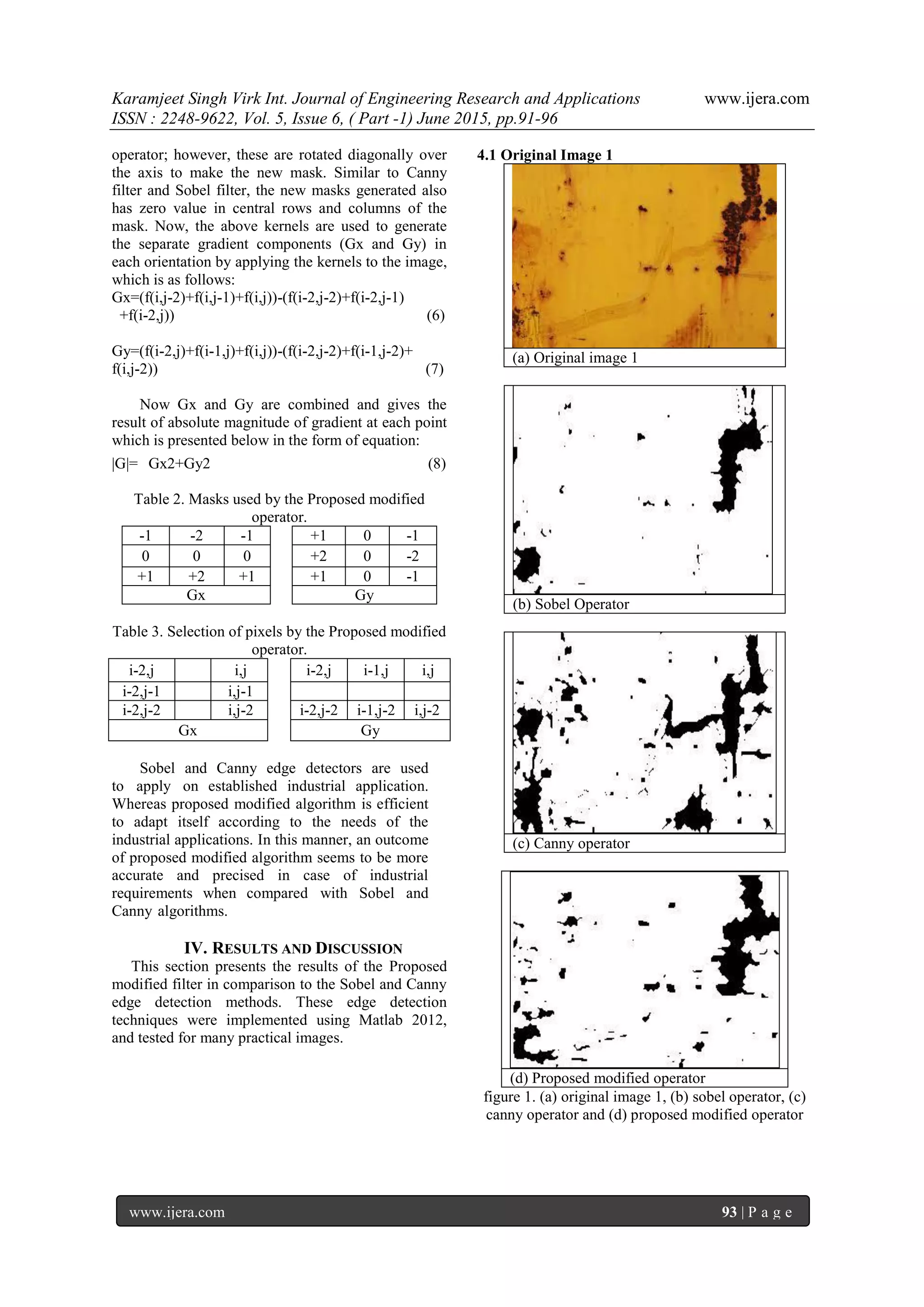
This paper introduces a modified algorithm for edge detection specifically aimed at identifying corroded surfaces in industrial applications. The proposed method enhances the detection process by minimizing false edges and improving accuracy compared to traditional algorithms like Sobel and Canny. Results demonstrate that the new algorithm offers superior performance in edge detection, particularly in noisy images associated with industrial inspection.



