Max Area of Island - Largest in Boolean Matrix
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Given a binary 2D matrix, find area of the largest region of 1s which are connected horizontally, vertically or diagonally.
Examples:
Input: M[][]= {{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}}
Output: 6
Explanation: The region in red has the largest area of 6 cells.
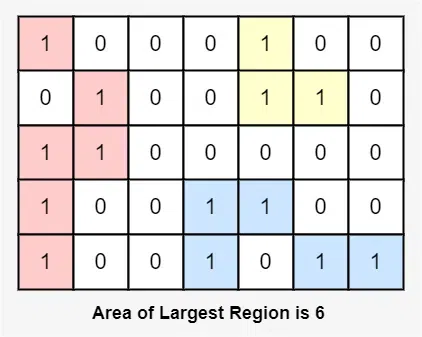 Area of Largest Region is 6
Area of Largest Region is 6
Input: M[][] = {{0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1}}
Output: 6
Explanation: In the following example, there are 2 regions. One with area = 1 and other with area = 6. So, largest area = 6.
Using DFS - O(rows * cols) Time and O(rows * cols) Space
The idea is to traverse the input matrix and if the value of any cell is 1, then run a DFS from the cell to visit all the cells in the connected component. In DFS, keep track of the area of the region and make recursive calls for all the eight neighbors. Also, while visiting any cell, update its value to 0 to mark it as visited. So, using the input matrix to mark the visited cells will avoid maintaining an extra 2D matrix to store the visited cells.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Program to find area of the largest region of 1s #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS bool isSafe(vector<vector<int>> &M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range and // value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island void DFS(vector<vector<int>> &M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols, int &area) { // These arrays are used to get row and column // numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell vector<int> dirR = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; vector<int> dirC = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; // Increment area of region by 1 area += 1; // Mark this cell as visited M[r][c] = 0; // Recur for all connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = r + dirR[i]; int newC = c + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) DFS(M, newR, newC, rows, cols, area); } } // function to find area of the largest region of 1s int largestRegion(vector<vector<int>> &M) { int rows = M.size(), cols = M[0].size(); // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the // all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = 0; DFS(M, i, j, rows, cols, area); // maximize the area maxArea = max(maxArea, area); } } } return maxArea; } int main() { vector<vector<int>> M = {{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}}; cout << largestRegion(M); return 0; } // C Program to find area of the largest region of 1s #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Define constants for rows and columns #define ROWS 5 #define COLS 7 // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS int isSafe(int M[ROWS][COLS], int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // Row number is in range, column number is in range, // and value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island void DFS(int M[ROWS][COLS], int r, int c, int rows, int cols, int *area) { // These arrays are used to get row and column numbers of 8 // neighbours of a given cell int dirR[] = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; int dirC[] = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; // Increment area of region by 1 (*area)++; // Mark this cell as visited M[r][c] = 0; // Recur for all connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = r + dirR[i]; int newC = c + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { DFS(M, newR, newC, rows, cols, area); } } } // Function to find area of the largest region of 1s int largestRegion(int M[ROWS][COLS], int rows, int cols) { // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through // all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = 0; DFS(M, i, j, rows, cols, &area); // Maximize the area if (area > maxArea) { maxArea = area; } } } } return maxArea; } int main() { int M[ROWS][COLS] = { {1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1} }; printf("%d\n", largestRegion(M, ROWS, COLS)); return 0; } // Java Program to find area of the largest region of 1s import java.util.*; class GfG { // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS static boolean isSafe(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range and // value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island static void DFS(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols, int[] area) { // These arrays are used to get row and column // numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell int[] dirR = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; int[] dirC = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; // Increment area of region by 1 area[0] += 1; // Mark this cell as visited M[r][c] = 0; // Recur for all connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = r + dirR[i]; int newC = c + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { DFS(M, newR, newC, rows, cols, area); } } } // function to find area of the largest region of 1s static int largestRegion(int[][] M) { int rows = M.length; int cols = M[0].length; // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the // all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { // area is taken as an array of size 1 to // achieve pass by reference