AVL tree is a self-balancing Binary Search Tree (BST) where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees cannot be more than one for all nodes.
Insertion in an AVL Tree follows the same basic rules as in a Binary Search Tree (BST):
- A new key is placed in its correct position based on BST rules (left < node < right).
However, after the insertion, the balance factor of each node is checked during the path back up to the root. If any node becomes unbalanced (i.e., its balance factor becomes less than -1 or greater than +1), a rotation is required to restore the AVL property.
In an AVL Tree, rotations are used to maintain balance after insertion or deletion of nodes. The balance factor must be between -1 and 1 for all nodes. When this balance is violated, one of the following four types of rotations is applied:
Example of AVL Tree:

The above tree is AVL tree because the differences between the heights of left and right subtrees for every node are lies in the range -1 to +1.
Example of a Tree that is NOT an AVL Tree:
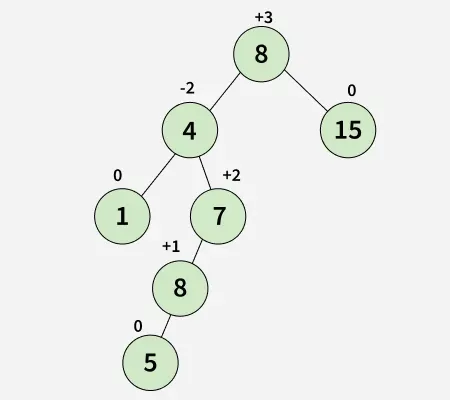
The above tree is not an AVL tree because the differences between the heights of the left and right subtrees for 8 and 12 are greater than 1.
Why AVL Trees? Most of the BST operations (e.g., search, max, min, insert, delete, floor and ceiling) take O(h) time where h is the height of the BST. The cost of these operations may become O(n) for a skewed Binary tree. If we make sure that the height of the tree remains O(log(n)) after every insertion and deletion, then we can guarantee an upper bound of O(log(n)) for all these operations. The height of an AVL tree is always O(log(n)) where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
Insertion in AVL Tree:
To make sure that the given tree remains AVL after every insertion, we must augment the standard BST insert operation to perform some re-balancing. Following are two basic operations that can be performed to balance a BST without violating the BST property (keys(left) < key(root) < keys(right)).
- Left Rotation
- Right Rotation
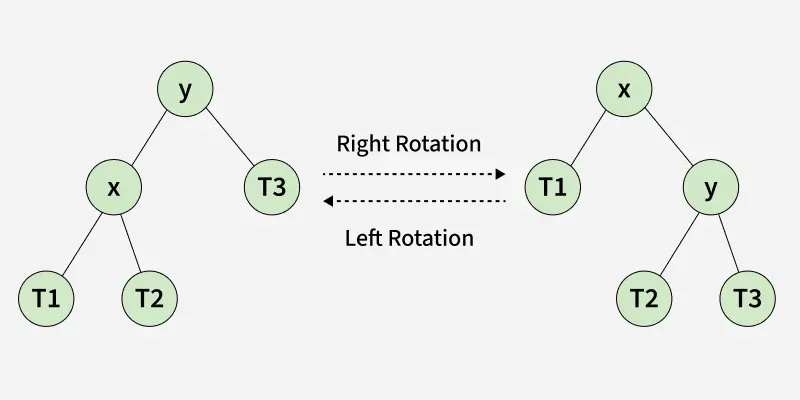 keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3)
keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3)Illustration of Insertion at AVL Tree:
Approach: The idea is to use recursive BST insert, after insertion, we get pointers to all ancestors one by one in a bottom-up manner. So we don't need a parent pointer to travel up. The recursive code itself travels up and visits all the ancestors of the newly inserted node.
Follow the steps mentioned below to implement the idea:
- Perform the normal BST insertion.
- The current node must be one of the ancestors of the newly inserted node. Update the height of the current node.
- Get the balance factor (left subtree height - right subtree height) of the current node.
- If the balance factor is greater than 1, then the current node is unbalanced and we are either in the Left Left case or left Right case. To check whether it is left left case or not, compare the newly inserted key with the key in the left subtree root.
