Introduction to Kali Linux
Last Updated : 19 Nov, 2025
Kali Linux is a Debian-based open-source Linux distribution specially designed for cybersecurity professionals and ethical hackers. Developed and maintained by Offensive Security, Kali Linux is one of the most popular platforms for ethical hacking and information security training.
It provides a vast collection of pre-installed tools for tasks such as:
- Penetration testing
- Security auditing
- Digital forensics
- Network monitoring
- Reverse engineering
Key Features
Given below the mainly key features of Kali Linux:
- Includes 600+ built-in tools for ethical hacking, penetration testing, digital forensics, and network security tasks.
- Eliminates the need for manual installation, giving users an instant, ready-to-use security environment.
2. Free and Open Source
- Completely free to download, use, customize, and distribute under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
- Users and developers can modify the system to suit their needs, promoting transparency and flexibility.
- Runs efficiently on desktops, laptops, VMs, cloud platforms, and ARM devices like Raspberry Pi.
- Designed to be lightweight, ensuring smooth performance even on low-spec systems.
4. Live Boot and Customization
- Can be booted directly from a USB drive without installing it on the system.
- Allows users to create customized Kali ISO images with selected tools and configurations.
5. Regular Updates and Strong Community Support
- Frequently updated with the latest tools, patches, and security improvements.
- Supported by a large cybersecurity community and the Offensive Security team for continuous development.
Deploy Kali Linux for penetration testing in a secure, high-performance environment with Hostinger’s VPS hosting solutions. Benefit from NVMe SSD storage, AMD EPYC processors, and a 300 Mb/s network for faster performance and superior uptime. With a one-click app installer, you can set up Kali Linux quickly. Managed VPS hosting ensures expert server support, so you can focus on your penetration testing tasks while leaving maintenance to the professionals.
History and Development
Kali Linux originated from BackTrack Linux and was officially released in 2013 as a rebuilt, modern, and more secure penetration-testing distribution developed by Offensive Security.
1. Origin
- Kali Linux evolved from BackTrack, an earlier security-focused Linux distribution used widely in penetration testing.
- BackTrack was based on Ubuntu, but Kali Linux was rebuilt completely for better structure, performance, and flexibility.
- The transition created a cleaner, more professional, and maintainable platform for cybersecurity work.
2. Initial Release
- Officially launched in March 2013 by Offensive Security.
- Introduced major improvements over BackTrack in usability, stability, and tool integration.
- Marked the beginning of a modern, standardized penetration-testing environment.
3. Base System
- Built on the Debian Testing repository to ensure frequent updates and newer packages.
- Provides a balance between stability and cutting-edge features.
- Ensures efficient compatibility with tools and hardware.
4. Developer
- Maintained by Offensive Security, a global leader in cybersecurity certifications.
- Ensures continuous updates, security patches, and reliable tool maintenance.
- Backed by experts who design real-world penetration-testing training.
5. Goal
- Created to offer a complete, ready-to-use toolkit for ethical hackers and penetration testers.
- Includes preinstalled tools for network attacks, digital forensics, wireless testing, and exploitation.
- Designed to support both beginners and professionals in cybersecurity fields.
Basic Commands in Kali Linux
Kali Linux uses standard Linux terminal commands to manage tools, update the system, and configure services. Mastering these commands ensures a faster, smoother, and more efficient workflow for cybersecurity operations.
[Command 1]: Update Package Lists
sudo apt update
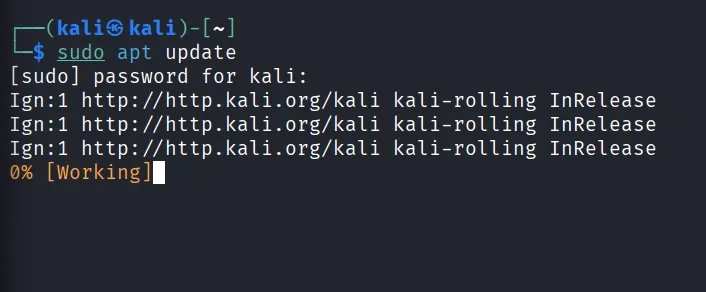
- Fetches the latest list of available packages and their versions from repositories (but doesn’t install them yet).
