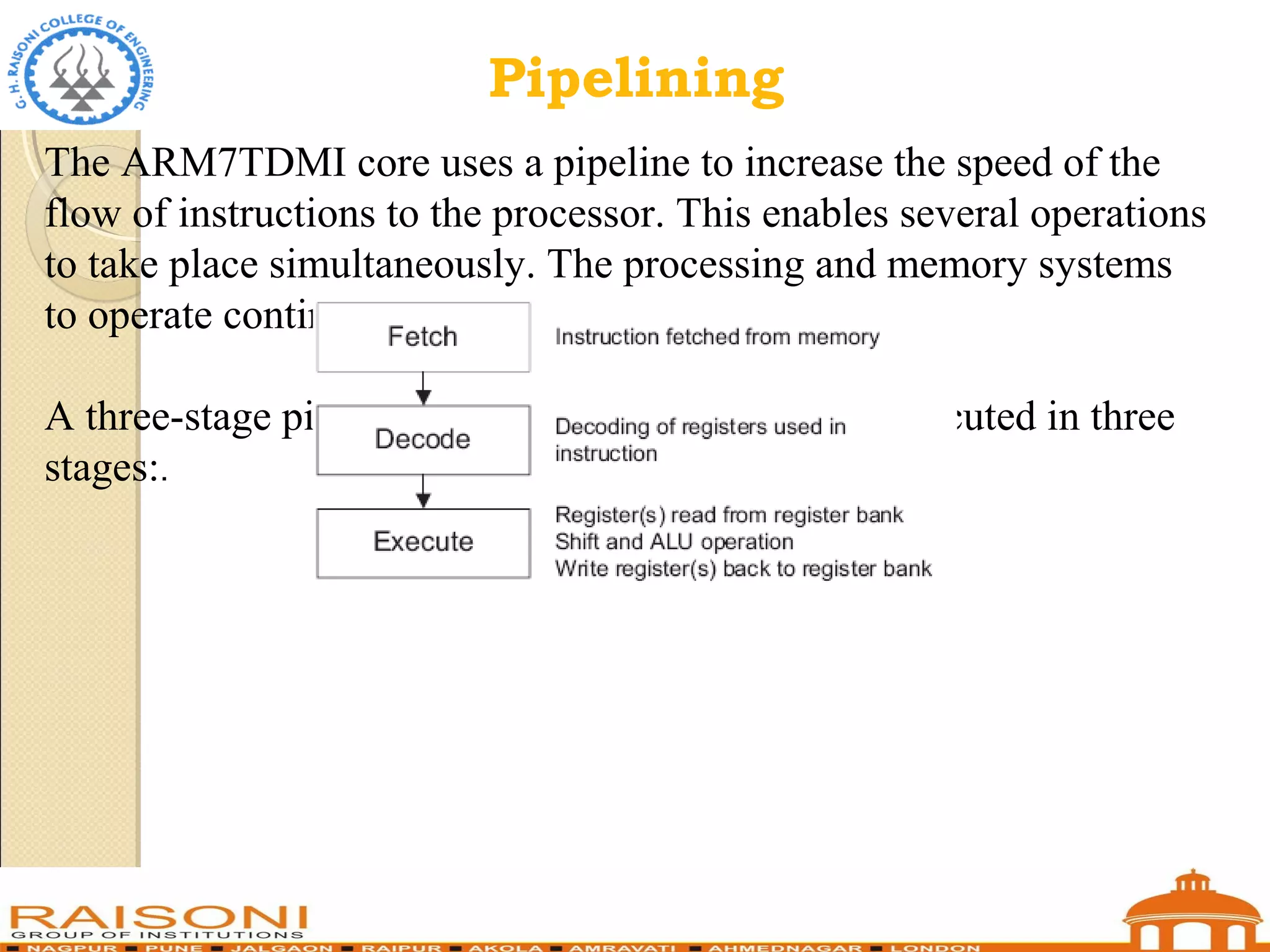
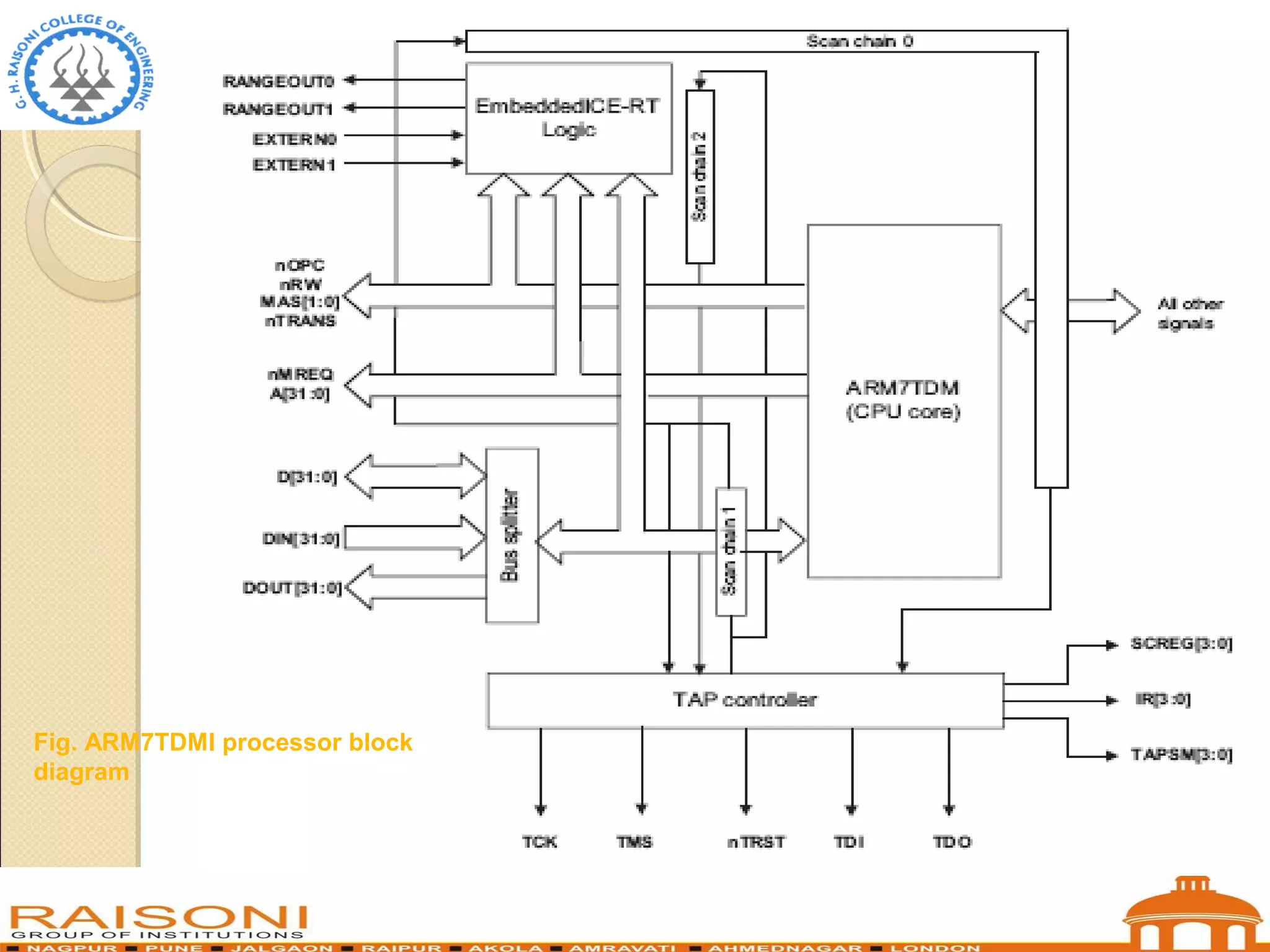
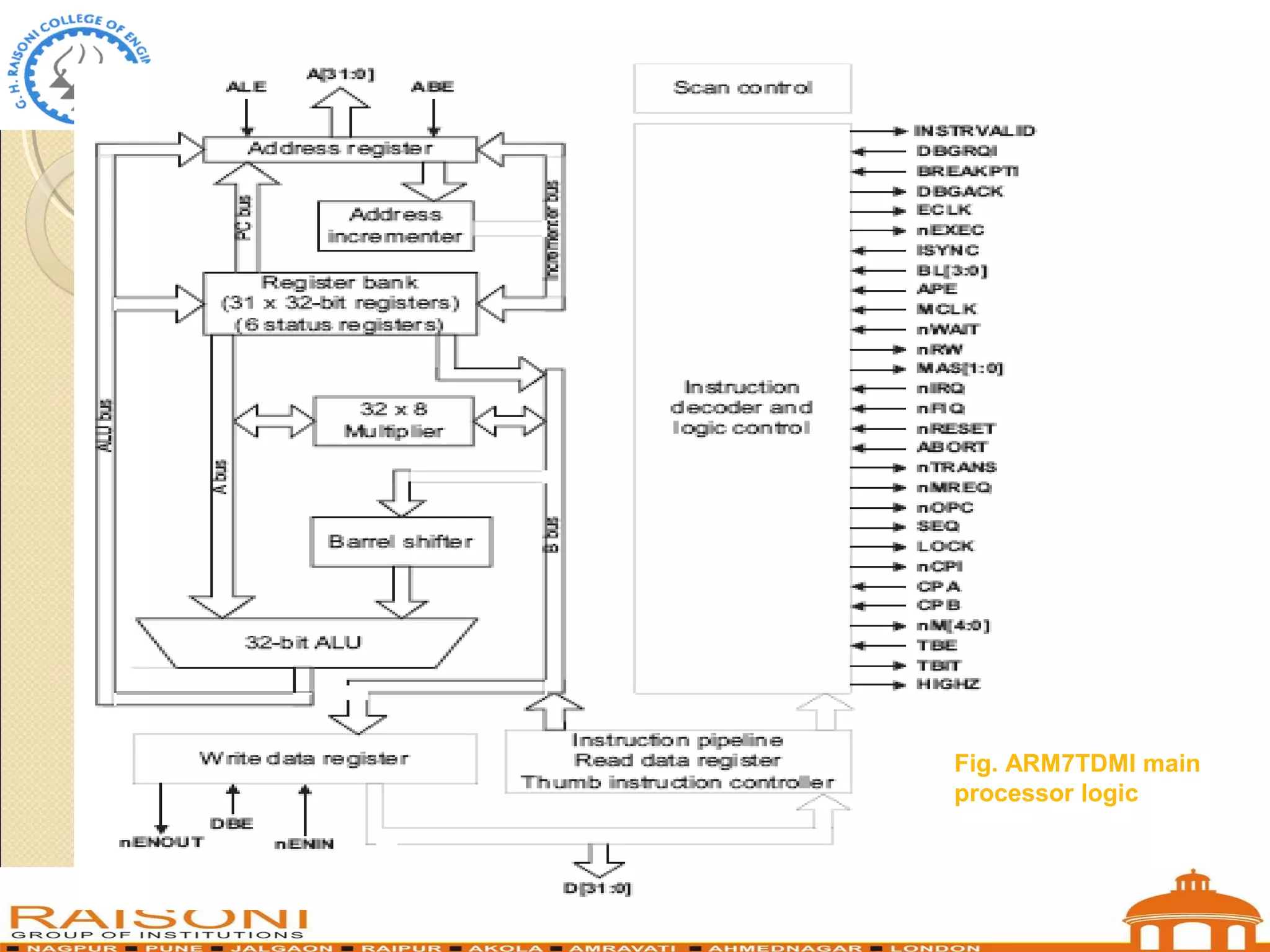
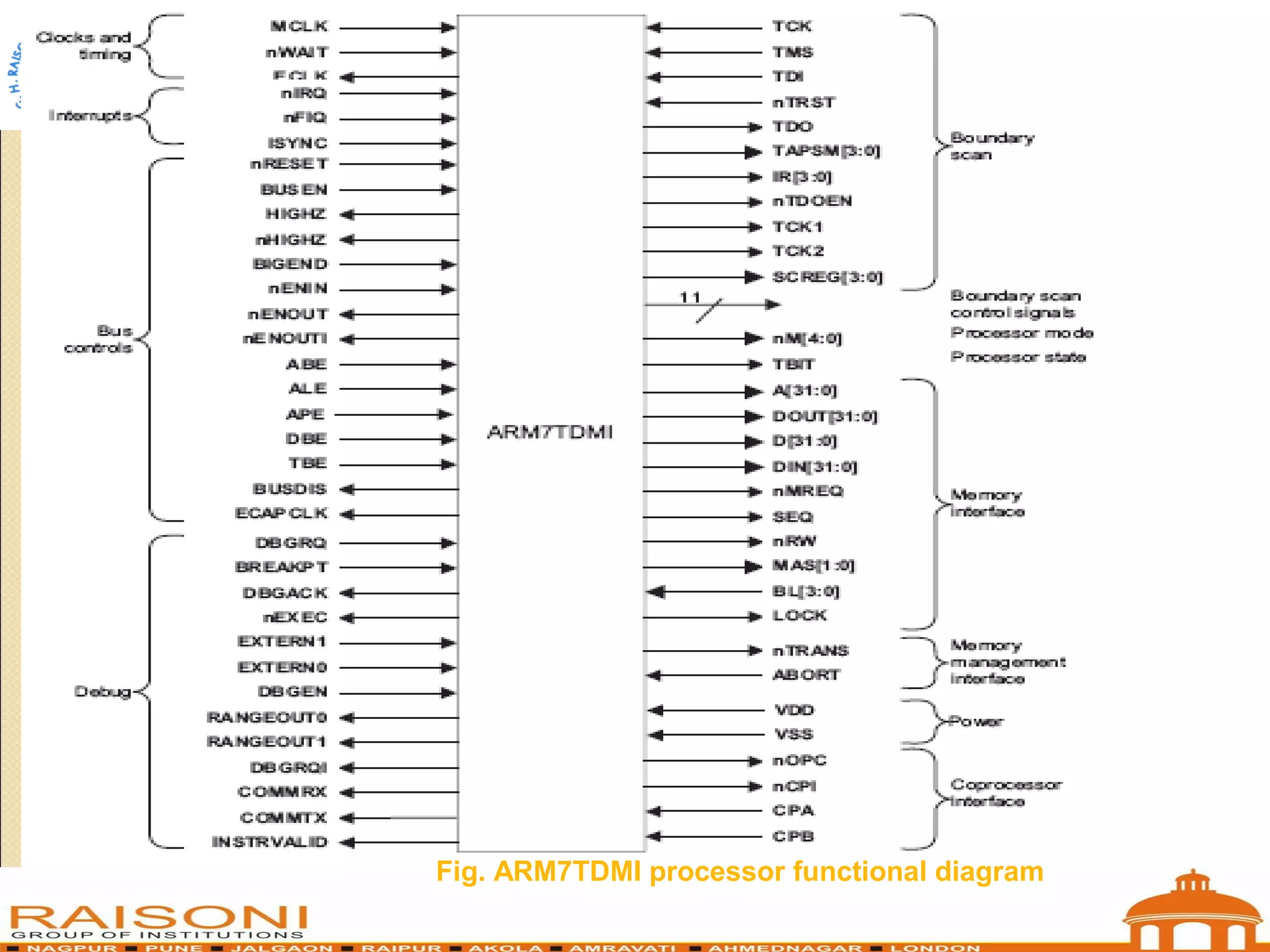
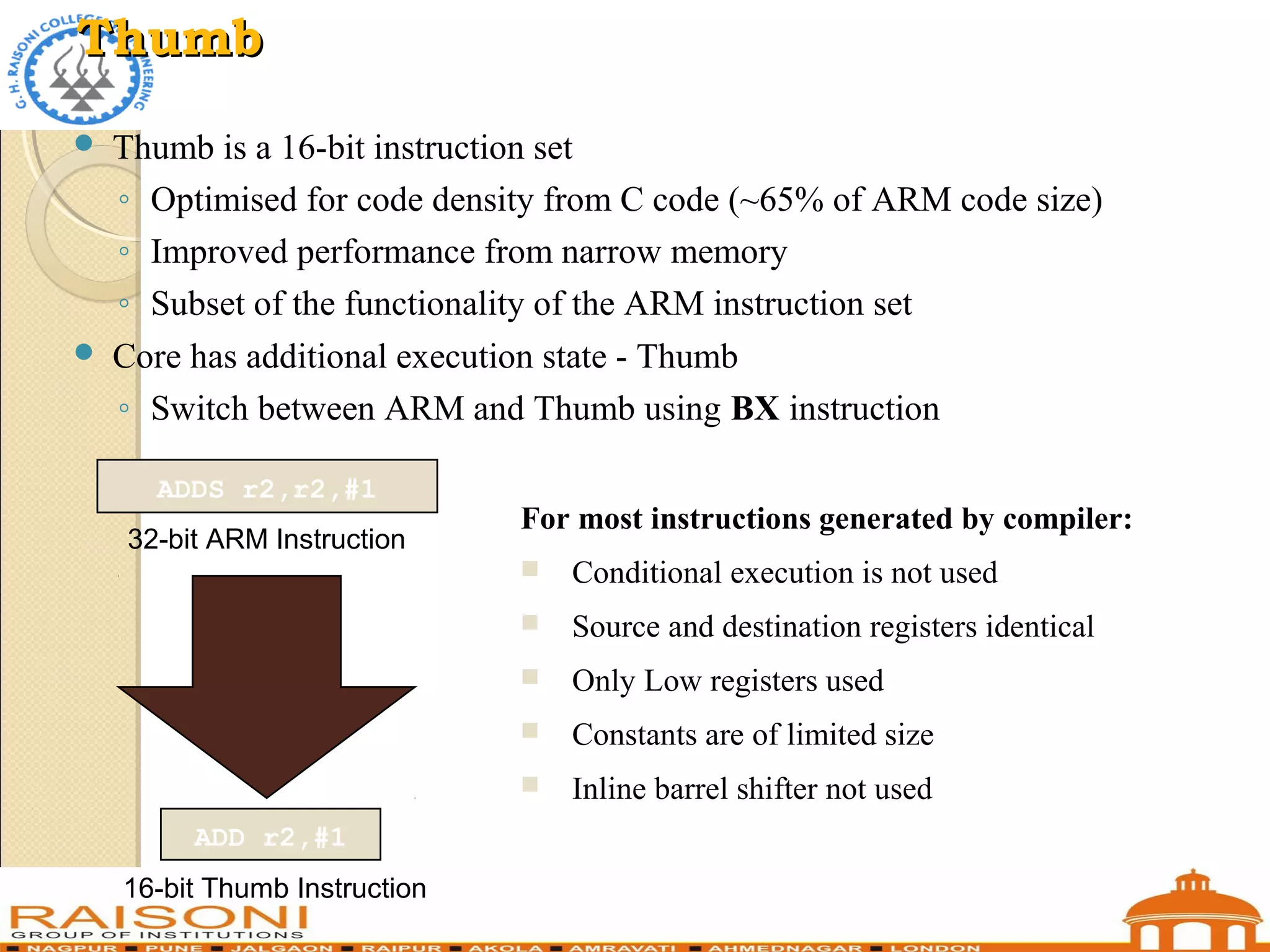
This document provides an introduction to ARM microcontrollers. It discusses that ARM designs RISC processor cores that are used in many microcontrollers produced by various manufacturers. The popular ARM7TDMI architecture is a 32-bit RISC processor that can operate in both 32-bit ARM and 16-bit THUMB modes. It has 31 registers and 7 operating modes. The ARM instruction set allows conditional execution and includes instructions for arithmetic, logical operations, and loading/storing data. Using THUMB instructions reduces code size by 30-40% compared to ARM.