The document discusses features of Angular 2, highlighting its performance improvements, component-based architecture, and the use of TypeScript for development. It explains key concepts such as data binding, dependency injection, and compares Angular 2 to its predecessor, Angular 1.x. Additionally, it provides guidance on setting up Angular 2 applications, using TypeScript, and offers resources for further learning and development.










![Display List of Users (app/main.ts) • import {bootstrap} from 'angular2/platform/browser'; • import {Component} from 'angular2/core'; • @Component({ • selector: 'my-app', • template: `<div><ul> • <li *ngFor='user of users'> {{ user }} </li> • </ul></div>` • }) • class MyApp { • users:string[]; // or users:Array<string>; • constructor() { • this.users = ['Jane', 'Dave', 'Tom']; • } • } • bootstrap(MyApp);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160216010205/75/Angular2-for-Beginners-14-2048.jpg)


![Angular 2 Template Syntax • [attribute] syntax: <input [value]="name"> • (method) syntax: <input #myname (keyup)="vm.myCtrlMethod()"> • ^ symbol handles bubble up events: <div (^click)="handleClick()"> <div></div> </div> • [(method)] syntax for two-way binding: <input [(ng-model)]="vm.foo"> <p>Hello {{vm.foo}}</p>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160216010205/75/Angular2-for-Beginners-17-2048.jpg)






![TypeScript Variables • var isDone: boolean = false; • var height: number = 6; • var name: string = "dave"; • var myList:number[] = [1, 2, 3]; // option #1 • var myList:Array<number> = [1, 2, 3]; // option #2 • var changeMe: any = 4; • changeMe = ”I’m a string now"; • var myList:any[] = [1, true, ”pizza"];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160216010205/75/Angular2-for-Beginners-26-2048.jpg)


![Convert JSON Data to TS Class (1) • Consider the following array of data: var people = [ {fname:"Jane",lname:"Smith",zip:"94043"}, {fname:"John",lname:"Jones",zip:"94539"}, {fname:"Dave",lname:"Starr",zip:"67800"} ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160216010205/75/Angular2-for-Beginners-33-2048.jpg)
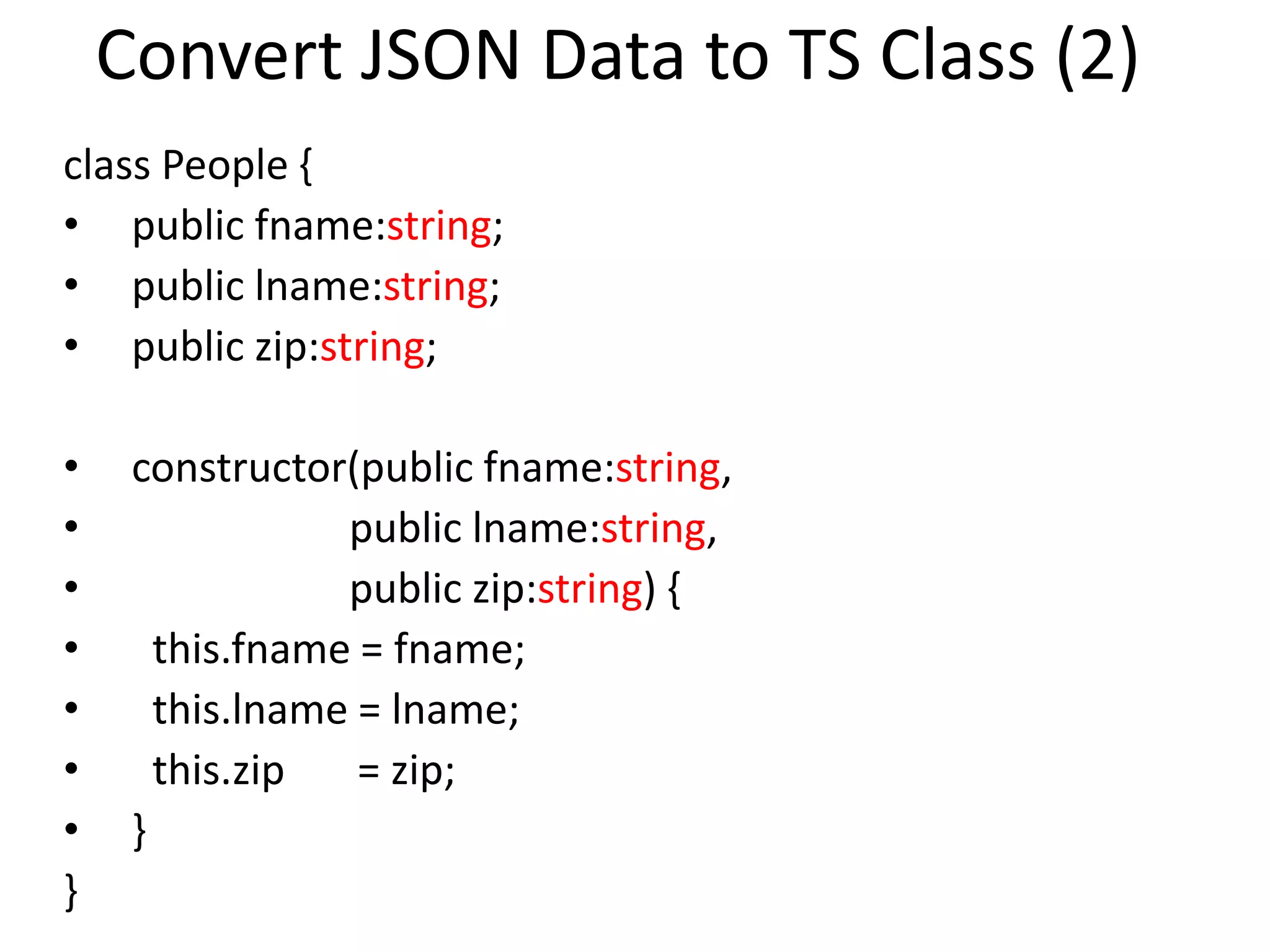
![Convert JSON Data to TS Class (3) • Array of TypeScript objects: var TSPeople = [ new People("Jane","Smith","94043"), new People("John","Jones","94539"), new People("Dave","Starr","67800") ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160216010205/75/Angular2-for-Beginners-35-2048.jpg)