Implementation of Elastic Net Regression From Scratch
Last Updated : 05 Aug, 2025
Elastic Net Regression is a type of linear regression that adds two types of penalties, L1 (from Lasso) and L2 (from Ridge) to its cost function. This helps picking out important features by setting some coefficients to zero and also handle situations where some features are highly similar or correlated. This makes the model less likely to overfit and more stable, especially when working with lots of features or data where some variables are related to each other.
In this article we will implement Elastic Net Regression From Scratch in python.
Step 1: Import Libraries
Here we will use numpy, pandas, scikit-learn and matplotlib.
Python import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Step 2: Build the Elastic Net Regression Class
- init: Initializes learning rate, iterations and penalty strengths.
- fit: Initializes weights, learns via gradient descent.
- update_weights: Computes gradients, applies L1 and L2 penalties, updates parameters.
- predict: Returns predictions from input features.
Python class ElasticRegression: def __init__(self, learning_rate, iterations, l1_penalty, l2_penalty): self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.iterations = iterations self.l1_penalty = l1_penalty self.l2_penalty = l2_penalty def fit(self, X, Y): self.m, self.n = X.shape self.W = np.zeros(self.n) self.b = 0 self.X = X self.Y = Y for i in range(self.iterations): self.update_weights() return self def update_weights(self): Y_pred = self.predict(self.X) dW = np.zeros(self.n) for j in range(self.n): l1_grad = self.l1_penalty if self.W[j] > 0 else -self.l1_penalty dW[j] = ( -2 * (self.X[:, j]).dot(self.Y - Y_pred) + l1_grad + 2 * self.l2_penalty * self.W[j] ) / self.m db = -2 * np.sum(self.Y - Y_pred) / self.m self.W -= self.learning_rate * dW self.b -= self.learning_rate * db return self def predict(self, X): return X.dot(self.W) + self.b
Step 3: Data Preparation
- The CSV file is loaded. To download the used dataset, click here.
- Features and target variables are separated.
- Data is split into training and test sets.
Python df = pd.read_csv("salary_data.csv") X = df.iloc[:, :-1].values Y = df.iloc[:, 1].values X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split( X, Y, test_size=1 / 3, random_state=0) Step 4: Model Initialization and Training
- The Elastic Net Regression model is created with specified parameters.
- The model is trained on the training data.
Python model = ElasticRegression( iterations=1000, learning_rate=0.01, l1_penalty=500, l2_penalty=1 ) model.fit(X_train, Y_train)
Step 5: Prediction and Evaluation
- Predictions are made for the test set.
- The first few predicted and actual salary values and the model parameters, are printed for inspection.
Python Y_pred = model.predict(X_test) print("Predicted values ", np.round(Y_pred[:3], 2)) print("Real values ", Y_test[:3]) print("Trained W ", round(model.W[0], 2)) print("Trained b ", round(model.b, 2)) Output:
Predicted values [ 40837.61 122887.43 65079.6 ]
Real values [ 37731 122391 57081]
Trained W 9323.84
Trained b 26851.84
Step 6: Visualization
Python plt.scatter(X_test, Y_test, color="green") plt.plot(X_test, Y_pred, color="orange") plt.title("Salary vs Experience") plt.xlabel("Years of Experience") plt.ylabel("Salary") plt.show() Output:
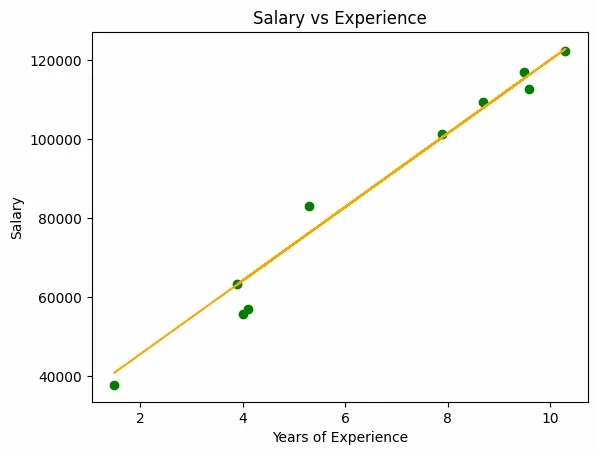 Visualization of Results
Visualization of ResultsElastic Net Regression effectively balances feature selection and model stability by combining Lasso and Ridge regularization. It’s a practical choice for handling datasets with many or highly correlated features, leading to more reliable and interpretable results.
What is Elastic Net Regression in Machine Learning
Explore
Machine Learning Basics
Python for Machine Learning
Feature Engineering
Supervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning
Model Evaluation and Tuning
Advanced Techniques
Machine Learning Practice