Seaborn Heatmap - A comprehensive guide
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
A heatmap is a graphical representation of data where individual values are represented by color intensity. It is widely used in data analysis and visualization to identify patterns, correlations and trends within a dataset. Heatmaps in Seaborn can be plotted using the seaborn.heatmap() function, which offers extensive customization options. Let's explore different methods to create and enhance heatmaps using Seaborn.
Example: The following example demonstrates how to create a simple heatmap using the Seaborn library.
Python import numpy as np import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Generating a 10x10 matrix of random numbers data = np.random.randint(1, 100, (10, 10)) sns.heatmap(data) plt.show()
 Basic heatmap
Basic heatmapExplanation: This will produce a heatmap where the intensity of color represents the magnitude of values in the matrix.
Syntax of seaborn.heatmap()
seaborn.heatmap(data, *, vmin=None, vmax=None, cmap=None, center=None, annot_kws=None, linewidths=0, linecolor='white', cbar=True, **kwargs)
Parameters:
- data: A 2D dataset that can be coerced into a NumPy ndarray.
- vmin, vmax: Values to anchor the colormap; if not specified, they are inferred from the data.
- cmap: The colormap for mapping data values to colors.
- center: Value at which to center the colormap when plotting divergent data.
- annot: If True, displays numerical values inside the cells.
- fmt: String format for annotations.
- linewidths: Width of the lines separating cells.
- linecolor: Color of the separating lines.
- cbar: Whether to display a color bar.
Note: All parameters except data are optional.
Returns: returns an object of type matplotlib.axes.Axes
Examples
Example 1: By setting vmin and vmax, we explicitly define the range of values that influence the color scaling in the heatmap. This ensures consistency across multiple heatmaps, preventing extreme values from distorting the visualization.
Python import numpy as np import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt data = np.random.randint(1, 100, (10, 10)) sns.heatmap(data, vmin=30, vmax=70) plt.show()
Output:
 Anchoring the Colormap
Anchoring the ColormapExplanation: The parameters vmin=30 and vmax=70 define the limits of the color scale range. Values lower than 30 are represented by the lowest intensity color, while values higher than 70 are mapped to the highest intensity color.
Example 2: The cmap parameter allows us to modify the color scheme of the heatmap, improving its visual appeal and making it easier to distinguish between different values.
Python import numpy as np import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt data = np.random.randint(1, 100, (10, 10)) sns.heatmap(data, cmap='tab20') plt.show()
Output:
 Choosing a Colormap
Choosing a ColormapExplanation: The argument cmap='tab20' sets a categorical colormap. Sequential colormaps (Blues, Reds, Greens) suit continuous data, while diverging colormaps (coolwarm, RdBu) highlight variations.
Example 3: By setting the center parameter, we ensure that a specific value (such as the mean or median) appears neutral in the colormap. This adjustment makes deviations above and below this value more distinguishable.
Python import numpy as np import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt data = np.random.randint(1, 100, (10, 10)) sns.heatmap(data, cmap='coolwarm', center=50) plt.show()
Output:
 Centering the Colormap
Centering the ColormapExplanation: The center=50 parameter sets 50 as a neutral color. Values above it are shaded in one color (e.g., red) and below in another (e.g., blue), making it useful for highlighting deviations from a reference point.
Advanced customizations in seaborn heatmap
Seaborn's heatmap() function provides various options for customization, allowing users to enhance visualization by adjusting color schemes, labels, scaling and spacing.
Python import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns import numpy as np import matplotlib.colors as mcolors data = np.random.rand(10, 10) * 100 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) # Adjust figure size sns.heatmap( data, xticklabels=list("ABCDEFGHIJ"), # Custom x-axis labels yticklabels=False, # Hide y-axis labels norm=mcolors.LogNorm(), # Logarithmic scaling cmap="coolwarm", # Color map linewidths=0.5 # Cell spacing ) # Add title and labels plt.title("Custom Heatmap", fontsize=16) plt.xlabel("X-axis") plt.ylabel("Y-axis") plt.show() Output:
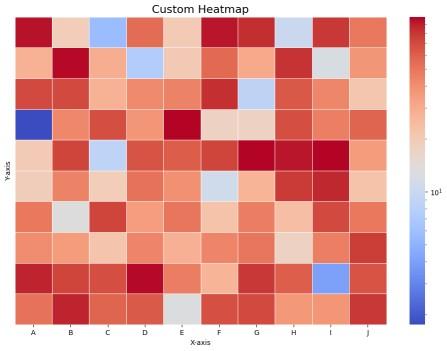 Advanced customization
Advanced customizationExplanation:
- plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) enlarges the figure for better visibility.
- xticklabels=list("ABCDEFGHIJ") replaces default labels with A-J.
- yticklabels=False removes y-axis labels for clarity.
- norm=mcolors.LogNorm() enhances contrast for varied data.
- cmap="coolwarm" uses a blue-to-red gradient.
- linewidths=0.5 adds thin separation lines.
- plt.title("Custom Heatmap", fontsize=16) adds a title with a readable font size.
- plt.xlabel("X-axis") & plt.ylabel("Y-axis") labels the axes for clear understanding.
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice