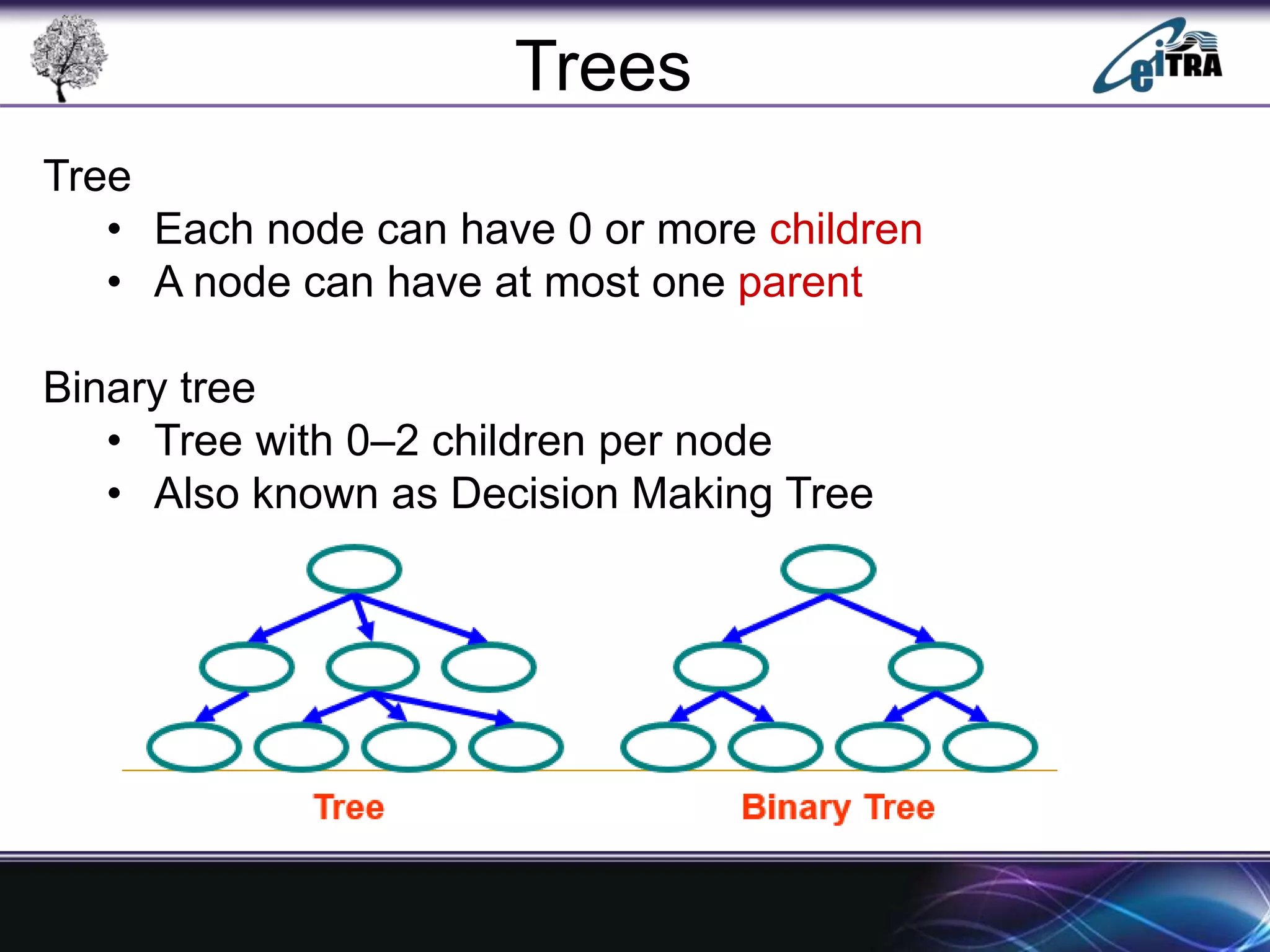
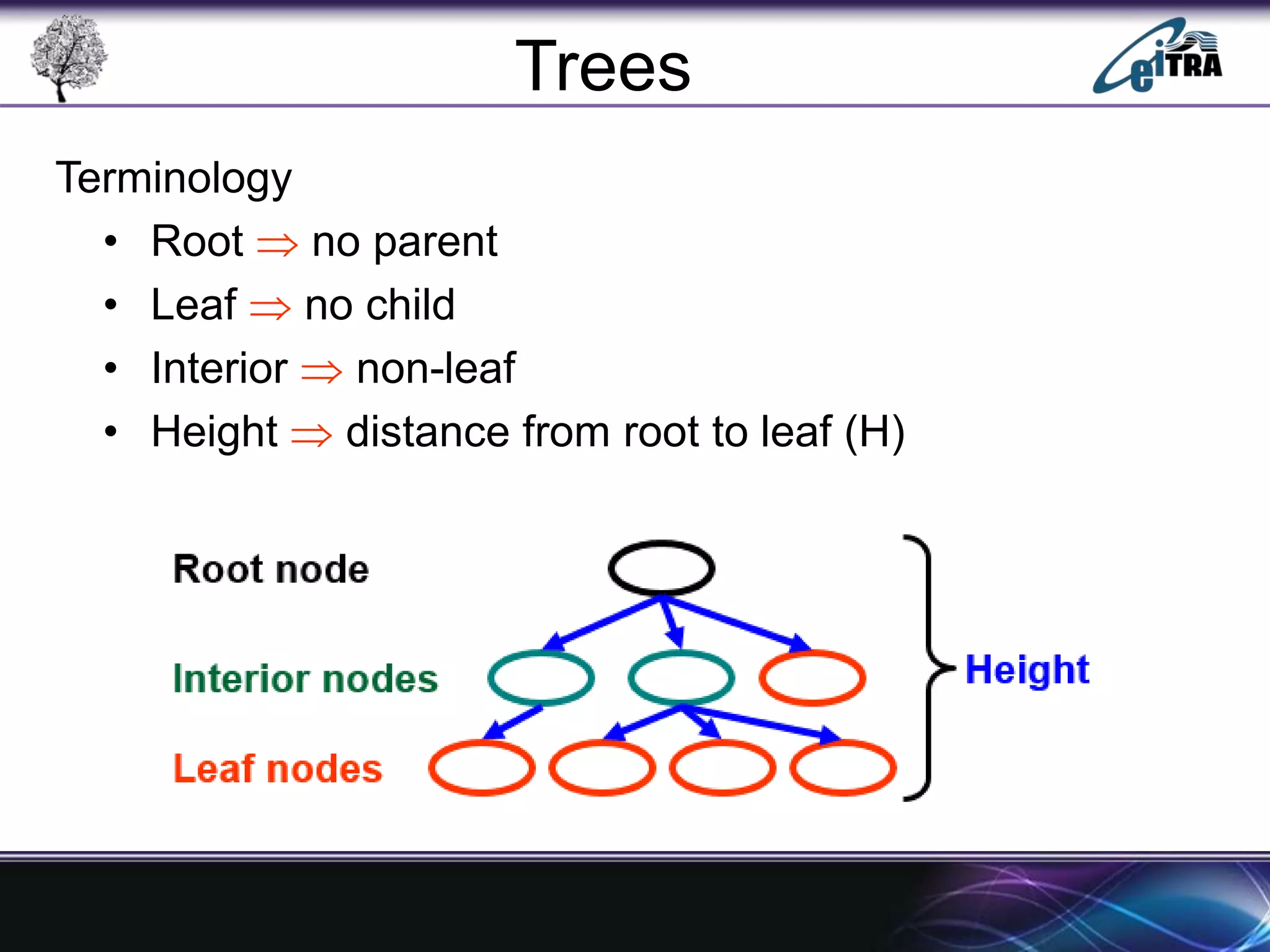
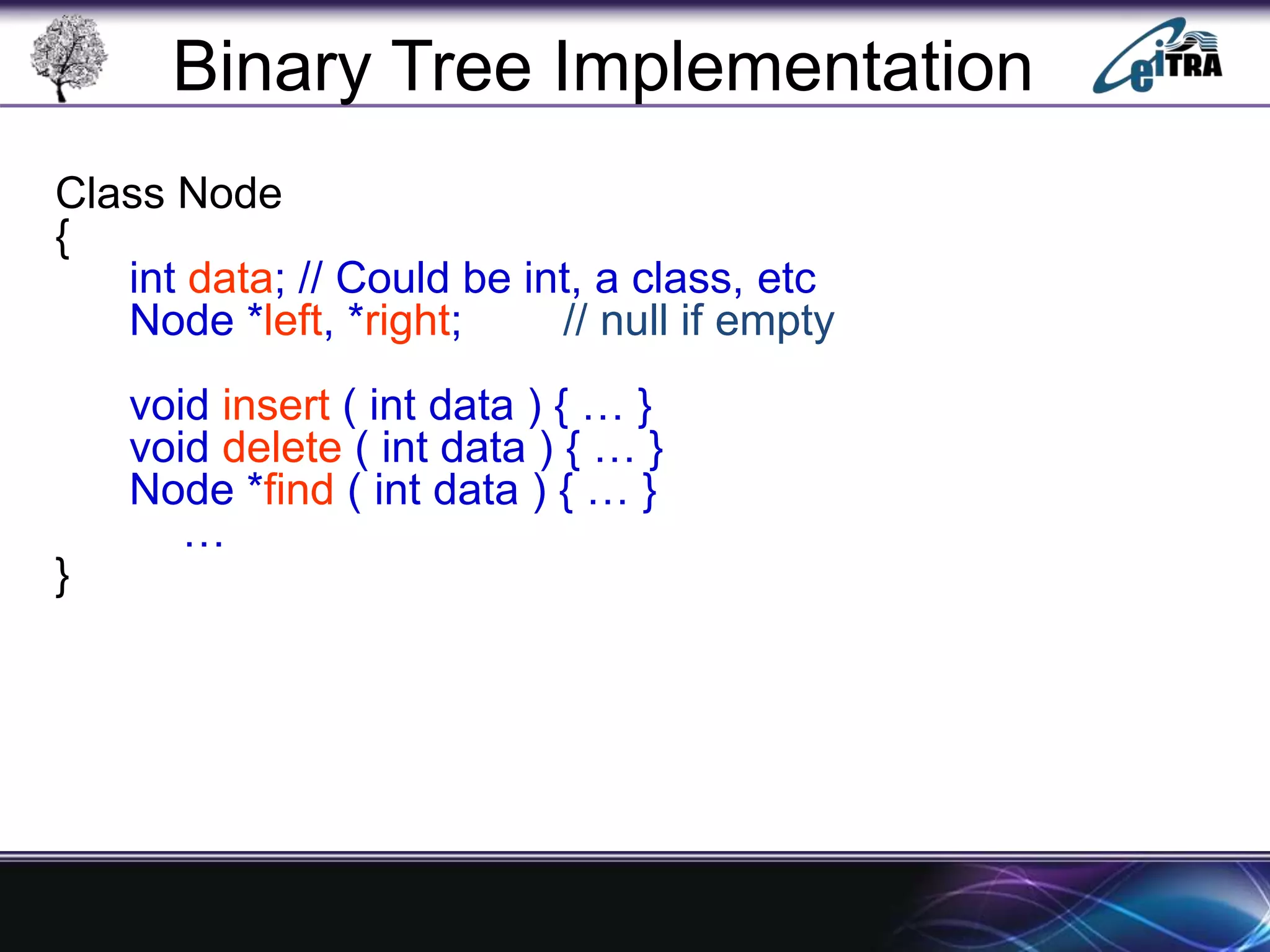
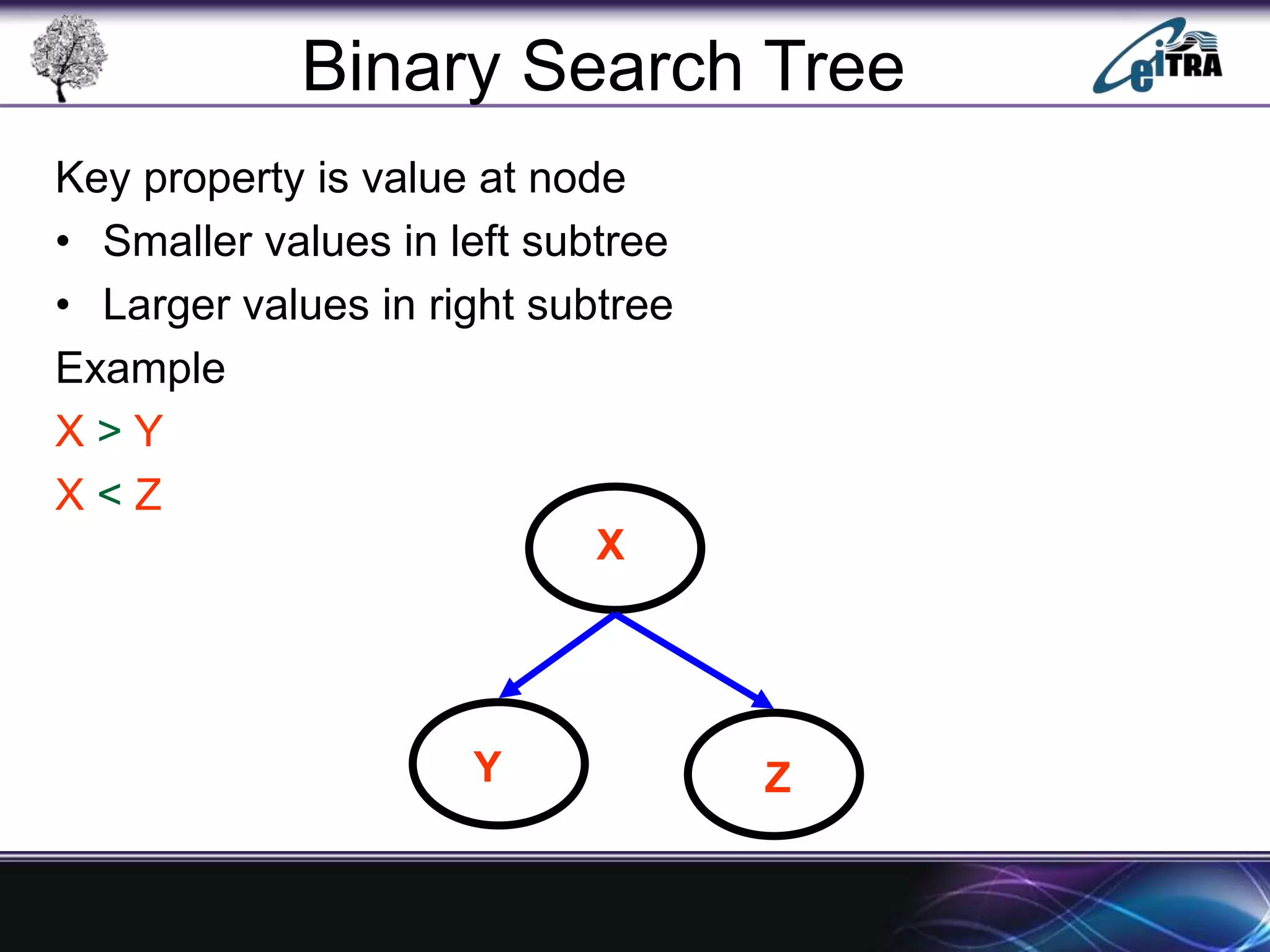
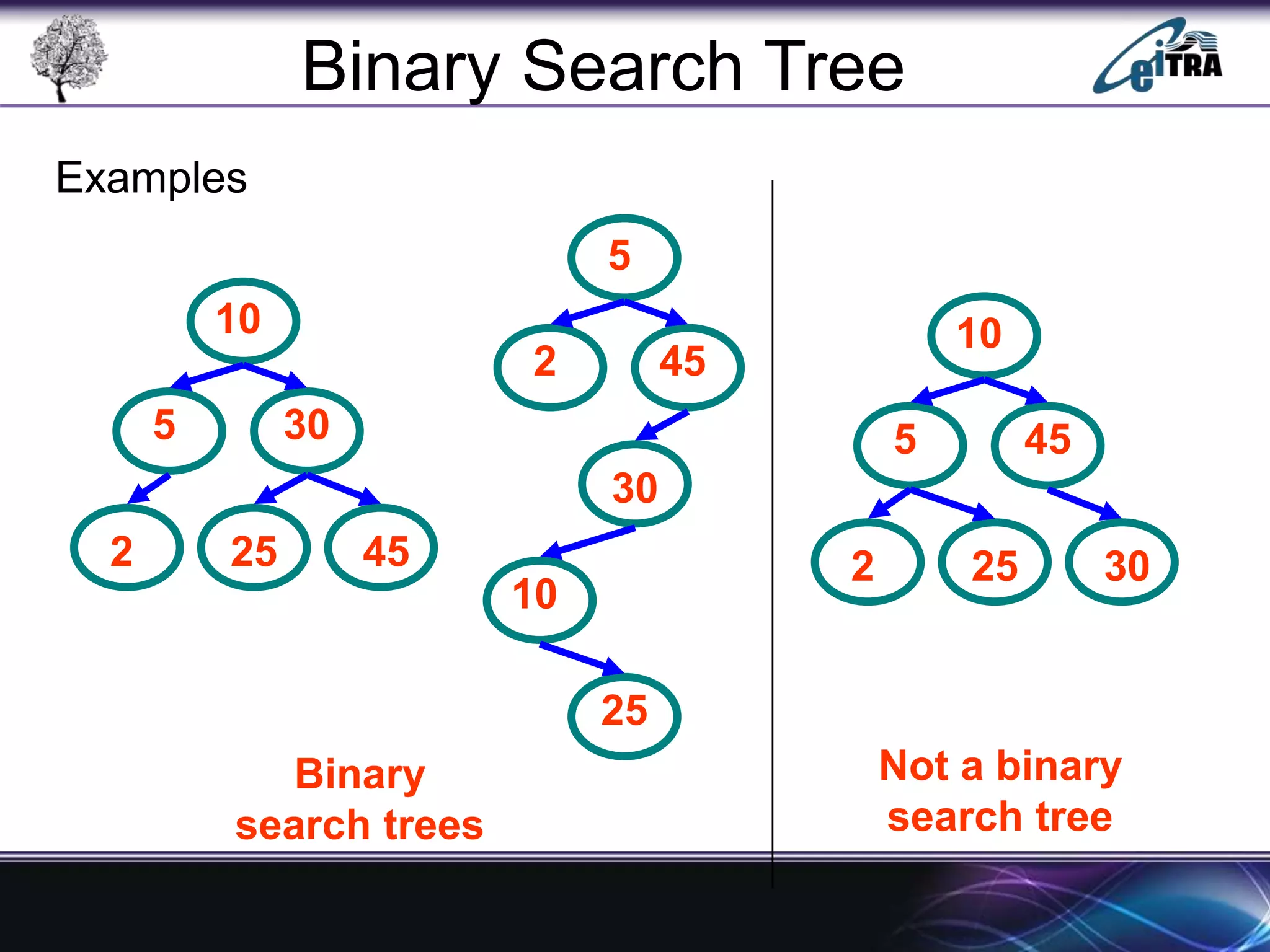
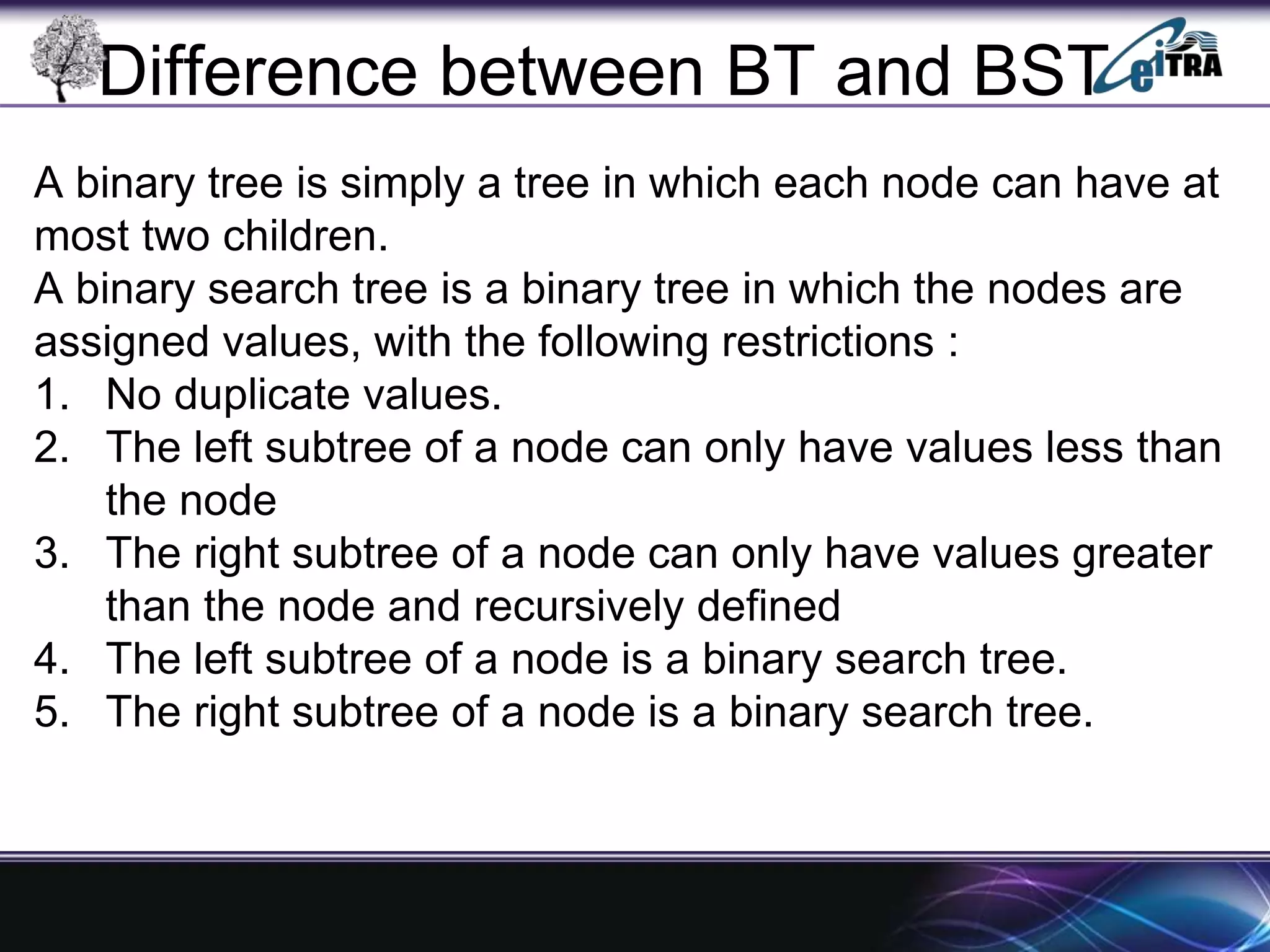
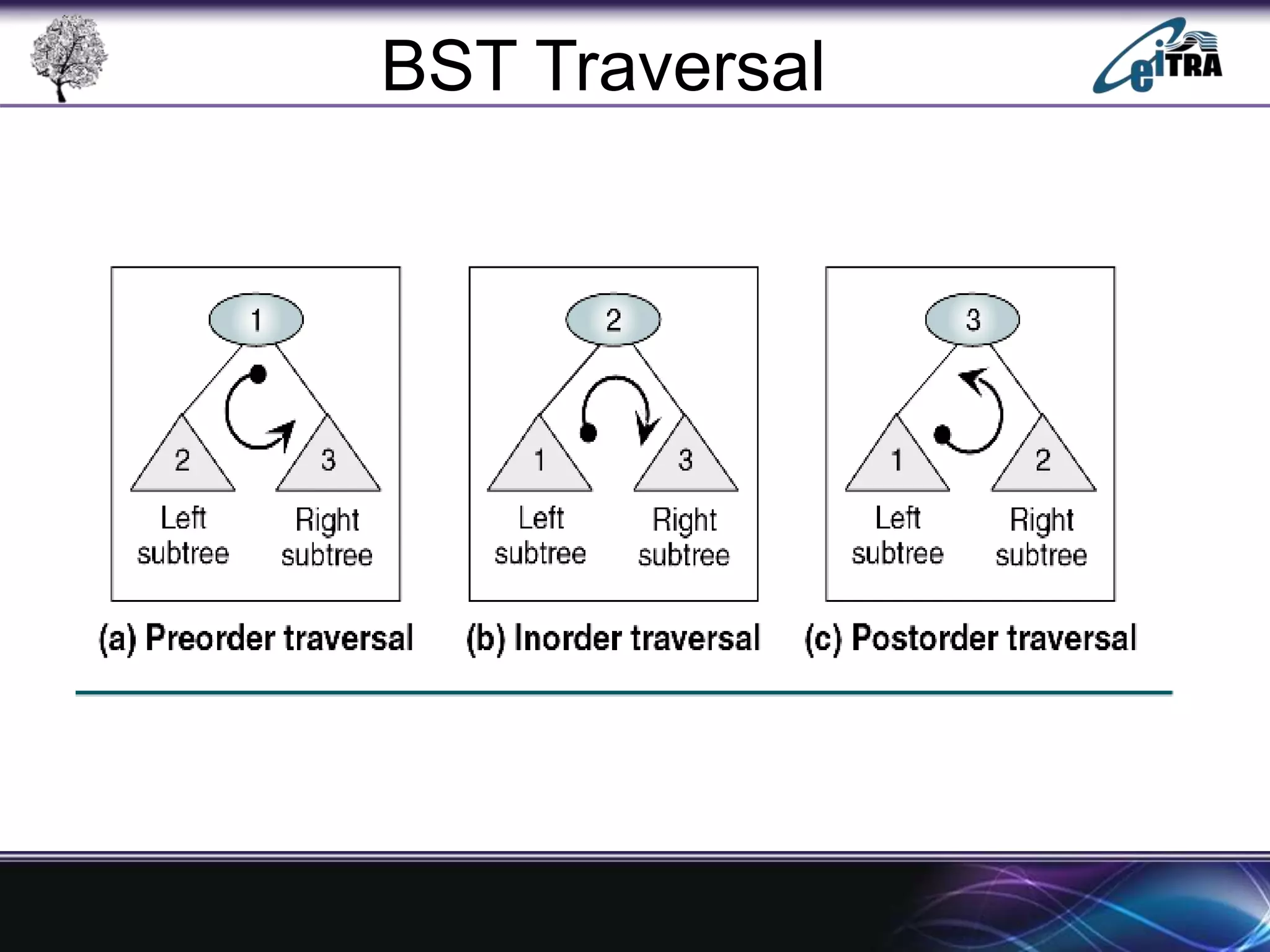
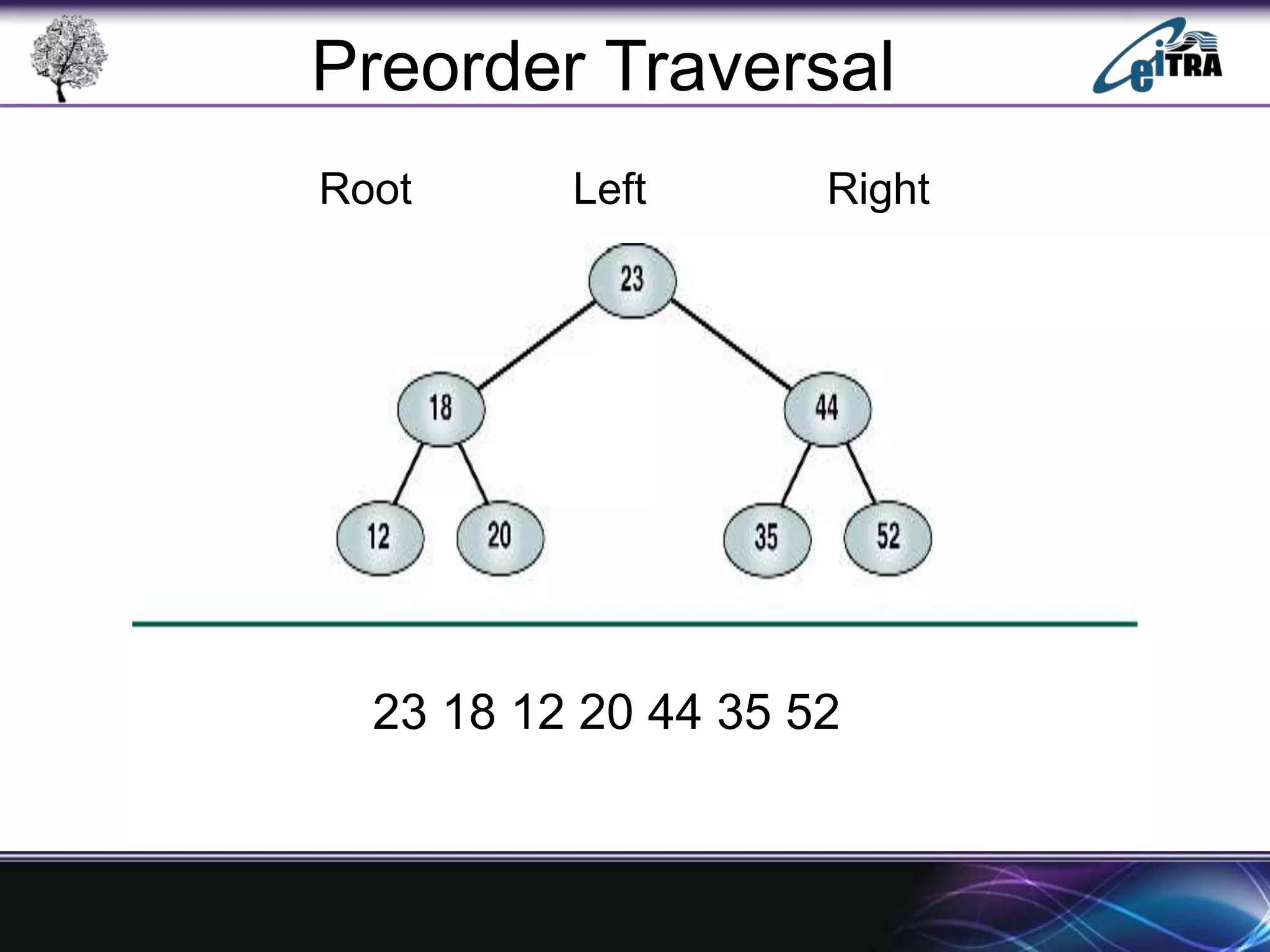
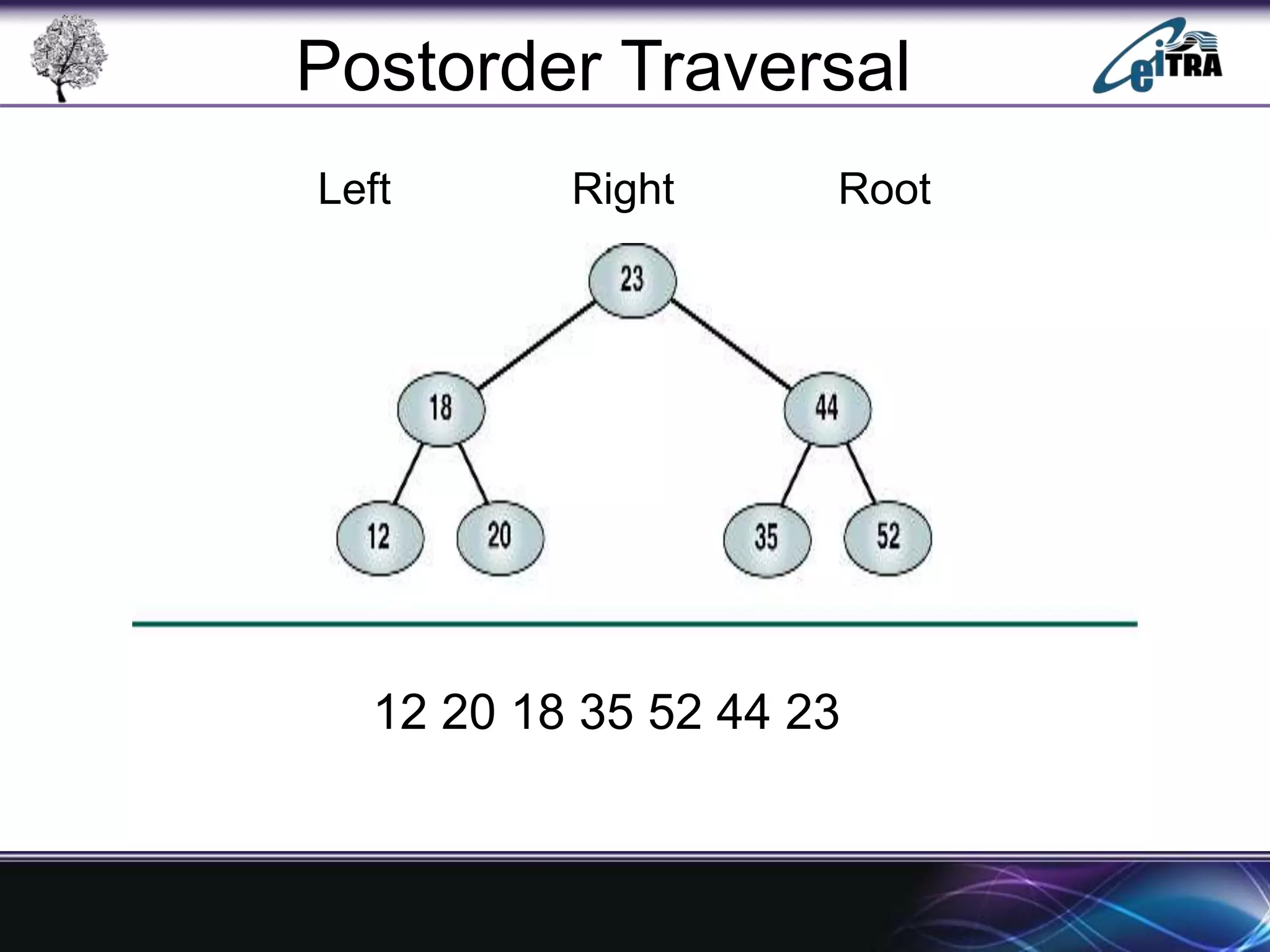
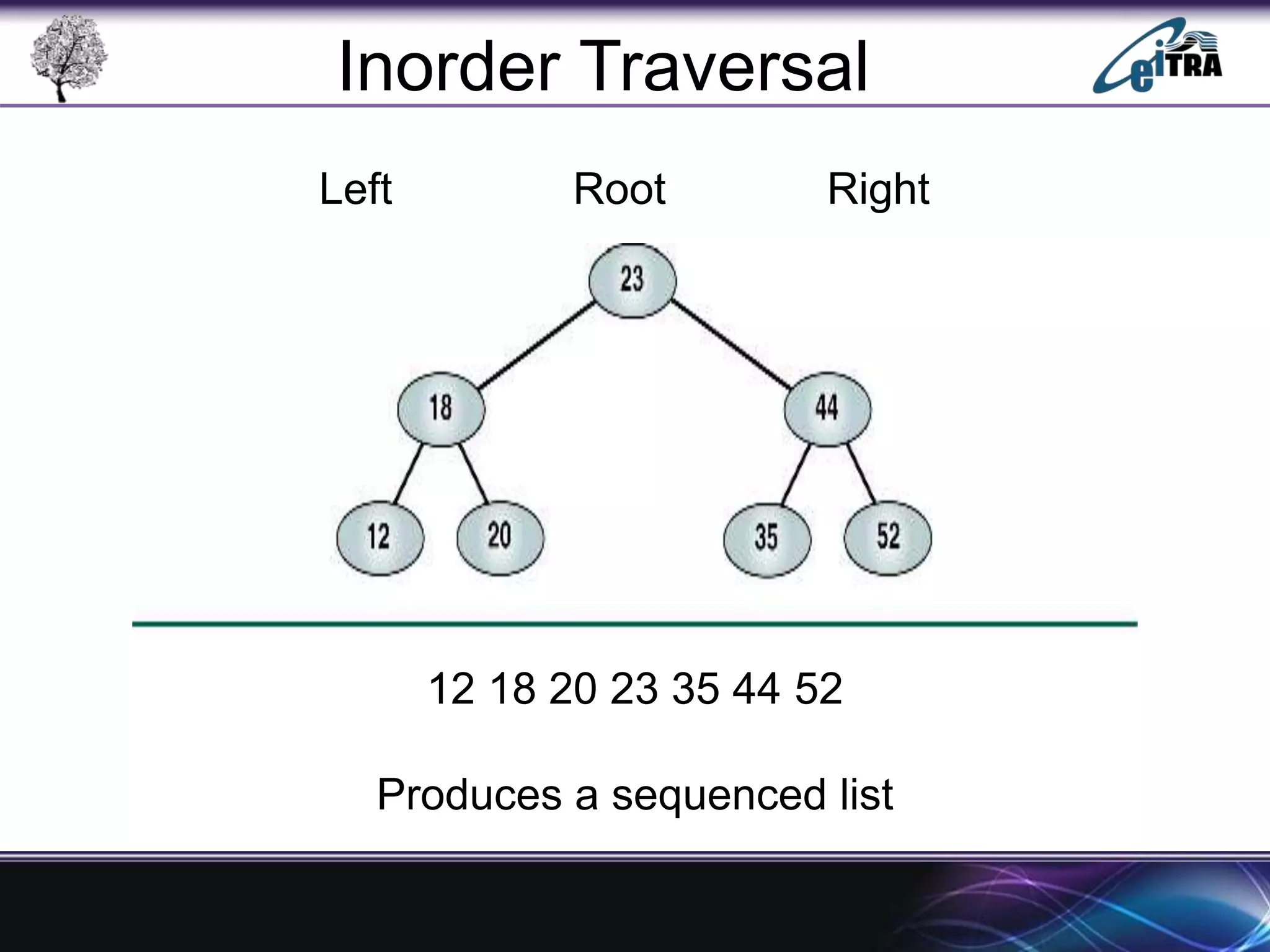
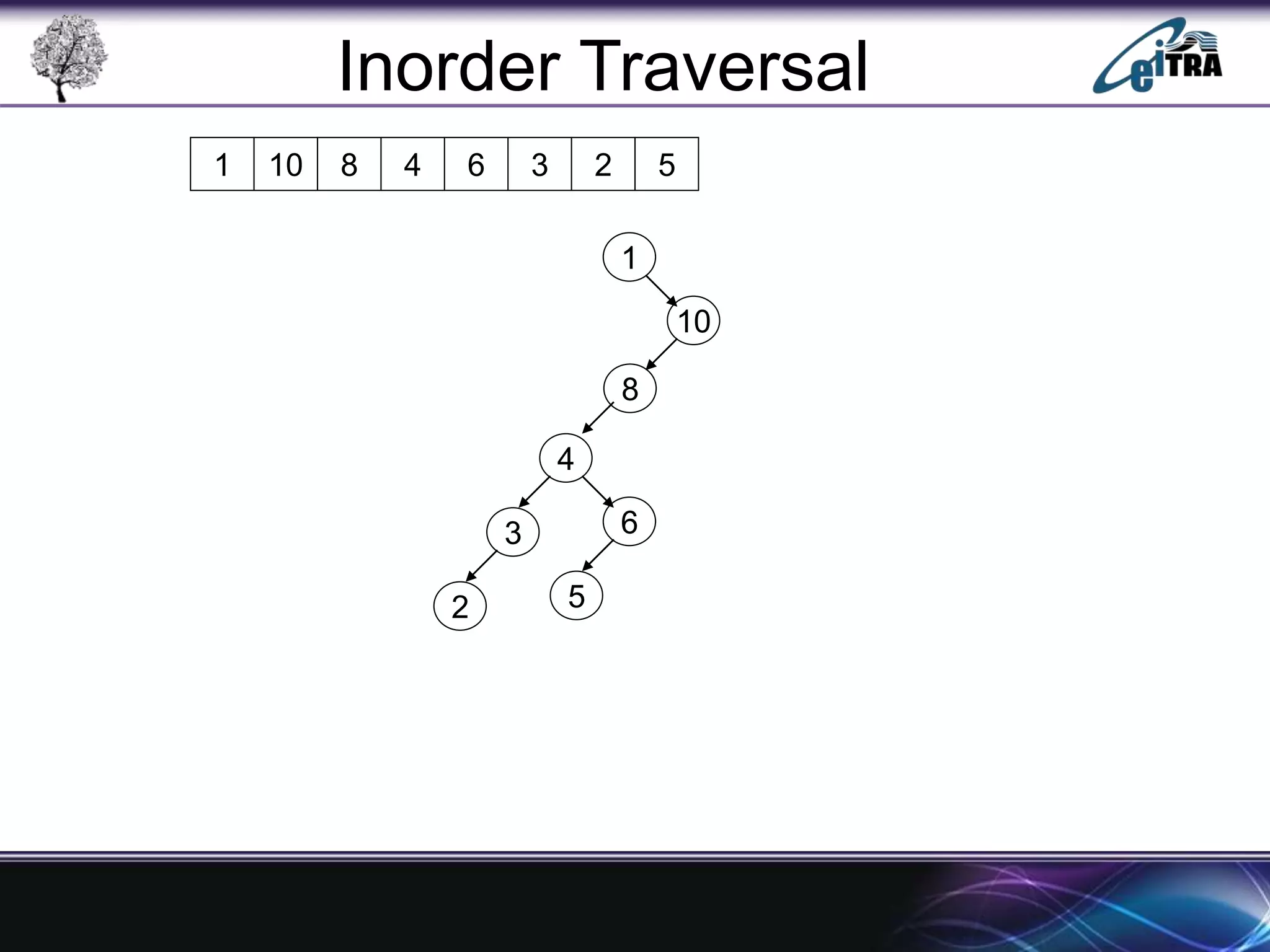
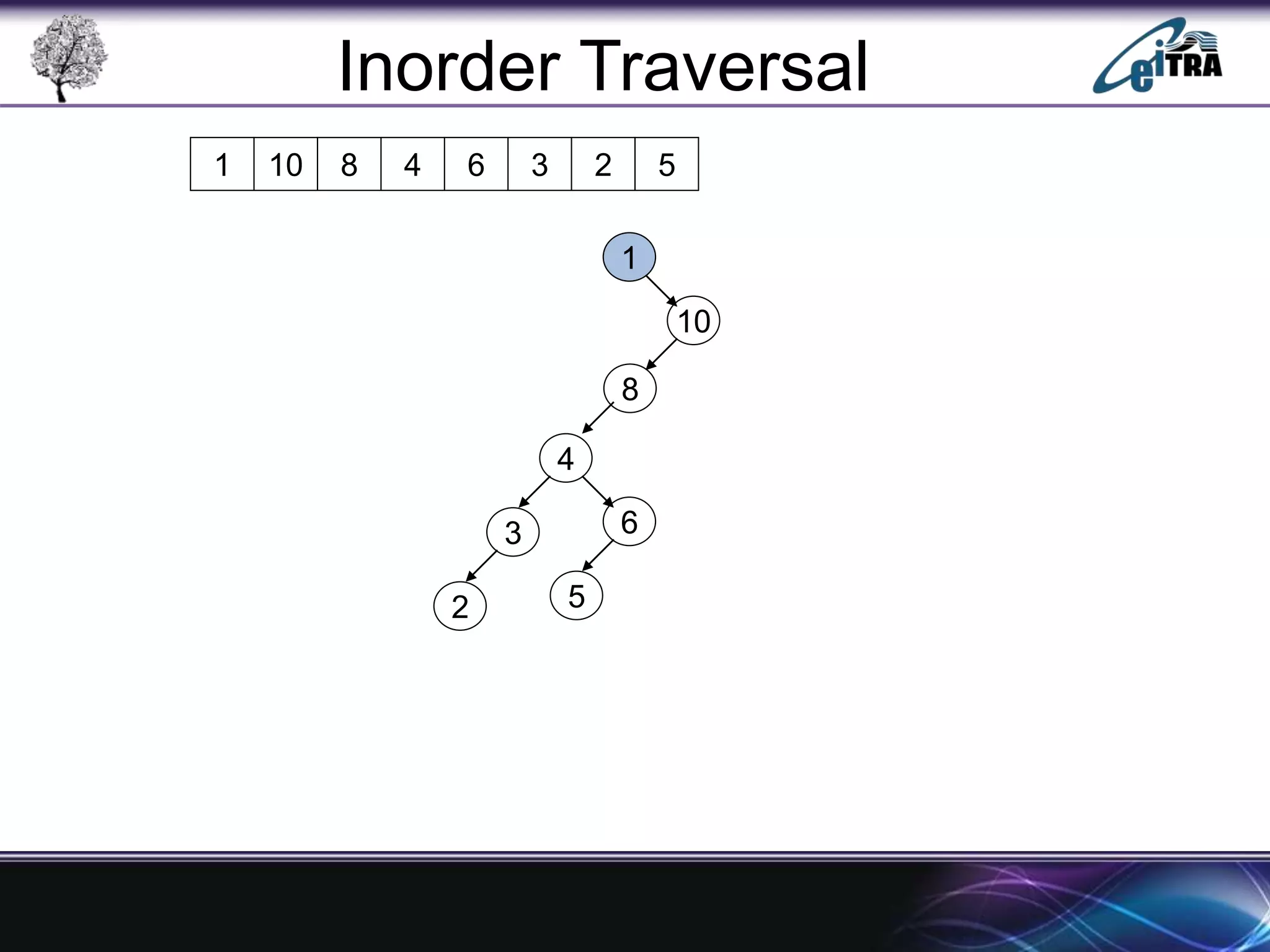
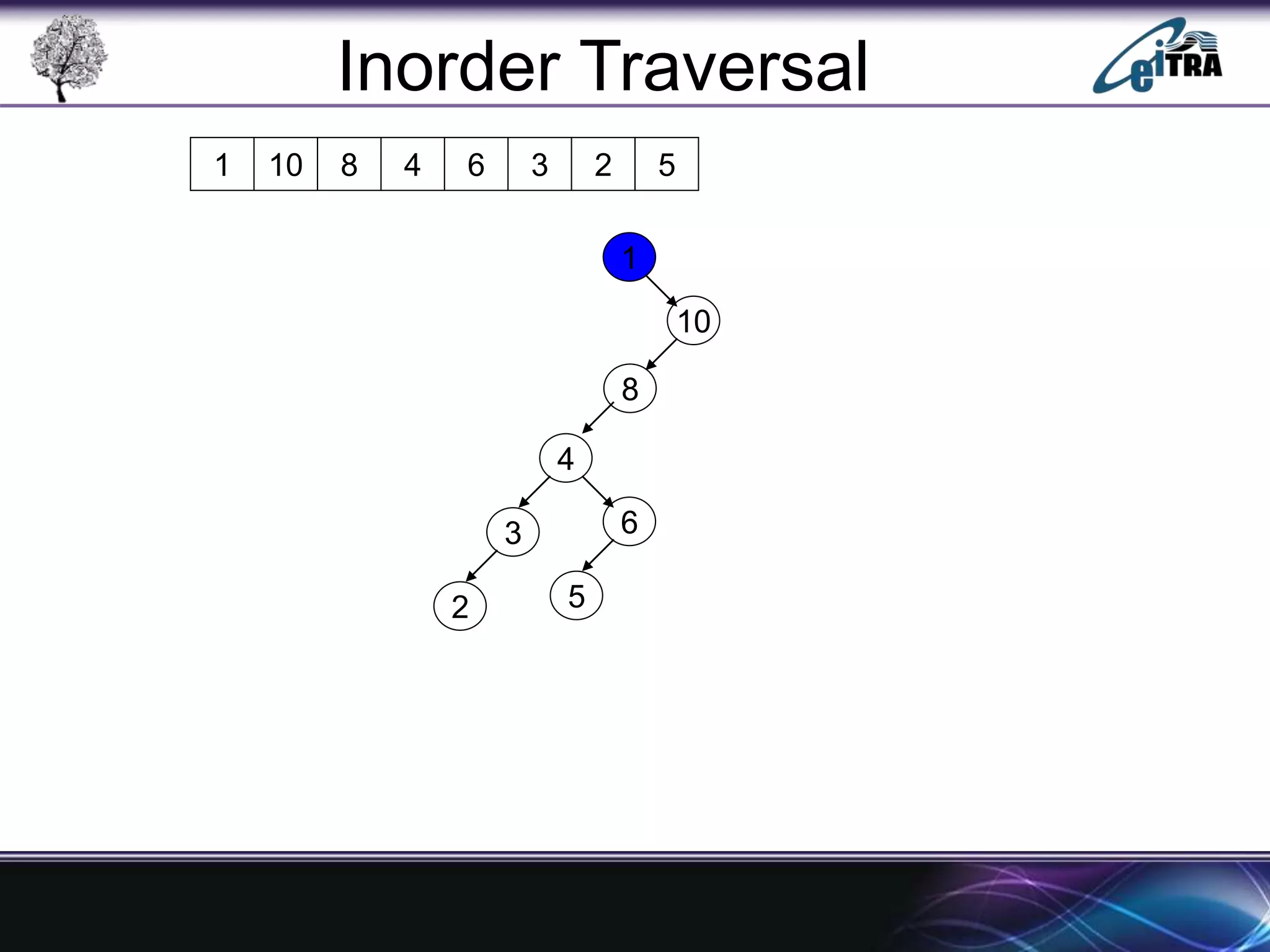
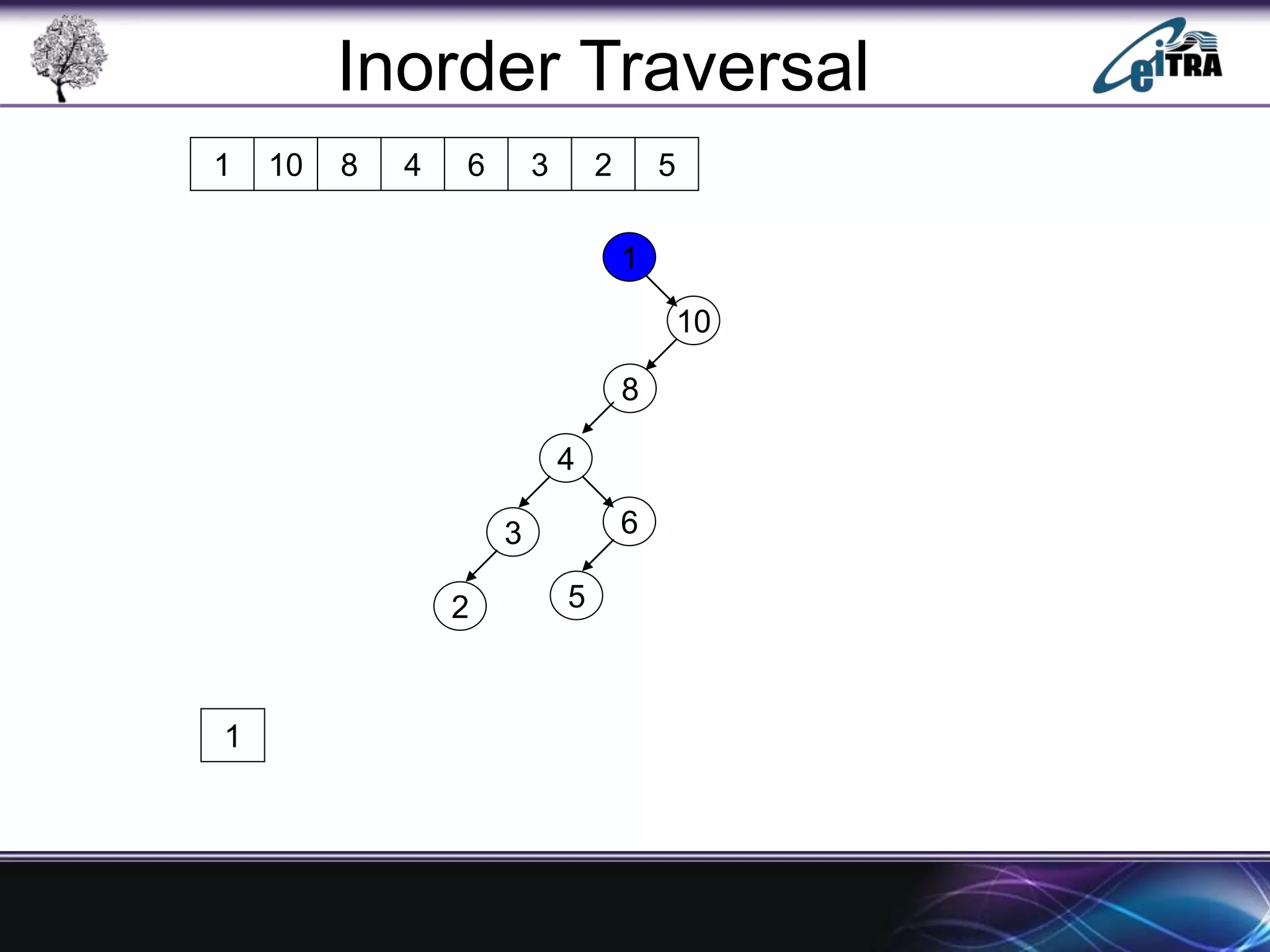
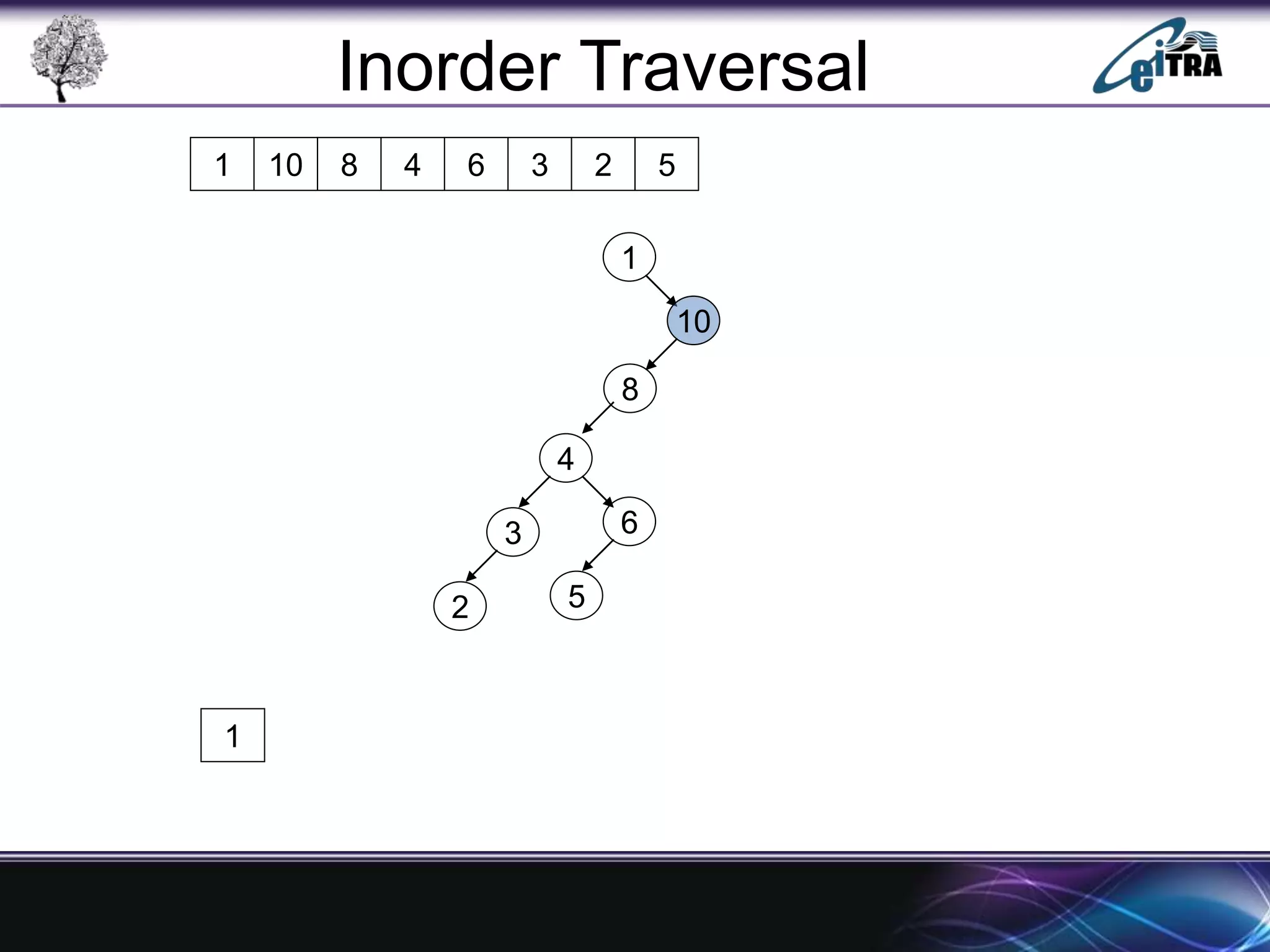
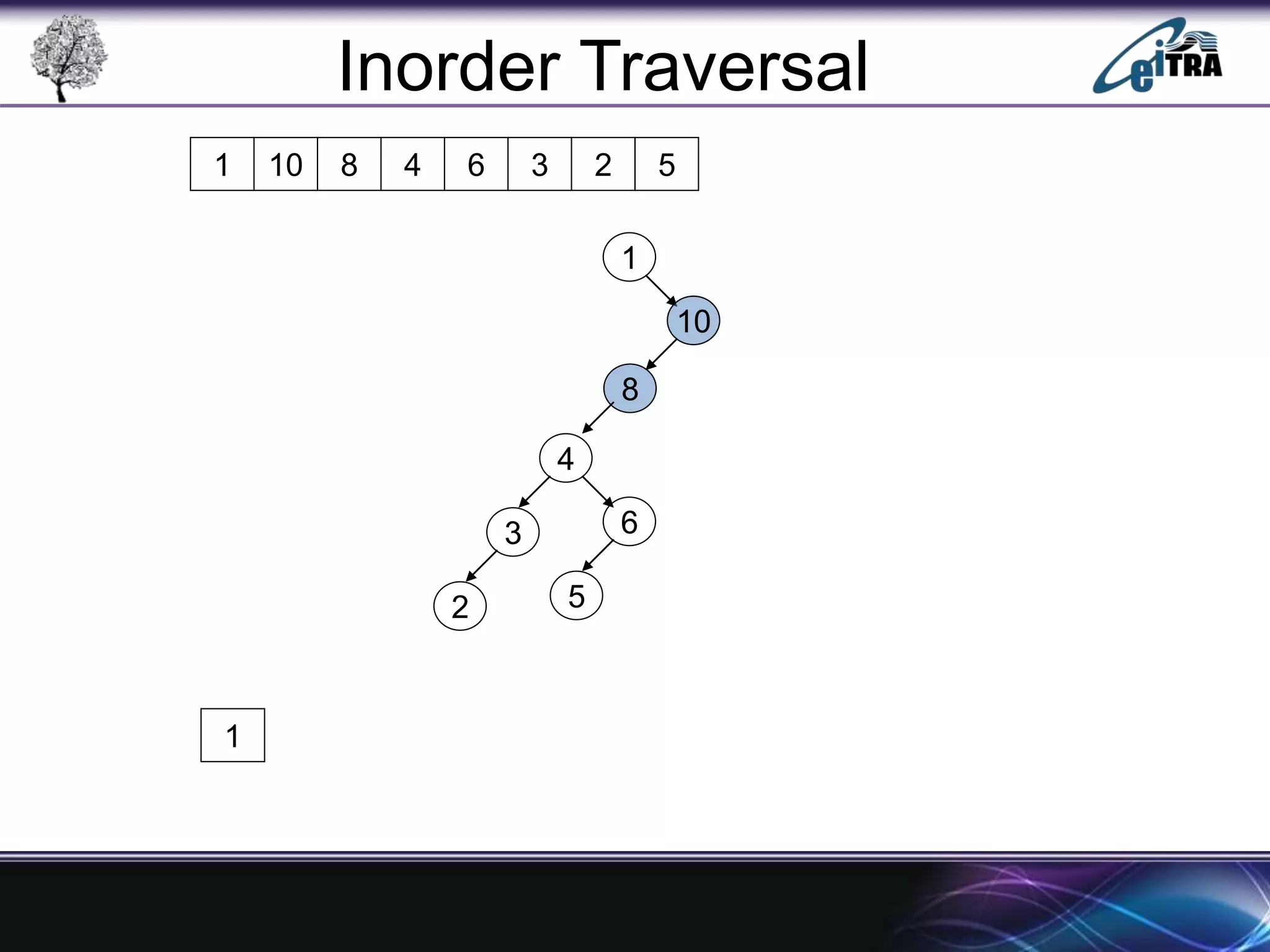
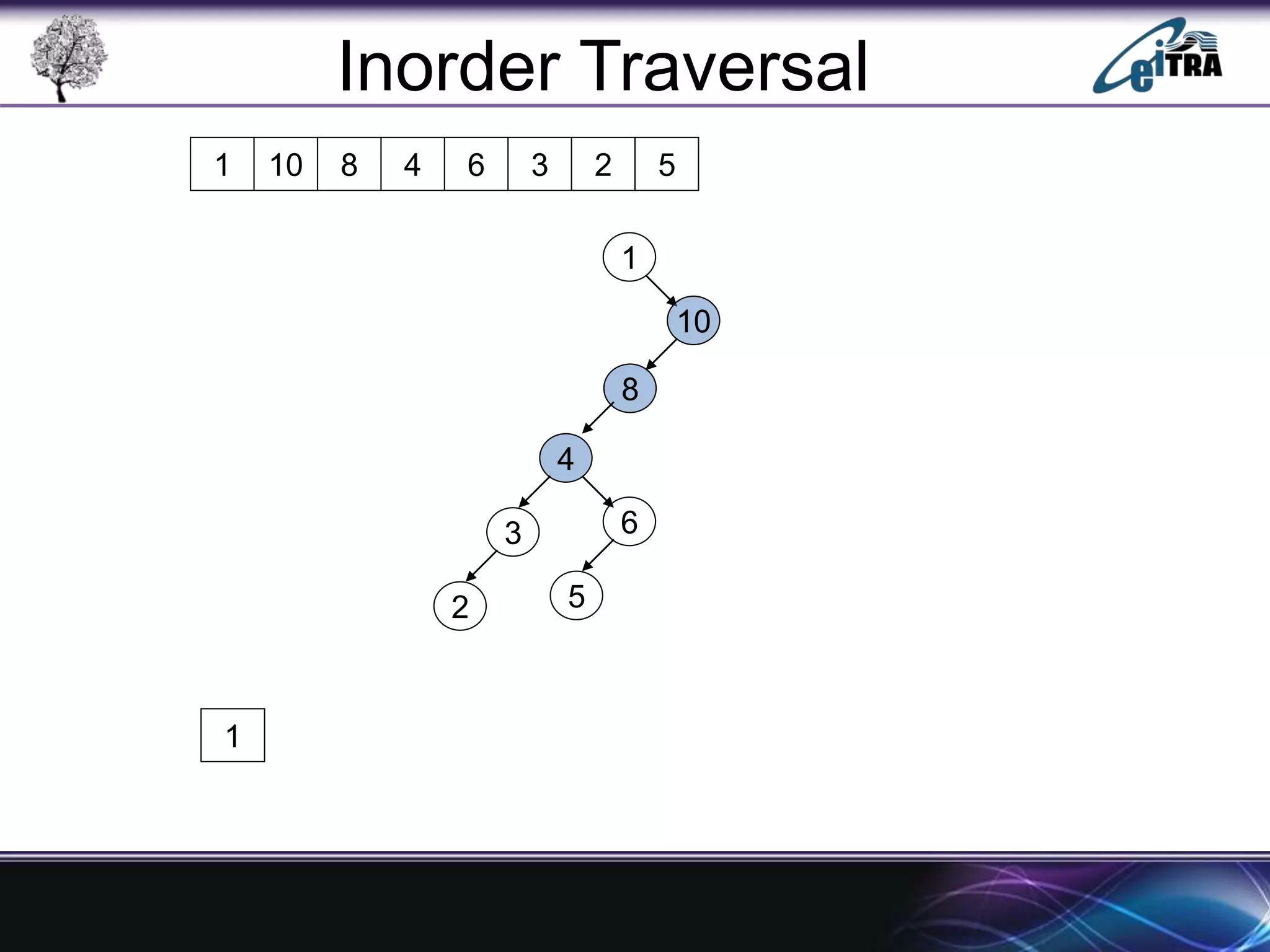
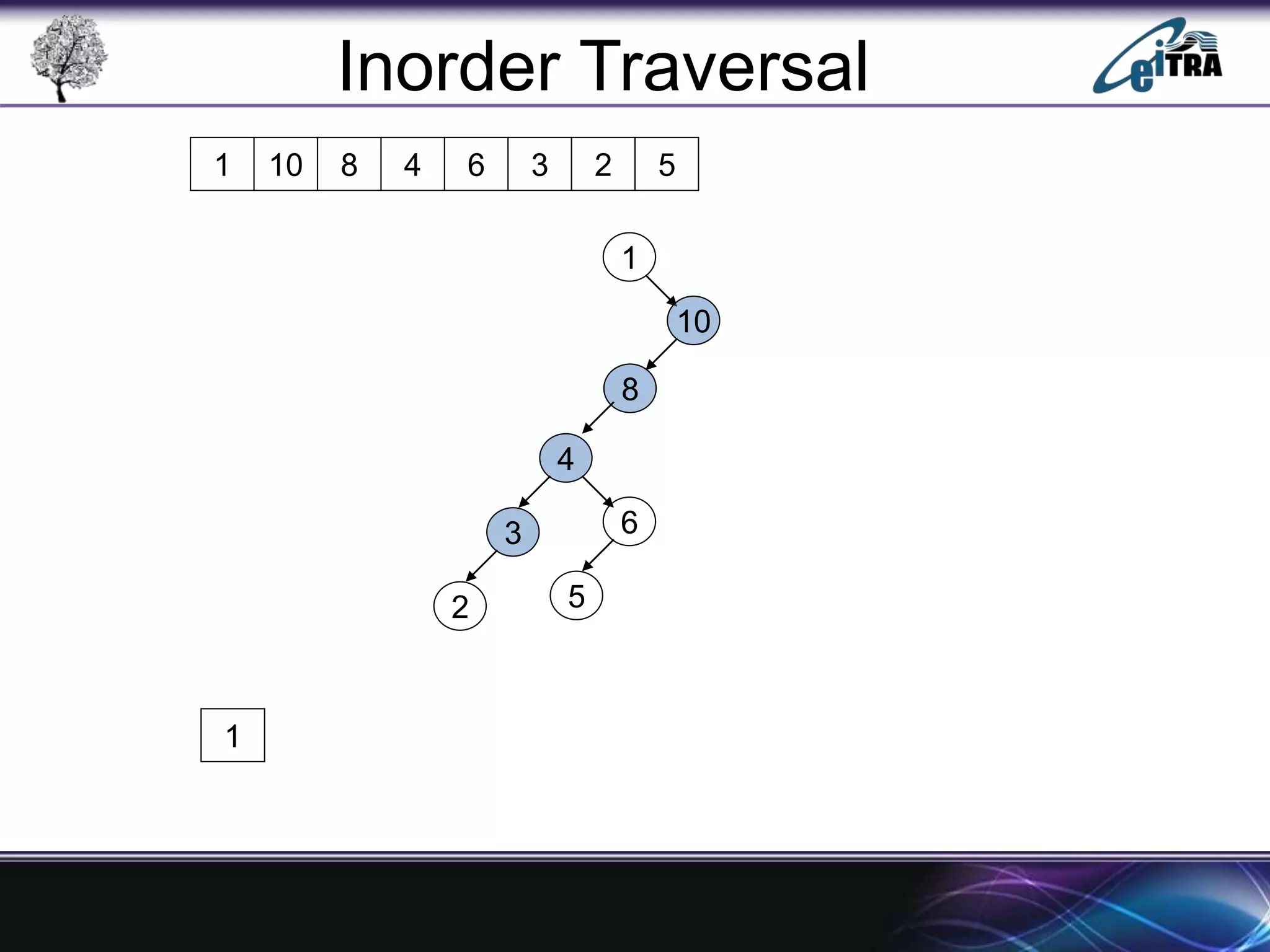
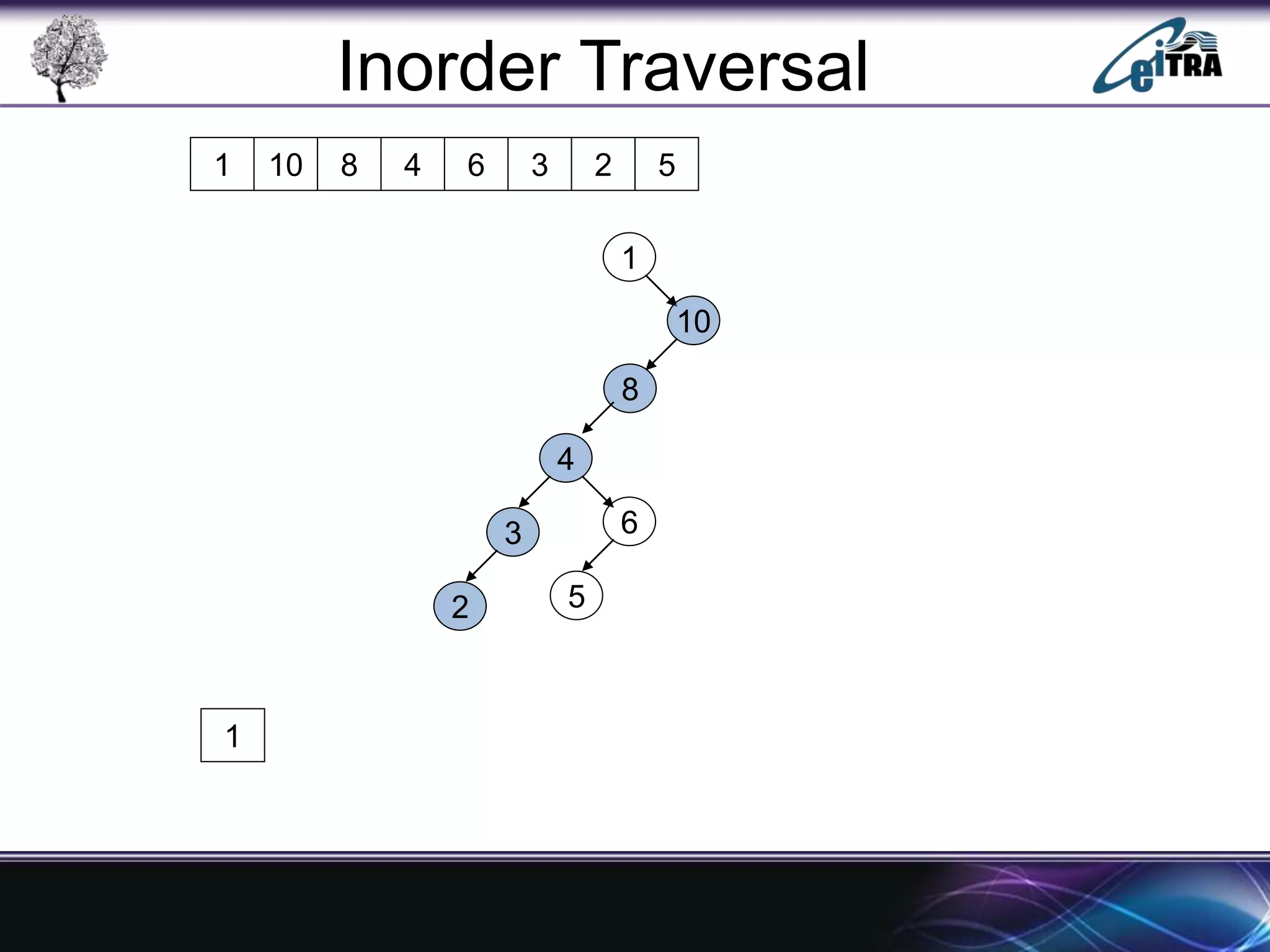
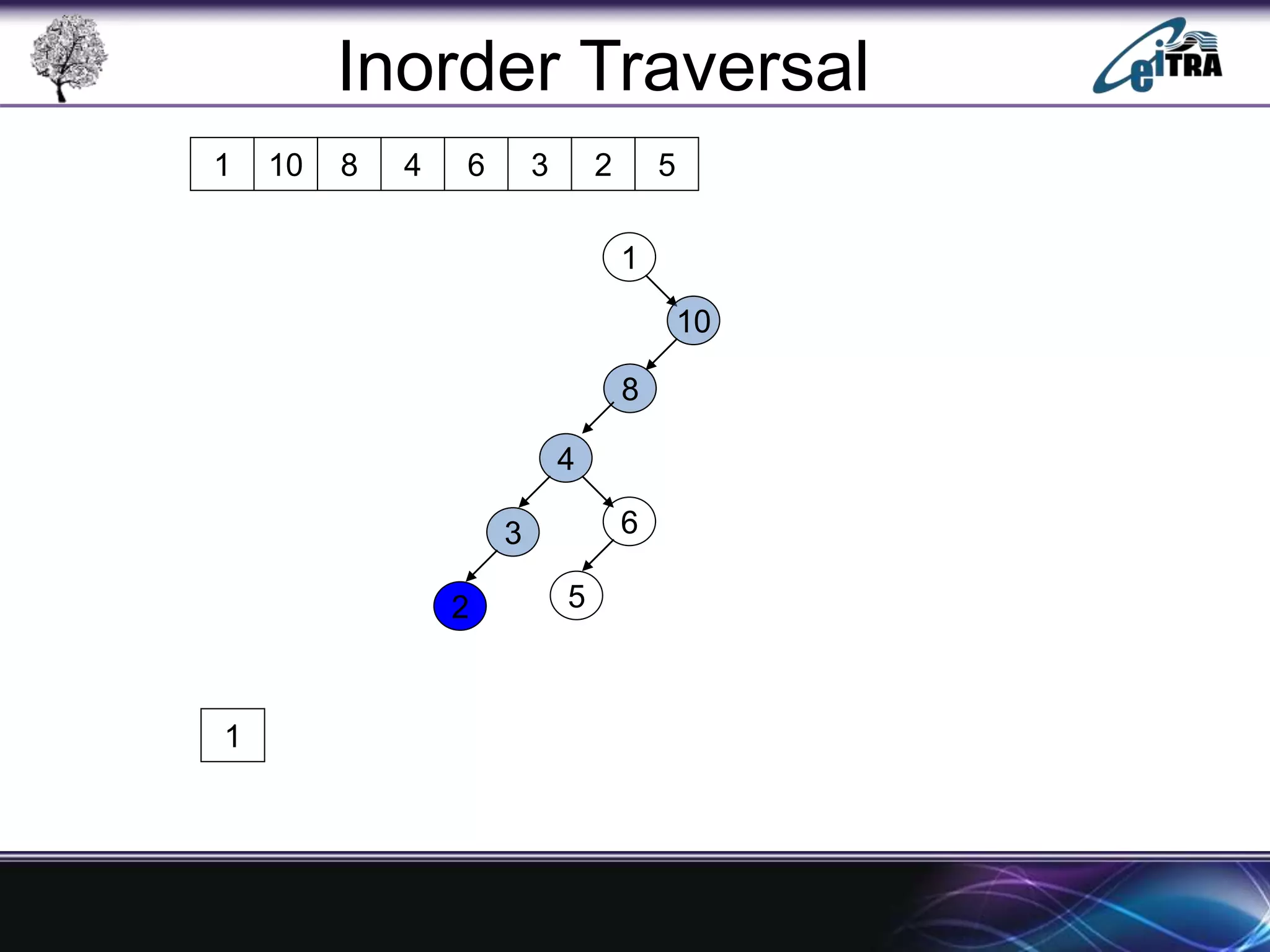
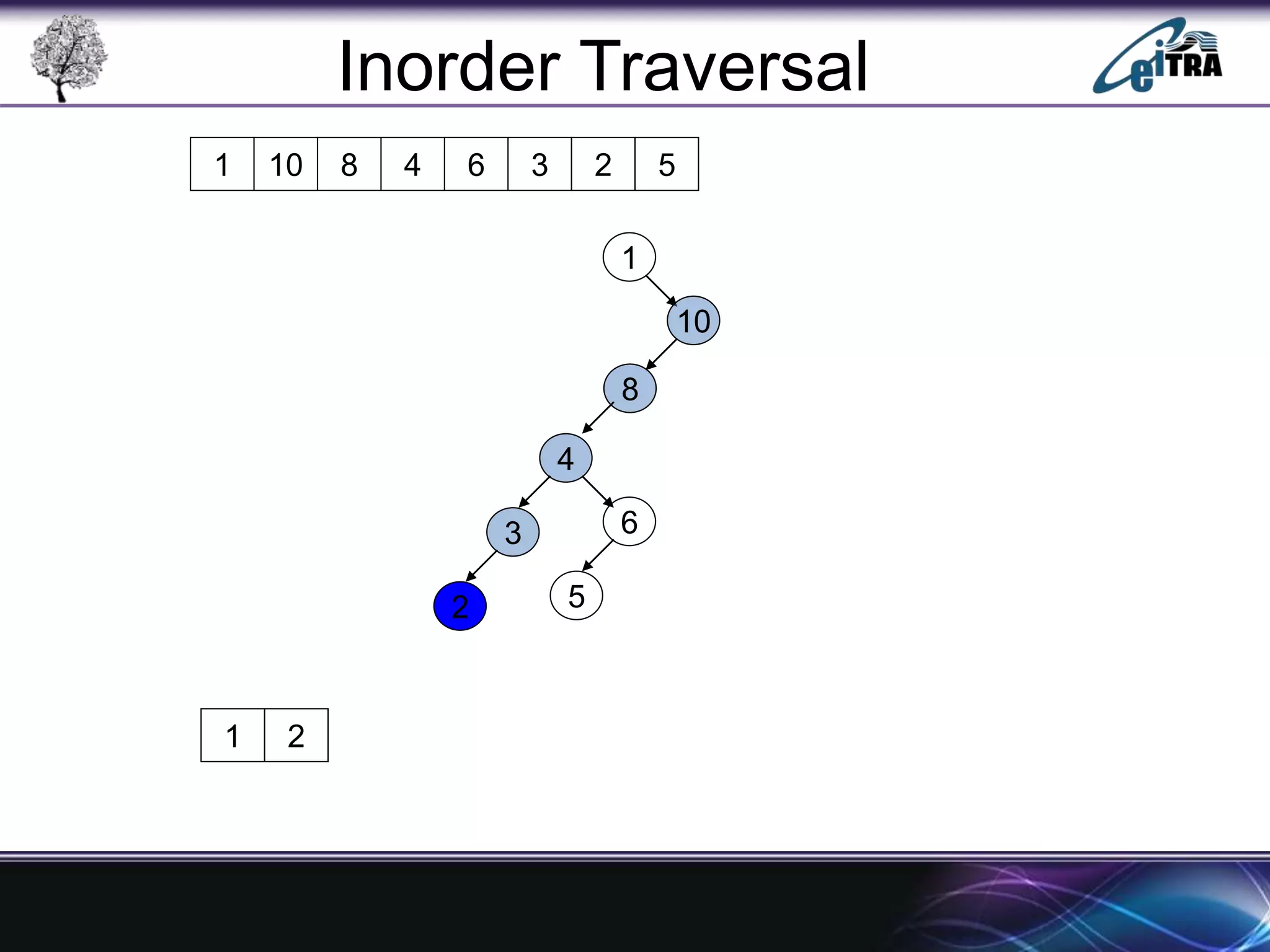
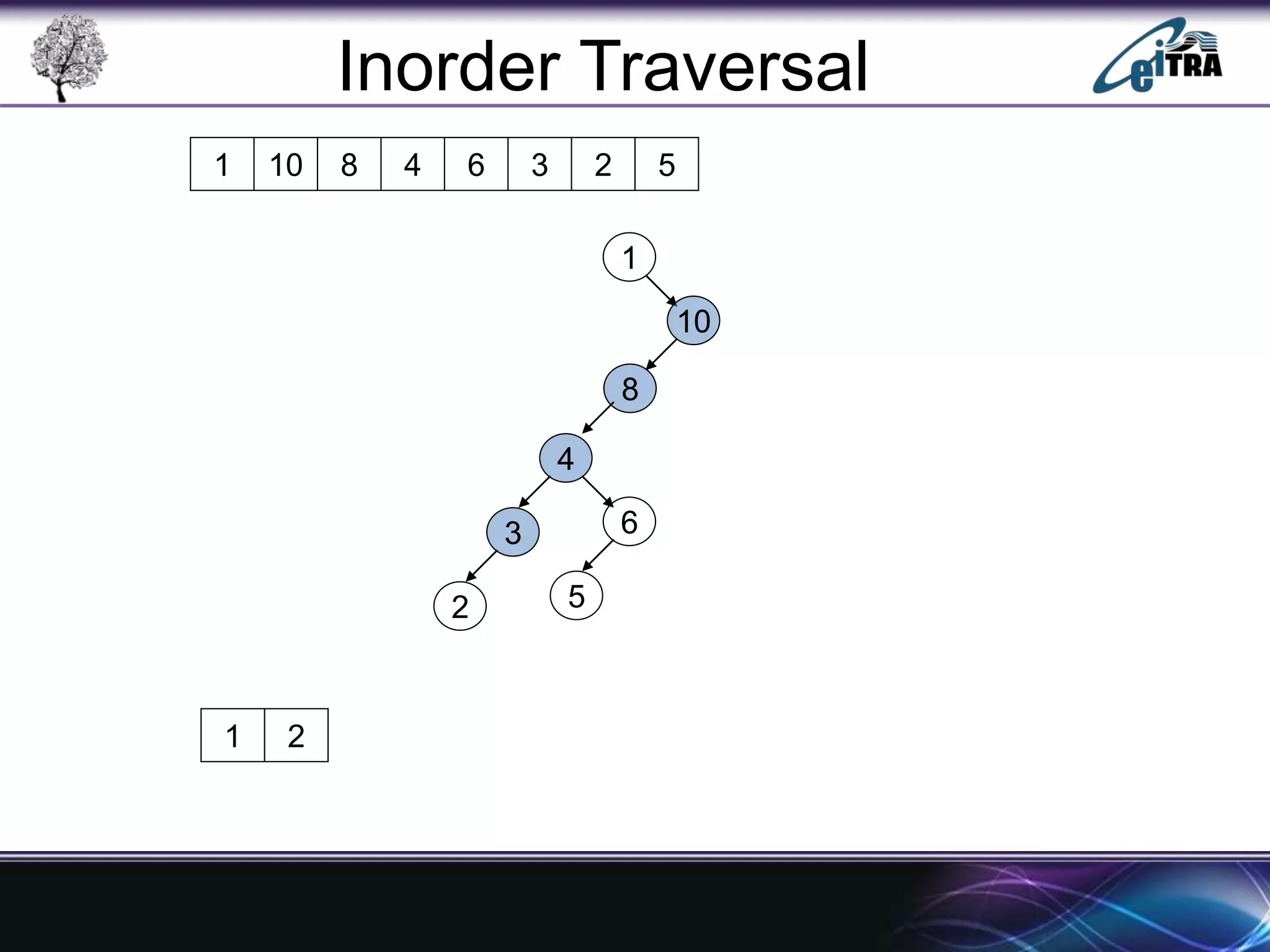
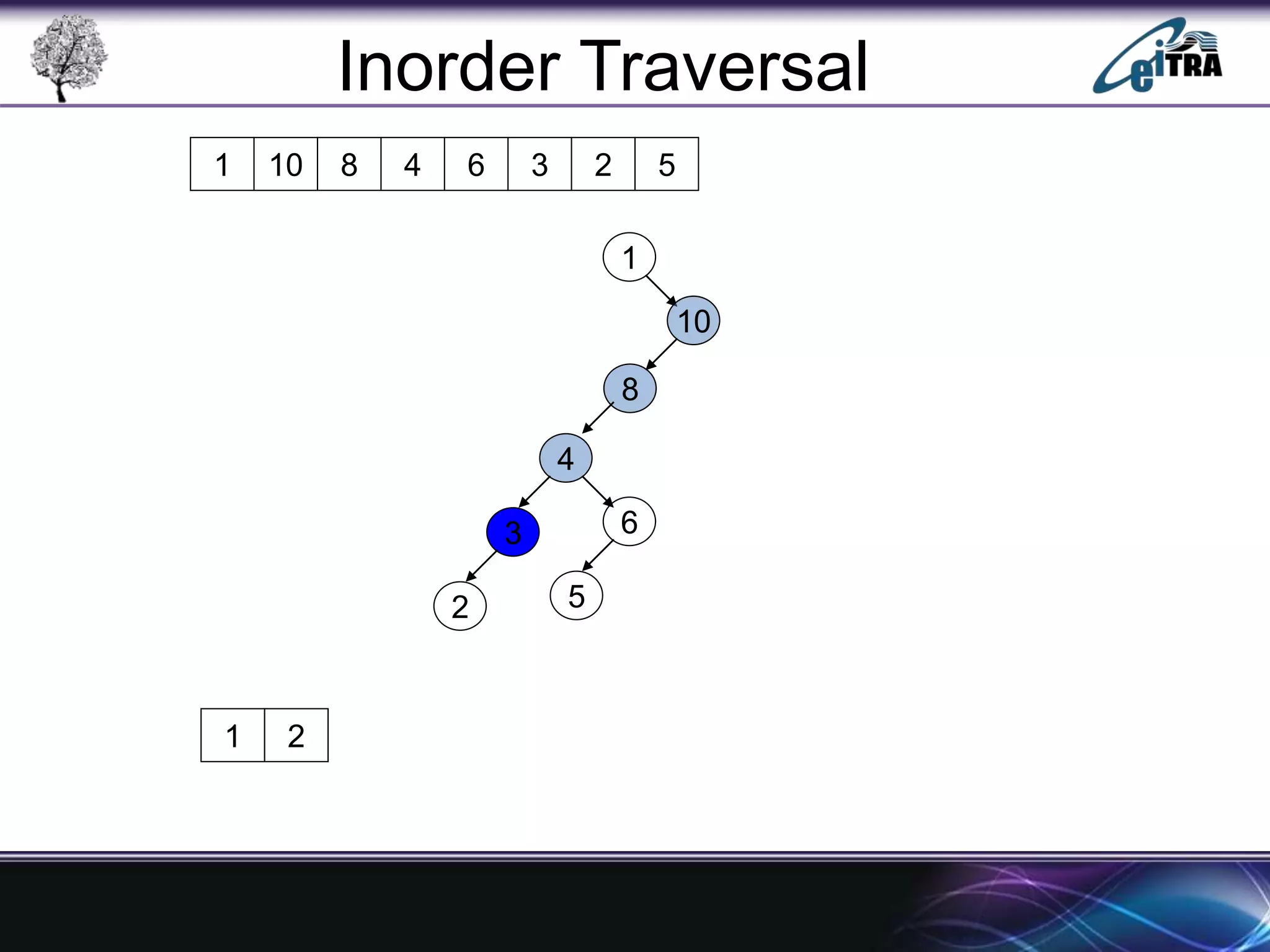
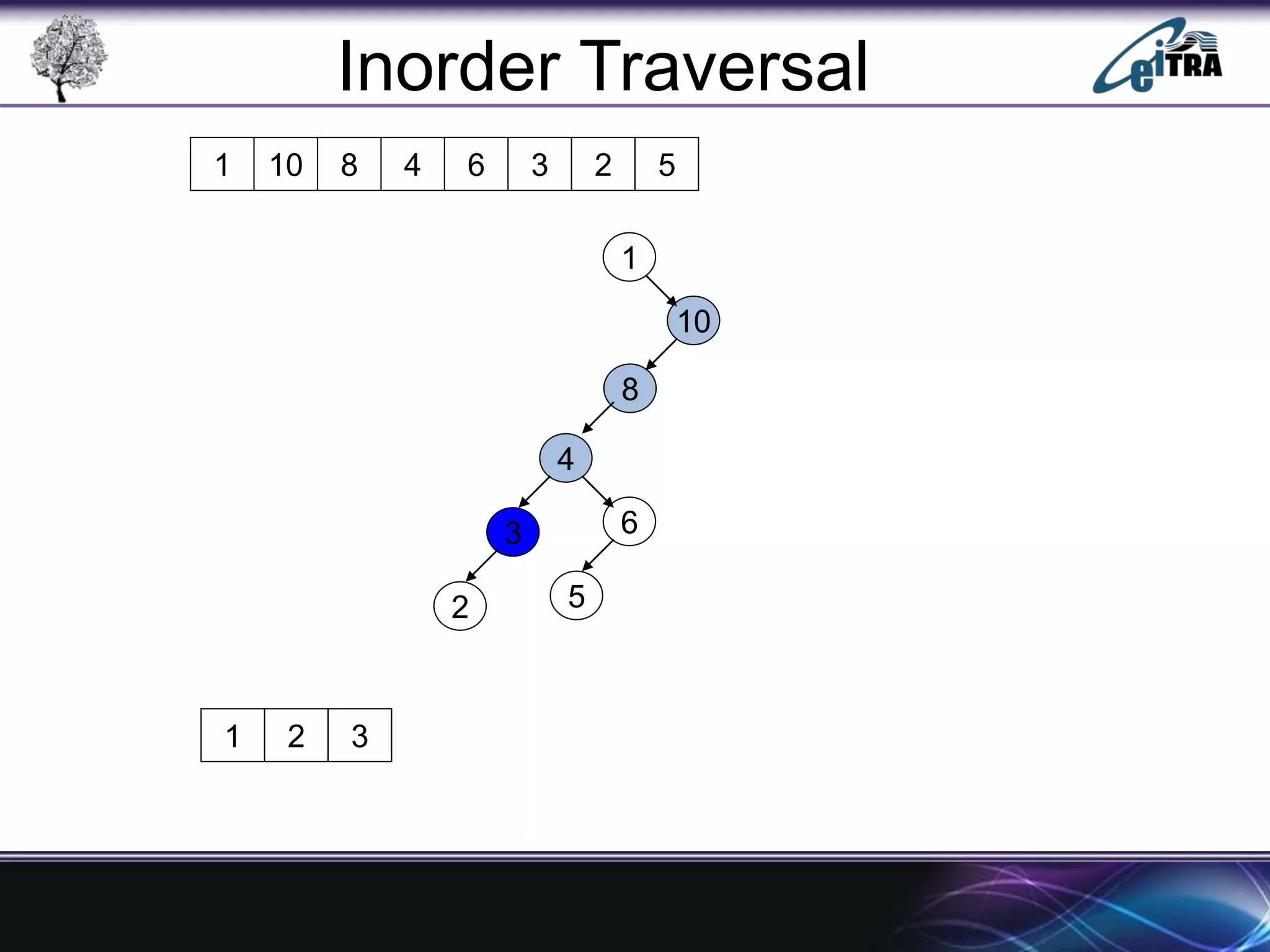
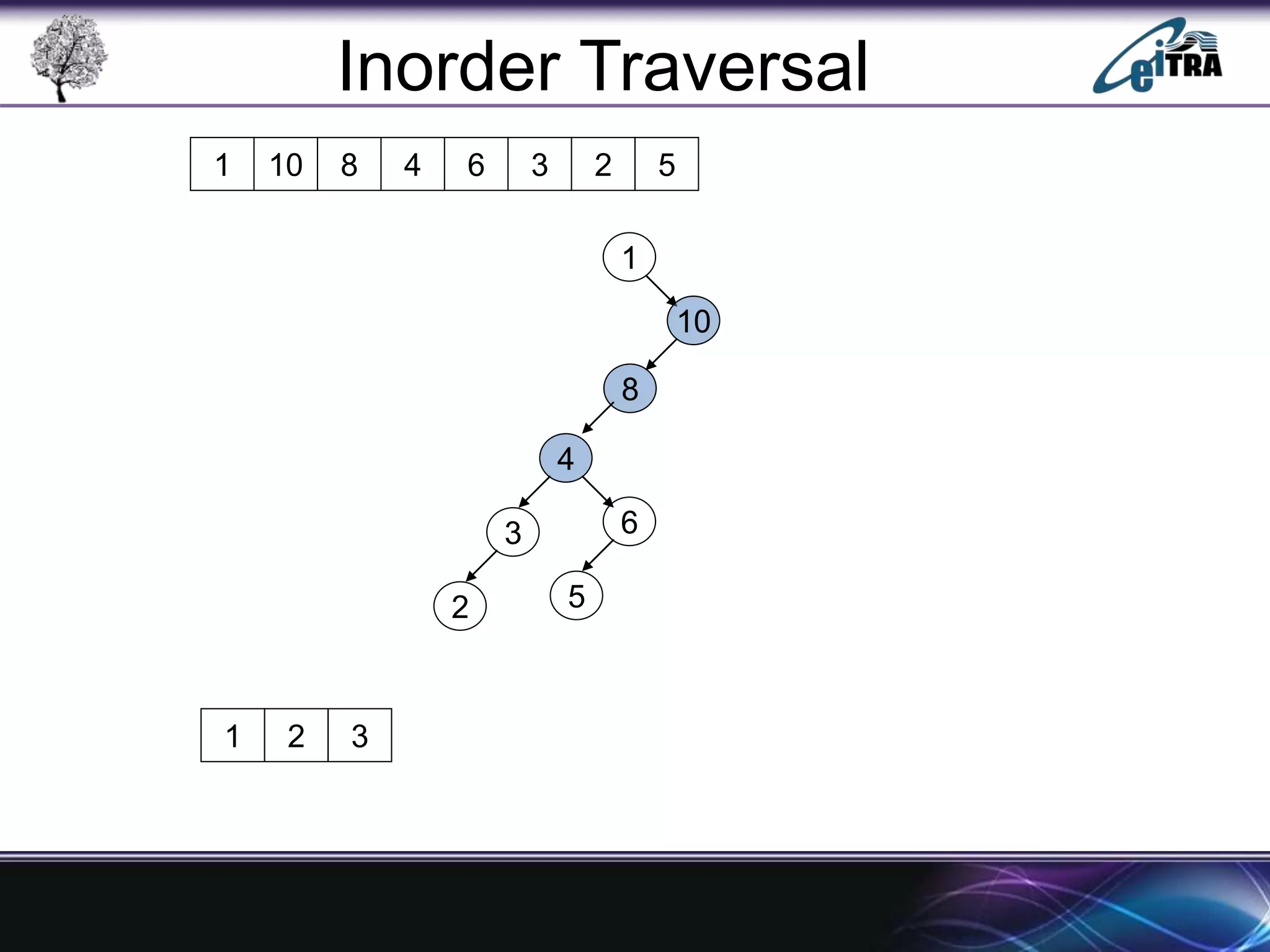
