In this tutorial, I will show you how to implement Angular 16 Form Validation example (and Submit) with Reactive Forms Module and Bootstrap 4.
More Practice:
– Angular 16 File upload example with progress bar
– Angular 16 CRUD example with Web API
– Angular 16 JWT Authentication & Authorization example
Serverless with Firebase:
– Angular 16 Firebase CRUD example
– Angular 16 Firestore CRUD example
– Angular 16 File Upload with Firebase Storage
Using Template Driven Forms instead:
Angular 16 Template Driven Form Validation example
Contents
Overview of Angular 16 Form Validation example
We will implement validation for a Angular Form using Reactive Forms Module and Bootstrap. The form has:
- Full Name: required
- Username: required, from 6 to 20 characters
- Email: required, email format
- Password: required, from 6 to 40 characters
- Confirm Password: required, same as Password
- Accept Terms Checkbox: required
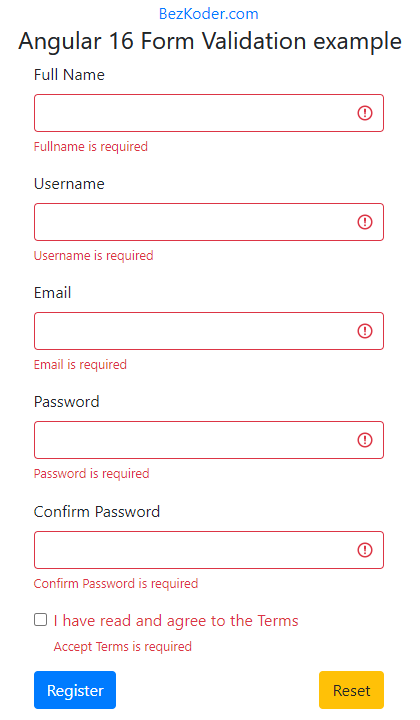
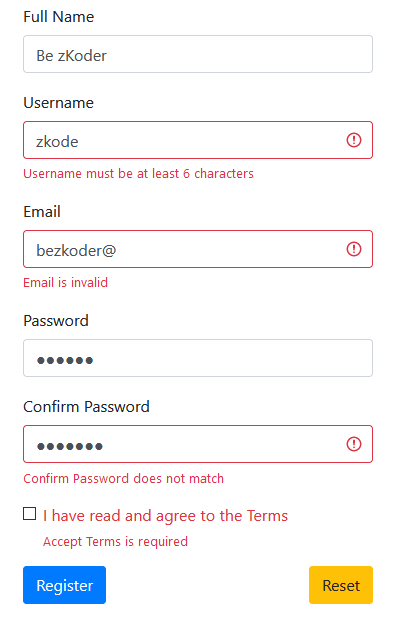
Some fields could be wrong:
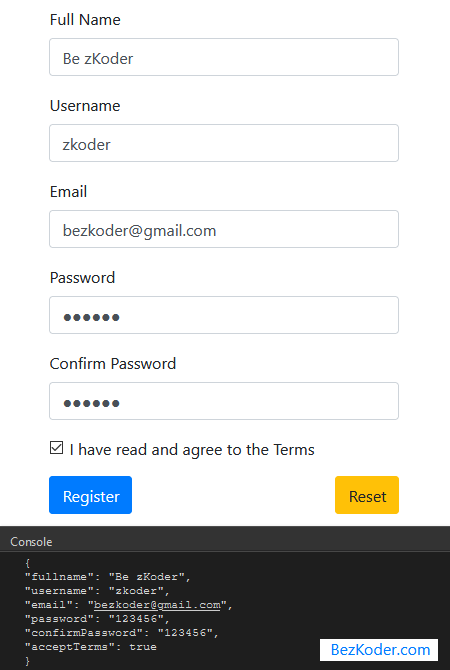
Successful Submission will look like this:
Technology
We’re gonna use following modules:
- Angular 16
- Bootstrap 4
- @angular/forms 16
Setup Project
First we need to add the ReactiveFormsModule into our App Module.
Open src/app/app.module.ts and import ReactiveFormsModule from @angular/forms:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, ReactiveFormsModule ], providers: [], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { } Import Bootstrap
Run the command: npm install [email protected].
Next, open src/style.css and add following code:
@import "~bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css"; Angular 16 Form Validation with Reactive Forms
The app component contains Form Validation example built with the @angular/forms version 16.
Open app/app.component.ts, we’re gonna import necessary library first:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { AbstractControl, FormBuilder, FormGroup, Validators } from '@angular/forms'; import Validation from './utils/validation'; We use Angular FormBuilder to create a FormGroup object (form property) which is then bound to the template <form> element (using the [formGroup] directive later).
Validators provides a set of built-in validators (required, minLength, maxLength…) that can be used by form controls.
A validator is a function that processes a FormControl or collection of controls and returns an error map or null (meaning validation has passed).
Validation is our custom class that provides custom validator function. I will explain it later.
export class AppComponent implements OnInit { form: FormGroup = new FormGroup({ fullname: new FormControl(''), username: new FormControl(''), email: new FormControl(''), password: new FormControl(''), confirmPassword: new FormControl(''), acceptTerms: new FormControl(false), }); submitted = false; constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder) {} ngOnInit(): void { this.form = this.formBuilder.group( { fullname: ['', Validators.required], username: [ '', [ Validators.required, Validators.minLength(6), Validators.maxLength(20) ] ], email: ['', [Validators.required, Validators.email]], password: [ '', [ Validators.required, Validators.minLength(6), Validators.maxLength(40) ] ], confirmPassword: ['', Validators.required], acceptTerms: [false, Validators.requiredTrue] }, { validators: [Validation.match('password', 'confirmPassword')] } ); } ... } We also have getter f to access form controls (form.controls) from the template. For example, we can get username field in the template using f.username instead of form.controls.username.
