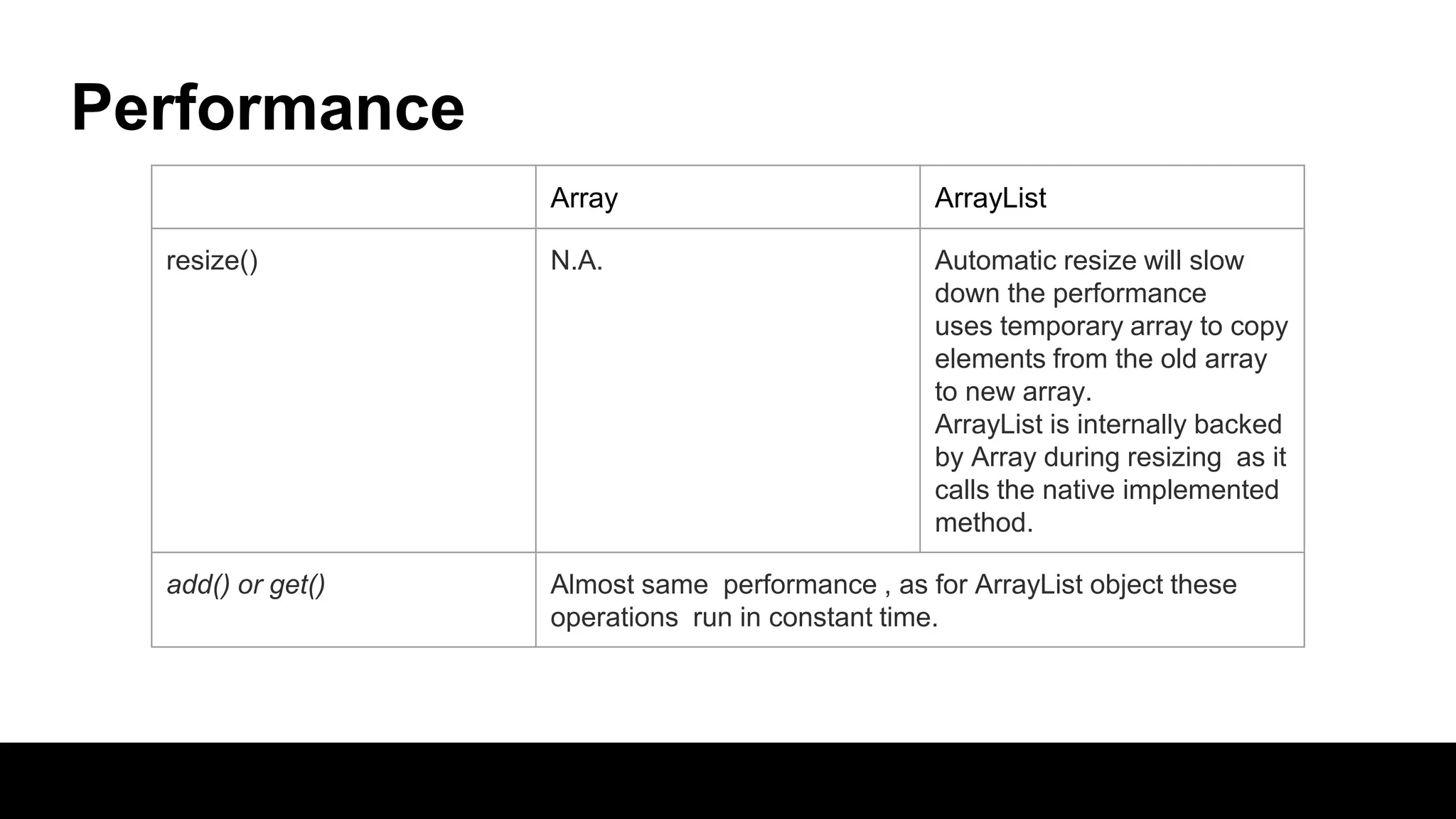
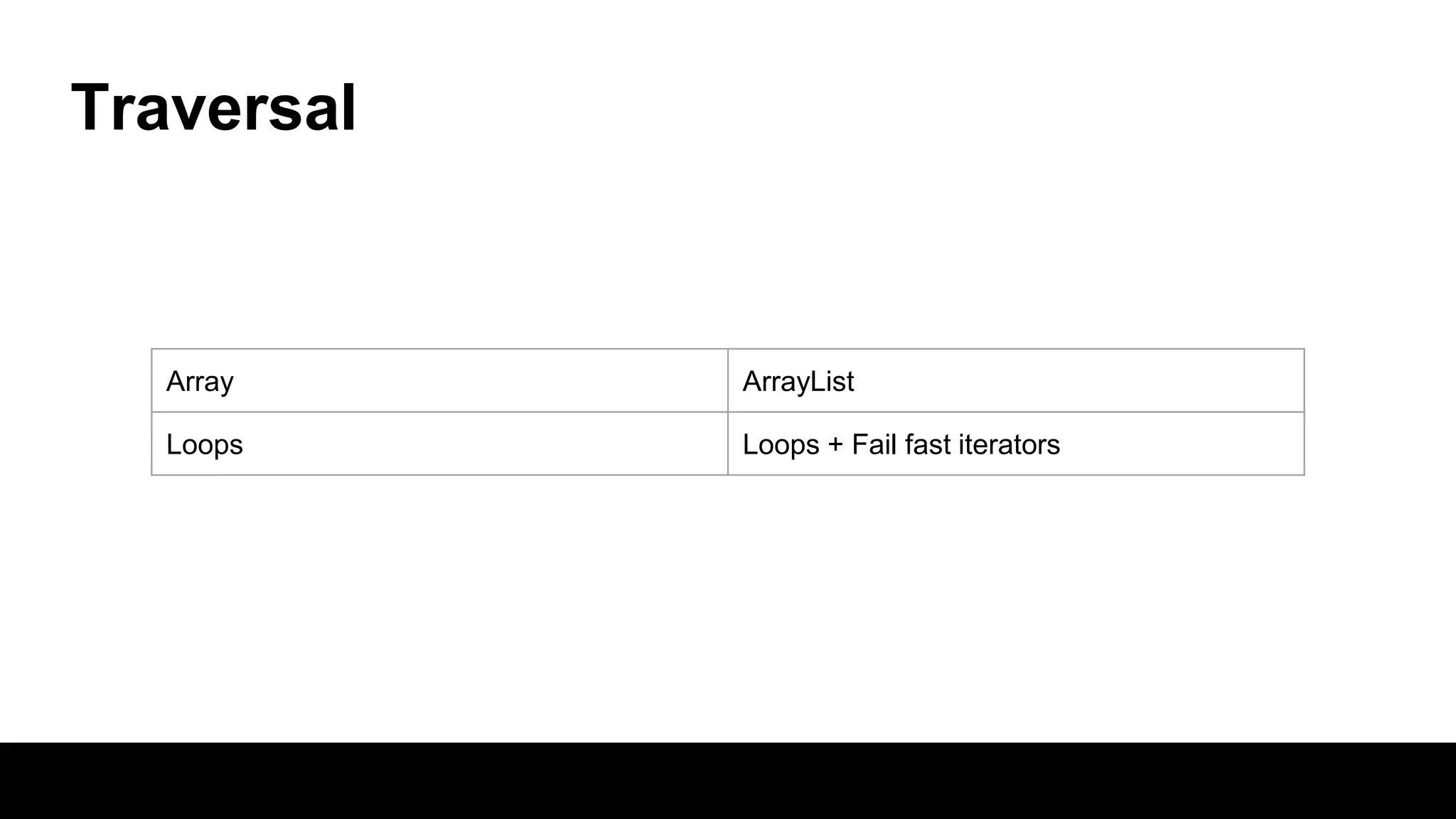
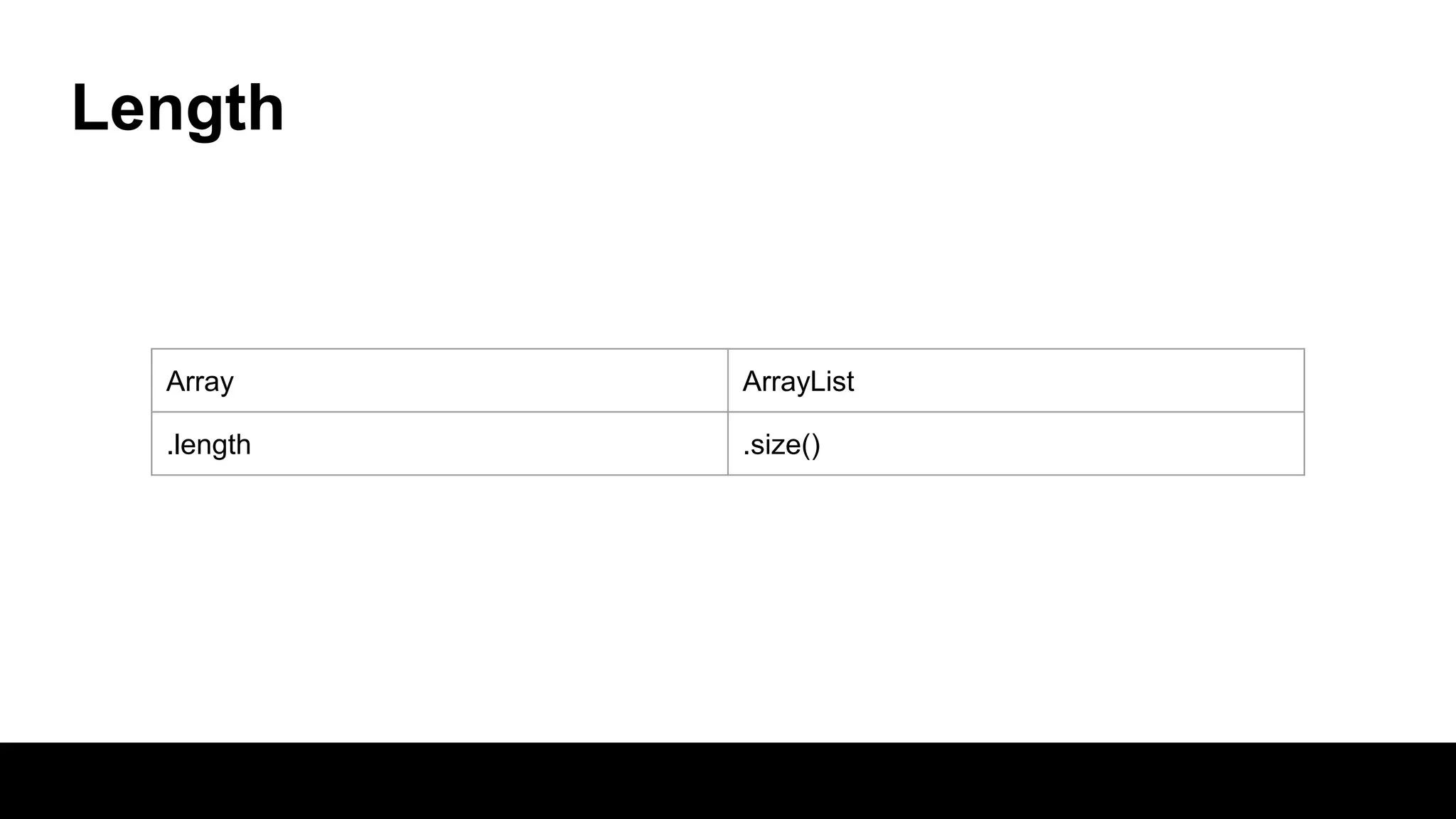
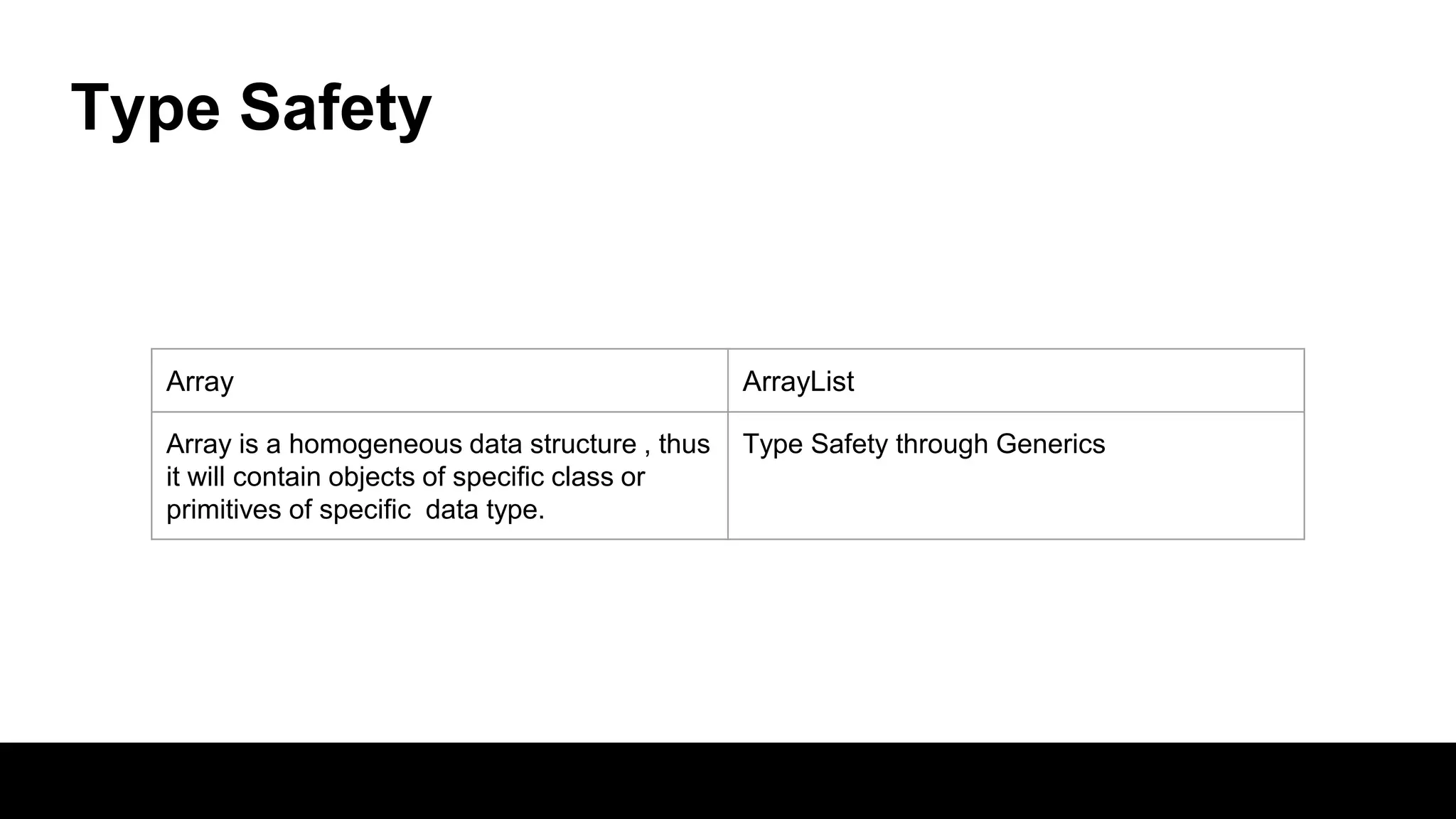
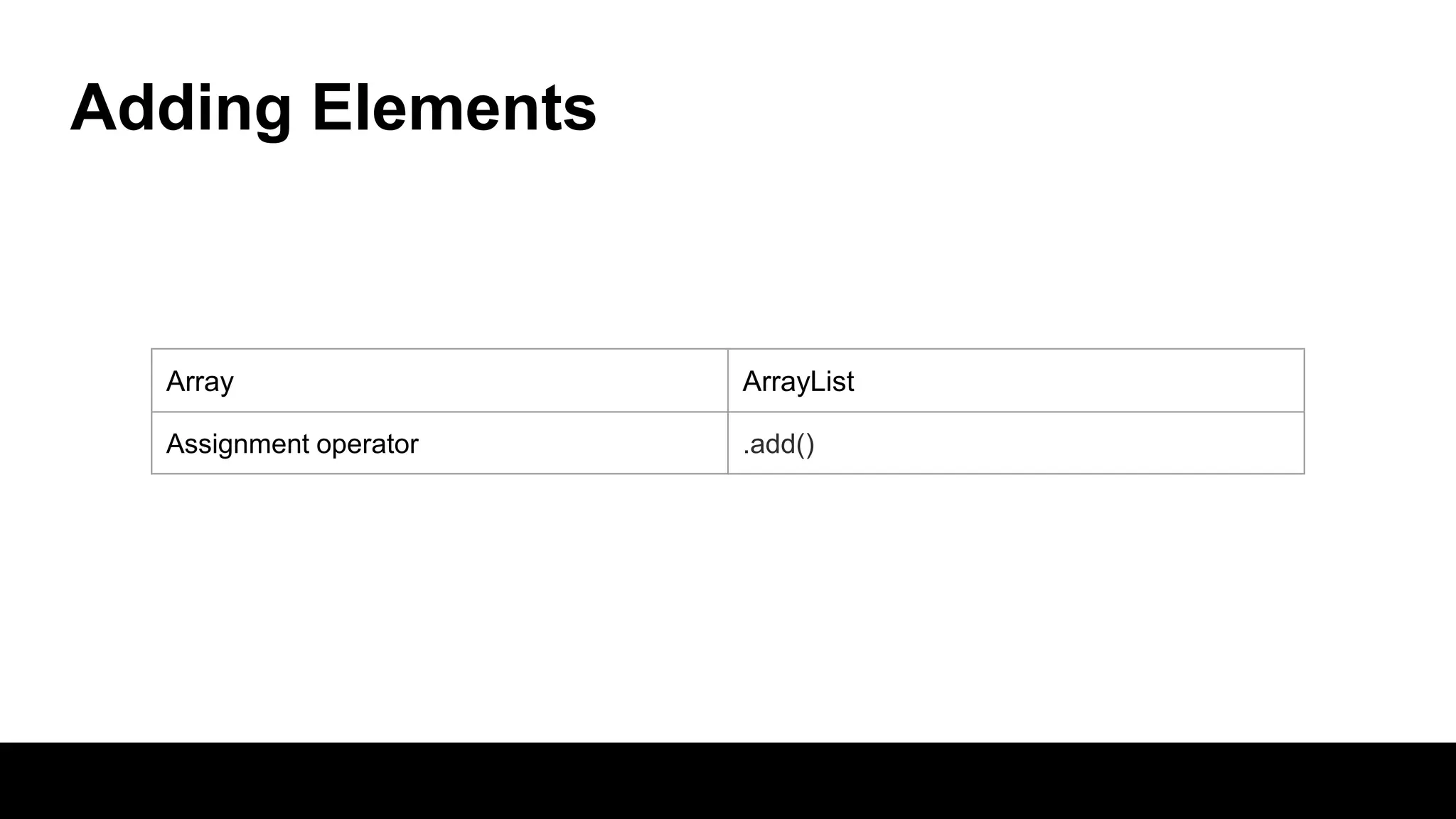
This document compares arrays and ArrayLists in Java. Arrays have a fixed length that is declared, while ArrayLists are dynamically sized. ArrayLists provide benefits like automatic resizing, type safety through generics, and the ability to add elements through the add() method rather than assignment. However, resizing can impact performance, and arrays allow for multi-dimensional structures while ArrayLists are always single dimensional.


![Declaration Array ArrayList int arr[] = new int[10] ArrayList<Type>arrL=new ArrayList<Type>();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayvsarraylist-170101051333/75/Array-vs-array-list-3-2048.jpg)