- If the balance factor is less than -1, then the current node is unbalanced and we are either in the Right Right case or Right-Left case. To check whether it is the Right Right case or not, compare the newly inserted key with the key in the right subtree root.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++14 // C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // An AVL tree node struct Node { int key; Node *left; Node *right; int height; Node(int k) { key = k; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; height = 1; } }; // A utility function to // get the height of the tree int height(Node *N) { if (N == nullptr) return 0; return N->height; } // A utility function to right // rotate subtree rooted with y Node *rightRotate(Node *y) { Node *x = y->left; Node *T2 = x->right; // Perform rotation x->right = y; y->left = T2; // Update heights y->height = 1 + max(height(y->left), height(y->right)); x->height = 1 + max(height(x->left), height(x->right)); // Return new root return x; } // A utility function to left rotate // subtree rooted with x Node *leftRotate(Node *x) { Node *y = x->right; Node *T2 = y->left; // Perform rotation y->left = x; x->right = T2; // Update heights x->height = 1 + max(height(x->left), height(x->right)); y->height = 1 + max(height(y->left), height(y->right)); // Return new root return y; } // Get balance factor of node N int getBalance(Node *N) { if (N == nullptr) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); } // Recursive function to insert a key in // the subtree rooted with node Node* insert(Node* node, int key) { // Perform the normal BST insertion if (node == nullptr) return new Node(key); if (key < node->key) node->left = insert(node->left, key); else if (key > node->key) node->right = insert(node->right, key); else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node; // Update height of this ancestor node node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); // Get the balance factor of this ancestor node int balance = getBalance(node); // If this node becomes unbalanced, // then there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && key < node->left->key) return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && key > node->right->key) return leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && key > node->left->key) { node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); } // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && key < node->right->key) { node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); } // Return the (unchanged) node pointer return node; } // A utility function to print // preorder traversal of the tree void preOrder(Node *root) { if (root != nullptr) { cout << root->key << " "; preOrder(root->left); preOrder(root->right); } } // Driver Code int main() { Node *root = nullptr; // Constructing tree given in the above figure root = insert(root, 10); root = insert(root, 20); root = insert(root, 30); root = insert(root, 40); root = insert(root, 50); root = insert(root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / \ 20 40 / \ \ 10 25 50 */ // Preorder traversal preOrder(root); return 0; } // C program to insert a node in AVL tree #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> // An AVL tree node struct Node { int key; struct Node *left; struct Node *right; int height; }; // A utility function to get the height of the tree int height(struct Node *N) { if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; } // A utility function to get maximum of two integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b)? a : b; } /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and NULL left and right pointers. */ struct Node* newNode(int key) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; // new node is initially added at leaf return(node); } // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y // See the diagram given above. struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y) { struct Node *x = y->left; struct Node *T2 = x->right; // Perform rotation x->right = y; y->left = T2; // Update heights y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; // Return new root return x; } // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x // See the diagram given above. struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x) { struct Node *y = x->right; struct Node *T2 = y->left; // Perform rotation y->left = x; x->right = T2; // Update heights x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; // Return new root return y; } // Get Balance factor of node N int getBalance(struct Node *N) { if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); } // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted // with node and returns the new root of the subtree. struct Node* insert(struct Node* node, int key) { /* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */ if (node == NULL) return(newNode(key)); if (key < node->key) node->left = insert(node->left, key); else if (key > node->key) node->right = insert(node->right, key); else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node; /* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */ node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor node to check whether this node became unbalanced */ int balance = getBalance(node); // If this node becomes unbalanced, then // there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && key < node->left->key) return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && key > node->right->key) return leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && key > node->left->key) { node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); } // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && key < node->right->key) { node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(struct Node *root) { if(root != NULL) { printf("%d ", root->key); preOrder(root->left); preOrder(root->right); } } /* Driver program to test above function*/ int main() { struct Node *root = NULL; /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ root = insert(root, 10); root = insert(root, 20); root = insert(root, 30); root = insert(root, 40); root = insert(root, 50); root = insert(root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / \ 20 40 / \ \ 10 25 50 */ // Preorder traversal preOrder(root); return 0; } // Java program to insert a node in AVL tree import java.util.