An encoder is a digital combinational circuit that converts multiple input signals into a binary code. It typically has one active input at a time and generates a binary output representing the position of that active input. For example, a 4-to-2 encoder has four inputs and produces a 2-bit output code. Encoders are useful in digital systems for data compression and efficient transmission. Variants like priority encoders assign importance to inputs to manage simultaneous signals.
- The number of inputs is usually 2n, with n output lines.
- Inputs are usually active high, meaning high voltage represents an active signal.
- Binary-weighted encoders assign codes based on input position using binary values.
- Encoders help convert parallel inputs into compact binary formats for processing.
 Encoder
EncoderTypes of Encoders
There are different types of Encoders which are mentioned below:
1. 4 to 2 Encoder
The 4 to 2 Encoder consists of four inputs Y3, Y2, Y1 & Y0, and two outputs A1 & A0. At any time, only one of these 4 inputs can be ‘1’ in order to get the respective binary code at the output. The figure below shows the logic symbol of the 4 to 2 encoder.
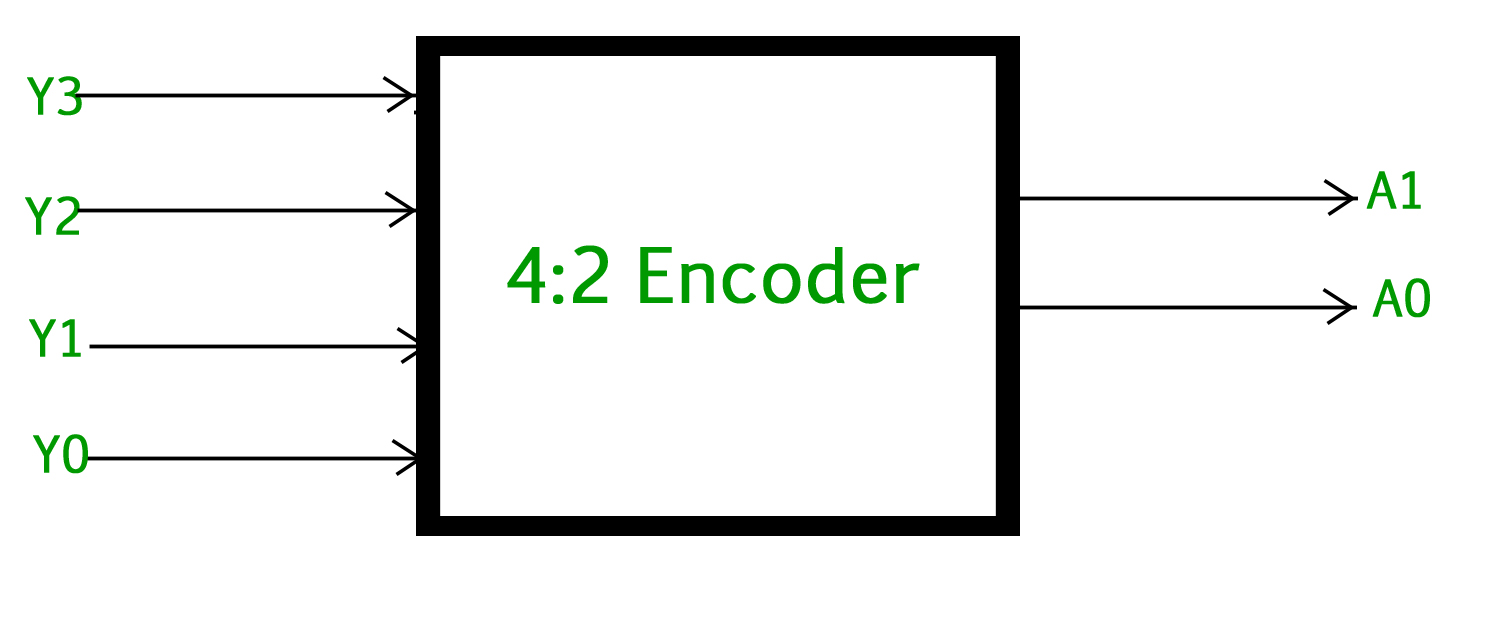 4 to 2 Encoder
4 to 2 EncoderTruth Table
The Truth table of 4 to 2 encoders is as follows:
| INPUTS(Y3Y2Y1Y0) | OUTPUTS(A1A0) |
|---|
| 0001 | 00 |
| 0010 | 01 |
| 0100 | 10 |
| 1000 | 11 |
Logical expression for A1 and A0:
A1 = Y3 + Y2
A0 = Y3 + Y1
Circuit Diagram
The above two Boolean functions A1 and A0 can be implemented using two input OR gates:
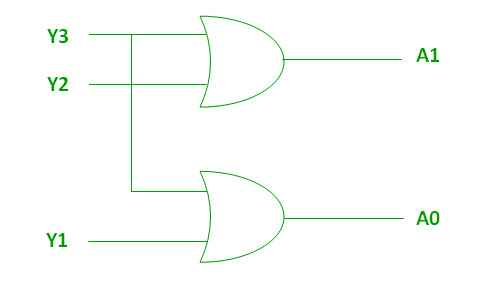 Implementation using OR Gate
Implementation using OR Gate2. Octal to Binary Encoder (8 to 3 Encoder)
The 8 to 3 Encoder or octal to Binary encoder consists of 8 inputs: Y7 to Y0 and 3 outputs: A2, A1 & A0. Each input line corresponds to each octal digit value and three outputs generate corresponding binary code. The figure below shows the logic symbol of octal to the binary encoder.
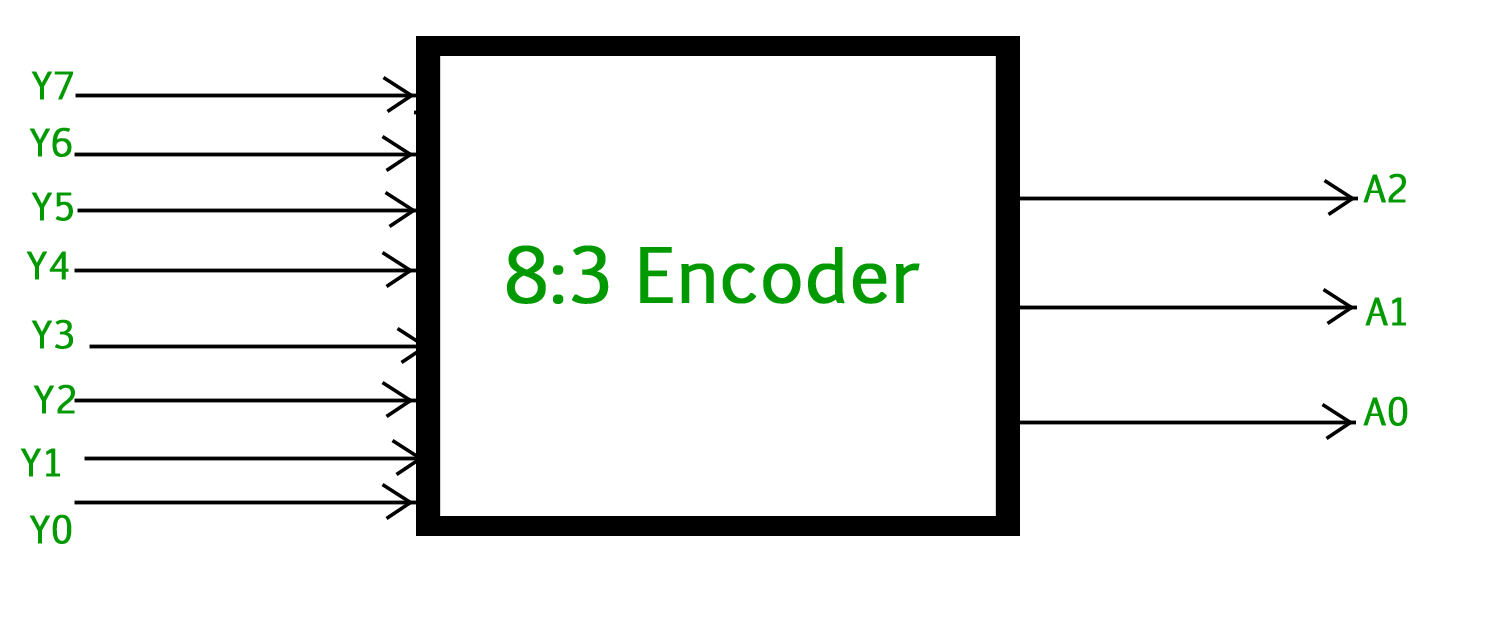 Octal to Binary Encoder (8 to 3 Encoder)
Octal to Binary Encoder (8 to 3 Encoder)Truth Table
The truth table for the 8 to 3 encoder is as follows:
| INPUTS(Y7Y6Y5Y4Y3Y2Y1Y0) | OUTPUTS(A2A1A0) |
|---|
| 00000001 | 000 |
| 00000010 | 001 |
| 00000100 | 010 |
| 00001000 | 011 |
| 00010000 | 100 |
| 00100000 | 101 |
| 01000000 | 110 |
| 10000000 | 111 |
Logical expression for A2, A1, and A0:
A2 = Y7 + Y6 + Y5 + Y4
A1 = Y7 + Y6 + Y3 + Y2
A0 = Y7 + Y5 + Y3 + Y1
Circuit Diagram
The above two Boolean functions A2, A1, and A0 can be implemented using four input OR gates:
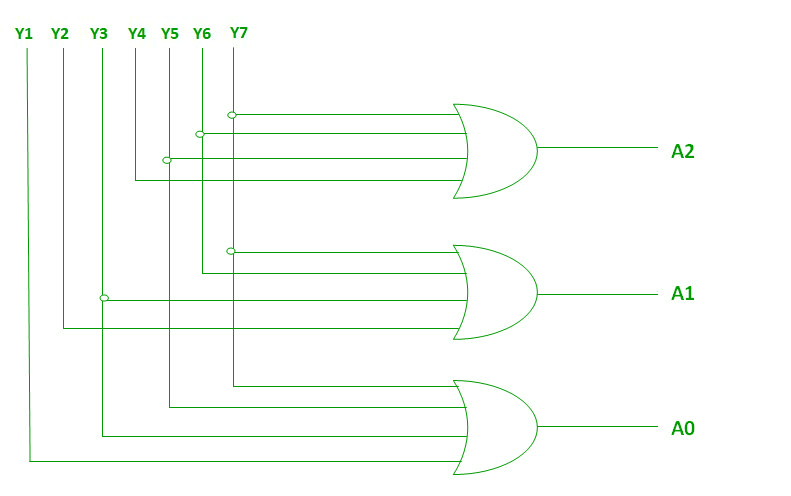 Implementation using OR Gate
Implementation using OR Gate3. Decimal to BCD Encoder
