Agile Methodology in Software Testing
⚡ Smart Summary
Agile Methodology in Software Testing involves continuous iteration of development and testing throughout the software lifecycle, ensuring concurrent activity and rapid adaptation to evolving requirements, delivering minimally shippable features in short cycles.

What is Agile Methodology in Testing?
Agile Methodology is a practice that promotes continuous iteration of development and testing throughout the software development lifecycle of the project. In the Agile model in software testing, both development and testing activities are concurrent, unlike the Waterfall model.

👉 Enroll for Free Live Software Testing Project
Core Principles and Values of Agile Testing
Agile Testing is guided by a set of principles and values that foster collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement throughout development.
Customer Collaboration: Agile testing emphasizes close interaction with customers to ensure the software meets real-world needs.
Continuous Testing: Testing happens early and throughout development, not just at the end.
Adaptability to Change: Welcomes evolving requirements, promoting flexibility and faster delivery.
Working Software Over Documentation: Focuses on functional results rather than lengthy documentation.
Team Collaboration: Encourages strong communication among developers, testers, and stakeholders.
Constant Feedback: Regular feedback loops help identify and resolve issues quickly.
Simplicity and Efficiency: Prioritizes essential tasks to maximize value and minimize waste.
Sustainable Pace: Promotes balanced workloads to maintain long-term productivity and quality.
Lifecycle of Agile Testing
Here’s a brief explanation of the lifecycle of agile testing:
1. Test Planning
In this initial stage, the agile team defines testing scope, objectives, resources, and timelines. Testers collaborate with developers and stakeholders to align testing goals with sprint requirements.
2. Test Design
Here, testers design test cases, scenarios, and acceptance criteria based on user stories. The focus is on modular, reusable, and automated tests that align with continuous integration principles.
3. Test Execution
Testing happens iteratively alongside development. Testers perform unit, integration, and system tests within each sprint to validate new features and identify defects early.
4. Defect Reporting and Retesting
Any defects found are logged, prioritized, and fixed quickly. Retesting ensures that bug fixes don’t break existing functionality.
5. Regression Testing
Automated regression tests verify that new code changes don’t affect existing modules. This step safeguards product stability across sprints.
6. Test Closure
After the sprint ends, teams review test metrics, document lessons learned, and ensure deliverables meet the Definition of Done.
Agile Process
Check the Agile methodology process given below to deliver successful systems quickly:
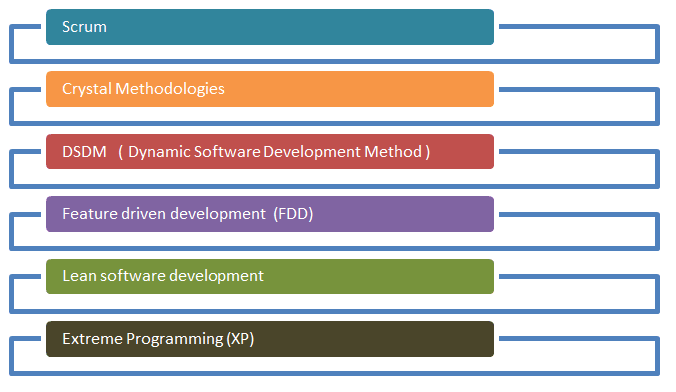
There are various Agile methods present in agile testing, and those are listed below:
Scrum
SCRUM is an agile development method that concentrates specifically on how to manage tasks within a team-based development environment. Basically, Scrum is derived from a concept that occurs during a rugby match. Scrum believes in empowering the development team and advocates working in small teams (say, 7 to 9 members). Agile and Scrum consist of three roles, and their responsibilities are explained as follows:
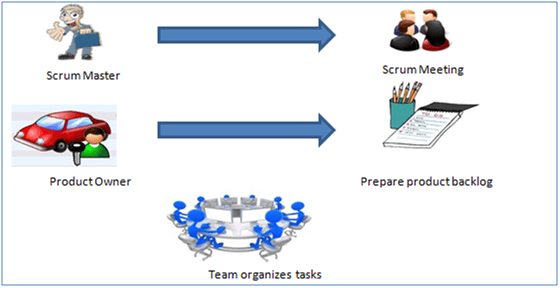
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is responsible for setting up the team, sprint meetings, and removing obstacles to progress.
Product owner
The Product Owner creates the product backlog, prioritizes the backlog, and is responsible for the delivery of the functionality at each iteration.
Scrum Team
Team manages its own work and organizes the work to complete the sprint or cycle.
Product Backlog
This is a repository where requirements are tracked with details on the no of requirements(user stories) to be completed for each release. It should be maintained and prioritized by the Product Owner, and it should be distributed to the Scrum team. The team can also request a new requirement addition, modification, or deletion.
Scrum Practices
Practices are described in detail in this section:
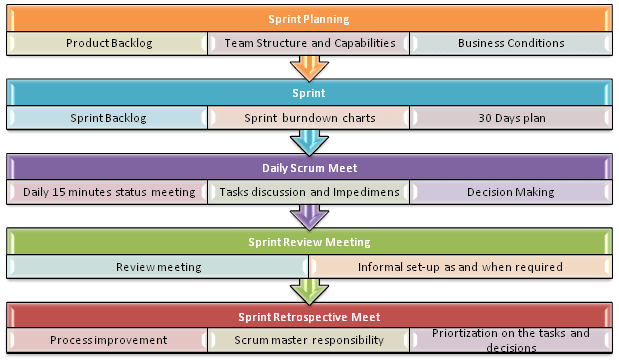
Process flow of Scrum Methodologies:
Process flow of Scrum testing is as follows:
- Each iteration of a scrum is known as a Sprint
- A product backlog is a list where all details are entered to get the end product
- During each Sprint, the top user stories of the Product backlog are selected and turned into the Sprint backlog
- The team works on the defined sprint backlog
- Team checks for the daily work
- At the end of the sprint, the team delivers product functionality
Extreme Programming (XP)
The Extreme Programming technique is very helpful when there are constantly changing demands or requirements from the customers, or when they are not sure about the functionality of the system. It advocates frequent “releases” of the product in short development cycles, which inherently improves the productivity of the system and also introduces a checkpoint where any customer requirements can be easily implemented. The XP develops software, keeping the customer in mind.
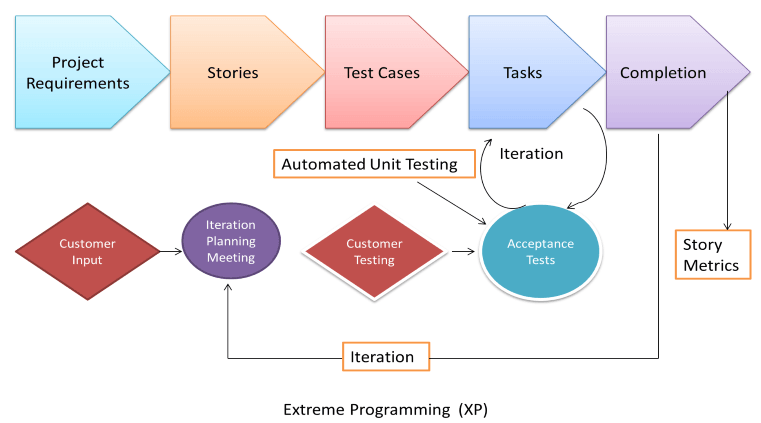
Business requirements are gathered in terms of stories. All those stories are stored in a place called the parking lot.
In this type of methodology, releases are based on shorter cycles called Iterations with a span of a 14-day time period. Each iteration includes phases like coding, unit testing, and system testing, where at each phase, some minor or major functionality will be built into the application.
Phases of Extreme Programming
There are 6 phases available in the Agile XP method, and those are explained as follows:
Planning
- Identification of stakeholders and sponsors
- Infrastructure Requirements
- Security-related information and gathering
- Service Level Agreements and their conditions
Analysis
- Capturing of Stories in the Parking lot
- Prioritize stories in the Parking lot
- Scrubbing of stories for estimation
- Define Iteration SPAN(Time)
- Resource planning for both the Development and QA teams
Design
- Breakdown of tasks
- Test Scenario preparation for each task
- Regression Automation Framework
Execution
- Coding
- Unit Testing
- Execution of Manual test scenarios
- Defect Report generation
- Conversion of Manual to Automation regression test cases
- Mid-iteration review
- End of Iteration review
Wrapping
- Small Releases
- Regression Testing
- Demos and reviews
- Develop new stories based on the need
- Process Improvements based on end-of-iteration review comments
Closure
- Pilot Launch
- Training
- Production Launch
- SLA Guarantee assurance
- Review SOA strategy
- Production Support
There are two storyboards available to track the work on a daily basis, and those are listed below for reference.
Story Cardboard
This is a traditional way of collecting all the stories on a board in the form of sticky notes to track daily XP activities. As this manual activity involves more effort and time, it is better to switch to an online form.
Online Storyboard
The online tool Storyboard can be used to store the stories. Several teams can use it for different purposes.
Crystal Methodologies
Crystal Methodology is based on three concepts
- Chartering: Various activities involved in this phase are creating a development team, performing a preliminary feasibility analysis, developing an initial plan, and fine-tuning the development methodology
- Cyclic delivery: The main development phase consists of two or more delivery cycles, during which the
- Team updates and refines the release plan.
- Implements a subset of the requirements through one or more program test integration iterations
- Integrated product is delivered to real users
- Review of the project plan and adopted development methodology
- Wrap Up: The activities performed in this phase are deployment into the user environment, and deployment reviews and reflections are performed.
Dynamic Software Development Method (DSDM)
DSDM is a Rapid Application Development (RAD) approach to software development and provides an agile project delivery framework. The important aspect of DSDM is that the users are required to be actively involved, and the teams are given the power to make decisions. Frequent delivery of product becomes the active focus with DSDM. The techniques used in DSDM are
- Time Boxing
- MoSCoW Rules
- Prototyping
The DSDM project consists of 7 phases
- Pre-project
- Feasibility Study
- Business Study
- Functional Model Iteration
- Design and build an Iteration
- Implementation
- Post-project
Feature Driven Development (FDD)
This method is focused on “designing & building” features. Unlike other Agile methods in software engineering, FDD describes very specific and short phases of work that have to be accomplished separately per feature. It includes domain walkthrough, design inspection, promote to build, code inspection, and design. FDD develops a product keeping the following things in mind
- Domain Object Modeling
- Development by feature
- Component/ Class Ownership
- Feature Teams
- Inspections
- Configuration Management
- Regular Builds
- Visibility of progress and results
Lean Software Development
The Lean software development method is based on the principle of “Just in time production”. It aims at increasing the speed of software development and decreasing cost. Lean development can be summarized in seven steps.
- Eliminating Waste
- Amplifying learning
- Defer commitment (deciding as late as possible)
- Early delivery
- Empowering the team
- Building Integrity
- Optimize the whole
Kanban
Kanban originally emerged from the Japanese word that means a card containing all the information needed to be done on the product at each stage along its path to completion. This framework or method is widely adopted in software testing, especially in Agile concepts.
What are the Benefits of Agile Testing?
Here’s why agile testing is helpful:
- Early and Continuous Feedback: Testing starts from the beginning of the project, so bugs and design flaws are caught early — before they become expensive disasters.
- Faster Delivery: Testing runs alongside development, enabling quicker releases and ensuring usable software is delivered in shorter, continuous cycles.
- Better Collaboration: Testers, developers, and product owners work closely together, fostering shared understanding and reducing miscommunication.
- Improved Quality: Frequent testing and automation help maintain consistent quality and catch issues early in every iteration.
- Flexibility to Change: Agile testing adapts easily to evolving requirements, allowing teams to pivot without derailing the entire project.
- Higher Customer Satisfaction: Regular feedback loops ensure the end product aligns with user expectations and real-world needs.
How to Overcome the Challenges of Agile Testing?
Here are the best ways to overcome the challenges that appear in agile testing:
- Challenge: Rapid requirement changes make maintaining stable test plans difficult.
Solution: Implement adaptive test strategies with flexible automation frameworks and continuous feedback loops to accommodate evolving requirements efficiently. - Challenge: Short development cycles reduce available time for comprehensive testing.
Solution: Prioritize risk-based testing, automate regression suites, and integrate continuous testing early in the development pipeline. - Challenge: Frequent code changes make maintaining sufficient test coverage difficult.
Solution: Use automated unit and integration tests, supported by continuous integration tools, to ensure consistent coverage and quick validation. - Challenge: Lack of collaboration causes misunderstandings between developers and testers.
Solution: Foster collaboration through daily stand-ups, shared documentation, and cross-functional pairing to align testing objectives with development goals. - Challenge: Managing consistent and accurate test data becomes increasingly challenging.
Solution: Utilize synthetic data generation and version-controlled test datasets to ensure repeatable and reliable test environments. - Challenge: Balancing fast delivery timelines with maintaining high-quality assurance.
Solution: Integrate quality gates within CI/CD pipelines and enforce automated quality checks without slowing down delivery cycles. - Challenge: Agile teams often struggle due to minimal or missing documentation.
Solution: Maintain lightweight, living documentation linked to user stories and test cases to preserve clarity without sacrificing agility. - Challenge: Testing environments often fall out of sync with production setups.
Solution: Adopt containerized environments and configuration management tools to maintain consistent setups across development, testing, and production.
Agile Model Vs Waterfall Model
Agile and Waterfall models are two different methods for the software development process. Though they are different in their approach, both methods are useful at times, depending on the requirement and the type of project.
| Agile Model | Waterfall Model |
|---|---|
| Agile methodology in software testing definition: Agile methodologies propose an incremental and iterative approach to software design | Development of the software flows sequentially from the start point to the end point |
| The Agile process in software testing is broken into individual models that designers work on | The design process is not broken into individual models |
| The customer has early and frequent opportunities to look at the product and make decisions and changes to the project | The customer can only see the product at the end of the project |
| Agile model in testing is considered unstructured compared to the waterfall model | Waterfall models are more secure because they are so plan-oriented |
| Small projects can be implemented very quickly. For large projects, it is difficult to estimate the development time | All sorts of projects can be estimated and completed |
| The error can be fixed in the middle of the project | Only at the end is the whole product tested. If the requirement error is found or any changes have to be made, the project has to start from the beginning |
| The development process is iterative, and the project is executed in short (2-4 week) iterations. Planning is very little. | The development process is phased, and the phase is much bigger than an iteration. Every phase ends with a detailed description of the next phase. |
| Documentation receives less priority than software development | Documentation is a top priority and can even be used for training staff and upgrading the software with another team |
| Every iteration has its own testing phase. It allows implementing regression testing every time new functions or logic are released | Only after the development phase is the testing phase executed, because separate parts are not fully functional |
| In agile testing, when an iteration ends, shippable features of the product are delivered to the customer. New features are usable right after shipment. It is useful when you have good contact with customers | All features developed are delivered at once after the long implementation phase |
| Testers and developers work together | Testers work separately from developers |
| At the end of every sprint, user acceptance is performed | User acceptance is performed at the end of the project |
| It requires close communication with developers and together analyze requirements and planning | Developer is not involved in the requirement and planning process. Usually, time delays between tests and coding |
Also Check:- Agile Vs Waterfall: Know the Difference Between Methodologies