*; class Node { int key; Node left; Node right; int height; Node(int k) { key = k; left = null; right = null; height = 1; } } class GfG { // A utility function to get the // height of the tree static int height(Node N) { if (N == null) return 0; return N.height; } // A utility function to right rotate // subtree rooted with y static Node rightRotate(Node y) { Node x = y.left; Node T2 = x.right; // Perform rotation x.right = y; y.left = T2; // Update heights y.height = 1 + Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)); x.height = 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)); // Return new root return x; } // A utility function to left rotate // subtree rooted with x static Node leftRotate(Node x) { Node y = x.right; Node T2 = y.left; // Perform rotation y.left = x; x.right = T2; // Update heights x.height = 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)); y.height = 1 + Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)); // Return new root return y; } // Get balance factor of node N static int getBalance(Node N) { if (N == null) return 0; return height(N.left) - height(N.right); } // Recursive function to insert a key in // the subtree rooted with node static Node insert(Node node, int key) { // Perform the normal BST insertion if (node == null) return new Node(key); if (key < node.key) node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key > node.key) node.right = insert(node.right, key); else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node; // Update height of this ancestor node node.height = 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); // Get the balance factor of this ancestor node int balance = getBalance(node); // If this node becomes unbalanced, // then there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key) return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key) return leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); } // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } // Return the (unchanged) node pointer return node; } // A utility function to print preorder // traversal of the tree static void preOrder(Node root) { if (root != null) { System.out.print(root.key + " "); preOrder(root.left); preOrder(root.right); } } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = null; // Constructing tree given in the above figure root = insert(root, 10); root = insert(root, 20); root = insert(root, 30); root = insert(root, 40); root = insert(root, 50); root = insert(root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / \ 20 40 / \ \ 10 25 50 */ // Preorder traversal preOrder(root); } } class Node: def __init__(self, key): self.key = key self.left = None self.right = None self.height = 1 # A utility function to get the # height of the tree def height(node): if not node: return 0 return node.height # A utility function to right rotate # subtree rooted with y def right_rotate(y): x = y.left T2 = x.right # Perform rotation x.right = y y.left = T2 # Update heights y.height = 1 + max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) x.height = 1 + max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) # Return new root return x # A utility function to left rotate # subtree rooted with x def left_rotate(x): y = x.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = x x.right = T2 # Update heights x.height = 1 + max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) y.height = 1 + max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) # Return new root return y # Get balance factor of node N def get_balance(node): if not node: return 0 return height(node.left) - height(node.right) # Recursive function to insert a key in # the subtree rooted with node def insert(node, key): # Perform the normal BST insertion if not node: return Node(key) if key < node.key: node.left = insert(node.left, key) elif key > node.key: node.right = insert(node.right, key) else: # Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node # Update height of this ancestor node node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)) # Get the balance factor of this ancestor node balance = get_balance(node) # If this node becomes unbalanced, # then there are 4 cases # Left Left Case if balance > 1 and key < node.left.key: return right_rotate(node) # Right Right Case if balance < -1 and key > node.right.key: return left_rotate(node) # Left Right Case if balance > 1 and key > node.left.key: node.left = left_rotate(node.left) return right_rotate(node) # Right Left Case if balance < -1 and key < node.right.key: node.right = right_rotate(node.right) return left_rotate(node) # Return the (unchanged) node pointer return node # A utility function to print preorder # traversal of the tree def pre_order(root): if root: print(root.key, end=" ") pre_order(root.left) pre_order(root.right) # Driver code root = None # Constructing tree given in the above figure root = insert(root, 10) root = insert(root, 20) root = insert(root, 30) root = insert(root, 40) root = insert(root, 50) root = insert(root, 25) # The constructed AVL Tree would be # 30 # / \ # 20 40 # / \ \ # 10 25 50 # Preorder traversal pre_order(root)