[Command 2]: Upgrade Installed Packages
sudo apt upgrade
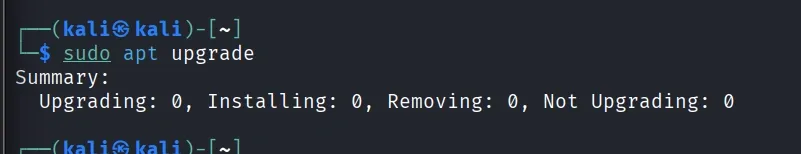
- Installs the latest versions of all installed packages and security updates.
- By using
-y flag automatically confirms the upgrade process.
sudo apt install <tool name>
Example:
sudo apt install nmap
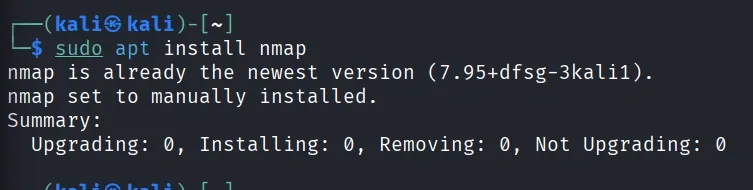
- Installs new tools from the Kali Linux repositories - here, the Nmap network scanner tool.
[Command 4]: Start a System Service
sudo service <service_name> start
Example:
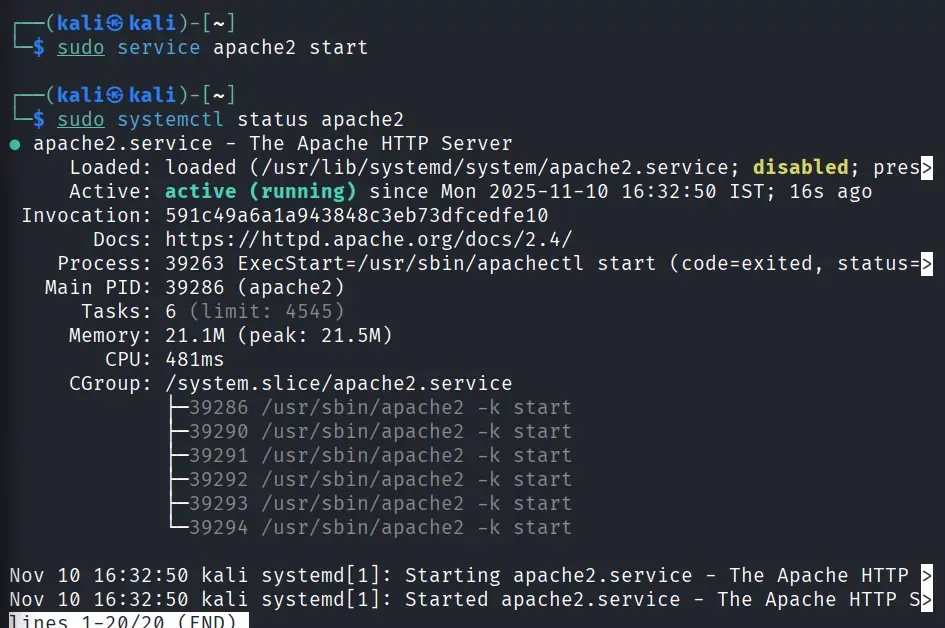
sudo service apache2 start
- Starts a specific service - here, the Apache web server.
- You can verify it’s running with:
sudo systemctl status apache2
[Command 5]: View Network Interface Details
ifconfig
Alternative:
ip a
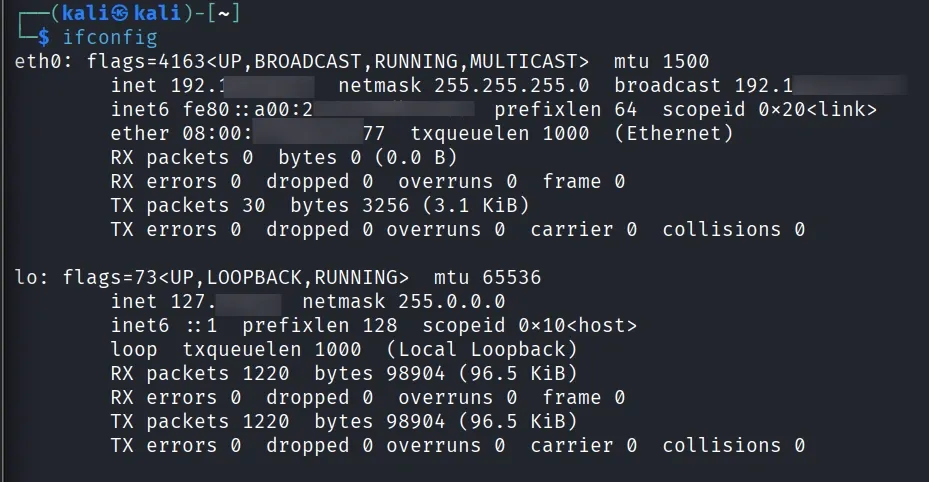
- Displays all network interfaces, IP addresses, and their status — useful for identifying network configurations before scanning or testing.
System Requirements for Kali Linux
Kali Linux needs a moderate hardware setup to run efficiently, ensuring smooth performance for security tools. It requires adequate CPU power, memory, storage, and internet connectivity to support updates and operations.
- Processor (CPU): Dual-core Intel or AMD processor for smooth performance.
- Memory (RAM): Minimum 2 GB, though 4 GB or more is recommended for better multitasking and tool execution.
- Storage (Disk Space): At least 20 GB of free space required for installation and tool storage.
- Bootable Media: 8 GB or larger USB drive needed to create a bootable Kali installer.
- Network Connection: Stable internet connection for system updates, package installation, and tool downloads.
Desktop Environments in Kali Linux
Kali Linux offers multiple desktop environments (DEs), giving users the flexibility to choose between performance, appearance, and system resource usage.
1. Xfce(Default)
- Lightweight, fast, and stable, making it ideal for both beginners and professionals.
- Uses minimal system resources, ensuring smooth performance even on older hardware.
2. GNOME
- Provides a modern, elegant interface with a clean and user-friendly design.
- Offers strong integration and productivity features, suitable for daily use.
3. KDE Plasma
- Highly customizable with extensive visual and functional personalization options.
- Feature-rich environment recommended for users who prefer a polished and dynamic experience.
4. LXDE
- Extremely lightweight, making it perfect for low-end or older systems.
- Prioritizes speed and simplicity, with minimal resource consumption.
Kali Linux Usage Guidelines
Kali Linux must be used strictly for ethical, authorized, and educational purposes. Any misuse or unauthorized hacking is illegal and punishable by law.
Ethical and Educational Use Only
- Kali Linux is created for ethical hacking, cybersecurity learning, and legitimate security research.
- It must never be used for malicious, harmful, or unauthorized activities.
Obtain Permission Before Testing
- Always get written consent or explicit authorization before testing any system or network.
- Penetration testing without permission is considered illegal access.
Unauthorized Hacking is Illegal
- Attacking or accessing systems without permission violates cybersecurity laws.
- Such actions can lead to heavy penalties, fines, or imprisonment.
Use in a Safe, Controlled Environment
- Conduct all practice work in a secure lab setup using tools like VirtualBox, VMware, or isolated test systems.
- Avoid experimenting on real networks or devices you do not own.
Be a Responsible Security Professional
- Follow ethical hacking guidelines and respect user privacy while conducting security work.
- Use your skills to protect systems and contribute positively to the cybersecurity community.
Explore
Getting Started with Linux
Installation with Linux
Linux Commands
Linux File System
Linux Kernel
Linux Networking Tools
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting
Linux Administrator System