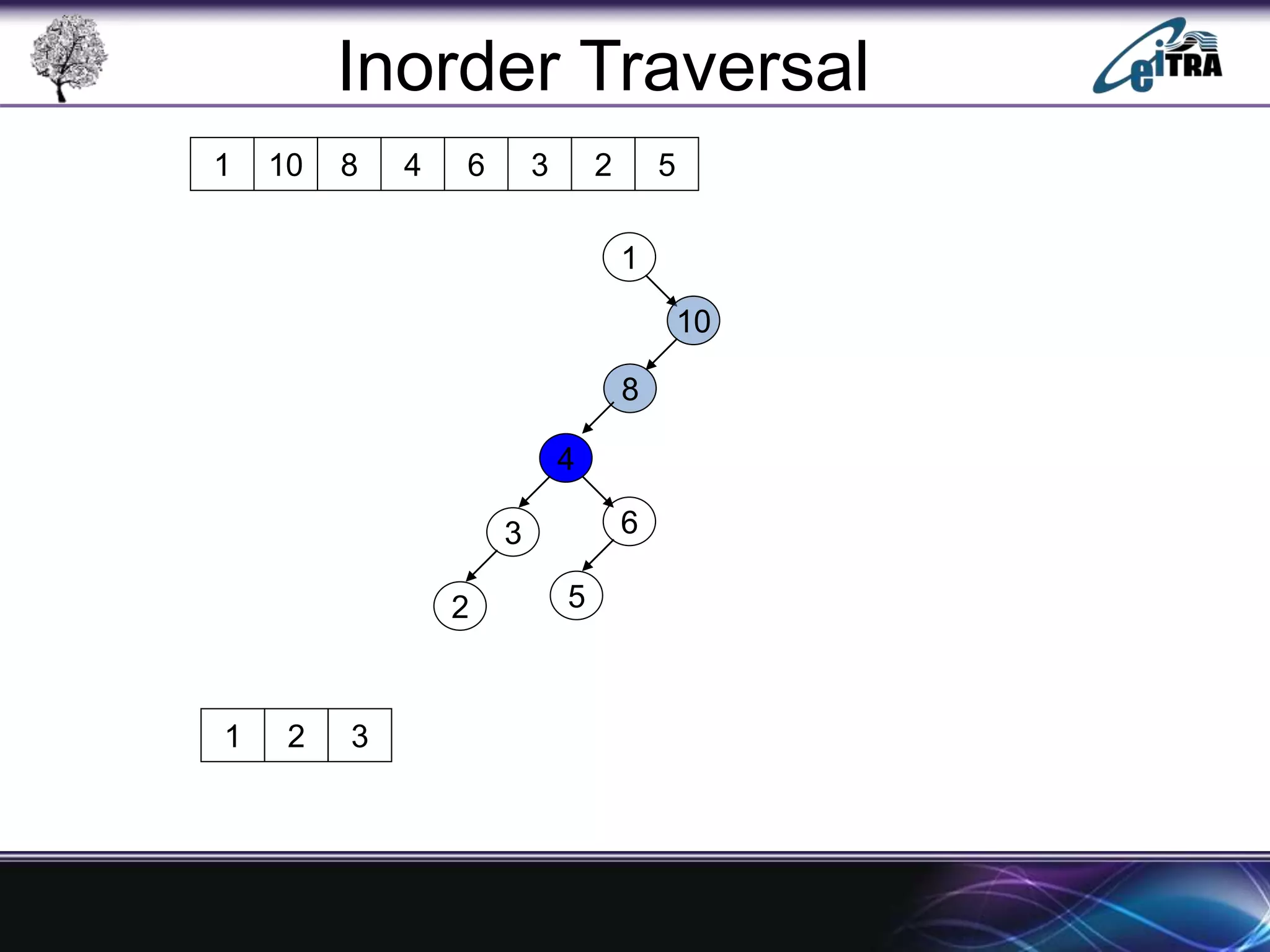
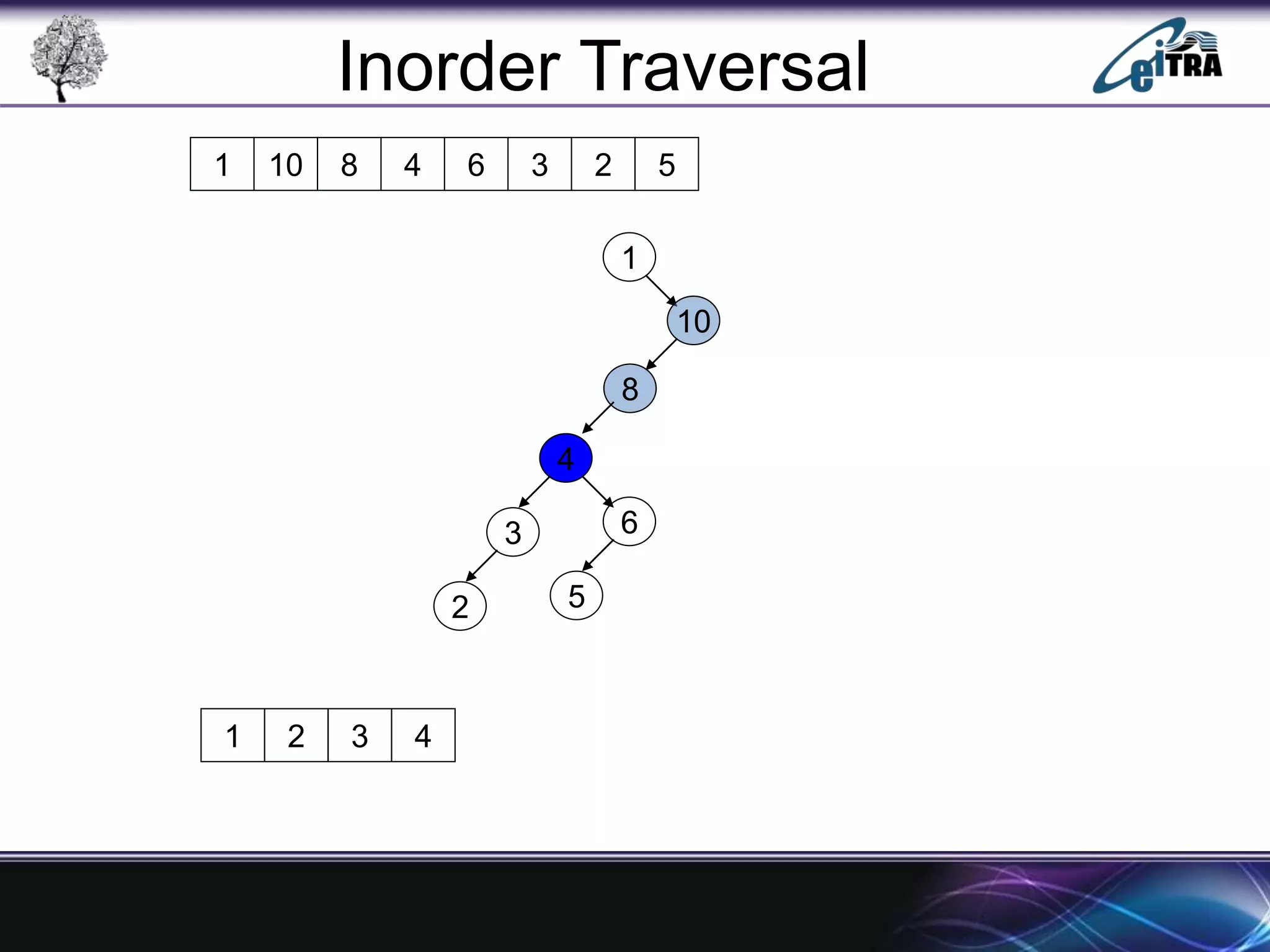
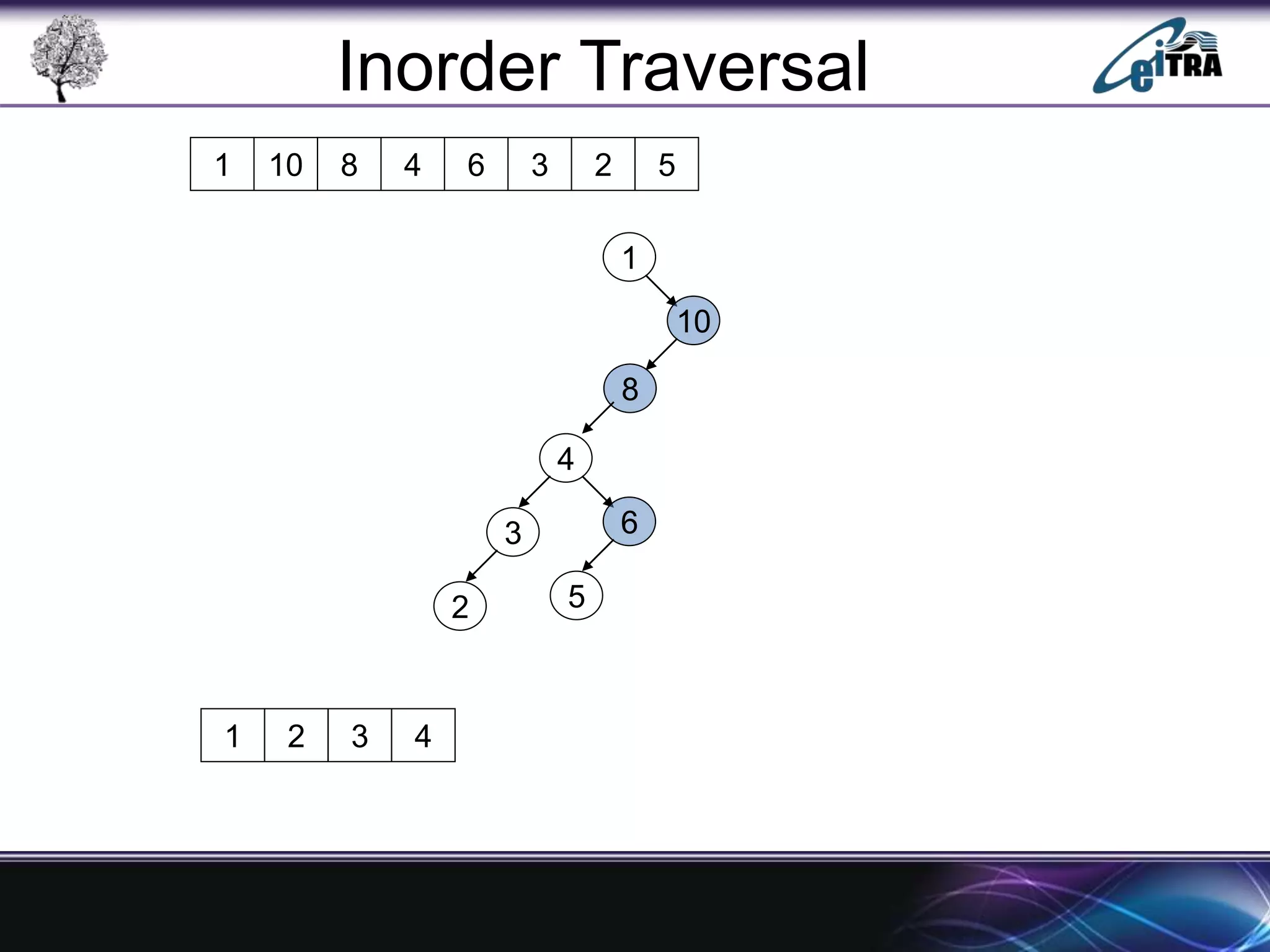
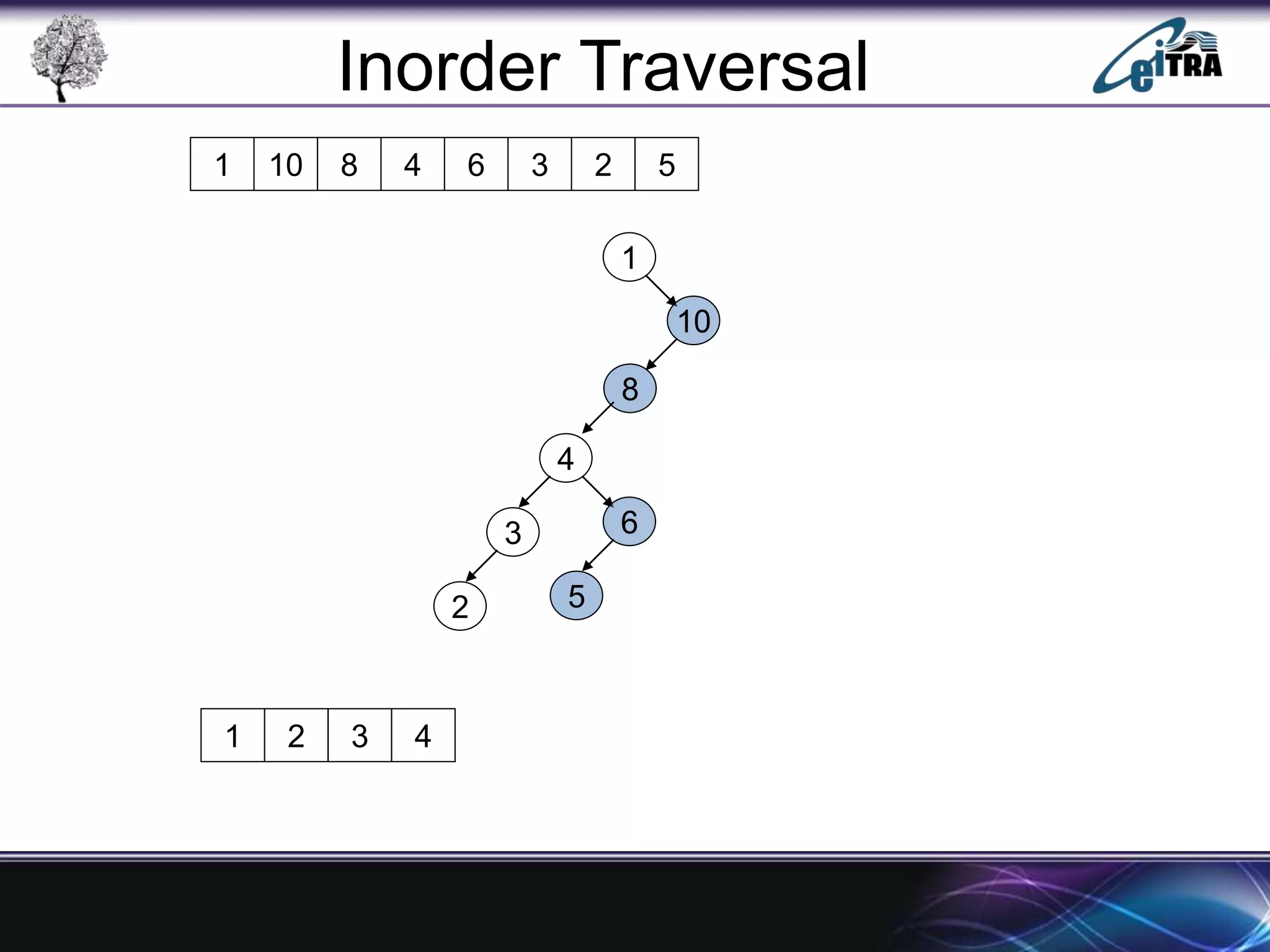
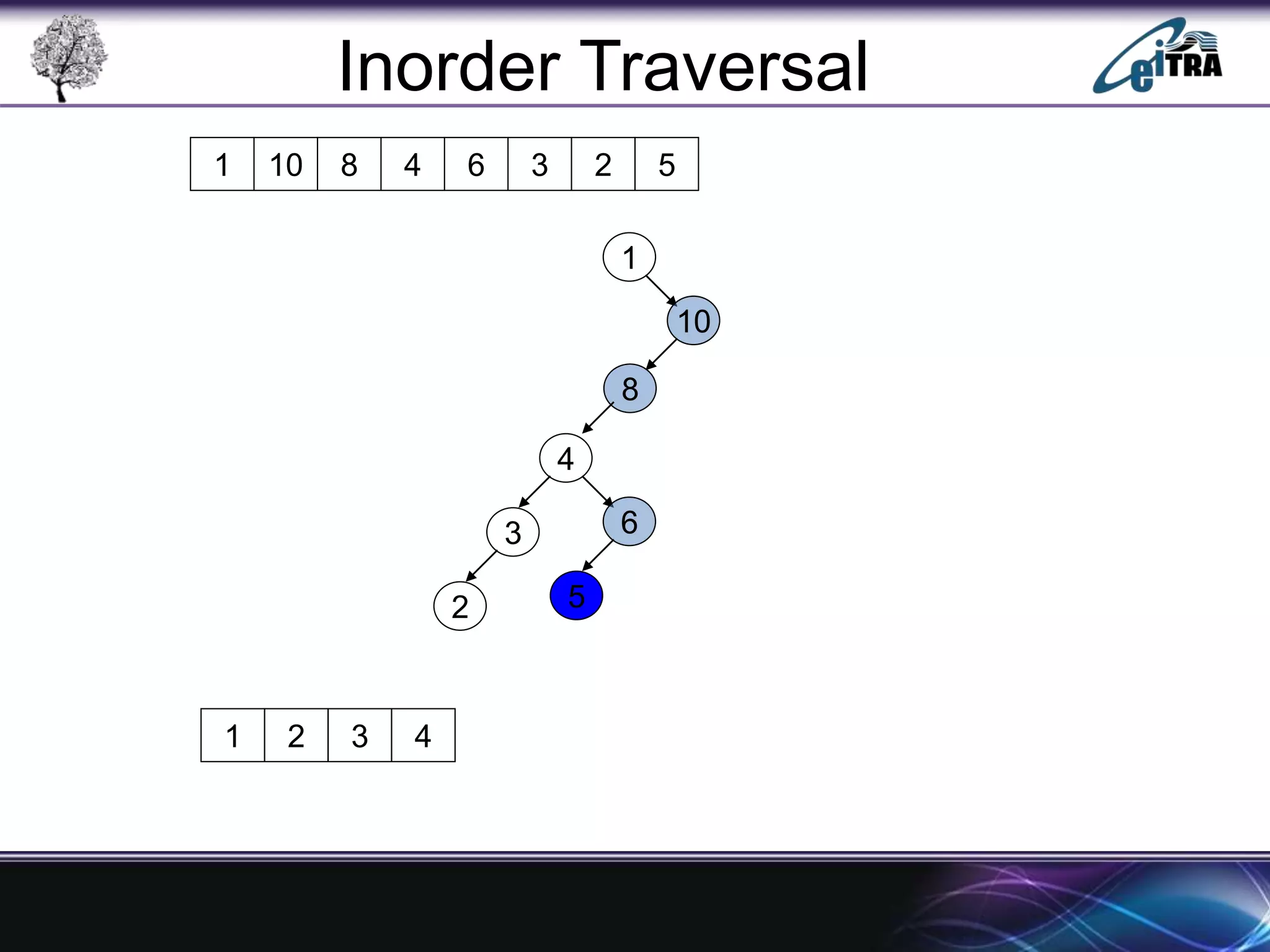
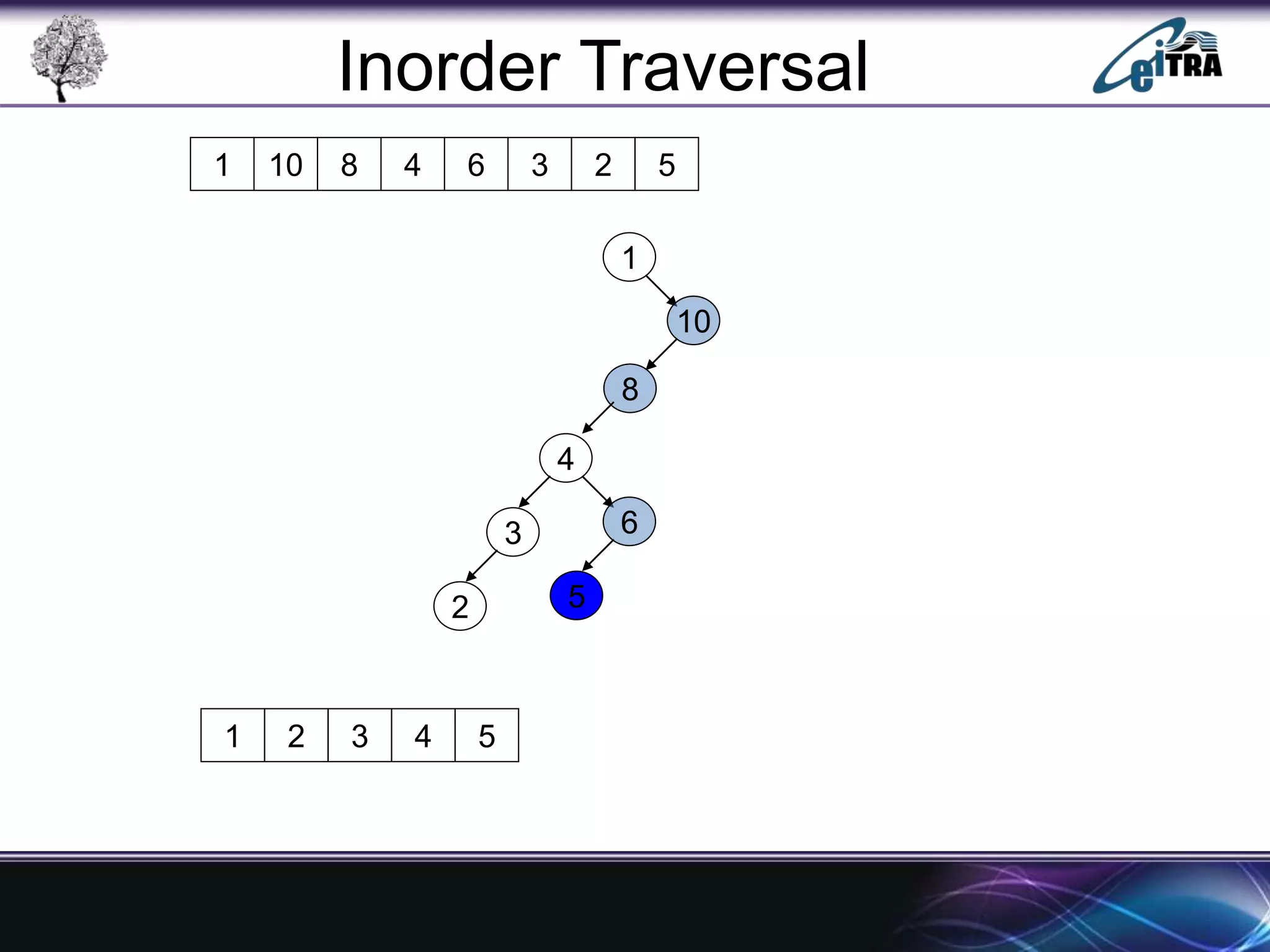
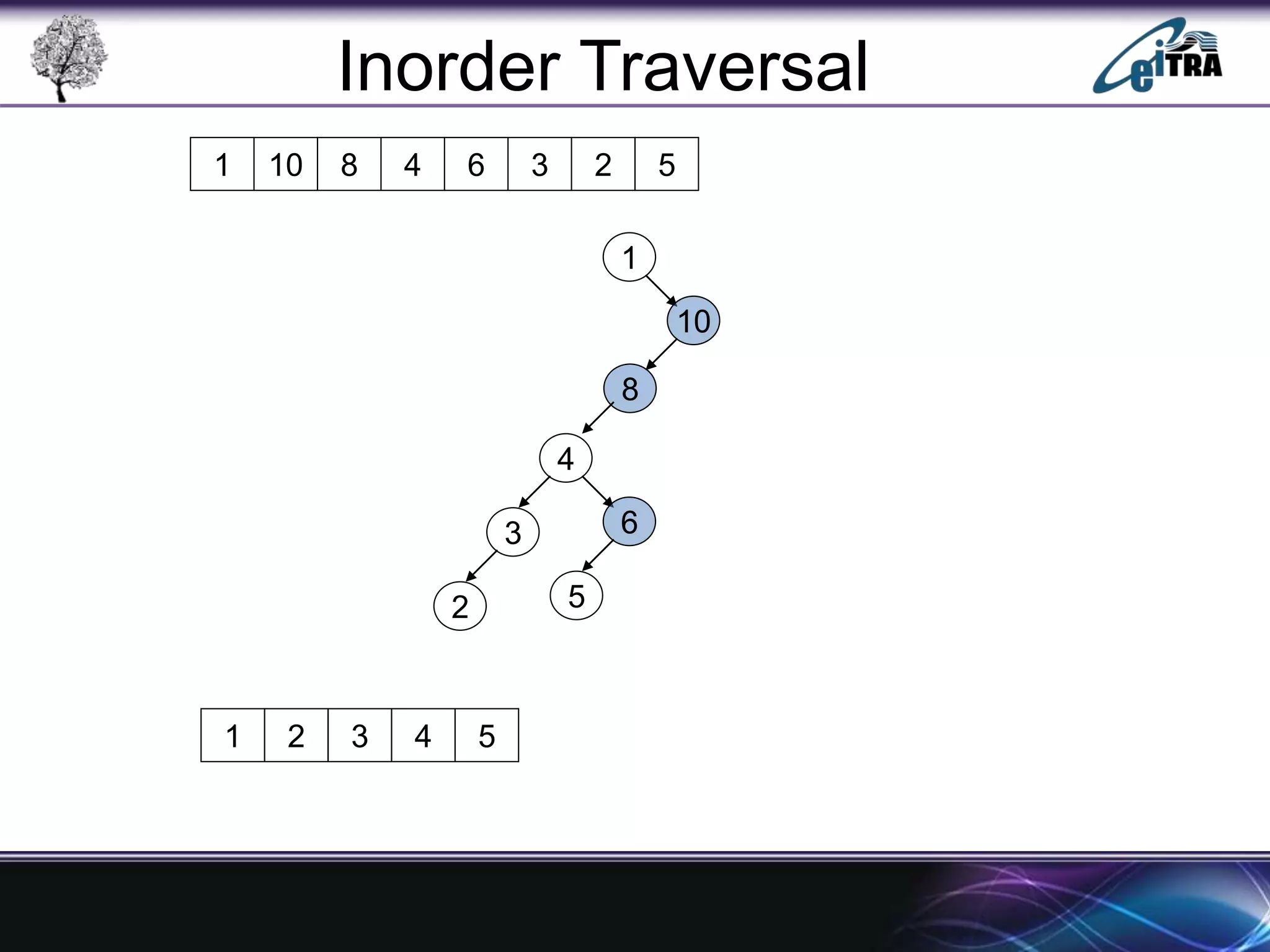
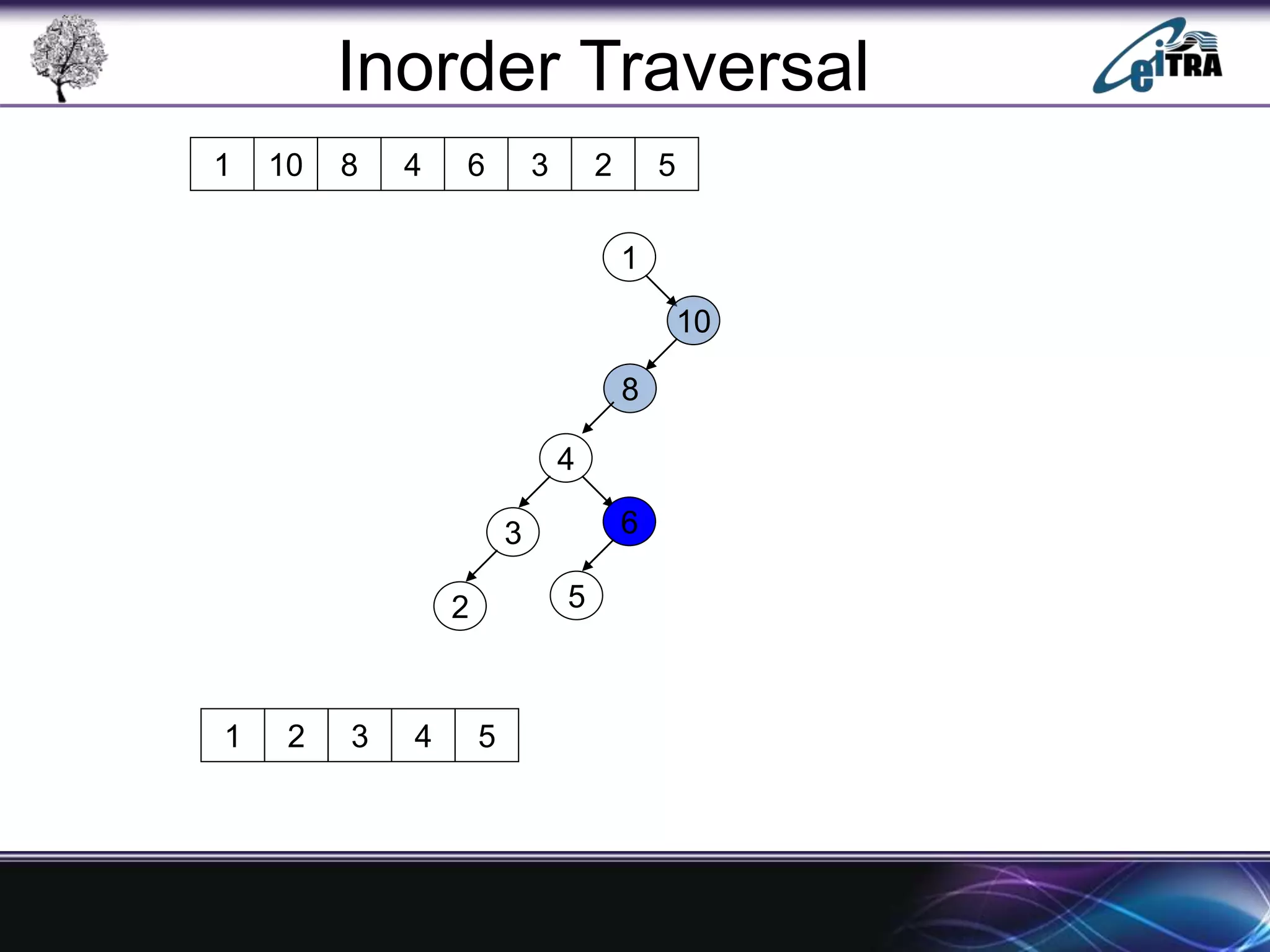
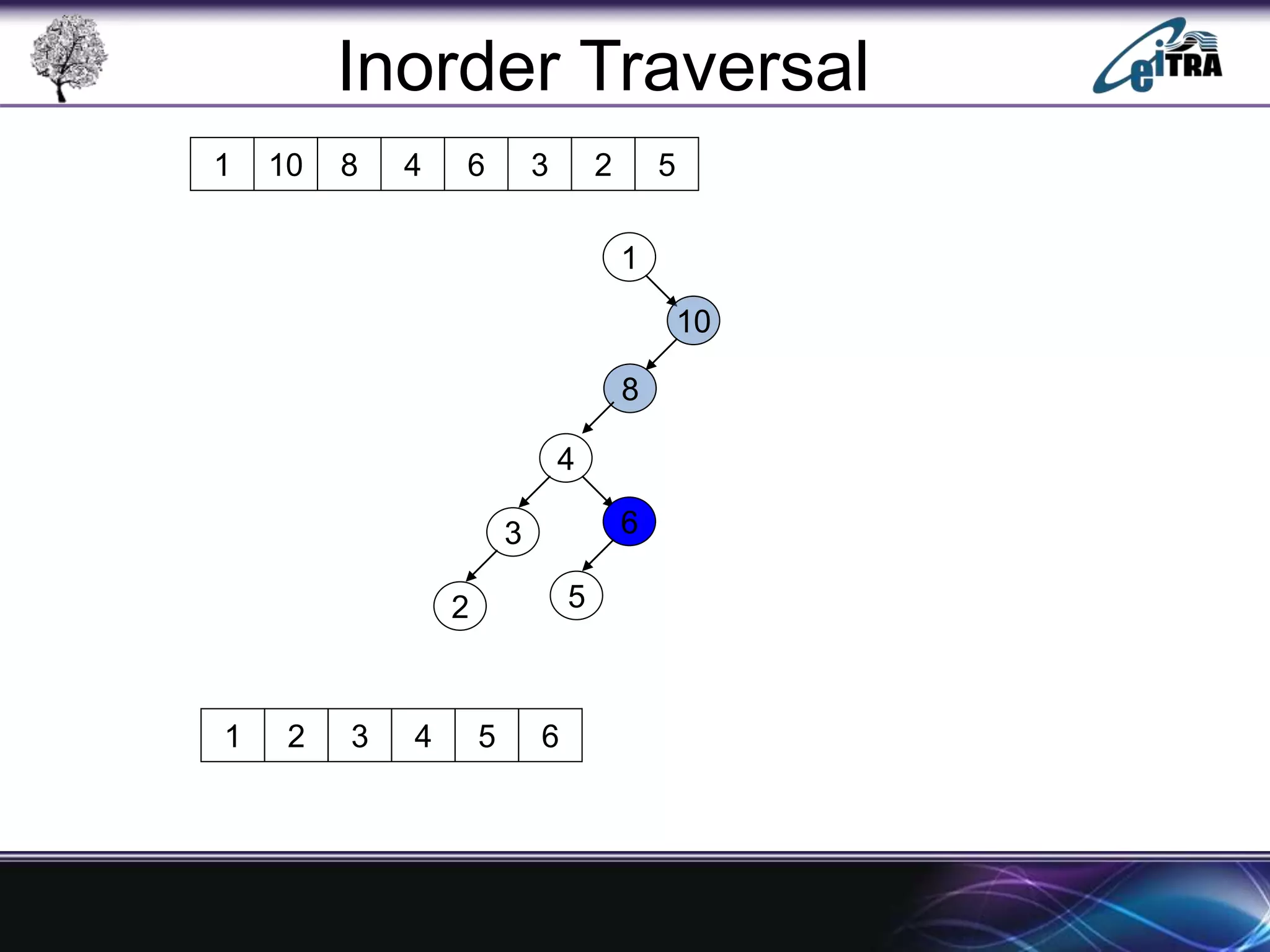
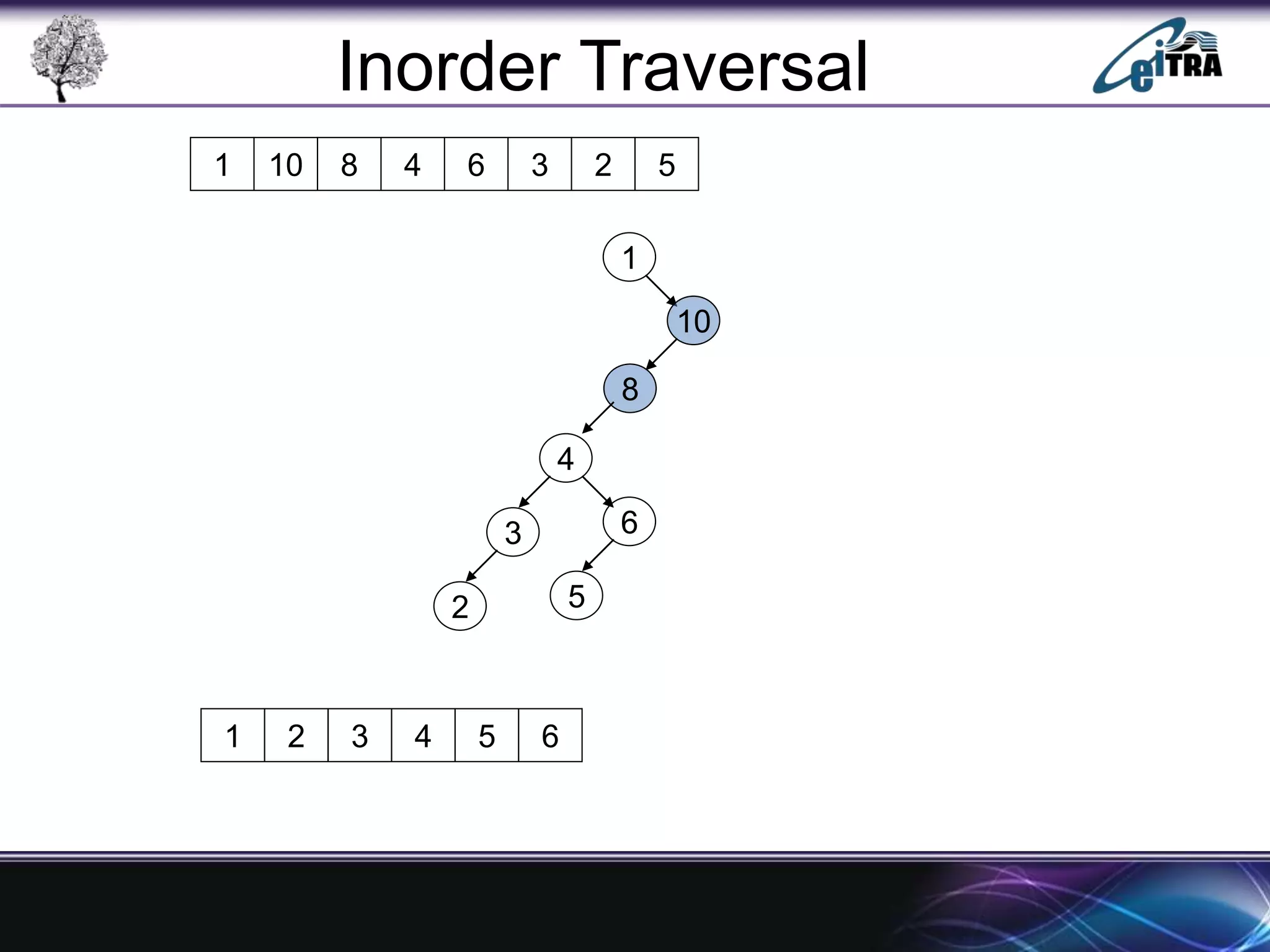
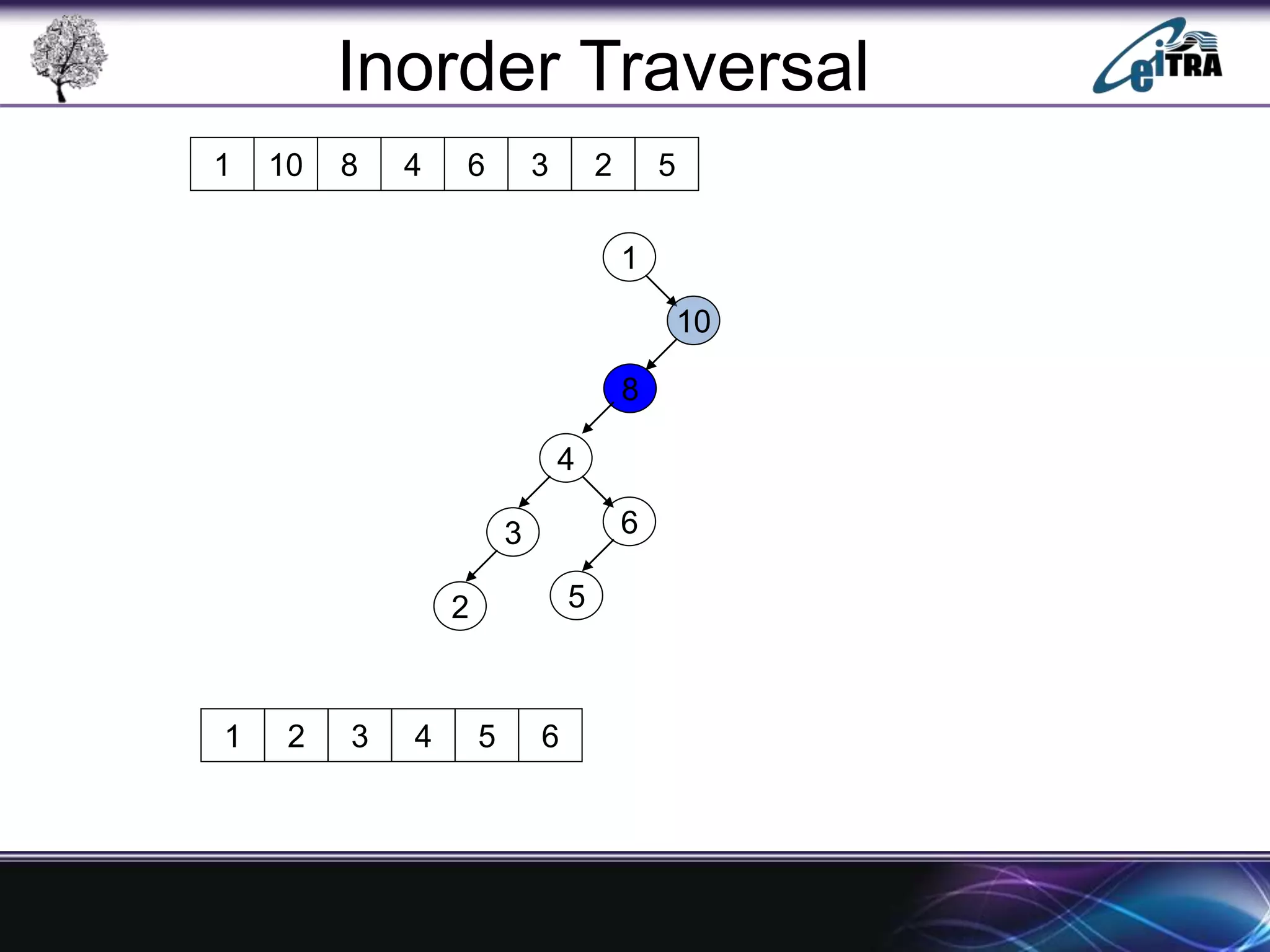
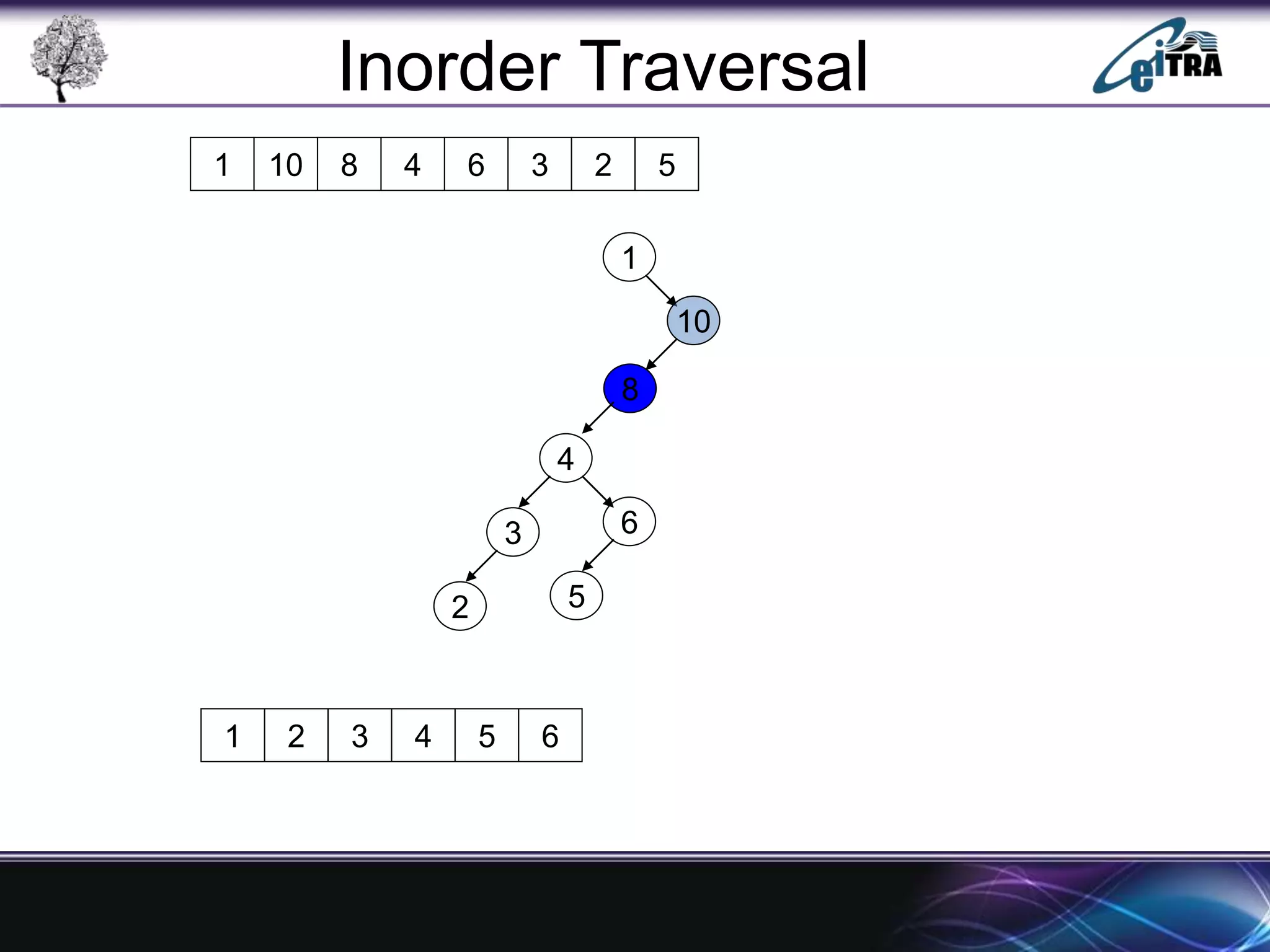