int[] area = {0}; DFS(M, i, j, rows, cols, area); // maximize the area maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area[0]); } } } return maxArea; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] M = { {1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1} }; System.out.println(largestRegion(M)); } } # Python Program to find area of the largest region of 1s # A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS def is_safe(M, r, c, rows, cols): # row number is in range, column number is in range and # value is 1 return (r >= 0 and r < rows) and (c >= 0 and c < cols) \ and (M[r][c] == 1) # Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island def dfs(M, r, c, rows, cols, area): # Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island # These arrays are used to get row and column # numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell dirR = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1] dirC = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1] # Increment area of region by 1 area[0] += 1 # Mark this cell as visited M[r][c] = 0 # Recur for all connected neighbours for i in range(8): new_r = r + dirR[i] new_c = c + dirC[i] if is_safe(M, new_r, new_c, rows, cols): dfs(M, new_r, new_c, rows, cols, area) # function to find area of the largest region of 1s def largest_region(M): # function to find area of the largest region of 1s rows = len(M) cols = len(M[0]) # Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the # all cells of given matrix max_area = 0 for i in range(rows): for j in range(cols): # If a cell with value 1 is found if M[i][j] == 1: # area is taken as a list of size 1 to # achieve pass by reference area = [0] dfs(M, i, j, rows, cols, area) # maximize the area max_area = max(max_area, area[0]) return max_area if __name__ == "__main__": M = [ [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1] ] print(largest_region(M))
// C# Program to find area of the largest region of 1s using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS static bool IsSafe(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range // and value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island static void DFS(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols, ref int area) { // These arrays are used to get row and column // numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell int[] dirR = { -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 }; int[] dirC = { -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1 }; // Increment area of region by 1 area += 1; // Mark this cell as visited M[r][c] = 0; // Recur for all connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = r + dirR[i]; int newC = c + dirC[i]; if (IsSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) DFS(M, newR, newC, rows, cols, ref area); } } // function to find area of the largest region of 1s static int LargestRegion(int[][] M) { int rows = M.GetLength(0); int cols = M[0].GetLength(0); // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the // all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = 0; DFS(M, i, j, rows, cols, ref area); // maximize the area maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, area); } } } return maxArea; } static void Main() { int[][] M = { new int[] { 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, new int[] { 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 }, new int[] { 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, new int[] { 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, new int[] { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 } }; Console.WriteLine(LargestRegion(M)); } } // JavaScript Program to find area of the largest region of 1s // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS function isSafe(M, r, c, rows, cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range and // value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] === 1); } // Depth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island function DFS(M, r, c, rows, cols, area) { // These arrays are used to get row and column // numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell const dirR = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]; const dirC = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1]; // Increment area of region by 1 area[0] += 1; // Mark this cell as visited M[r][c] = 0; // Recur for all connected neighbours for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) { const newR = r + dirR[i]; const newC = c + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { DFS(M, newR, newC, rows, cols, area); } } } // Function to find area of the largest region of 1s function largestRegion(M) { const rows = M.length; const cols = M[0].length; // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the // all cells of given matrix let maxArea = 0; for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] === 1) { // area is taken as list to achieve // pass by reference let area = [0]; DFS(M, i, j, rows, cols, area); // Maximize the area maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area[0]); } } } return maxArea; } // Example usage const M = [ [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1] ]; console.log(largestRegion(M)); Time complexity: O(rows * cols). In the worst case, all the cells will be visited so the time complexity is O(rows * cols).
Auxiliary Space: O(rows * cols) for recursive stack space.