The decimal-to-binary encoder usually consists of 10 input lines and 4 output lines. Each input line corresponds to each decimal digit and 4 outputs correspond to the BCD code. This encoder accepts the decoded decimal data as an input and encodes it to the BCD output which is available on the output lines. The figure below shows the logic symbol of the decimal to BCD encoder.
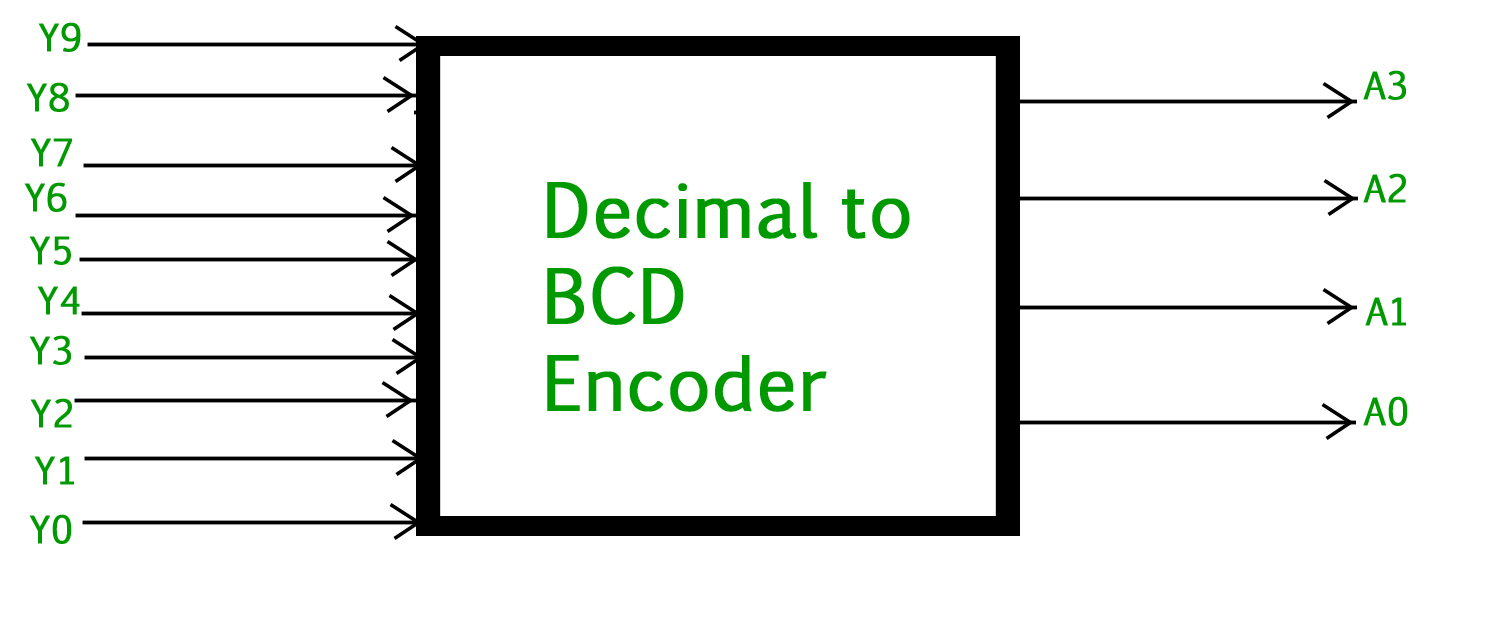 Decimal to BCD Encoder
Decimal to BCD EncoderTruth Table
The truth table for decimal to BCD encoder is as follows:
| INPUTS(Y9Y8Y7Y6Y5Y4Y3Y2Y1Y0) | OUTPUTS(A3A2A1A0) |
|---|
| 0000000001 | 0000 |
| 0000000010 | 0001 |
| 0000000100 | 0010 |
| 0000001000 | 0011 |
| 0000010000 | 0100 |
| 0000100000 | 0101 |
| 0001000000 | 0110 |