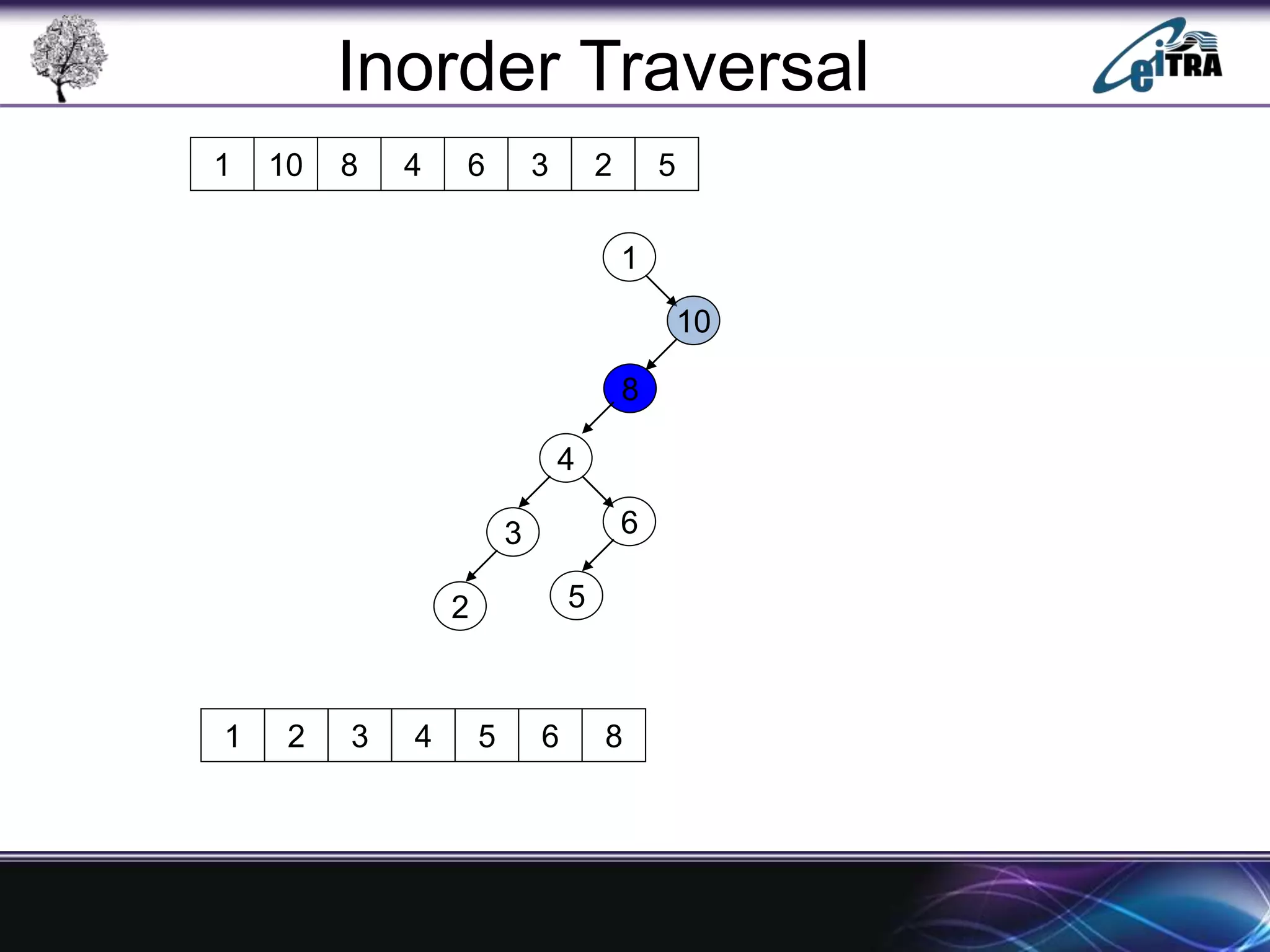
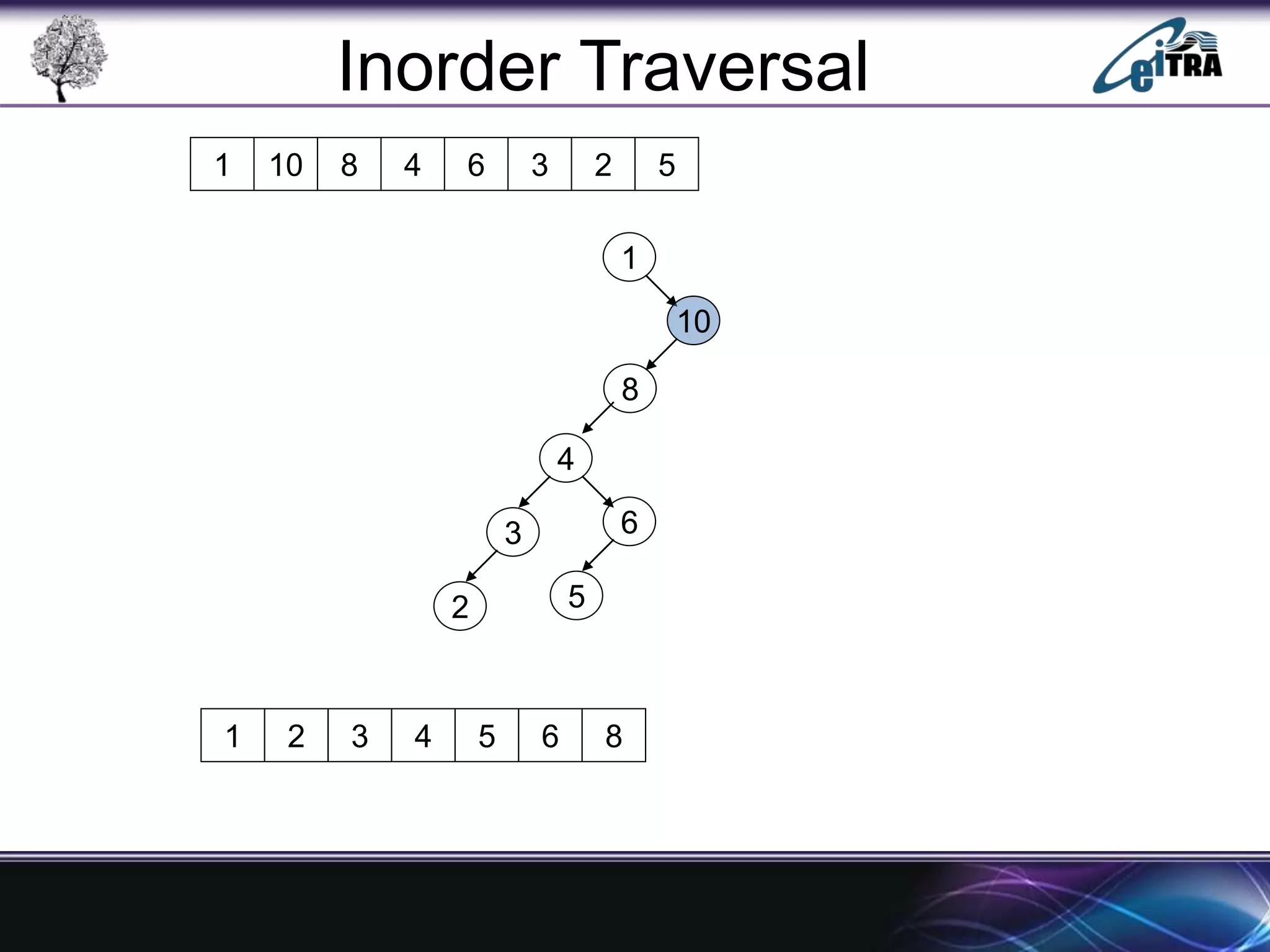
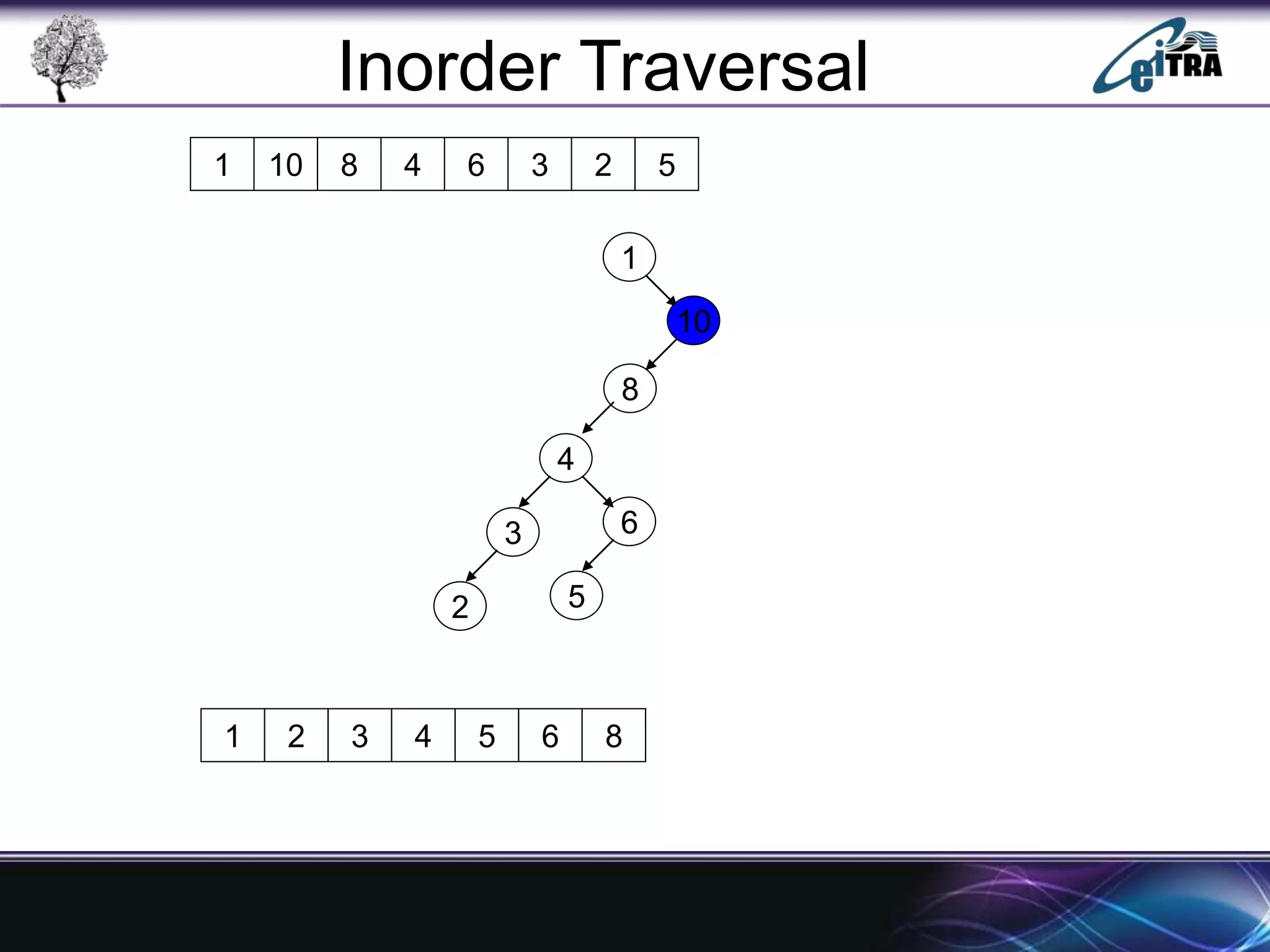
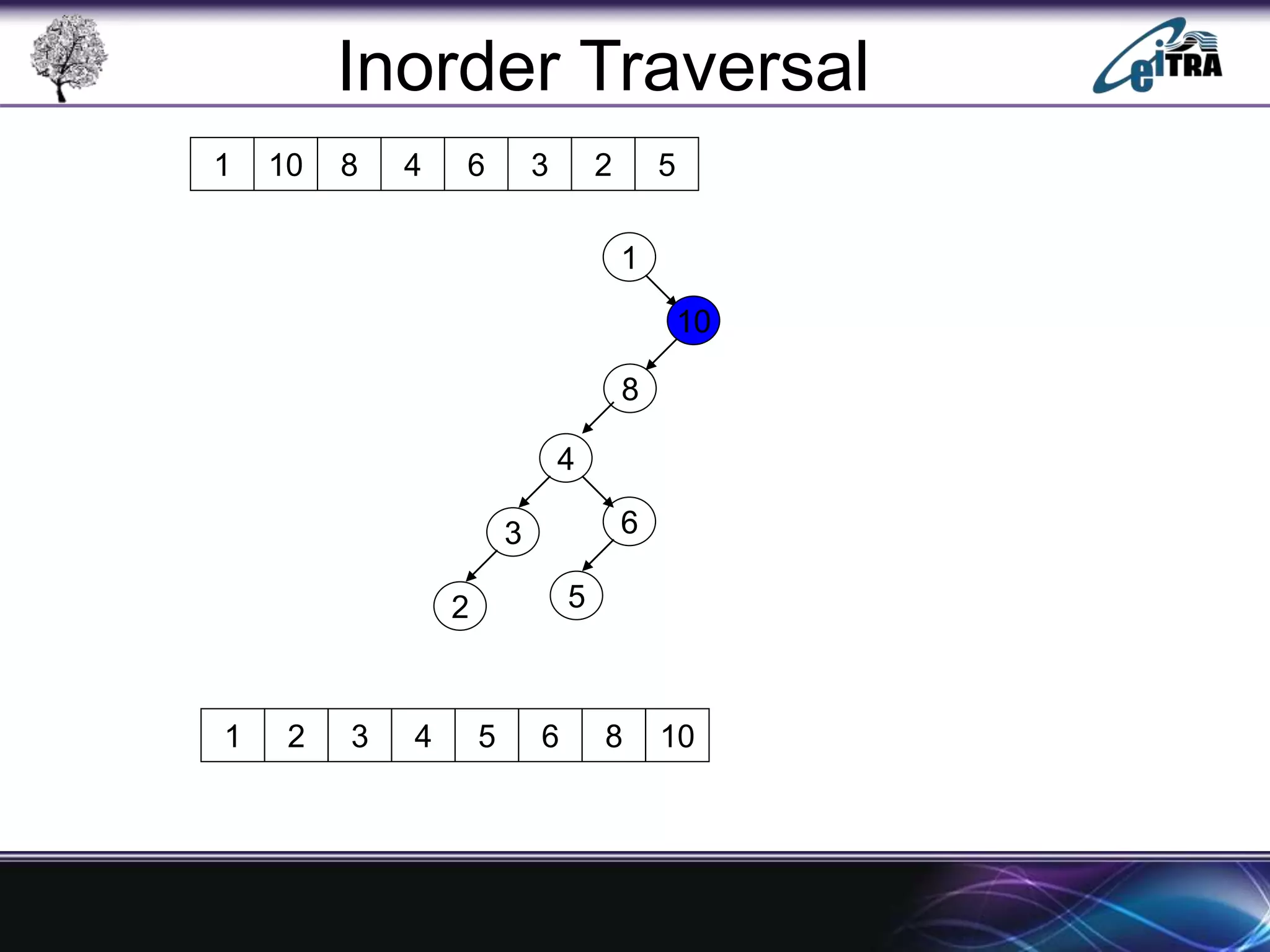
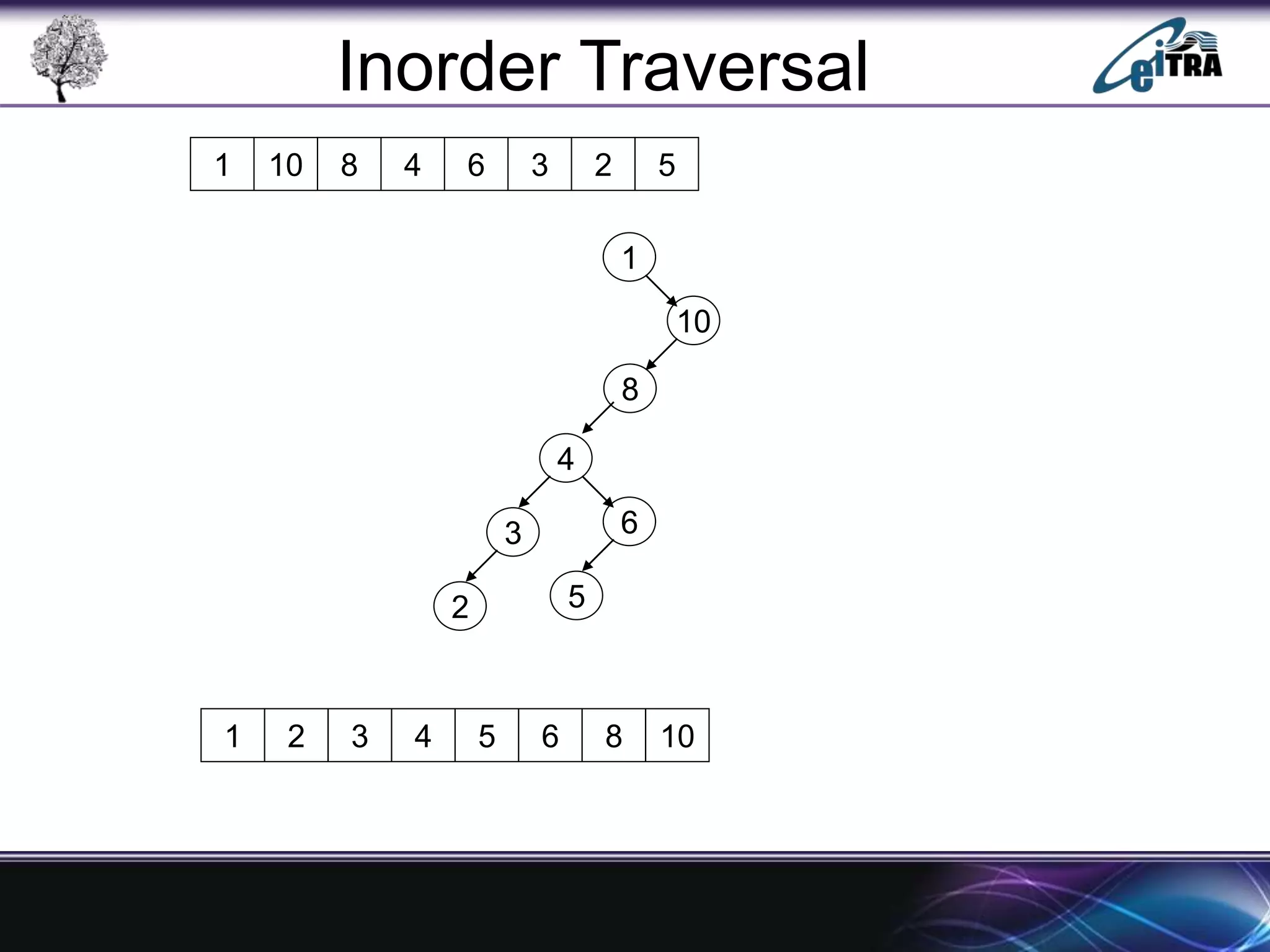
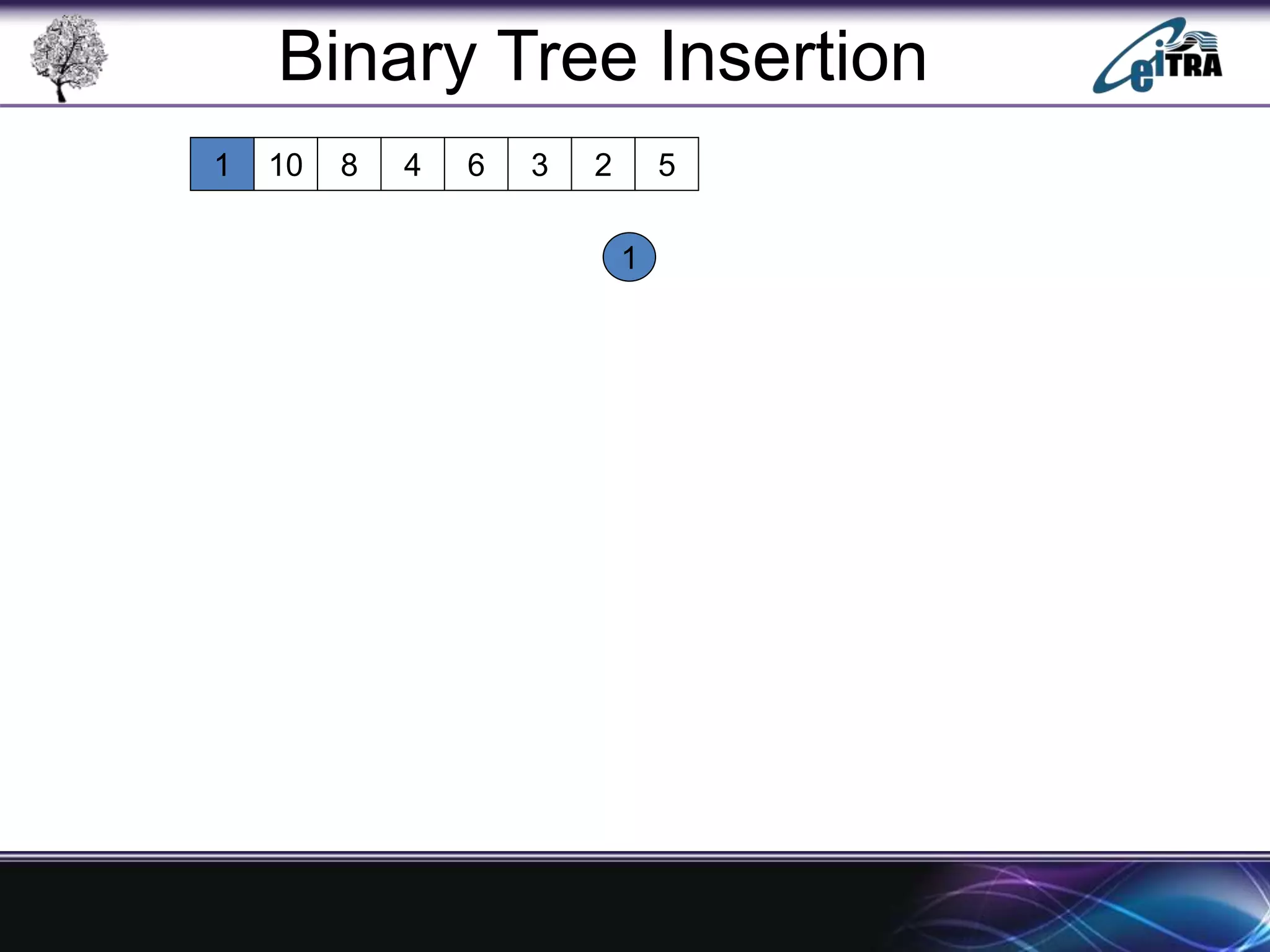
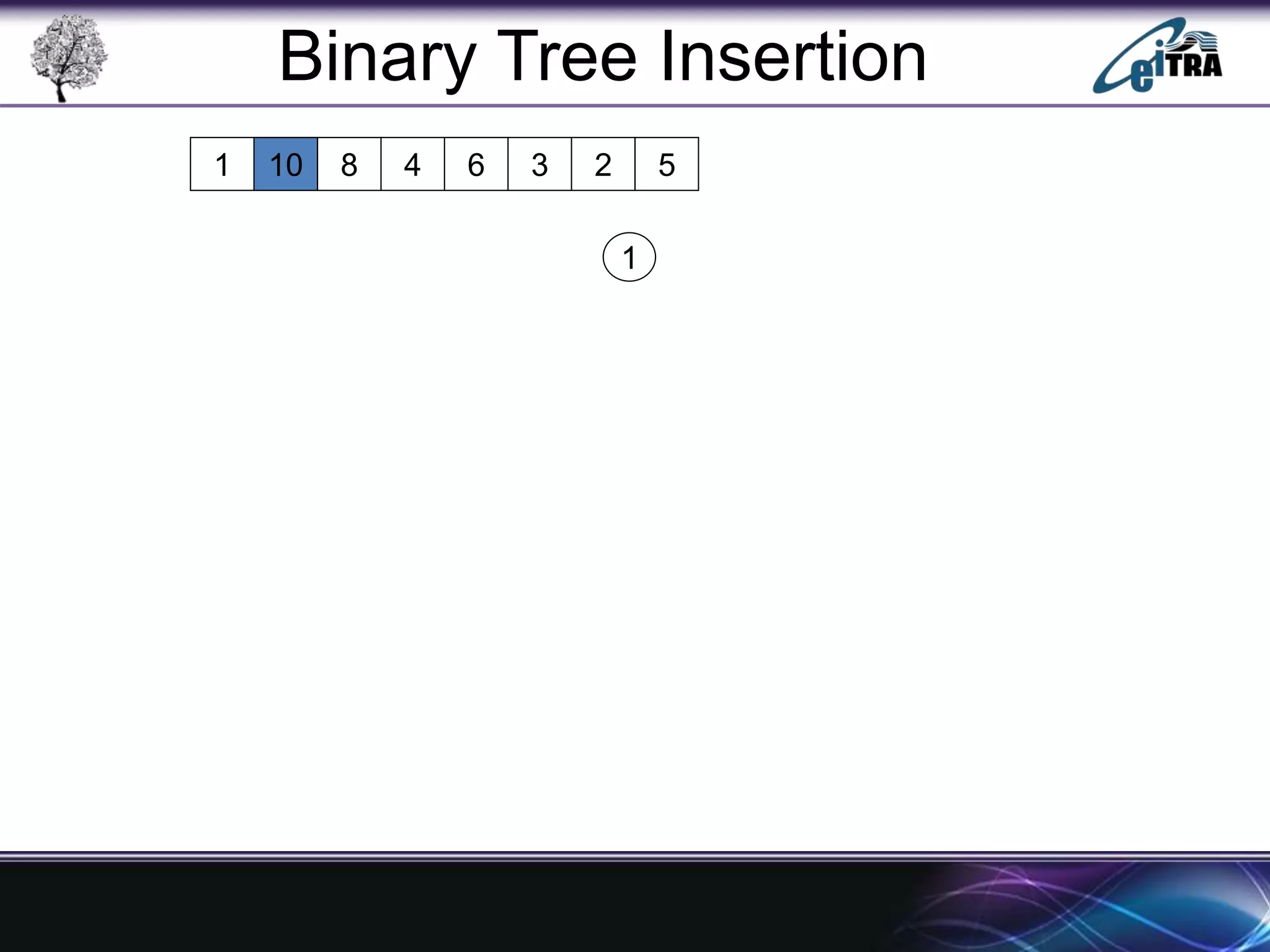
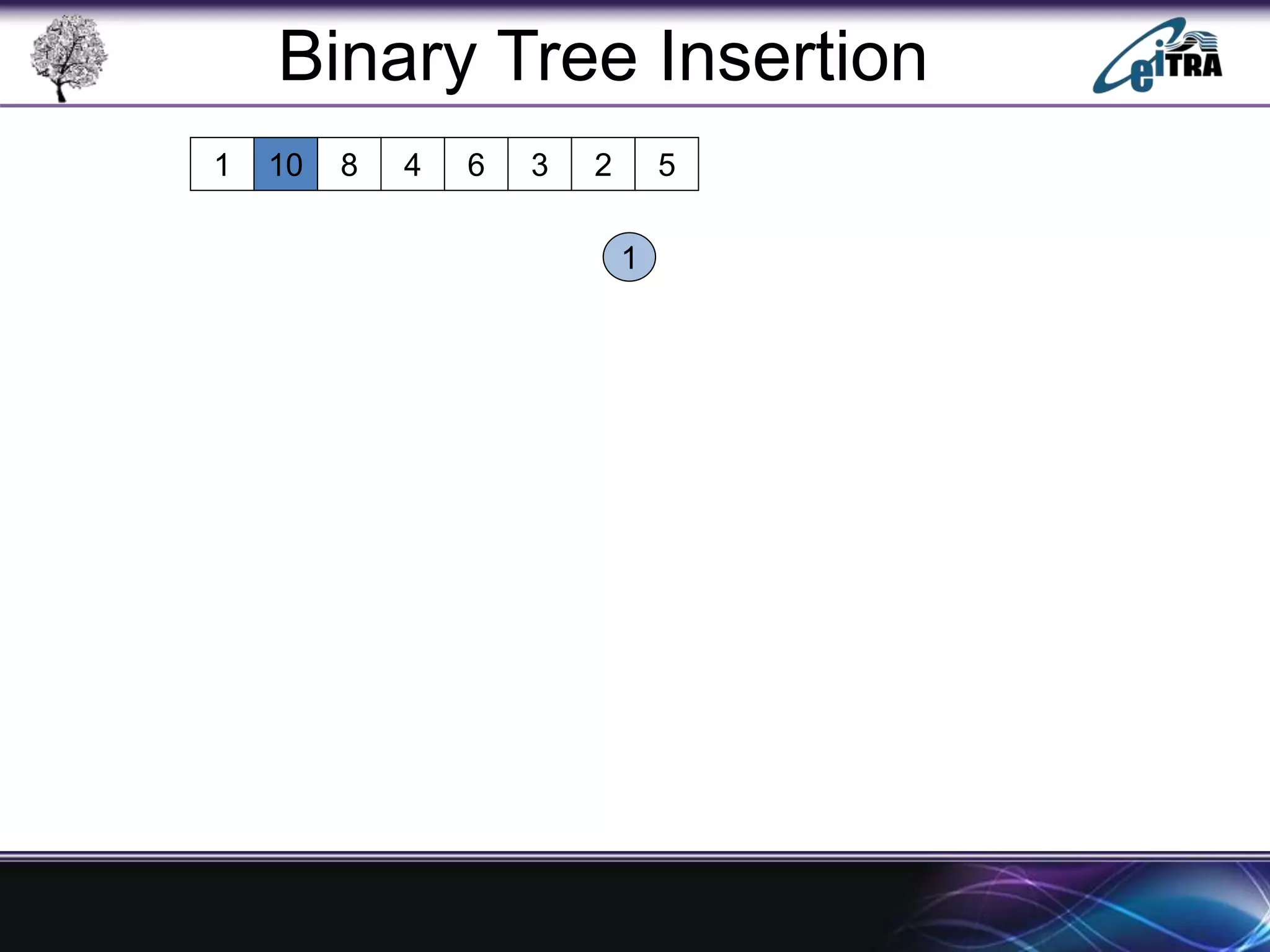
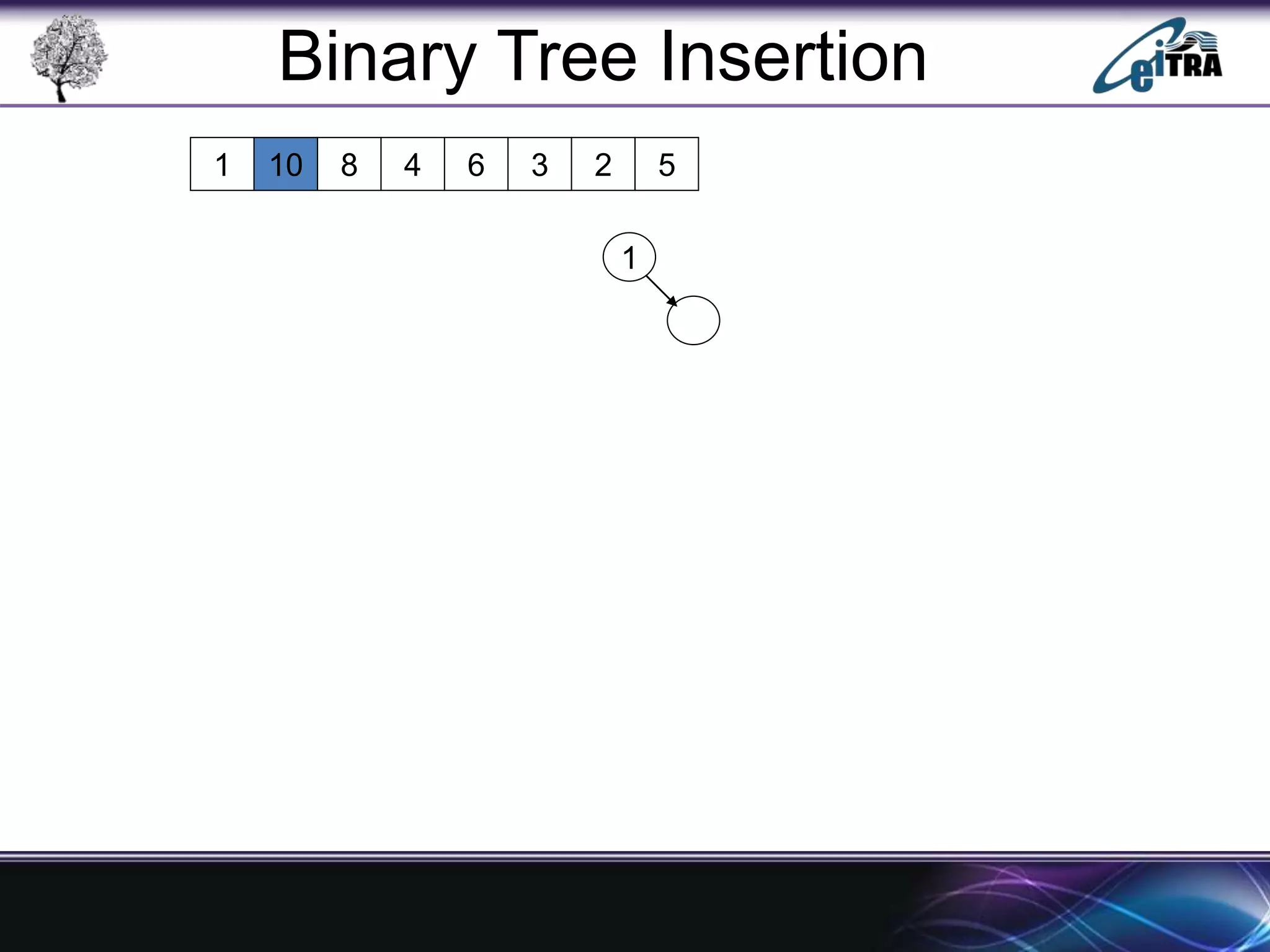
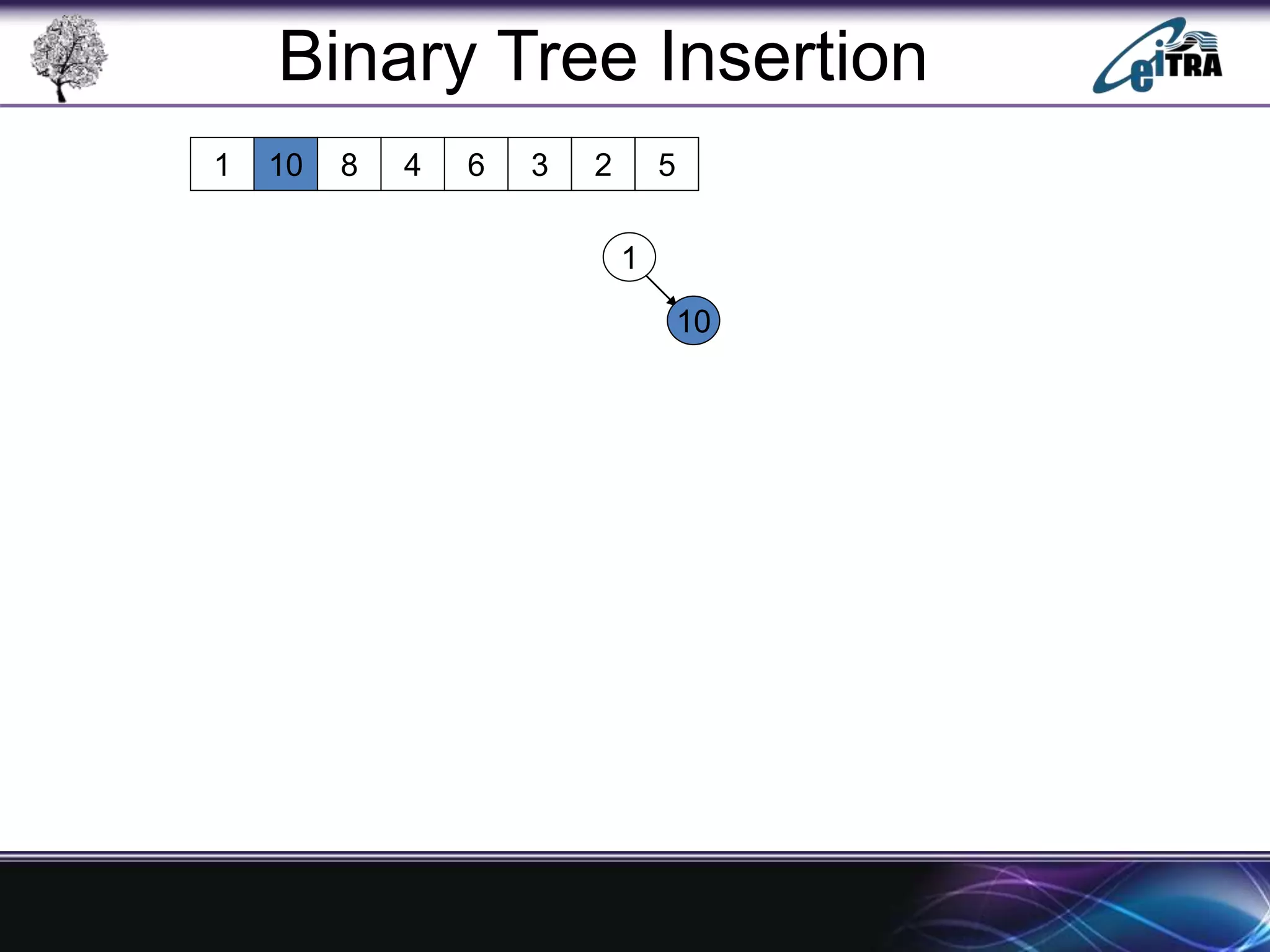
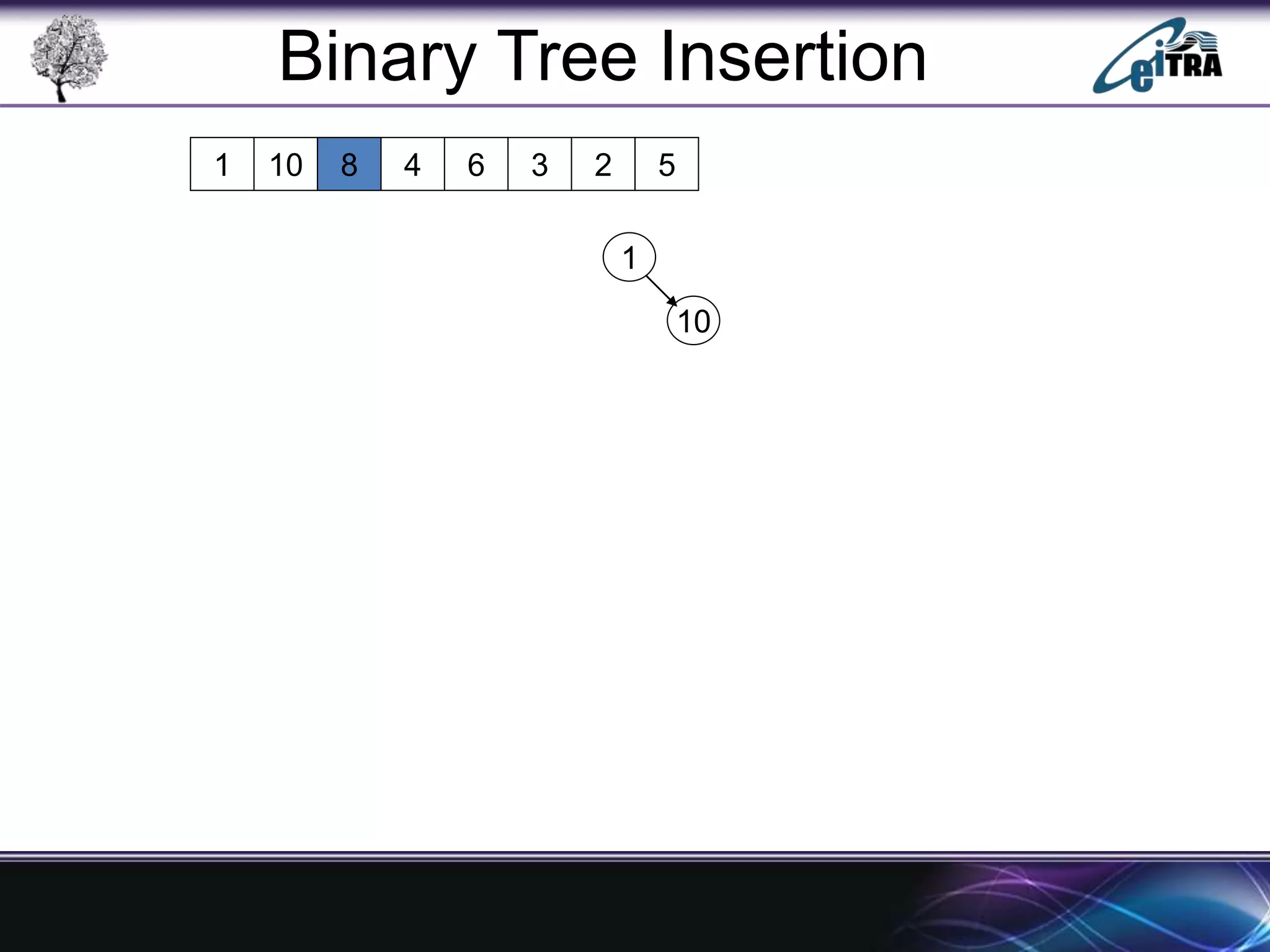
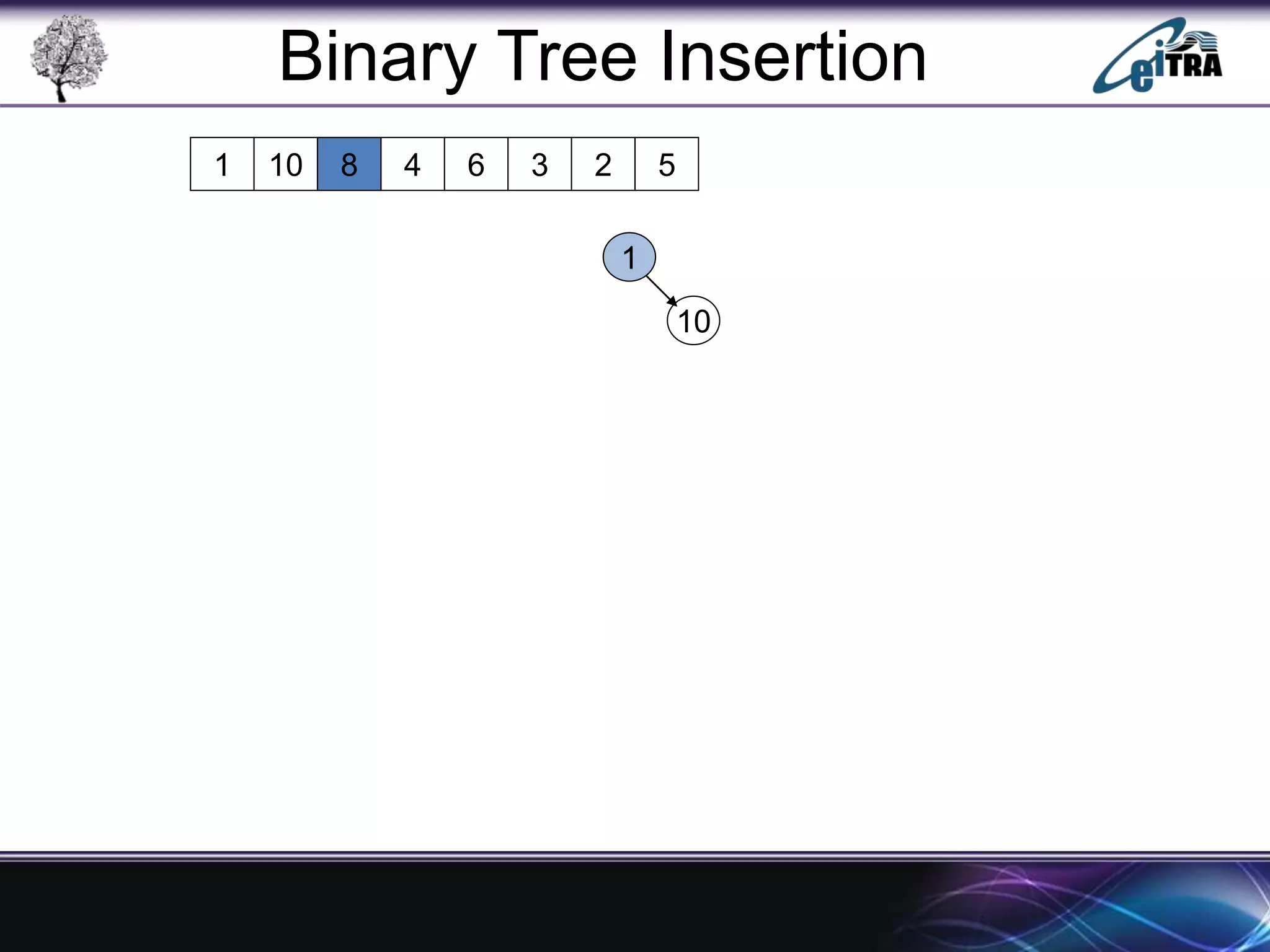
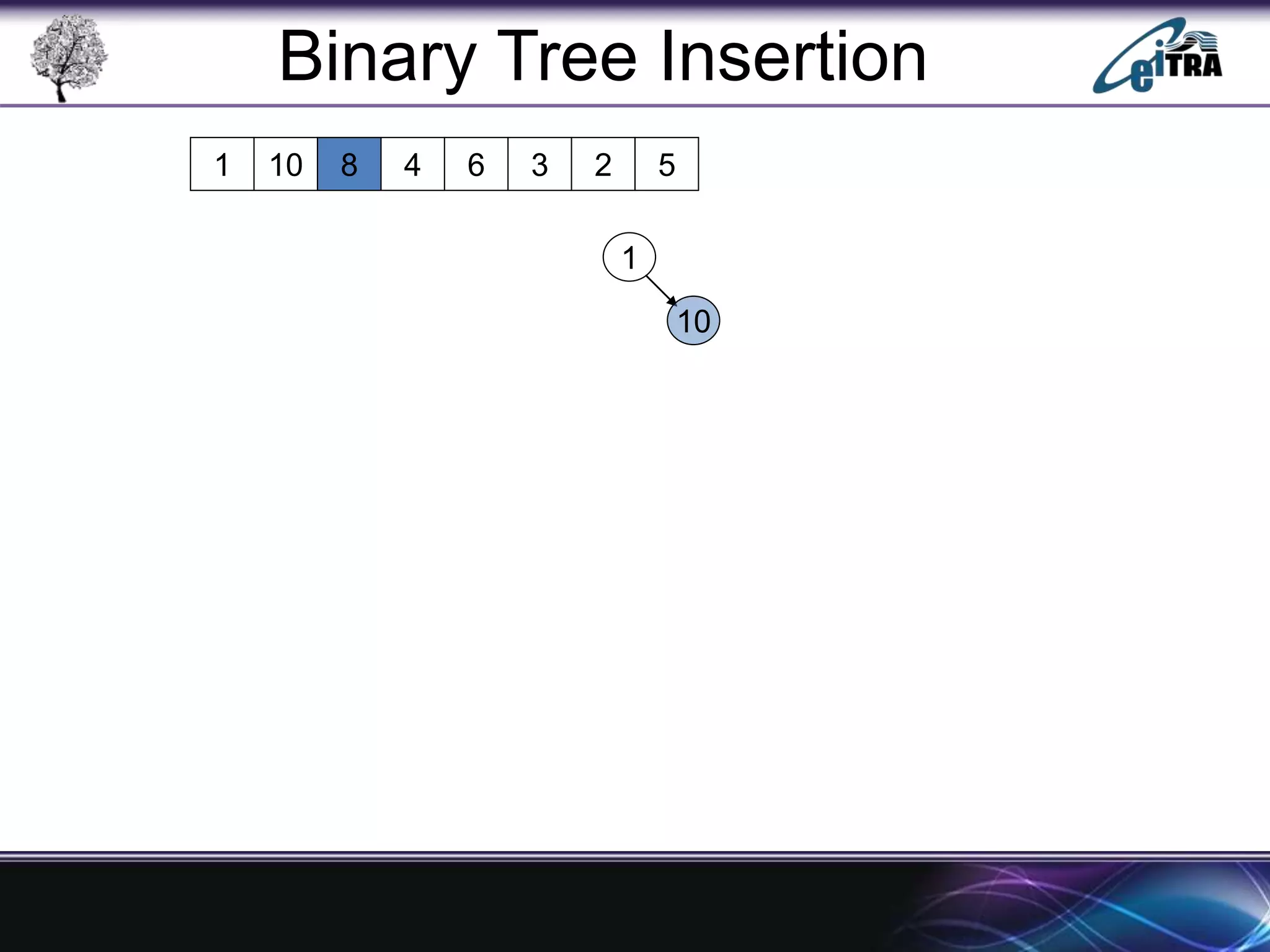
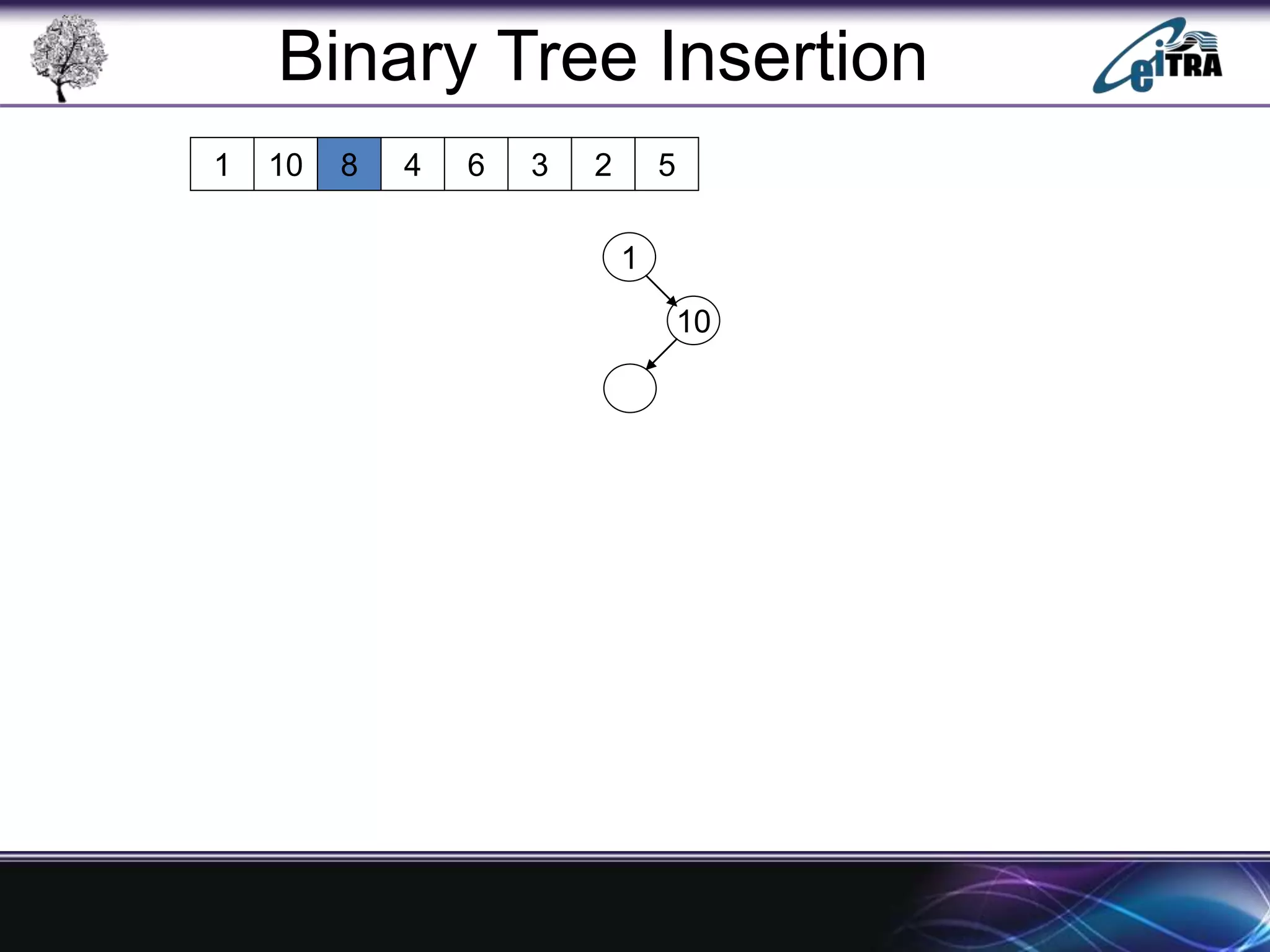
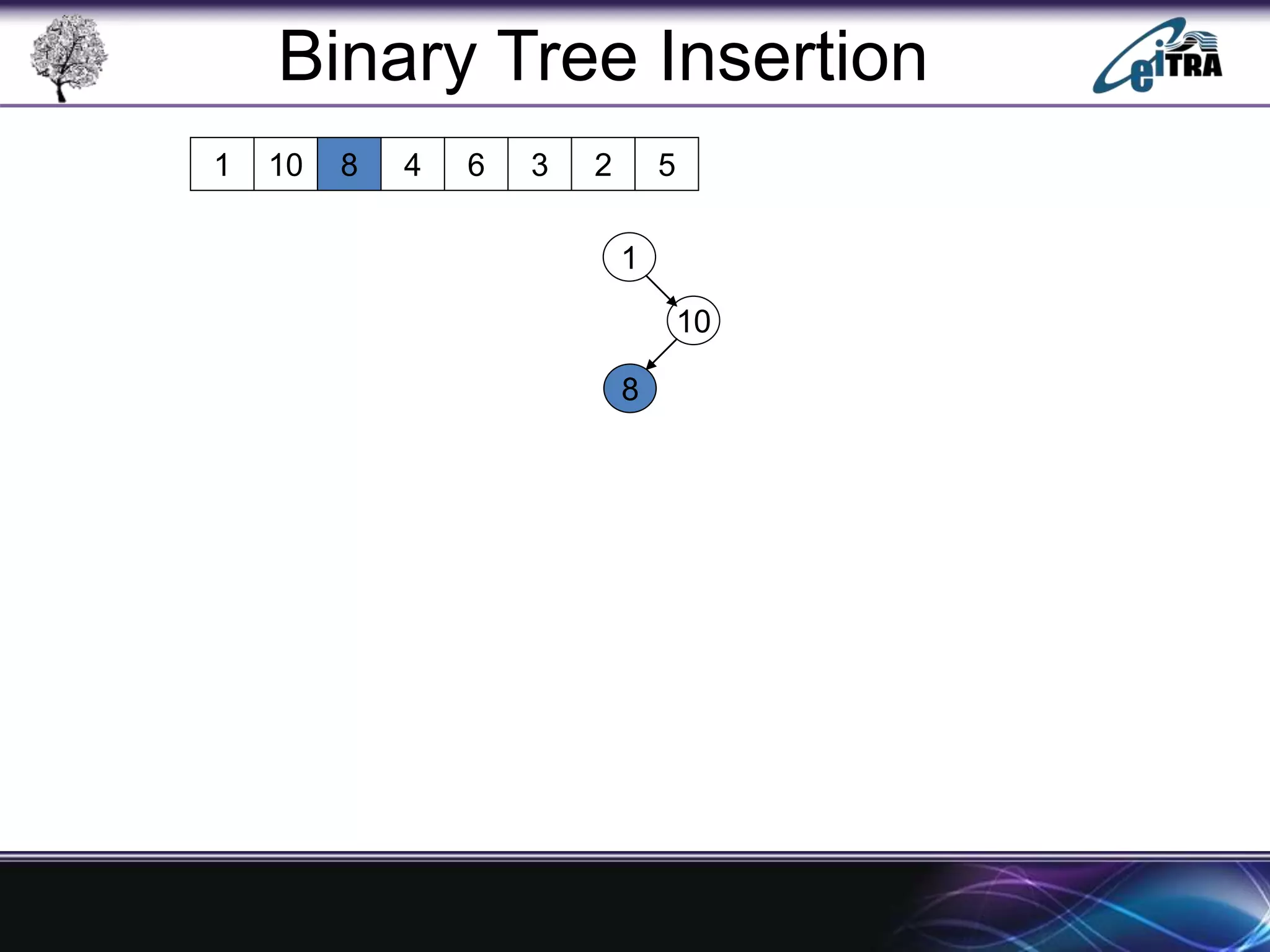
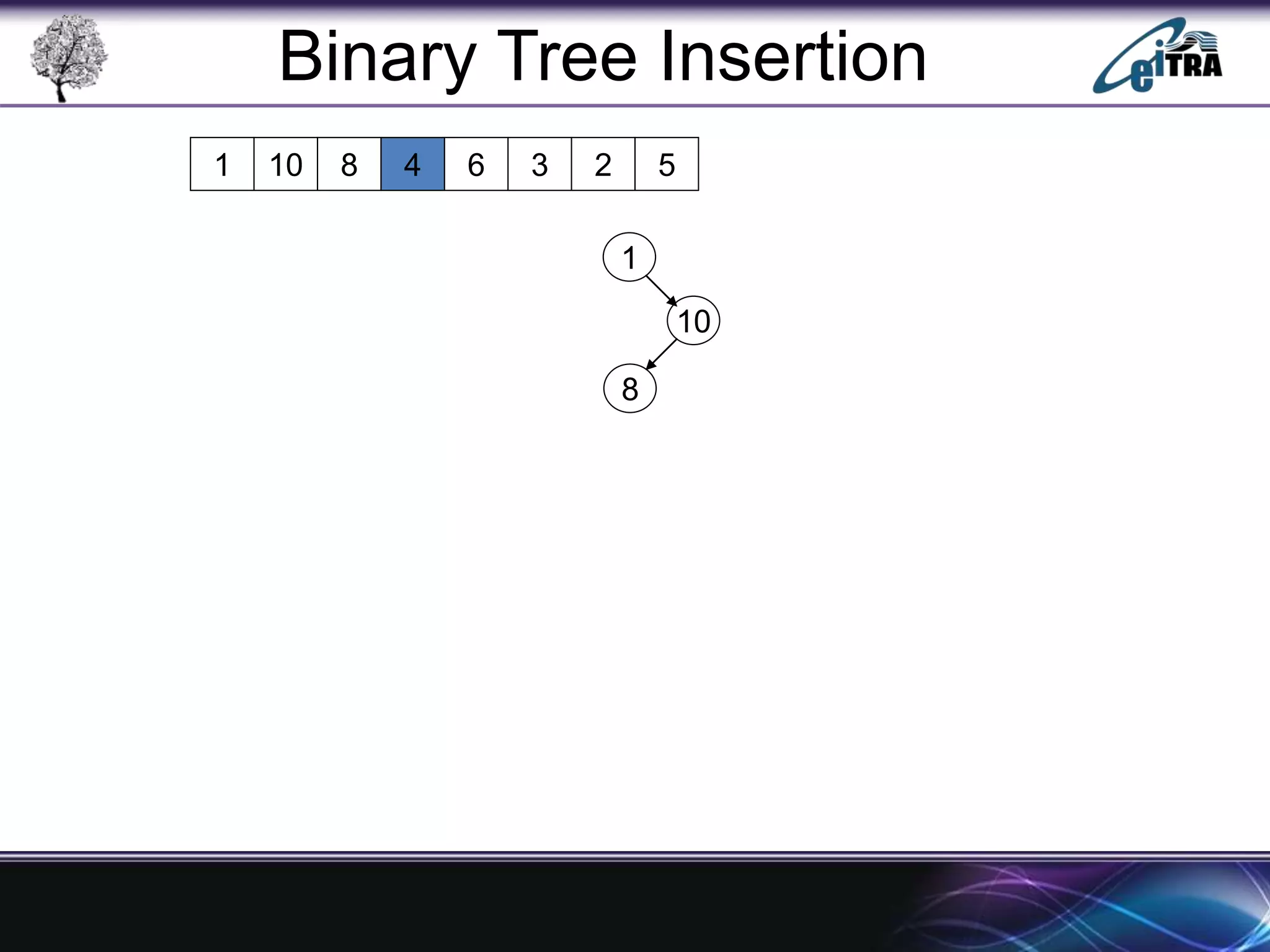
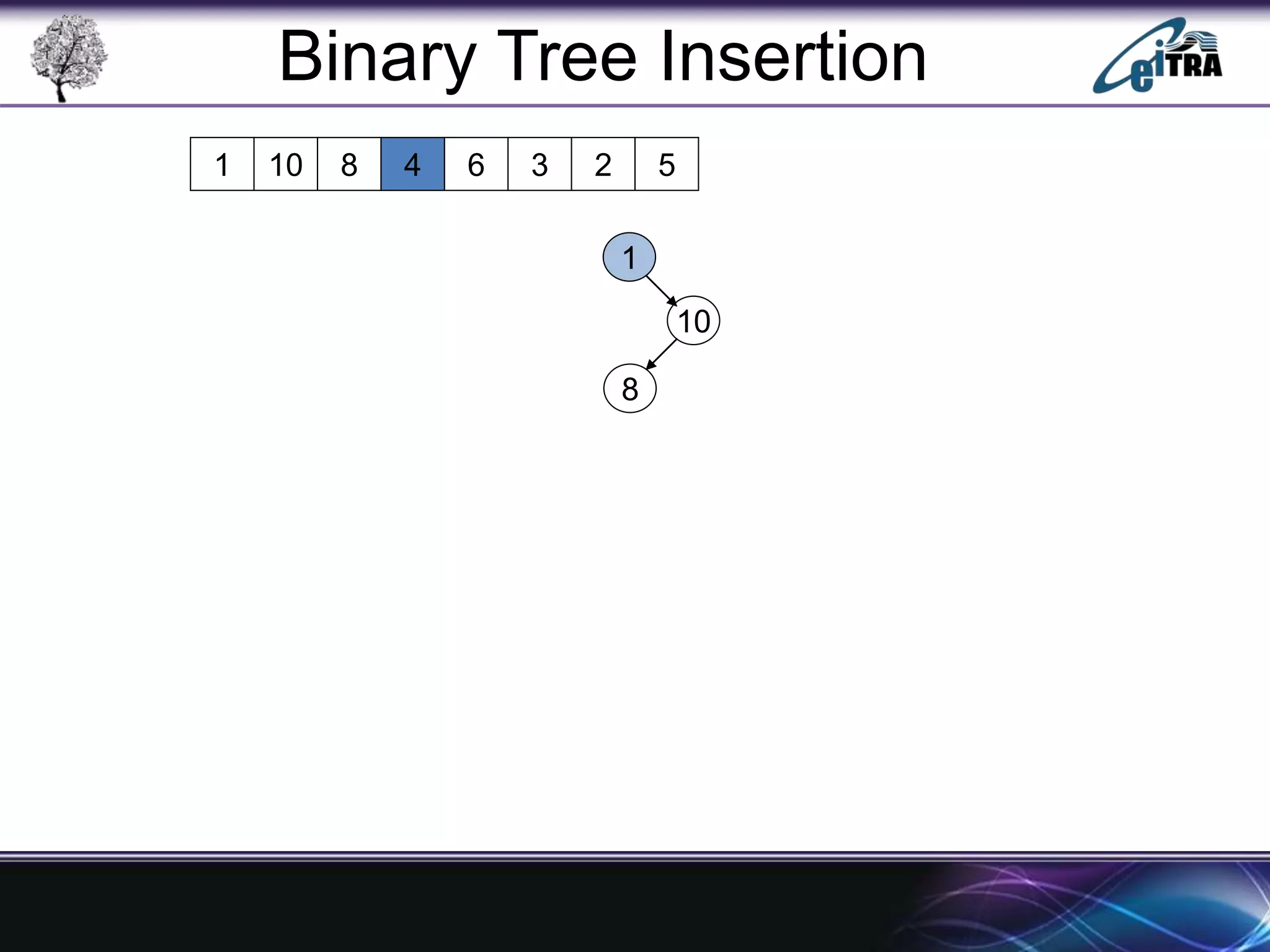
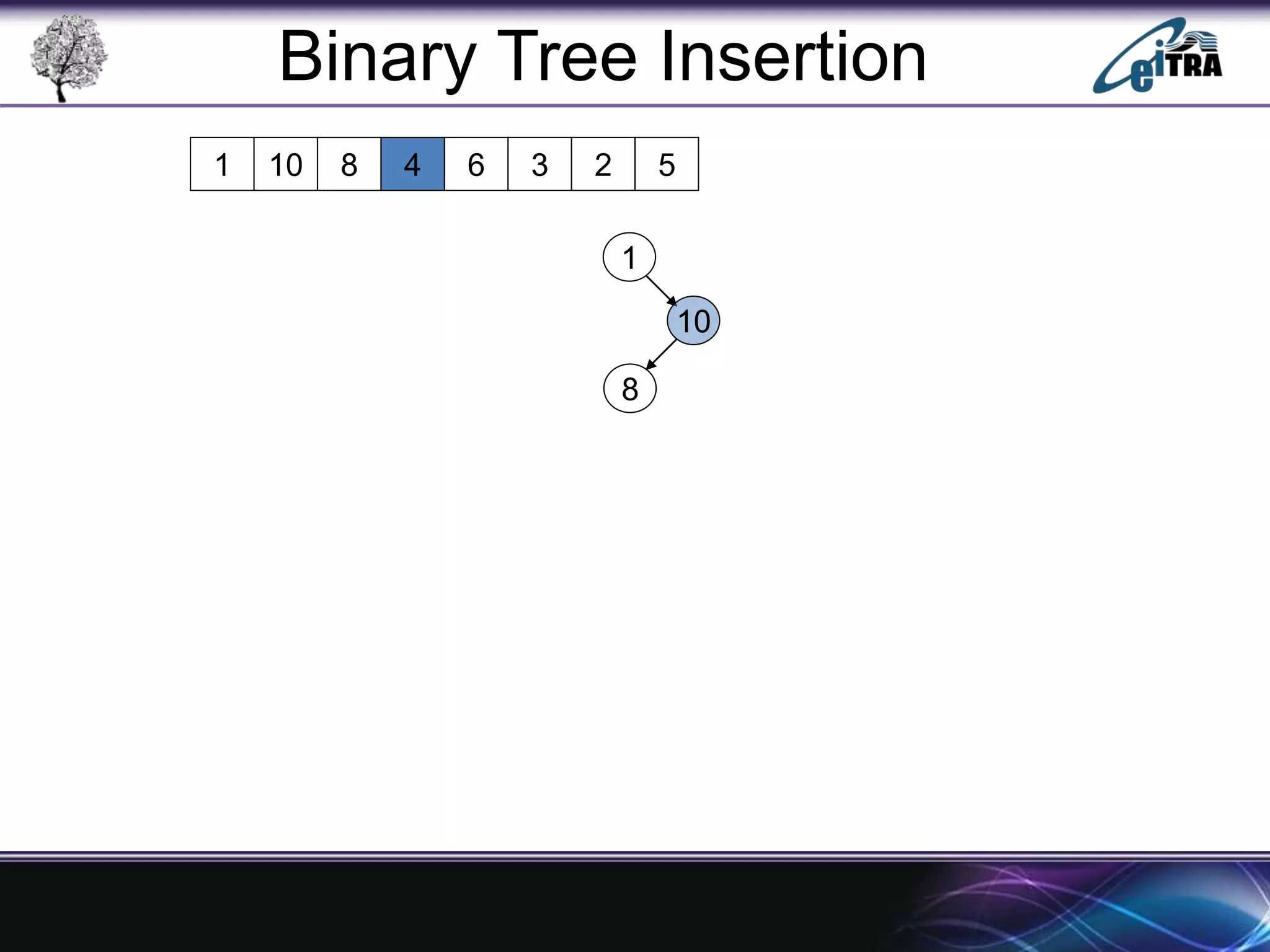
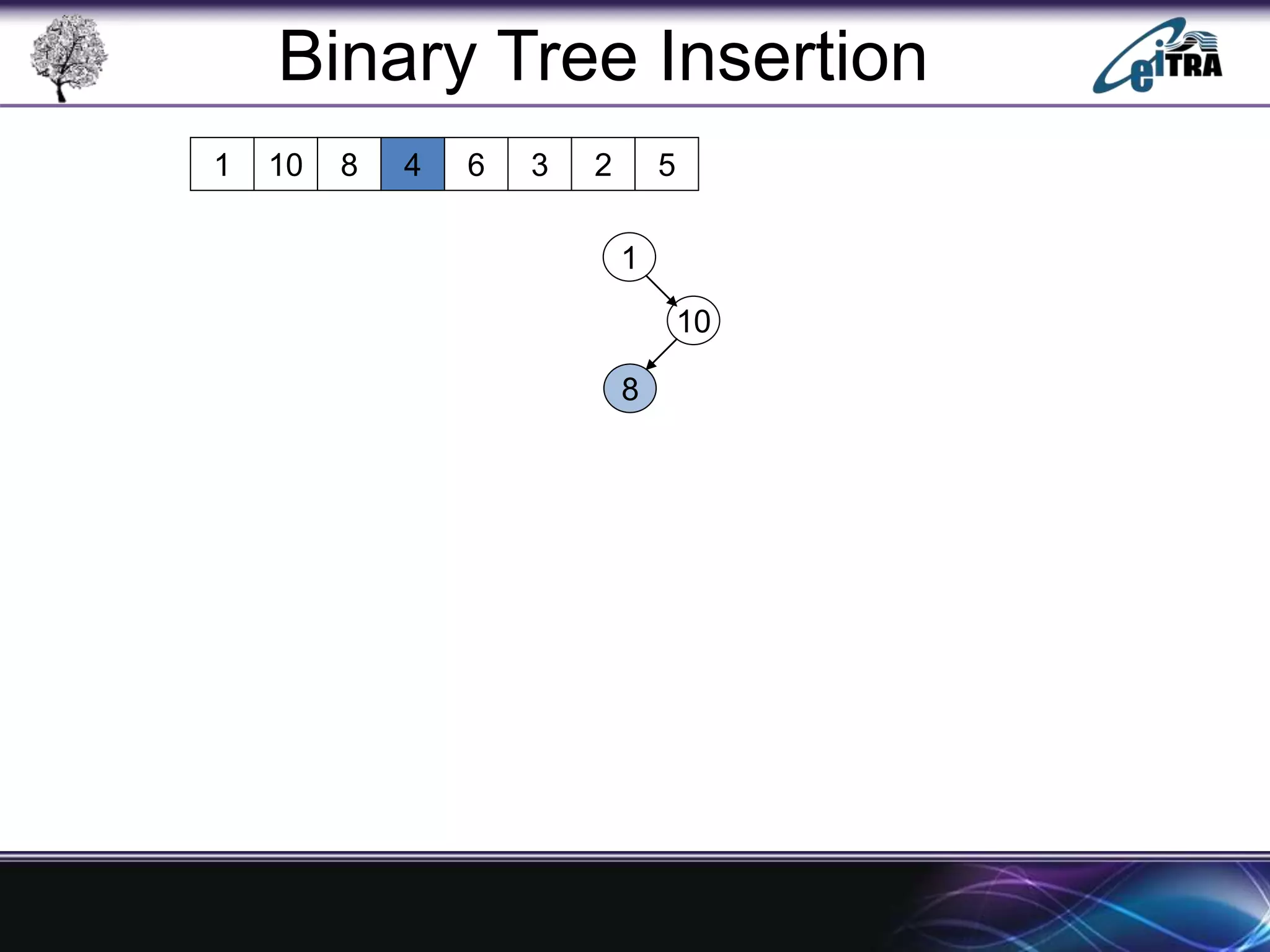
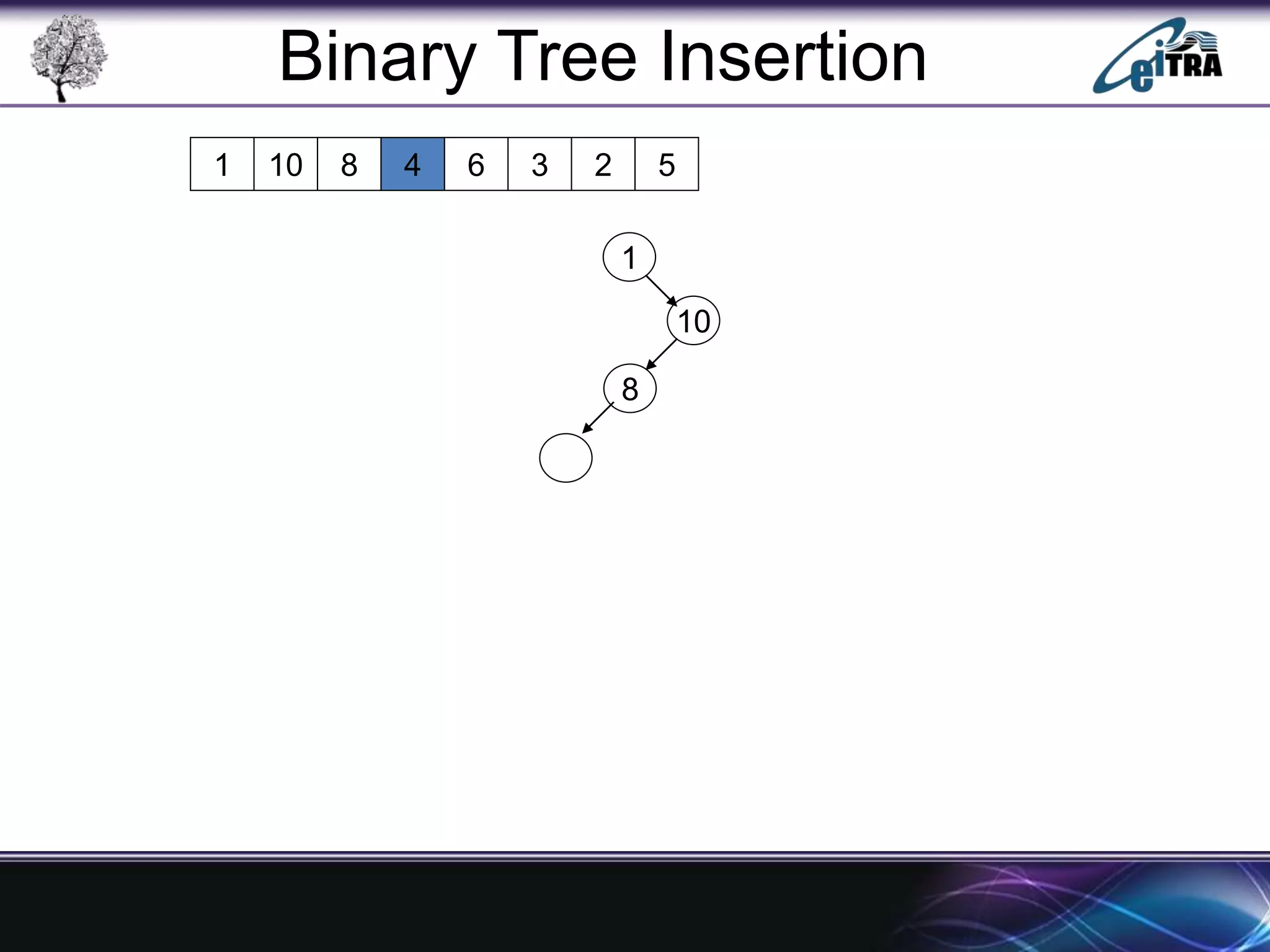
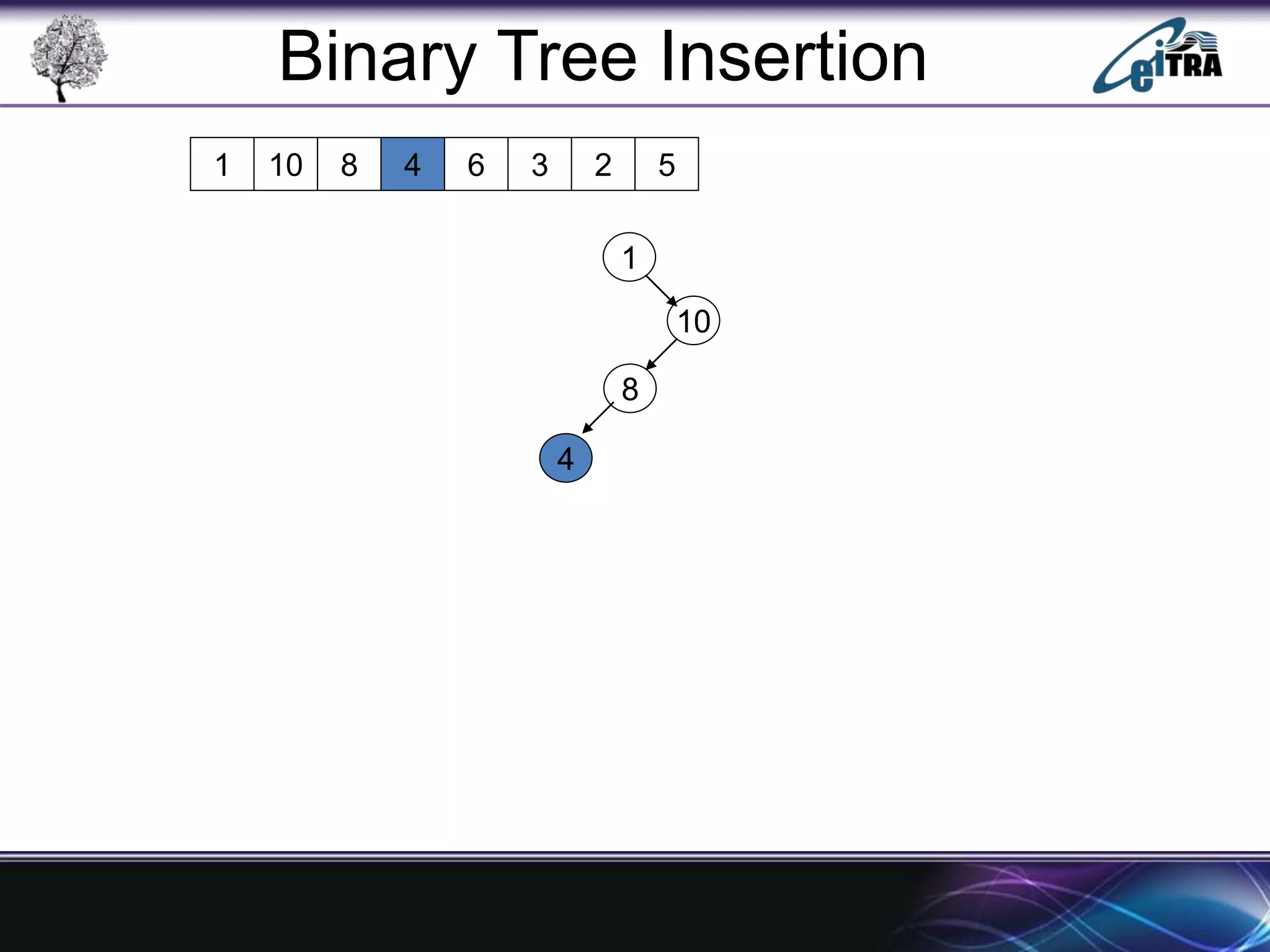
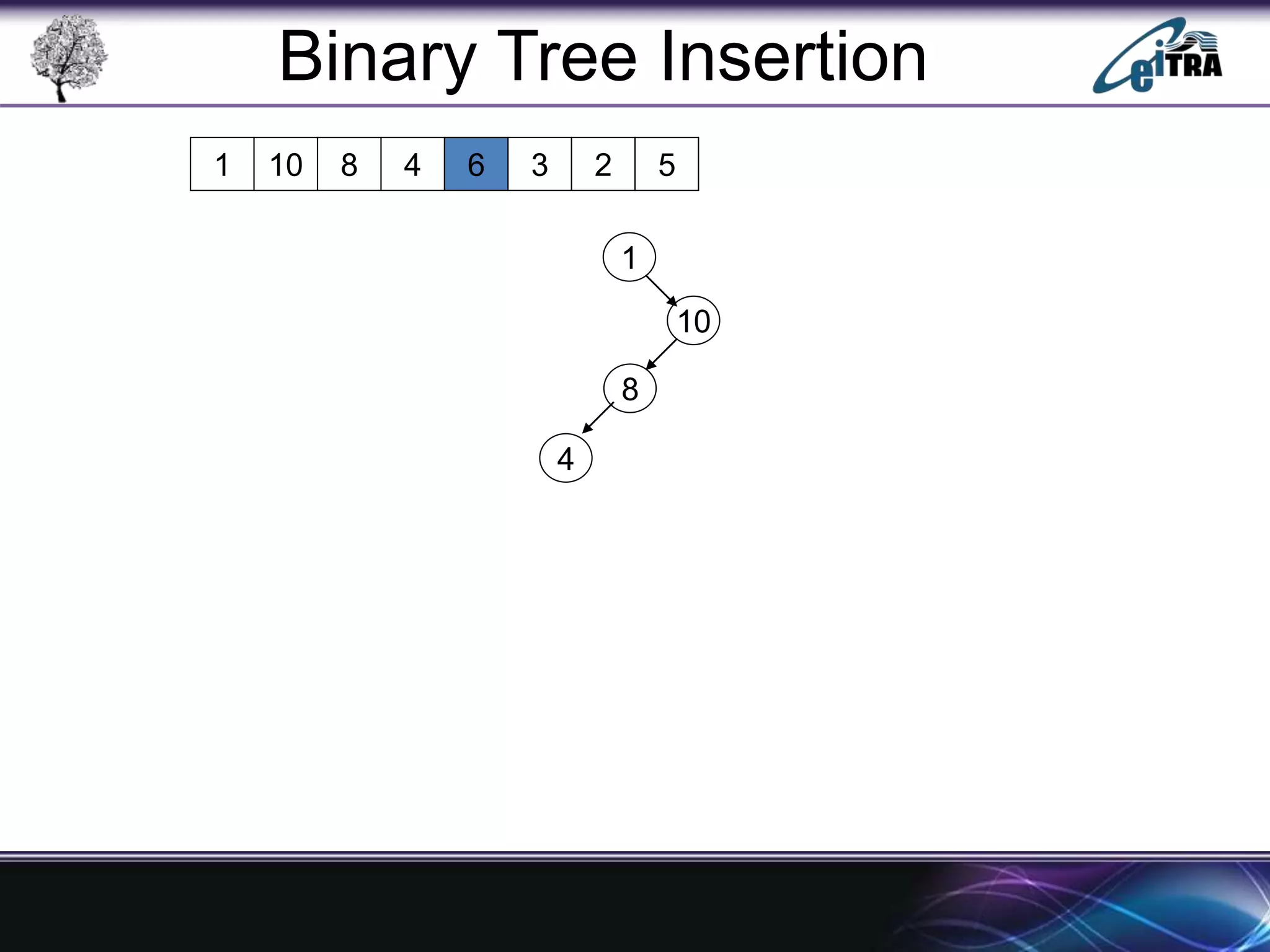
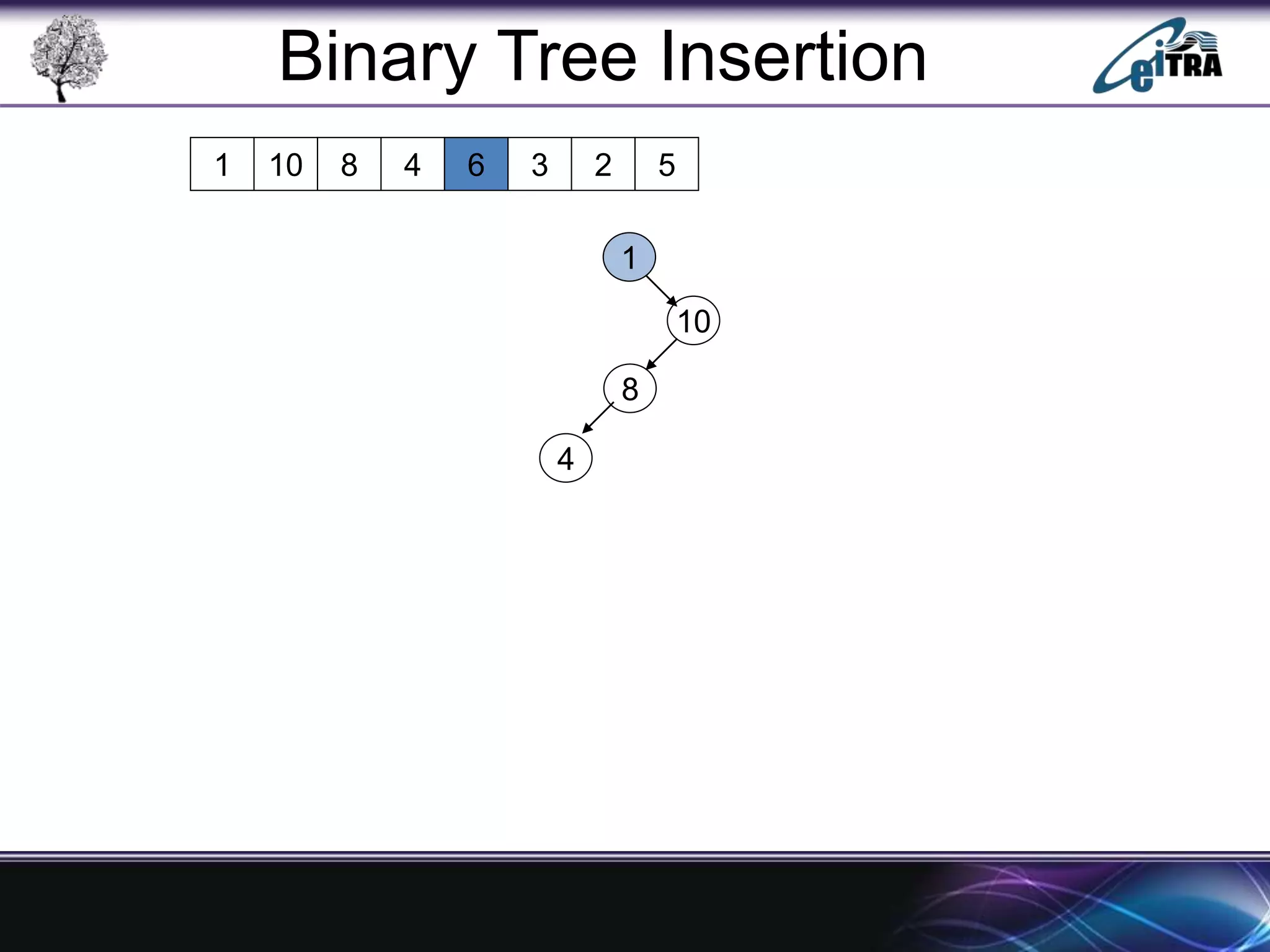
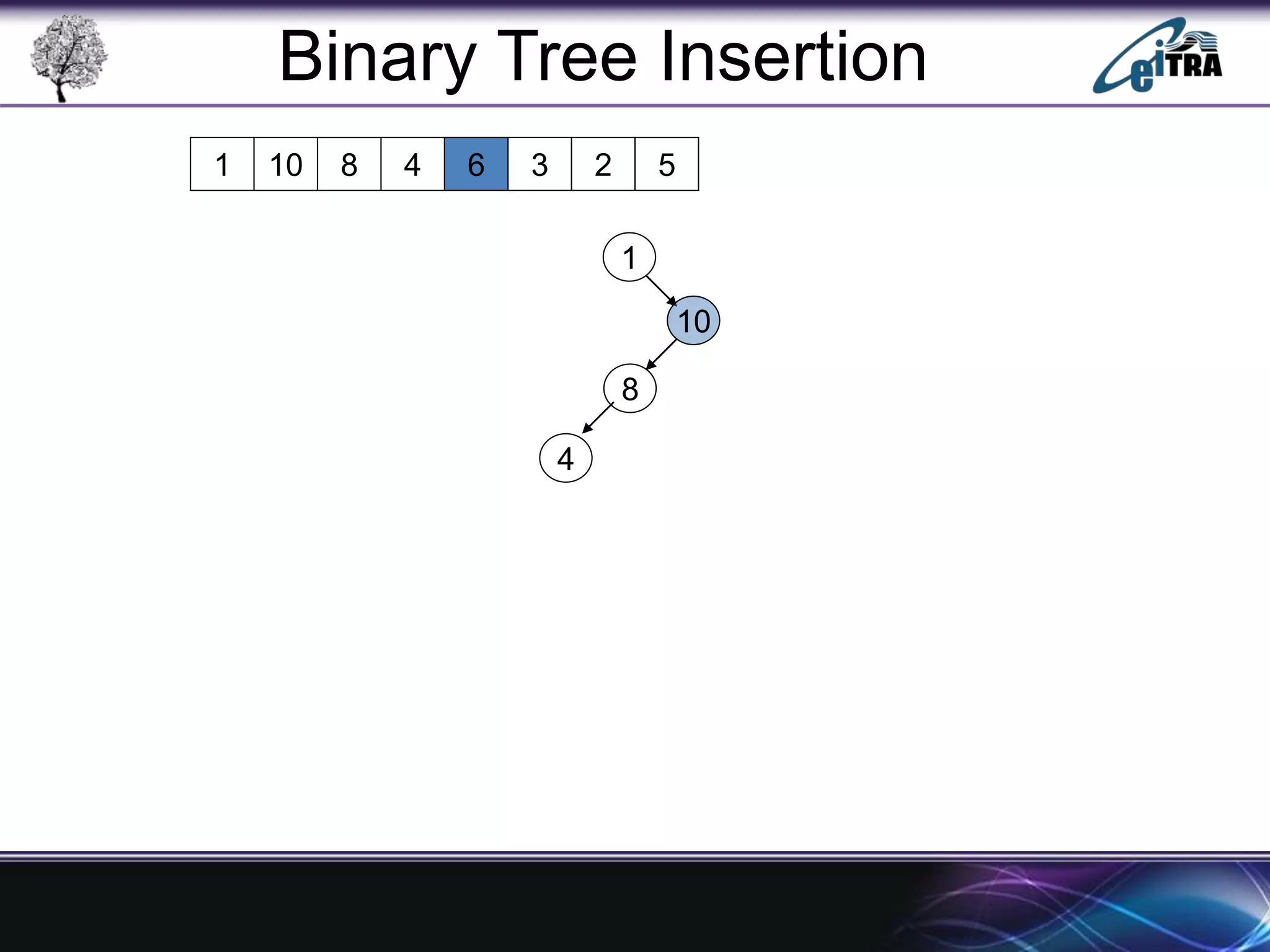
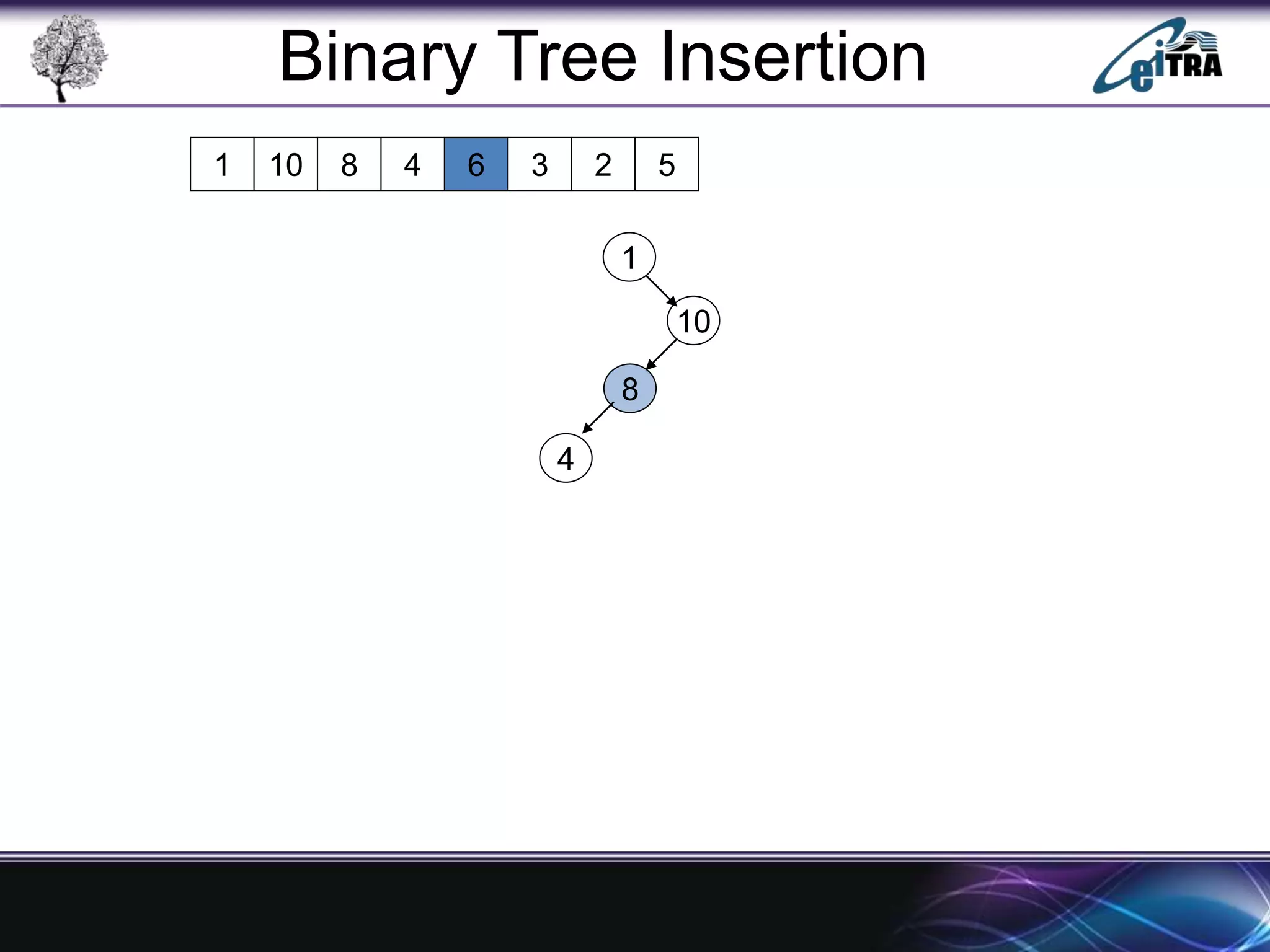
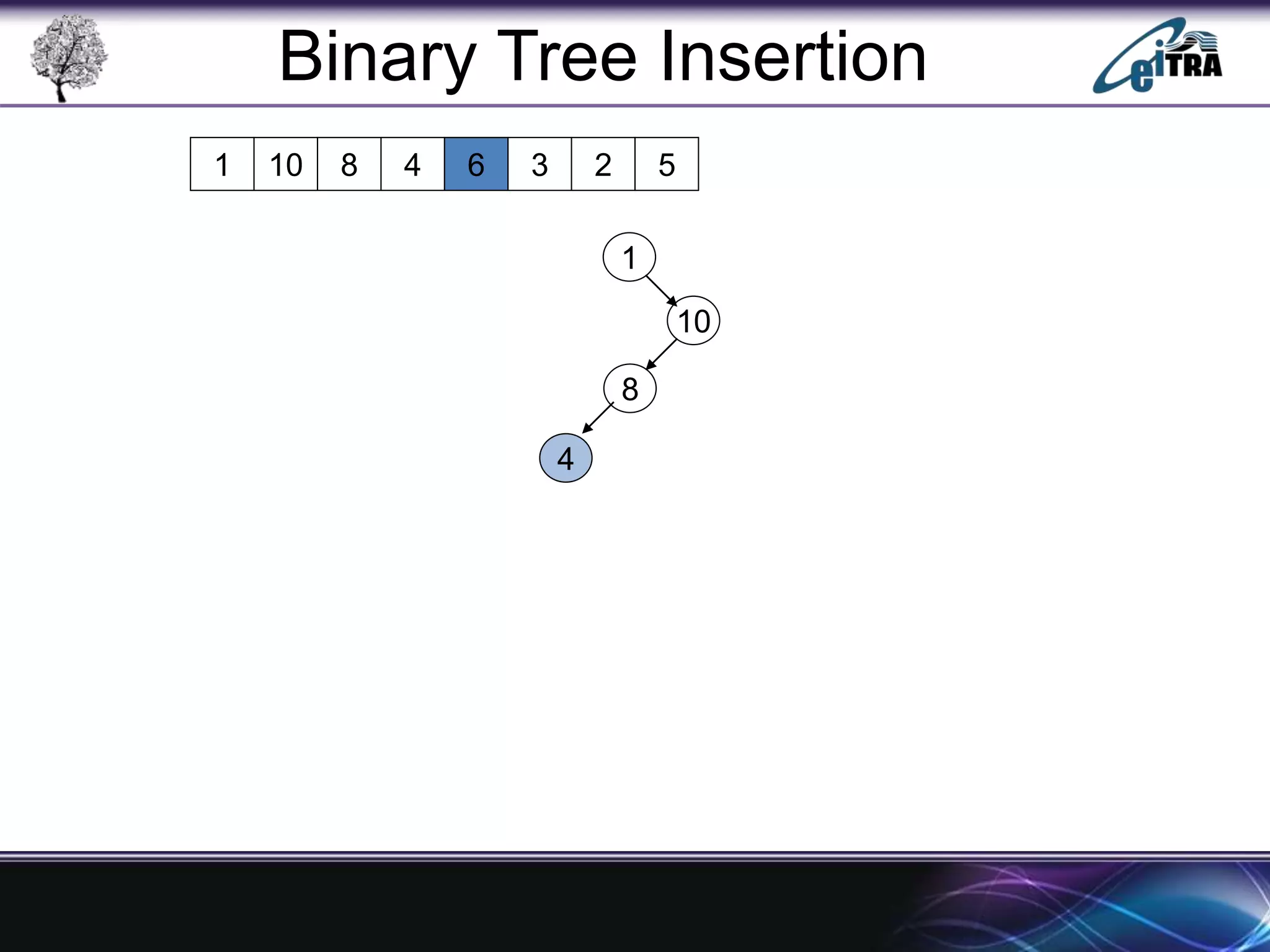
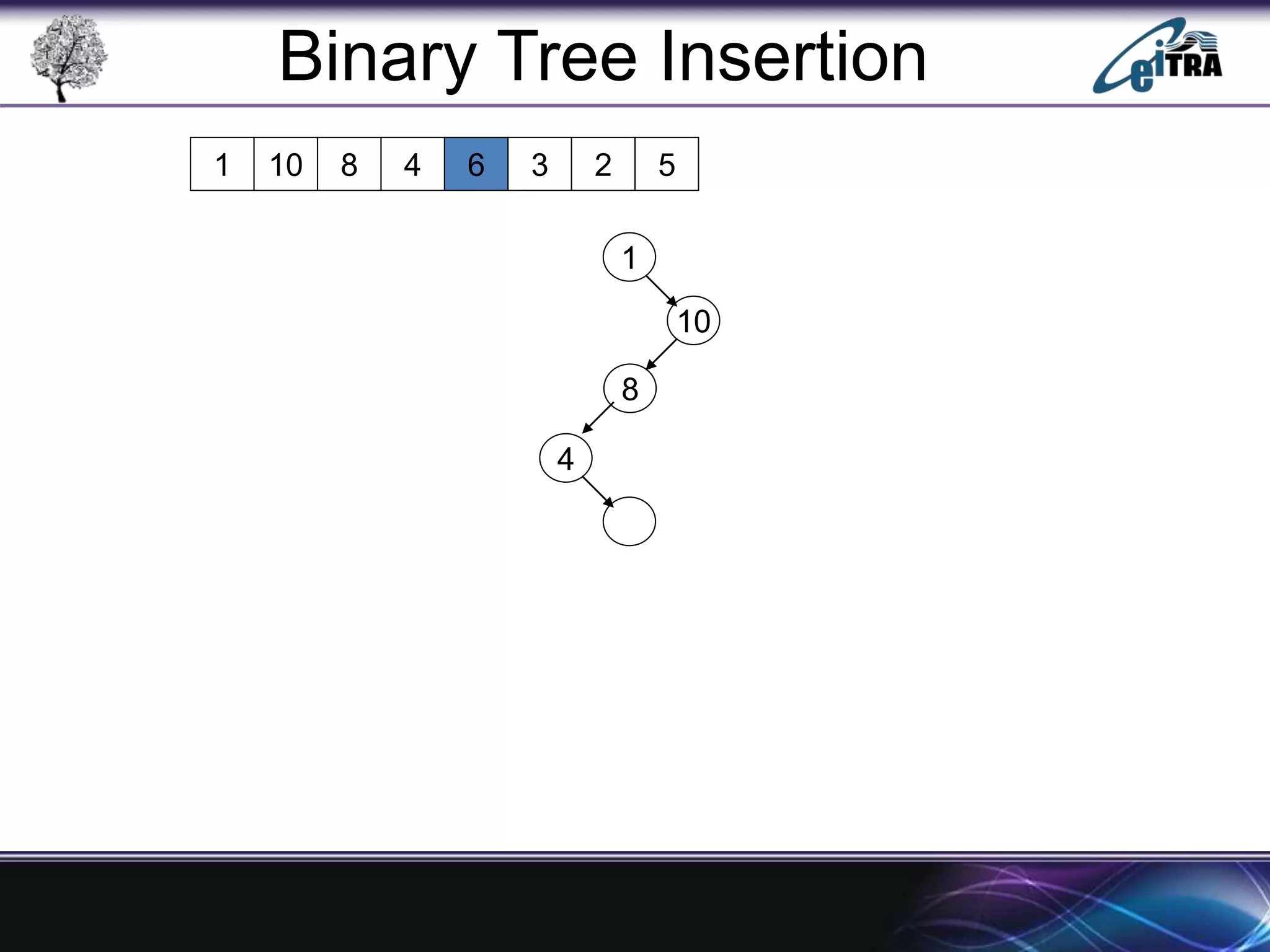
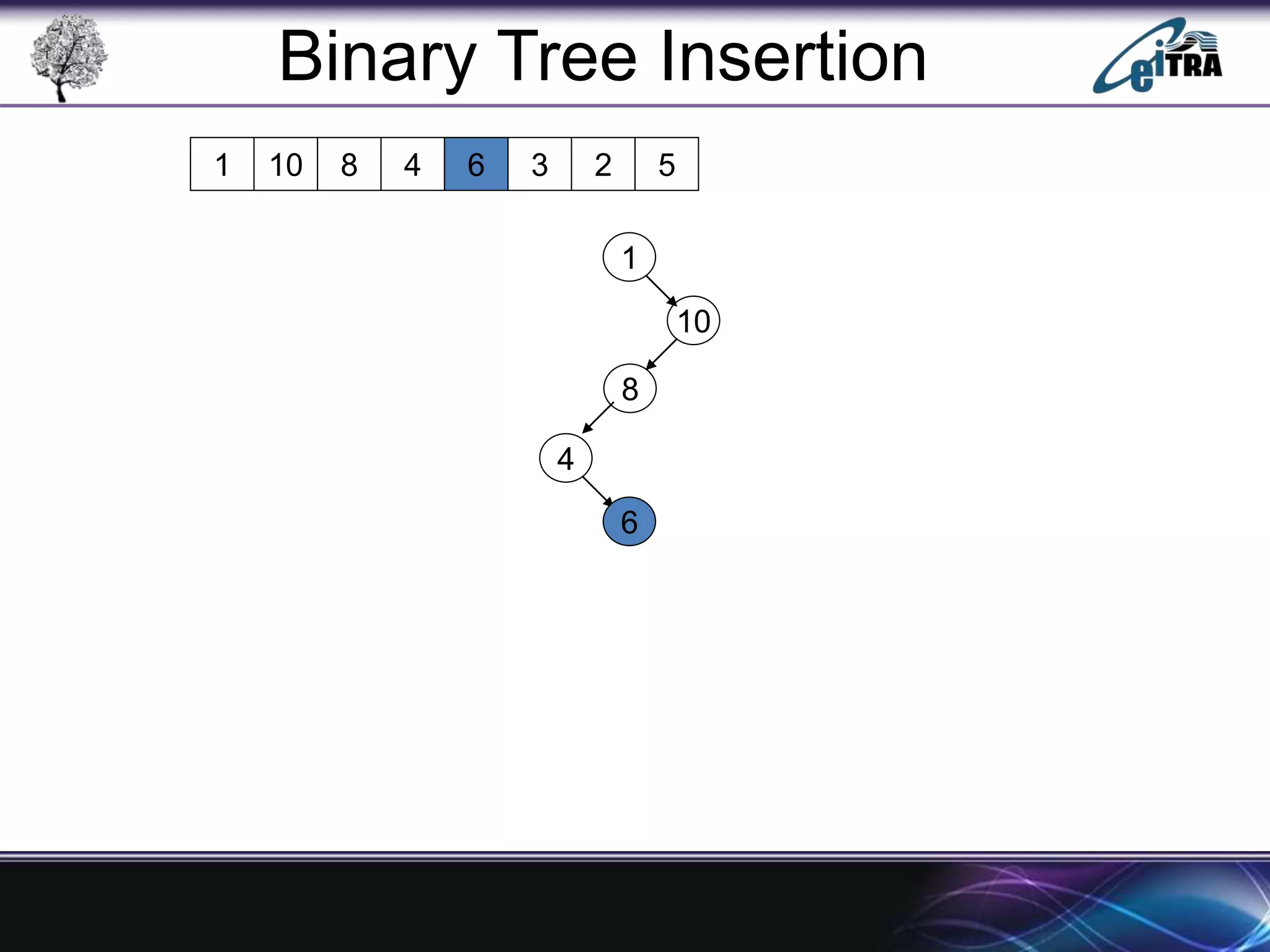
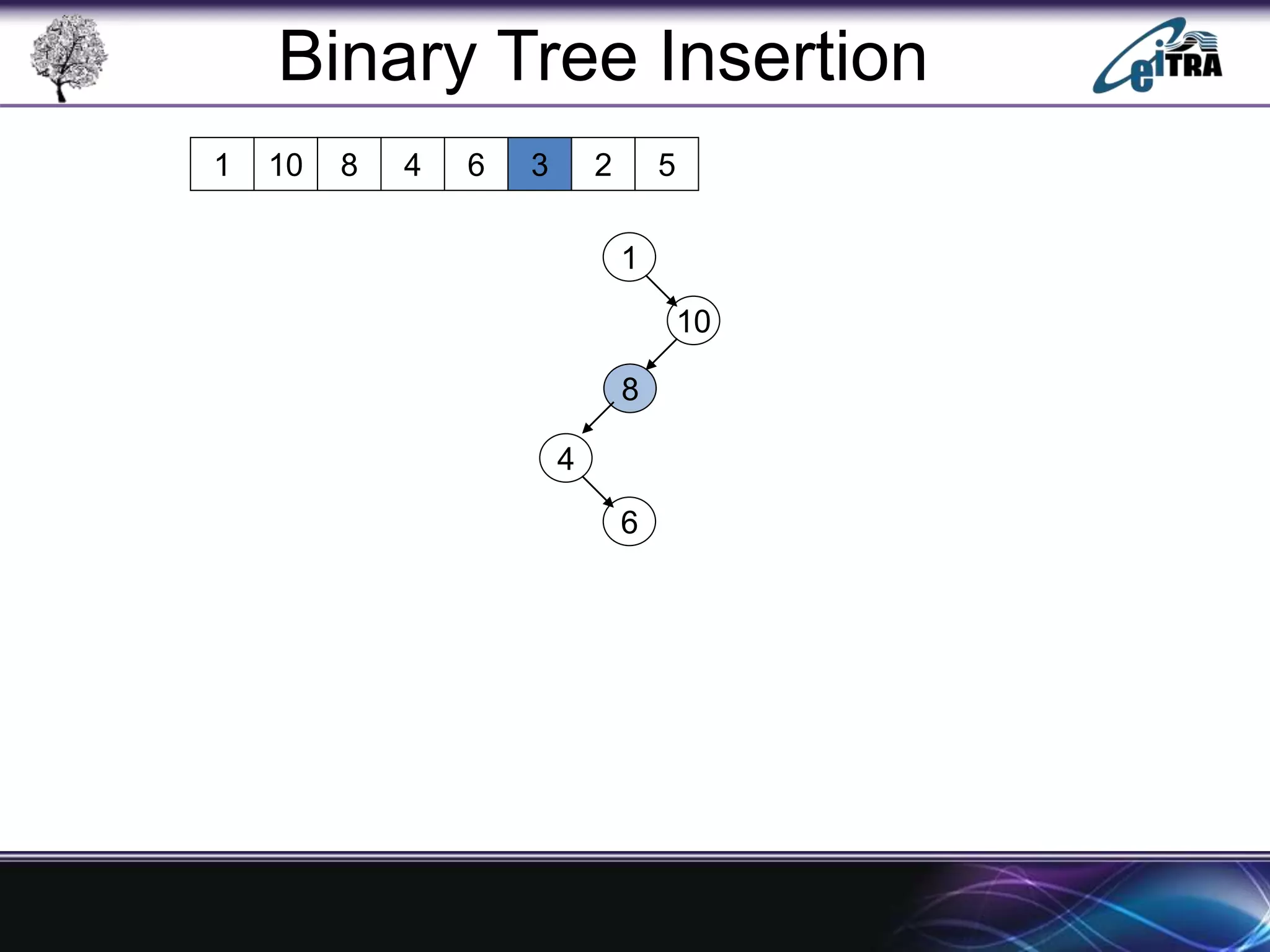
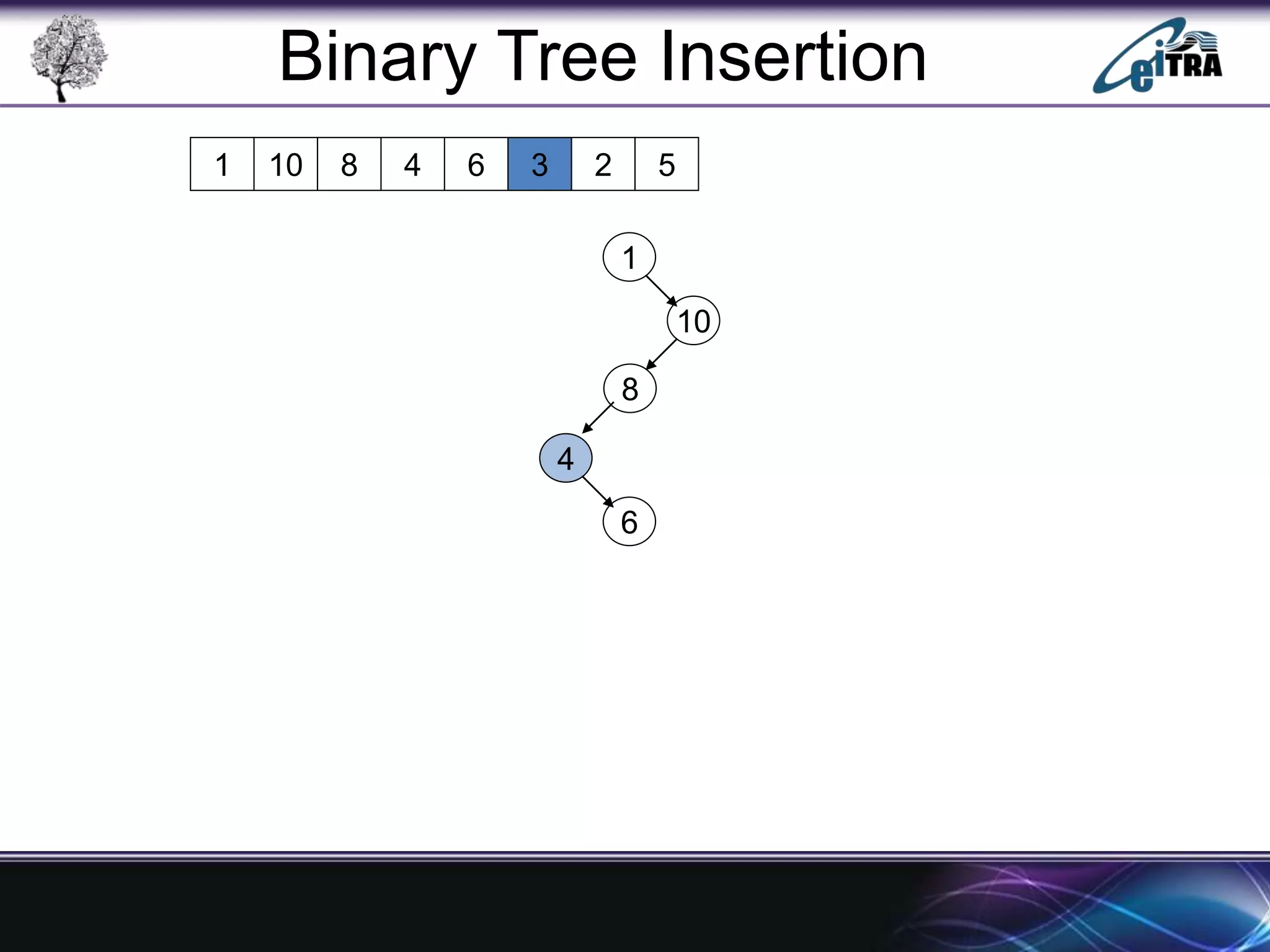
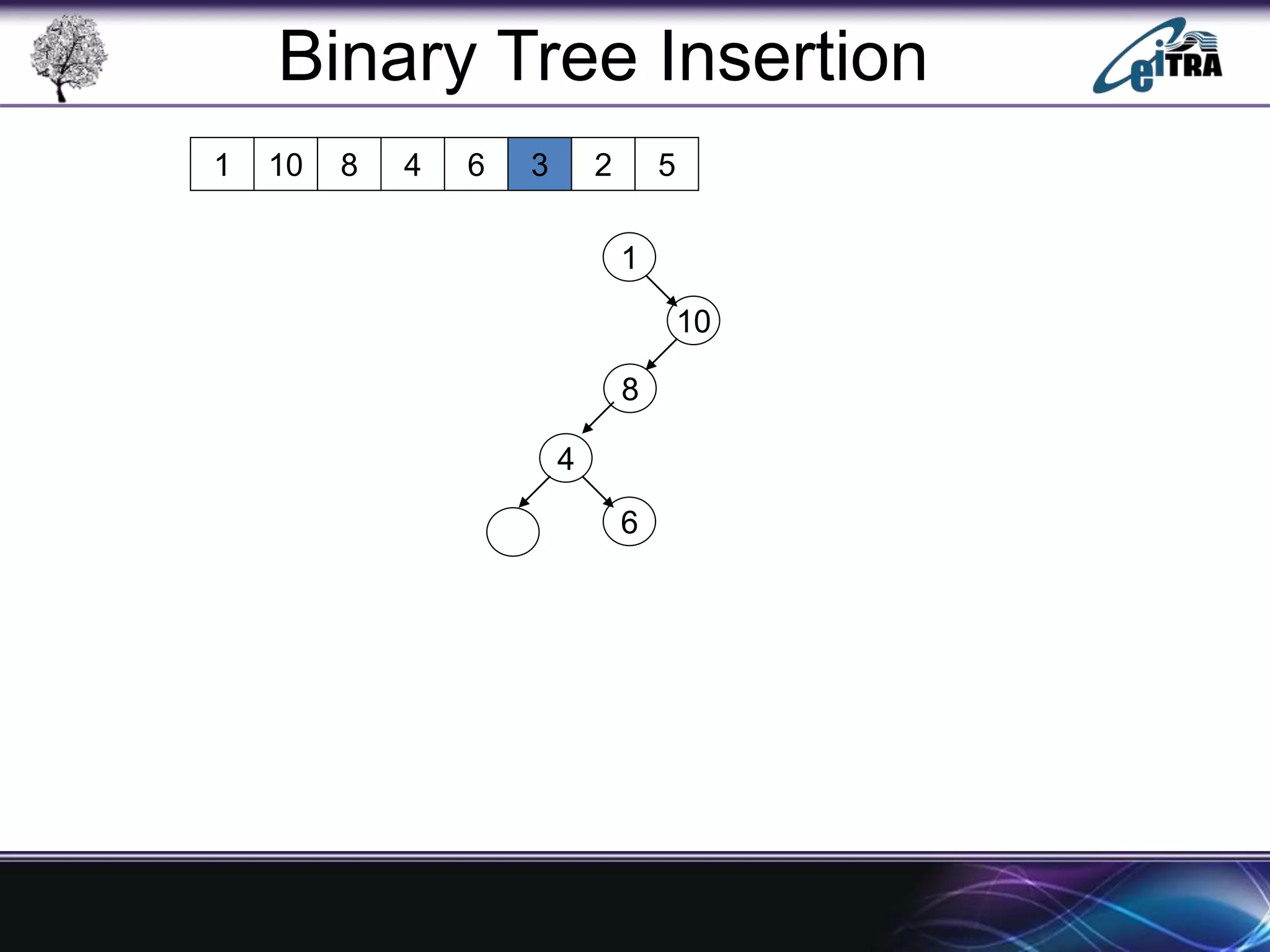
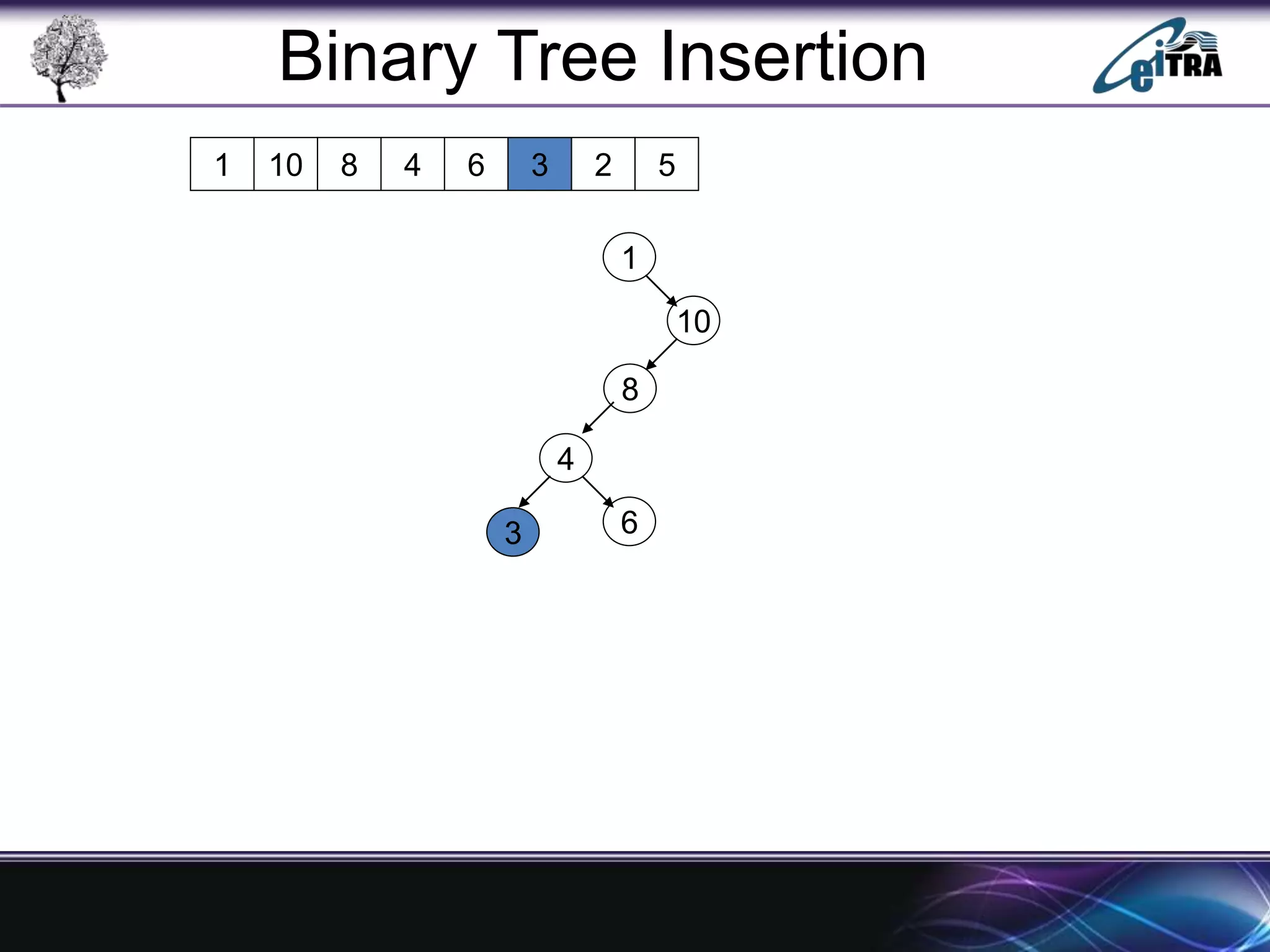
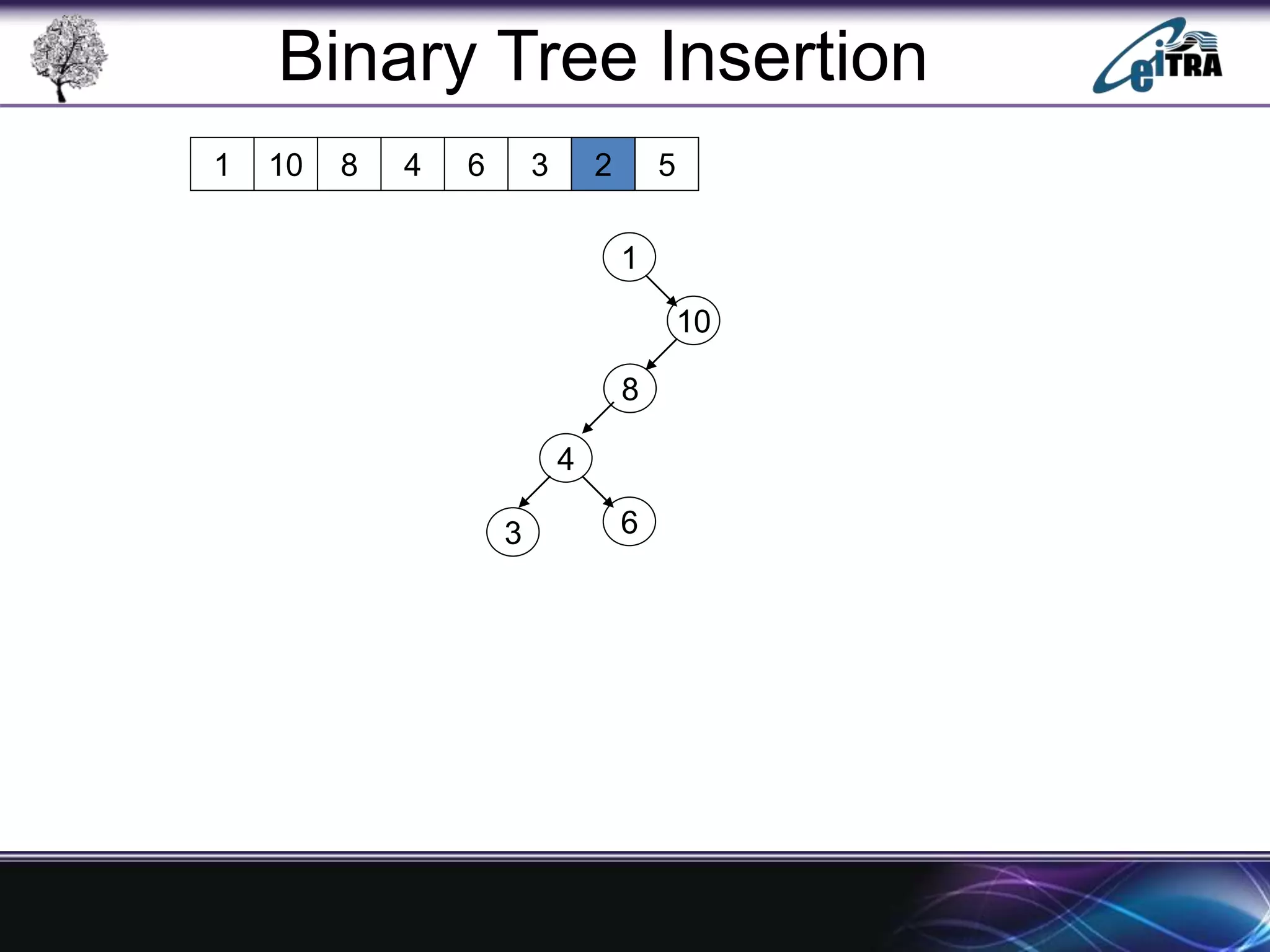
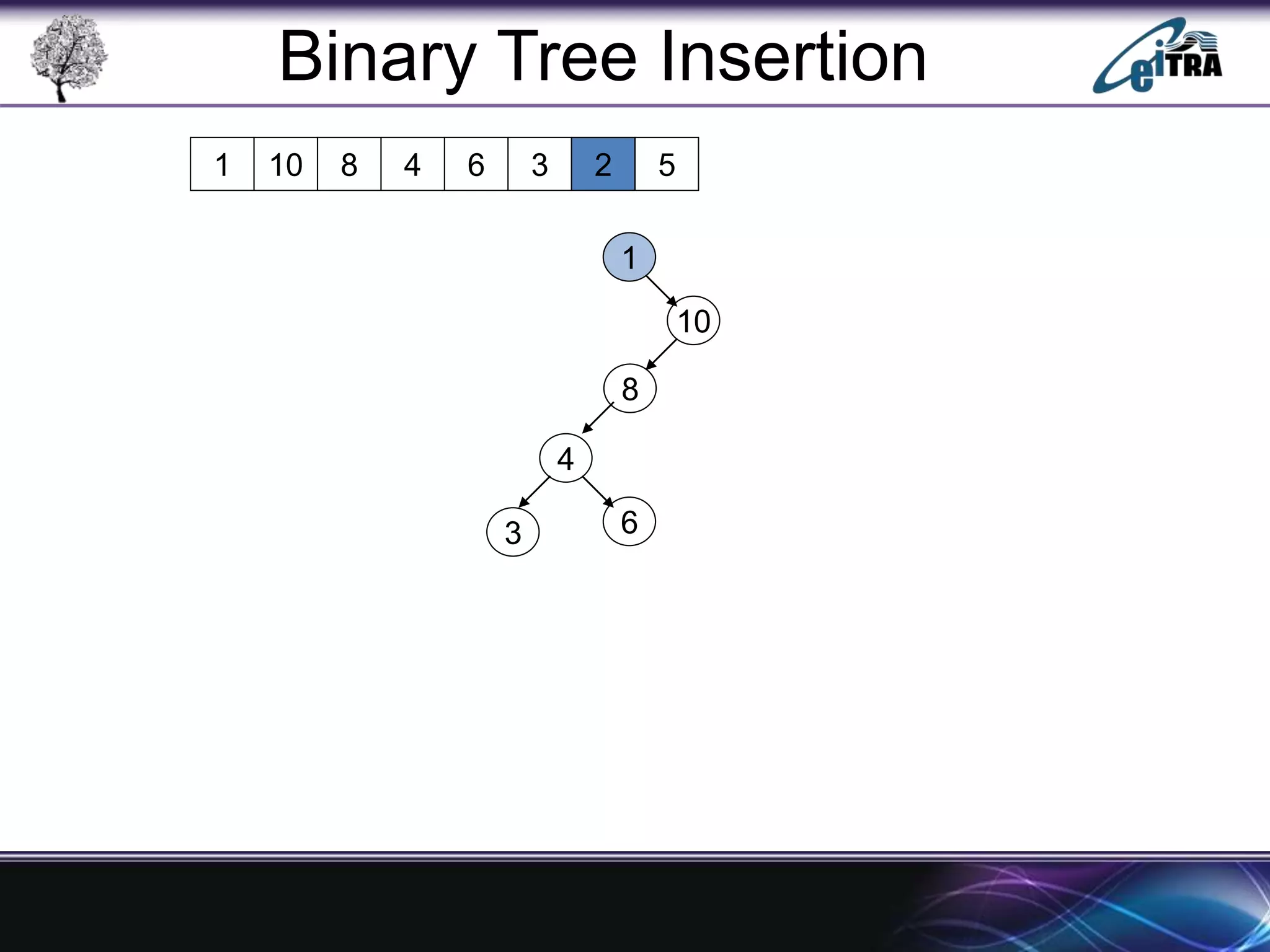
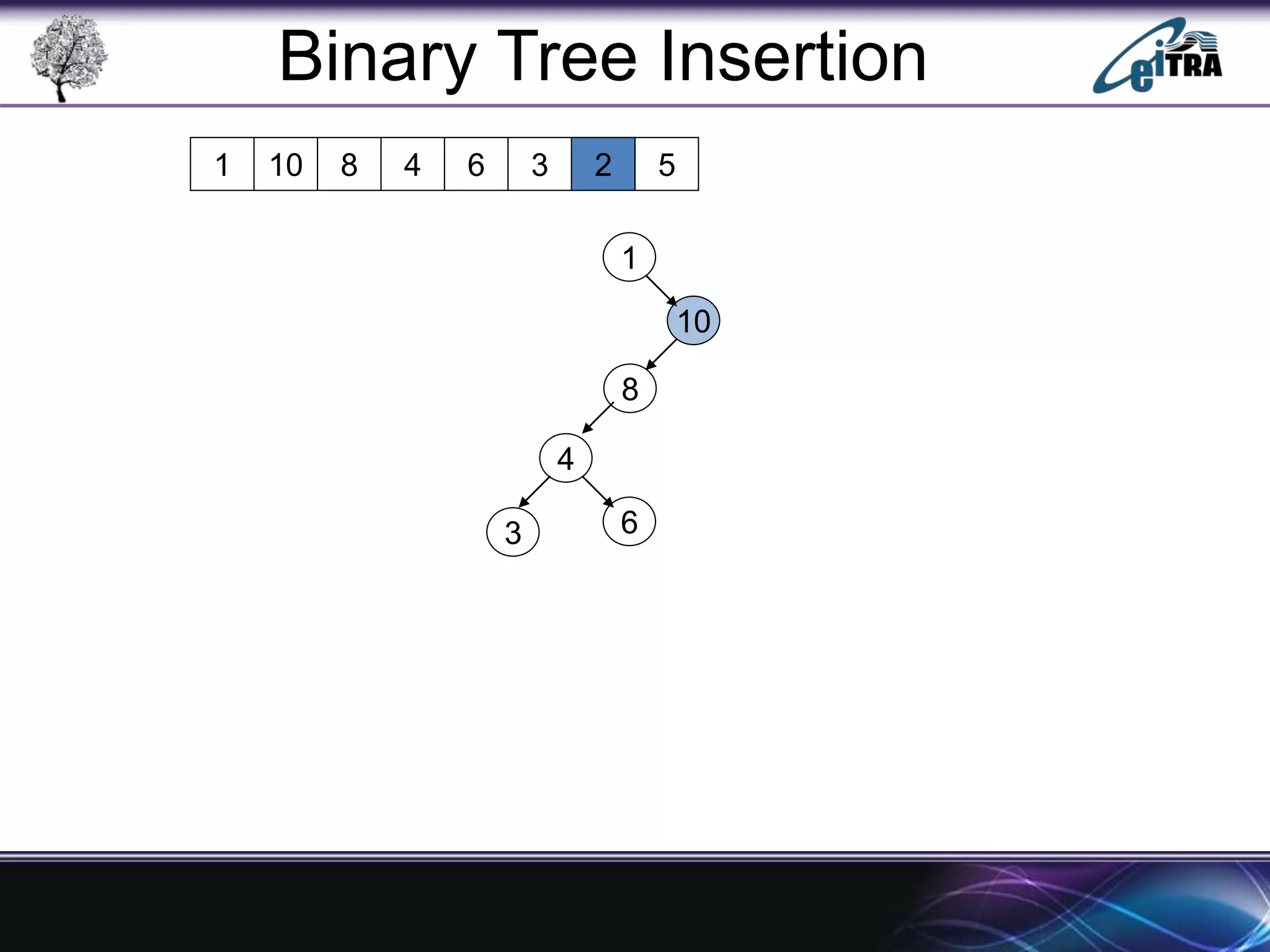
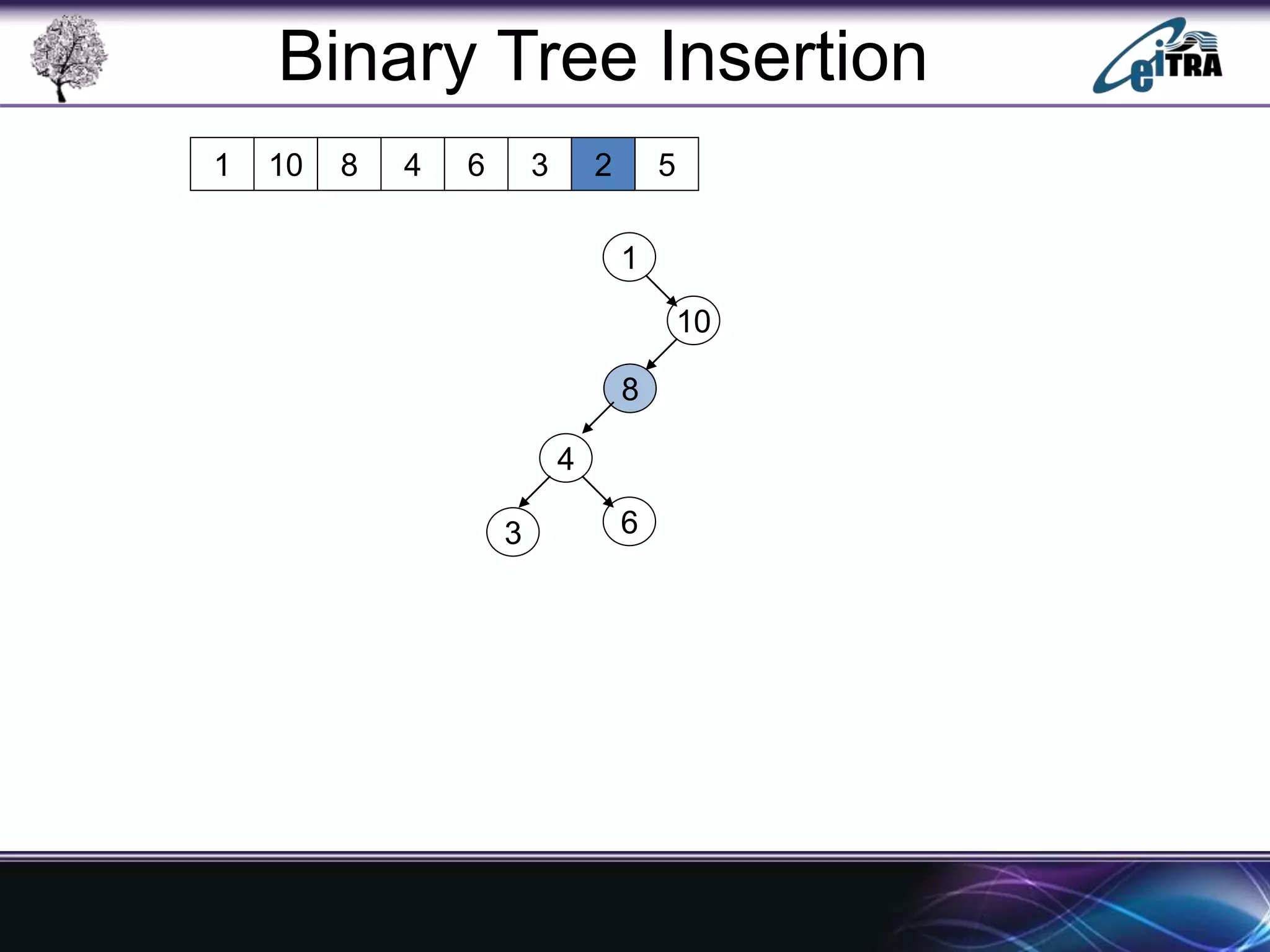
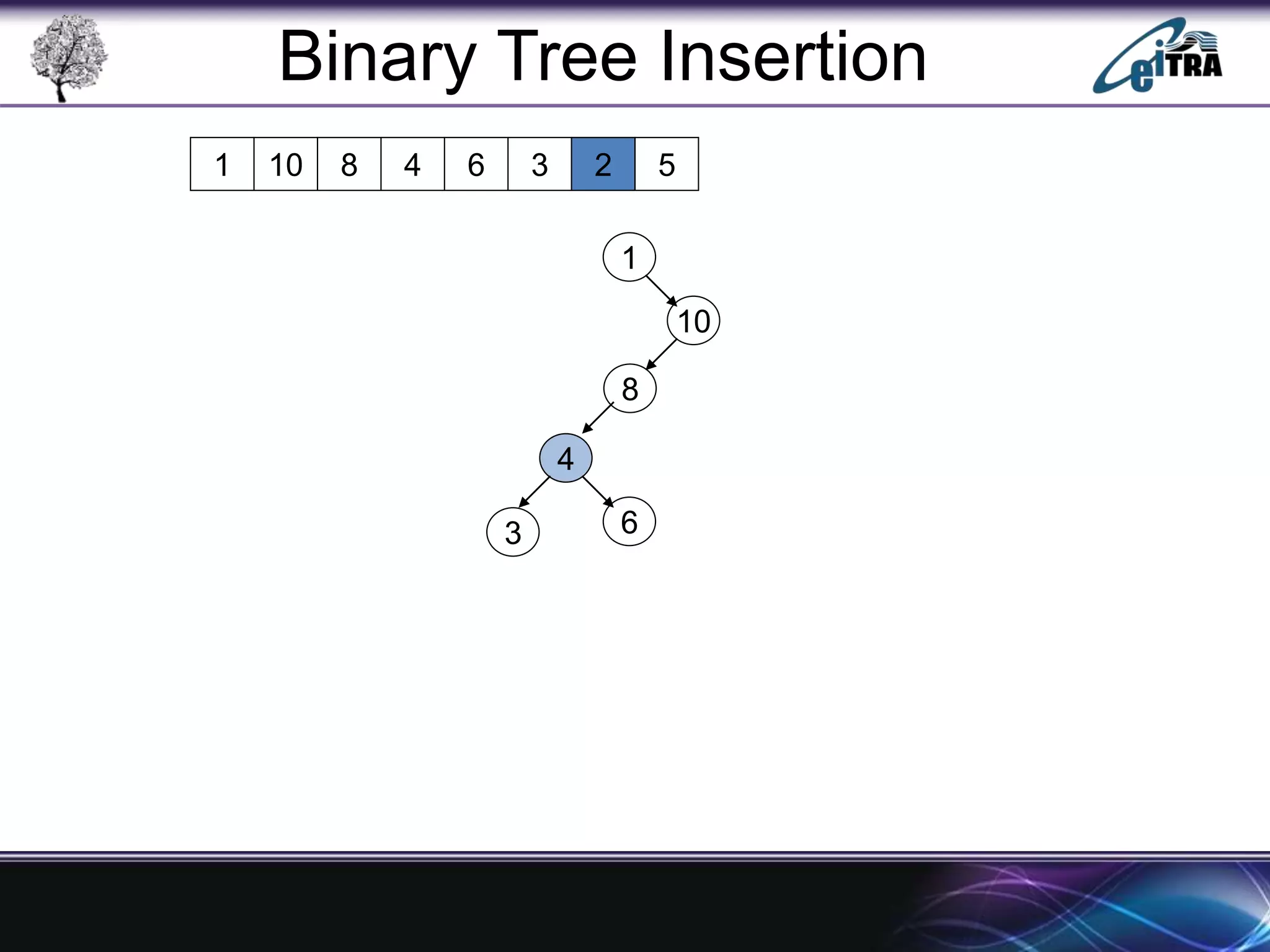