Using BFS - O(rows * cols) Time and O(rows + cols) Space
The idea is to traverse the input matrix and if the value of any cell is 1, then run a BFS from the cell to visit all the cells in the connected component. In BFS, maintain a queue to store the nodes and its neighbors. Also, while visiting any cell, update its value to 0 to mark it as visited. So, using the input matrix to mark the visited cells will avoid maintaining an extra 2D matrix to store the visited cells.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Program to find area of the largest region of 1s #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in DFS bool isSafe(vector<vector<int>> &M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range and // value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Breadth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island int BFS(vector<vector<int>> &M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // These arrays are used to get row and column // numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell vector<int> dirR = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; vector<int> dirC = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; int area = 0; // create a queue for bfs traversal queue<pair<int, int>> q; // Push the cell(r, c) into queue and mark it as visited q.push({r, c}); M[r][c] = 0; while (!q.empty()) { pair<int, int> curr = q.front(); q.pop(); // Increment the area of region area += 1; // Recur for all 8 connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = curr.first + dirR[i]; int newC = curr.second + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { M[newR][newC] = 0; q.push({newR, newC}); } } } return area; } // function to find area of the largest region of 1s int largestRegion(vector<vector<int>> &M) { int rows = M.size(), cols = M[0].size(); // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the // all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = BFS(M, i, j, rows, cols); // maximize the area maxArea = max(maxArea, area); } } } return maxArea; } int main() { vector<vector<int>> M = {{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}}; cout << largestRegion(M); return 0; } // C Program to find area of the largest region of 1s #include <stdio.h> // Define the maximum size of the matrix and queue #define MAX_ROWS 100 #define MAX_COLS 100 #define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE MAX_ROWS * MAX_COLS // Define a structure for the queue to store pairs of integers struct Pair { int row, col; }; int isSafe(int M[MAX_ROWS][MAX_COLS], int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // Row number is in range, column number is in range, and value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Breadth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island int BFS(int M[MAX_ROWS][MAX_COLS], int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // These arrays are used to get row and column numbers of // 8 neighbours of a given cell int dirR[] = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; int dirC[] = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; int area = 0; // Create a queue for BFS traversal struct Pair queue[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE]; int front = 0, rear = 0; // Push the cell(r, c) into queue and mark it as visited queue[rear++] = (struct Pair){r, c}; M[r][c] = 0; while (front < rear) { struct Pair curr = queue[front++]; // Increment the area of region area += 1; // Recur for all 8 connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = curr.row + dirR[i]; int newC = curr.col + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { M[newR][newC] = 0; queue[rear++] = (struct Pair){newR, newC}; } } } return area; } // Function to find the area of the largest region of 1s int largestRegion(int M[MAX_ROWS][MAX_COLS], int rows, int cols) { // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through all cells // of the given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = BFS(M, i, j, rows, cols); // Maximize the area if (area > maxArea) { maxArea = area; } } } } return maxArea; } int main() { // Define the matrix directly int M[MAX_ROWS][MAX_COLS] = { {1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1} }; int rows = 5, cols = 7; // Matrix dimensions printf("%d\n", largestRegion(M, rows, cols)); return 0; } // Java Program to find area of the largest region of 1s import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class GfG { // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in BFS static boolean isSafe(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range and // value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Breadth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island static int BFS(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // These arrays are used to get row and column // numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell int[] dirR = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; int[] dirC = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; int area = 0; // Create a queue for BFS traversal Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Push the cell(r, c) into queue and mark it as visited q.add(new int[]{r, c}); M[r][c] = 0; while (!q.isEmpty()) { int[] curr = q.poll(); int currR = curr[0]; int currC = curr[1]; // Increment the area of region area += 1; // Recur for all 8 connected neighbours for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = currR + dirR[i]; int newC = currC + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { M[newR][newC] = 0; q.add(new int[]{newR, newC}); } } } return area; } // Function to find area of the largest region of 1s static int largestRegion(int[][] M) { int rows = M.length; int cols = M[0].length; // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the // all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = BFS(M, i, j, rows, cols); // Maximize the area maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area); } } } return maxArea; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] M = { {1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1} }; System.out.println(largestRegion(M)); } } # Python Program to find area of the largest region of 1s from collections import deque # A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in BFS def isSafe(M, r, c, rows, cols): # row number is in range, column number is in range and # value is 1 return (r >= 0 and r < rows) and (c >= 0 and c < cols) and (M[r][c] == 1) # Breadth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island def BFS(M, r, c, rows, cols): # These arrays are used to get row and column # numbers of 8 neighbours of a given cell dirR = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1] dirC = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1] area = 0 # create a queue for bfs traversal q = deque() # Push the cell(r, c) into queue and mark it as visited q.append((r, c)) M[r][c] = 0 while q: curr = q.popleft() # Increment the area of region area += 1 # Recur for all 8 connected neighbours for i in range(8): newR = curr[0] + dirR[i] newC = curr[1] + dirC[i] if isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols): M[newR][newC] = 0 q.append((newR, newC)) return area # Function to find area of the largest region of 1s def largestRegion(M): rows = len(M) cols = len(M[0]) # Initialize result as 0 and traverse through the # all cells of given matrix maxArea = 0 for i in range(rows): for j in range(cols): # If a cell with value 1 is found if M[i][j] == 1: area = BFS(M, i, j, rows, cols) # Maximize the area maxArea = max(maxArea, area) return maxArea if __name__ == "__main__": M = [ [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1] ] print(largestRegion(M))
// C# Program to find area of the largest region of 1s using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // A function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in BFS static bool IsSafe(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // row number is in range, column number is in range and value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] == 1); } // Breadth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island static int BFS(int[][] M, int r, int c, int rows, int cols) { // These arrays are used to get row and column numbers of 8 neighbors of a given cell int[] dirR = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}; int[] dirC = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1}; int area = 0; // Create a queue for BFS traversal Queue<Tuple<int, int>> q = new Queue<Tuple<int, int>>(); // Push the cell(r, c) into queue and mark it as visited q.Enqueue(Tuple.Create(r, c)); M[r][c] = 0; while (q.Count > 0) { var curr = q.Dequeue(); int currR = curr.Item1; int currC = curr.Item2; // Increment the area of region area += 1; // Recur for all 8 connected neighbors for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int newR = currR + dirR[i]; int newC = currC + dirC[i]; if (IsSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { M[newR][newC] = 0; q.Enqueue(Tuple.Create(newR, newC)); } } } return area; } // Function to find area of the largest region of 1s static int LargestRegion(int[][] M) { int rows = M.Length; int cols = M[0].Length; // Initialize result as 0 and traverse through all cells of given matrix int maxArea = 0; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] == 1) { int area = BFS(M, i, j, rows, cols); // Maximize the area maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, area); } } } return maxArea; } static void Main() { int[][] M = { new int[] {1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, new int[] {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, new int[] {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, new int[] {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, new int[] {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1} }; Console.WriteLine(LargestRegion(M)); } } // JavaScript Program to find area of the largest region of 1s // Function to check if cell(r, c) can be included in BFS function isSafe(M, r, c, rows, cols) { // Row number is in range, column number is in range and value is 1 return (r >= 0 && r < rows) && (c >= 0 && c < cols) && (M[r][c] === 1); } // Breadth-First-Search to visit all cells in the current island function BFS(M, r, c, rows, cols) { // These arrays are used to get row and column numbers // of 8 neighbors of a given cell const dirR = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]; const dirC = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1]; let area = 0; // Create a queue for BFS traversal const queue = []; // Push the cell(r, c) into queue and mark it as visited queue.push([r, c]); M[r][c] = 0; while (queue.length > 0) { const [currR, currC] = queue.shift(); // Increment the area of region area += 1; // Recur for all 8 connected neighbors for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) { const newR = currR + dirR[i]; const newC = currC + dirC[i]; if (isSafe(M, newR, newC, rows, cols)) { M[newR][newC] = 0; queue.push([newR, newC]); } } } return area; } // Function to find area of the largest region of 1s function largestRegion(M) { const rows = M.length; const cols = M[0].length; let maxArea = 0; for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) { // If a cell with value 1 is found if (M[i][j] === 1) { const area = BFS(M, i, j, rows, cols); // Maximize the area maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area); } } } return maxArea; } const M = [ [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1] ]; console.log(largestRegion(M)); Time complexity: O(rows * cols). In the worst case, all the cells will be visited so the time complexity is O(rows * cols).
Auxiliary Space: O(rows + cols), in the worst case when all the cells are 1, then the size of queue can grow up to (rows + cols).
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem