Mongoose Populate() Method
Last Updated : 10 Oct, 2025
The populate() method in Mongoose automatically replaces a referenced field (ObjectId) with the actual document from another collection. It makes working with related data easier by fetching linked documents in a single query, eliminating the need to manually query multiple collections.
How Mongoose populate() Works
- References: Replaces ObjectId fields with actual documents from the referenced collection using the ref option in the schema.
- Field Target: The argument passed to populate() specifies the reference field (e.g., postedBy).
- Multiple Fields: Chain populate() to populate multiple fields in one query.
- Selective Fields: Populate only specific fields from the referenced document using field selection.
- Nested Population: Supports deep population for nested references through chained populate() calls.
Now let's understand this with the help of example:
JavaScript const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ username: String, email: String }) const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ title: String, postedBy: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: "User" } }) const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema); const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema); module.exports = { Source, Destination, User, Post } In this example:
- Define two Mongoose schemas: User and Post.
- In the Post schema, add a field postedBy.
- Set postedBy to reference a document from the User model.
- This establishes a relationship between posts and their corresponding users.
Implementation Of Populate() Method
Here are the steps to implement populate() method:
Step 1: Install mongoose
If we do not have Mongoose, start by installing Mongoose in your Node.js project
npm install mongoose
Step 2: Set Up Your Database Connection
In your main.js file, establish a connection to the MongoDB database.
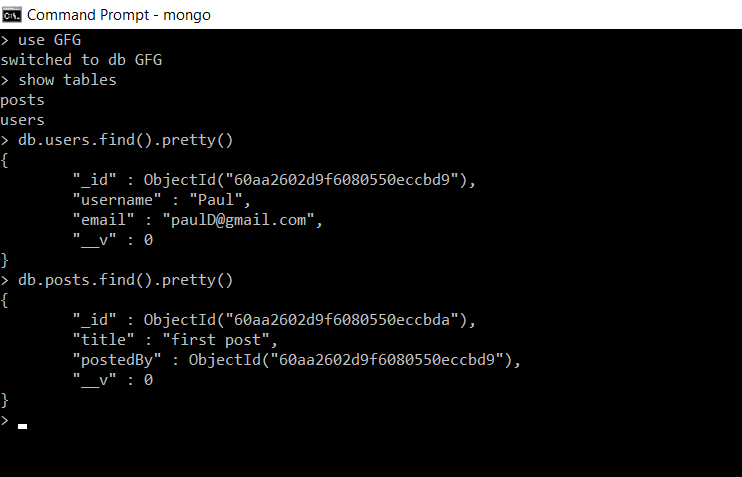
JavaScript const mongoose = require('mongoose'); // Connecting to database mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/GFG', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, useFindAndModify: false }); Database: Initially we have two collections users and posts in our database GFG. And each collection contains a single document.
Step 3: Query Without Using Populate()
We will perform the query to find all the posts without using populate() method. Create a folder and add the file main.js which is shown below:
JavaScript // Creating Schemas const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ username: String, email: String }) const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ title: String, postedBy: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: "User" } }) // Creating models from userSchema and postSchema const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema); const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema); // Query to find and show all the posts Post.find() .then(p => console.log(p)) .catch(error => console.log(error)); Steps to run main.js using the below command:
node main.js
Output:
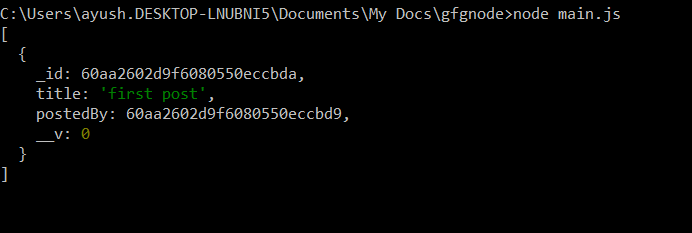 Mongoose Populate() Method
Mongoose Populate() MethodIn this example:
- You fetch documents from the Post collection.
- The postedBy field in each post contains only the ObjectId of the user.
- The query does not retrieve the full user details from the User collection.
- This means you only have a reference, not the complete user document.
Step 4: Query Using populate()
We will perform the query to find all the posts using populate() method. To overcome the above problem, populate() method is used to replace the user ObjectId field with the whole document consisting of all the user data. For this we only have to replace the query part in the above code in main.js file with:
Post.find() .populate("postedBy") .then(posts=>console.log(posts)) .catch(error=>console.log(error));Output:
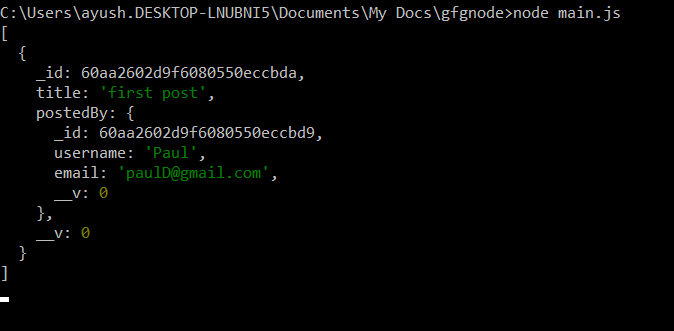 Mongoose Populate() Method
Mongoose Populate() MethodIn this example:
- Replaces the postedBy ObjectId with the full user document.
- Fetches all relevant user data automatically.
- Makes it easier to work with related data in a single query.
- Useful for displaying complete information without separate queries.
Note: In the argument of the populate() method we pass the field we want to populate with the user data.
Explore
MongoDB Tutorial
7 min read
Introduction
Installation
Basics of MongoDB
MongoDB Methods
Comparison Operators
Logical Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Field Update Operators
Array Expression Operators