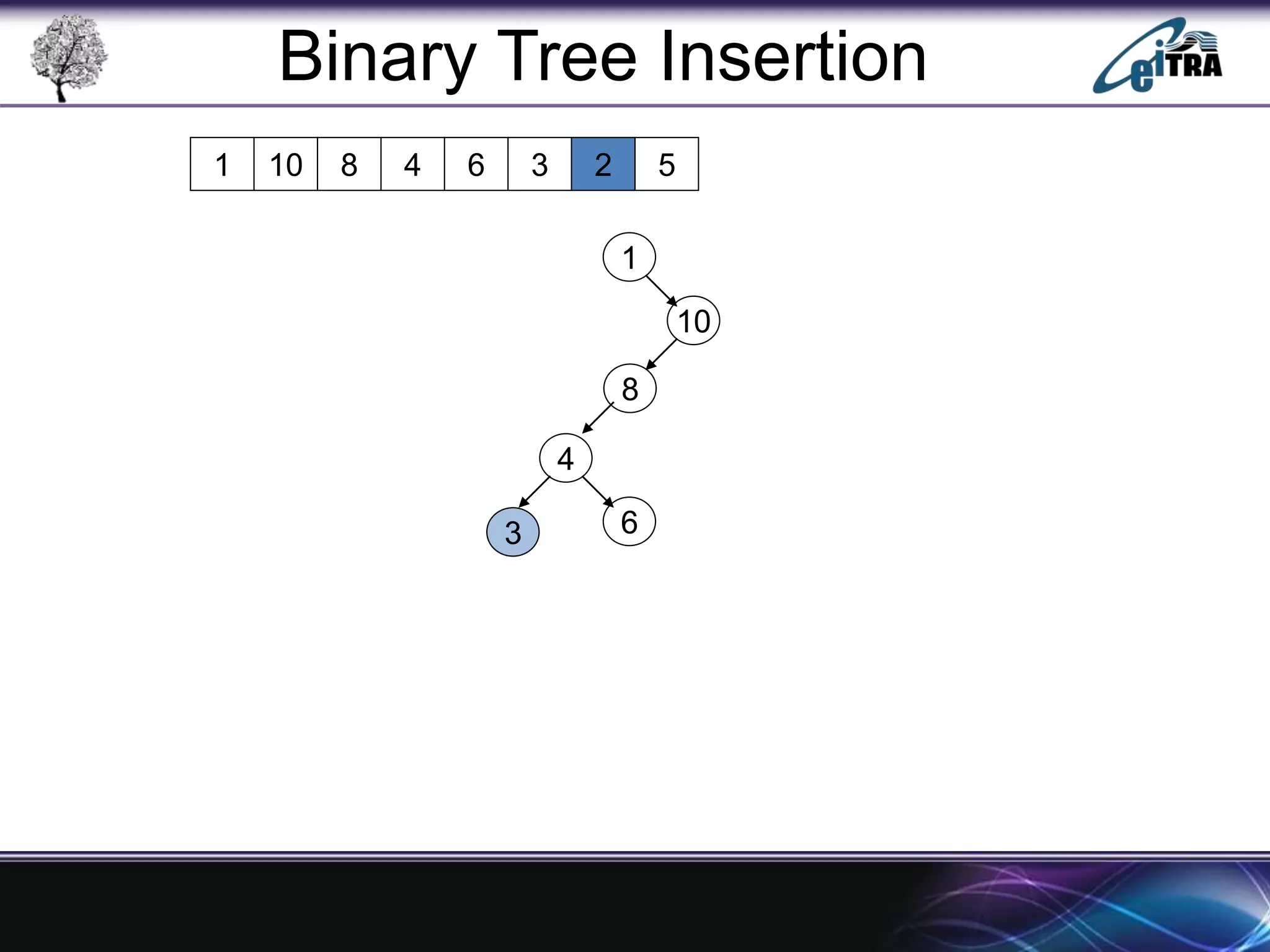
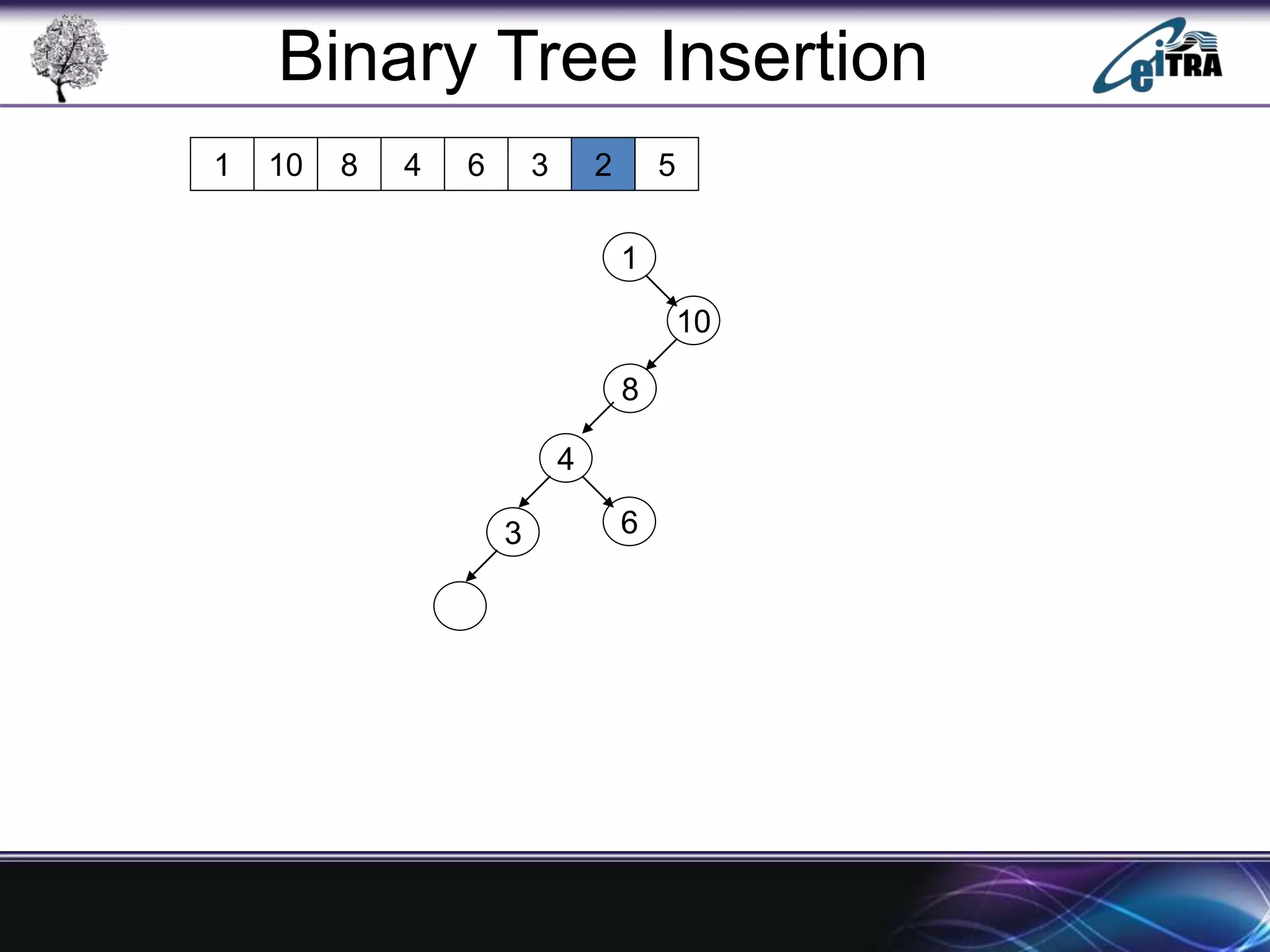
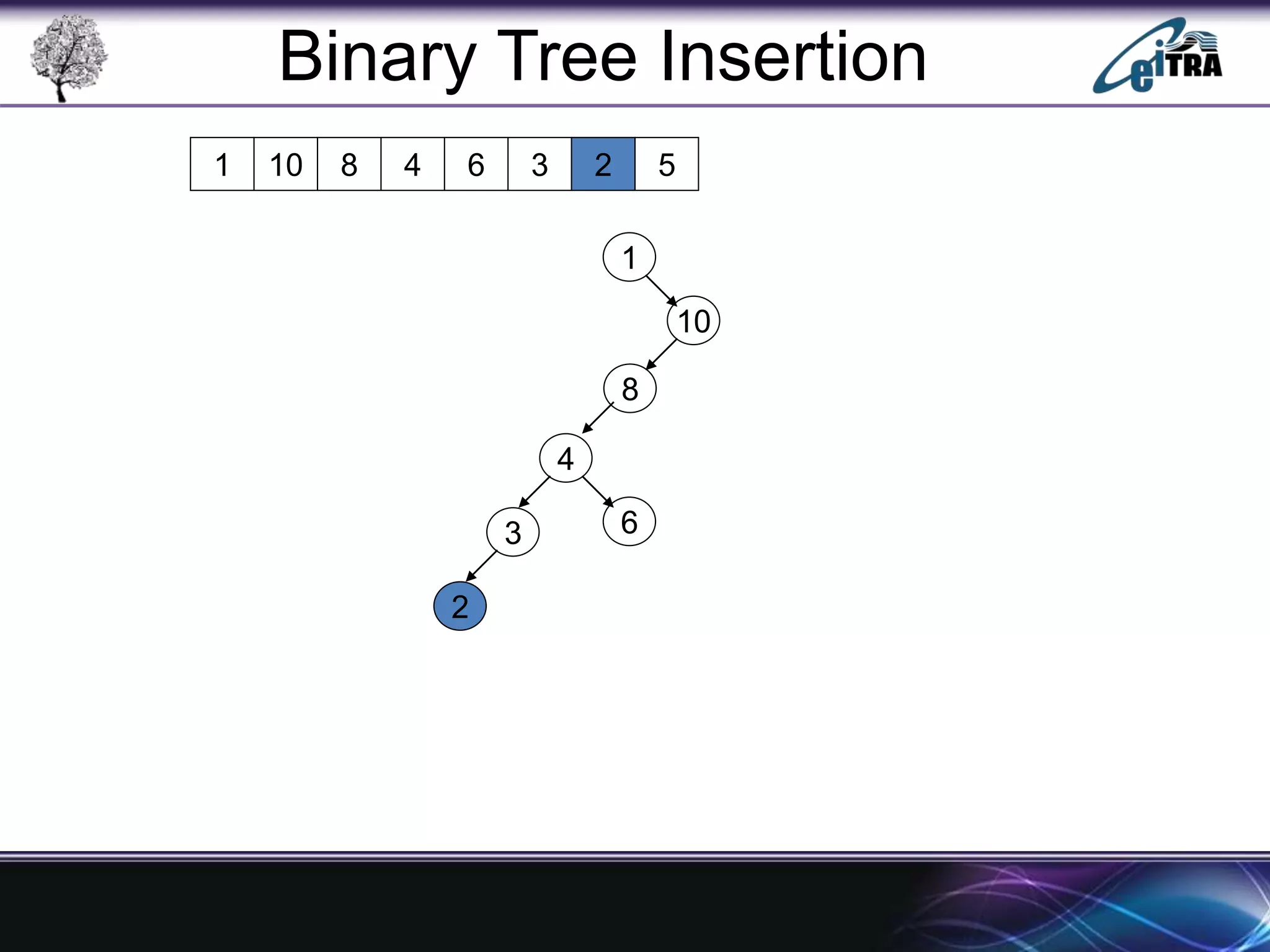
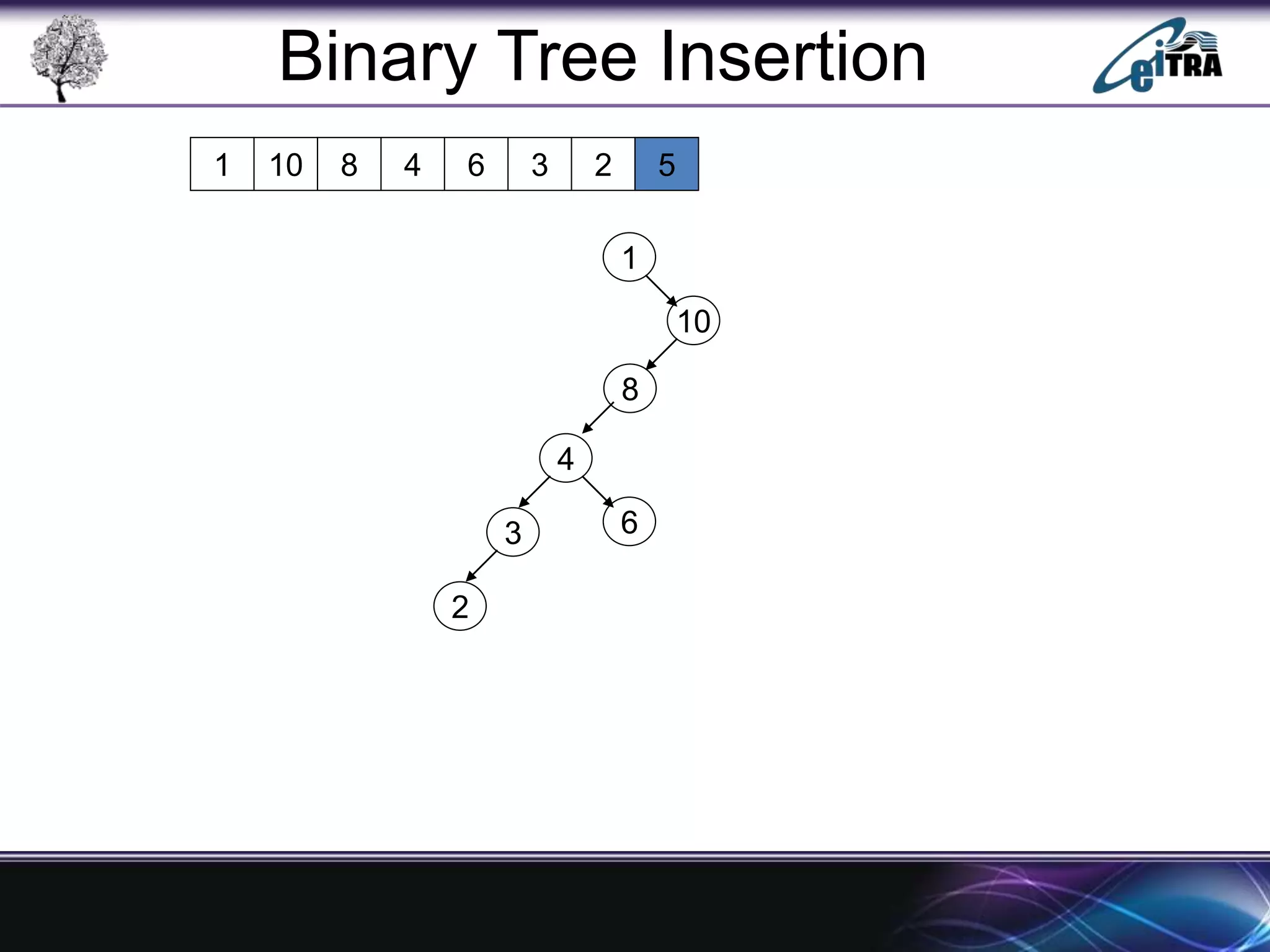
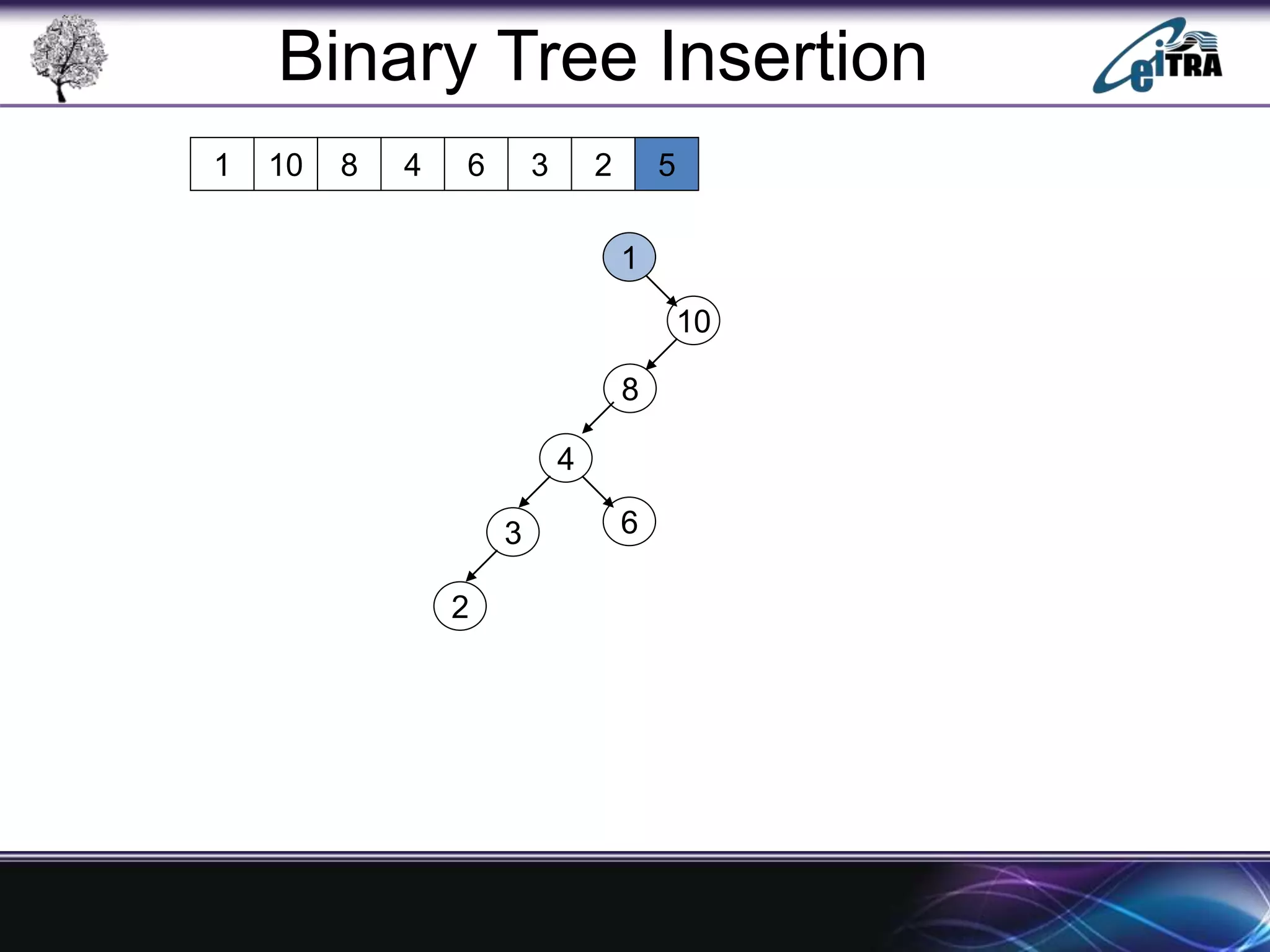
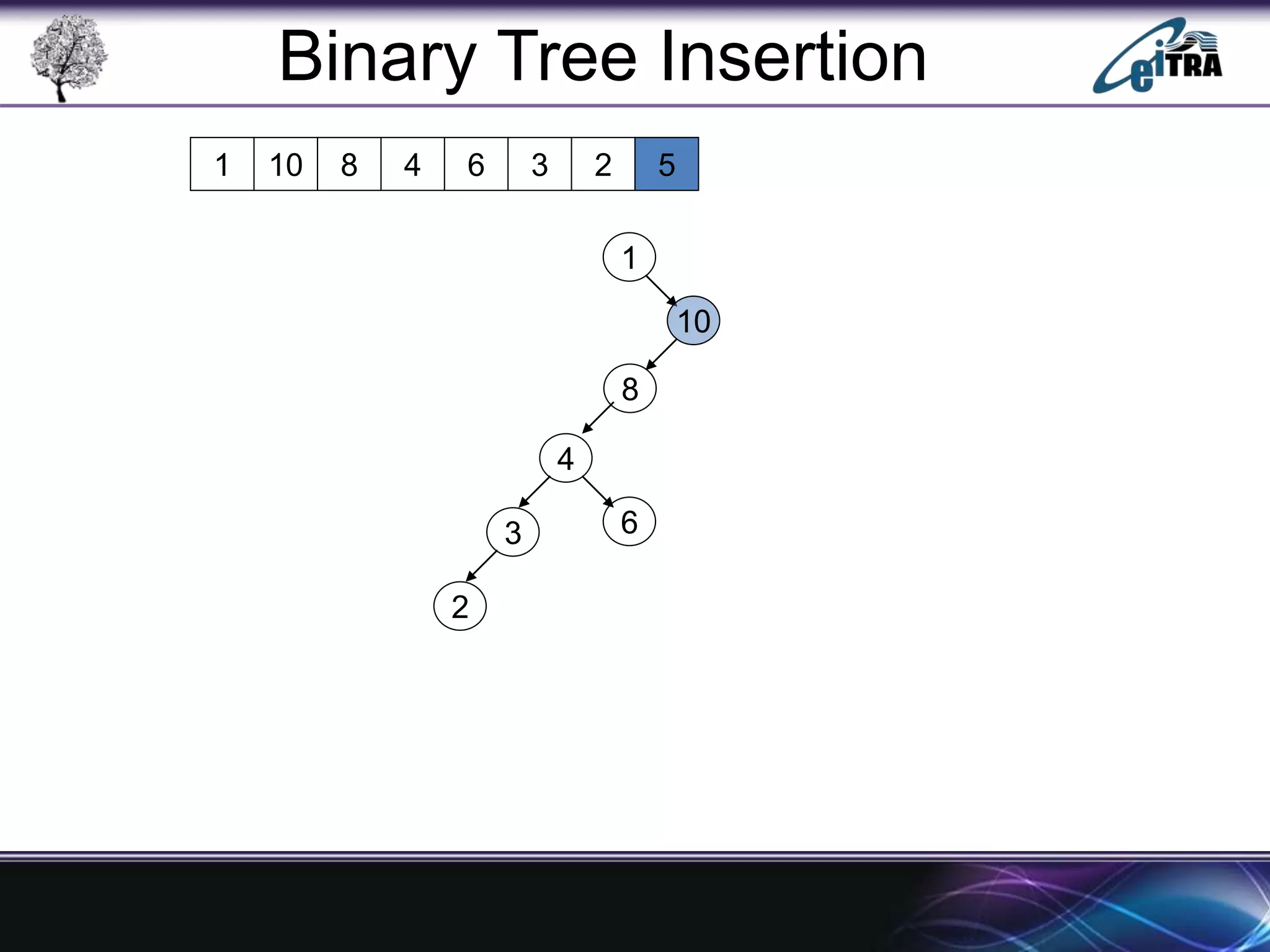
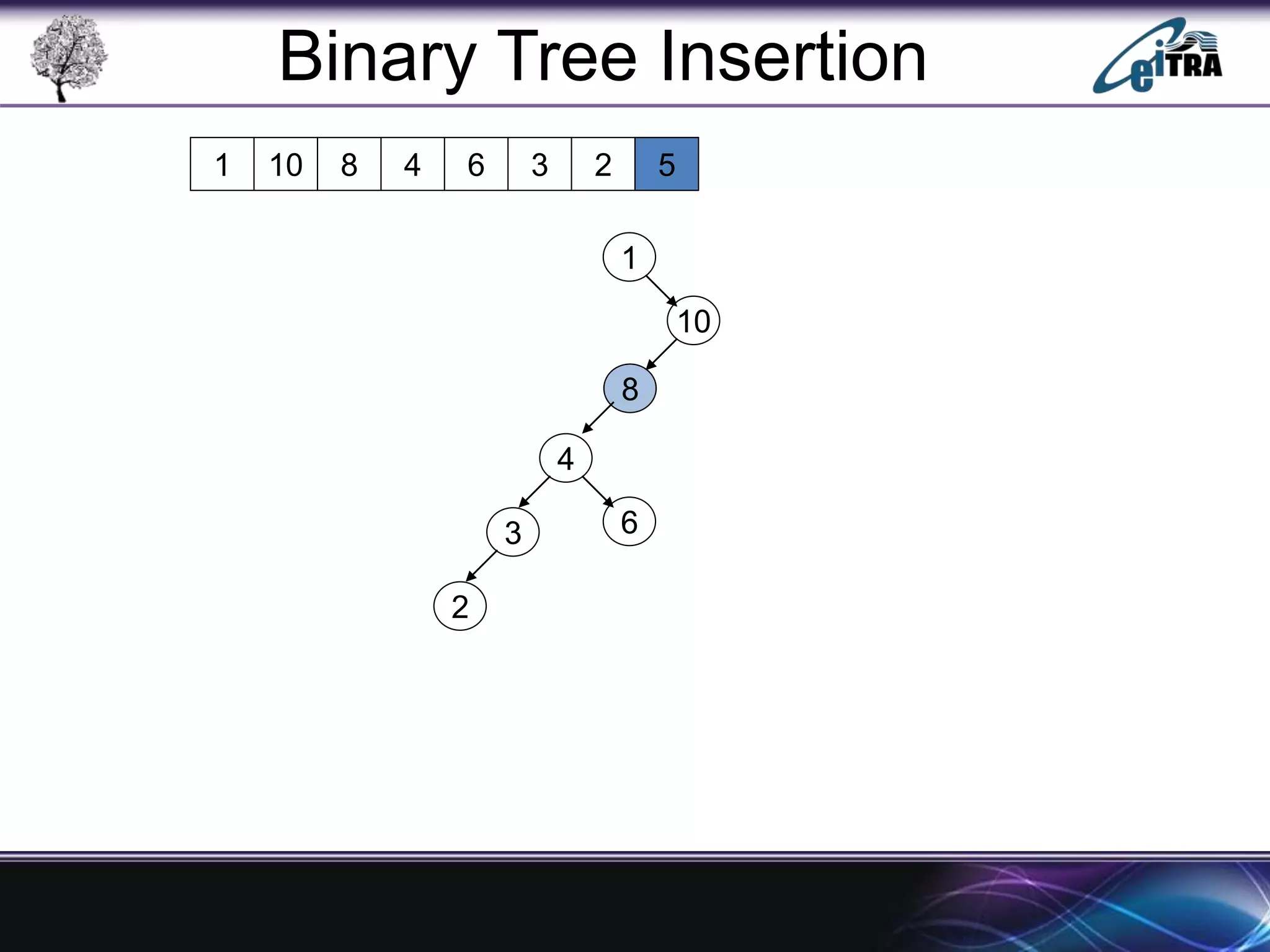
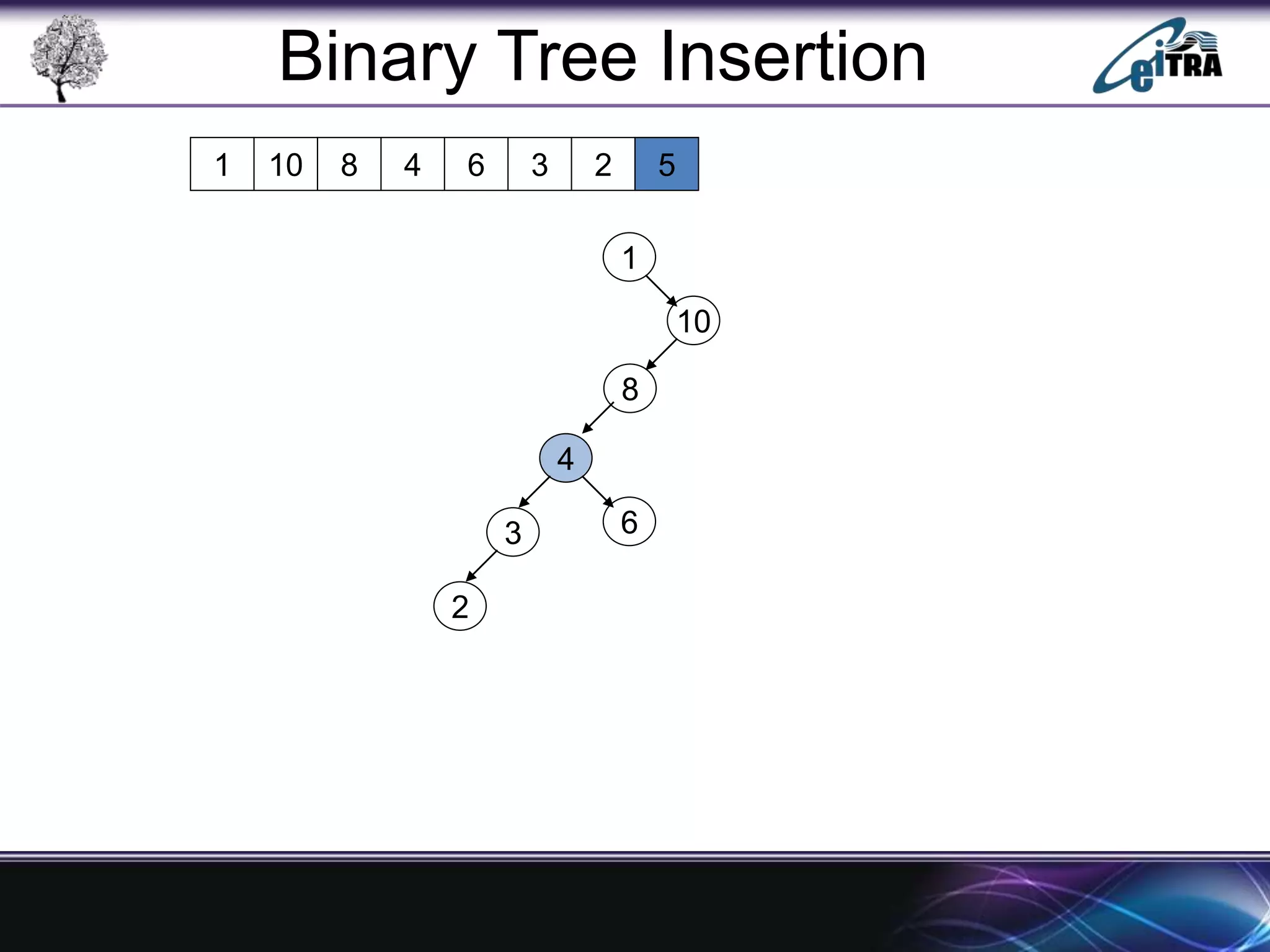
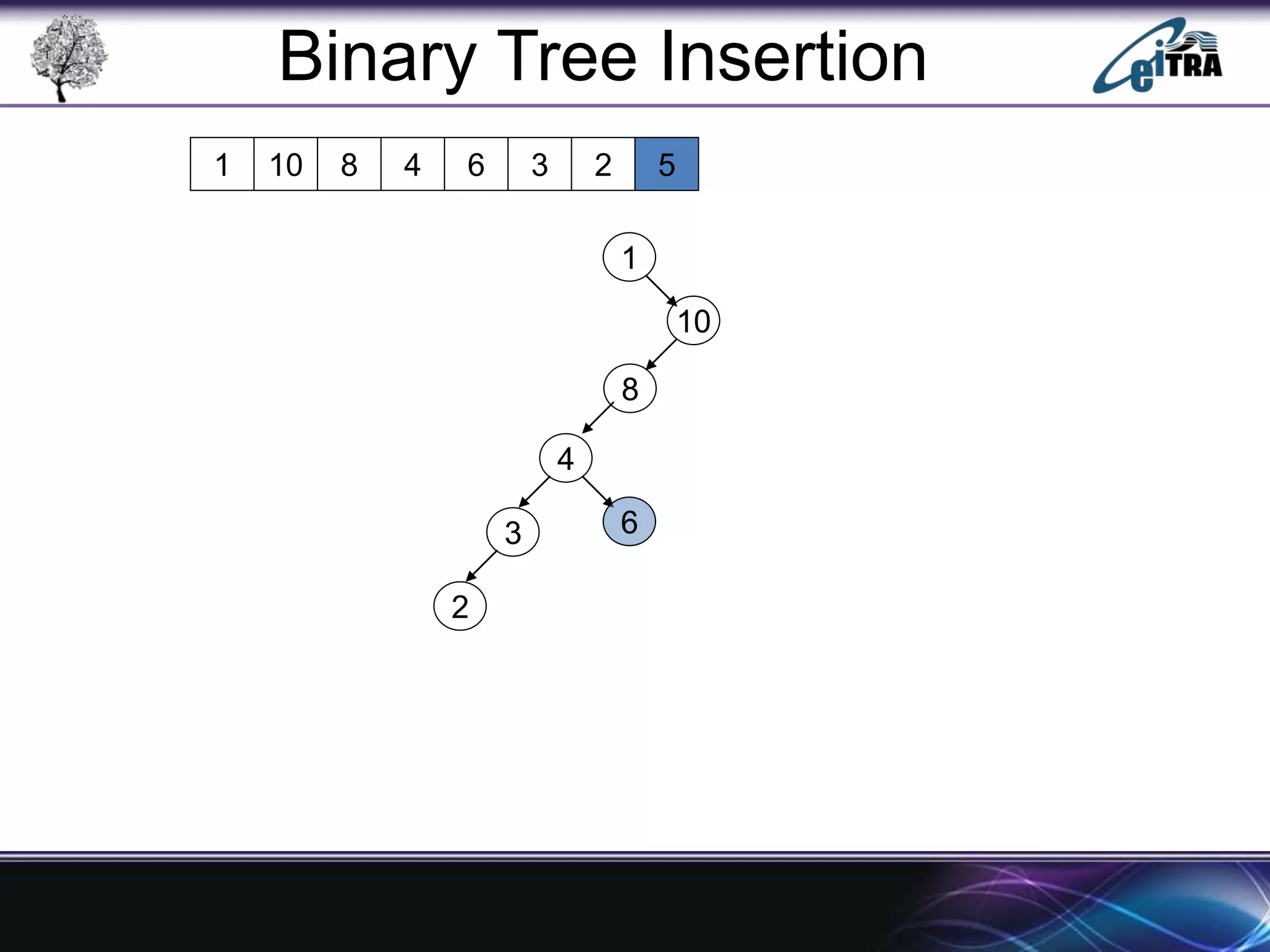
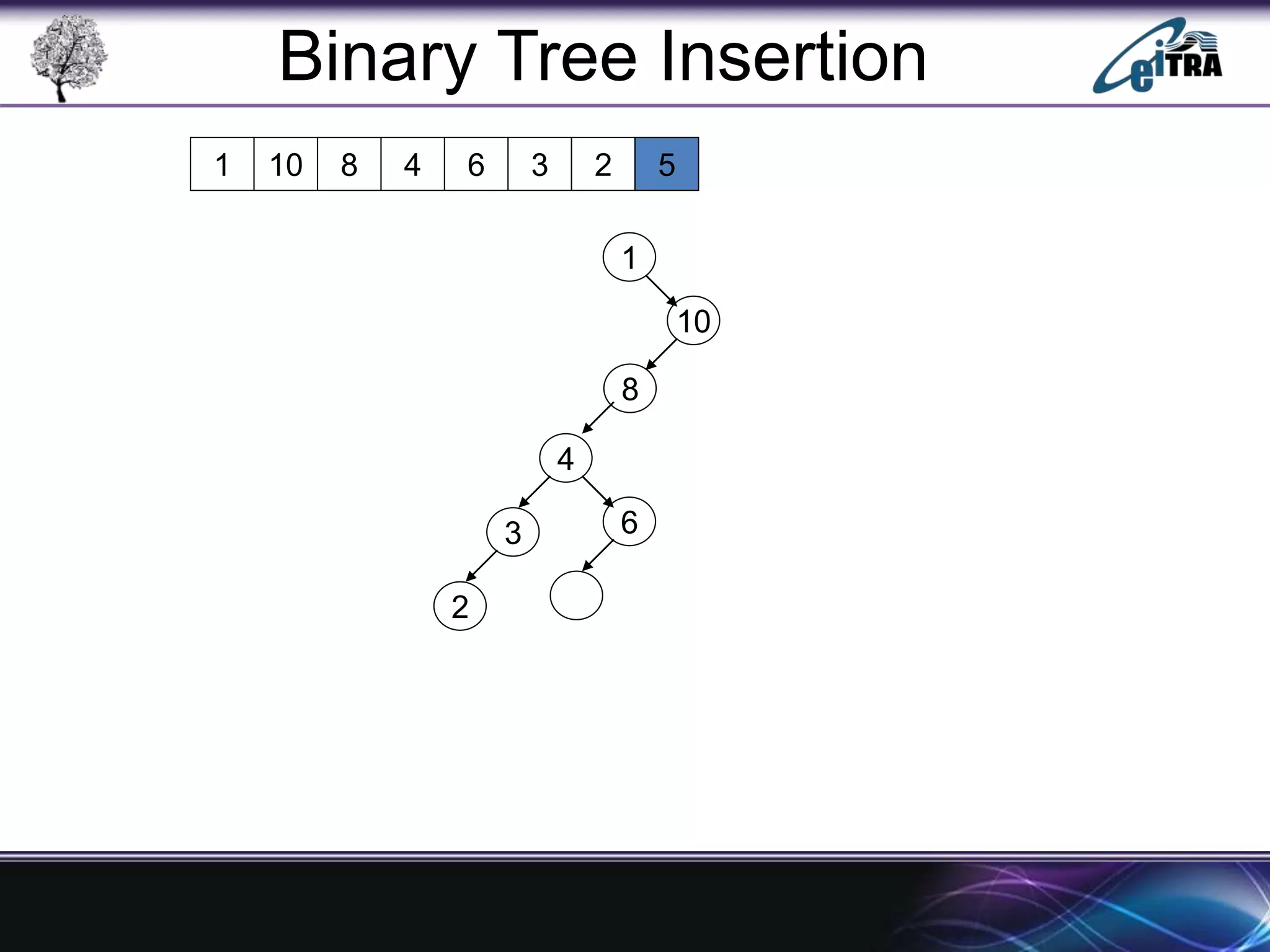
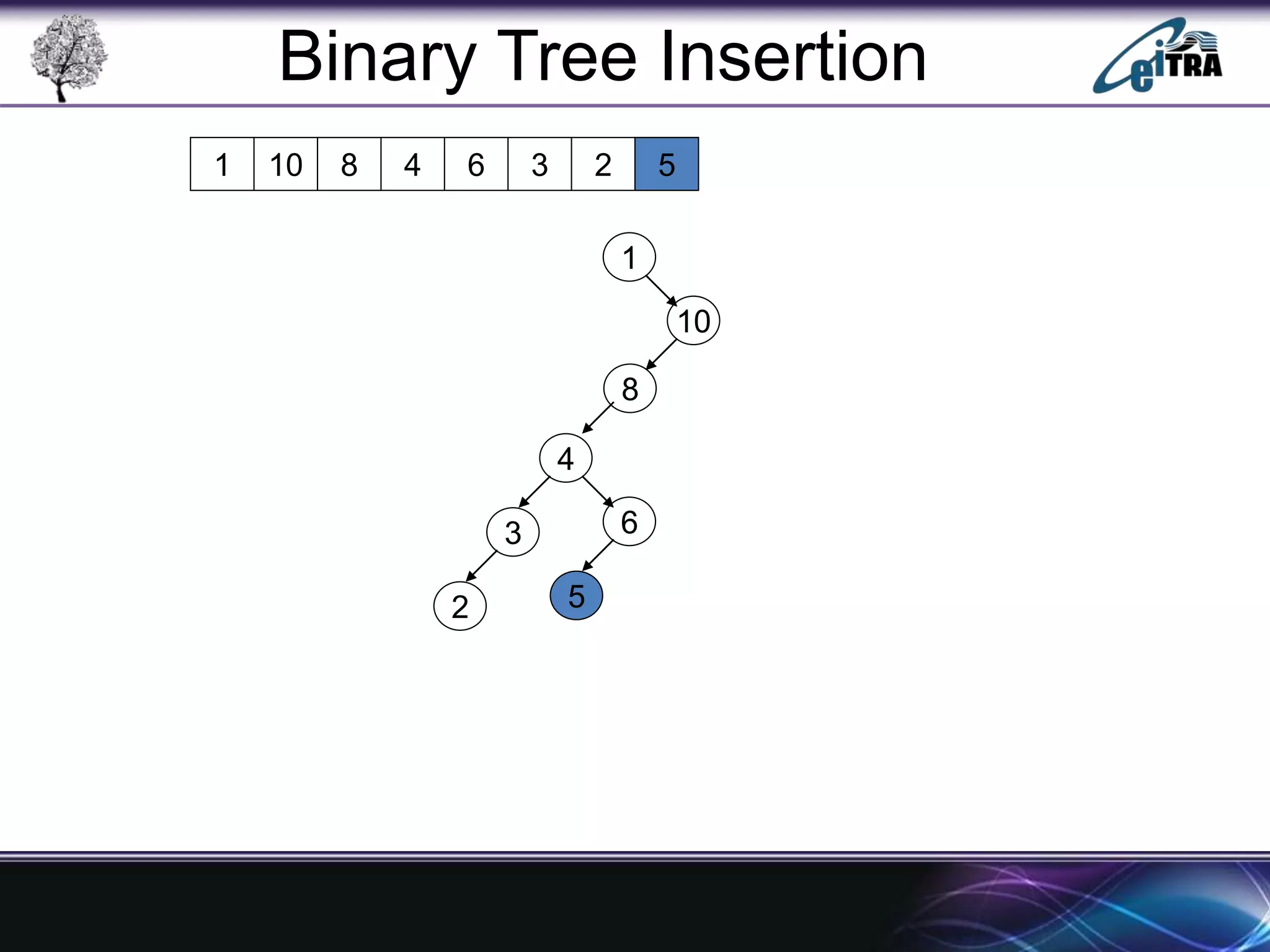
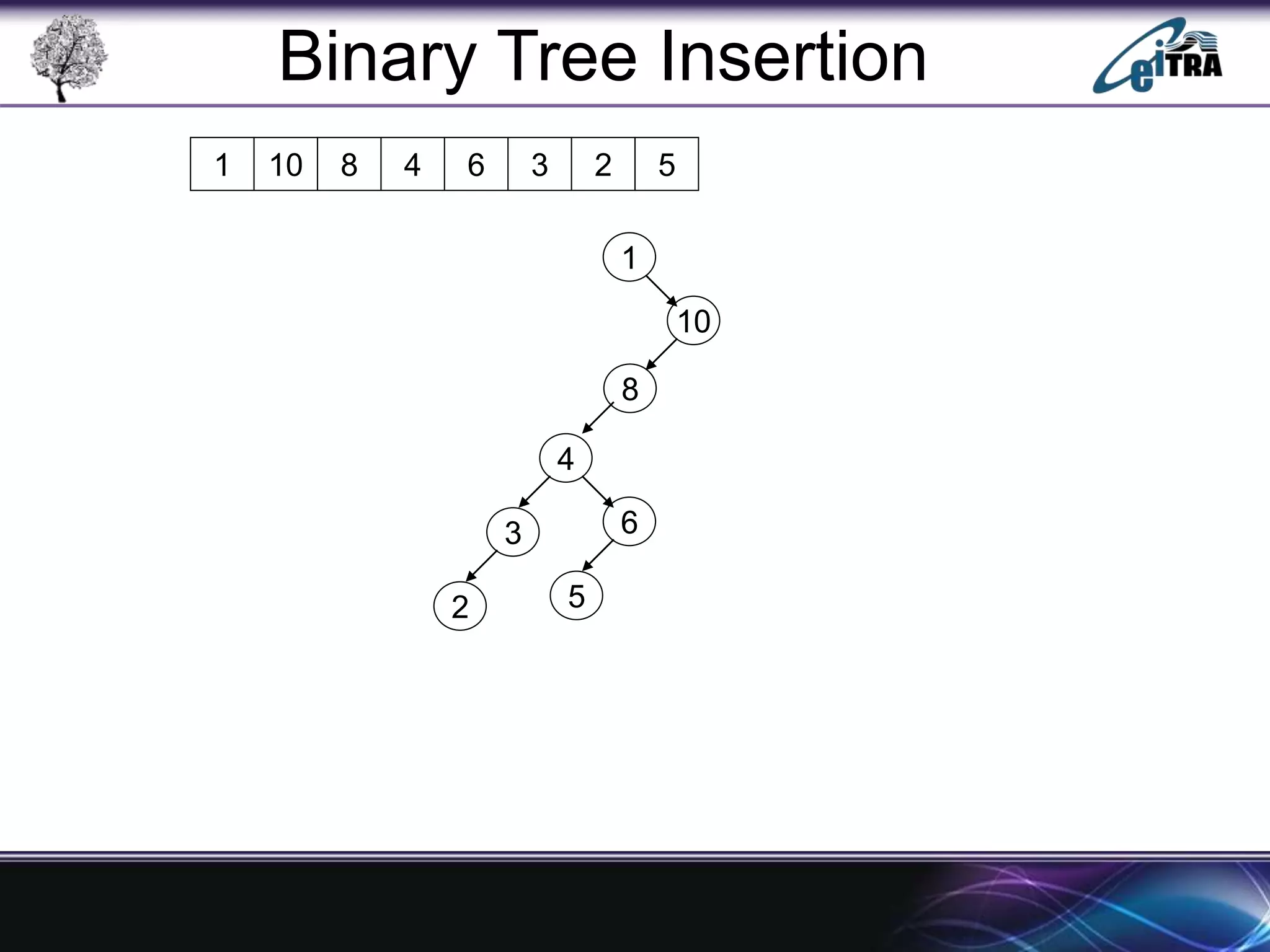
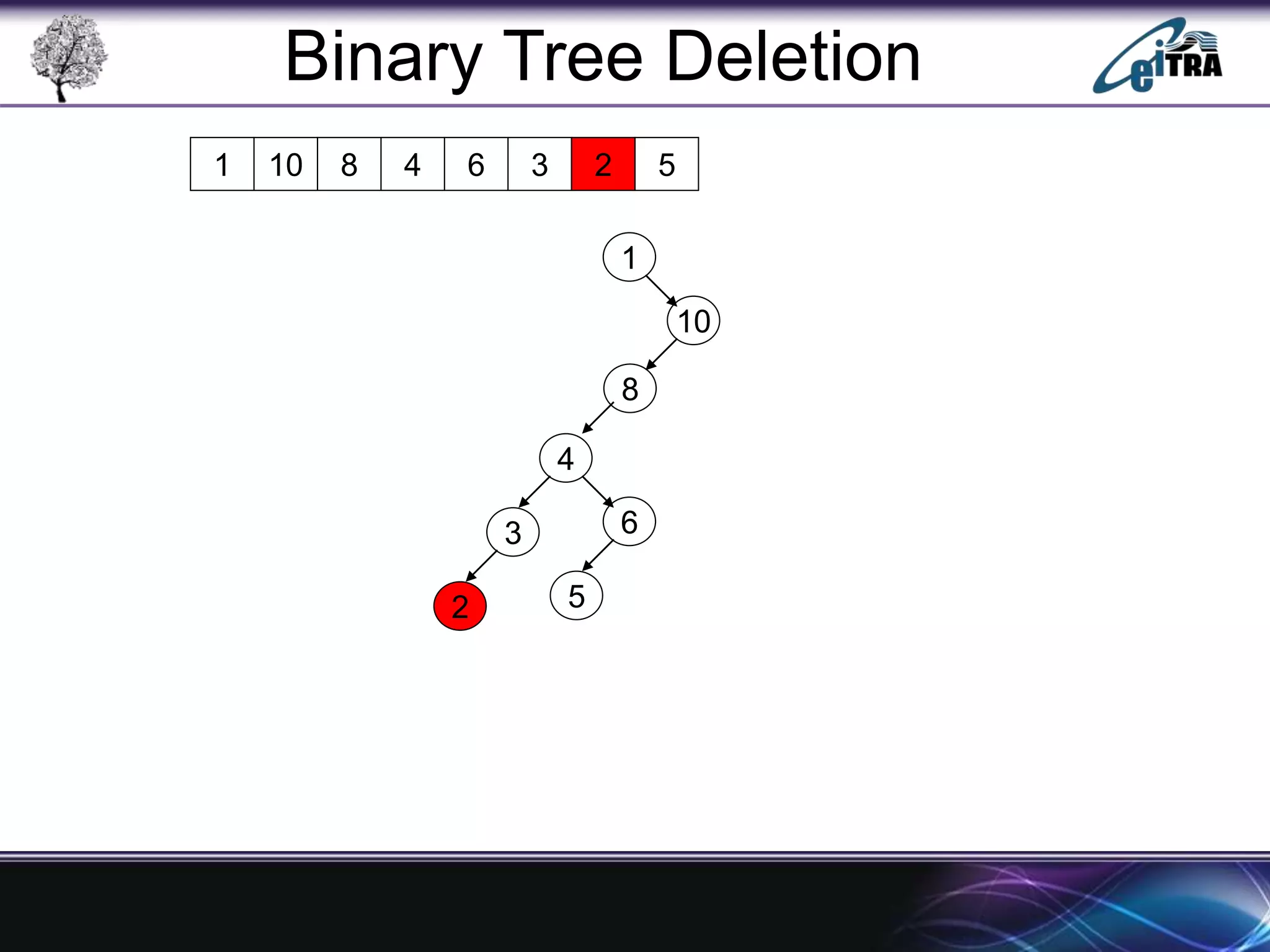
