Detect Cycle in a Directed Graph
Last Updated : 04 Nov, 2025
Given a directed graph represented by its adjacency list adj[][], determine whether the graph contains a cycle/Loop or not.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same vertex, following the direction of edges.
Examples:
Input: adj[][] = [[1], [2], [0, 3], []]
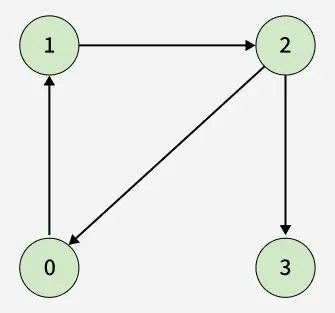
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0.
Input: adj[][] = [[2], [0], []]
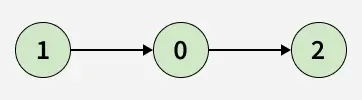
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the graph.
[Approach 1] Using DFS - O(V + E) Time and O(V) Space
To detect a cycle in a directed graph, we use Depth First Search (DFS). In DFS, we go as deep as possible from a starting node. If during this process, we reach a node that we’ve already visited in the same DFS path, it means we’ve gone back to an ancestor — this shows a cycle exists.
But there’s a problem: When we start DFS from one node, some nodes get marked as visited. Later, when we start DFS from another node, those visited nodes may appear again, even if there’s no cycle.
So, using only visited[] isn’t enough.
To fix this, we use two arrays:
- visited[] - marks nodes visited at least once.
- recStack[] - marks nodes currently in the recursion (active) path.
If during DFS we reach a node that’s already in the recStack, we’ve found a path from the current node back to one of its ancestors, forming a cycle. As soon as we finish exploring all paths from a node, we remove it from the recursion stack by marking recStack[node] = false. This ensures that only the nodes in the current DFS path are tracked.
Illustration:
C++ //Driver Code Starts #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; //Driver Code Ends // Utility DFS function to detect cycle in a directed graph bool isCyclicUtil(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int u, vector<bool>& visited, vector<bool>& recStack) { // node is already in recursion stack cycle found if (recStack[u]) return true; // already processed no need to visit again if (visited[u]) return false; visited[u] = true; recStack[u] = true; // Recur for all adjacent nodes for (int v : adj[u]) { if (isCyclicUtil(adj, v, visited, recStack)) return true; } // remove from recursion stack before backtracking recStack[u] = false; return false; } // Function to detect cycle in a directed graph bool isCyclic(vector<vector<int>>& adj) { int V = adj.size(); vector<bool> visited(V, false); vector<bool> recStack(V, false); // Run DFS from every unvisited node for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (!visited[i] && isCyclicUtil(adj, i, visited, recStack)) return true; } return false; } //Driver Code Starts int main() { vector<vector<int>> adj = {{1},{2},{0, 3}}; cout << (isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false") << endl; return 0; } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts import java.util.ArrayList; public class GFG { //Driver Code Ends // Utility DFS function to detect cycle in a directed graph static boolean isCyclicUtil(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, boolean[] visited, boolean[] recStack) { // Node already in recursion stack cycle found if (recStack[u]) return true; // Already processed no need to visit again if (visited[u]) return false; visited[u] = true; recStack[u] = true; // Recur for all adjacent nodes for (int v : adj.get(u)) { if (isCyclicUtil(adj, v, visited, recStack)) return true; } // Remove from recursion stack before backtracking recStack[u] = false; return false; } // Function to detect cycle in a directed graph static boolean isCyclic(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) { int V = adj.size(); boolean[] visited = new boolean[V]; boolean[] recStack = new boolean[V]; // Run DFS from every unvisited node for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (!visited[i] && isCyclicUtil(adj, i, visited, recStack)) return true; } return false; } //Driver Code Starts // Function to add an edge to the adjacency list static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) { adj.get(u).add(v); } public static void main(String[] args) { int V = 4; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { adj.add(new ArrayList<>()); } // Add directed edges addEdge(adj, 0, 1); addEdge(adj, 1, 2); addEdge(adj, 2, 0); addEdge(adj, 2, 3); System.out.println(isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false"); } } //Driver Code Ends # Utility DFS function to detect cycle in a directed graph def isCyclicUtil(adj, u, visited, recStack): # node is already in recursion stack cycle found if recStack[u]: return True # already processed no need to visit again if visited[u]: return False visited[u] = True recStack[u] = True # Recur for all adjacent nodes for v in adj[u]: if isCyclicUtil(adj, v, visited, recStack): return True # remove from recursion stack before backtracking recStack[u] = False return False # Function to detect cycle in a directed graph def isCyclic(adj): V = len(adj) visited = [False] * V recStack = [False] * V # Run DFS from every unvisited node for i in range(V): if not visited[i] and isCyclicUtil(adj, i, visited, recStack): return True return False #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == "__main__": adj = [[1], [2], [0, 3]] print("true" if isCyclic(adj) else "false") #Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { // Utility DFS function to detect cycle in a directed graph //Driver Code Ends static bool isCyclicUtil(List<List<int>> adj, int u, bool[] visited, bool[] recStack) { // Node already in recursion stack cycle found if (recStack[u]) return true; // Already processed → no need to visit again if (visited[u]) return false; visited[u] = true; recStack[u] = true; // Recur for all adjacent nodes foreach (int v in adj[u]) { if (isCyclicUtil(adj, v, visited, recStack)) return true; } // Remove from recursion stack before backtracking recStack[u] = false; return false; } // Function to detect cycle in a directed graph static bool isCyclic(List<List<int>> adj) { int V = adj.Count; bool[] visited = new bool[V]; bool[] recStack = new bool[V]; // Run DFS from every unvisited node for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (!visited[i] && isCyclicUtil(adj, i, visited, recStack)) return true; } return false; } //Driver Code Starts // Function to add an edge to the adjacency list static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v) { adj[u].Add(v); } static void Main() { int V = 4; List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>(); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { adj.Add(new List<int>()); } // Add directed edges addEdge(adj, 0, 1); addEdge(adj, 1, 2); addEdge(adj, 2, 0); addEdge(adj, 2, 3); Console.WriteLine(isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false"); } } //Driver Code Ends // Utility DFS function to detect cycle in a directed graph function isCyclicUtil(adj, u, visited, recStack) { // node is already in recursion stack cycle found if (recStack[u]) return true; // already processed no need to visit again if (visited[u]) return false; visited[u] = true; recStack[u] = true; // Recur for all adjacent nodes for (let v of adj[u]) { if (isCyclicUtil(adj, v, visited, recStack)) return true; } // remove from recursion stack before backtracking recStack[u] = false; return false; } // Function to detect cycle in a directed graph function isCyclic(adj) { const V = adj.length; const visited = Array(V).fill(false); const recStack = Array(V).fill(false); // Run DFS from every unvisited node for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (!visited[i] && isCyclicUtil(adj, i, visited, recStack)) return true; } return false; } // Driver Code //Driver Code Starts let V = 4; const adj = [[1],[2],[0, 3]]; console.log(isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false"); //Driver Code Ends [Approach 2] Using Topological Sorting - O(V + E) Time and O(V) Space
The idea is to use Kahn’s algorithm because it works only for Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). So, while performing topological sorting using Kahn’s algorithm, if we are able to include all the vertices in the topological order, it means the graph has no cycle and is a DAG.
However, if at the end there are still some vertices left (i.e., their in-degree never becomes 0), it means those vertices are part of a cycle. Hence, if we cannot get all the vertices in the topological sort, the graph must contain at least one cycle.
