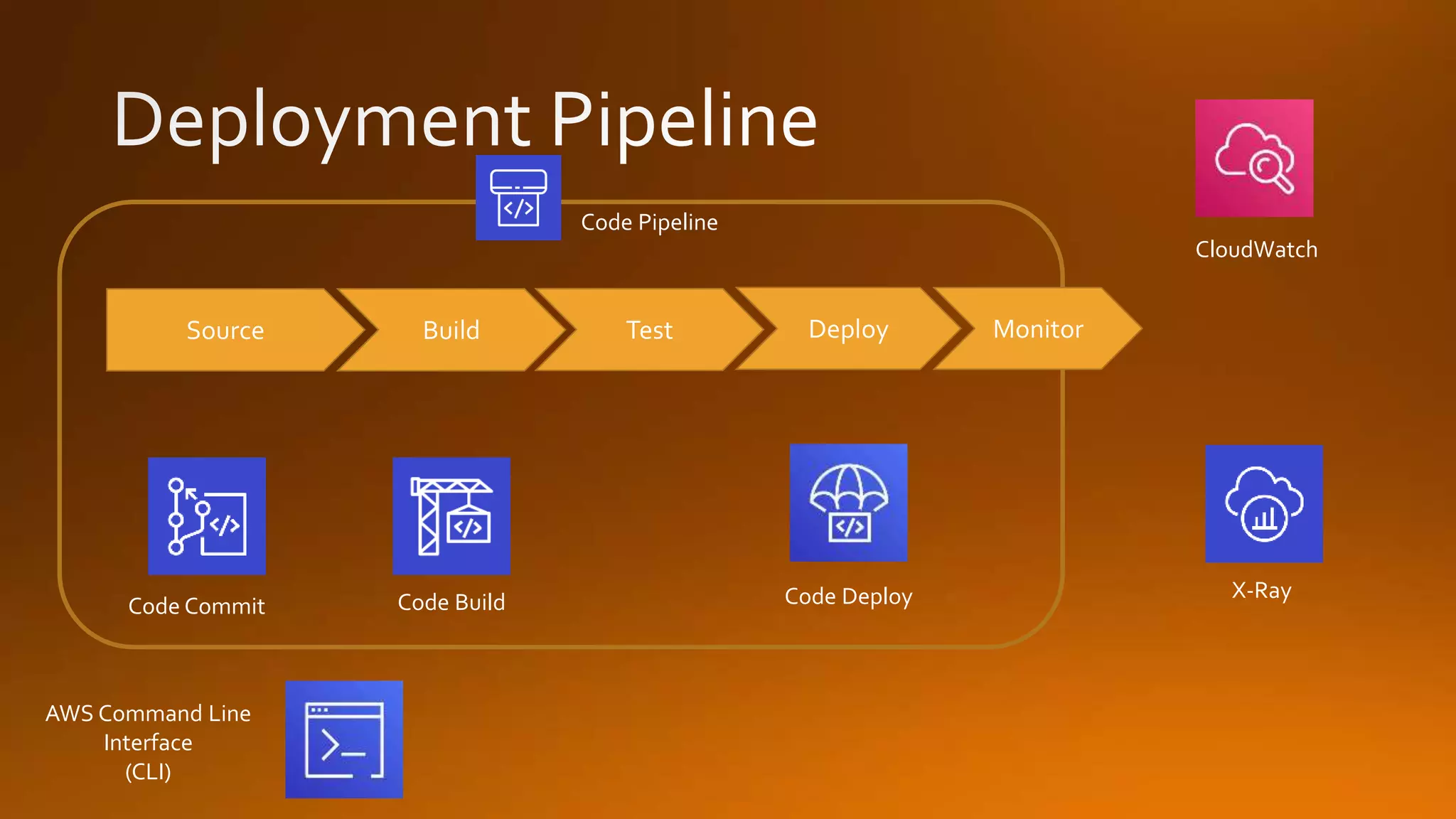
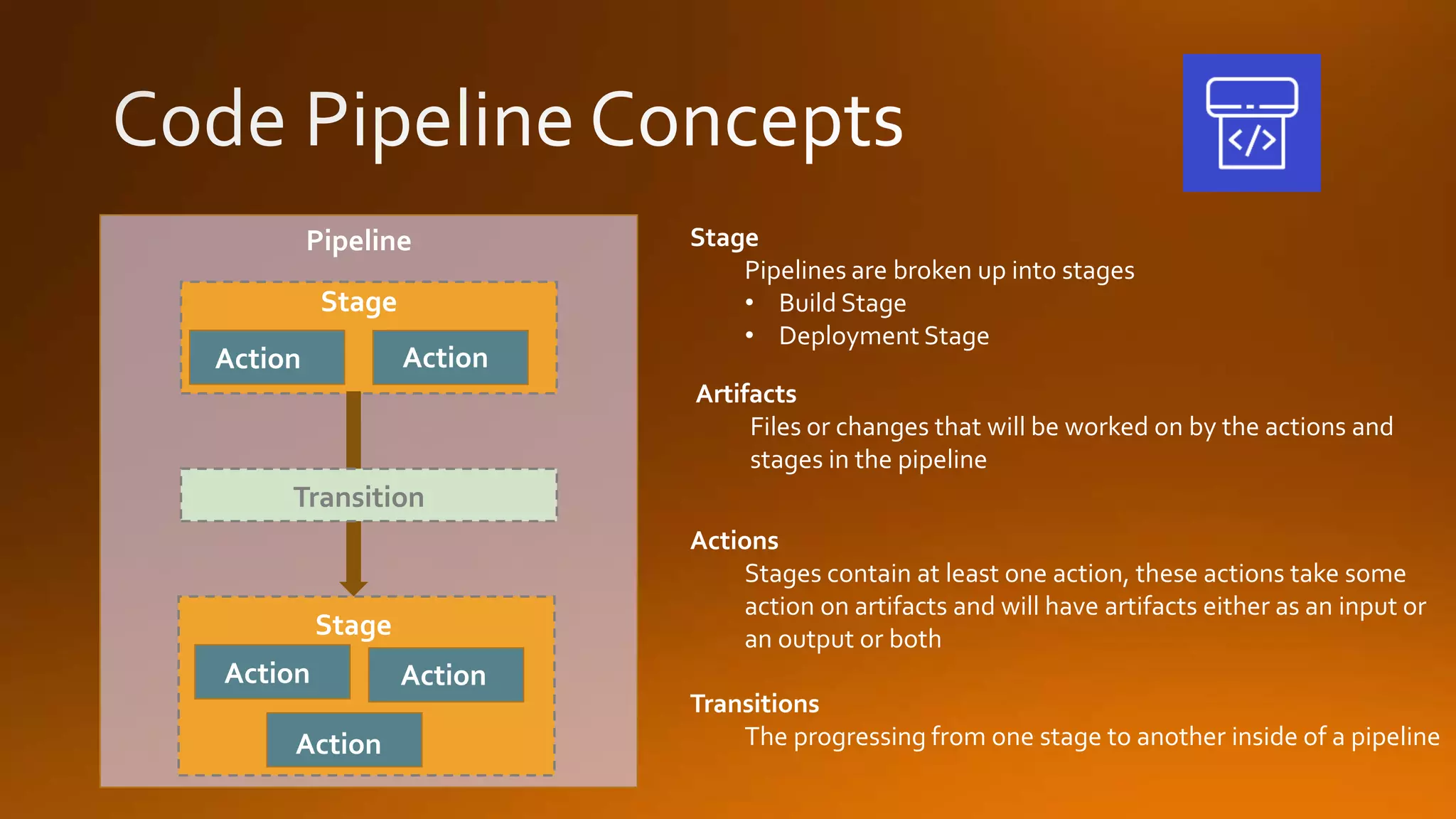
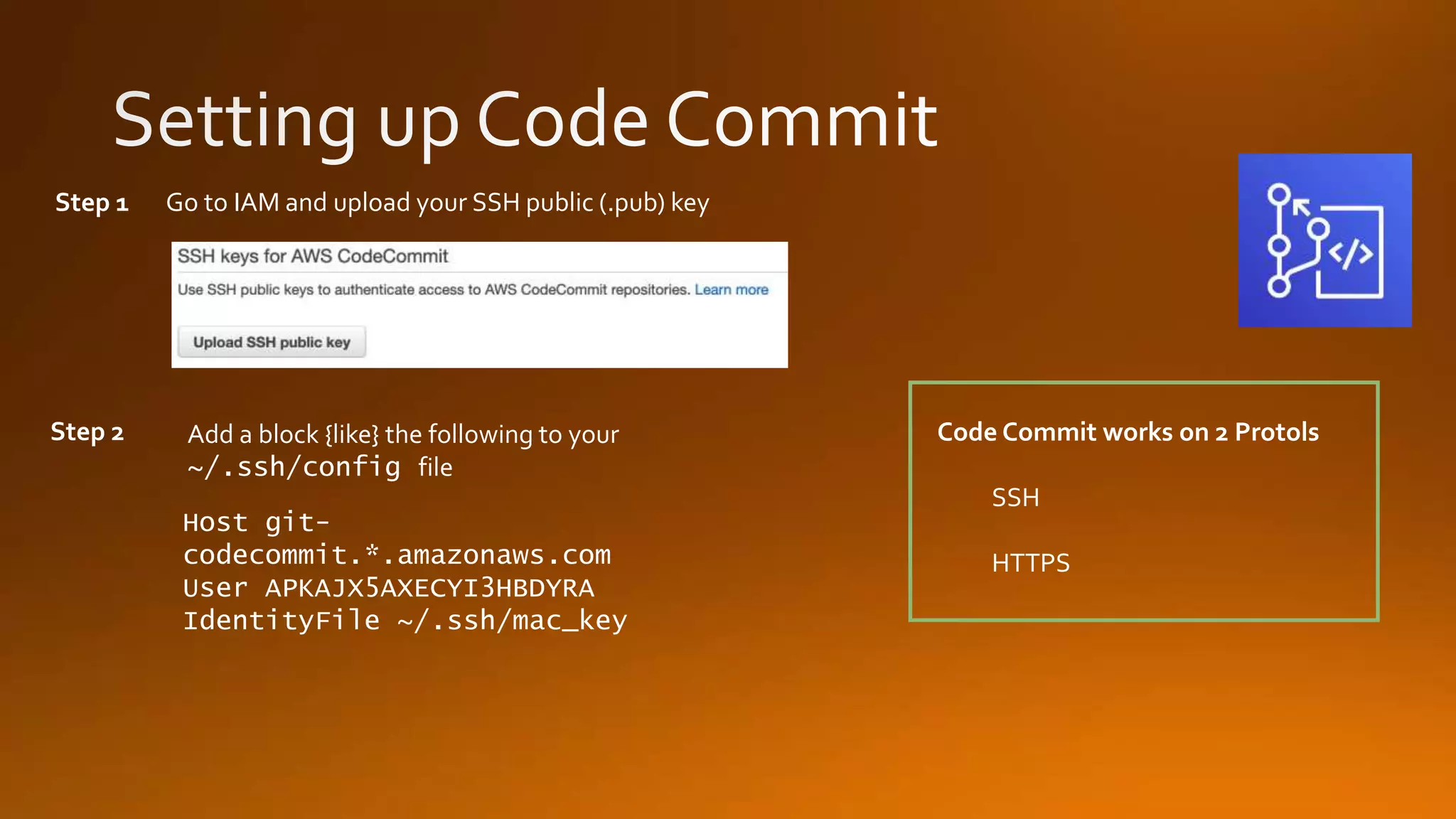
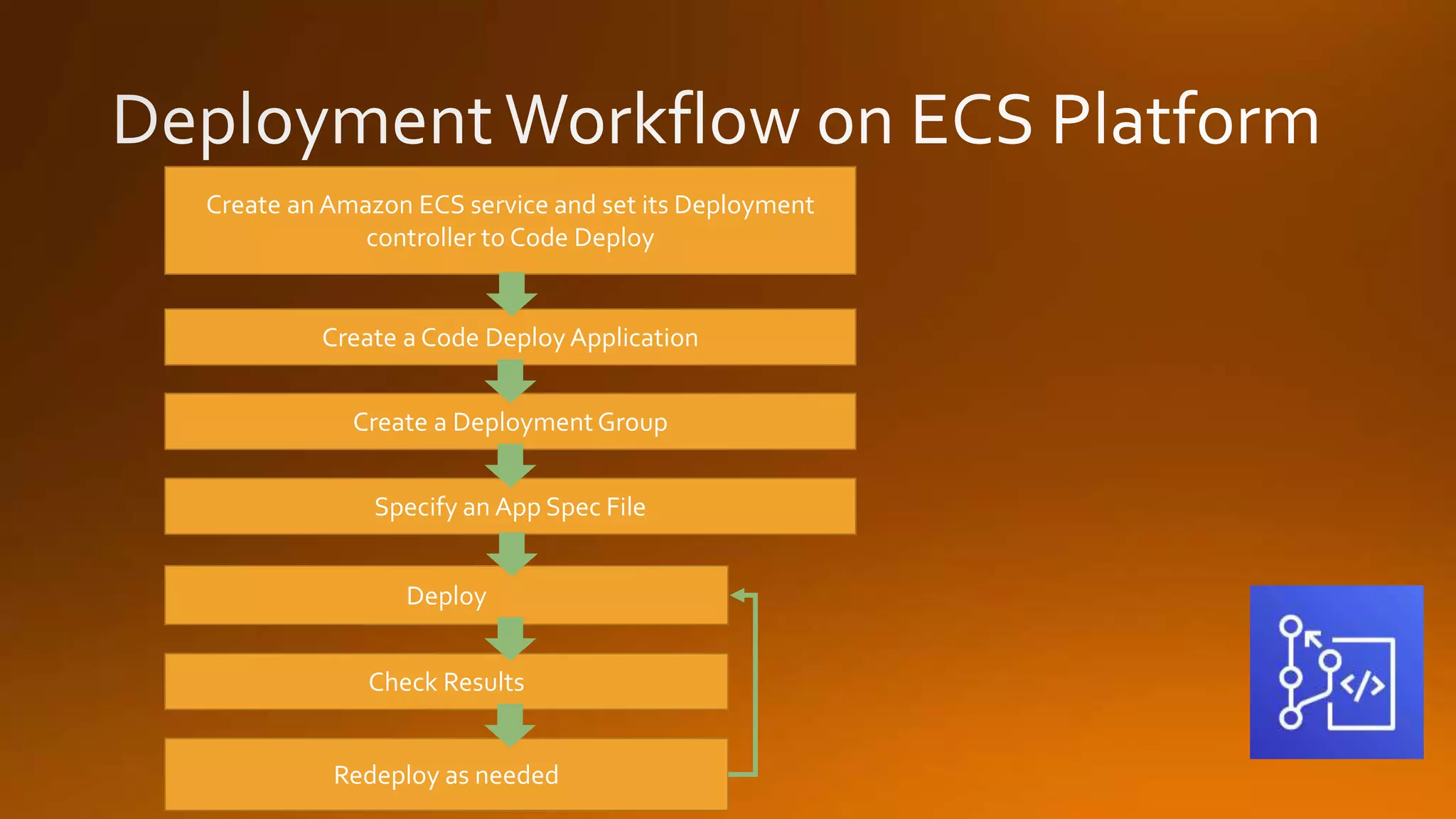
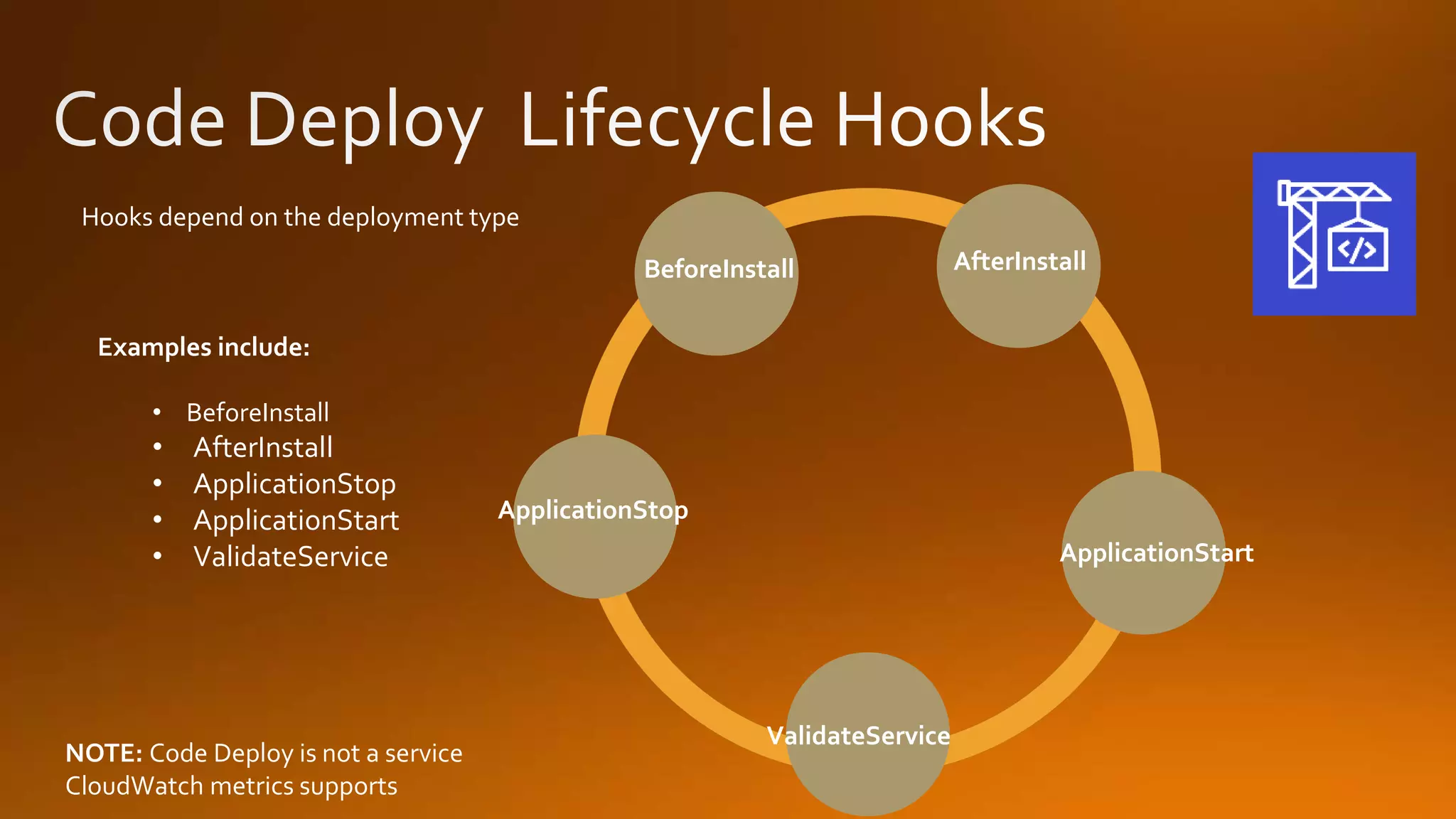
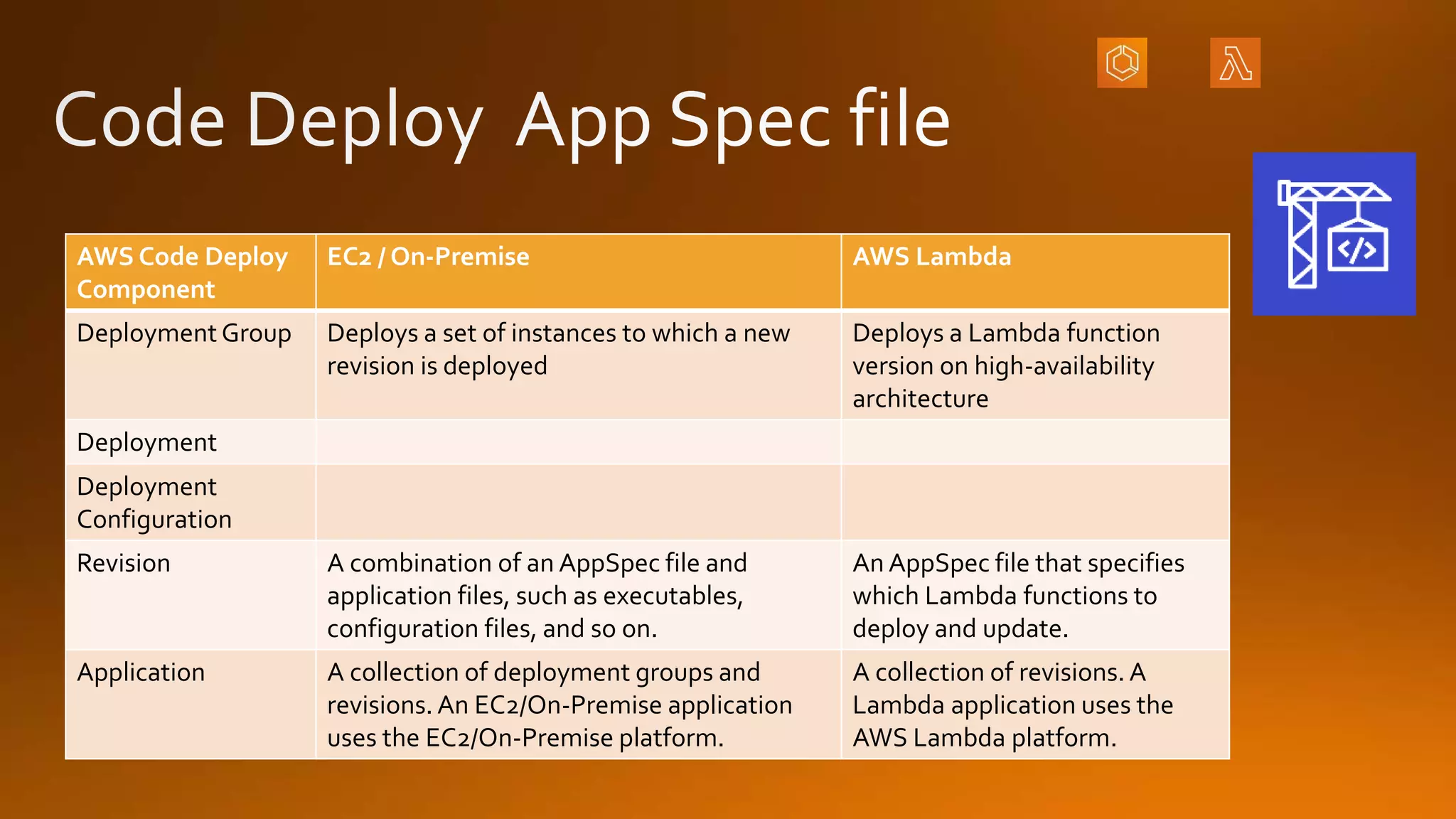
Continuous delivery is a software development discipline that allows for the frequent release of software to production, while continuous integration is the practice of merging developer changes to a shared mainline multiple times a day. AWS CodeCommit facilitates this process by hosting private git repositories and enabling automation of deployment pipelines through services like CodePipeline and CodeDeploy. This document outlines the steps to set up and manage these processes within AWS, including examples of deployment strategies like blue-green and canary deployments.