SimpleNet
import torch model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_5m_m1", pretrained=True) # or any of these variants # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_5m_m2", pretrained=True) # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_9m_m1", pretrained=True) # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_9m_m2", pretrained=True) # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_small_m1_05", pretrained=True) # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_small_m2_05", pretrained=True) # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_small_m1_075", pretrained=True) # model = torch.hub.load("coderx7/simplenet_pytorch:v1.0.0", "simplenetv1_small_m2_075", pretrained=True) model.eval() All pre-trained models expect input images normalized in the same way, i.e. mini-batches of 3-channel RGB images of shape (3 x H x W), where H and W are expected to be at least 224. The images have to be loaded in to a range of [0, 1] and then normalized using mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] and std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225].
Here’s a sample execution.
# Download an example image from the pytorch website import urllib url, filename = ("https://github.com/pytorch/hub/raw/master/images/dog.jpg", "dog.jpg") try: urllib.URLopener().retrieve(url, filename) except: urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename) # sample execution (requires torchvision) from PIL import Image from torchvision import transforms input_image = Image.open(filename) preprocess = transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(256), transforms.CenterCrop(224), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]), ]) input_tensor = preprocess(input_image) input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) # create a mini-batch as expected by the model # move the input and model to GPU for speed if available if torch.cuda.is_available(): input_batch = input_batch.to('cuda') model.to('cuda') with torch.no_grad(): output = model(input_batch) # Tensor of shape 1000, with confidence scores over ImageNet's 1000 classes print(output[0]) # The output has unnormalized scores. To get probabilities, you can run a softmax on it. probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(output[0], dim=0) print(probabilities) # Download ImageNet labels !wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/hub/master/imagenet_classes.txt # Read the categories with open("imagenet_classes.txt", "r") as f: categories = [s.strip() for s in f.readlines()] # Show top categories per image top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5) for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)): print(categories[top5_catid[i]], top5_prob[i].item()) Model Description
SimpleNet models were proposed in “Lets Keep it simple, Using simple architectures to outperform deeper and more complex architectures”.
Here we have the 8 versions of simplenet models, which contains 1.5m, 3.2m, 5.7m and 9.5m parameters respectively.
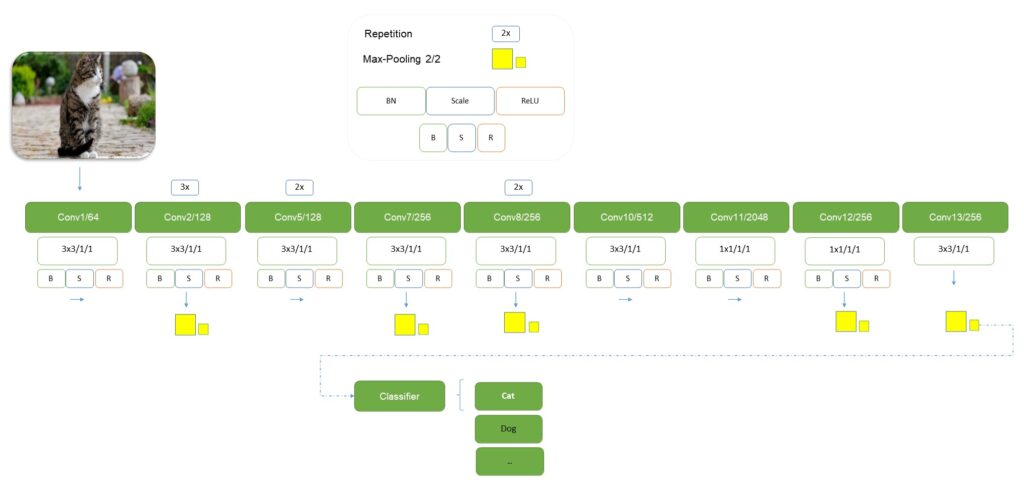
Detailed model architectures can be found in Table 1 and Table 2.
Their 1-crop errors on ImageNet dataset with pretrained models are listed below.
The m2 variants
| Model structure | Top-1 errors | Top-5 errors |
|---|---|---|
| simplenetv1_small_m2_05 | 38.33 | 16.512 |
| simplenetv1_small_m2_075 | 31.494 | 11.85 |
| simplenetv1_5m_m2 | 27.97 | 9.676 |
| simplenetv1_9m_m2 | 25.77 | 8.252 |
The m1 variants
| Model structure | Top-1 errors | Top-5 errors |
|---|---|---|
| simplenetv1_small_m1_05 | 38.878 | 17.012 |
| simplenetv1_small_m1_075 | 32.216 | 12.282 |
| simplenetv1_5m_m1 | 28.452 | 10.06 |
| simplenetv1_9m_m1 | 26.208 | 8.514 |
References