| 0010000000 | 0111 |
| 0100000000 | 1000 |
| 1000000000 | 1001 |
Logical expression for A3, A2, A1, and A0:
A3 = Y9 + Y8
A2 = Y7 + Y6 + Y5 +Y4
A1 = Y7 + Y6 + Y3 +Y2
A0 = Y9 + Y7 +Y5 +Y3 + Y1
Circuit Diagram
The above two Boolean functions can be implemented using OR gates:
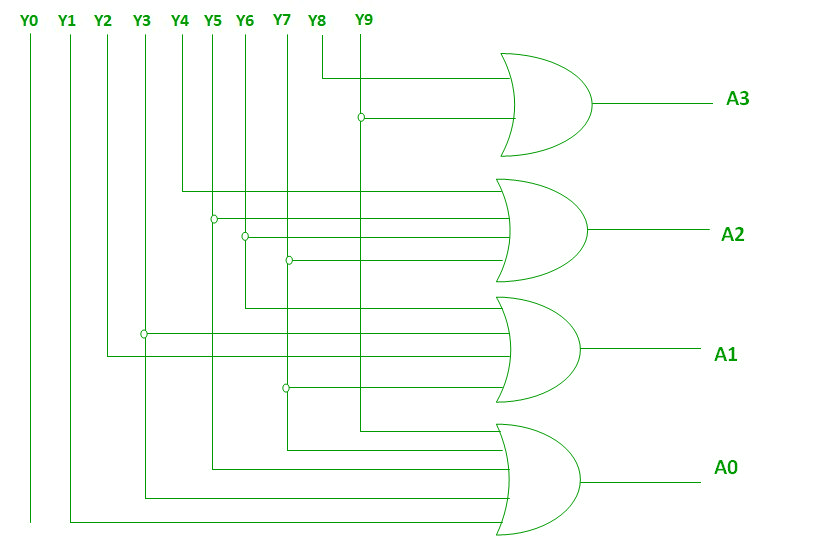 Implementation using OR Gate
Implementation using OR Gate4. Priority Encoder
A 4 to 2 priority encoder has 4 inputs: Y3, Y2, Y1 & Y0, and 2 outputs: A1 & A0. Here, the input, Y3 has the highest priority, whereas the input, Y0 has the lowest priority. In this case, even if more than one input is ‘1’ at the same time, the output will be the (binary) code corresponding to the input, which is having higher priority.
