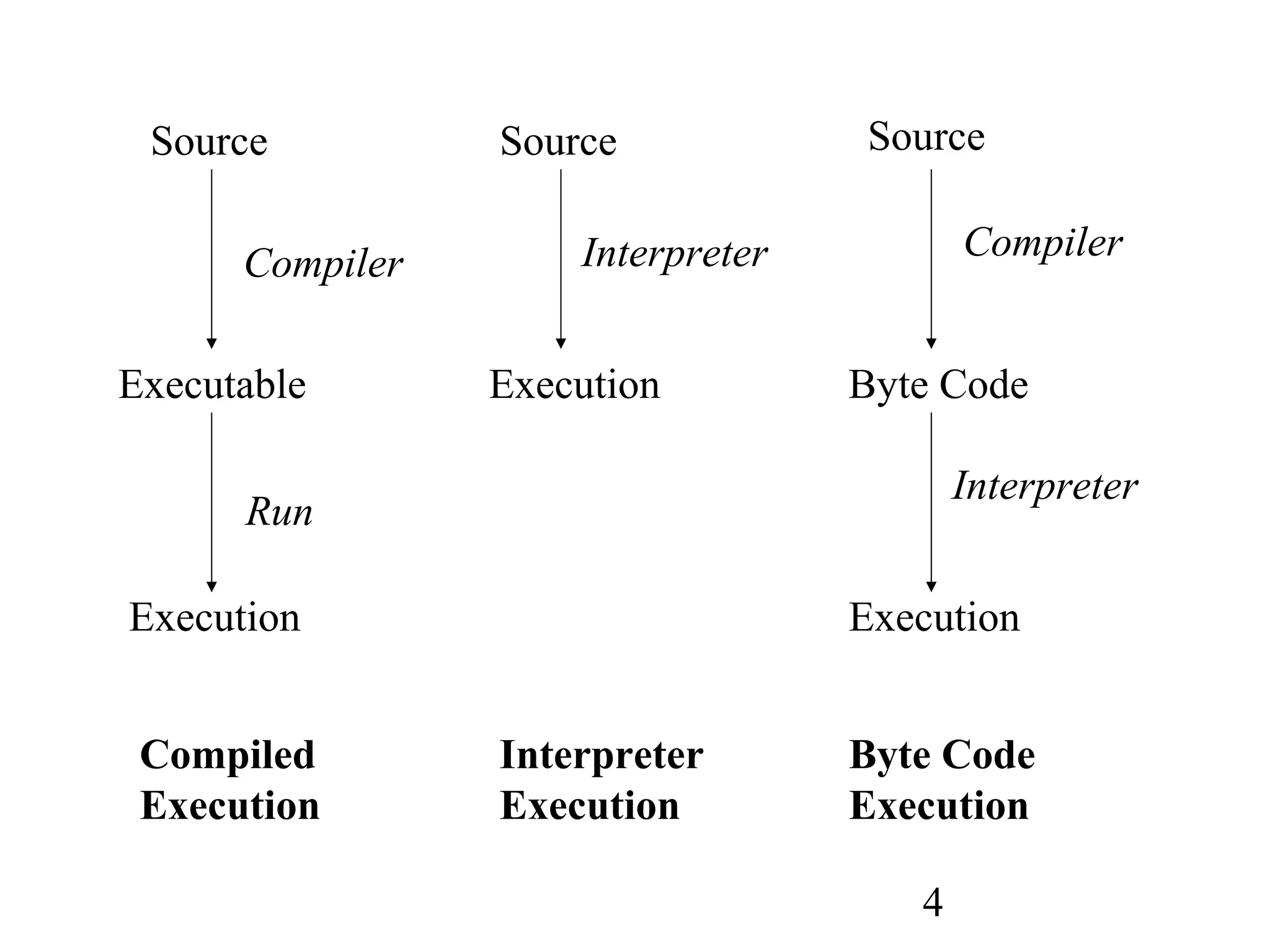
This document discusses scripting languages and their key characteristics. Scripting languages are generally interpreted rather than compiled, allowing for rapid development and changes. They have built-in support for high-level structures and libraries. Python uses a combination of compilation and interpretation through bytecode. Scripting languages are often used to combine the functionality of other programs by acting as an intermediary between them. They can also extend their functionality by binding existing programs. Many scripting languages support dynamic typing, automatic memory management, object-oriented structures, dynamic code creation, and built-in data structures like associative arrays and lists.