The SQL IS NULL operator checks whether a column contains a NULL (missing or unknown) value. Since NULL is not the same as zero or an empty string, IS NULL is used in the WHERE clause to filter rows where a value is absent.
- It can check multiple columns using OR.
- COUNT can be used to count NULL values.
- NULL rows can be updated or deleted after filtering with IS NULL.
Example: First, we create a demo SQL database and table, on which we will use the IS NULL command.
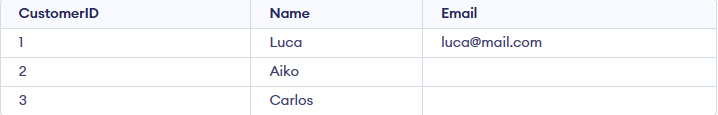
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM Customers
WHERE Email IS NULL;
Output:

SQL IS NULL Examples
Let's look at some examples of the IS NULL operator in SQL. First, we will create a demo SQL database and table, on which we will use the IS NULL operator.
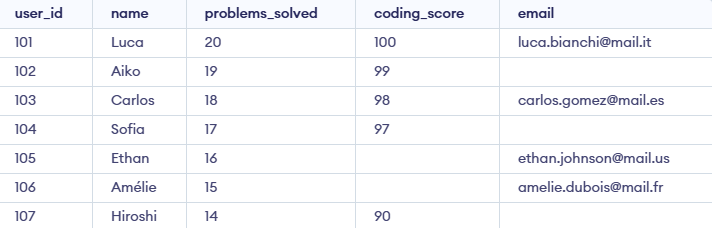
Example 1: IS NULL with WHERE clause
To filter rows where the email column contains NULL, use the IS NULL operator in a WHERE clause:
Query:
SELECT *
FROM Geeksforgeeks
WHERE email IS NULL;
Output:

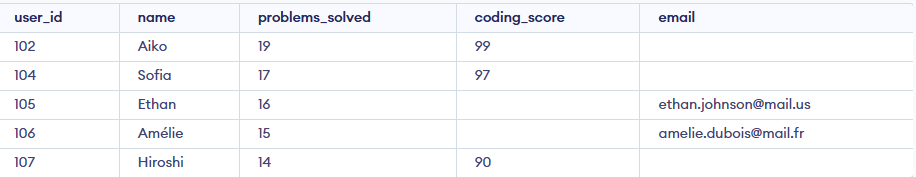
Example 2: IS NULL Operator on Multiple Columns
We can use the IS NULL operator with multiple columns. For instance, to filter rows where either email or coding_score is NULL, use the OR operator:
Query:
SELECT *
FROM Geeksforgeeks
WHERE email IS NULL OR coding_score IS NULL;
Output:
Example 3: IS NULL with COUNT() Function
The COUNT() function can be used to count the number of NULL values in a column. For example, to count how many rows have a NULL value in the coding_score column
SELECT COUNT(*) AS count_empty_coding_score
FROM Geeksforgeeks
WHERE coding_score IS NULL;
Output:

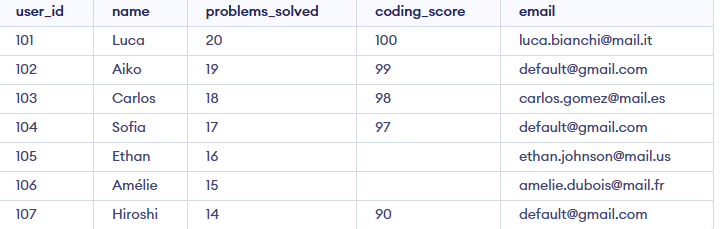
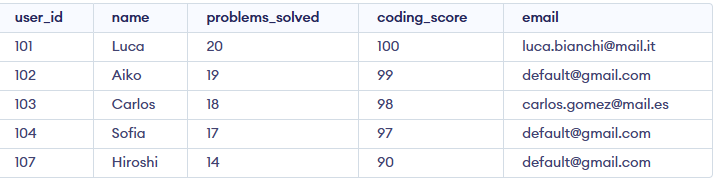
Example 4: IS NULL with UPDATE Statement
We can update NULL values using the IS NULL operator in an UPDATE statement. For example, let's set a default email for all users with a NULL value in the email column
Query:
UPDATE Geeksforgeeks
SET email = 'default@gmail.com'
WHERE email IS NULL;
Output:
Example 5: IS NULL with DELETE Statement
We can also use the IS NULL operator to delete rows where a column contains NULL values. For example, to delete rows where coding_score is NULL
Query:
DELETE FROM Geeksforgeeks
WHERE coding_score IS NULL;
Output:
Note: A NULL value is different from a Zero Value and Blank Spaces. A field that has NULL value means the field was left blank.
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security