The submitted property helps us to check whether the form is submitted or not.
export class AppComponent implements OnInit { form: FormGroup = ...; submitted = false; constructor(private formBuilder: FormBuilder) {} ngOnInit(): void { ... } get f(): { [key: string]: AbstractControl } { return this.form.controls; } onSubmit(): void { this.submitted = true; if (this.form.invalid) { return; } console.log(JSON.stringify(this.form.value, null, 2)); } onReset(): void { this.submitted = false; this.form.reset(); } } Angular 16 Form Validation template
Now we create the form with input fields and validation messages.
We bind to the FormGroup object (form) in the app component using [formGroup] directive. Form submit event will call onSubmit() handler above using event binding (ngSubmit).
Validation messages will display after form submission for the first time by submitted property.
app/app.component.html
<div class="register-form"> <form [formGroup]="form" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()"> <div class="form-group"> <label>Full Name</label> <input type="text" formControlName="fullname" class="form-control" [ngClass]="{ 'is-invalid': submitted && f['fullname'].errors }" /> <div *ngIf="submitted && f['fullname'].errors" class="invalid-feedback"> <div *ngIf="f['fullname'].errors['required']">Fullname is required</div> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Username</label> <input type="text" formControlName="username" class="form-control" [ngClass]="{ 'is-invalid': submitted && f['username'].errors }" /> <div *ngIf="submitted && f['username'].errors" class="invalid-feedback"> <div *ngIf="f['username'].errors['required']">Username is required</div> <div *ngIf="f['username'].errors['minlength']"> Username must be at least 6 characters </div> <div *ngIf="f['username'].errors['maxlength']"> Username must not exceed 20 characters </div> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Email</label> <input type="text" formControlName="email" class="form-control" [ngClass]="{ 'is-invalid': submitted && f['email'].errors }" /> <div *ngIf="submitted && f['email'].errors" class="invalid-feedback"> <div *ngIf="f['email'].errors['required']">Email is required</div> <div *ngIf="f['email'].errors['email']">Email is invalid</div> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Password</label> <input type="password" formControlName="password" class="form-control" [ngClass]="{ 'is-invalid': submitted && f['password'].errors }" /> <div *ngIf="submitted && f['password'].errors" class="invalid-feedback"> <div *ngIf="f['password'].errors['required']">Password is required</div> <div *ngIf="f['password'].errors['minlength']"> Password must be at least 6 characters </div> <div *ngIf="f['password'].errors['maxlength']"> Username must not exceed 40 characters </div> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label>Confirm Password</label> <input type="password" formControlName="confirmPassword" class="form-control" [ngClass]="{ 'is-invalid': submitted && f['confirmPassword'].errors }" /> <div *ngIf="submitted && f['confirmPassword'].errors" class="invalid-feedback" > <div *ngIf="f['confirmPassword'].errors['required']"> Confirm Password is required </div> <div *ngIf="f['confirmPassword'].errors['matching']"> Confirm Password does not match </div> </div> </div> <div class="form-group form-check"> <input type="checkbox" formControlName="acceptTerms" class="form-check-input" [ngClass]="{ 'is-invalid': submitted && f['acceptTerms'].errors }" /> <label for="acceptTerms" class="form-check-label" >I have read and agree to the Terms</label > <div *ngIf="submitted && f['acceptTerms'].errors" class="invalid-feedback"> Accept Terms is required </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Register</button> <button type="button" (click)="onReset()" class="btn btn-warning float-right" > Reset </button> </div> </form> </div> Angular 16 Confirm Password validation
Now we will use Angular Custom Validator to implement password and confirm password validation..
– First, the validator returns null (meaning validation has passed) if there is any error on the control that we want to check (confirm password).
– Then, the validator checks that two fields match or not and set error on checking control if validation fails.
utils/validation.ts
import { AbstractControl, ValidatorFn } from '@angular/forms'; export default class Validation { static match(controlName: string, checkControlName: string): ValidatorFn { return (controls: AbstractControl) => { const control = controls.get(controlName); const checkControl = controls.get(checkControlName); if (checkControl?.errors && !checkControl.errors['matching']) { return null; } if (control?.value !== checkControl?.value) { controls.get(checkControlName)?.setErrors({ matching: true }); return { matching: true }; } else { return null; } }; } } Run Angular 16 Form Validation example
You can run our App with command: ng serve.
If the process is successful, open Browser with Url: http://localhost:4200/ and check it.
Or run on Stackblitz:
Conclusion
Today we’ve built Angular 16 Form Validation example successfully with Reactive Forms Module & Bootstrap 4.
You can also use the Form Validation in following posts:
– Angular 16 File upload example with progress bar
– Angular 16 CRUD example with Web API
– Angular 16 JWT Authentication example with Web Api
Or using Template Driven Forms instead:
Angular 16 Template Driven Forms Validation example
Happy learning! See you again.
Further Reading
Serverless with Firebase:
– Angular 16 Firebase CRUD example
– Angular 16 Firestore CRUD example
– Angular 16 File Upload with Firebase Storage
Fullstack CRUD Application:
– Angular 16 + Node Express + MySQL example
– Angular 16 + Node Express + PostgreSQL example
– Angular 16 + Node Express + MongoDB example
– Angular 16 + Spring Boot + H2 example
– Angular 16 + Spring Boot + MySQL example
– Angular 16 + Spring Boot + PostgreSQL example
– Angular 16 + Spring Boot + MongoDB example
– Angular + Django example
– Angular + Django + MySQL example
– Angular + Django + PostgreSQL example
– Angular + Django + MongoDB example
