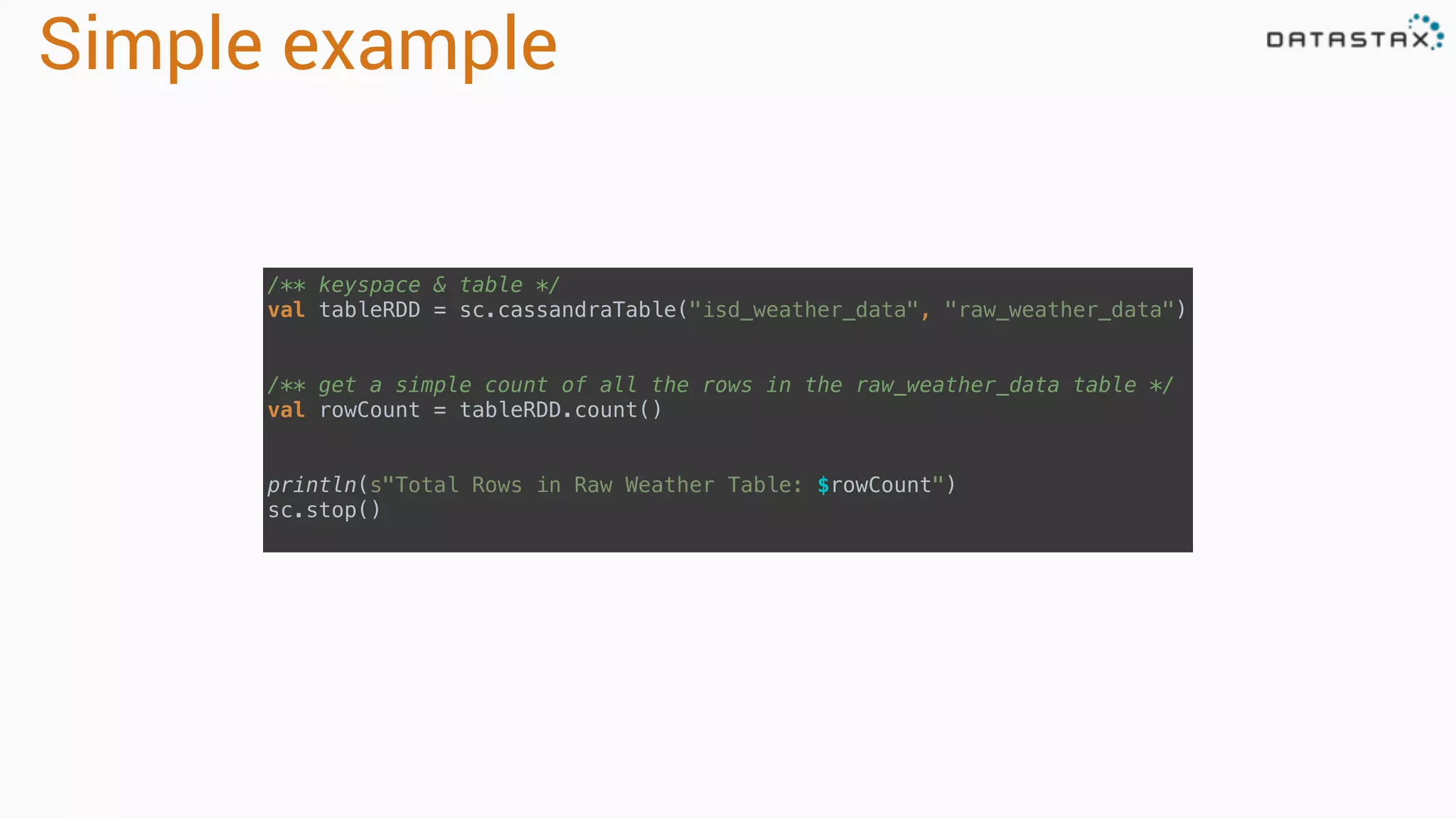
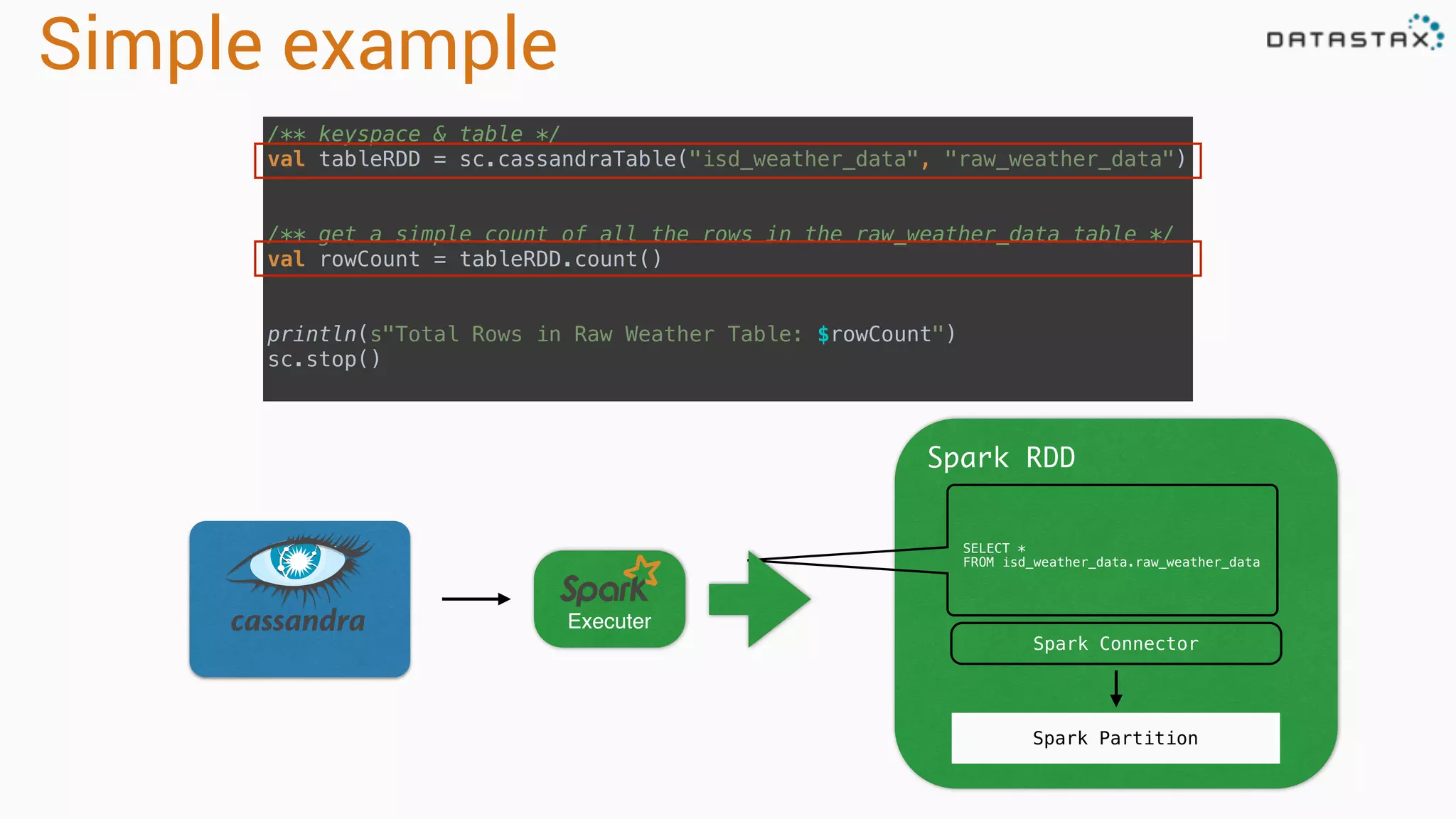
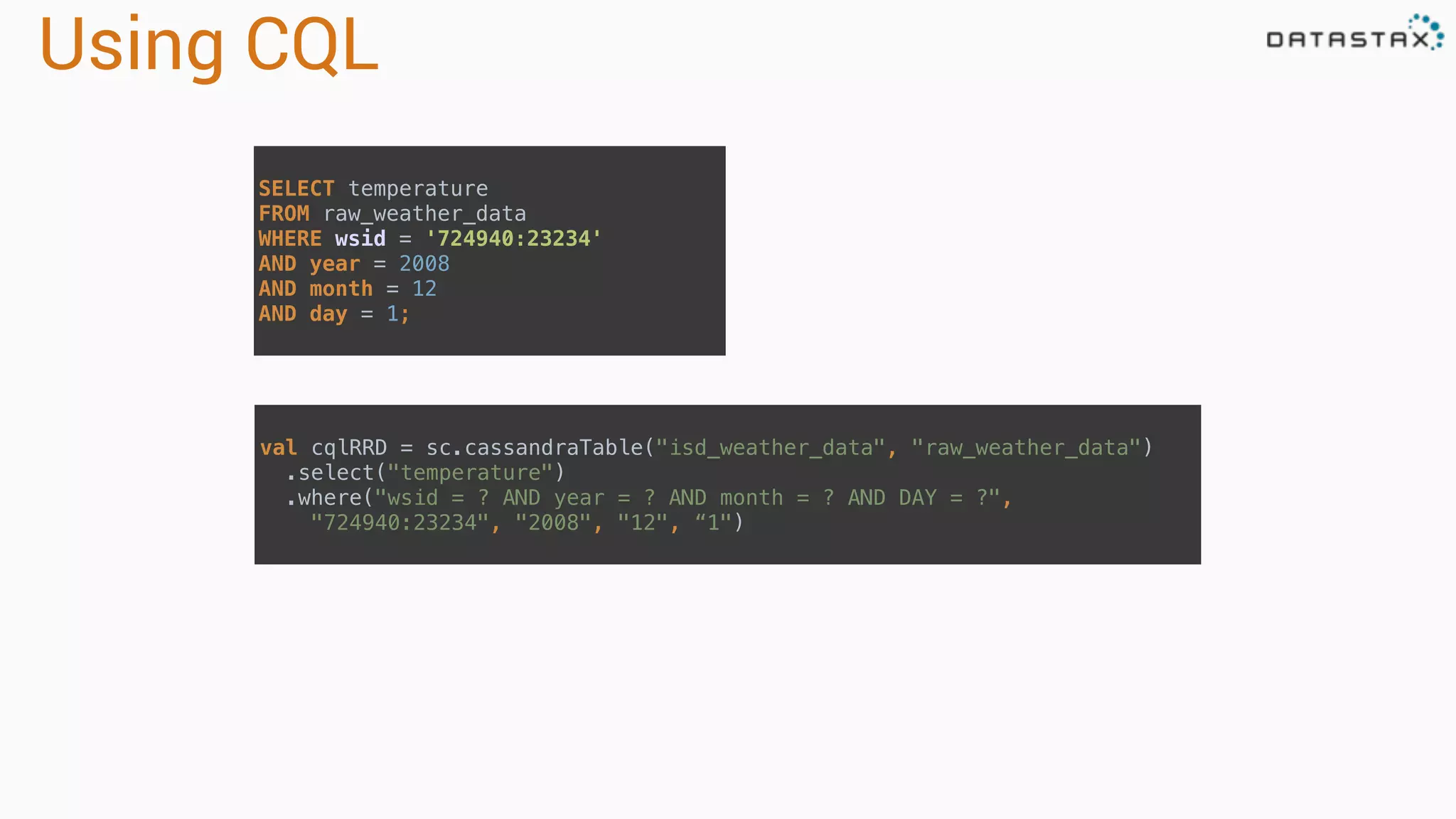
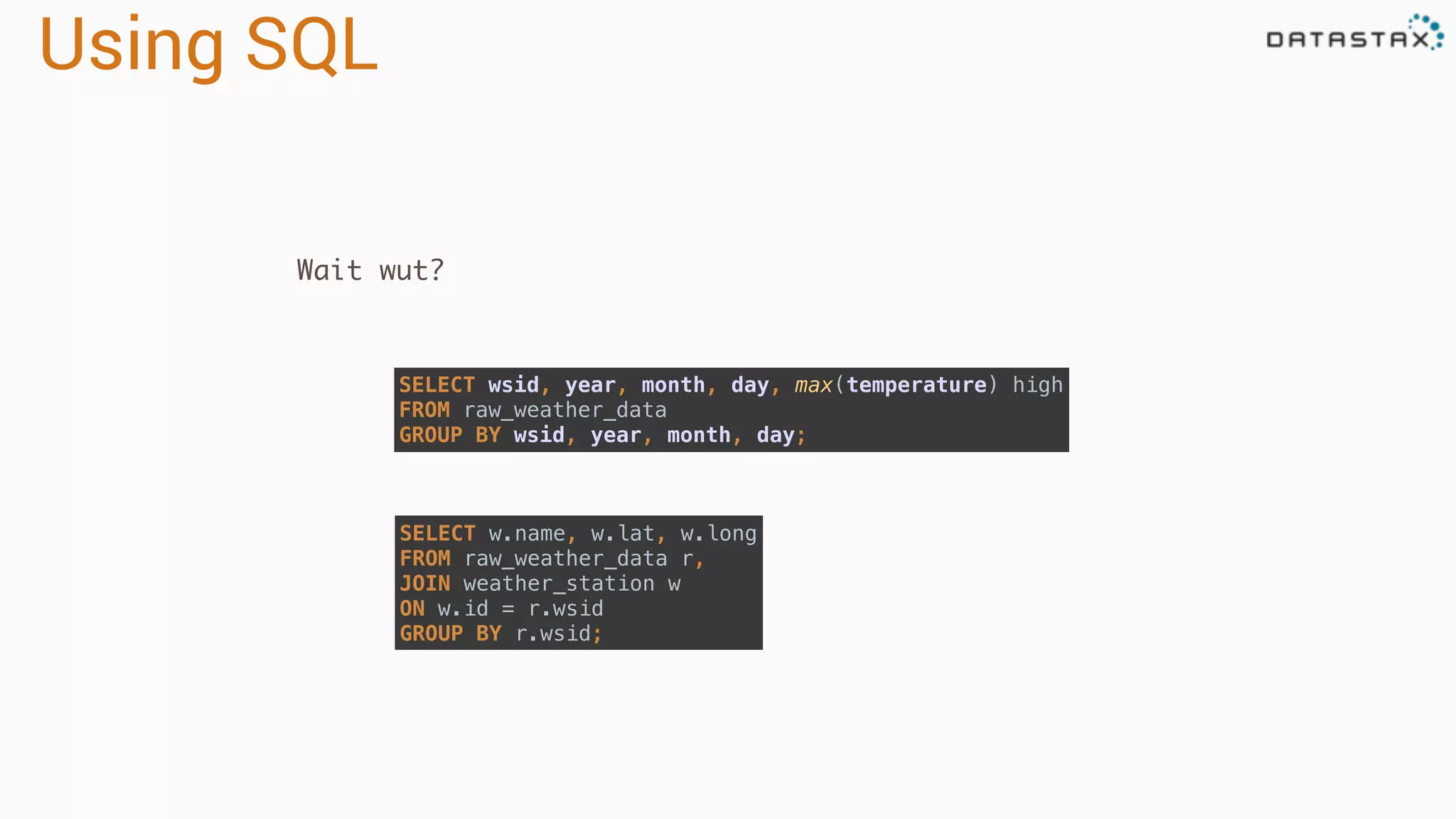
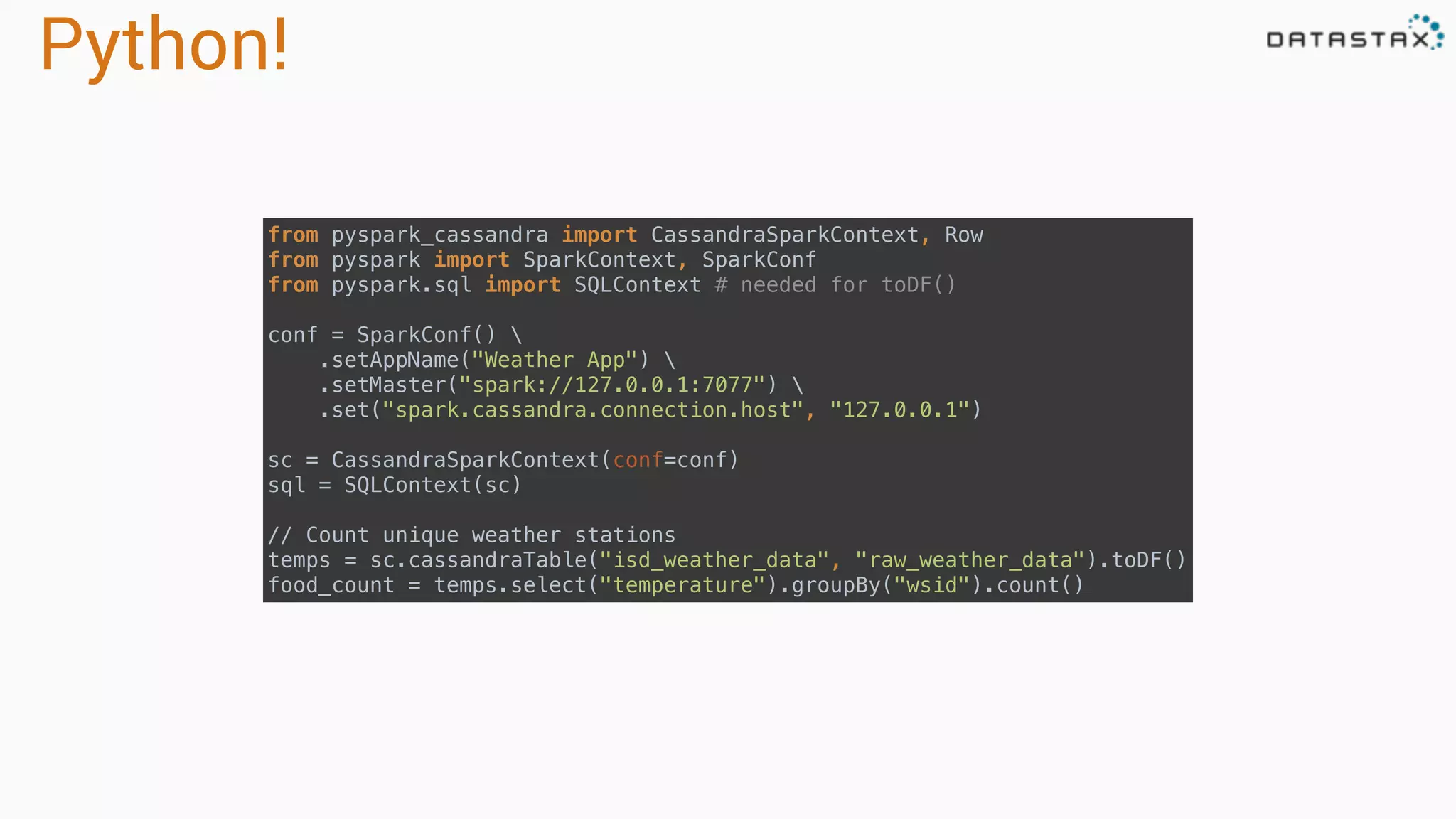
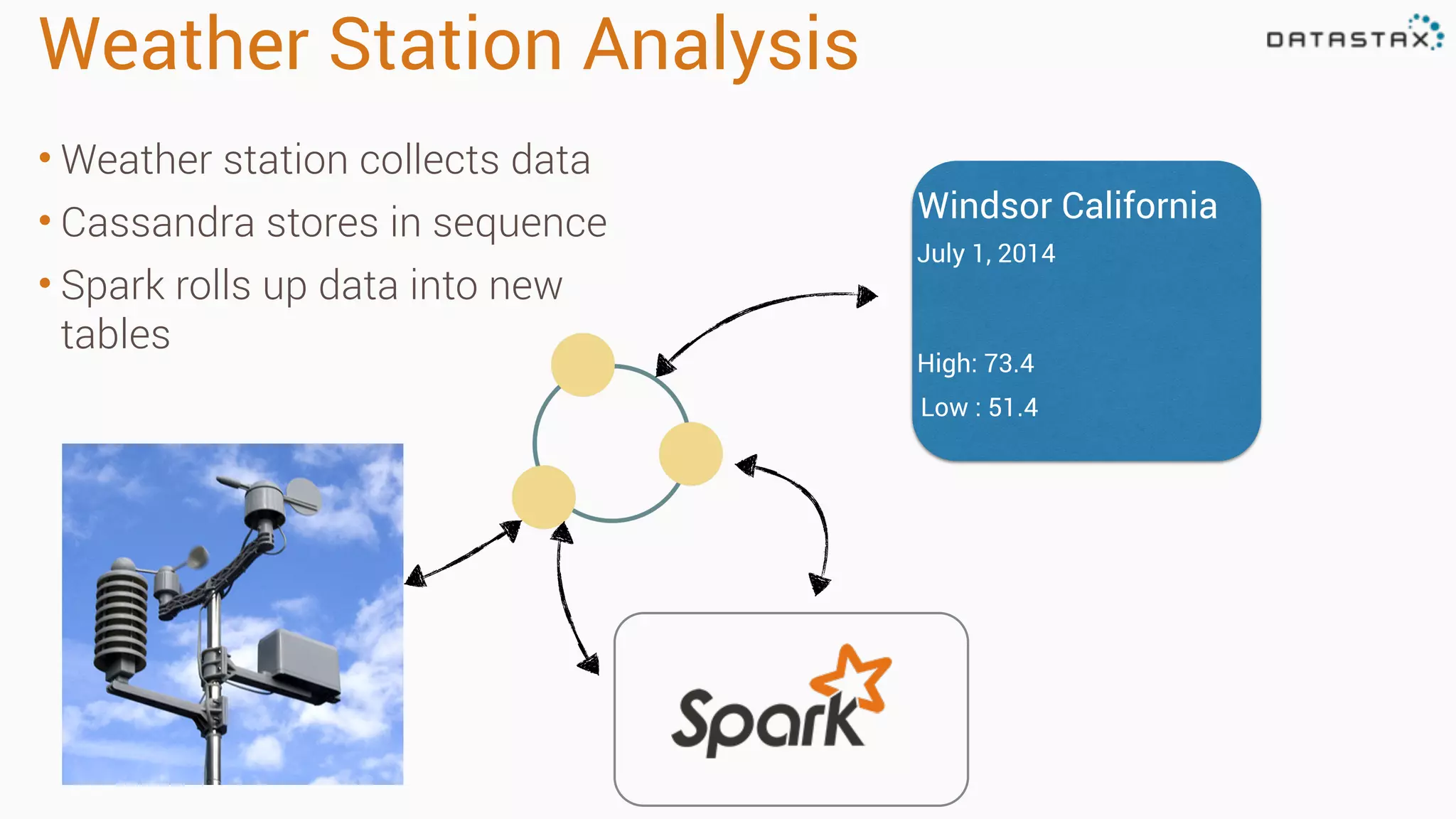
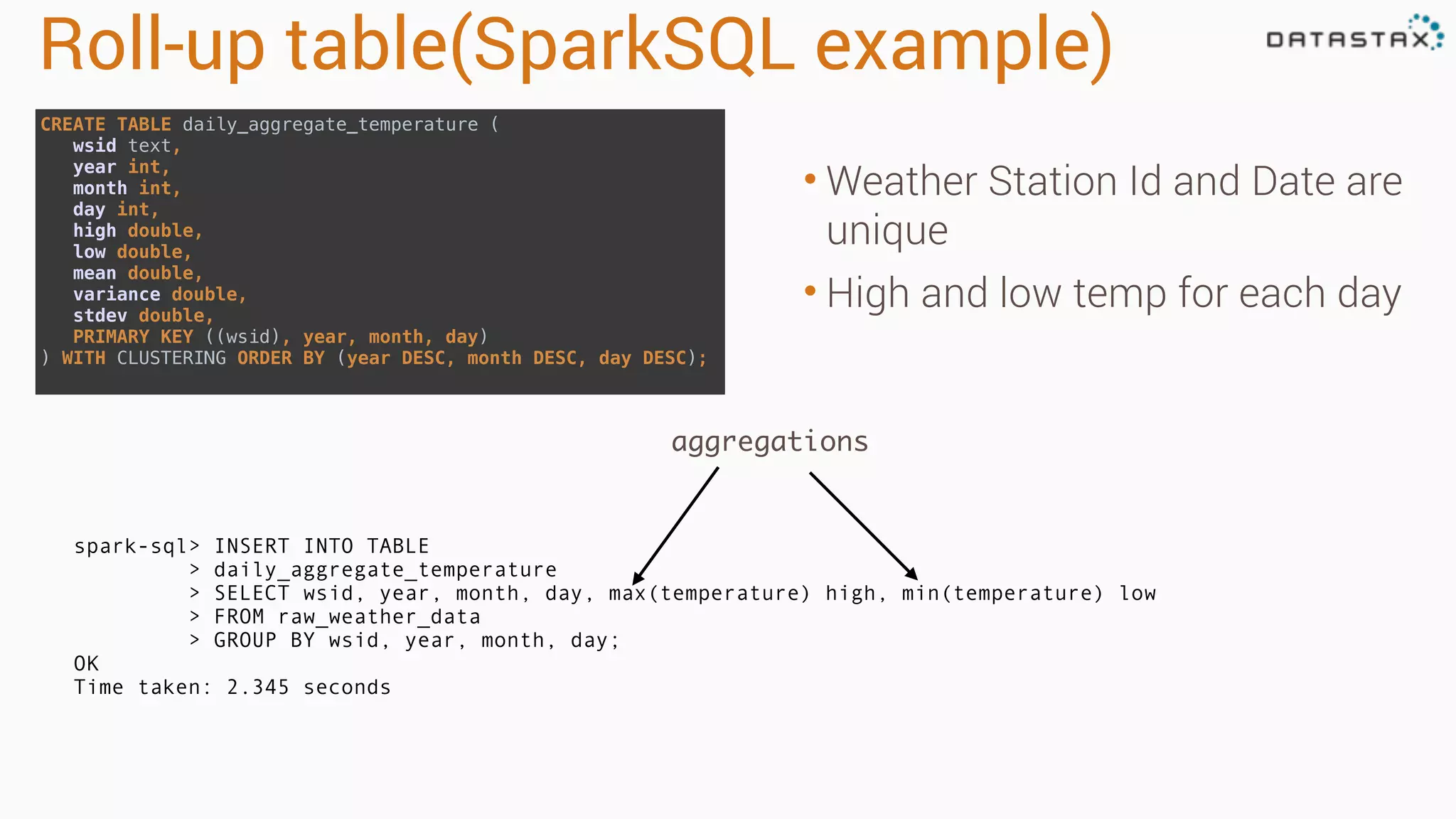
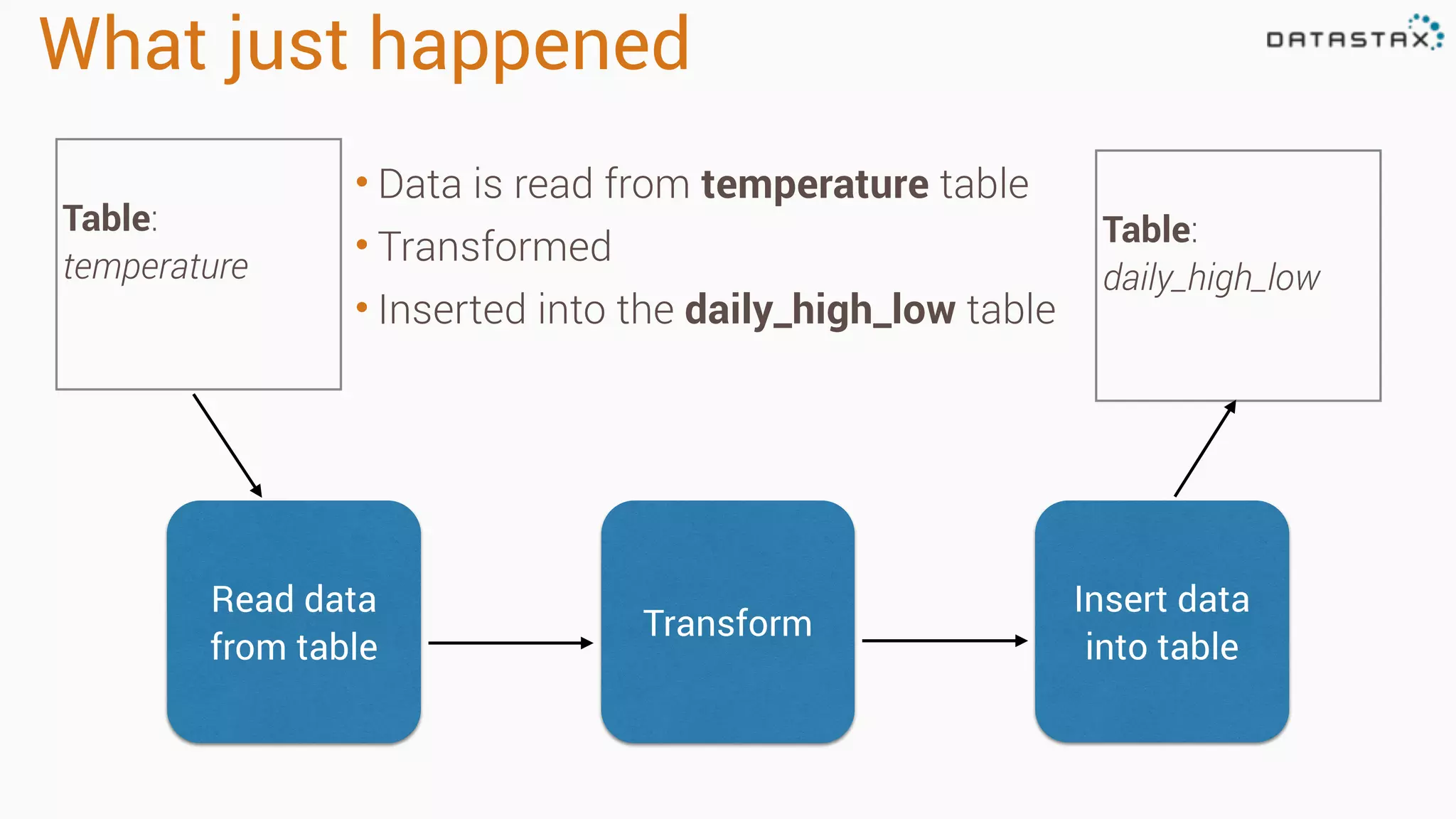
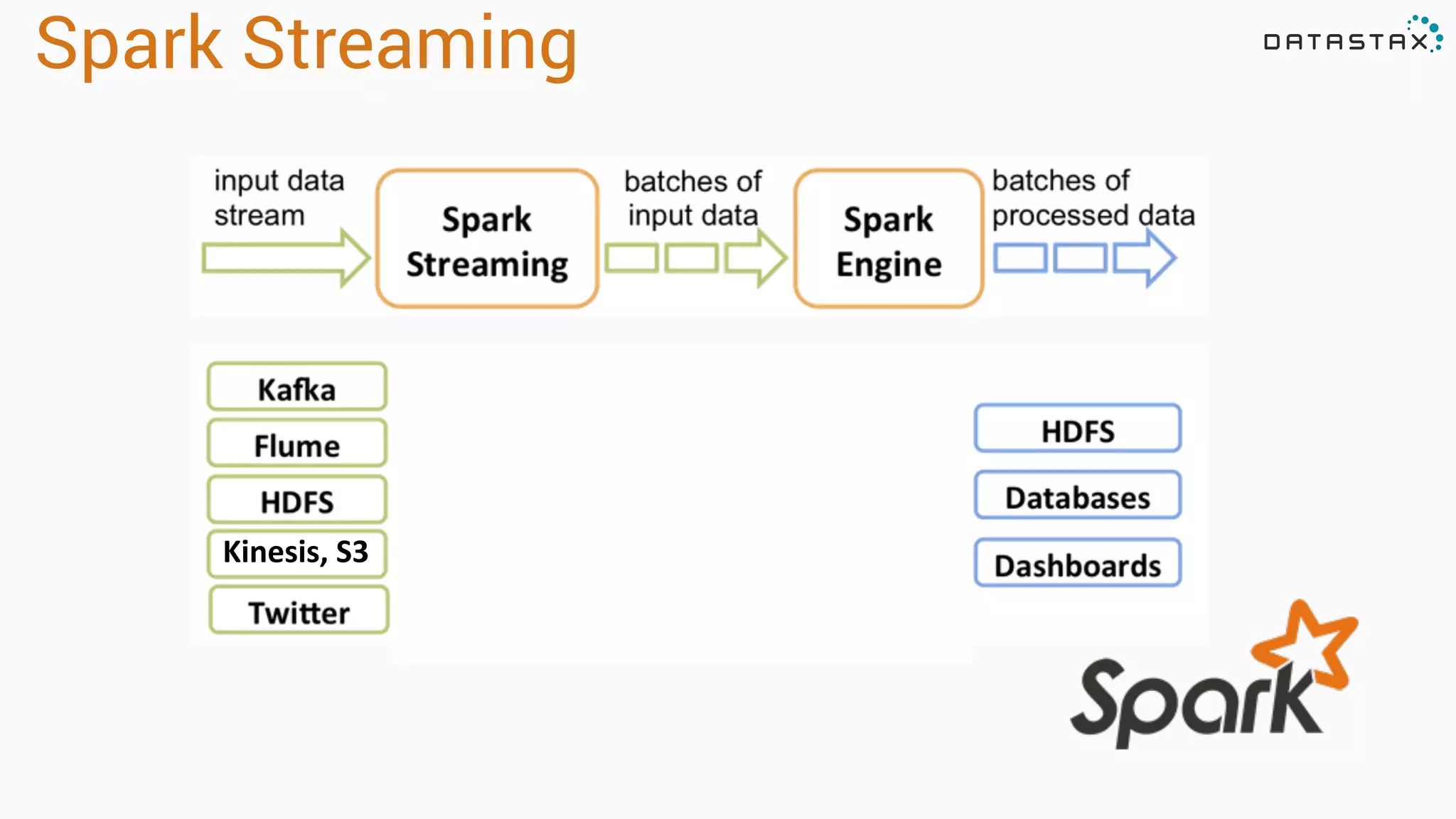
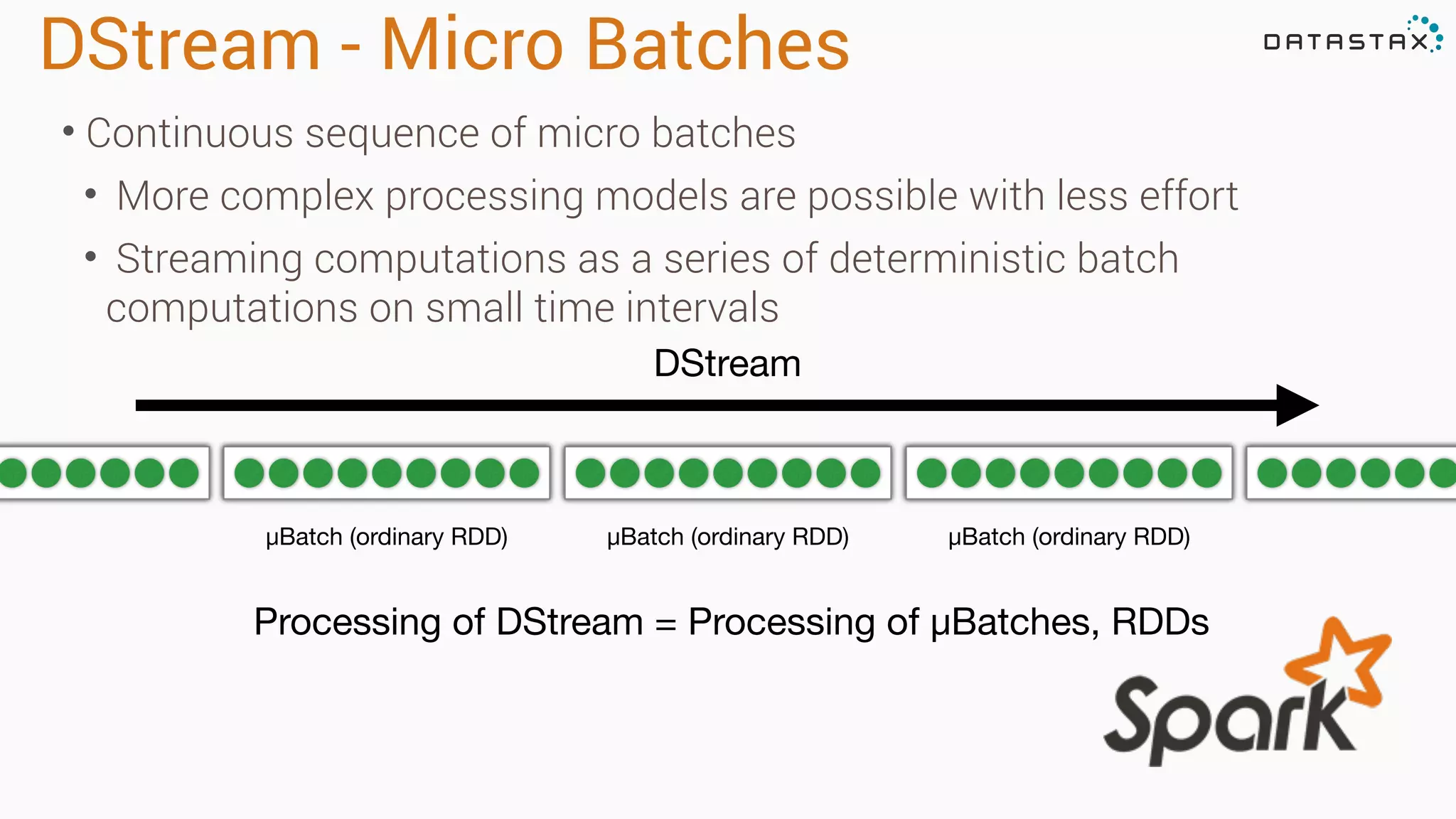
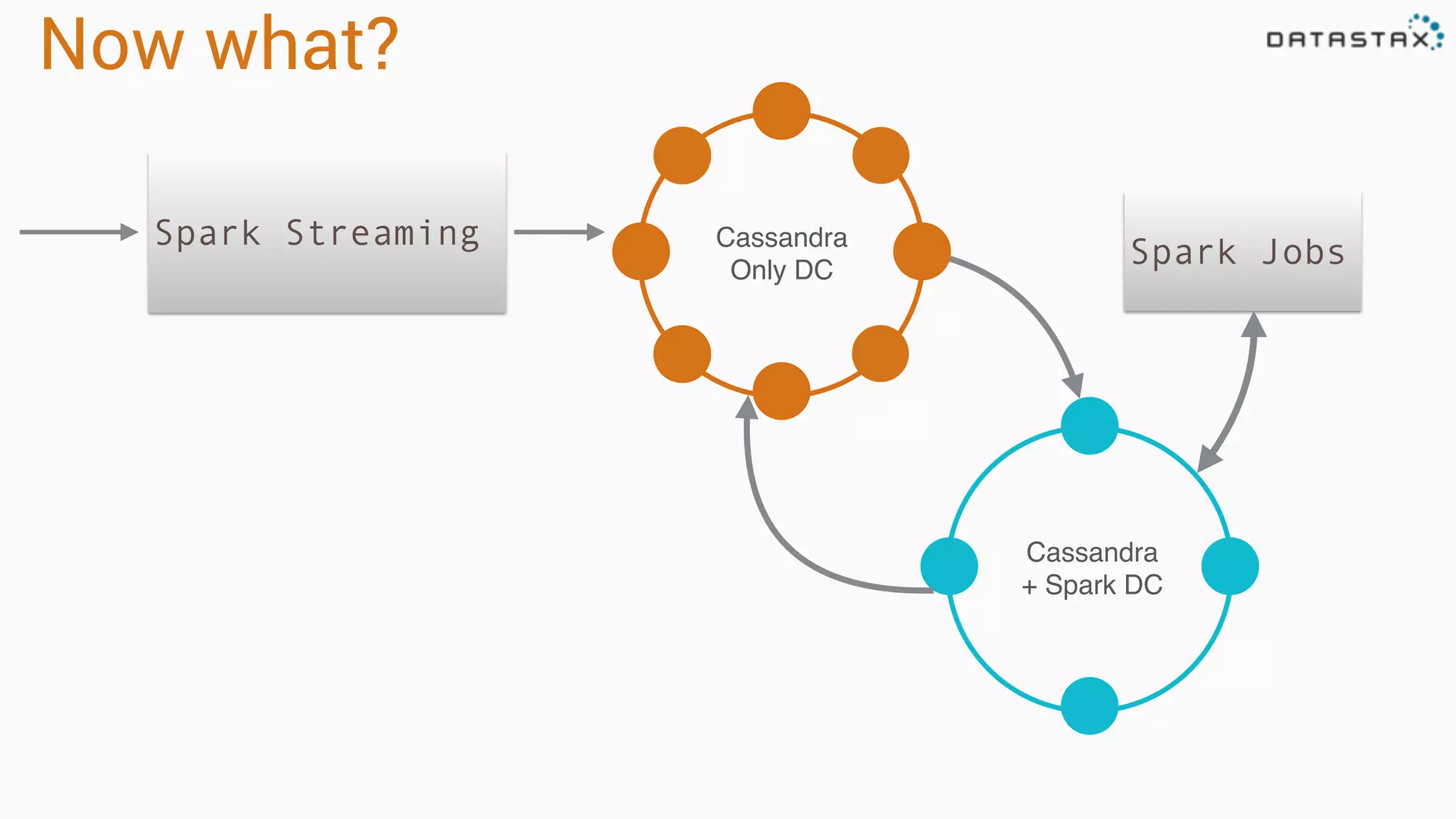
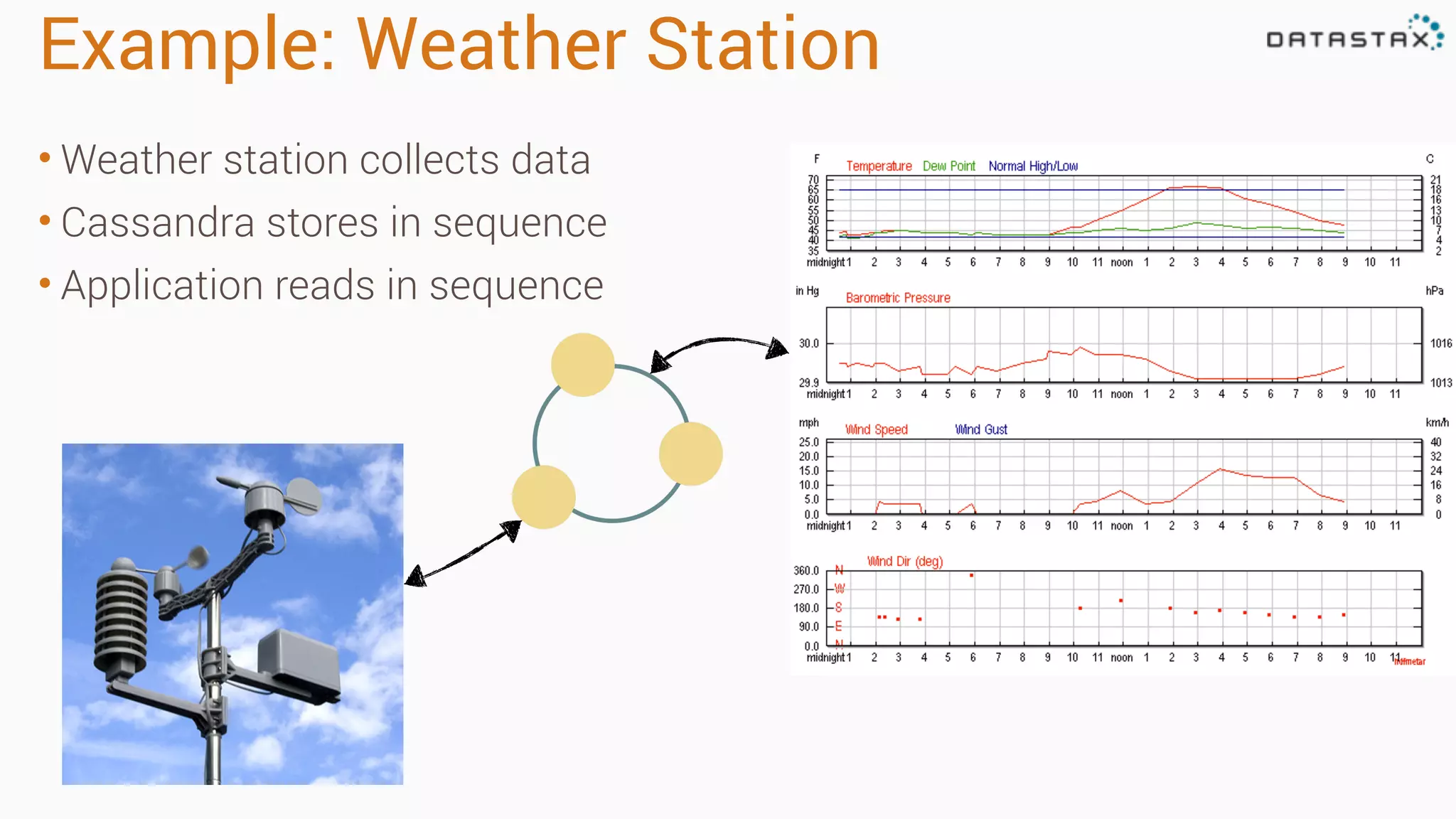
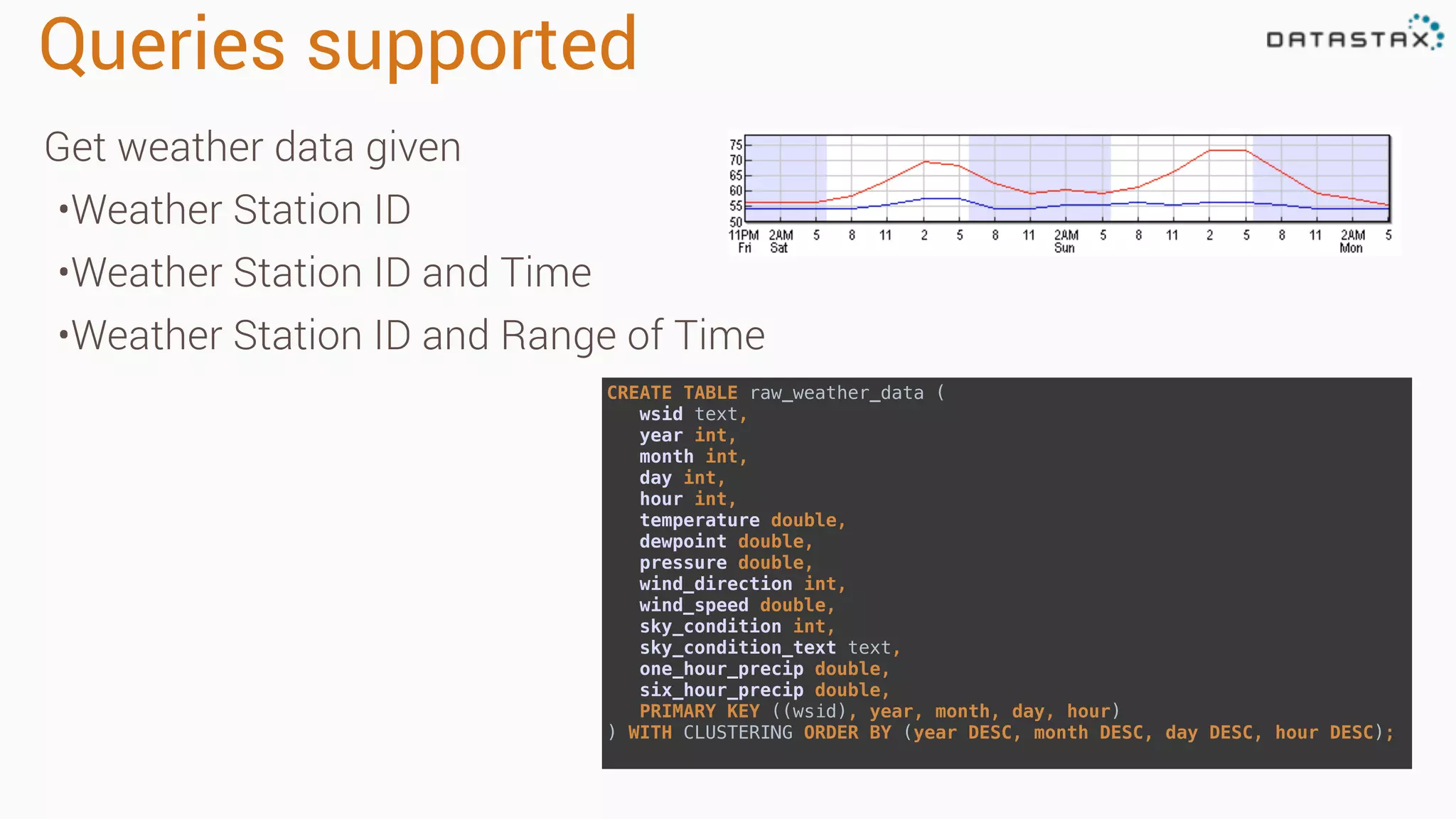
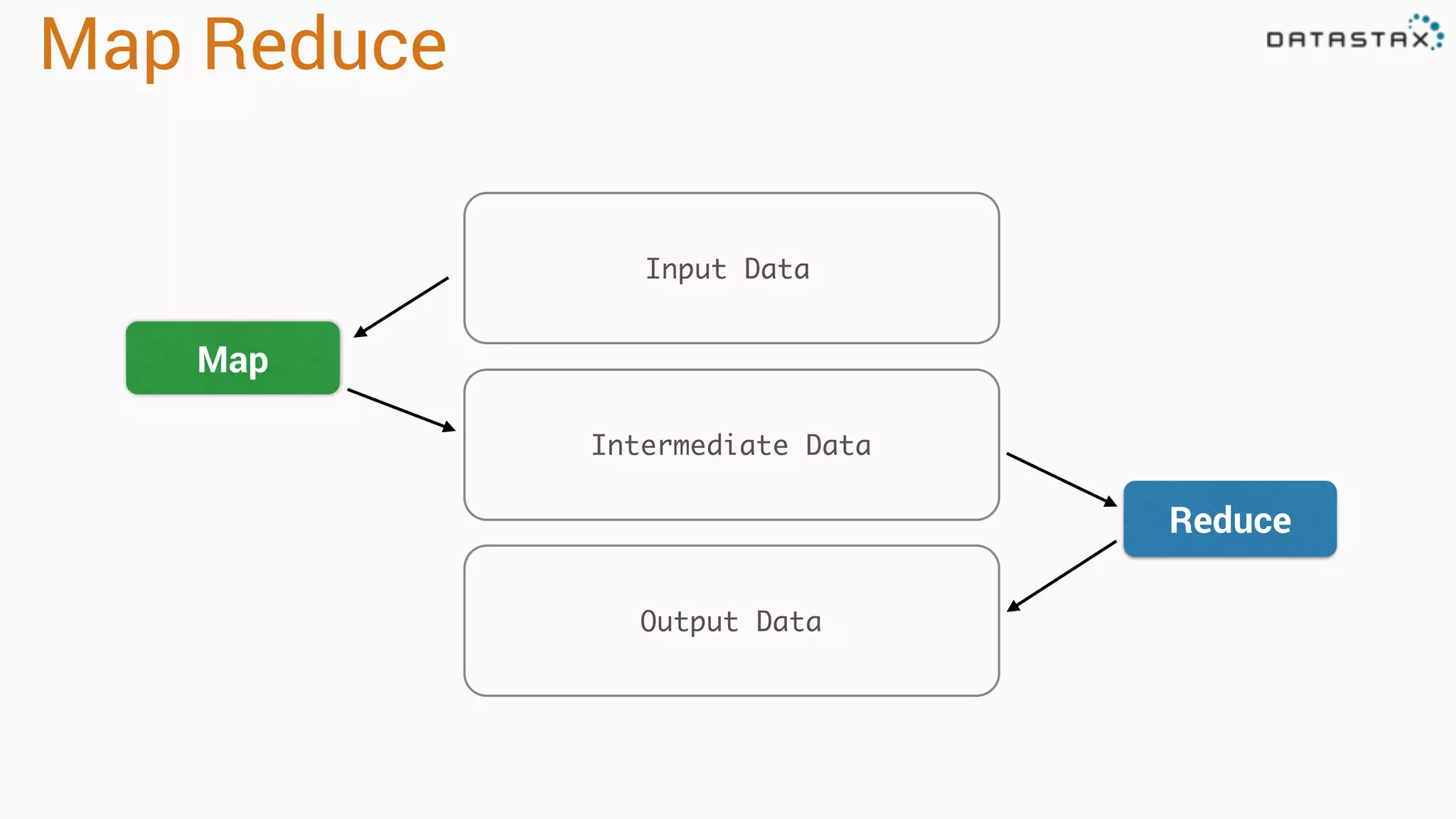
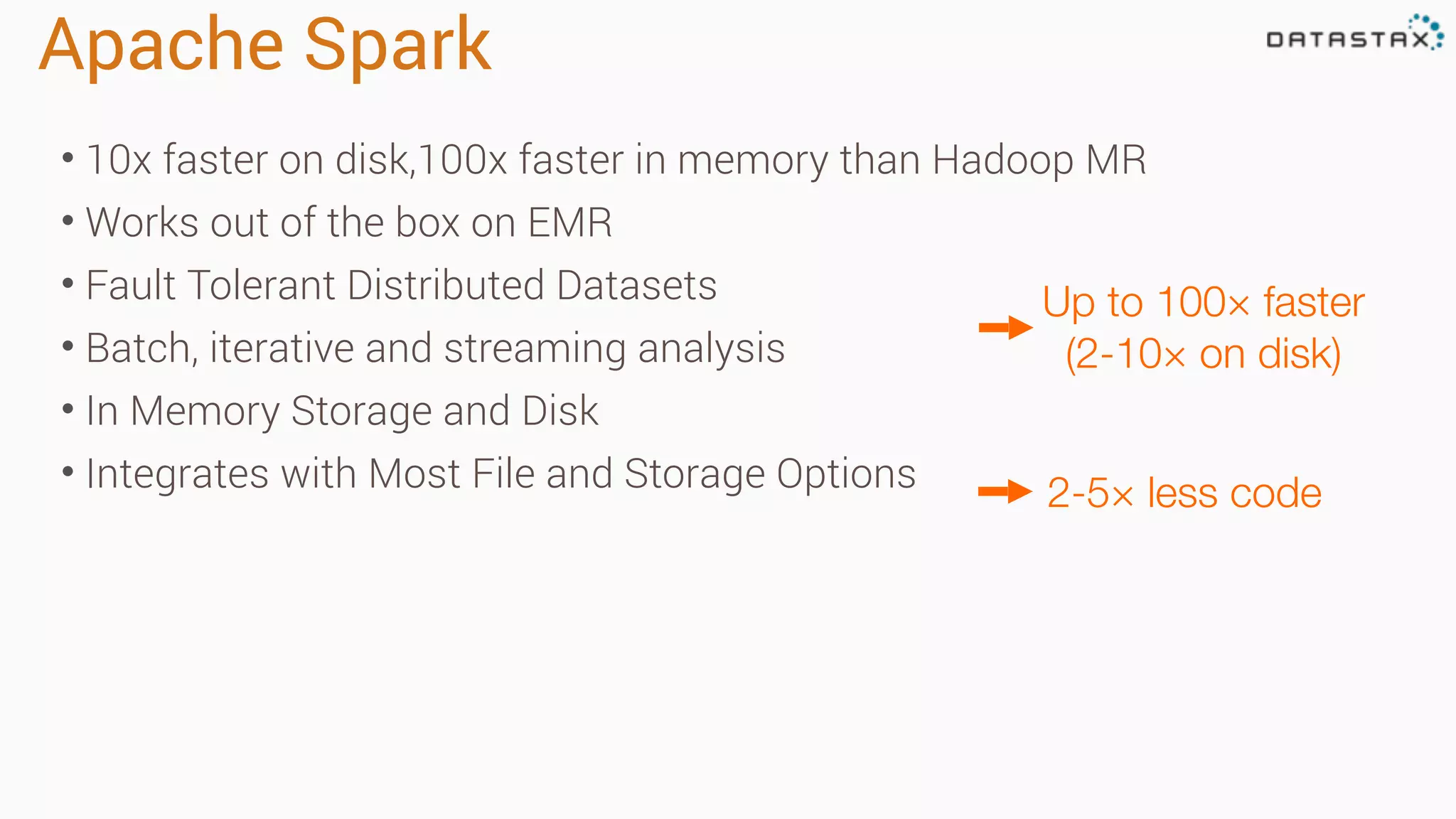
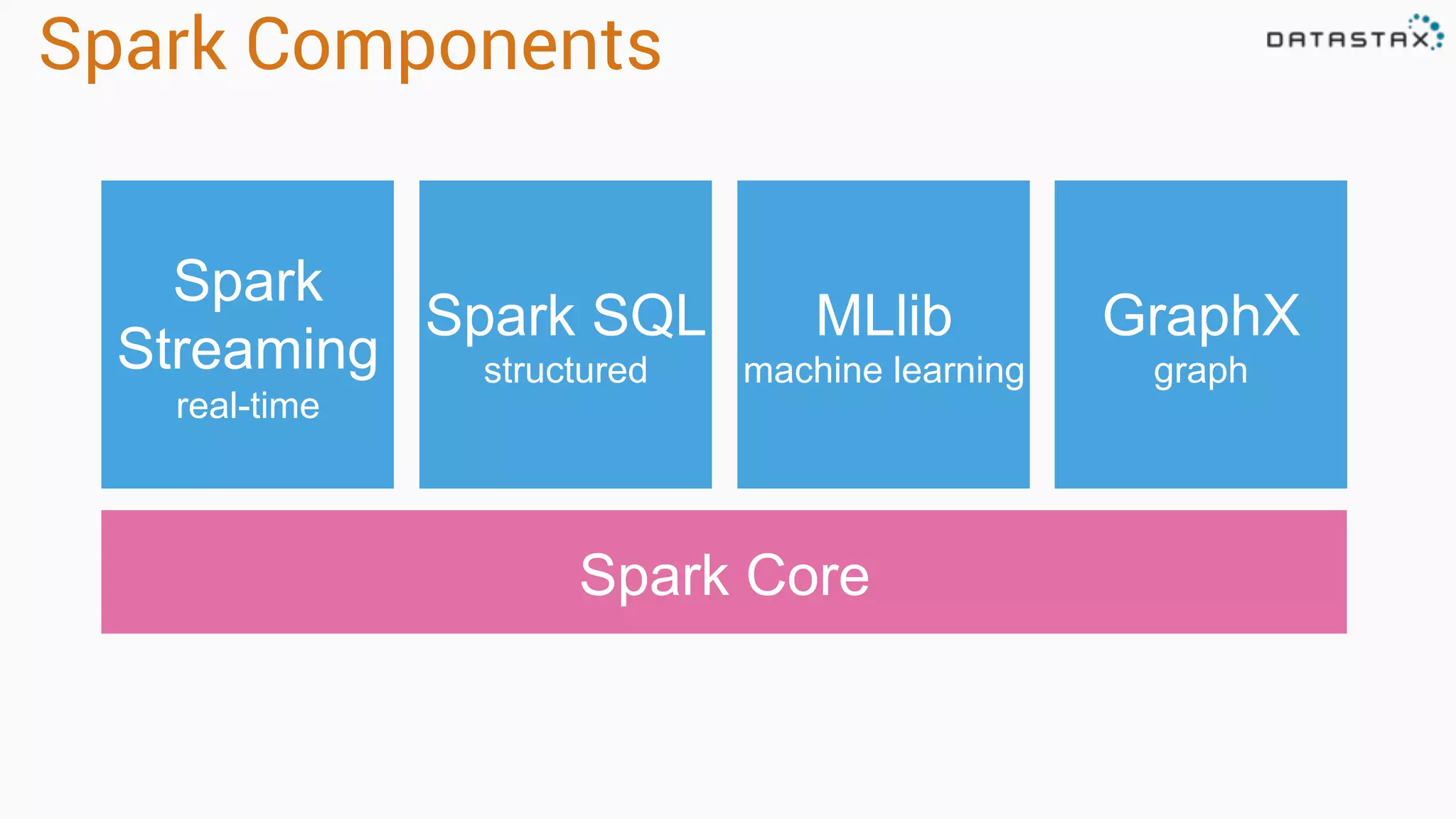
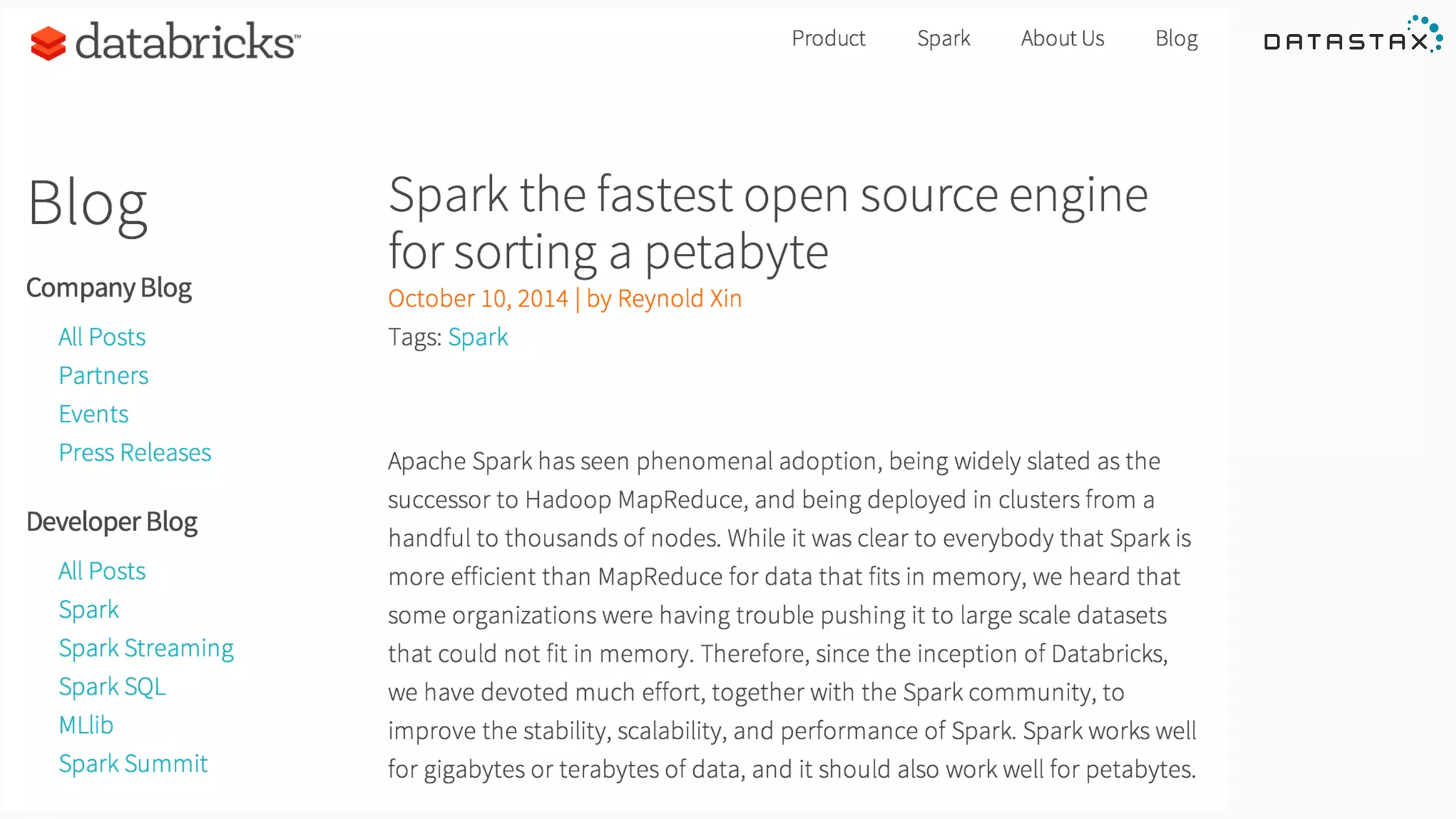
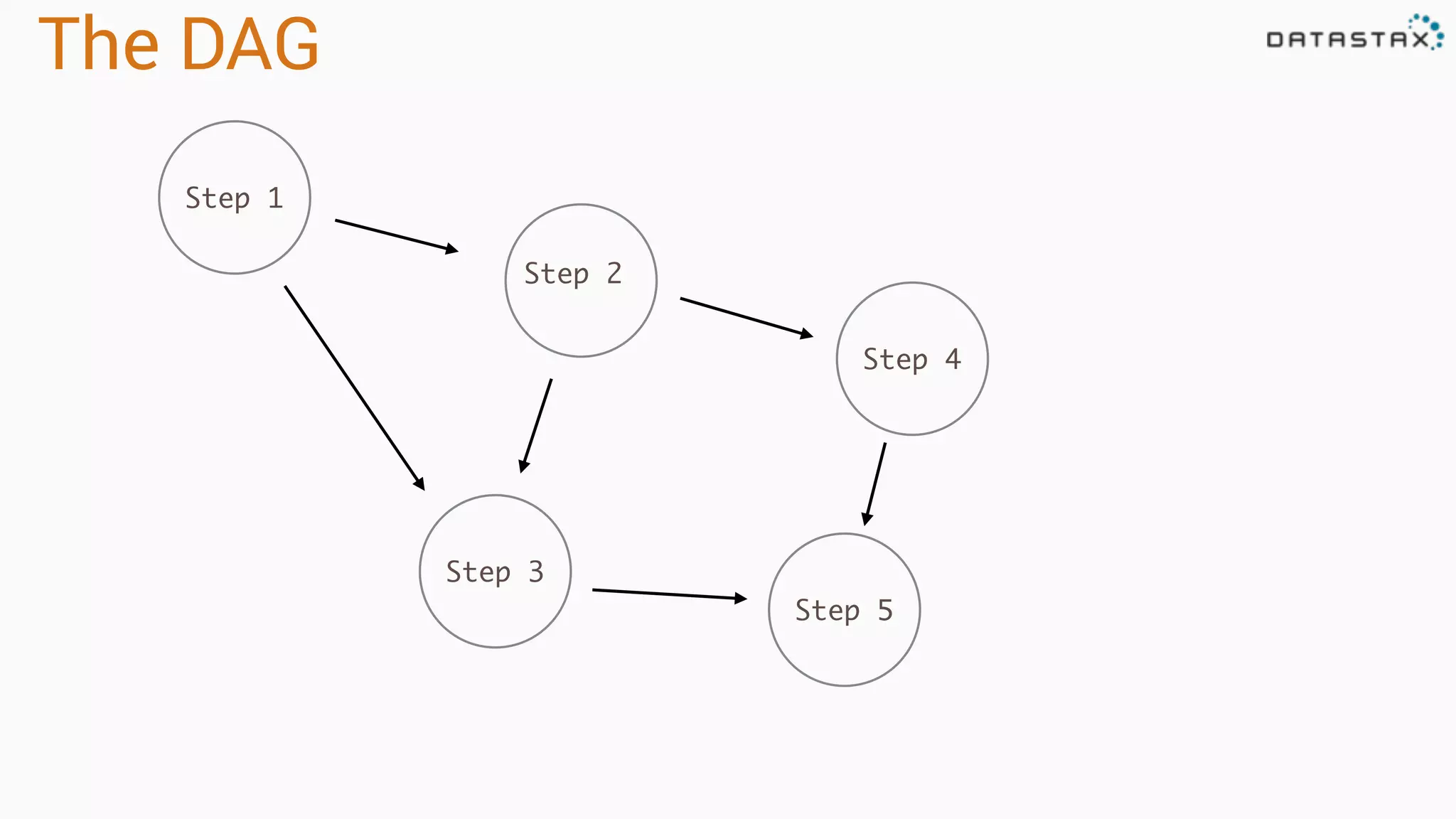
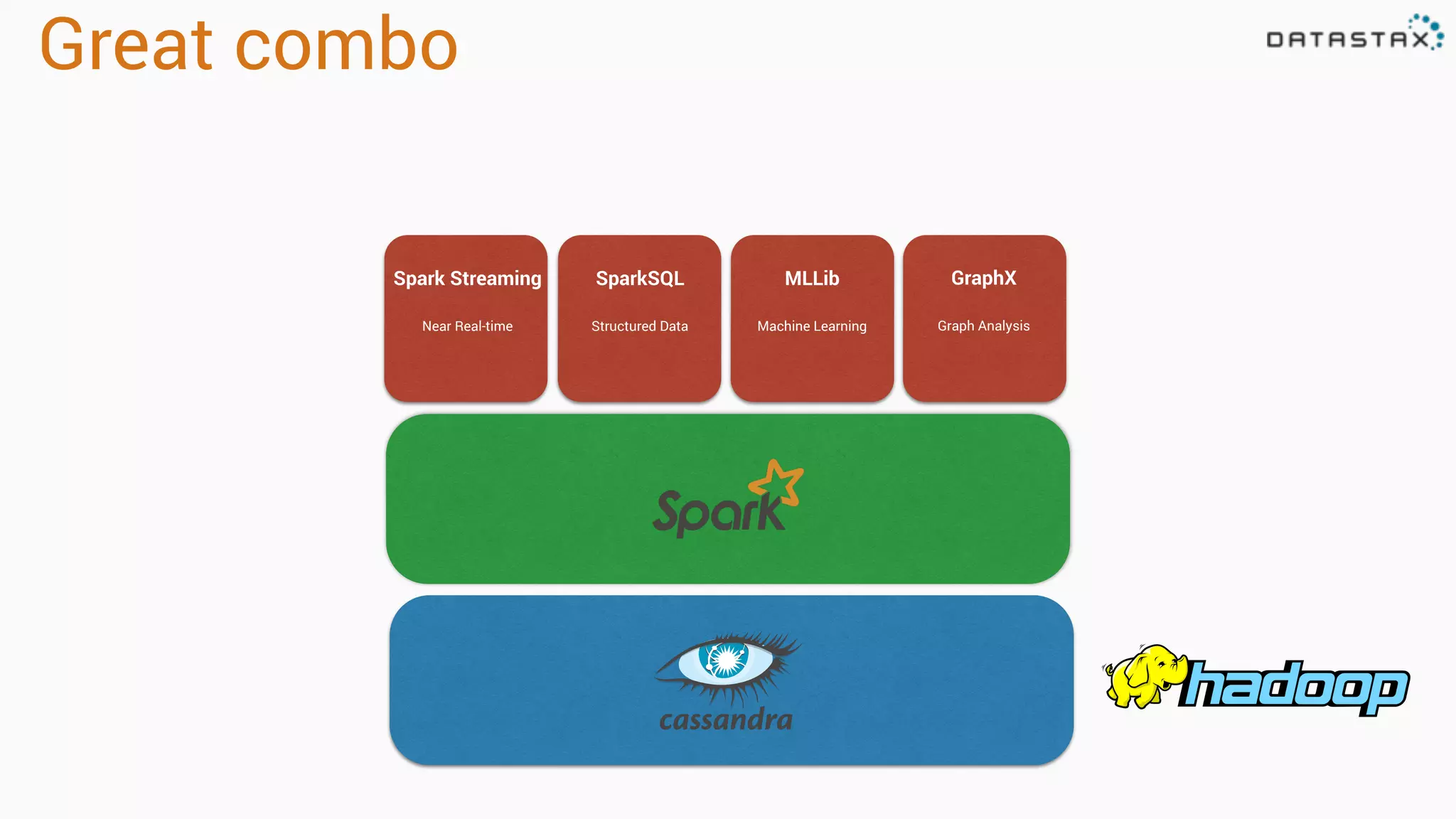
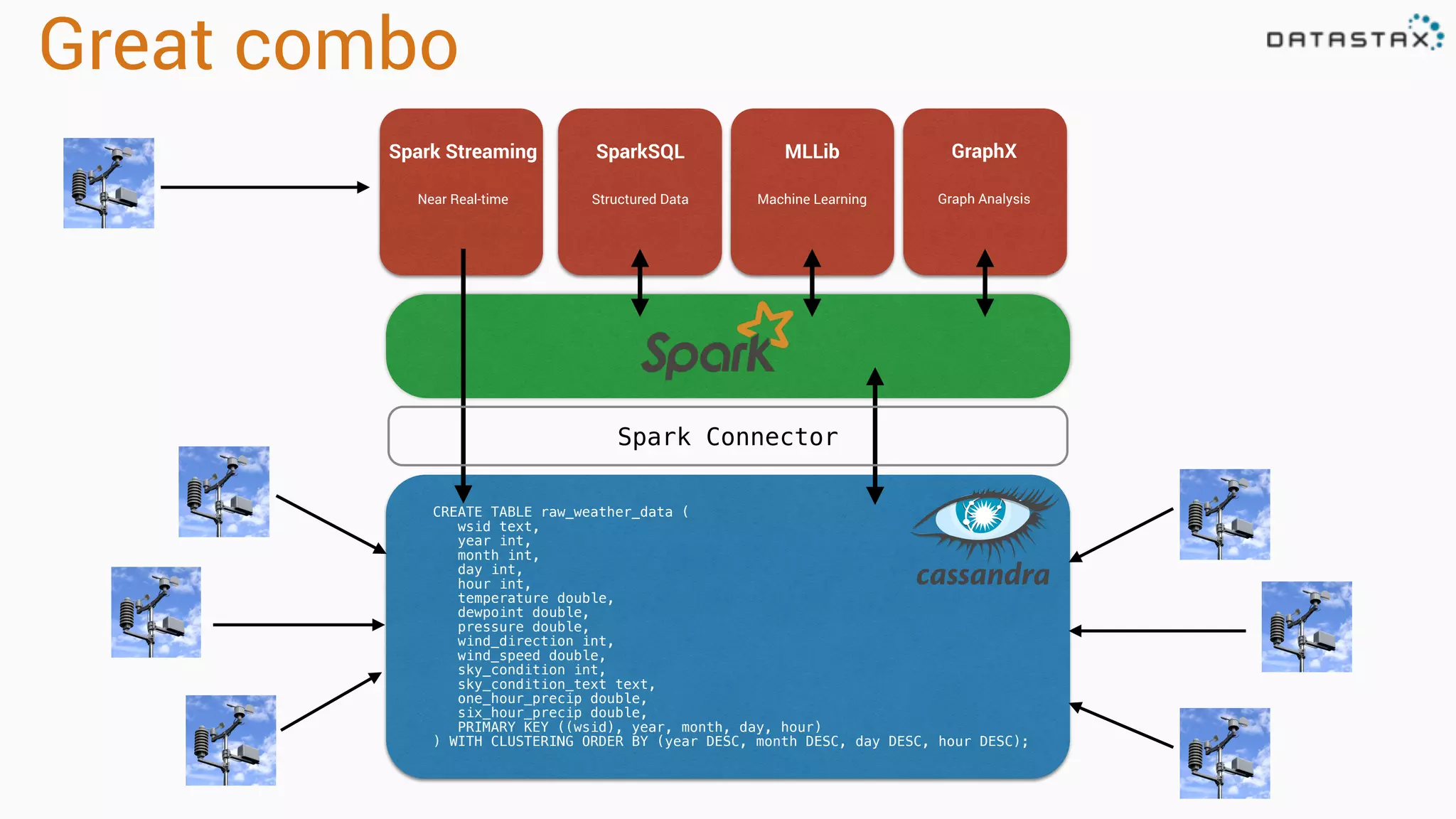
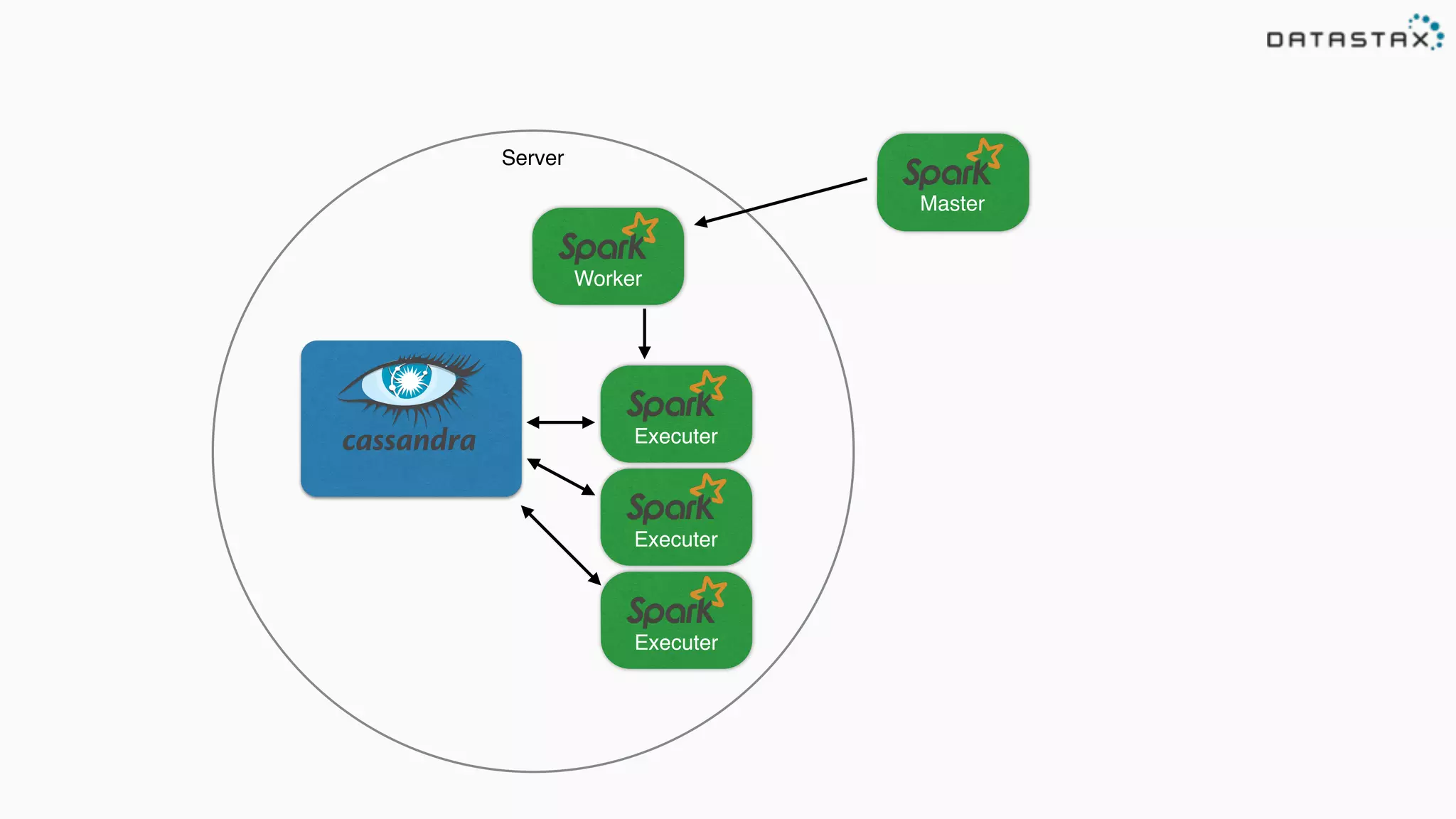
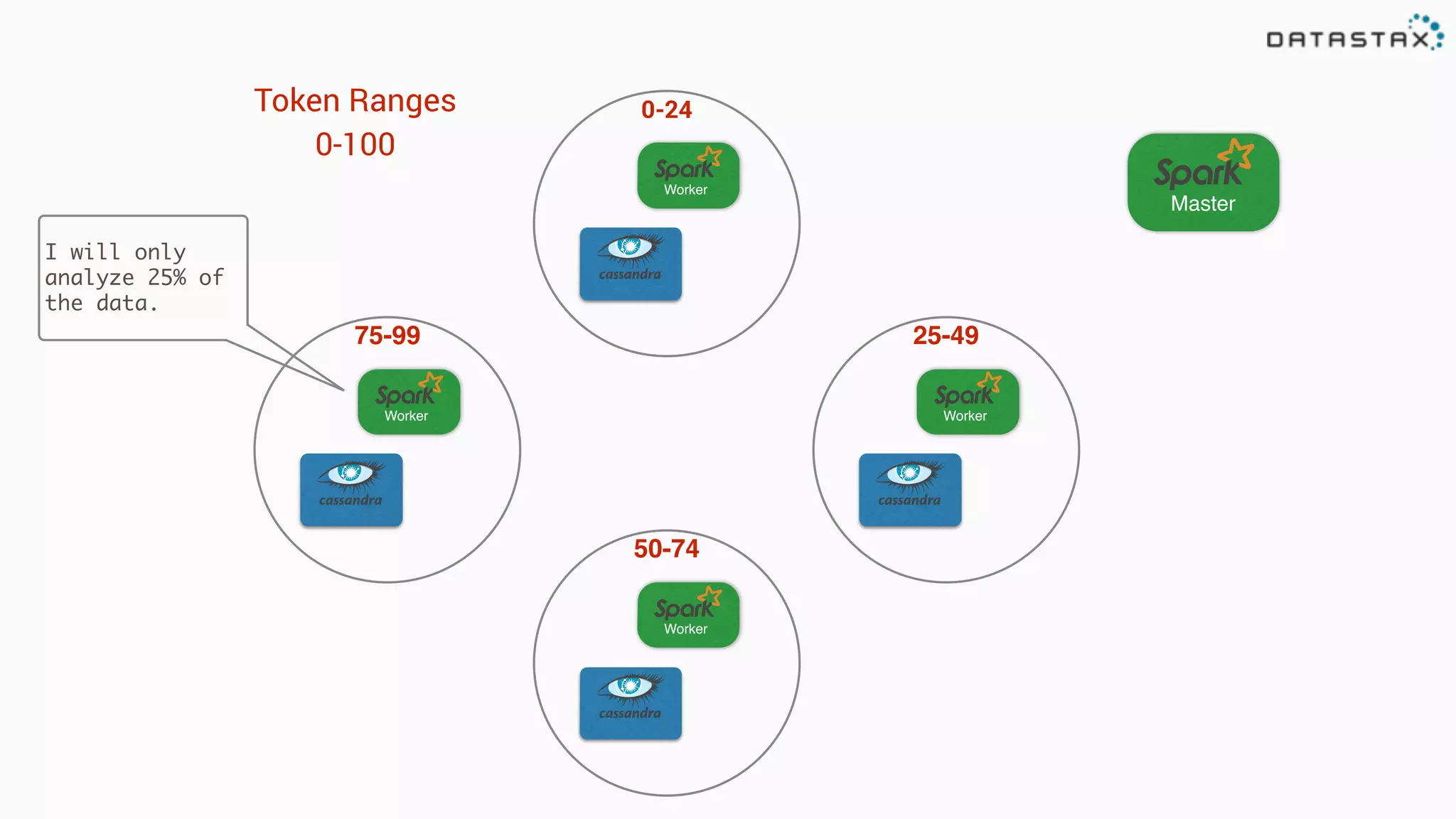
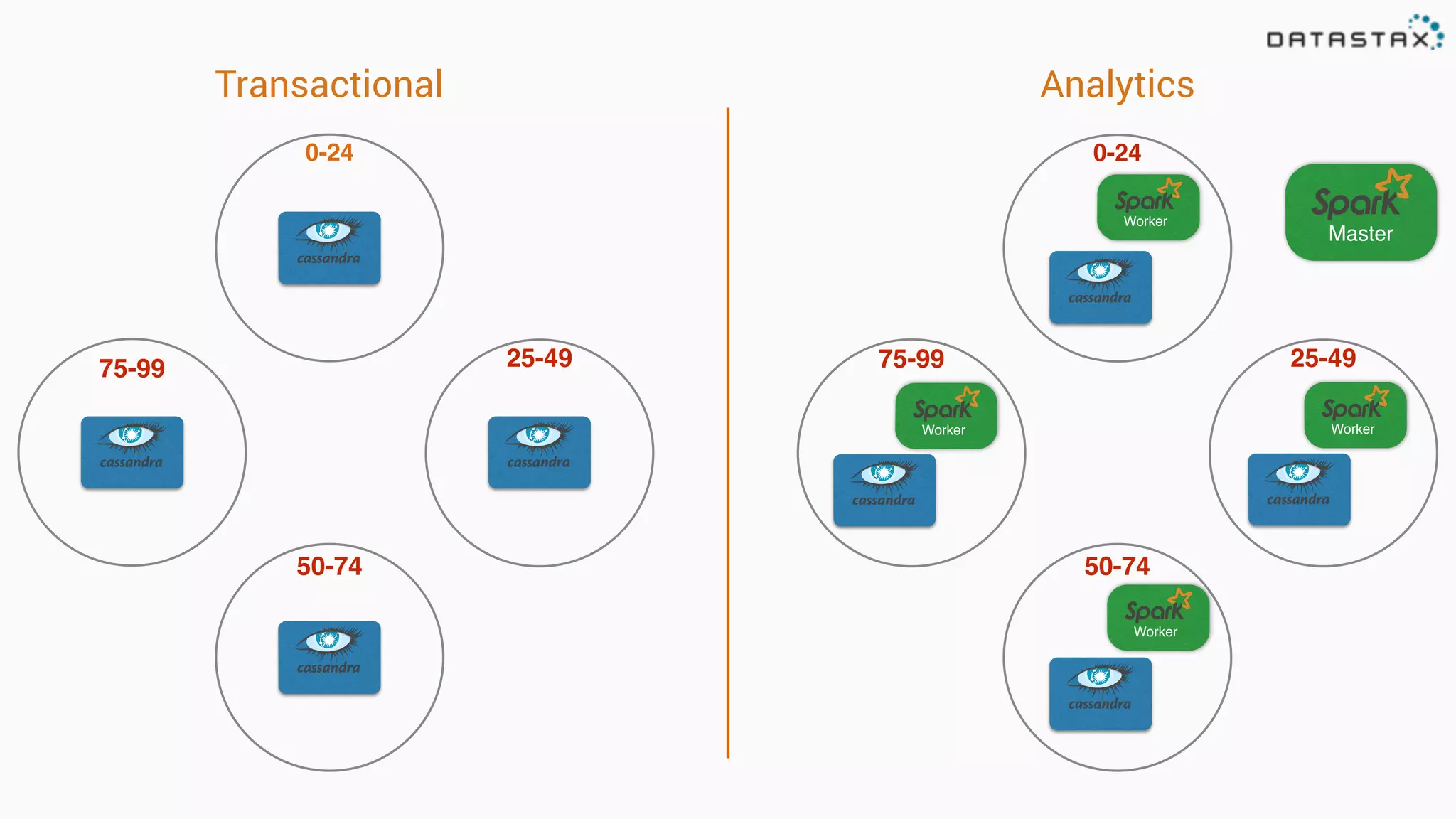
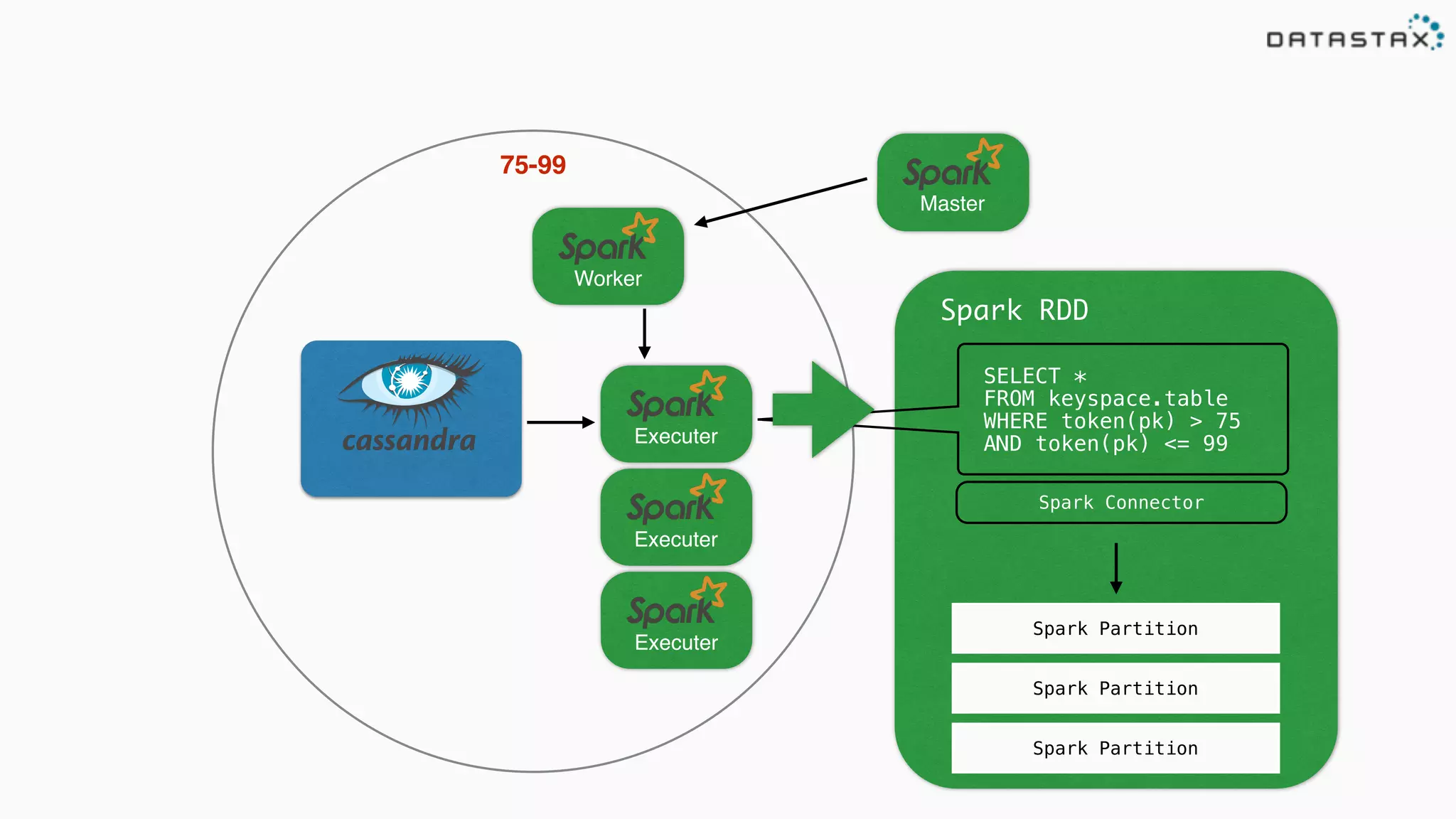
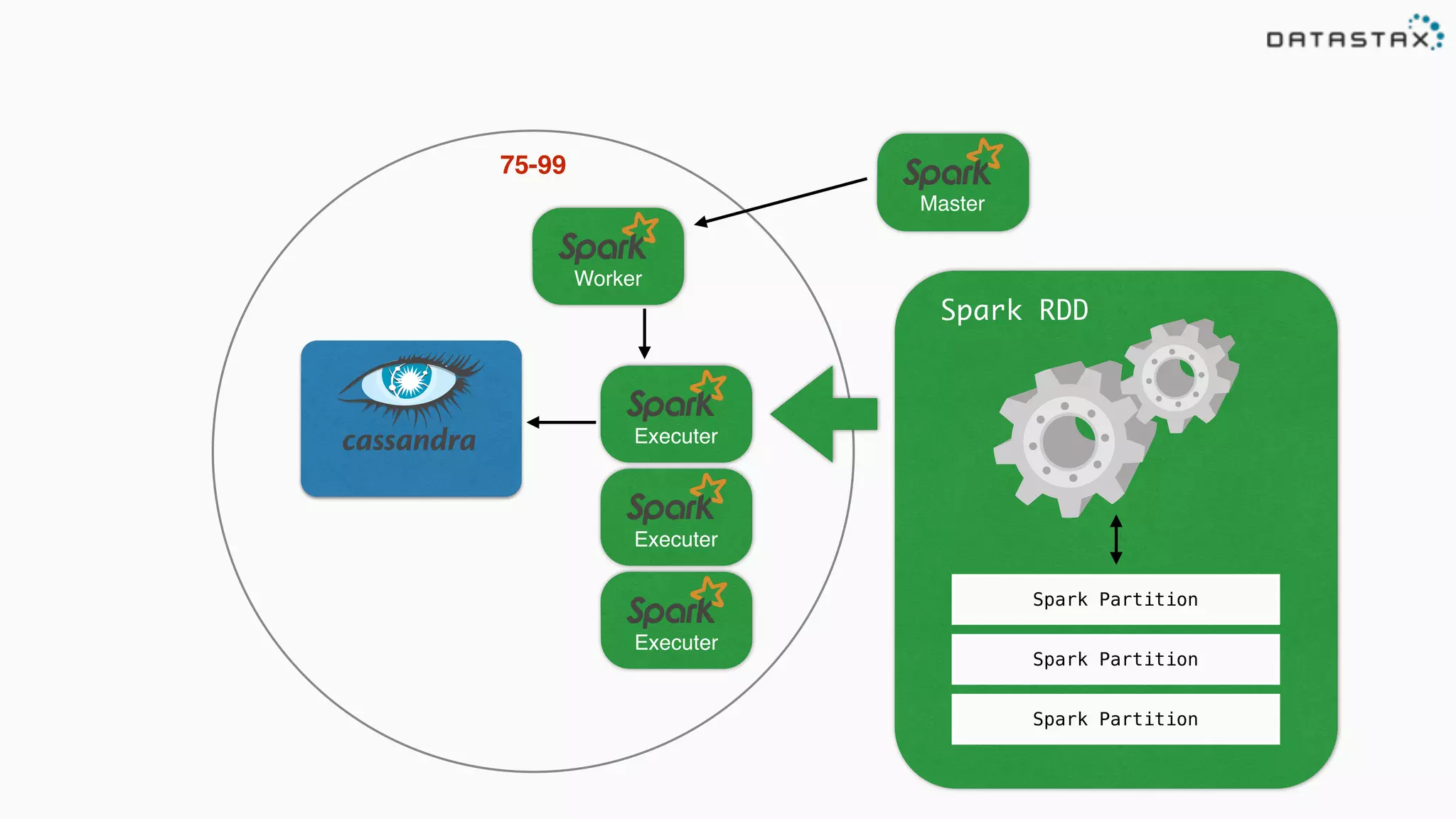
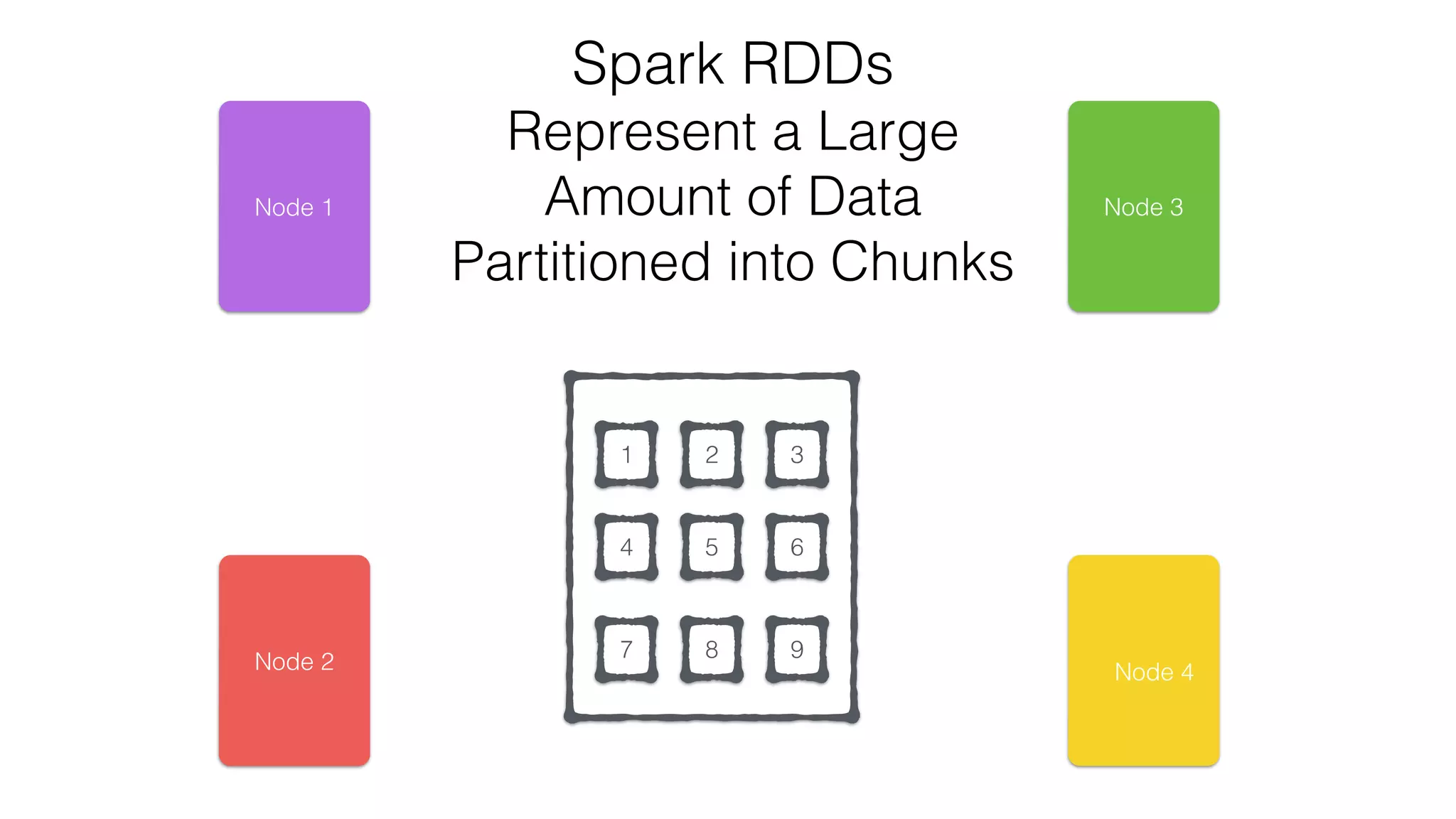
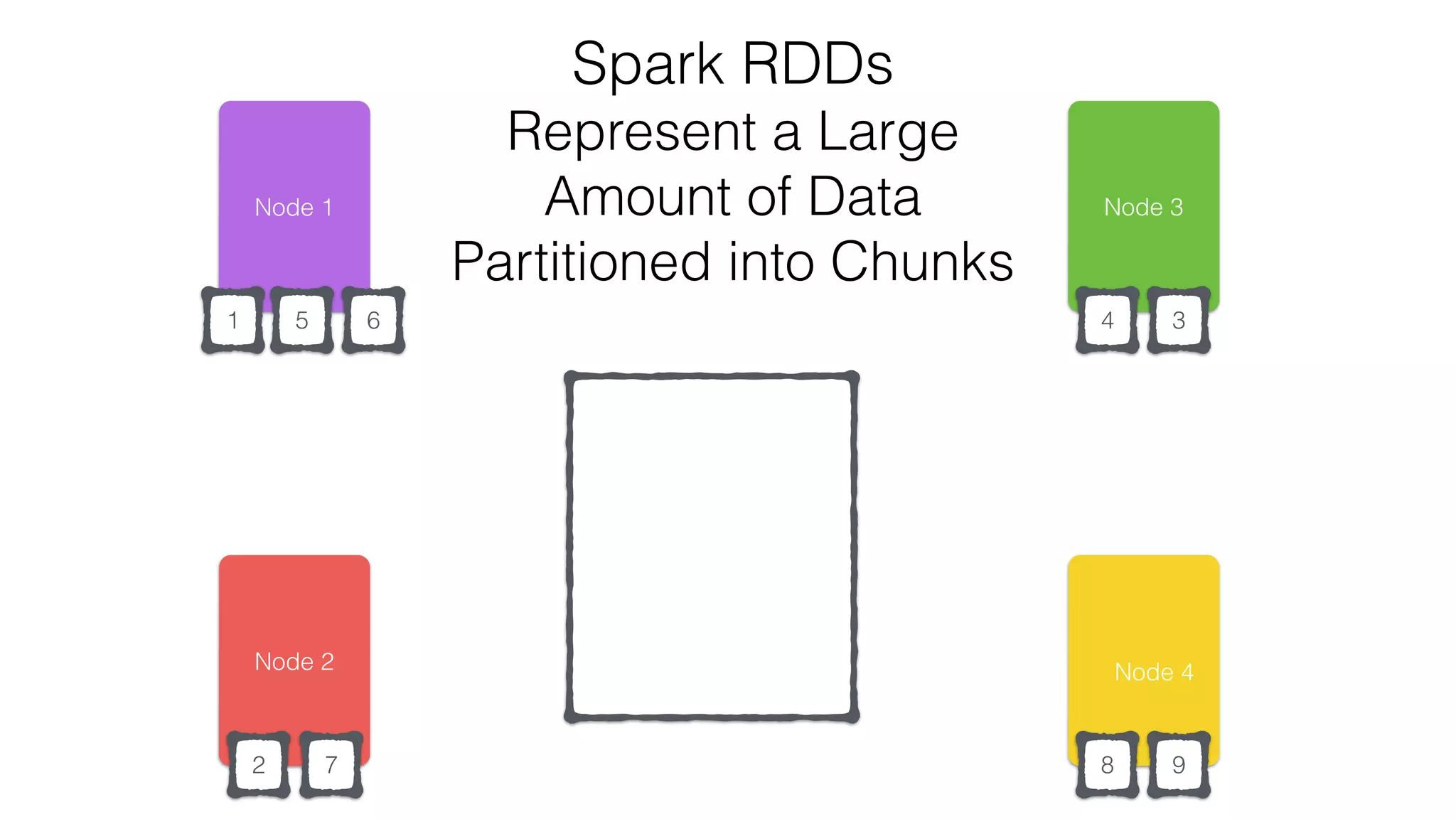
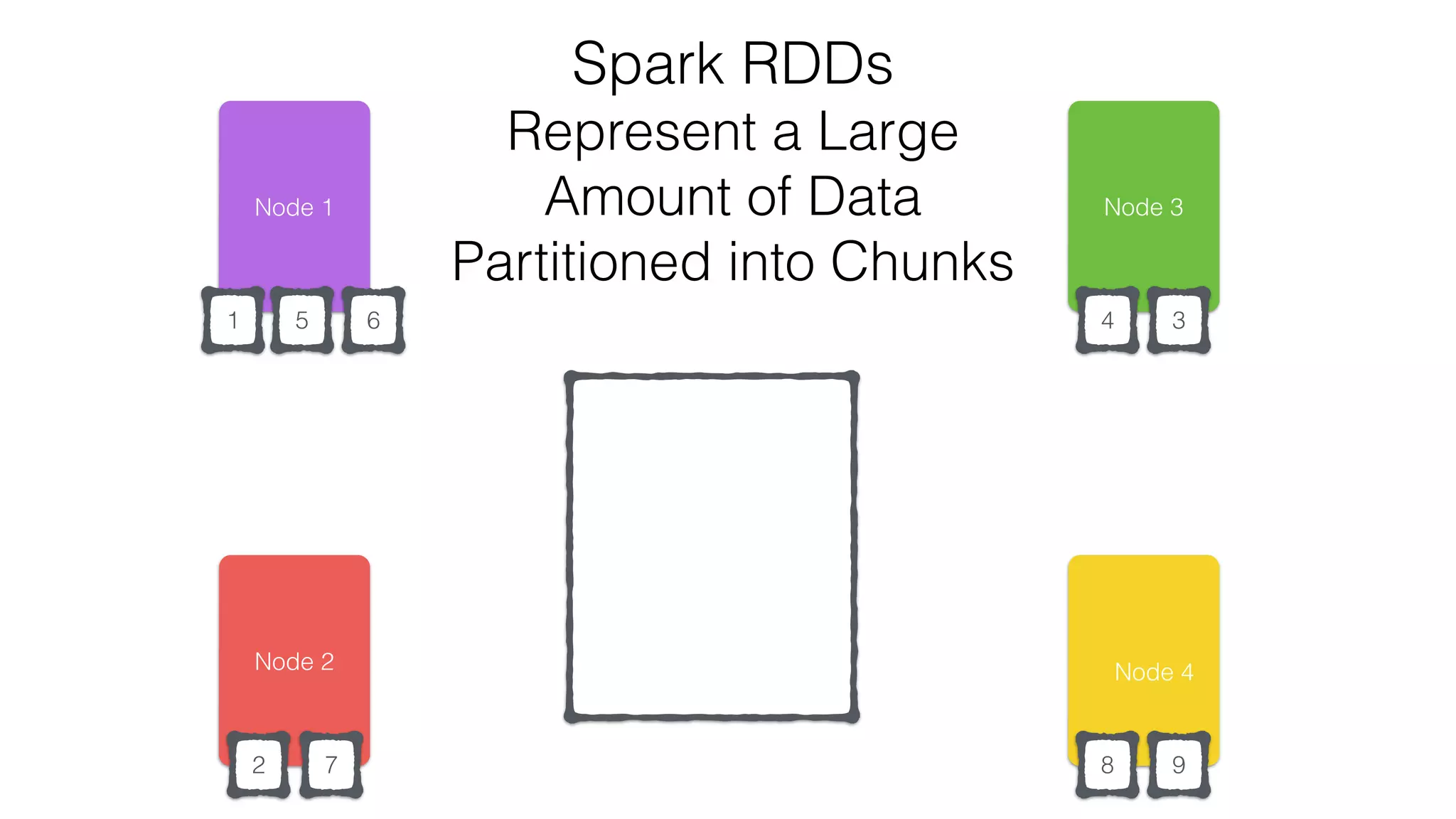
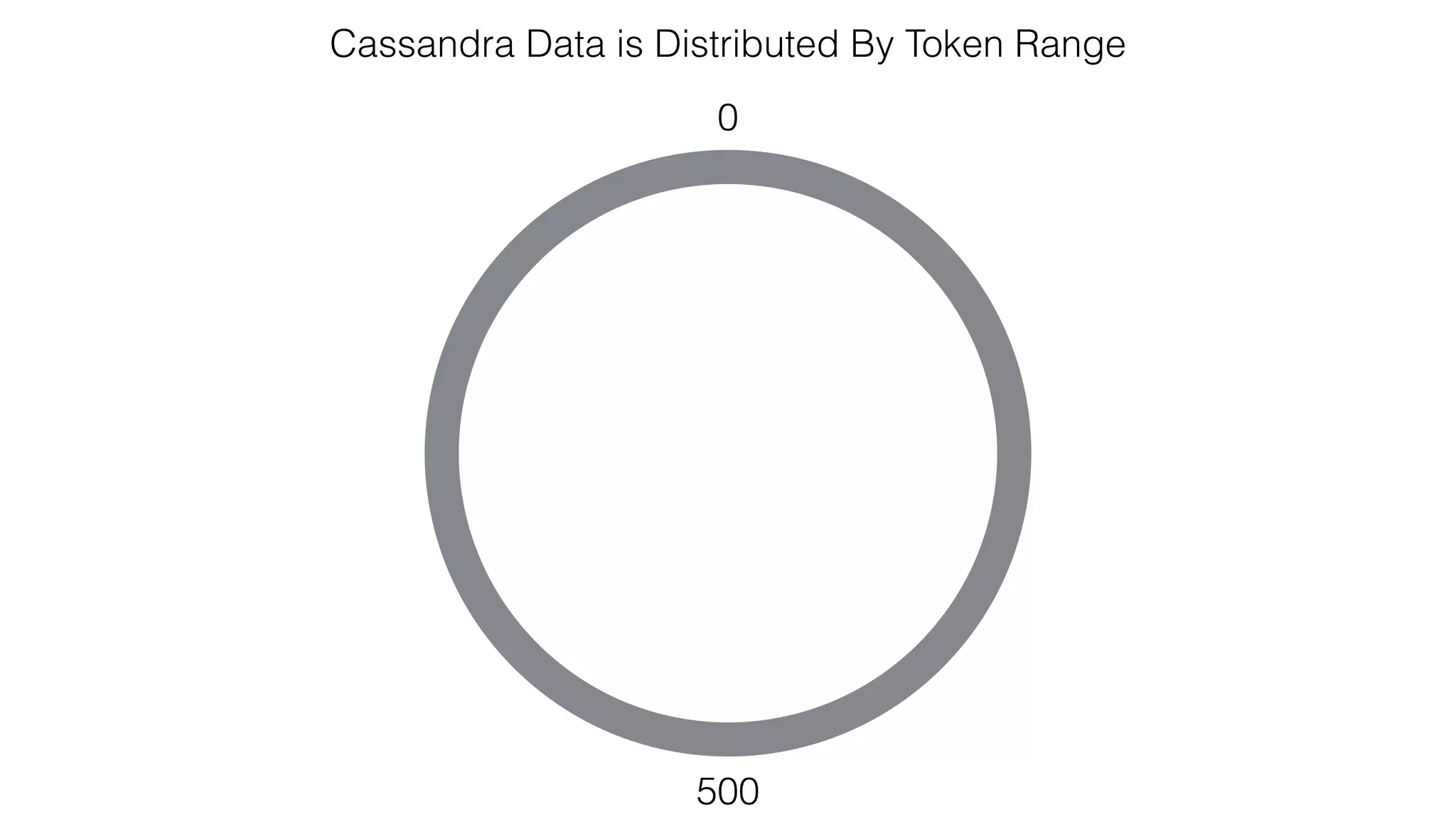
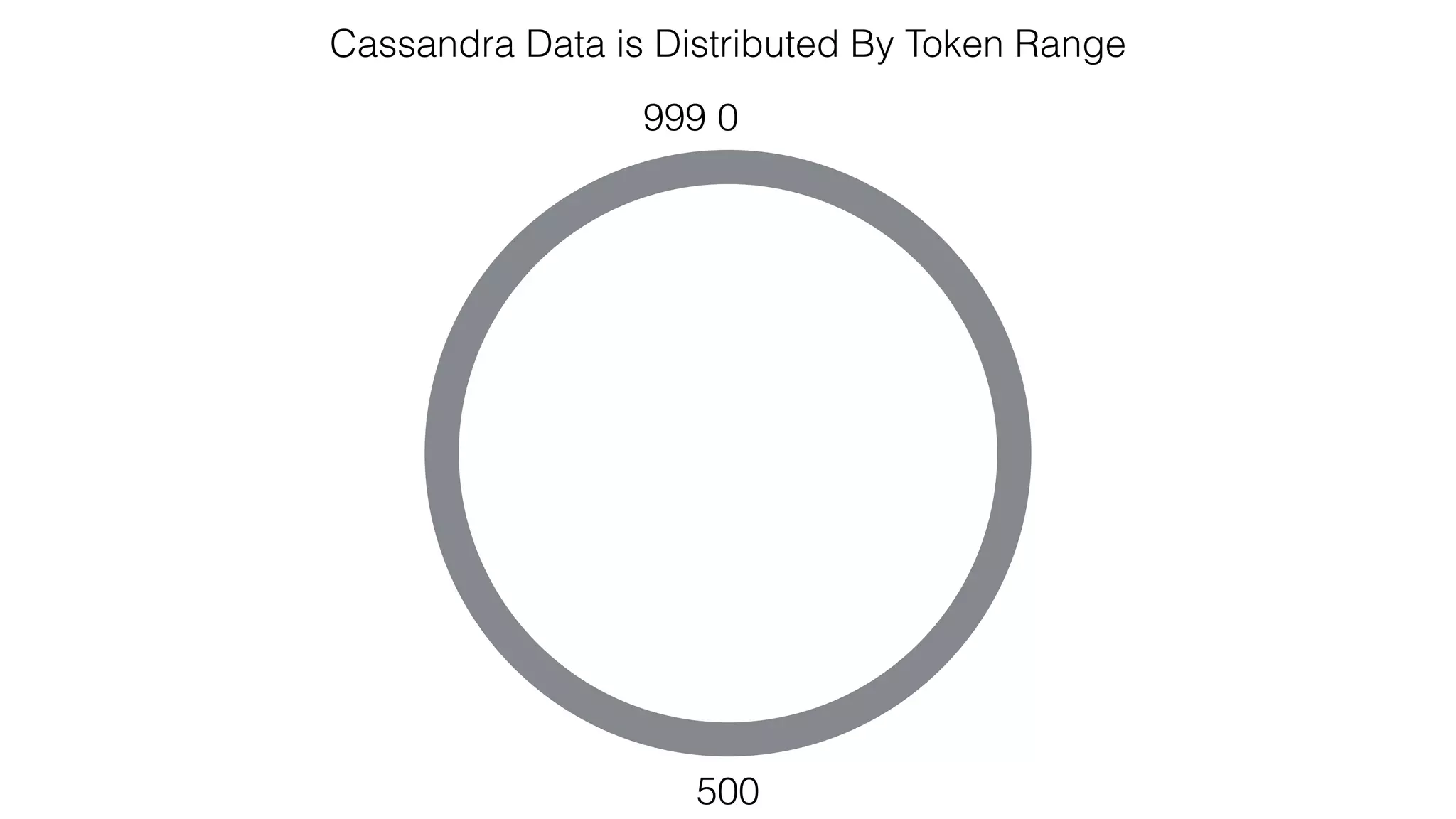
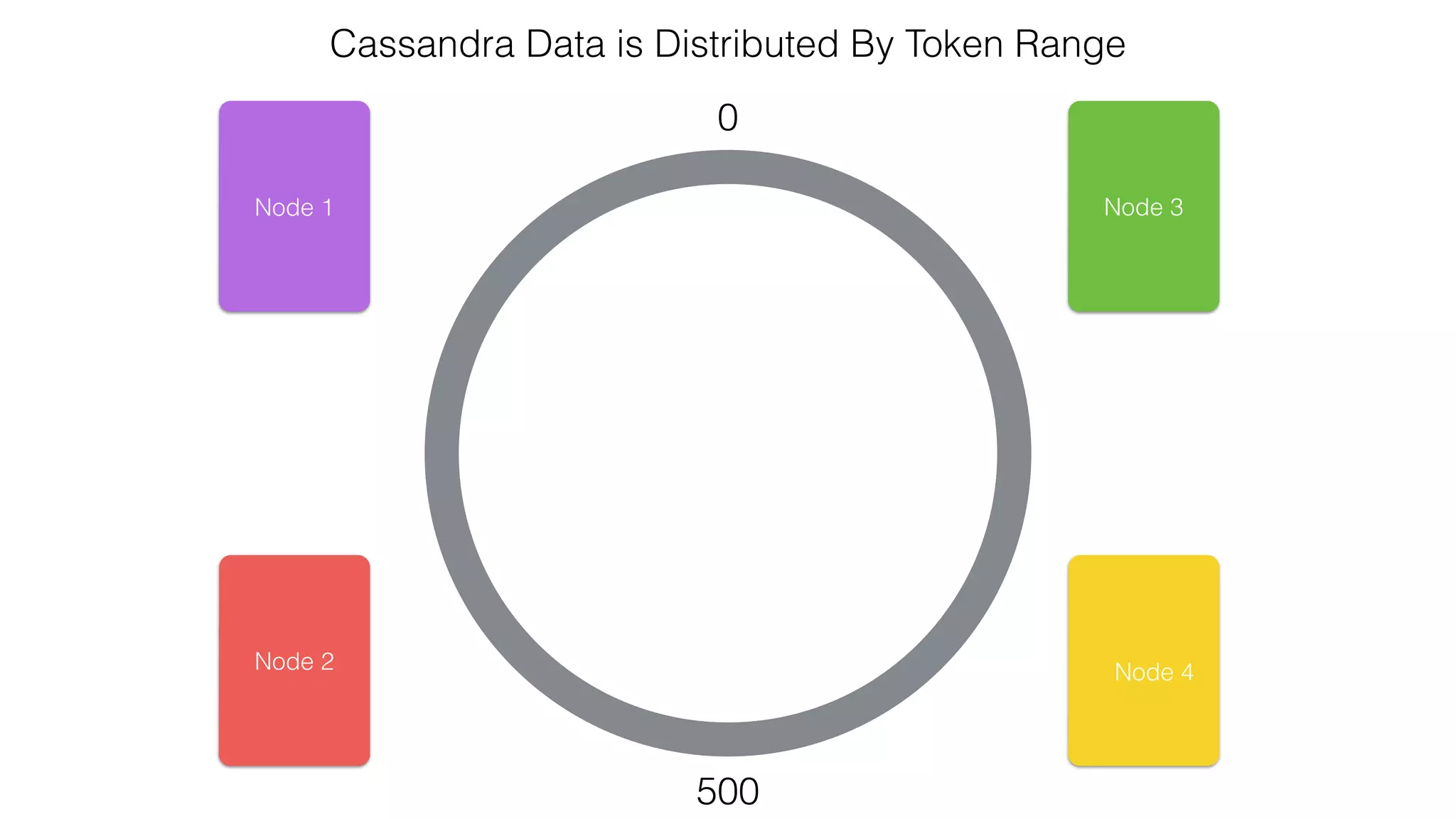
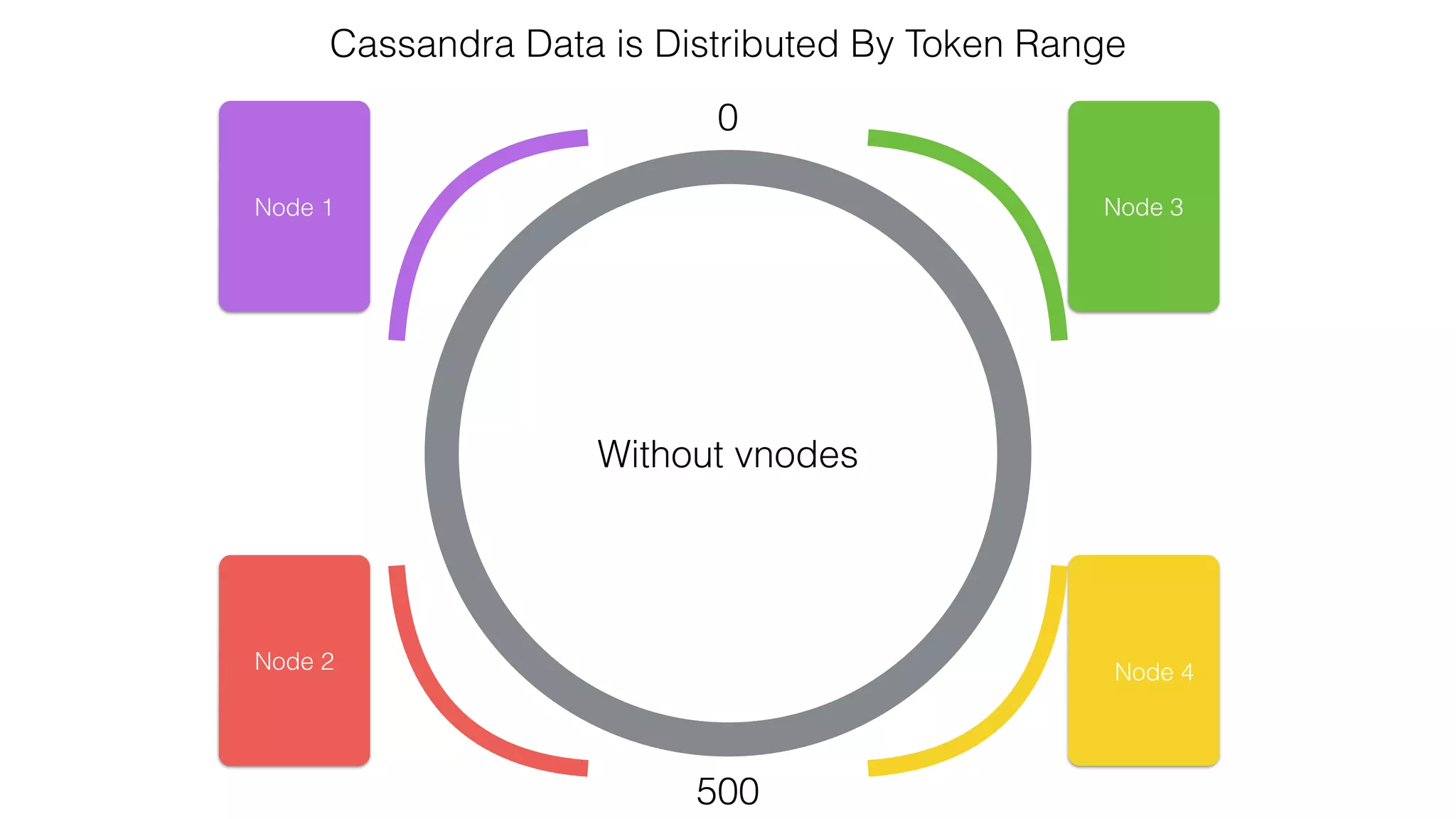
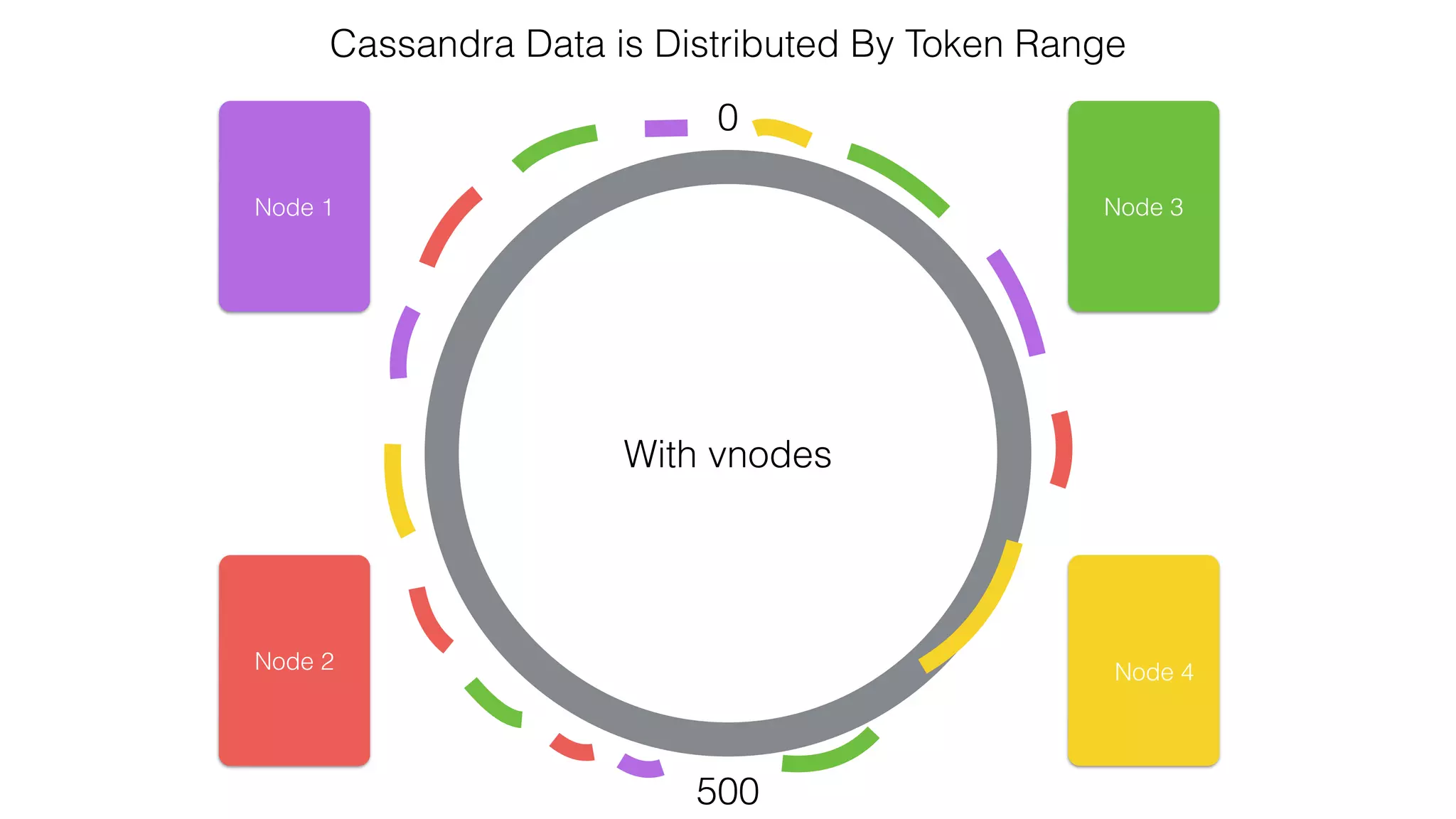
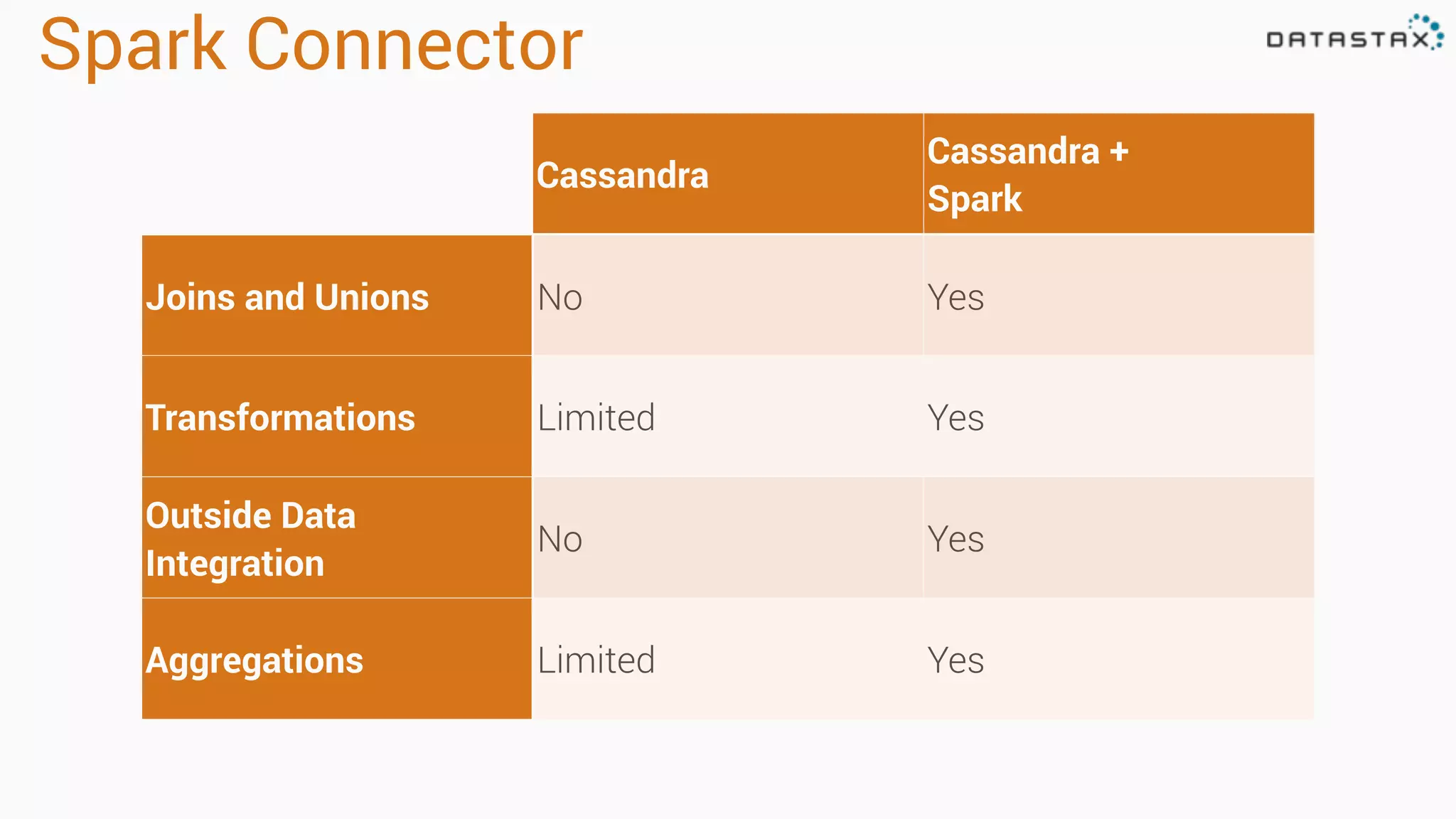
The document discusses the use of Apache Cassandra and Spark for analyzing time series data, specifically using a weather station example to demonstrate Cassandra's storage capabilities and Spark's processing speed. It outlines table structures for raw weather data and daily aggregates, along with various query capabilities supported by Cassandra and Spark's seamless integration. Additionally, it highlights Spark's advantages in terms of speed, flexibility, and fault tolerance in handling big data analysis.





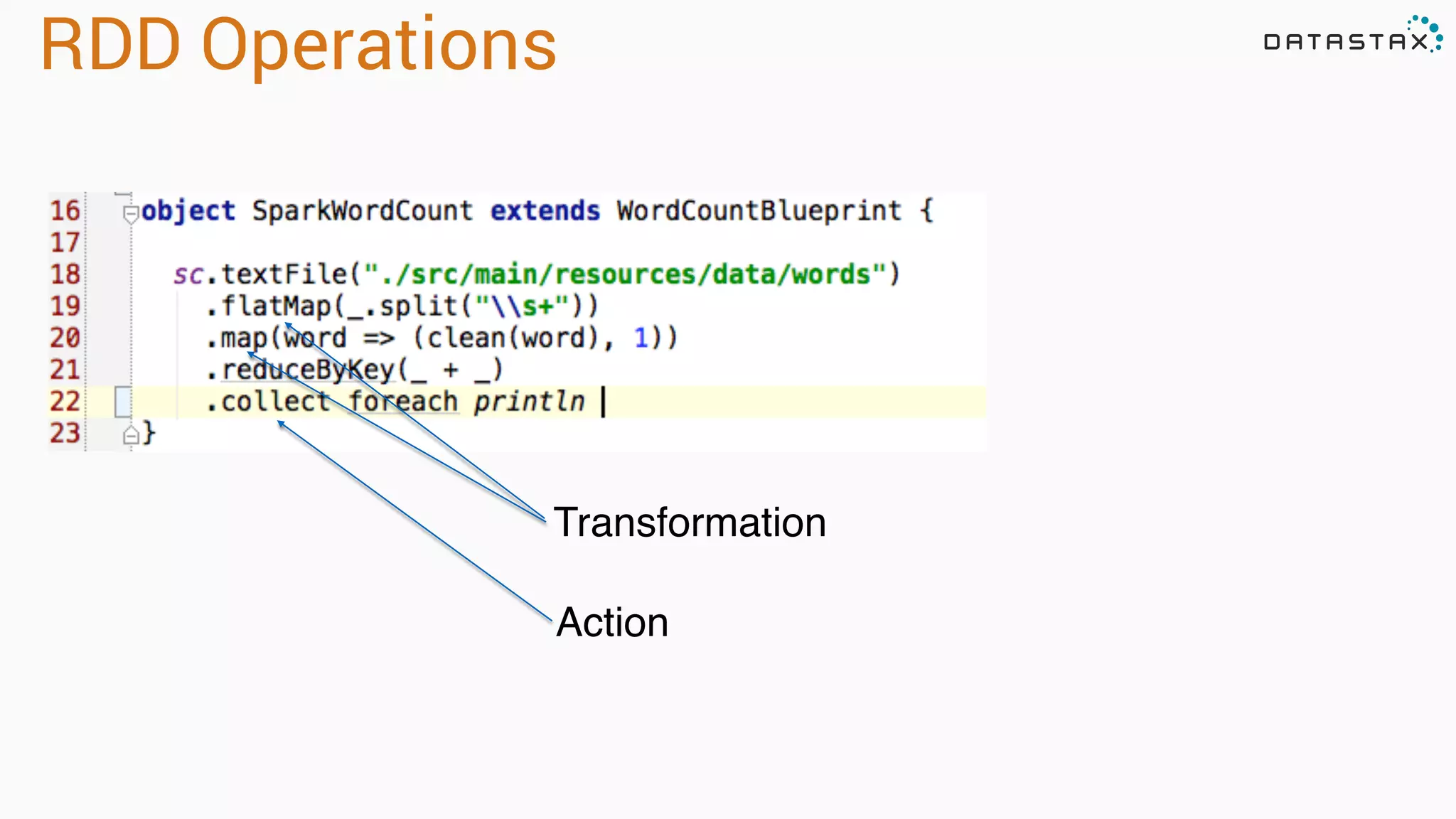
![RDD Operations •Transformations - Similar to scala collections API •Produce new RDDs •filter, flatmap, map, distinct, groupBy, union, zip, reduceByKey, subtract •Actions •Require materialization of the records to generate a value •collect: Array[T], count, fold, reduce..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyzingtimeseriesdatawithapachesparkandcassandra-150701140404-lva1-app6891/75/Analyzing-Time-Series-Data-with-Apache-Spark-and-Cassandra-15-2048.jpg)



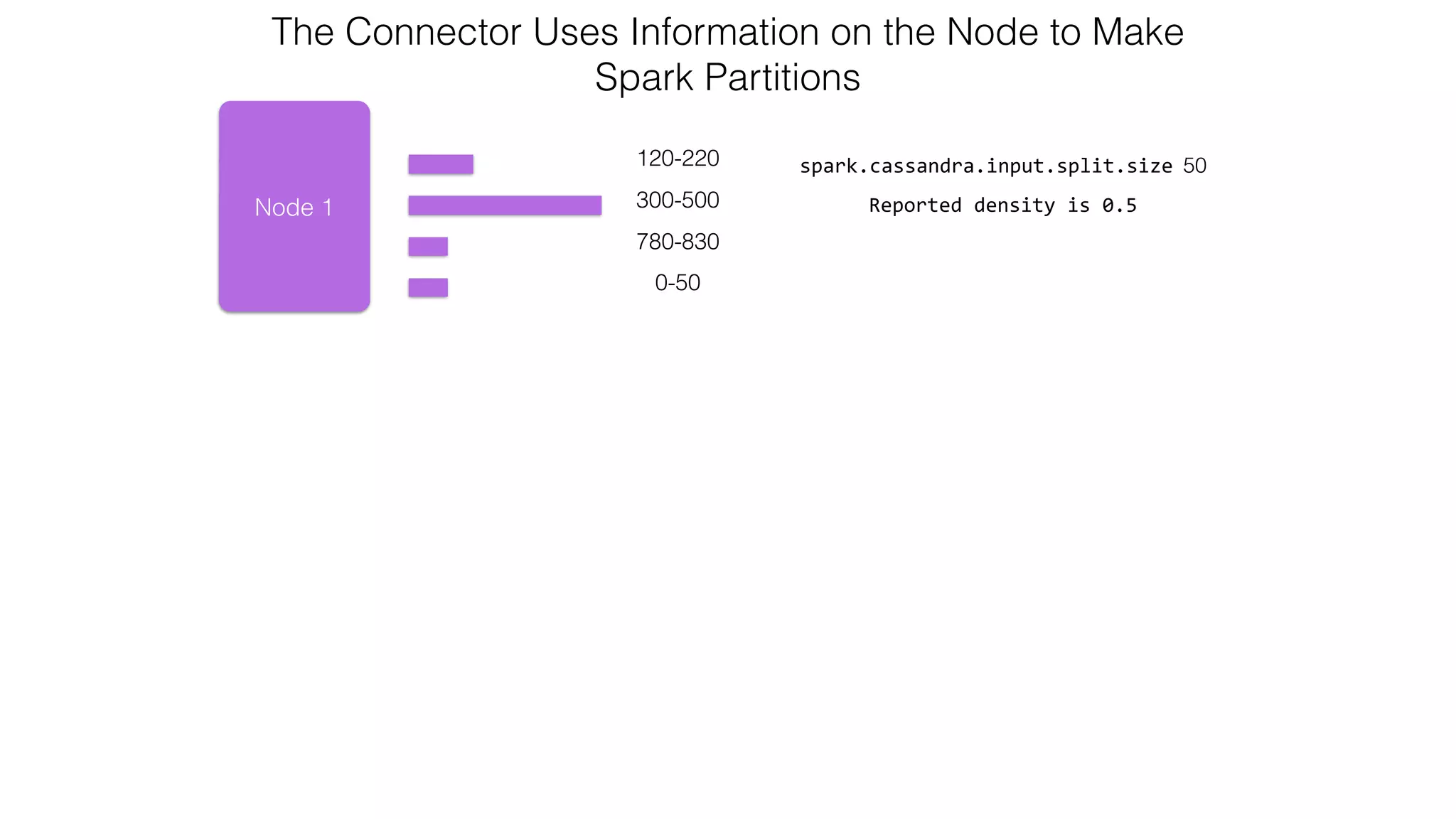
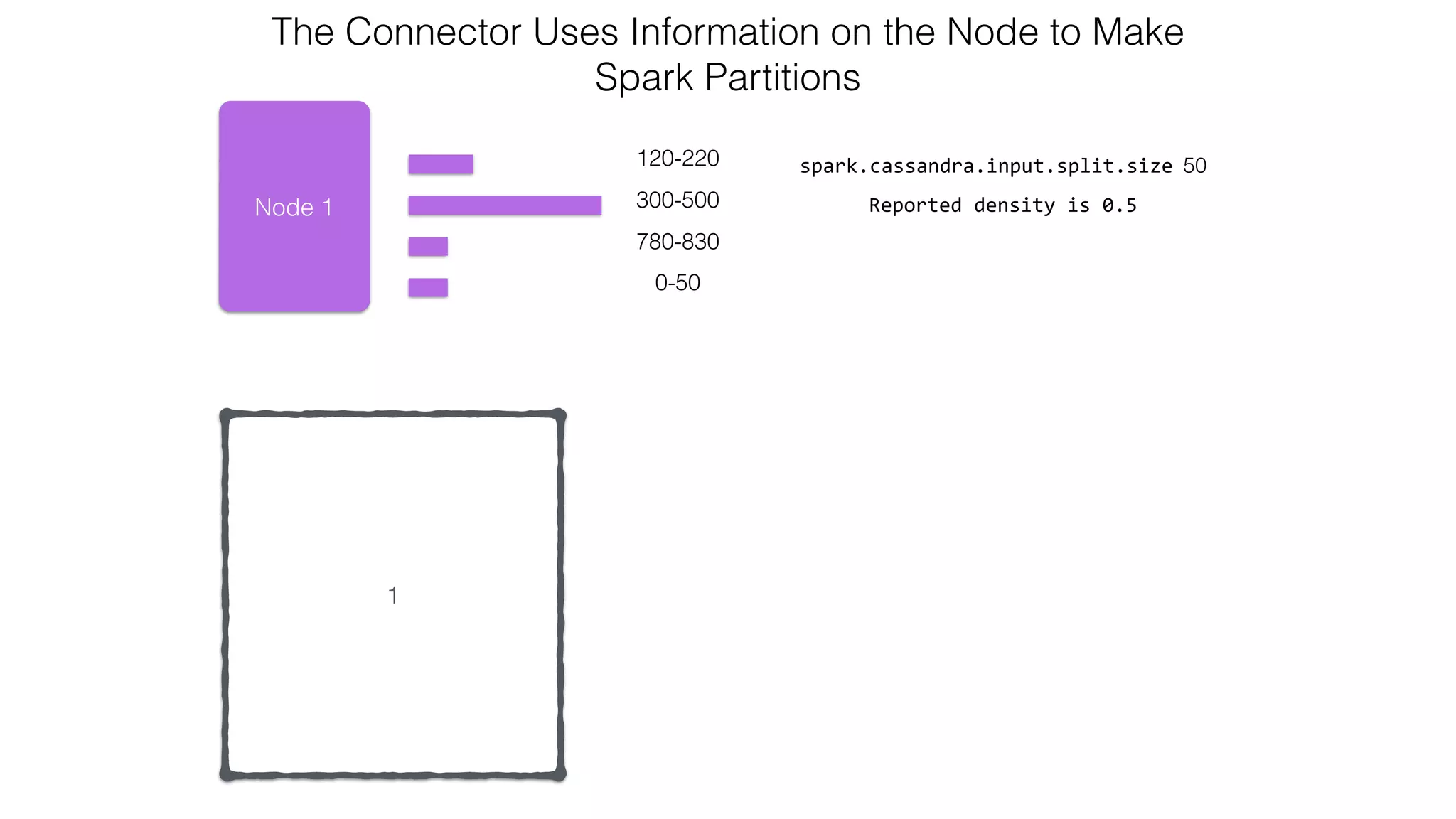
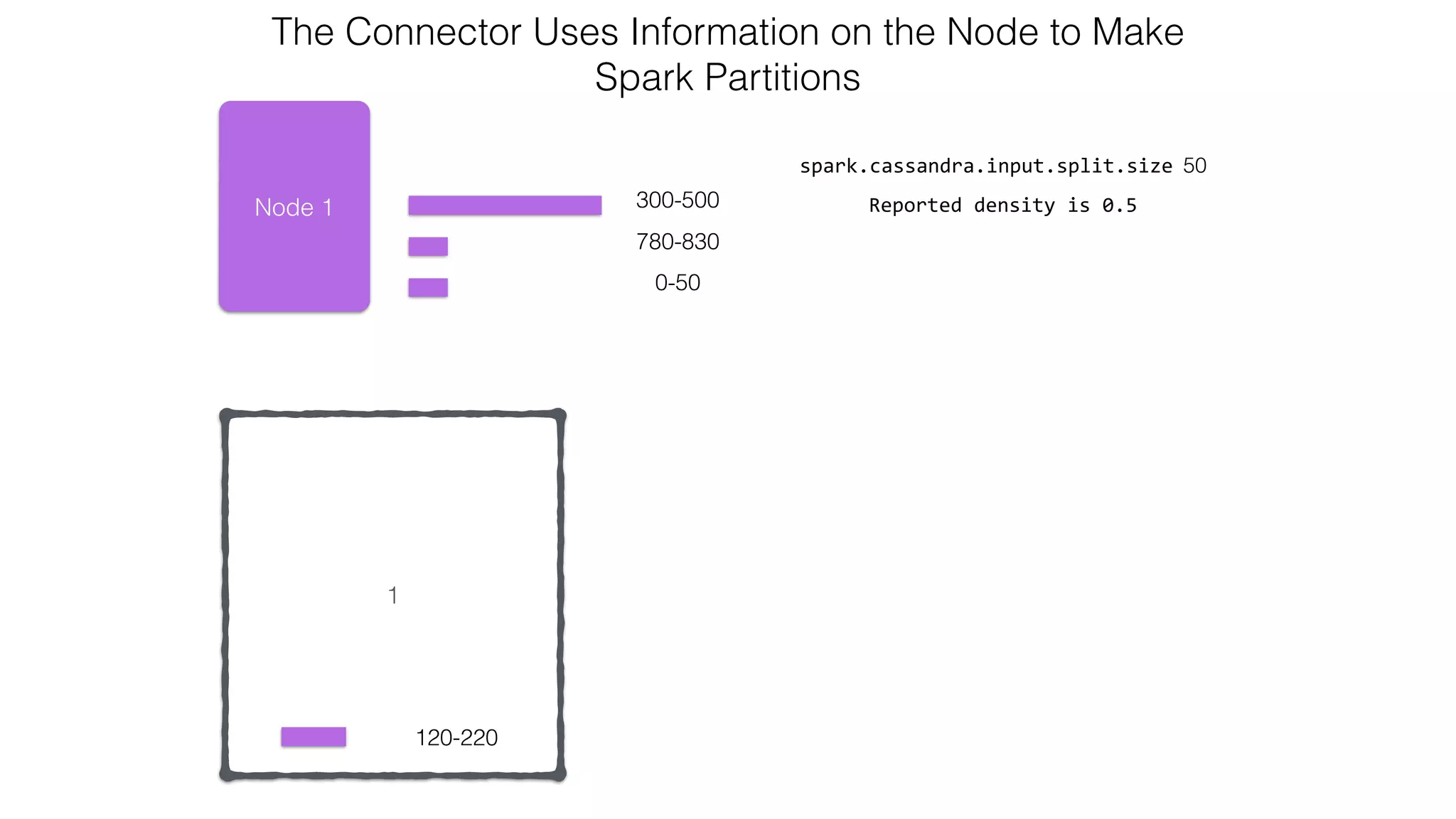
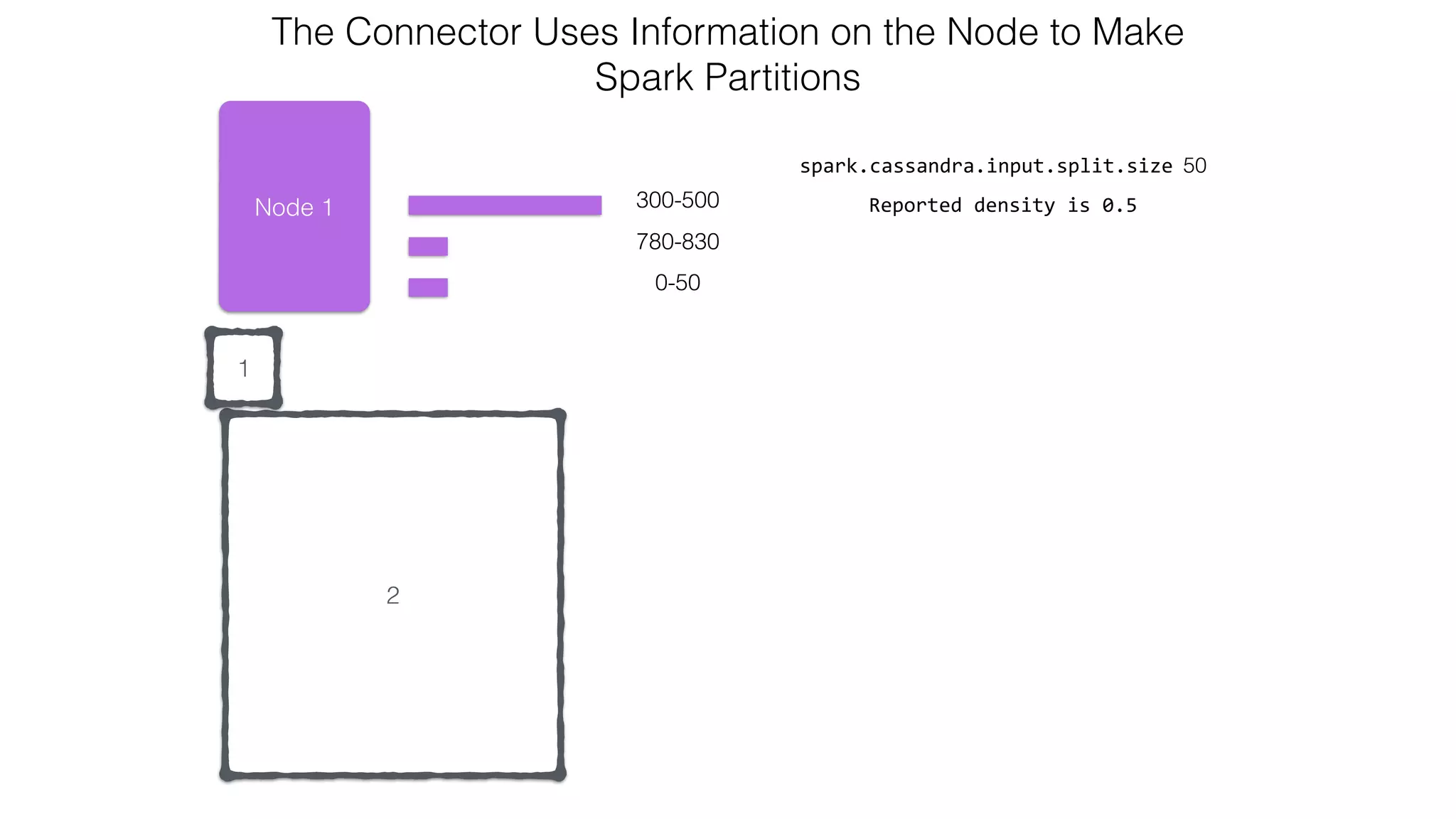
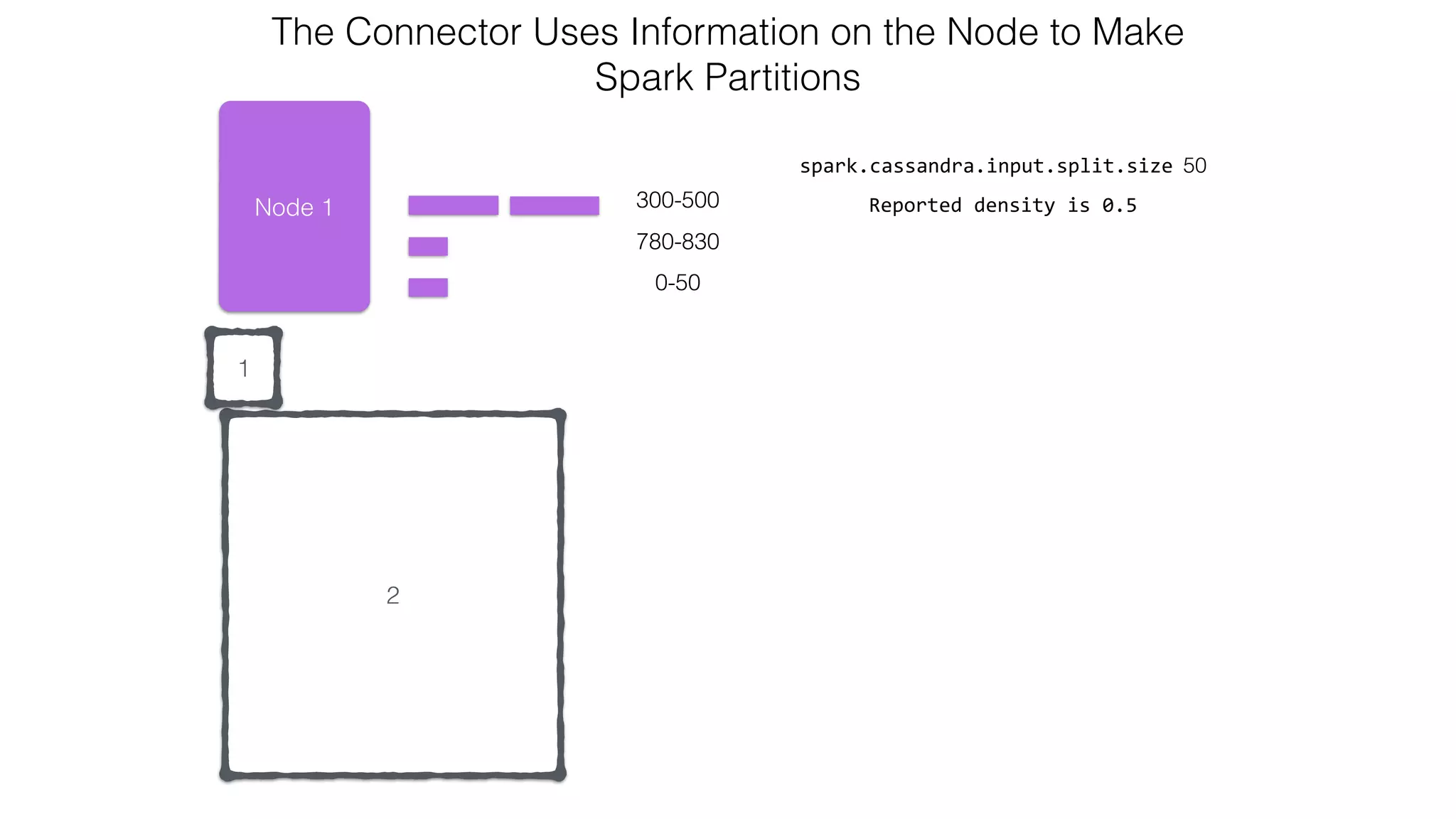
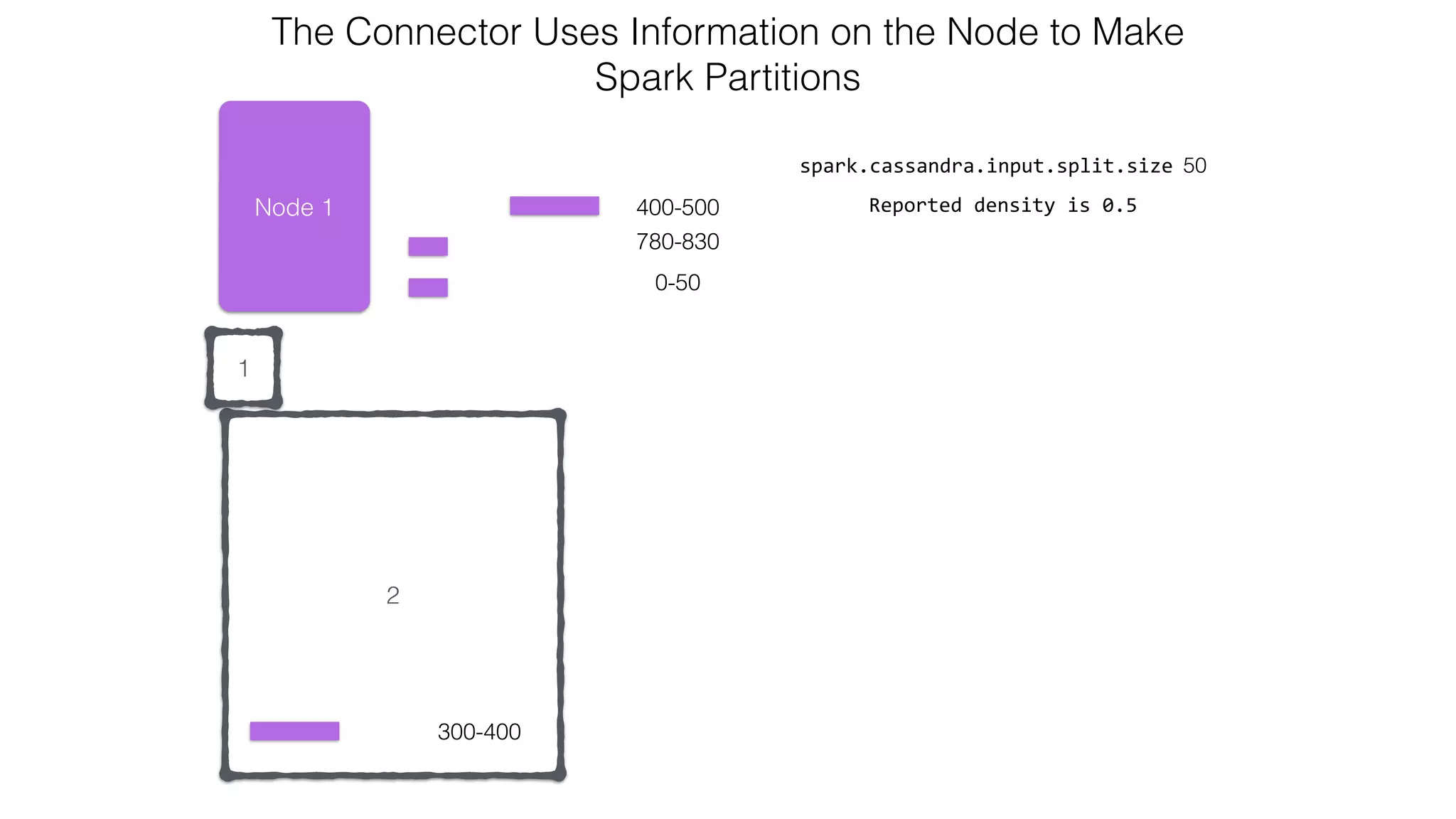
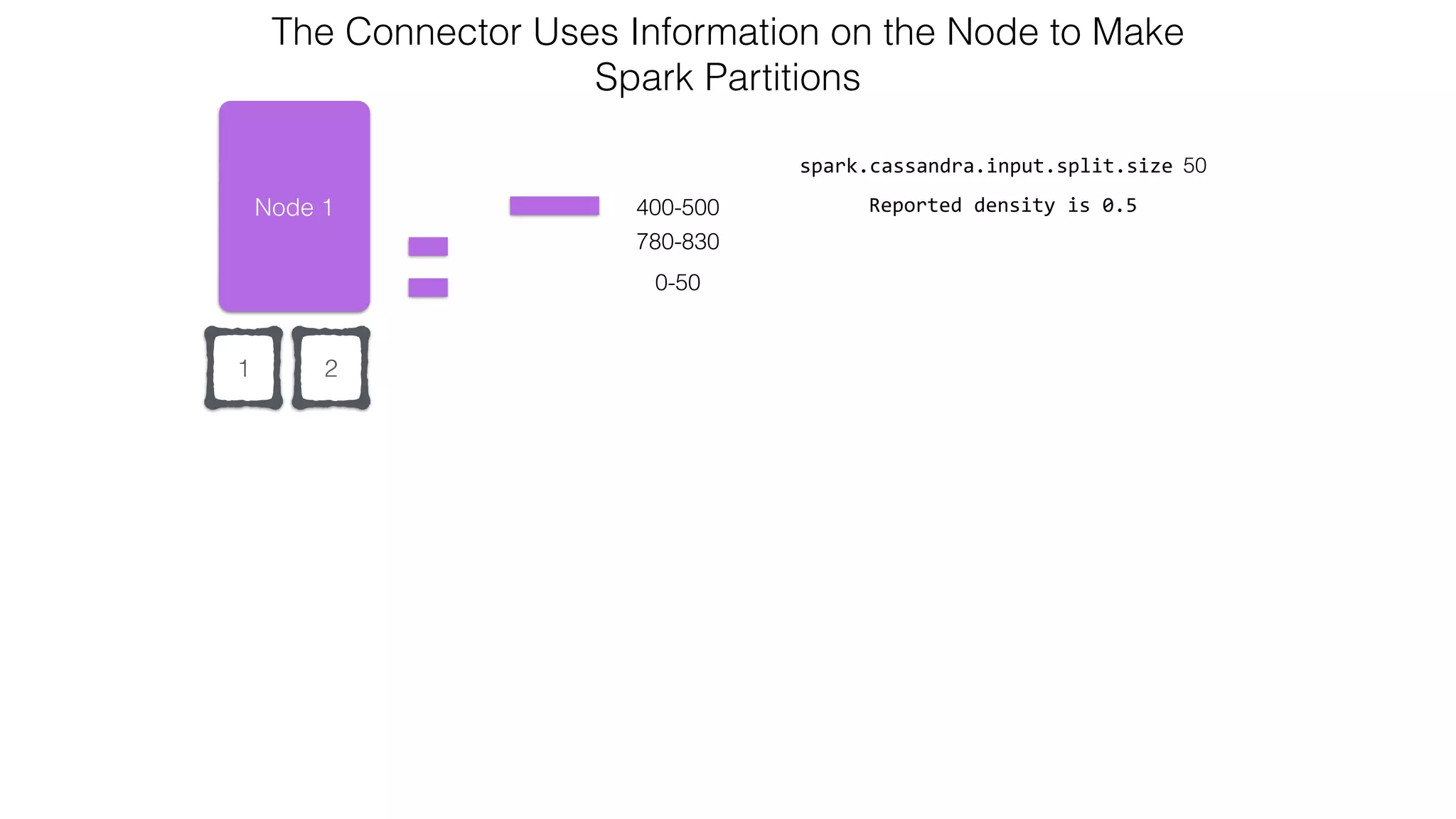
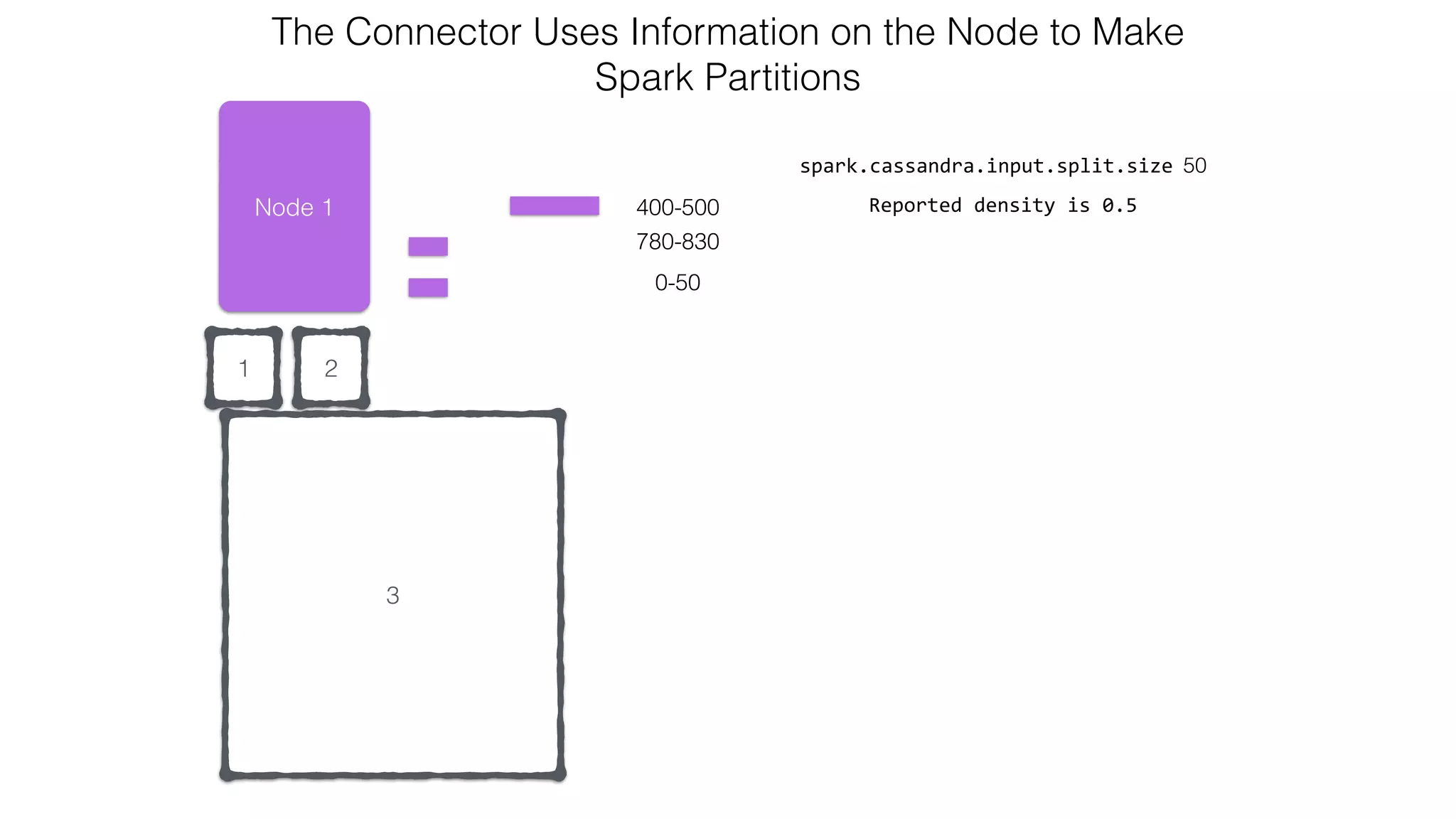
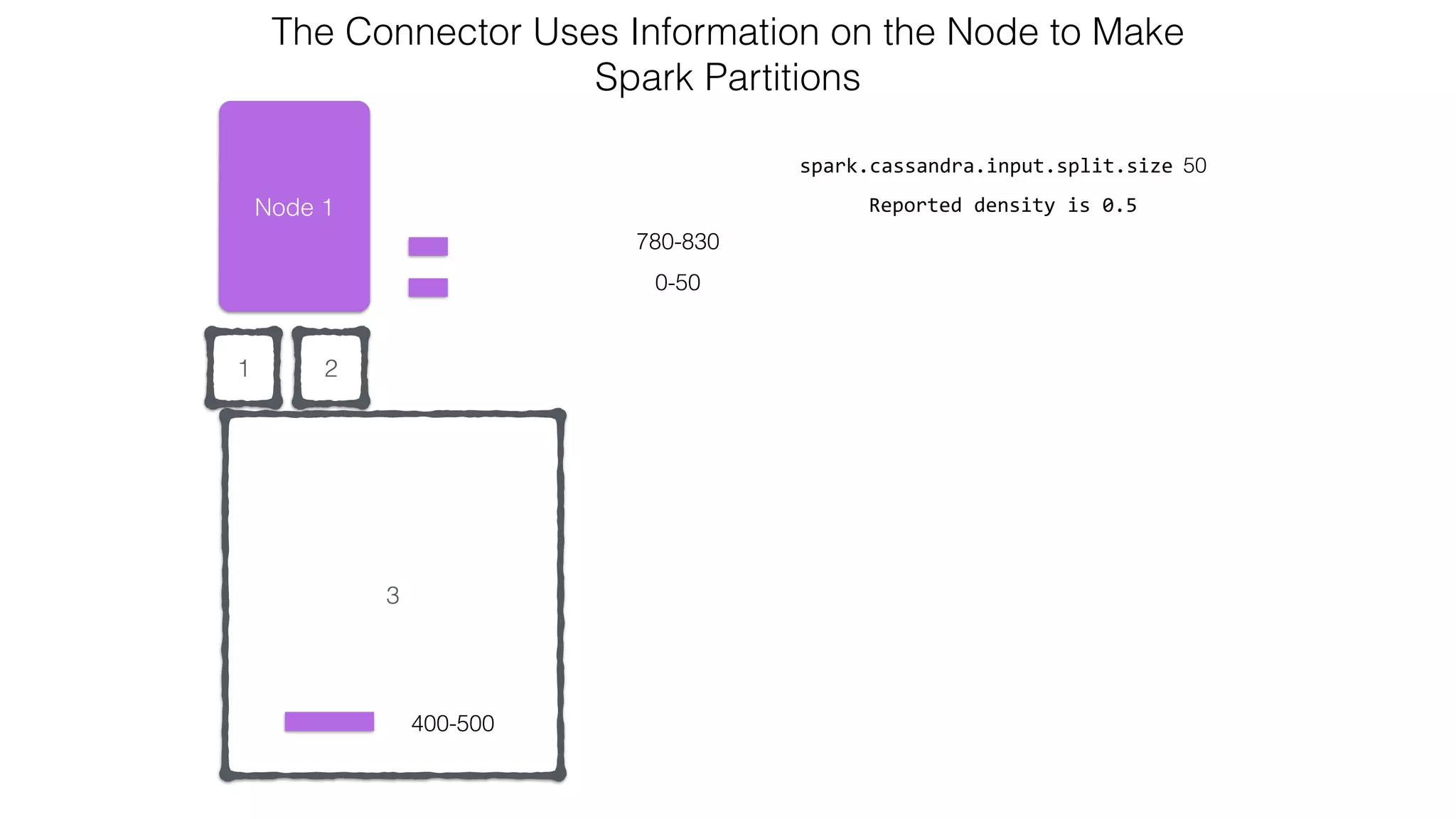
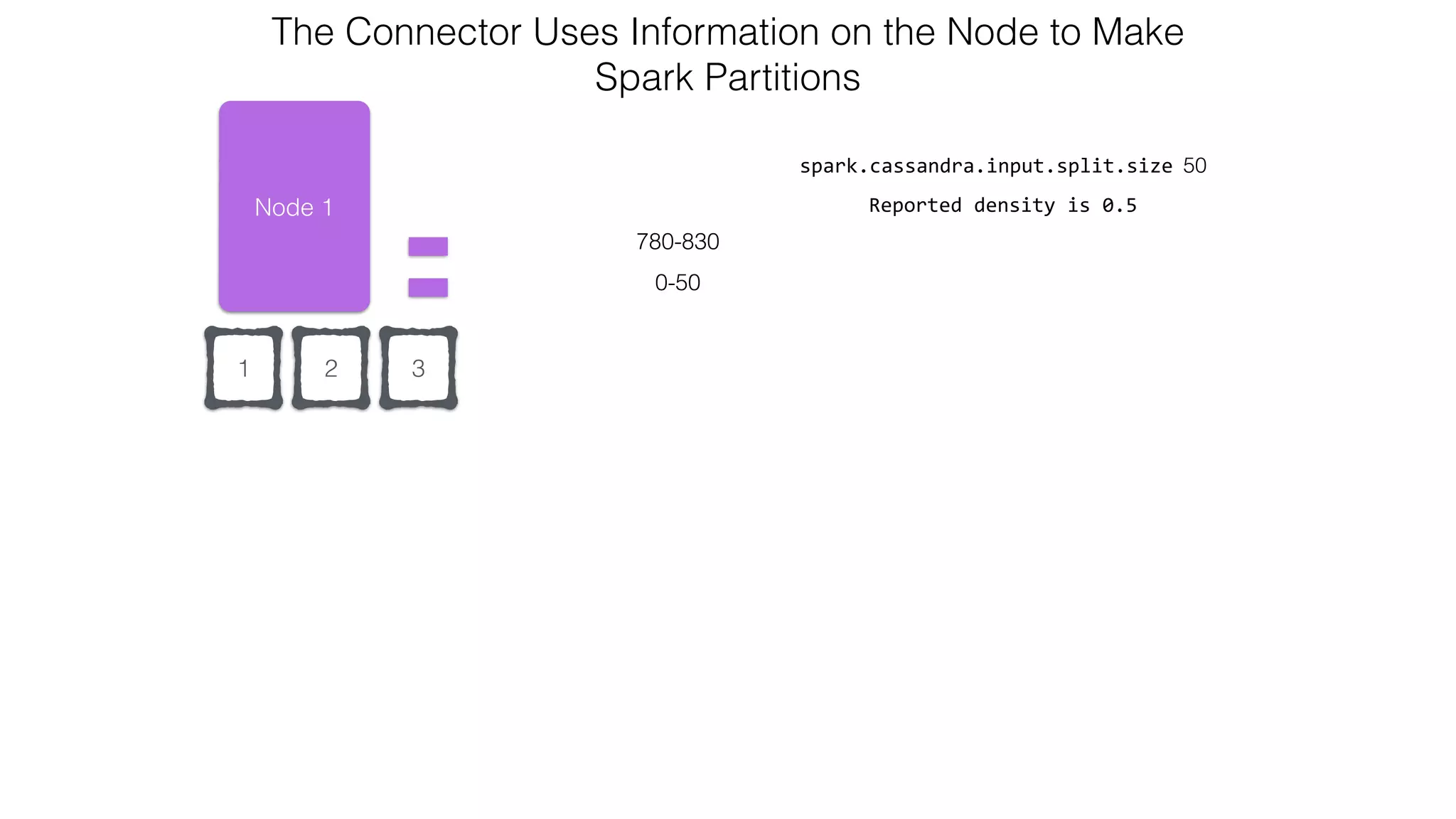
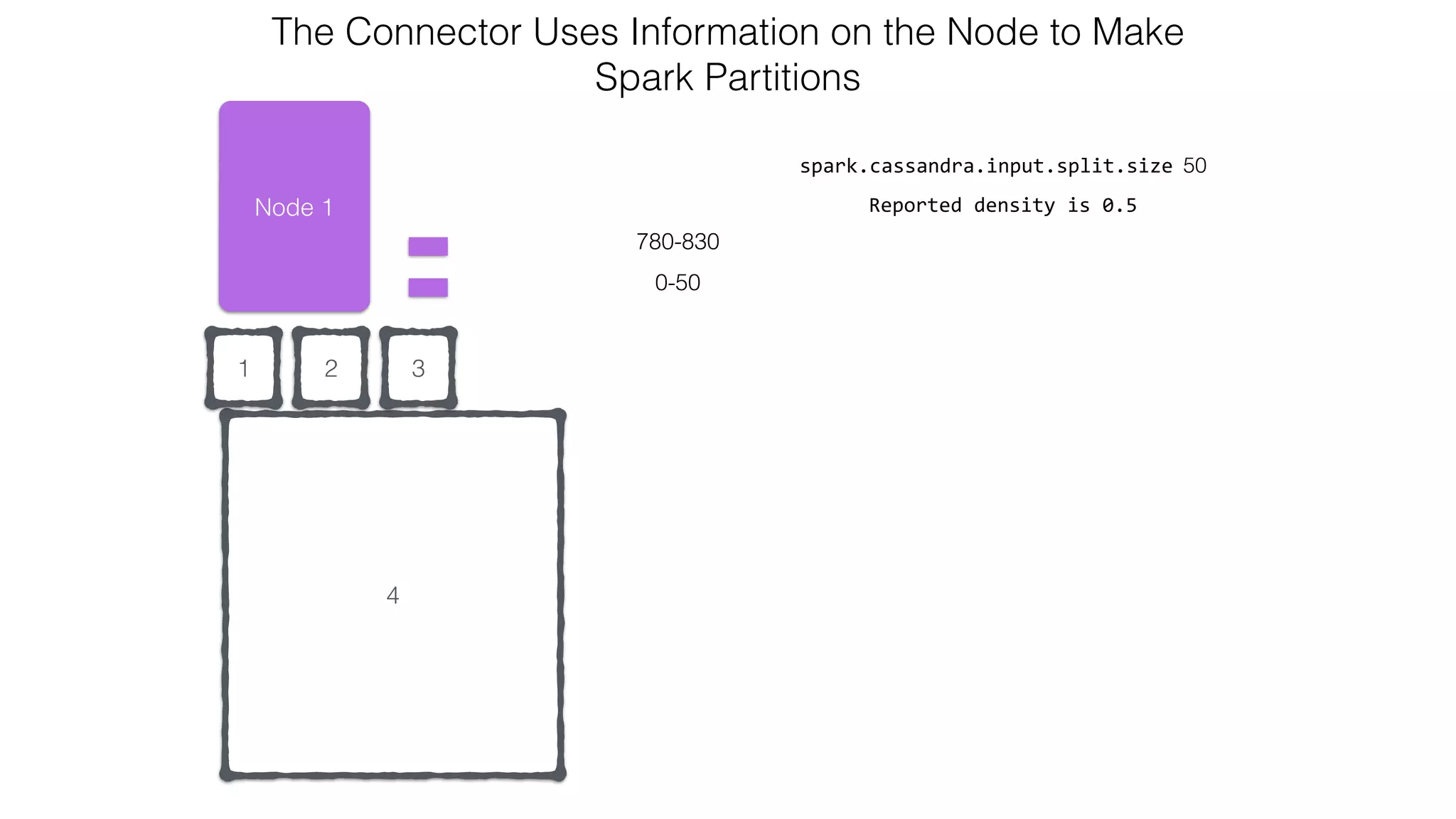
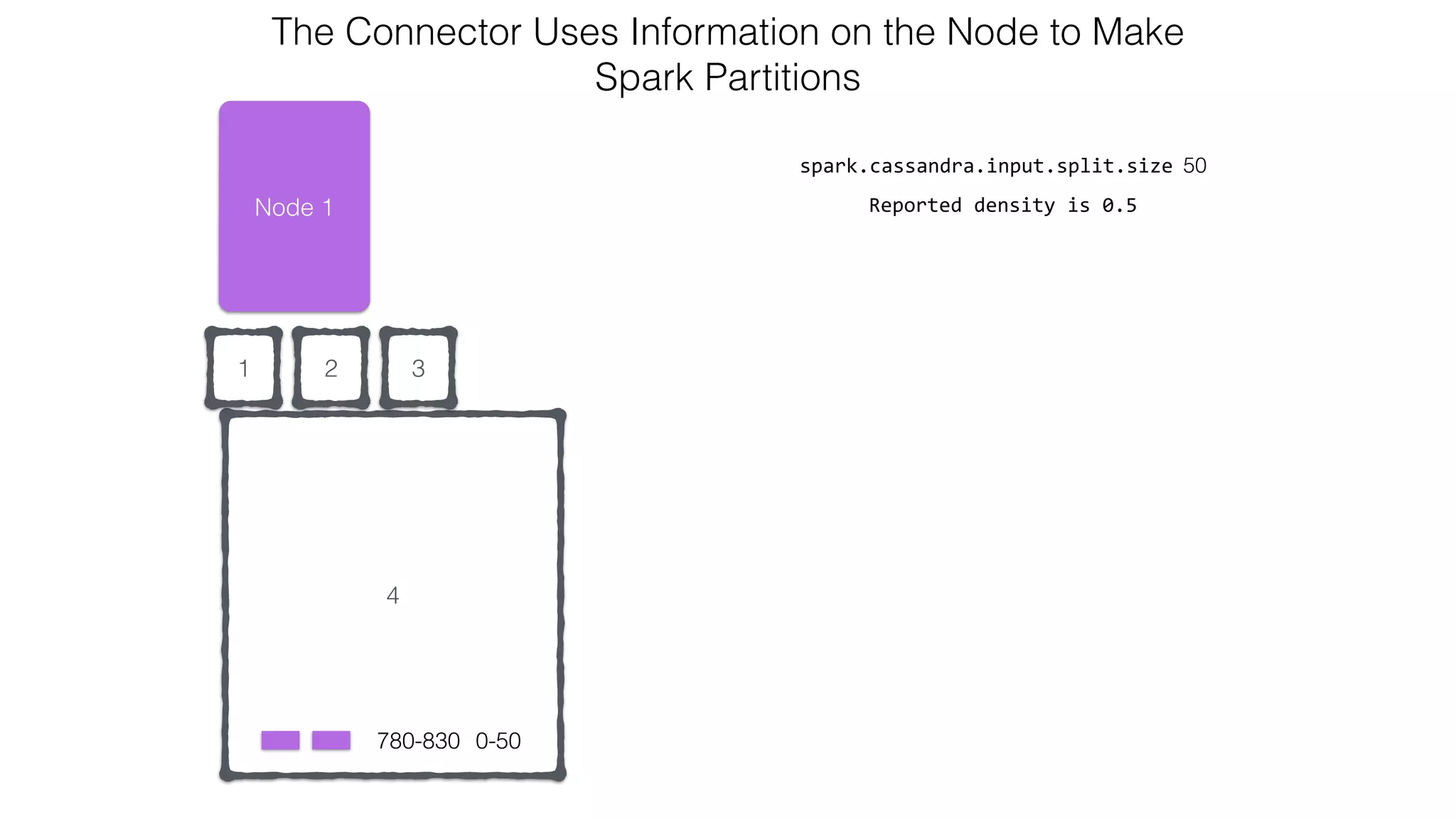
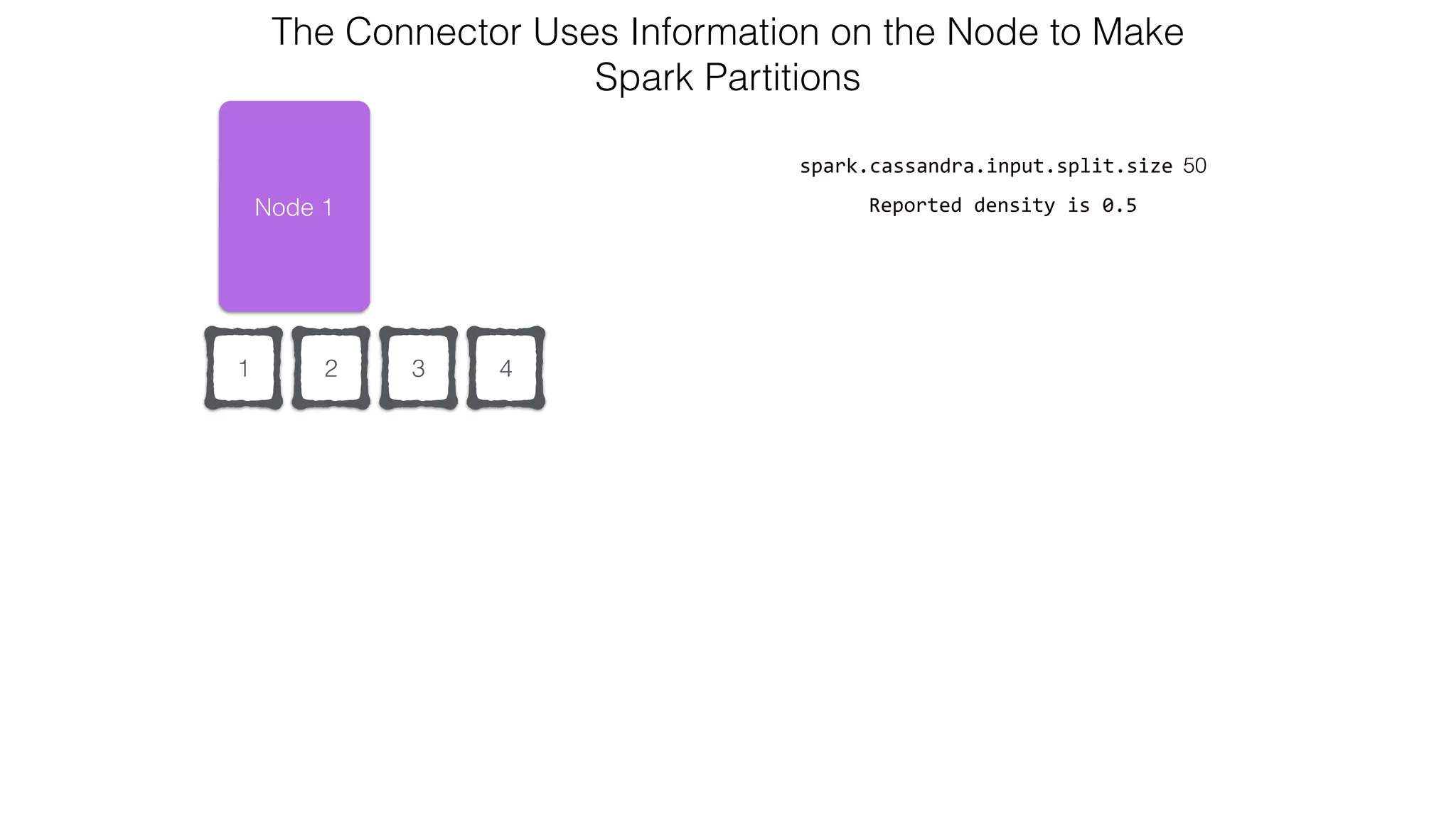
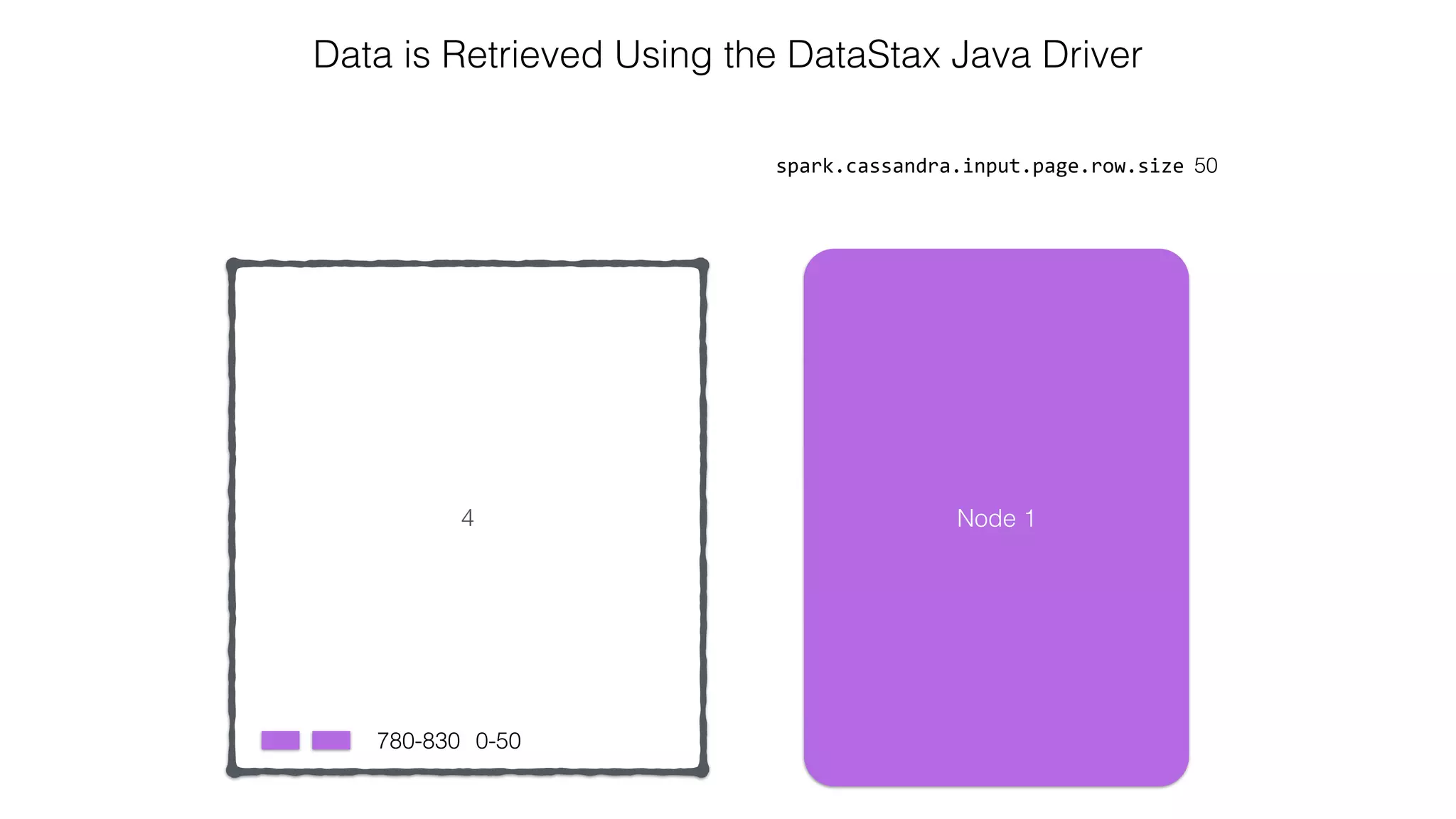
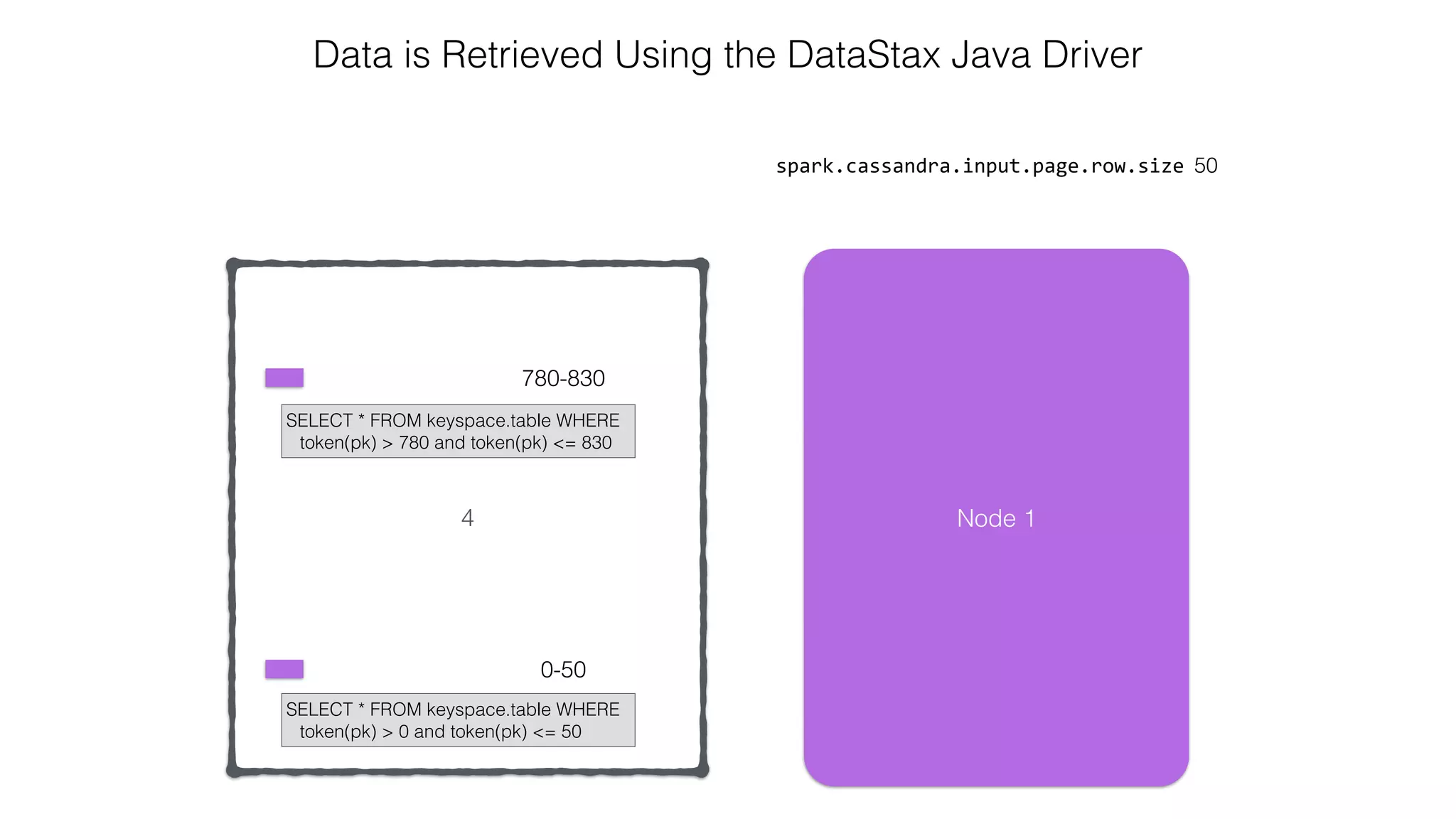
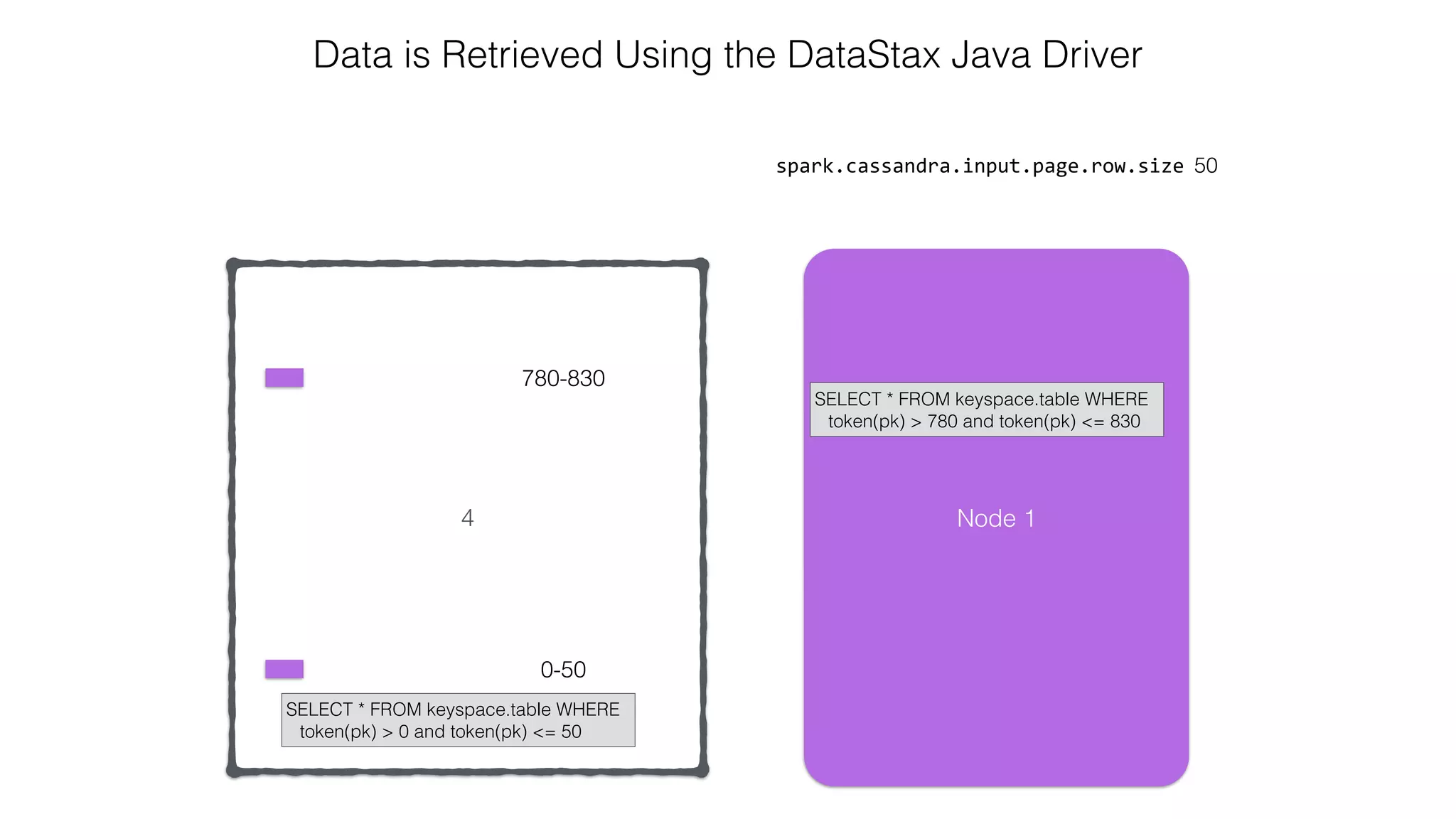
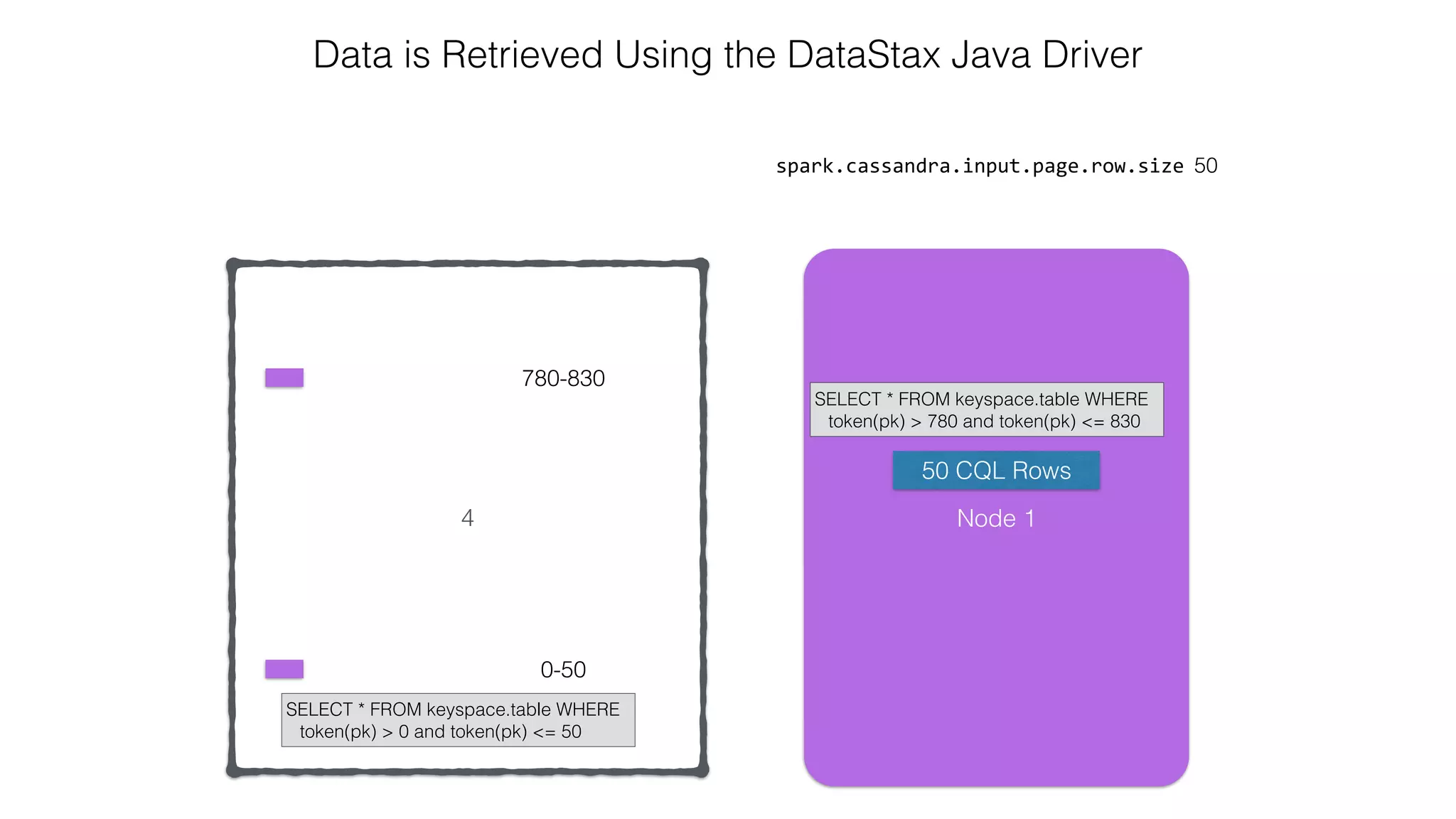

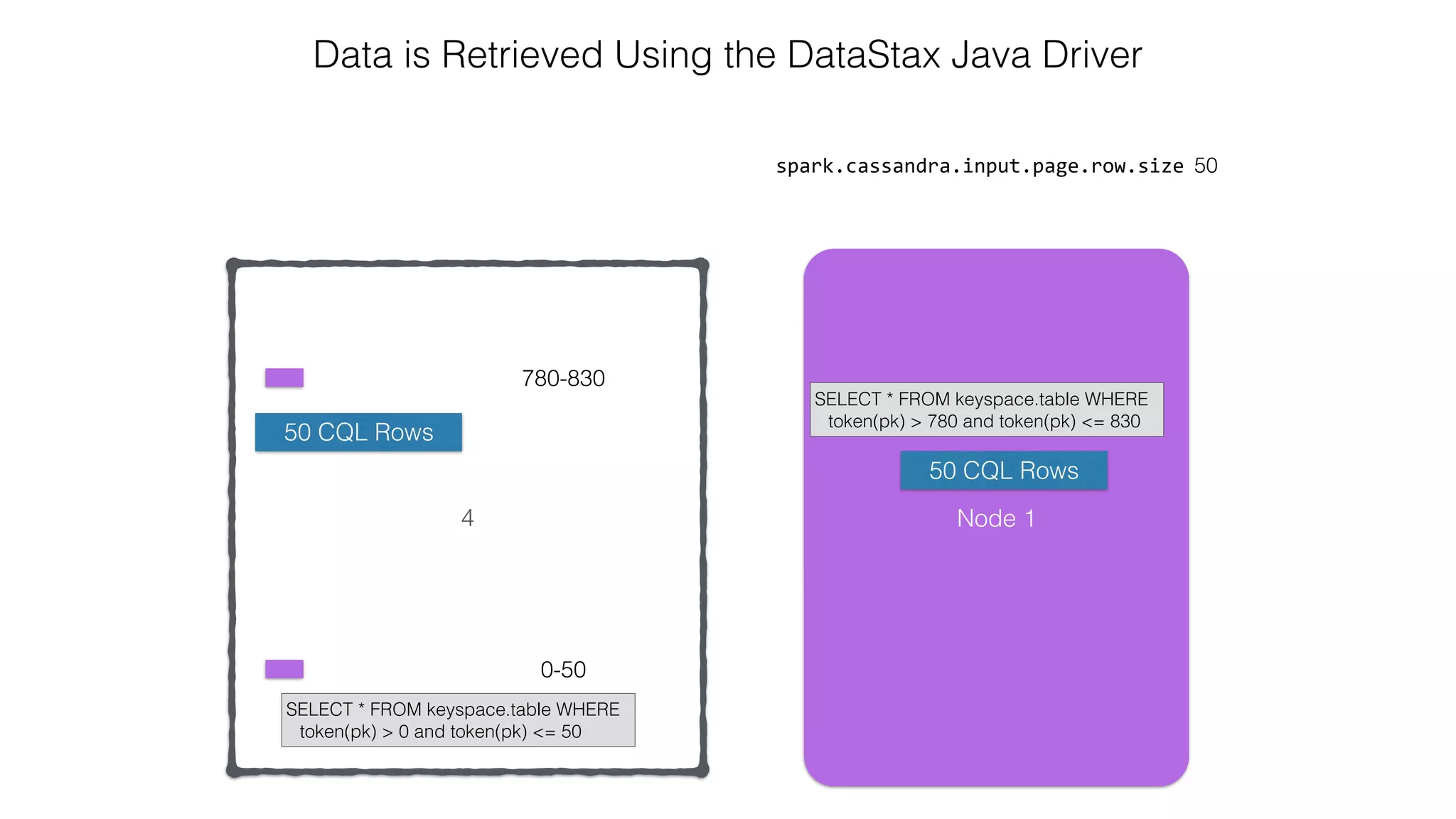
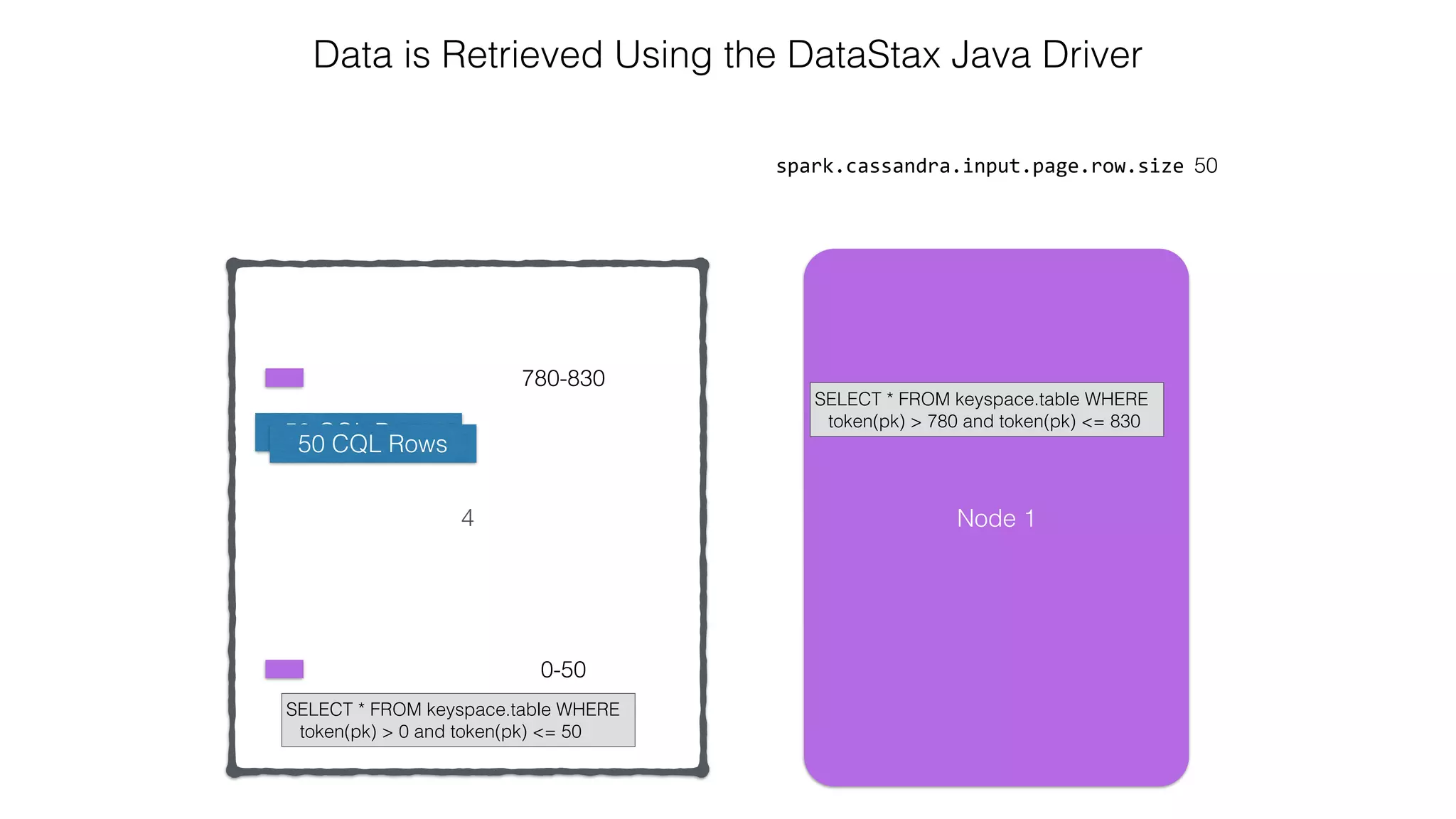
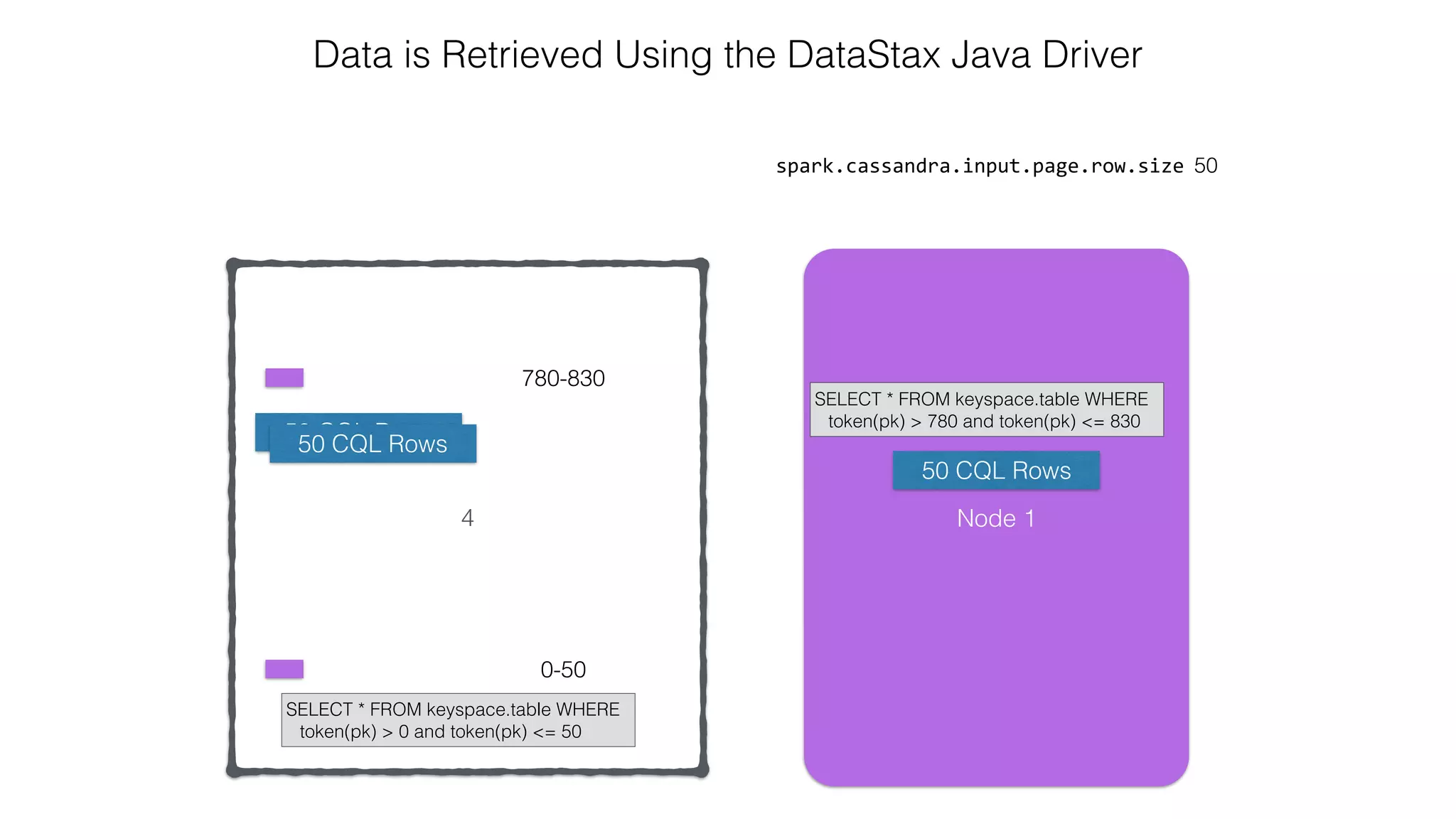
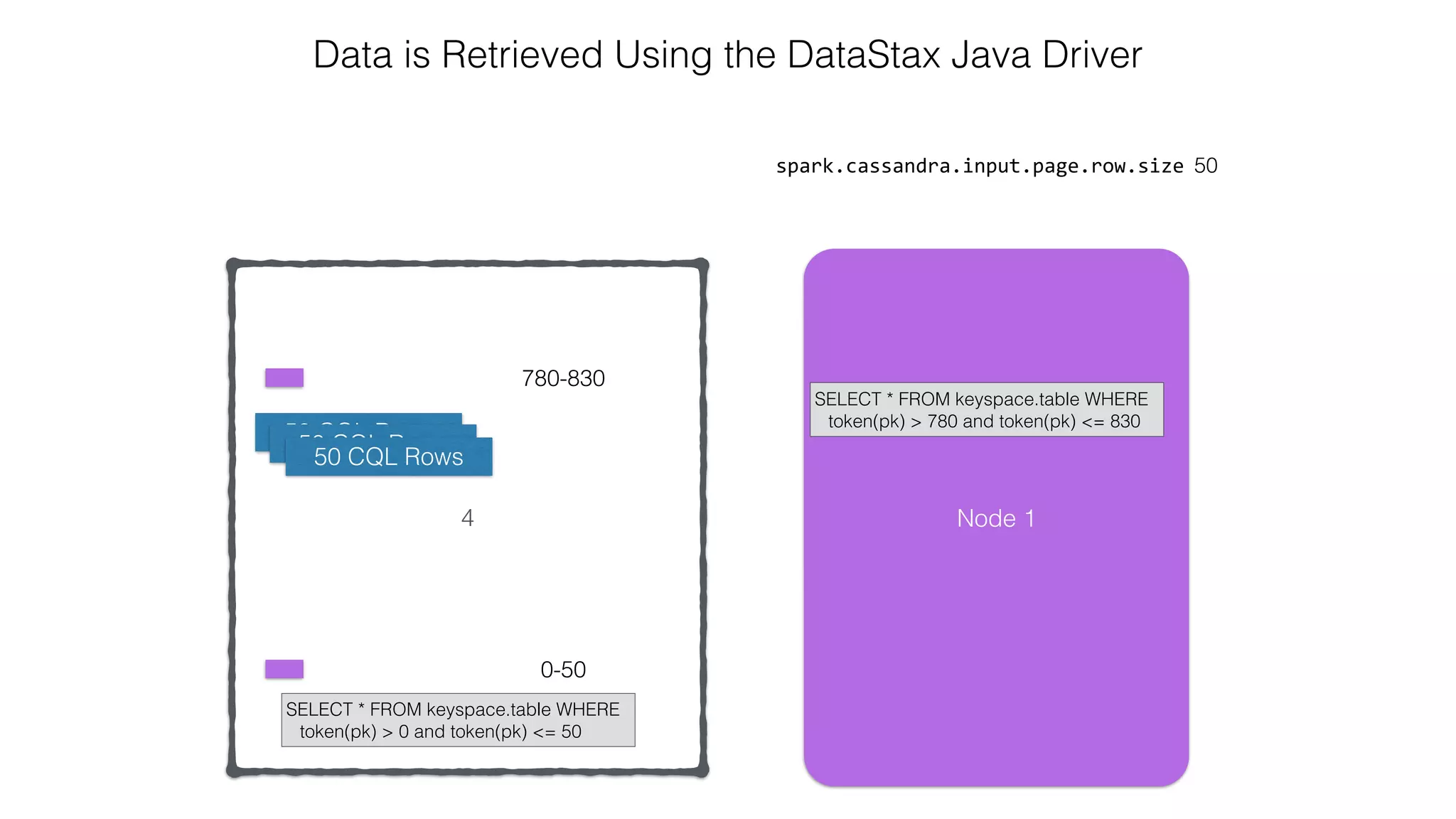
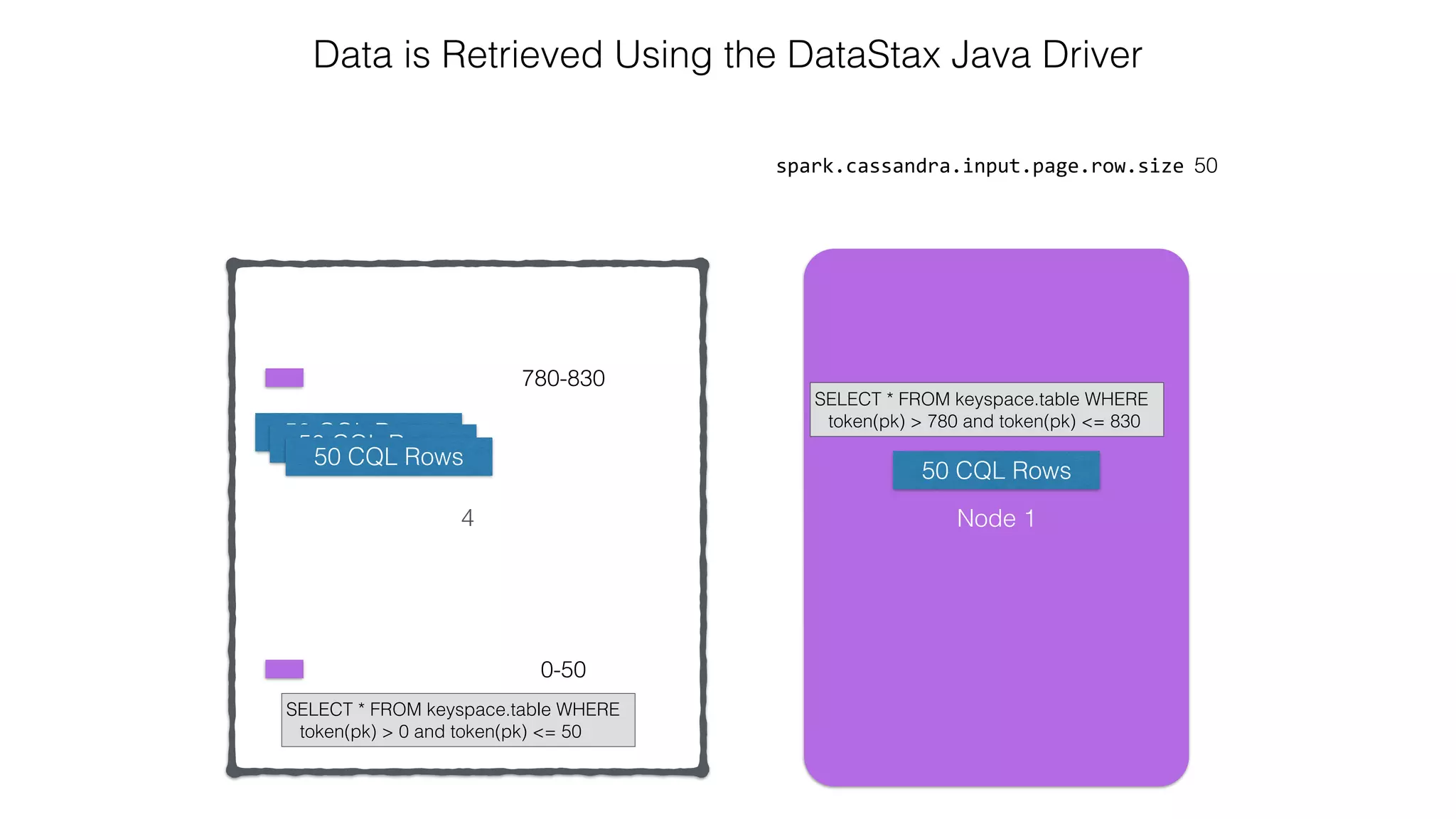
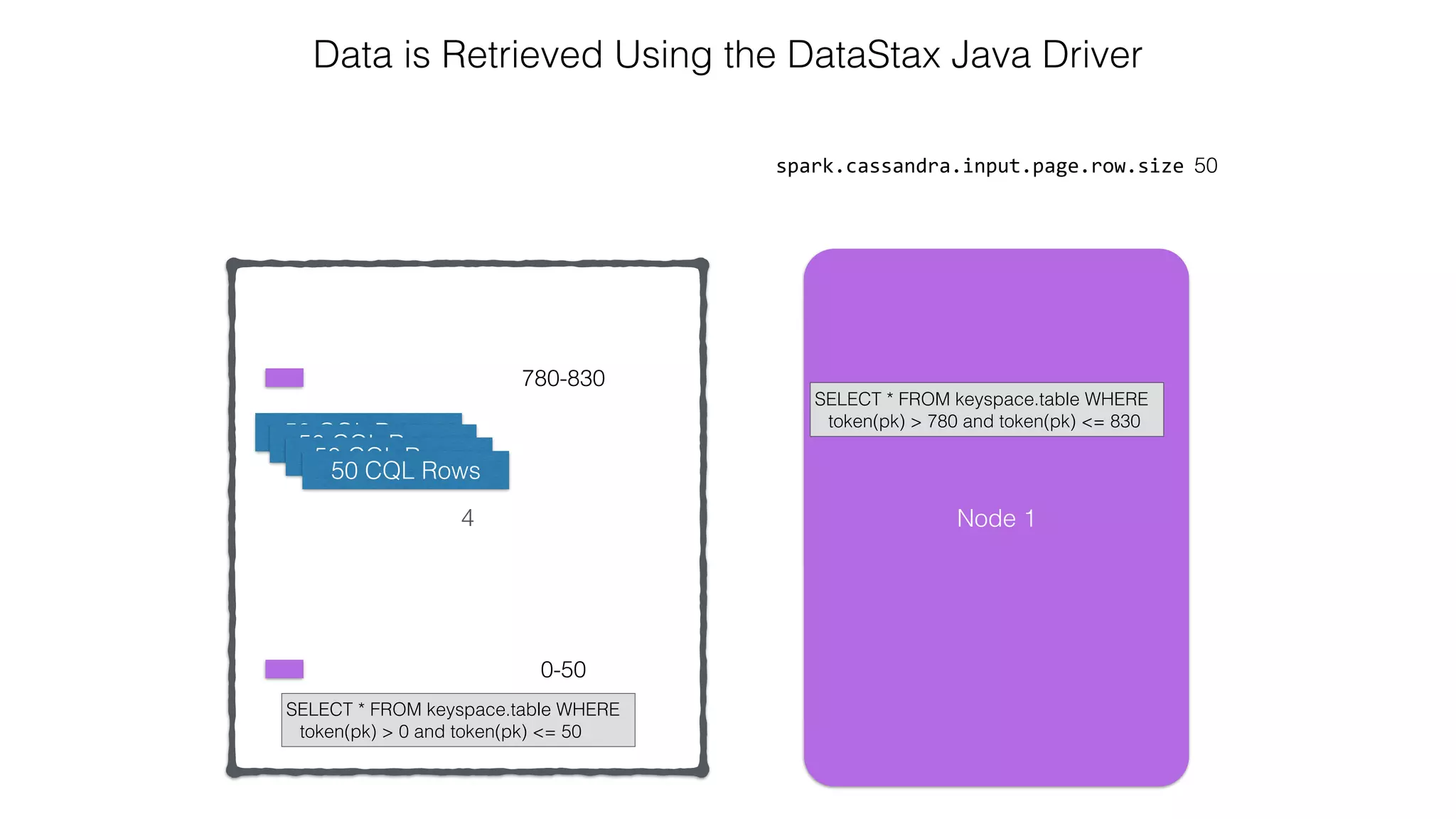
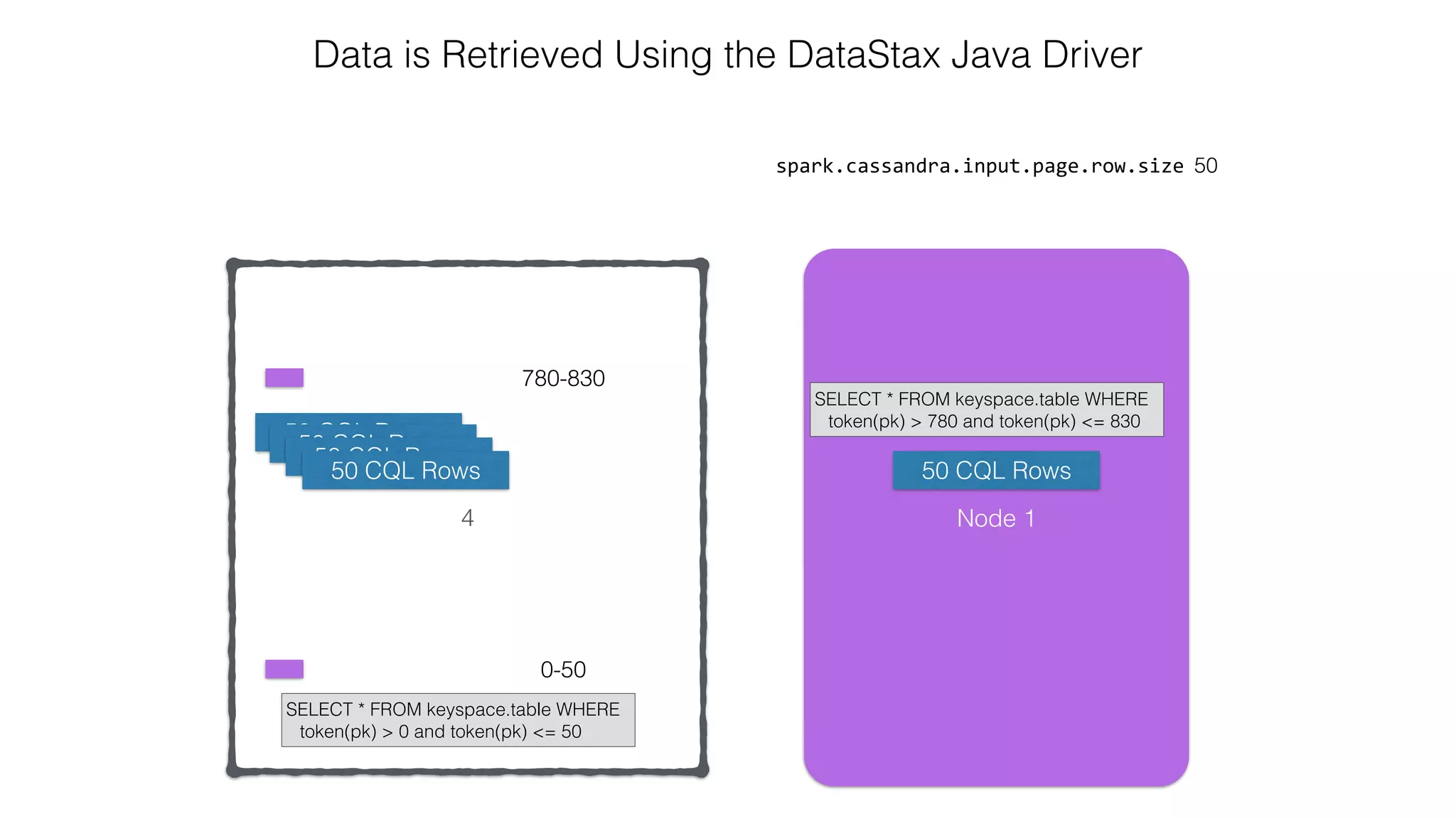
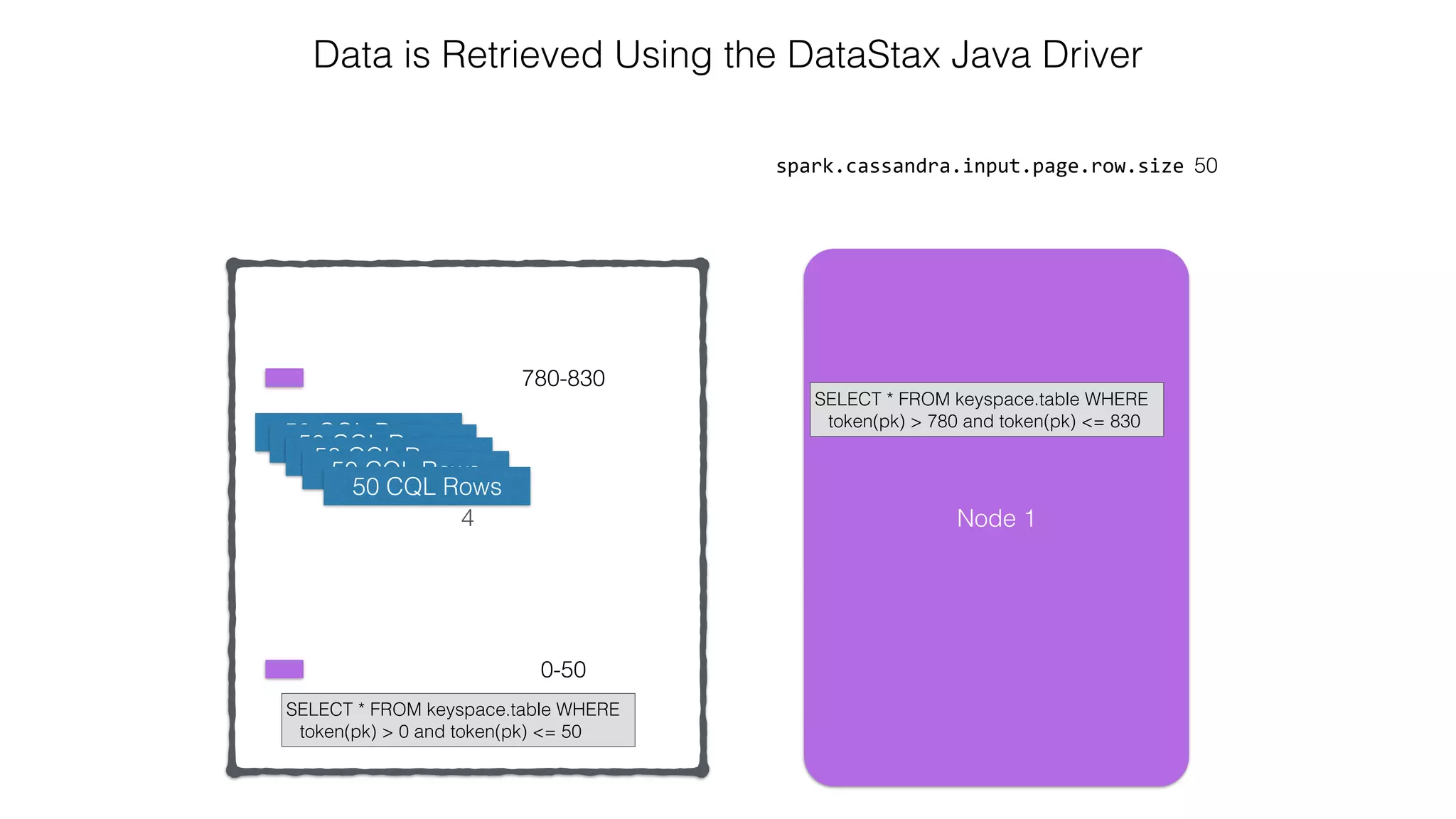
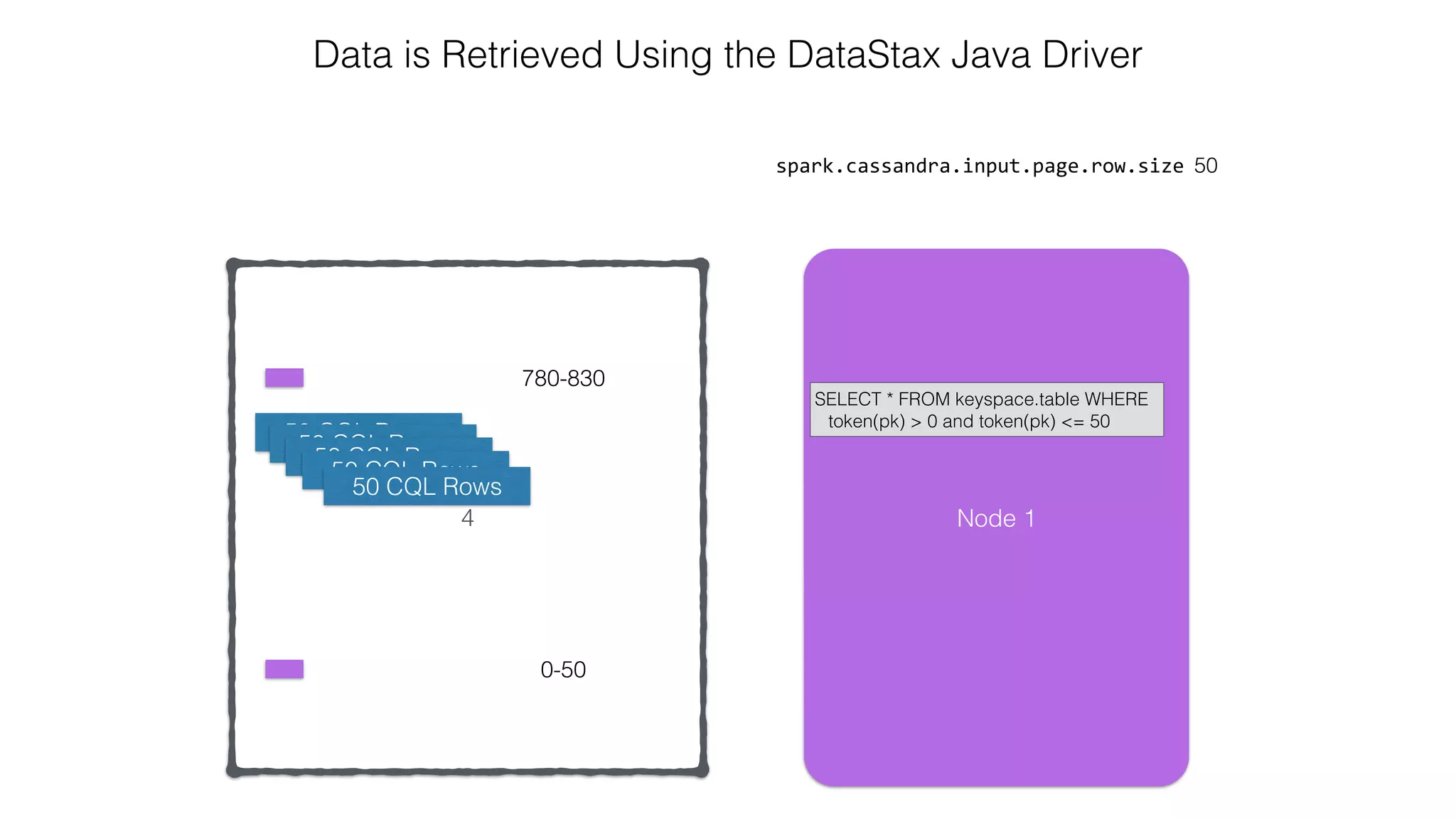
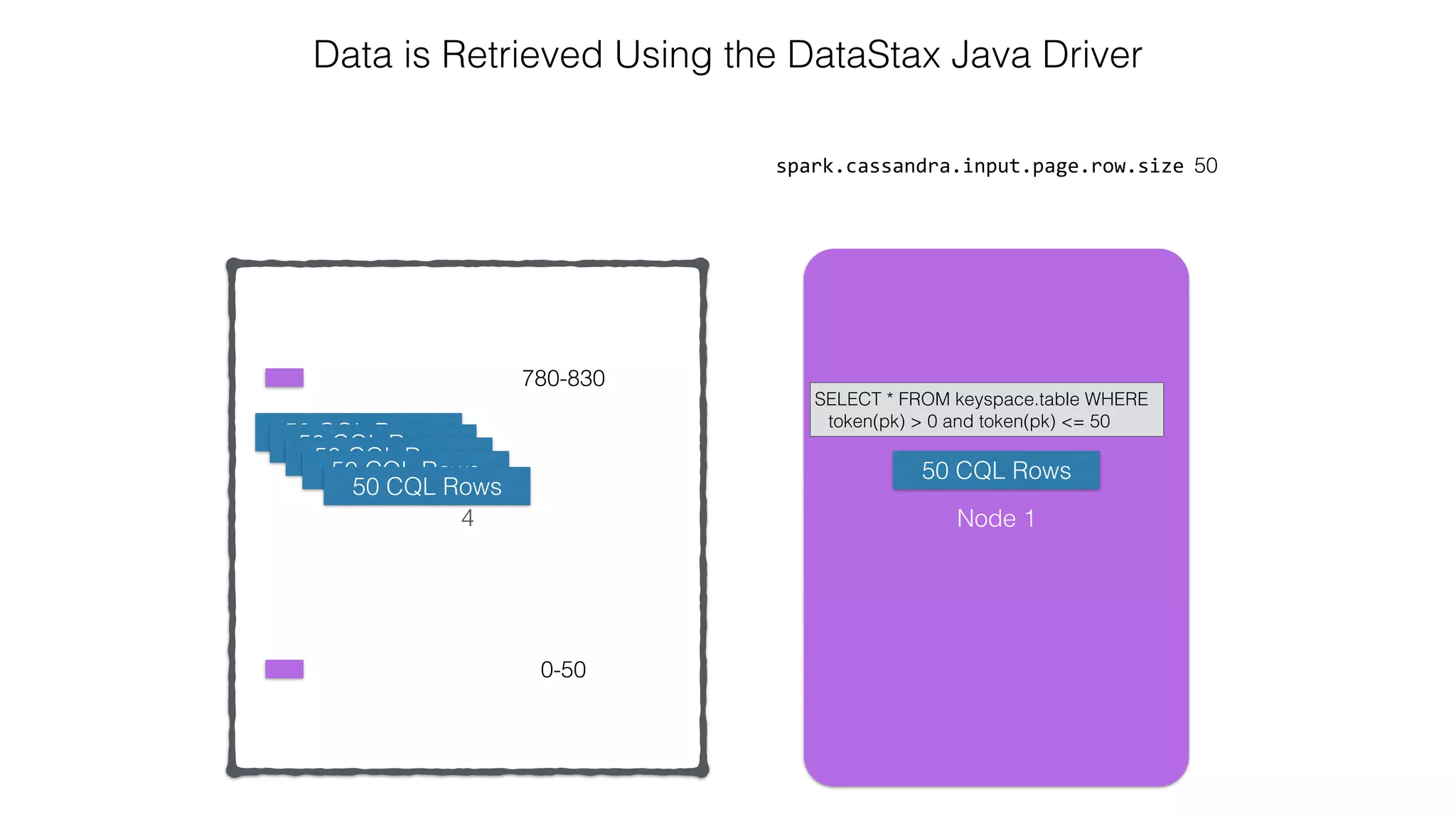
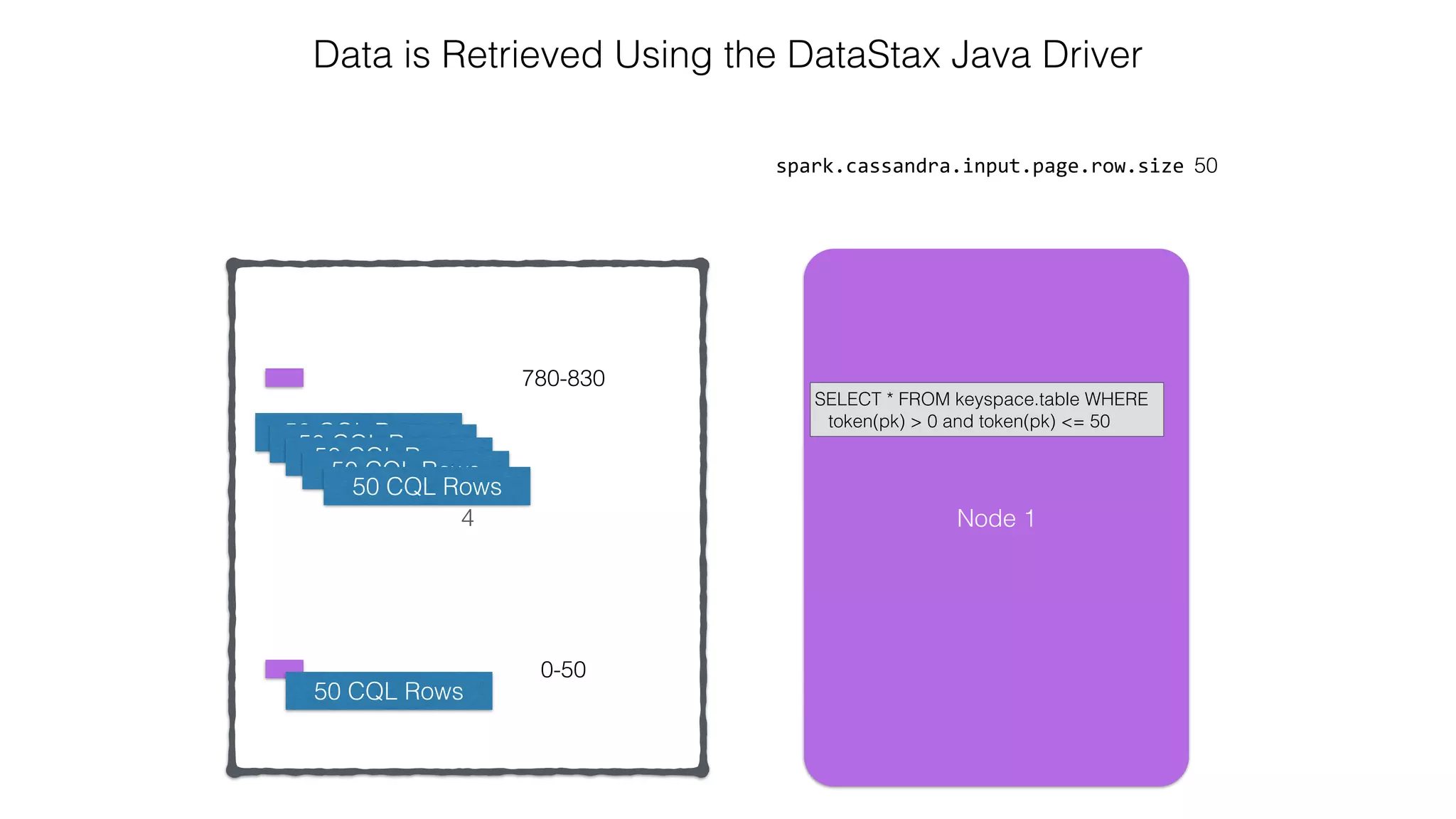
![Attaching to Spark and Cassandra // Import Cassandra-specific functions on SparkContext and RDD objects import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
import com.datastax.spark.connector._ /** The setMaster("local") lets us run & test the job right in our IDE */
val conf = new SparkConf(true) .set("spark.cassandra.connection.host", "127.0.0.1") .setMaster(“local[*]") .setAppName(getClass.getName) // Optionally
.set("cassandra.username", "cassandra")
.set("cassandra.password", “cassandra")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyzingtimeseriesdatawithapachesparkandcassandra-150701140404-lva1-app6891/75/Analyzing-Time-Series-Data-with-Apache-Spark-and-Cassandra-69-2048.jpg)