The Internet is a global network that connects millions of computers and devices, enabling people to communicate, share information, and access digital resources worldwide. It works like a vast highway system, where data travels in small packets between connected devices.
- Facilitates instant communication and information exchange across the world.
- Connects computers, smartphones, and servers through various wired and wireless networks.
- Powers daily activities such as emailing, online learning, shopping, and entertainment.
Internet vs. World Wide Web
Many people use the Internet and World Wide Web (WWW) interchangeably, but they are not the same.
- The Internet is the infrastructure — the physical network of cables, satellites, and routers.
- The World Wide Web is one of the services that runs on the Internet — it’s where websites and web pages exist, accessible through browsers like Chrome or Safari.
The Public Revolution
In 1989–1991, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, a British scientist, invented the World Wide Web while working at CERN. He created three key technologies:
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language) – for creating web pages
- HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) – for communication between browsers and servers
- URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) – for addressing pages on the Web
By the mid-1990s, web browsers like Mosaic and Netscape Navigator made the Internet easy for everyone to use. The digital revolution had begun.
How Does the Internet Work
Internetworking describes the process and technologies that allow millions of computers and devices to communicate and share data efficiently.
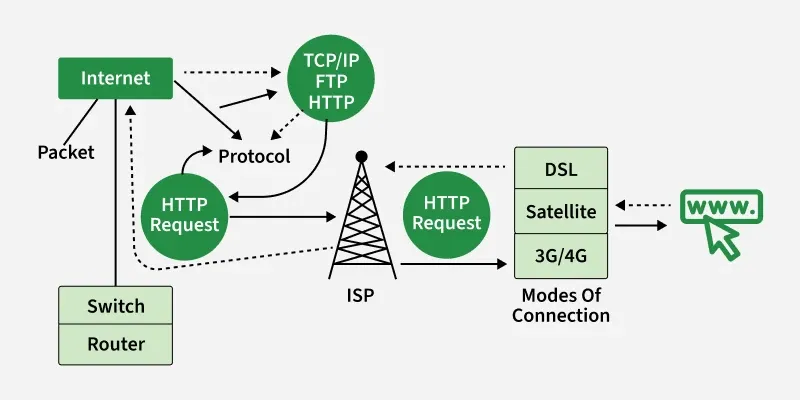 Basic Internet Working
Basic Internet WorkingProtocols – The Rules of the Road
All devices on the Internet follow a set of communication rules called protocols. The most important ones are:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – Breaks data into smaller packets and ensures they arrive safely.
- IP (Internet Protocol) – Assigns addresses and delivers packets to the correct destination.
- HTTP/HTTPS – Used for websites.
- SMTP – Used for sending emails.
These protocols ensure smooth, reliable, and secure communication worldwide.
IP Addresses – The Street Address
Every device connected to the Internet has a unique IP Address (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
It’s like a home address that tells data packets where to go and where they came from. Modern Internet systems are transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 to handle the massive number of connected devices.
Data Packets – The Small Boxes
When you send information — like a photo or an email — it’s divided into small chunks called packets. Each packet travels through the Internet independently, sometimes by different routes, and they are reassembled at the destination into the original file.
Internet Components
- Routers: Direct packets along the most efficient path.
- Servers: Store and deliver data like websites, emails, and videos.
- ISPs (Internet Service Providers): Companies like Airtel, Jio, AT&T, or Verizon that connect users to the Internet.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Translates website names (like google.com) into IP addresses.
Applications of Internet
The versatility of the Internet means it touches virtually every part of modern life. It's the platform that makes modern living possible.
A. Connect and Communicate
The Internet replaced slow communication with instant global interaction.
- Email: The standard for formal and professional written messages and documents worldwide.
- Instant Messaging & Video Calls: Services like WhatsApp, Zoom, and FaceTime allow for real-time chat and virtual presence. You can talk to someone across the street or across the globe just by tapping a screen.
The Internet is the largest collection of human knowledge ever assembled, making information instantly available.
- Search Engines: Tools like Google index billions of web pages to help you find exactly what you need using simple keywords. They are the gateway to information.
- Digital Education: The rise of online courses and digital libraries means you can access high-quality educational materials and learn new skills anytime, anywhere.
C. Shop and Manage Money
The Internet transformed how we buy goods and handle our finances.
- E-commerce (Online Shopping): Sites like Amazon allow you to buy and sell products globally from the comfort of your home, making retail a worldwide service.
- Online Banking & Digital Payments: Apps and websites let you manage your accounts, pay bills, and transfer money instantly and securely, reducing the need to visit a physical bank.
D. Entertain and Socialize
For many, the Internet is primarily a source of entertainment and a way to connect socially.
- Streaming Services: Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify offer on-demand entertainment. You can watch movies, listen to music, or view clips instantly without needing to download large files.
- Social Media & Gaming: Platforms like Instagram and online games connect users to communities and provide shared experiences, allowing millions to interact and play together in digital spaces.
Essential Internet Terminology
This section explains the key terms and concepts you need to understand to use and navigate the Internet effectively.
| Term | Meaning / Function |
|---|
| Web Client | The device or software (like a browser) used to access the Internet. |
| Web Browser | A program (Chrome, Firefox, Safari) that displays web pages. |
| Webpage | A single document on the Web written in HTML. |
| Website | A collection of connected web pages under one domain name. |
| Search Engine | A tool (like Google) used to find information on the Web. |
| URL (Uniform Resource Locator) | The address used to access a webpage. |
| Hyperlink | A clickable link connecting one page to another. |
| Download / Upload | Receiving or sending data from/to the Internet. |
| Firewall / Malware | Tools for network protection / harmful software. |
| The Cloud | Internet-based storage and services (e.g., Google Drive, iCloud). |
Internet Safety and the Future
Basic Security
As useful as the Internet is, it comes with risks such as viruses, hacking, identity theft, and misinformation. To stay safe:
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Avoid suspicious links or emails (phishing scams).
- Install antivirus software and enable firewalls.
- Be careful with sharing personal information online.
Digital awareness is essential to protect both privacy and data.
Looking Ahead
The Internet continues to evolve with exciting innovations:
- IoT (Internet of Things): Everyday devices like refrigerators and cars are now online.
- 5G and Fiber Optics: Providing ultra-fast Internet speeds.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Making online systems smarter and more personalized.
- Web 3.0: A decentralized, secure, and intelligent Internet future powered by blockchain and AI.
Which of the following best describes a "web browser"?
-
A tool for managing network hardware
-
A software application for retrieving and displaying web content
-
A protocol used for secure data transmission
-
A type of server that hosts websites
In the context of networking, what is the primary purpose of a router?
-
To store data for quick access
-
To connect multiple networks and direct data traffic between them
-
To provide wireless connectivity to devices
-
To encrypt data being transmitted
What describes the evolution from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0?
-
From static pages to user-generated content and social media
-
From mobile apps to desktop apps
-
From real-time chat to slow messaging
-
From email to postal mail
Explanation:
Web 1.0 featured static web pages. Web 2.0 introduced interactivity and platforms for user-generated content like blogs and social media
Which device forwards data packets between computer networks using routing protocols?
Explanation:
Routers use protocols like RIP to manage routing and direct packets between different networks.
What is a web browser used for?
-
-
-
It retrieves and displays internet content such as pages, images, and videos
-
It runs operating system commands
Explanation:
Spending too much time online can harm users' physical and mental health, especially in younger generations.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5 1/5 < Previous Next >
Explore
Basics of Computer
Application Software
System Software
Networks & Internet Protocols
Programming Languages