Truth Table
The truth table for the priority encoder is as follows:
| INPUTS(Y3Y2Y1Y0) | OUTPUTS(A1A0V) |
|---|
| 0000 | XX0 |
| 0001 | 001 |
| 001X | 011 |
| 01XX | 101 |
| 1XXX | 111 |
Logical Expressions using K-Map
The logical expression for A1 is shown below:
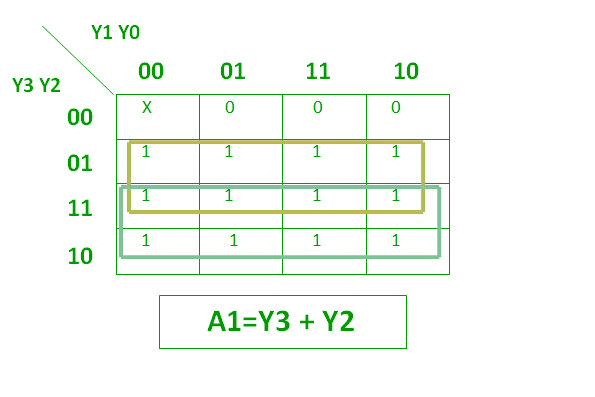 Logical Expression
Logical ExpressionThe Logical Expression for A0 is shown below:
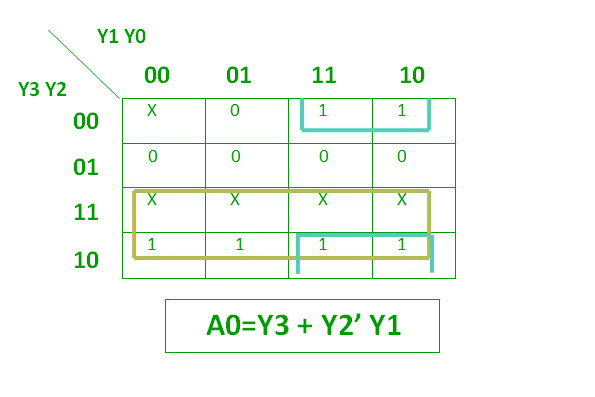 Logical Expression
Logical ExpressionCircuit Diagram
The above two Boolean functions can be implemented as:
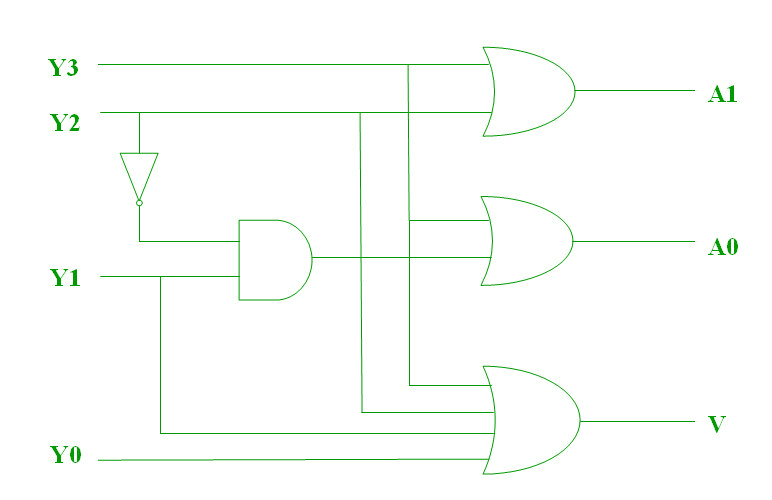 Priority Encoder
Priority EncoderErrors in Encoders
There are some errors that usually happen in Encoders are mentioned below:
- There is an ambiguity, when all outputs of the encoder are equal to zero.
- If more than one input is active High, then the encoder produces an output, which may not be the correct code.
So, to overcome these difficulties, we should assign priorities to each input of the encoder. Then, the output of the encoder will be the code corresponding to the active high inputs, which have higher priority.
Explore
Number Systems
Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates
Minimization Techniques
Combinational Circuits
Sequential Circuits
Conversion of Flip-Flop
Register, Counter, and Memory Unit
LMNs and GATE PYQs