C++ //Driver Code Starts #include <iostream> #include<vector> #include<queue> using namespace std; //Driver Code Ends bool isCyclic(vector<vector<int>> &adj) { int V = adj.size(); // Array to store in-degree of each vertex vector<int> inDegree(V, 0); queue<int> q; // Count of visited (processed) nodes int visited = 0; //Compute in-degrees of all vertices for (int u = 0; u < V; ++u) { for (int v : adj[u]) { inDegree[v]++; } } // Add all vertices with in-degree 0 to the queue for (int u = 0; u < V; ++u) { if (inDegree[u] == 0) { q.push(u); } } // Perform BFS (Topological Sort) while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); visited++; // Reduce in-degree of neighbors for (int v : adj[u]) { inDegree[v]--; if (inDegree[v] == 0) { // Add to queue when in-degree becomes 0 q.push(v); } } } // If visited nodes != total nodes, a cycle exists return visited != V; } //Driver Code Starts int main() { vector<vector<int>> adj = {{1},{2},{0, 3}}; cout << (isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false") << endl; return 0; } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts import java.util.Queue; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.ArrayList; public class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static boolean isCyclic(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) { int V = adj.size(); // Array to store in-degree of each vertex int[] inDegree = new int[V]; Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Count of visited (processed) nodes int visited = 0; // Compute in-degrees of all vertices for (int u = 0; u < V; ++u) { for (int v : adj.get(u)) { inDegree[v]++; } } // Add all vertices with in-degree 0 to the queue for (int u = 0; u < V; ++u) { if (inDegree[u] == 0) { q.add(u); } } // Perform BFS (Topological Sort) while (!q.isEmpty()) { int u = q.poll(); visited++; // Reduce in-degree of neighbors for (int v : adj.get(u)) { inDegree[v]--; if (inDegree[v] == 0) { // Add to queue when in-degree becomes 0 q.add(v); } } } // If visited nodes != total nodes, a cycle exists return visited != V; } //Driver Code Starts // Function to add an edge to the adjacency list static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v) { adj.get(u).add(v); } public static void main(String[] args) { int V = 4; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { adj.add(new ArrayList<>()); } // Add edges addEdge(adj, 0, 1); addEdge(adj, 1, 2); addEdge(adj, 2, 0); addEdge(adj, 2, 3); System.out.println(isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false"); } } //Driver Code Ends #Driver Code Starts from collections import deque #Driver Code Ends def isCyclic(adj): V = max(max(sub) if sub else 0 for sub in adj) + 1 # Array to store in-degree of each vertex inDegree = [0] * V q = deque() # Count of visited (processed) nodes visited = 0 # Compute in-degrees of all vertices for u in range(V): for v in adj[u]: inDegree[v] += 1 # Add all vertices with in-degree 0 to the queue for u in range(V): if inDegree[u] == 0: q.append(u) # Perform BFS (Topological Sort) while q: u = q.popleft() visited += 1 # Reduce in-degree of neighbors for v in adj[u]: inDegree[v] -= 1 if inDegree[v] == 0: # Add to queue when in-degree becomes 0 q.append(v) # If visited nodes != total nodes, a cycle exists return visited != V #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == "__main__": adj = [[1],[2],[0, 3], []] print("true" if isCyclic(adj) else "false") #Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static bool isCyclic(List<List<int>> adj) { int V = adj.Count; // Array to store in-degree of each vertex int[] inDegree = new int[V]; Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>(); // Count of visited (processed) nodes int visited = 0; // Compute in-degrees of all vertices for (int u = 0; u < V; ++u) { foreach (int v in adj[u]) { inDegree[v]++; } } // Add all vertices with in-degree 0 to the queue for (int u = 0; u < V; ++u) { if (inDegree[u] == 0) { q.Enqueue(u); } } // Perform BFS (Topological Sort) while (q.Count > 0) { int u = q.Dequeue(); visited++; // Reduce in-degree of neighbors foreach (int v in adj[u]) { inDegree[v]--; if (inDegree[v] == 0) { // Add to queue when in-degree becomes 0 q.Enqueue(v); } } } // If visited nodes != total nodes, a cycle exists return visited != V; } //Driver Code Starts // Function to add an edge to the adjacency list static void addEdge(List<List<int>> adj, int u, int v) { adj[u].Add(v); } static void Main() { int V = 4; List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>(); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { adj.Add(new List<int>()); } // Add edges addEdge(adj, 0, 1); addEdge(adj, 1, 2); addEdge(adj, 2, 0); addEdge(adj, 2, 3); Console.WriteLine(isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false"); } } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts const Denque = require("denque"); //Driver Code Ends function isCyclic(adj) { const V = adj.length; // Array to store in-degree of each vertex const inDegree = new Array(V).fill(0); const q = new Denque(); // Count of visited (processed) nodes let visited = 0; //Compute in-degrees of all vertices for (let u = 0; u < V; ++u) { for (let v of adj[u]) { inDegree[v]++; } } // Add all vertices with in-degree 0 to the queue for (let u = 0; u < V; ++u) { if (inDegree[u] === 0) { q.push(u); } } // Perform BFS (Topological Sort) while (!q.isEmpty()) { const u = q.shift(); visited++; // Reduce in-degree of neighbors for (let v of adj[u]) { inDegree[v]--; if (inDegree[v] === 0) { // Add to queue when in-degree becomes 0 q.push(v); } } } // If visited nodes != total nodes, a cycle exists return visited !== V; } //Driver Code Starts // Driver Code const adj = [ [1],[2],[0, 3],[]]; console.log(isCyclic(adj) ? "true" : "false"); //Driver Code Ends Similar Article:
Detect Cycle in a direct graph using colors
Detect Cycle in a Directed graph using colors
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem