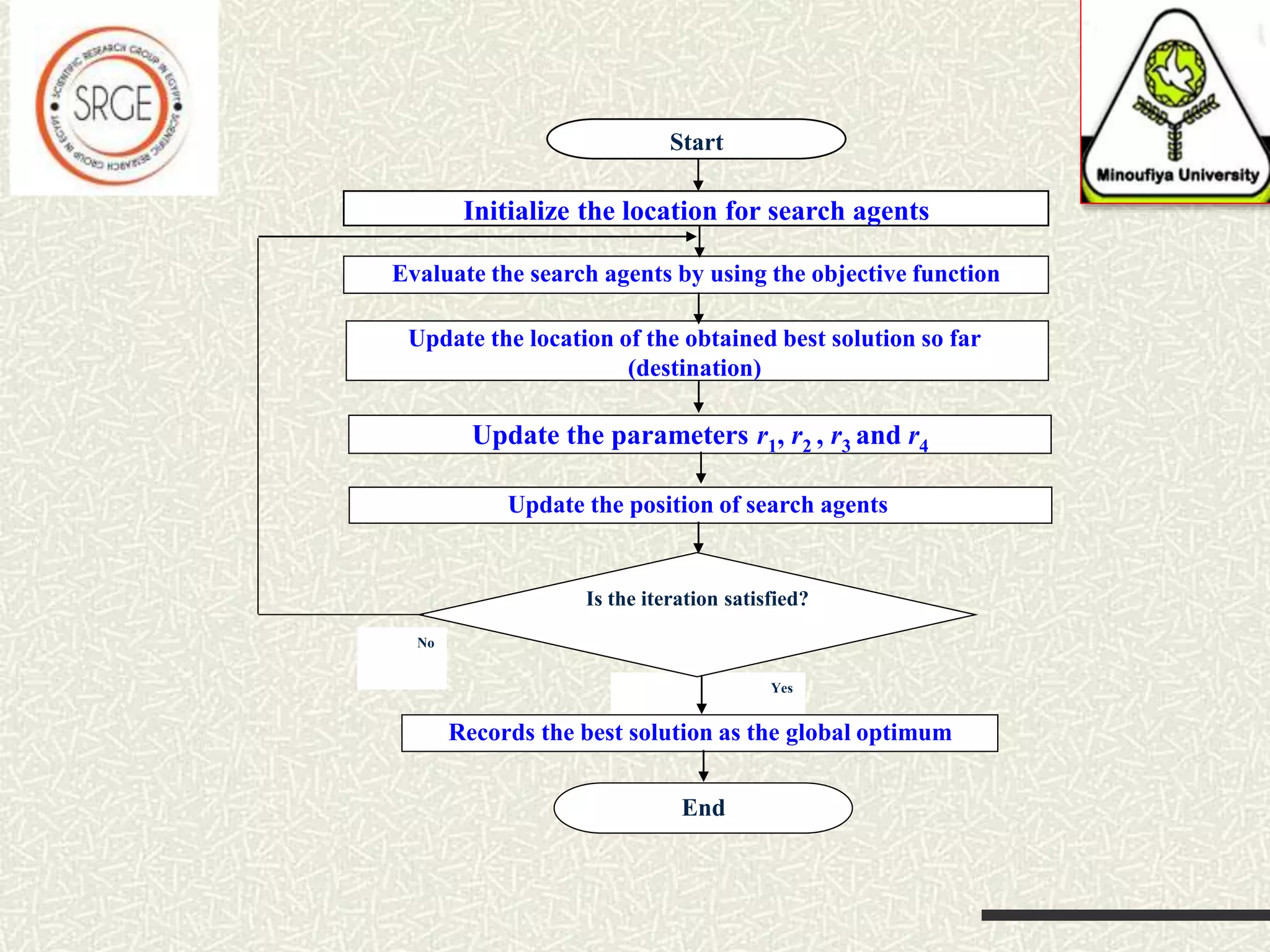
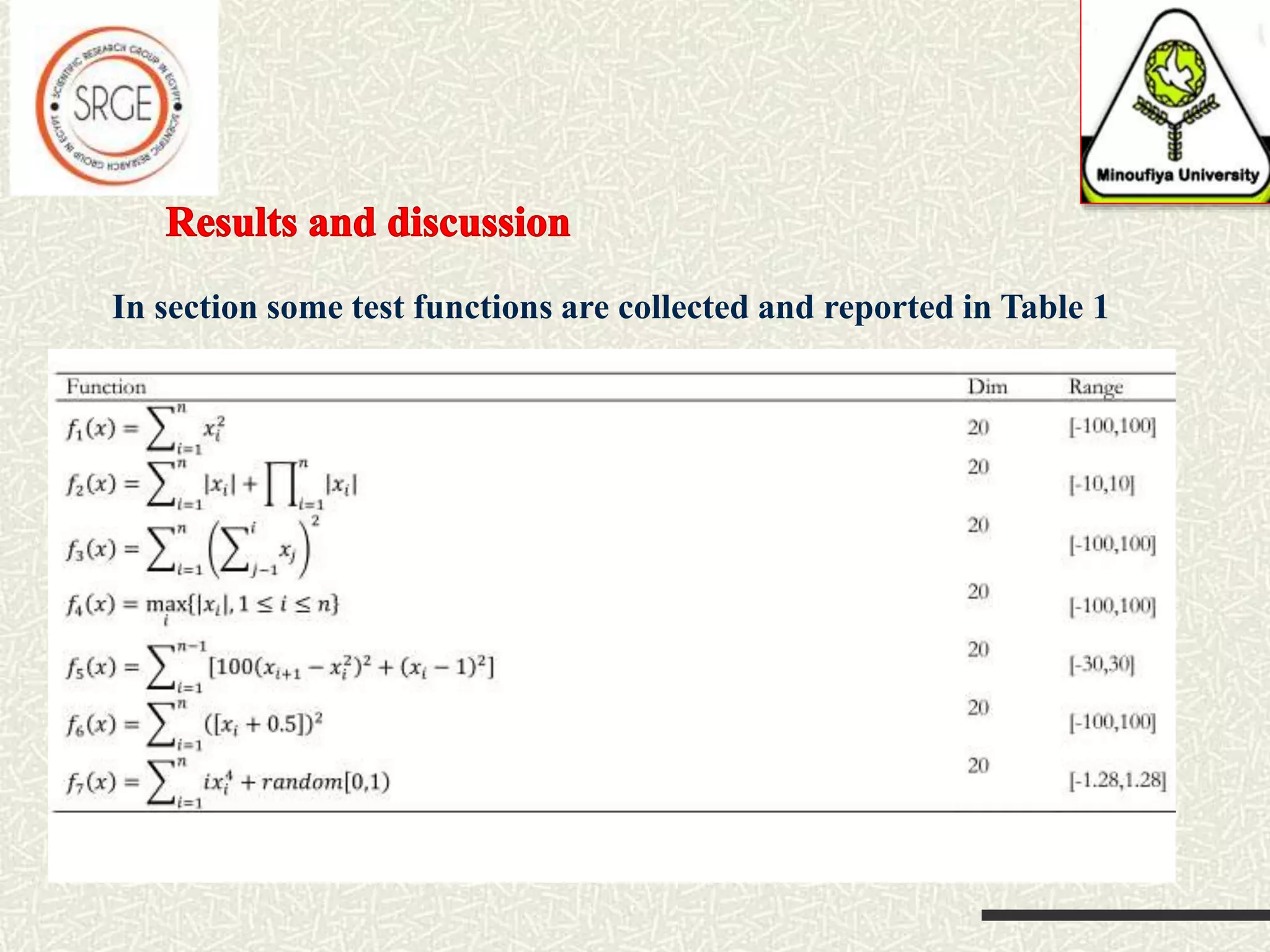
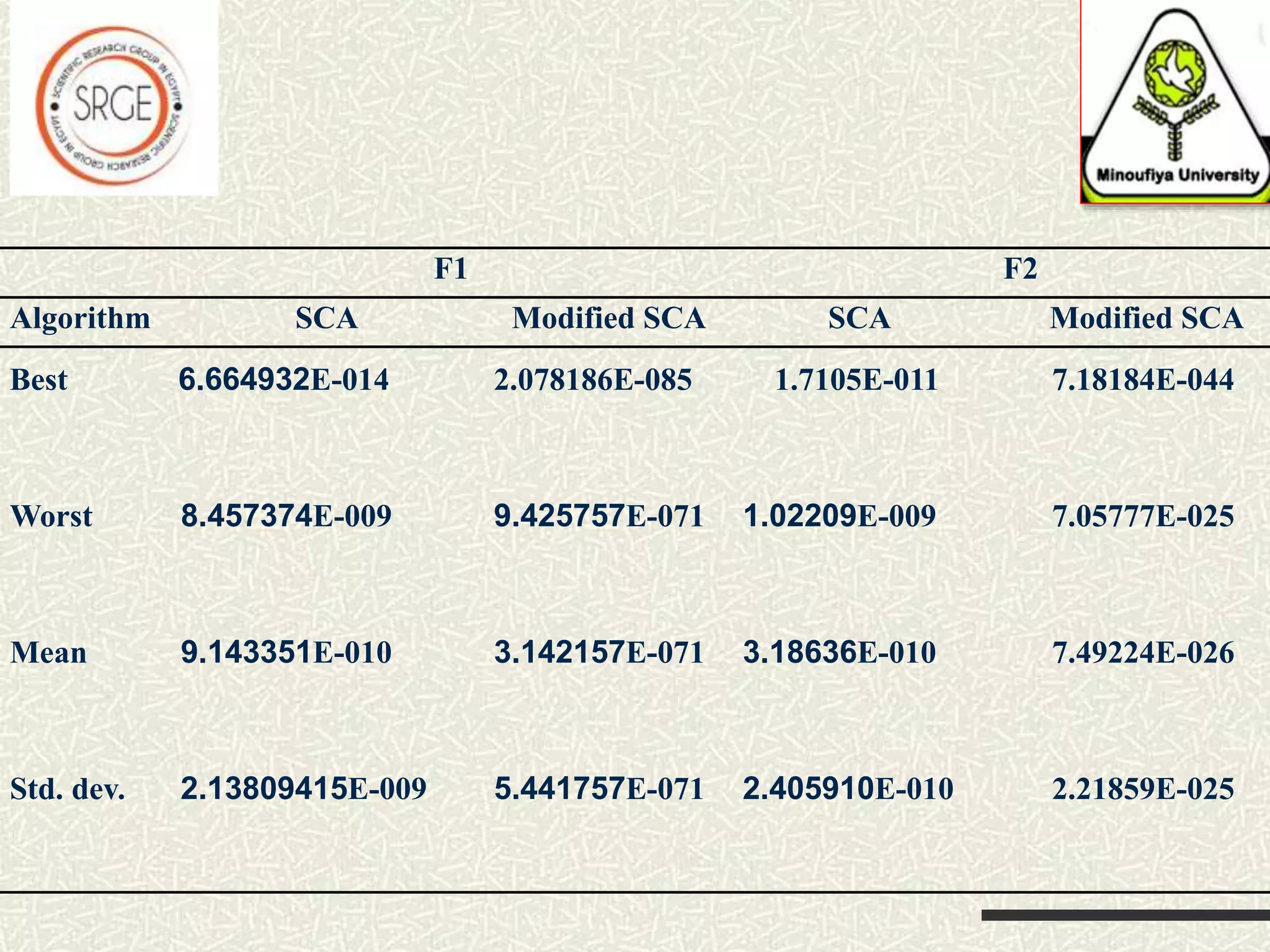
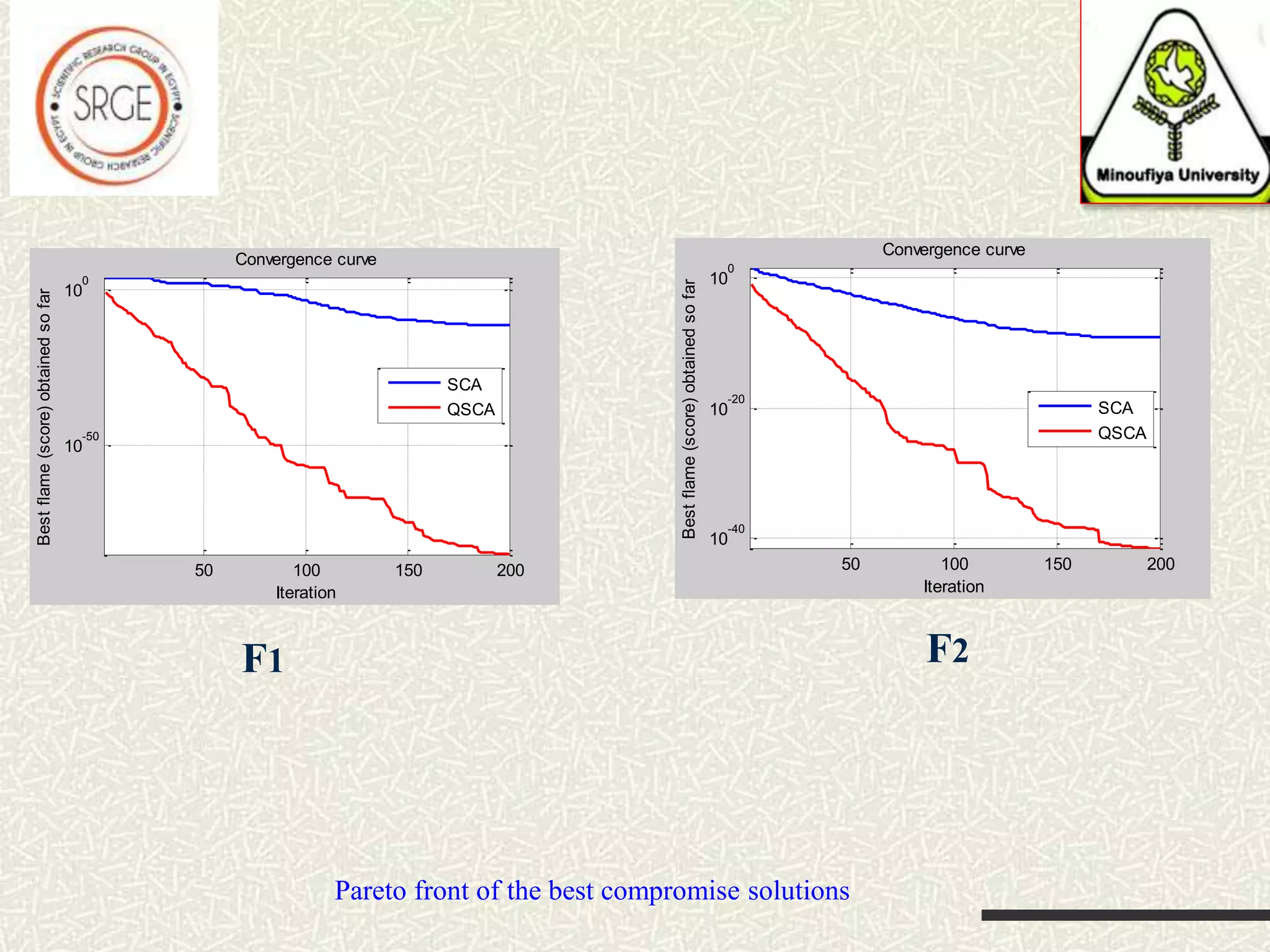
The document discusses a hybrid optimization algorithm, Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA), introduced in 2016, which aims to address global optimization problems but may become trapped in local optima. It integrates a local search technique for improved exploration and exploitation, showing superior performance in escaping local minima. The results indicate that this hybrid approach can efficiently converge to global minima, with potential for future applications to more complex problems.



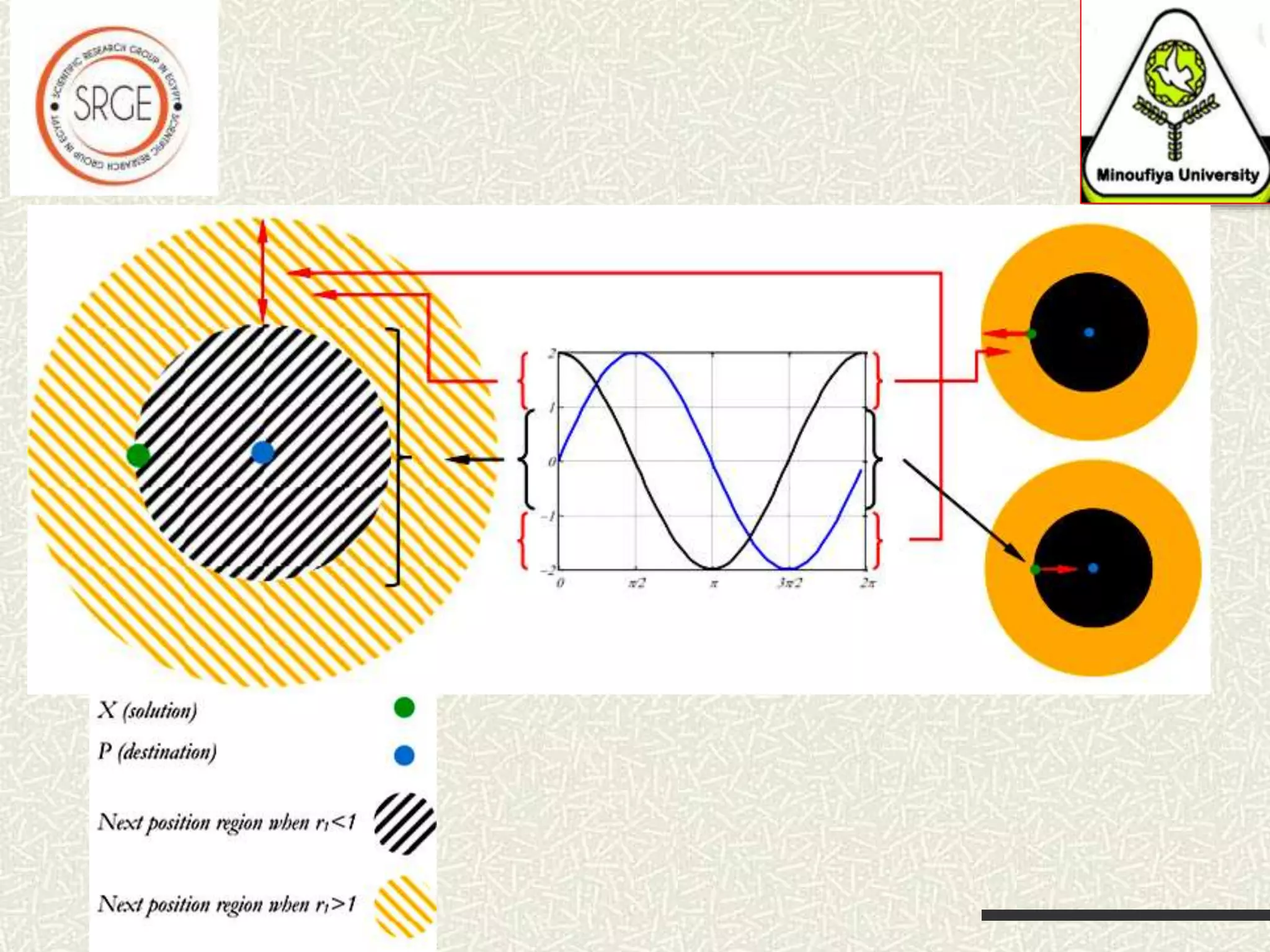
![SCA is population-based optimization algorithm that is established based on the mathematical sine and cosine functions Sine and cosine with range of [-2,2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahybridsinecosineoptimizationalgorithmforsolvingglobaloptimizationproblems-170514200506/75/A-hybrid-sine-cosine-optimization-algorithm-for-solving-global-optimization-problems-4-2048.jpg)