using System; class Node { public int Key; public Node Left; public Node Right; public int Height; public Node(int key) { Key = key; Left = null; Right = null; Height = 1; } } public class GfG { // A utility function to get // the height of the tree static int Height(Node node) { if (node == null) return 0; return node.Height; } // A utility function to right rotate // subtree rooted with y static Node RightRotate(Node y) { Node x = y.Left; Node T2 = x.Right; // Perform rotation x.Right = y; y.Left = T2; // Update heights y.Height = 1 + Math.Max(Height(y.Left), Height(y.Right)); x.Height = 1 + Math.Max(Height(x.Left), Height(x.Right)); // Return new root return x; } // A utility function to left rotate // subtree rooted with x static Node LeftRotate(Node x) { Node y = x.Right; Node T2 = y.Left; // Perform rotation y.Left = x; x.Right = T2; // Update heights x.Height = 1 + Math.Max(Height(x.Left), Height(x.Right)); y.Height = 1 + Math.Max(Height(y.Left), Height(y.Right)); // Return new root return y; } // Get balance factor of node N static int GetBalance(Node node) { if (node == null) return 0; return Height(node.Left) - Height(node.Right); } // Recursive function to insert a key in the // subtree rooted with node static Node Insert(Node node, int key) { // Perform the normal BST insertion if (node == null) return new Node(key); if (key < node.Key) node.Left = Insert(node.Left, key); else if (key > node.Key) node.Right = Insert(node.Right, key); else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node; // Update height of this ancestor node node.Height = 1 + Math.Max(Height(node.Left), Height(node.Right)); // Get the balance factor of this ancestor node int balance = GetBalance(node); // If this node becomes unbalanced, // then there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && key < node.Left.Key) return RightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && key > node.Right.Key) return LeftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && key > node.Left.Key) { node.Left = LeftRotate(node.Left); return RightRotate(node); } // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && key < node.Right.Key) { node.Right = RightRotate(node.Right); return LeftRotate(node); } // Return the (unchanged) node pointer return node; } // A utility function to print preorder // traversal of the tree static void PreOrder(Node root) { if (root != null) { Console.Write(root.Key + " "); PreOrder(root.Left); PreOrder(root.Right); } } // Driver code public static void Main() { Node root = null; // Constructing tree given in the above figure root = Insert(root, 10); root = Insert(root, 20); root = Insert(root, 30); root = Insert(root, 40); root = Insert(root, 50); root = Insert(root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / \ 20 40 / \ \ 10 25 50 */ // Preorder traversal PreOrder(root); } } class Node { constructor(key) { this.key = key; this.left = null; this.right = null; this.height = 1; } } // A utility function to get // the height of the tree function height(node) { if (node === null) { return 0; } return node.height; } // A utility function to right rotate // subtree rooted with y function rightRotate(y) { const x = y.left; const T2 = x.right; // Perform rotation x.right = y; y.left = T2; // Update heights y.height = 1 + Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)); x.height = 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)); // Return new root return x; } // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x function leftRotate(x) { const y = x.right; const T2 = y.left; // Perform rotation y.left = x; x.right = T2; // Update heights x.height = 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)); y.height = 1 + Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)); // Return new root return y; } // Get balance factor of node function getBalance(node) { if (node === null) { return 0; } return height(node.left) - height(node.right); } // Recursive function to insert a key in // the subtree rooted with node function insert(node, key) { // Perform the normal BST insertion if (node === null) { return new Node(key); } if (key < node.key) { node.left = insert(node.left, key); } else if (key > node.key) { node.right = insert(node.right, key); } else { // Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node; } // Update height of this ancestor node node.height = 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); // Get the balance factor of this ancestor node const balance = getBalance(node); // If this node becomes unbalanced, then there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key) { return rightRotate(node); } // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key) { return leftRotate(node); } // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); } // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } // Return the (unchanged) node pointer return node; } // A utility function to print preorder // traversal of the tree function preOrder(root) { if (root !== null) { console.log(root.key + " "); preOrder(root.left); preOrder(root.right); } } // Driver code let root = null; // Constructing tree given in the above figure root = insert(root, 10); root = insert(root, 20); root = insert(root, 30); root = insert(root, 40); root = insert(root, 50); root = insert(root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / \ 20 40 / \ \ 10 25 50 */ // Preorder traversal preOrder(root); Time Complexity: O(logn), for Insertion
Auxiliary Space: O(logn), for recursion call stack as we have written a recursive method to insert
The rotation operations (left and right rotate) take constant time as only a few pointers are being changed there. Updating the height and getting the balance factor also takes constant time. So the time complexity of the AVL insert remains the same as the BST insert which is O(h) where h is the height of the tree. Since the AVL tree is balanced, the height is O(logn). So time complexity of AVL insert is O(logn).
Comparison with Red Black Tree:
The AVL tree and other self-balancing search trees like Red Black are useful to get all basic operations done in O(logn) time. The AVL trees are more balanced compared to Red-Black Trees, but they may cause more rotations during insertion and deletion. So if your application involves many frequent insertions and deletions, then Red Black trees should be preferred. And if the insertions and deletions are less frequent and search is the more frequent operation, then the AVL tree should be preferred over Red Black Tree.
AVL Tree | Set 2 (Deletion)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem