SQL TOP, LIMIT, FETCH FIRST Clause
Last Updated : 10 Nov, 2025
The SQL TOP, LIMIT, and FETCH FIRST clauses are used to restrict the number of rows returned by a query. They help in retrieving only a small portion of data from a large table, which makes queries faster and easier to read.
- SQL TOP Clause is used in SQL Server and Sybase to limit the number of records returned.
- SQL LIMIT Clause is utilized in MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
- SQL FETCH FIRST Clause is supported by Oracle, DB2, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server via OFFSET-FETCH.
SQL SELECT TOP Clause
The SELECT TOP clause in SQL only returns the specified number of rows from the table. It is valuable on enormous tables with a large number of records. Returning countless records can affect execution.
The SQL TOP keyword is utilized with these database systems:
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, ... TOP count FROM table_name [WHERE conditions] [ORDER BY expression [ ASC | DESC ]];
- column1, column2: names of columns.
- count: number of records to be fetched.
- WHERE conditions: Optional. Filters the data based on conditions.
- ORDER BY expression: Optional. Sorts the result set in ascending or descending order.
Let’s understand this using an example of SQL SELECT TOP statement. We will use the following table for this example:

Example 1: Using SELECT TOP Clause in SQL
In this example, we will fetch the top 4 rows from the table.
Query:
SELECT TOP 4* FROM Employee;
Output:
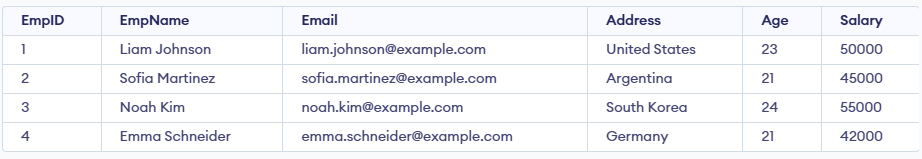
In this query:
- The query retrieves the first 4 rows from the Employee table.
- The TOP 4 clause limits the output to only four records from the result set.
Example 2: SQL SELECT TOP with ORDER BY Clause
In this example, we will use the SQL SELECT TOP clause with ORDER BY clause to sort the data in the results set.
Query
SELECT TOP 4* FROM Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC;
Output:
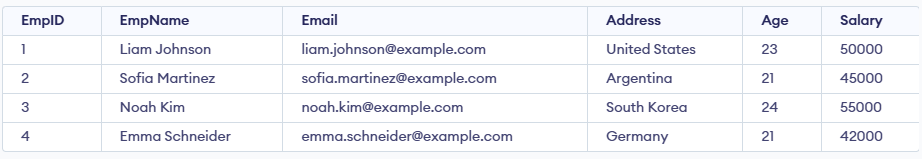
In this query:
- The query selects the top 4 employees from the Employee table.
- The results are sorted by Salary in descending order, so it returns the 4 highest-paid employees.
Example 3: SQL SELECT TOP Clause with WHERE Clause Example
In this example, we will use the SELECT TOP clause with WHERE clause to filter data on specific conditions.
Query:
SELECT TOP 2* FROM Employee WHERE Salary>2000 ORDER BY Salary;
Output:
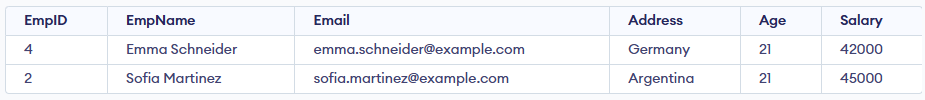
In this query:
- The query selects all employees who satisfy the condition (Salary > 2000).
- Employees with a salary less than 2000 are excluded.
- The results are sorted by Salary in ascending order (default for ORDER BY).
- Finally, the query returns the first 2 rows from the sorted result.
Example 4: SQL SELECT TOP PERCENT Clause Example
The PERCENT keyword is utilized to select the primary and percent of all-out rows. For example,
Query:
SELECT TOP 50 PERCENT* FROM Employee;
Output:
 SQL SELECT TOP PERCENT Clause Example Output
SQL SELECT TOP PERCENT Clause Example OutputIn this query:
- The query selects the first 50% of the total employee records.
- It calculates half of all available rows in the table.
- As a result, the first 3 rows from the table are returned.
Example 5: SQL TOP PERCENT with WHERE Clause Example
We can also include some situations using the TOP PERCENT with the WHERE clause in the above query.
Query:
SELECT TOP 50 PERCENT* FROM Employee WHERE Salary<50000;
Output:
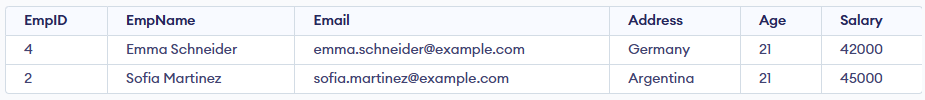
In this query:
- The query selects the top 50% of records from the Employee table.
- It only includes employees whose salary is less than 50,000.
- From those filtered rows, it returns half of the total records.
SQL LIMIT Clause
SQL LIMIT Clause limits the number of results returned in the results set. The LIMIT Clause is utilized with the accompanying database systems:
Example 1: SELECT LIMIT Clause in SQL
In this example, we will use the SELECT LIMIT clause to display only 2 results.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Salary = 45000 LIMIT 2;
Output:

In this query:
- The query selects all employees whose salary is 45,000.
- The LIMIT 2 clause restricts the result to only the first two matching rows.
Example 2: SQL LIMIT with WHERE Clause
The accompanying query selects the initial 4 records from the Employee table with a given condition.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Salary = 45000 LIMIT 2;
Output:

In this query:
- The query filters employees based on the condition Salary = 2000.
- It selects only the records that satisfy this condition.
- The LIMIT 2 clause restricts the result to two records.
- Finally, the query returns the first 2 matching rows.
Example 3: SQL LIMIT With OFFSET Clause
The OFFSET keyword is utilized to indicate beginning rows from where to select rows. For instance,
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee LIMIT 2 OFFSET 2;
Output:
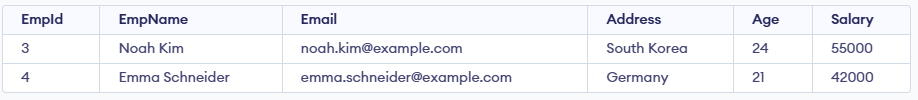
In this query:
- The query retrieves data from the Employee table.
- The OFFSET 2 clause skips the first two rows of the result.
- The LIMIT 2 clause then selects the next two rows after the skipped ones.
- In total, it returns rows 3 and 4 from the table.
SQL FETCH FIRST Clause
SQL FETCH FIRST clause fetches the first given number of rows from the table.
It is supported in database systems like:
Syntax:
The syntax to use the FETCH FIRST clause in SQL is:
SELECT columns FROM table WHERE condition FETCH FIRST n ROWS ONLY;
Example 1: SQL FETCH FIRST Clause
In this example, we will fetch the first 3 rows from the table.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee FETCH FIRST 3 ROWS ONLY;
Output:
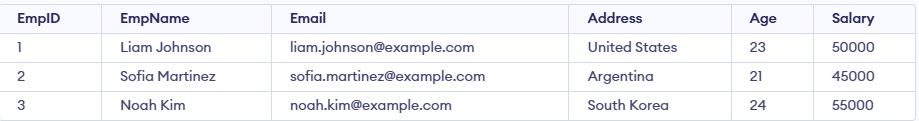
In this query:
- The query retrieves only the first 3 rows from the Employee table.
- It limits the number of rows returned using the FETCH FIRST clause.
- Additional conditions can be applied using FETCH FIRST PERCENT or a WHERE clause to refine the results.
Example 2: SQL FETCH FIRST PERCENT
In this example, we will fetch first 50% of the data from the table.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee FETCH FIRST (SELECT CEIL(COUNT(*) / 2) FROM Employee) ROWS ONLY;
Output:

In this query:
- The query retrieves records from the Employee table.
- The subquery (SELECT CEIL(COUNT(*) / 2) FROM Employee) calculates half of the total rows, rounded up.
- The FETCH FIRST clause then limits the result to that number of rows.
- In short, it returns the top 50% of rows from the Employee table.
Example 3: SQL FETCH FIRST with WHERE Clause
The "FETCH FIRST" syntax is not supported in MySQL. The correct syntax for limiting the number of rows in MySQL is by using the LIMIT clause.
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Salary = 45000 FETCH FIRST 1 ROW ONLY;
Output:

In this query:
- The query selects employees whose salary is 45,000.
- The FETCH FIRST 1 ROW ONLY clause returns only the first matching row from the result set.
SQL - TOP, LIMIT, FETCH FIRST Clause
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security