![Karamjeet Singh Virk Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications www.ijera.com ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 6, ( Part -1) June 2015, pp.91-96 www.ijera.com 95 | P a g e 4.4 Comparative study Table 4. Comparative study of Original Image 1 Image Total pixel (T) Accepte d pixel (A) Rejected pixel (R) Accurac y (%) Original image 1 (Grey) 50325 3662 46663 100 Sobel inverted segmented image 50325 2082 48243 56.8 Canny inverted segmented image 50325 4395 45930 80 Proposed inverted segmented image 51245 3343 47902 91.2 Table 5. Comparative study of Original Image 2 Image Total pixel (T) Accepted pixel (A) Rejecte d pixel (R) Accur acy (%) Original image 2 (Grey) 220675 35337 185338 100 Sobel inverted segmented image 220675 8996 211679 25.4 Canny inverted segmented image 220675 60092 160583 30 Proposed inverted segmented image 222559 37505 185054 93.9 Table 6. Comparative study of Original image 3 Image Total pixel (T) Accepted pixel (A) Rejected pixel (R) Accuracy (%) Original image 3 (Grey) 140125 25864 114261 100 Sobel inverted segmente d image 140125 4978 135147 19.2 Canny inverted segmente d image 140125 37815 102310 53.8 Proposed inverted segmente d image 141669 27008 114661 95.6 V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE SCOPE From the above study, we concluded the proposed modified edge detector is very effective for edge detection purposes. It is observed that for the four images used, there are less false edges in the proposed modified edge detector. From the results, it is concluded that results obtained from the modify detector shows that it detect less false edges and also improve intensity level of edges as compared to Sobel and Canny edge detector. Edge detection is the foremost field of inspection in modern industry in now a day. Canny detector is universally accepted technique but it is not suited all the way as it fails to give accurate performance in certain areas. It detects large number of weak edges also. Application of the corroded surfaces detection is one in which canny and sobel detector are not ideally performed. Thus, to overcome such type of problems a new edge detector is developed and outcome of this detector reflects its performance. The work can be improved in the future by using the same mask with image sharpening filters. For example, we can use median filtering to improve the method. Noisy contents are removed from the image by using the above filter. In some cases the noisy contents are taken as false edges. So the median filter can be used as a preprocessing step prior to image sharpening and can help to take out unwanted components present within an image. The improved filter can also further implemented on different type of applications. In the case of critical and complex application, evolutionary algorithms may evolve with this design. This can further improve the filter in the terms of performance. REFERENCES [1] Wang B. and Fan S. (2009) “An improved CANNY edge detection algorithm”, 2009 Second International Workshop on Computer Science and Engineering. [2] Zhao H., Qin G. and Wang X. (2010), “Improvement of Canny Algorithm Based on Pavement Edge Detection”, 2010 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP2010). [3] Gao W. and Yang L. (2010), “An Improved Sobel Edge Detection”, 978-1-4244-5540- 9/10/$26.00 ©2010 IEEE. [4] Hocenski Z. (2006), “Improved Canny Edge Detector in Ceramic Tiles Defect Detection”, 1-4244-0136-4/06/2006 IEEE. [5] Pithadiya K.J. (2011), “Selecting the Most Favourable Edge Detection Technique for Liquid Level Inspection in Bottles”, International Journal of Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications (IJCISIM) ISSN: 2150-7988 Vol.3 (2011), pp.034-044](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p56019196-150801062906-lva1-app6892/75/An-Efficient-Algorithm-for-Edge-Detection-of-Corroded-Surface-5-2048.jpg)
![Karamjeet Singh Virk Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications www.ijera.com ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 6, ( Part -1) June 2015, pp.91-96 www.ijera.com 96 | P a g e [6] Rui W. (2007, “Edge Enchancement and filtering of Medical Ultrasonic Images using a Hybrid Method”, 1-4244-1120- 3/07/$25.00 ©2007 IEEE. [7] Ma M., Liang J., Guo M., Fan Y. and Yin Y., "SAR image segmentation based on Artificial Bee Colony algorithm," Applied Soft Computing, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 5205- 5214, 2011. [8] Marr D. and Hildreth E. (1980), “Theory of edge detection”, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Vol. 207, pp. 187-217. [9] Canny J. (1983), “Finding Edges and Lines”, MIT Technical Report No. 720, 1983.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p56019196-150801062906-lva1-app6892/75/An-Efficient-Algorithm-for-Edge-Detection-of-Corroded-Surface-6-2048.jpg)