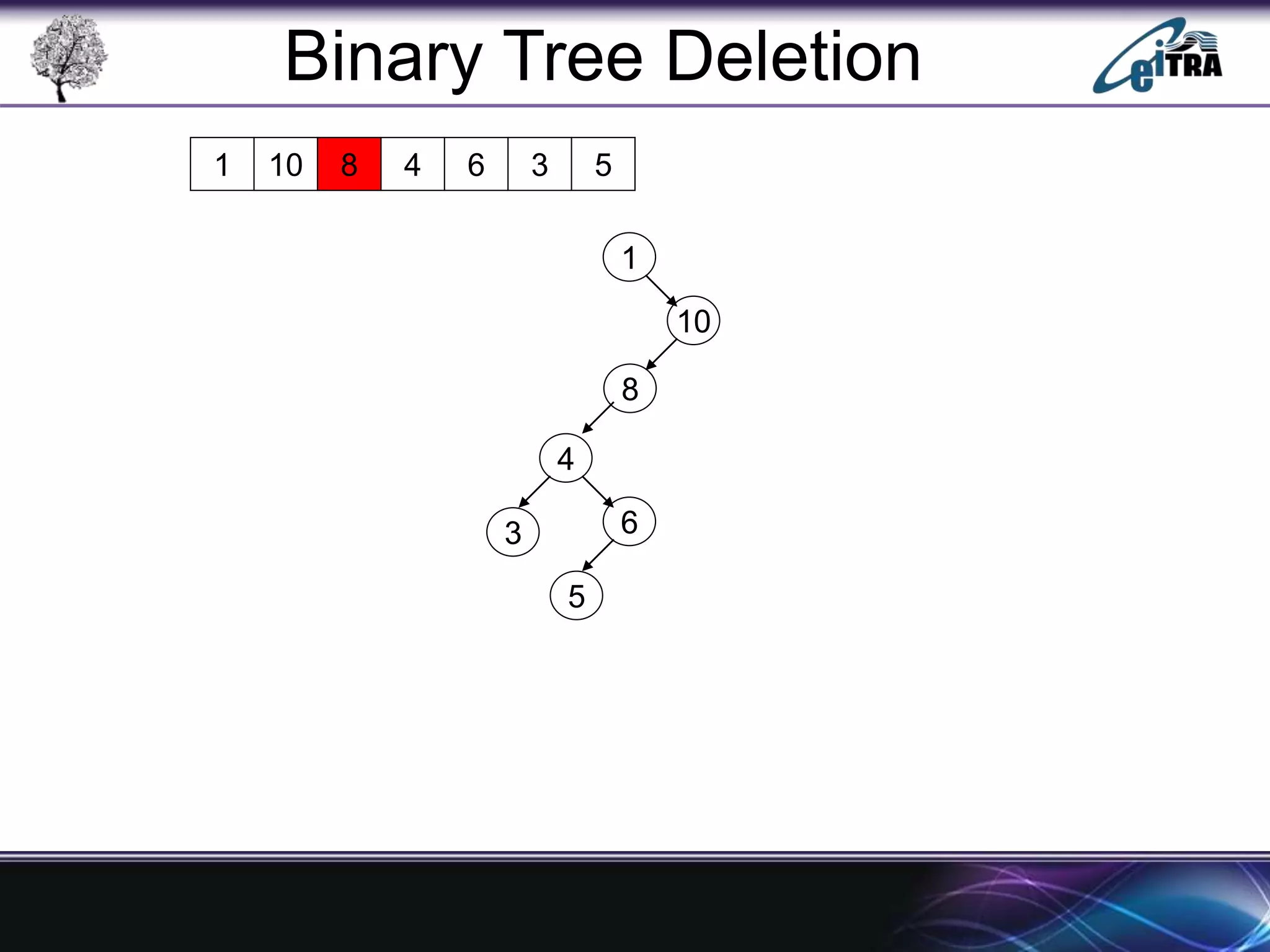
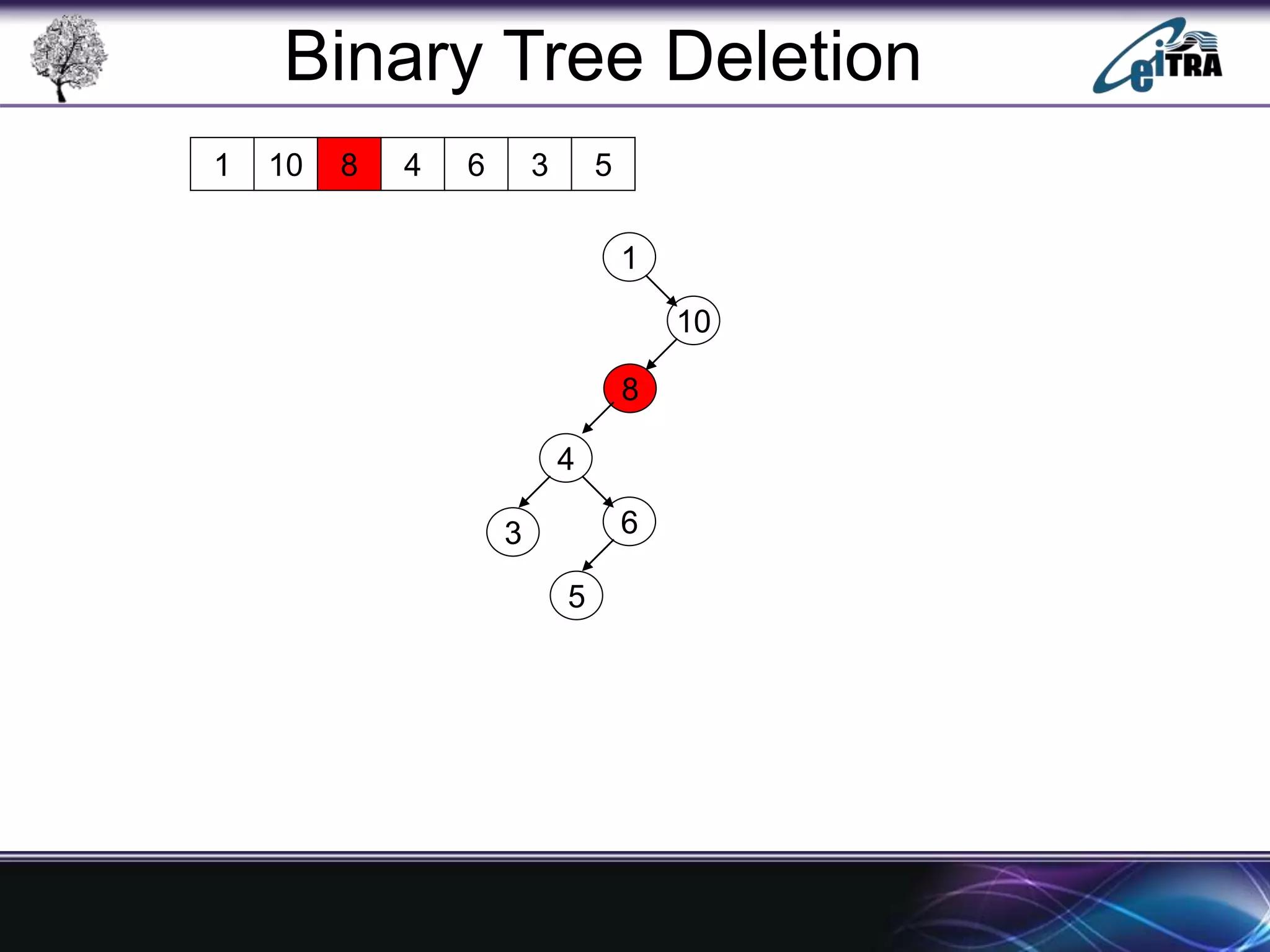
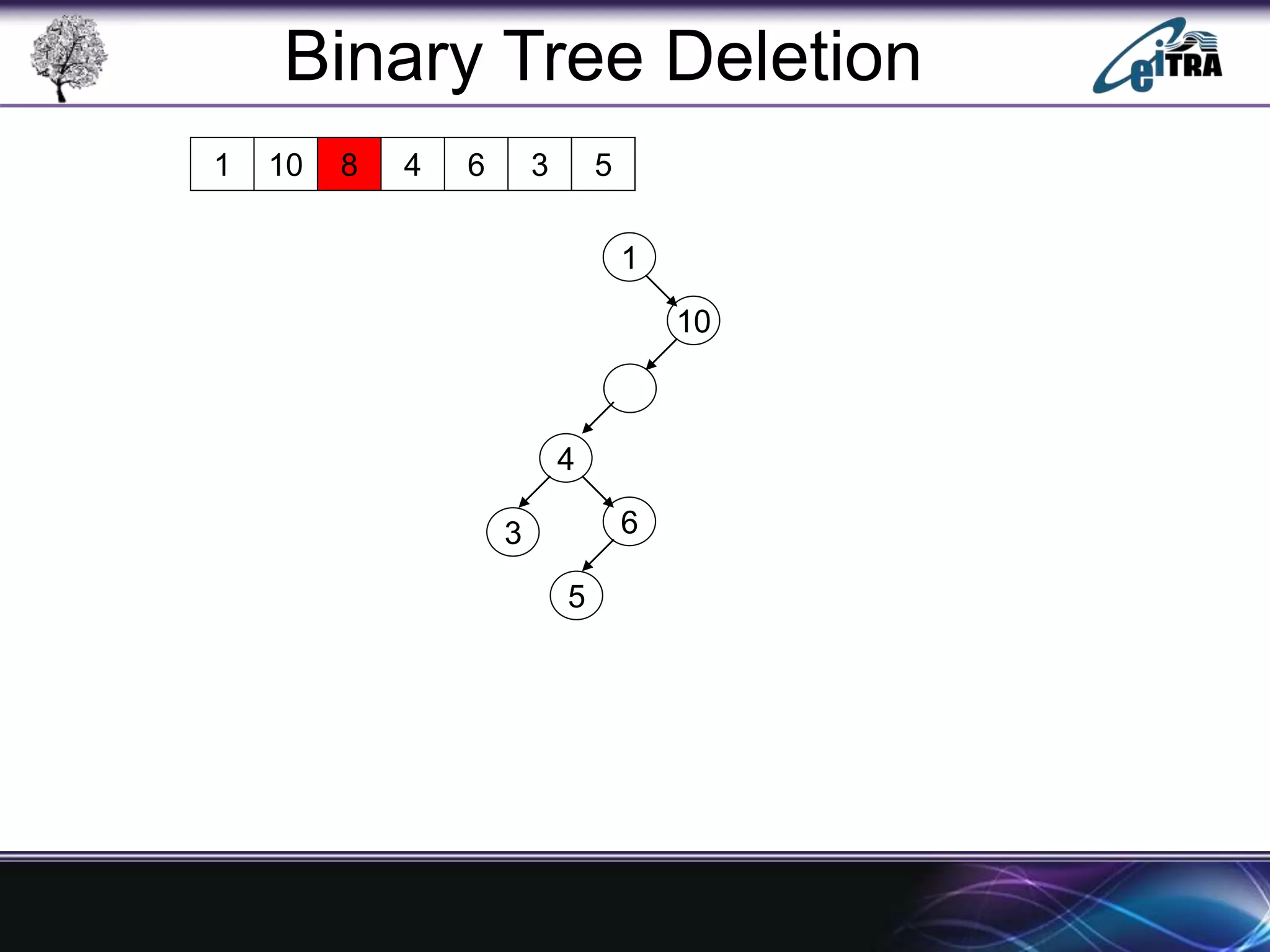
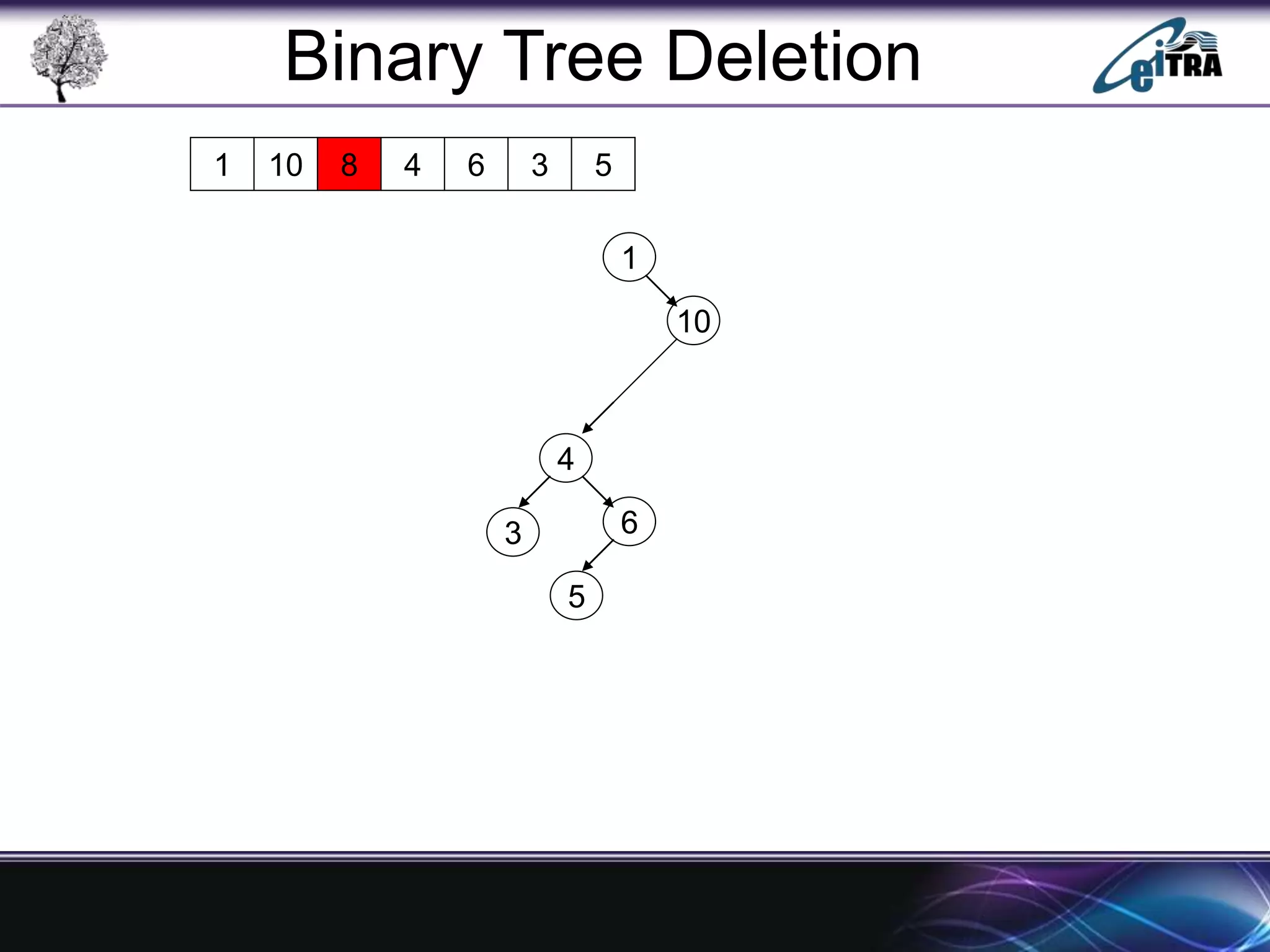
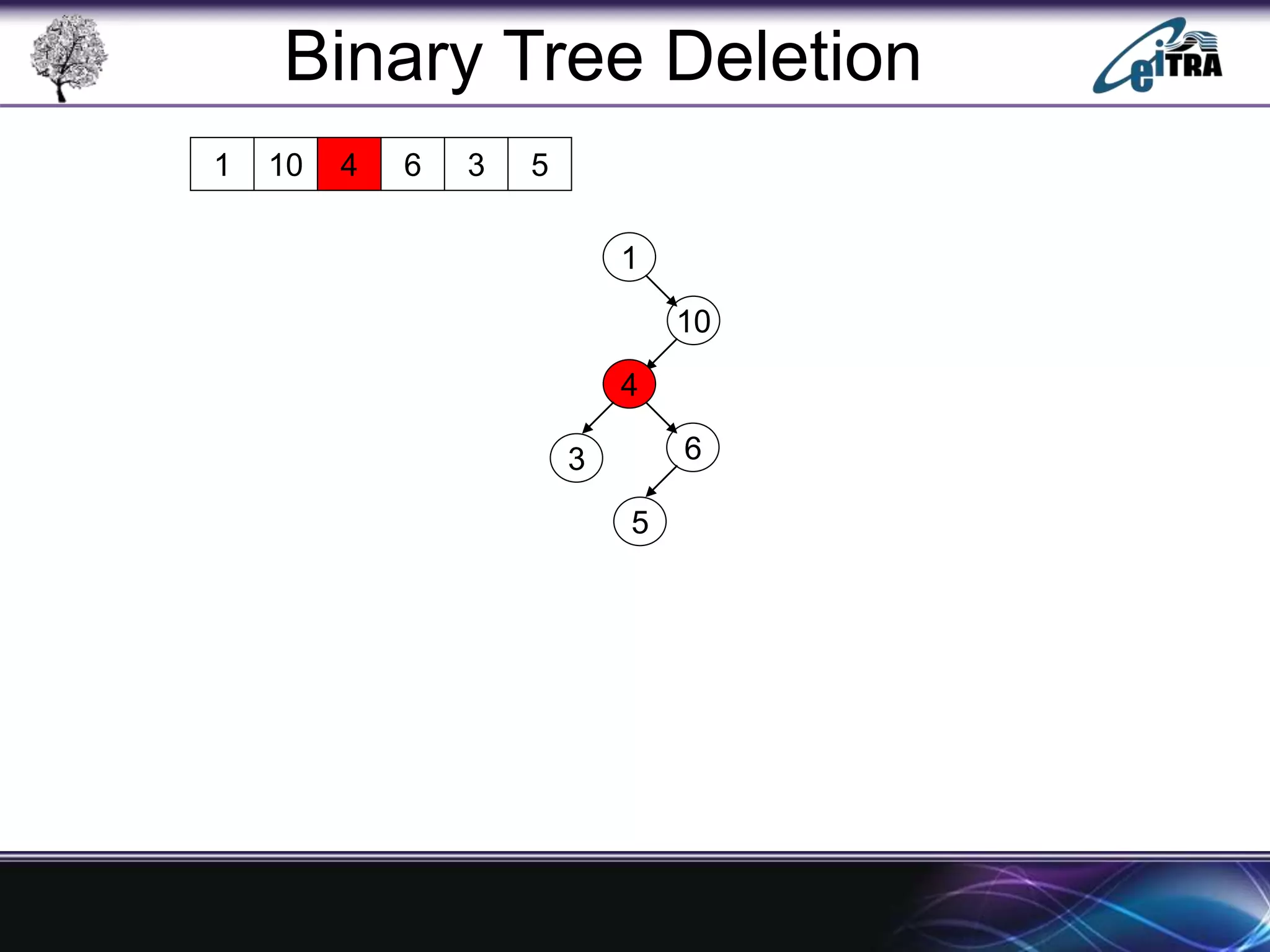
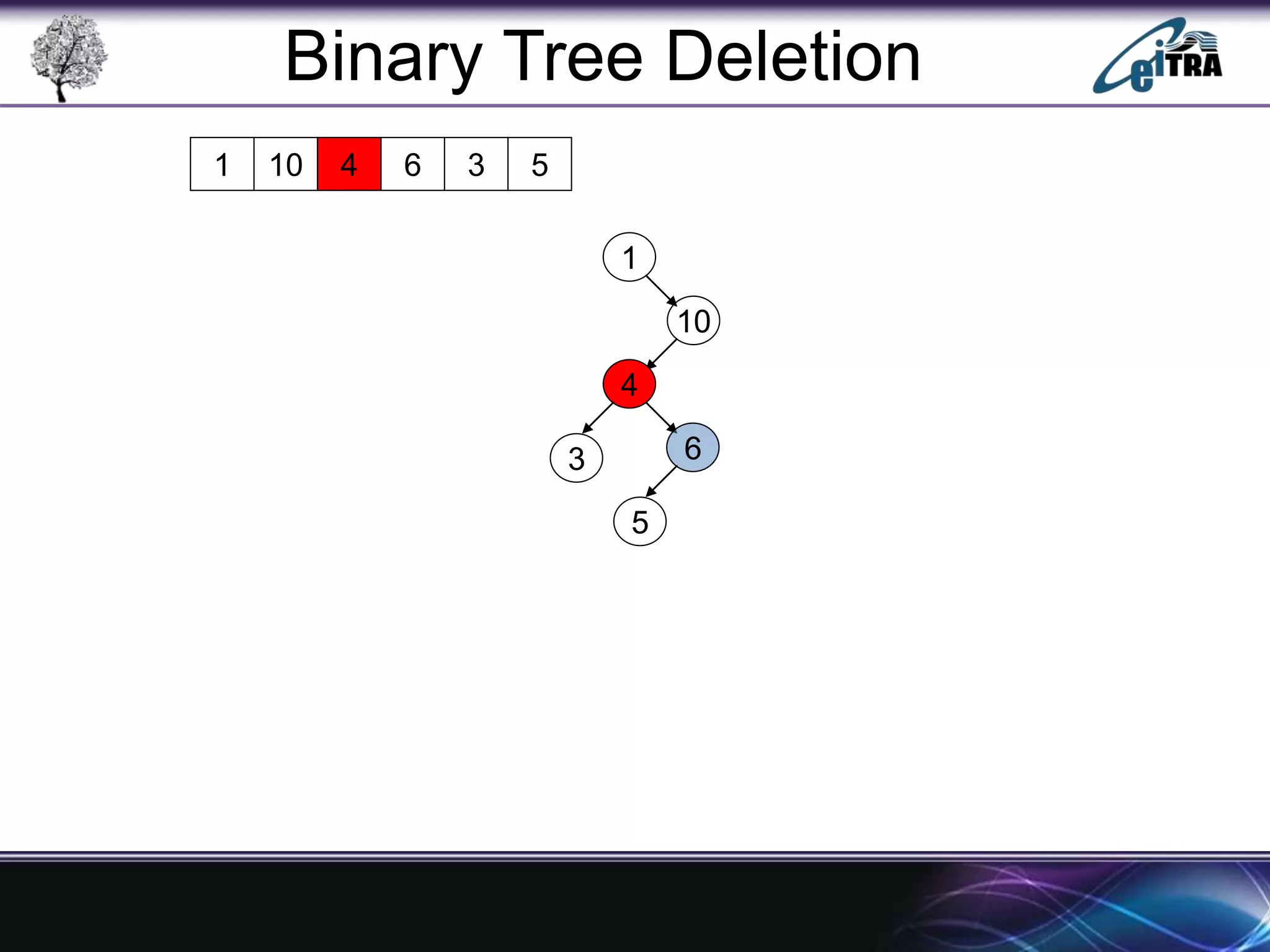
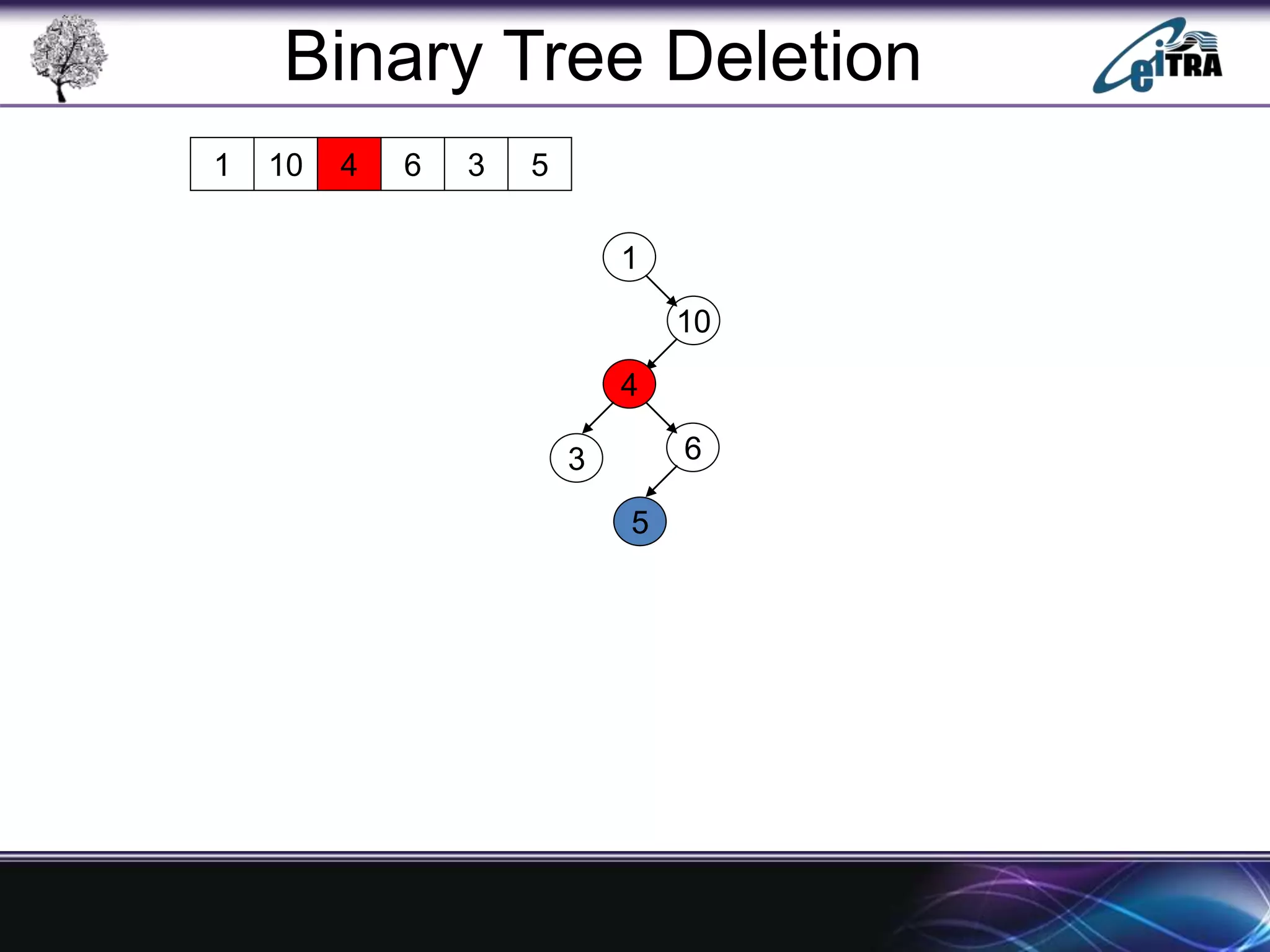
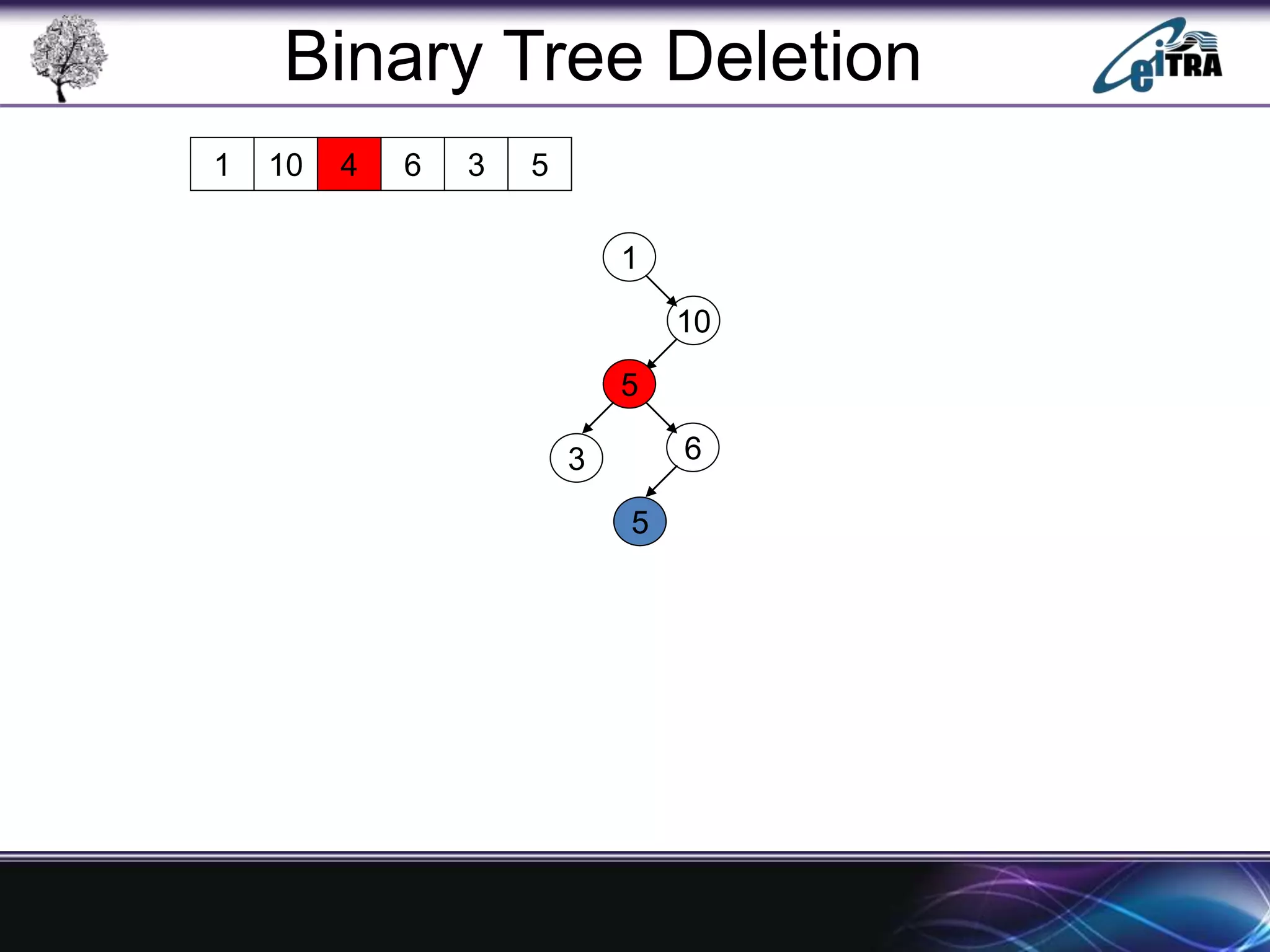
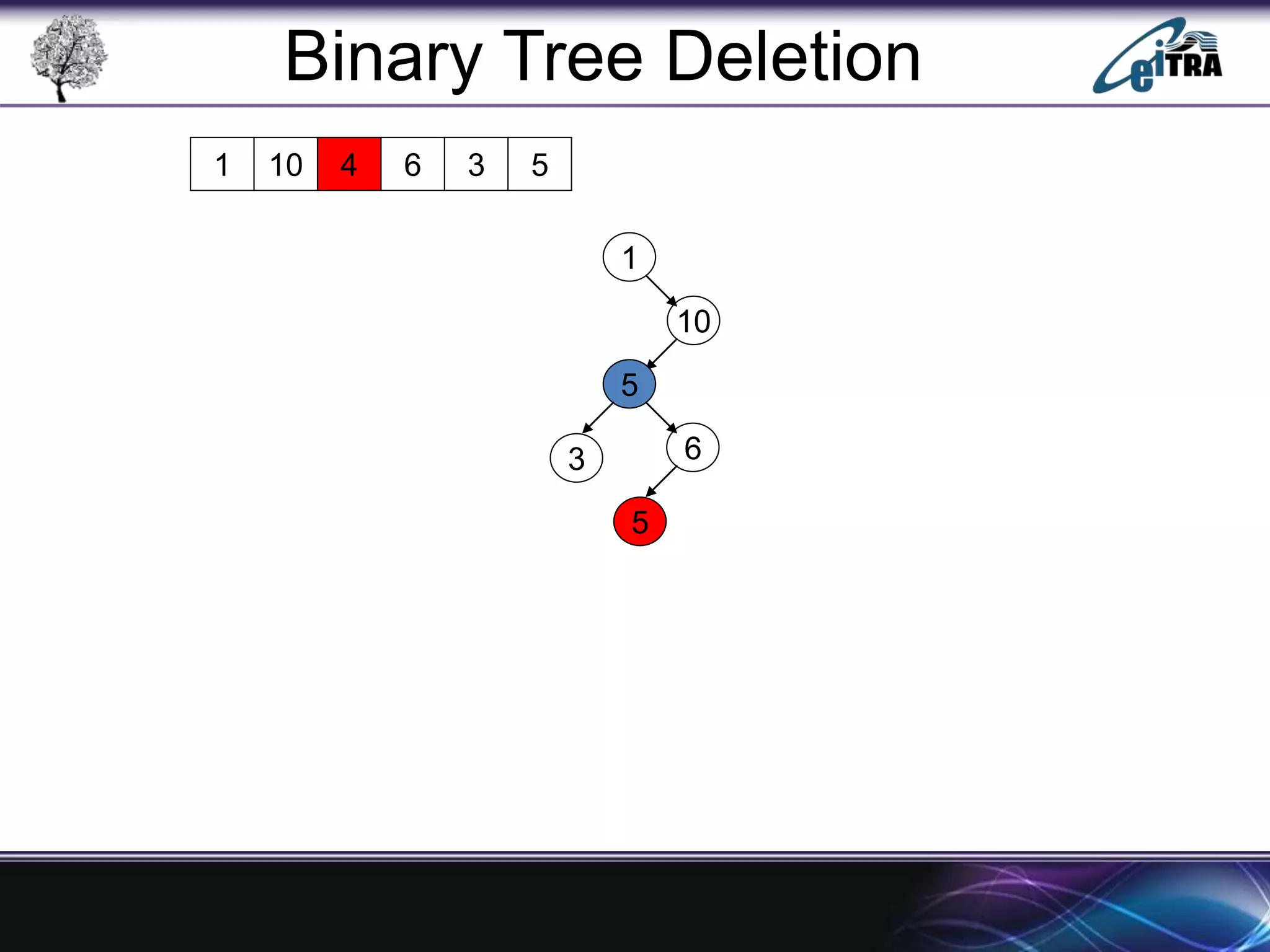
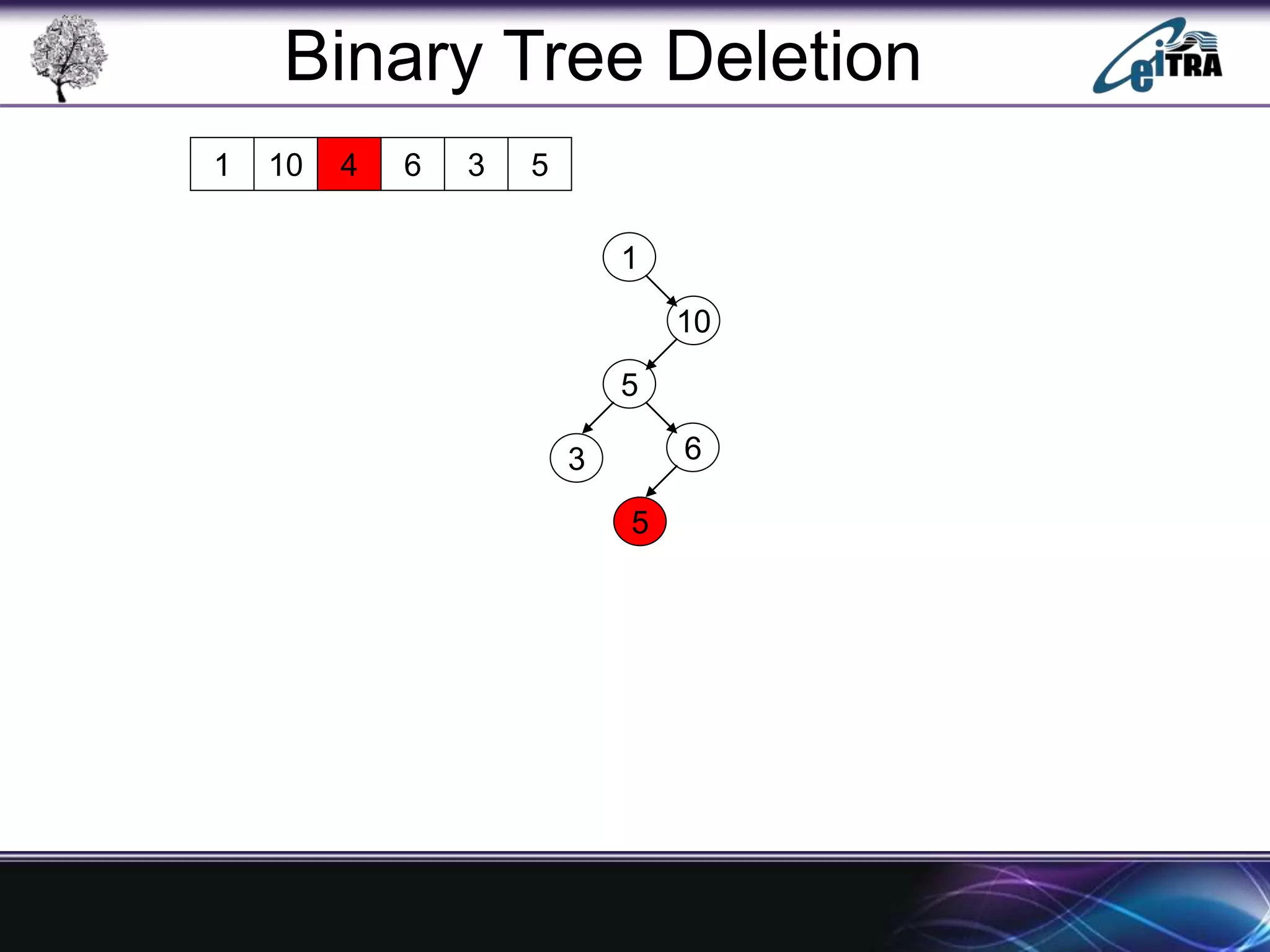
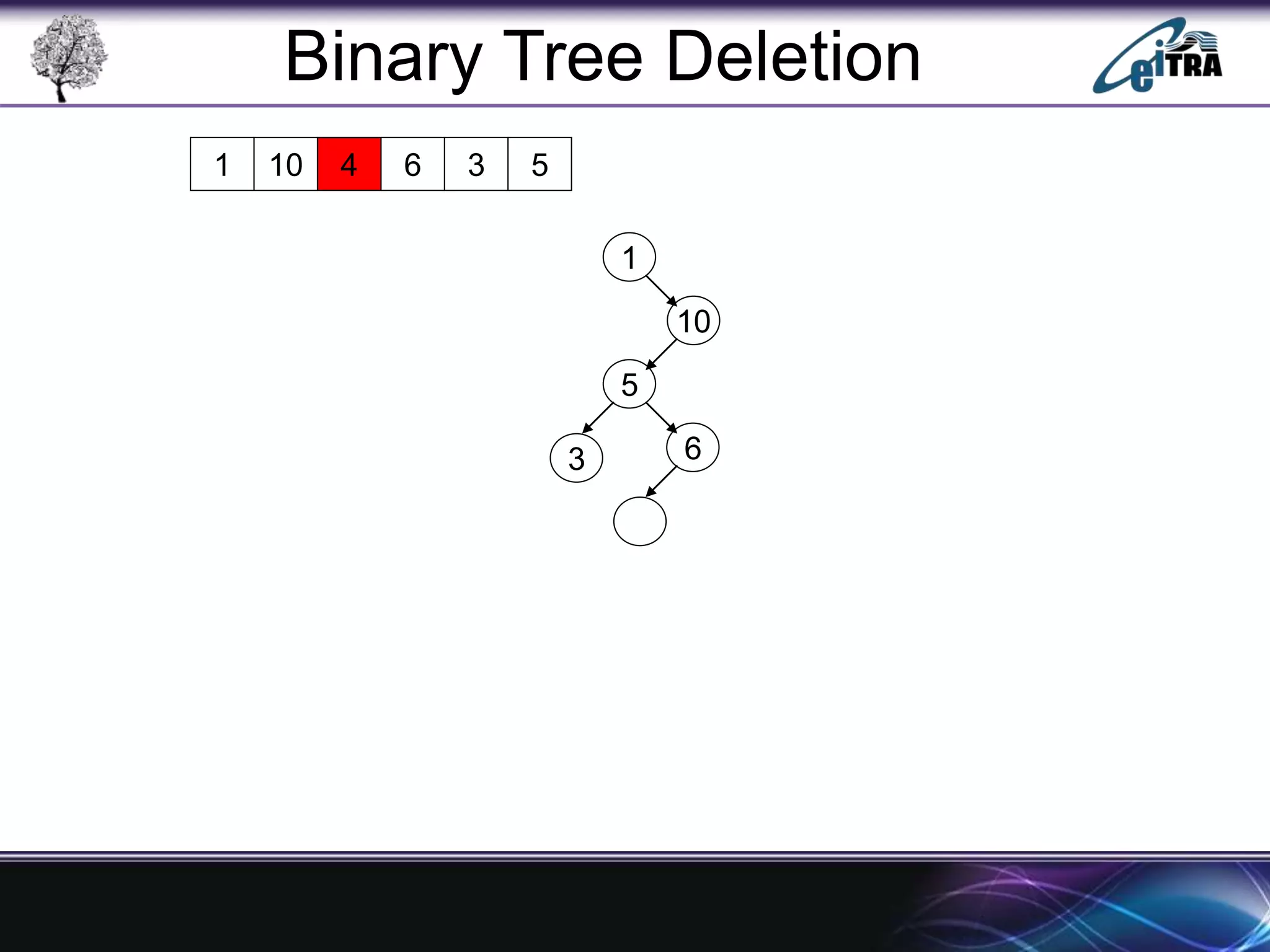
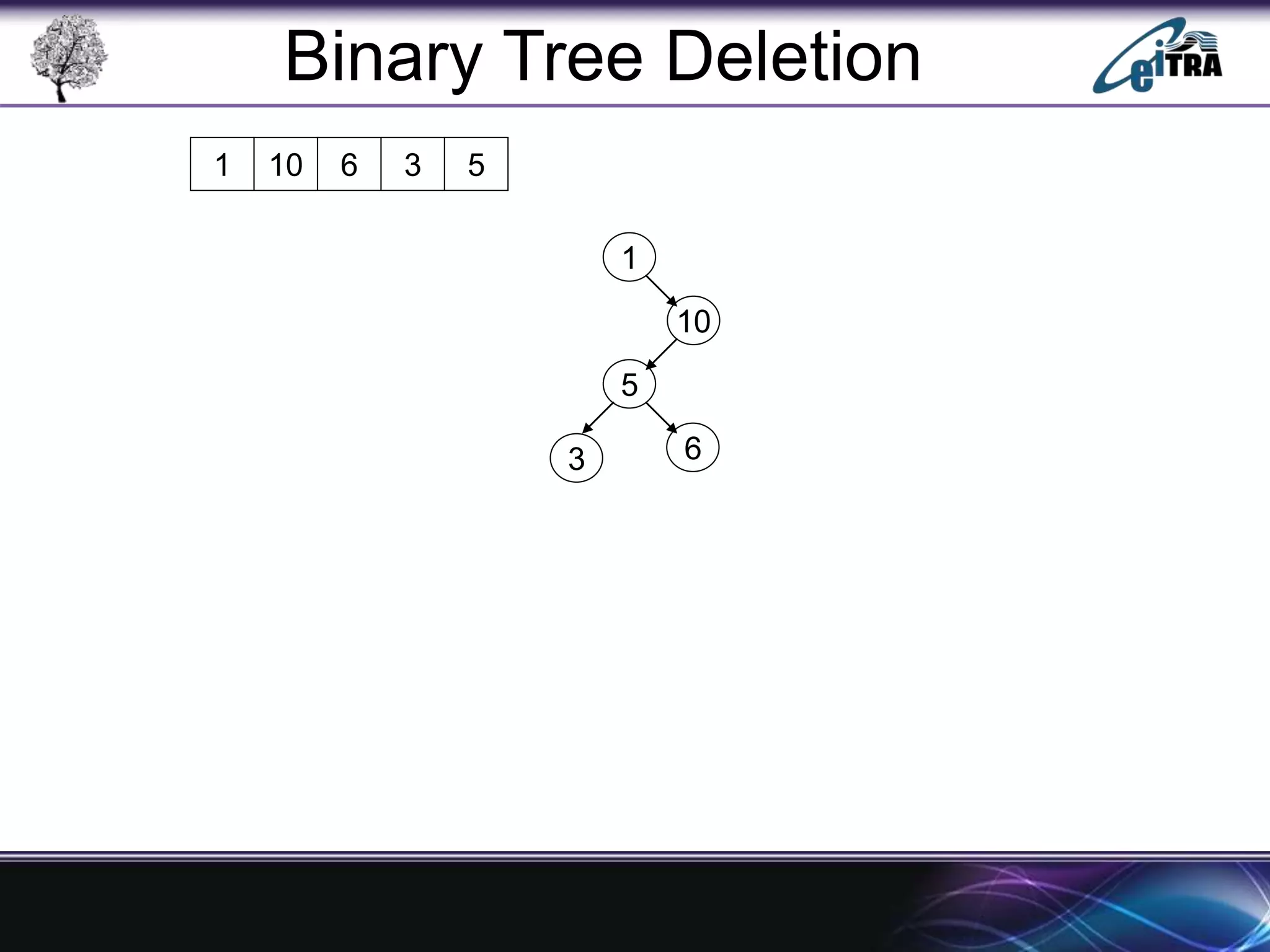
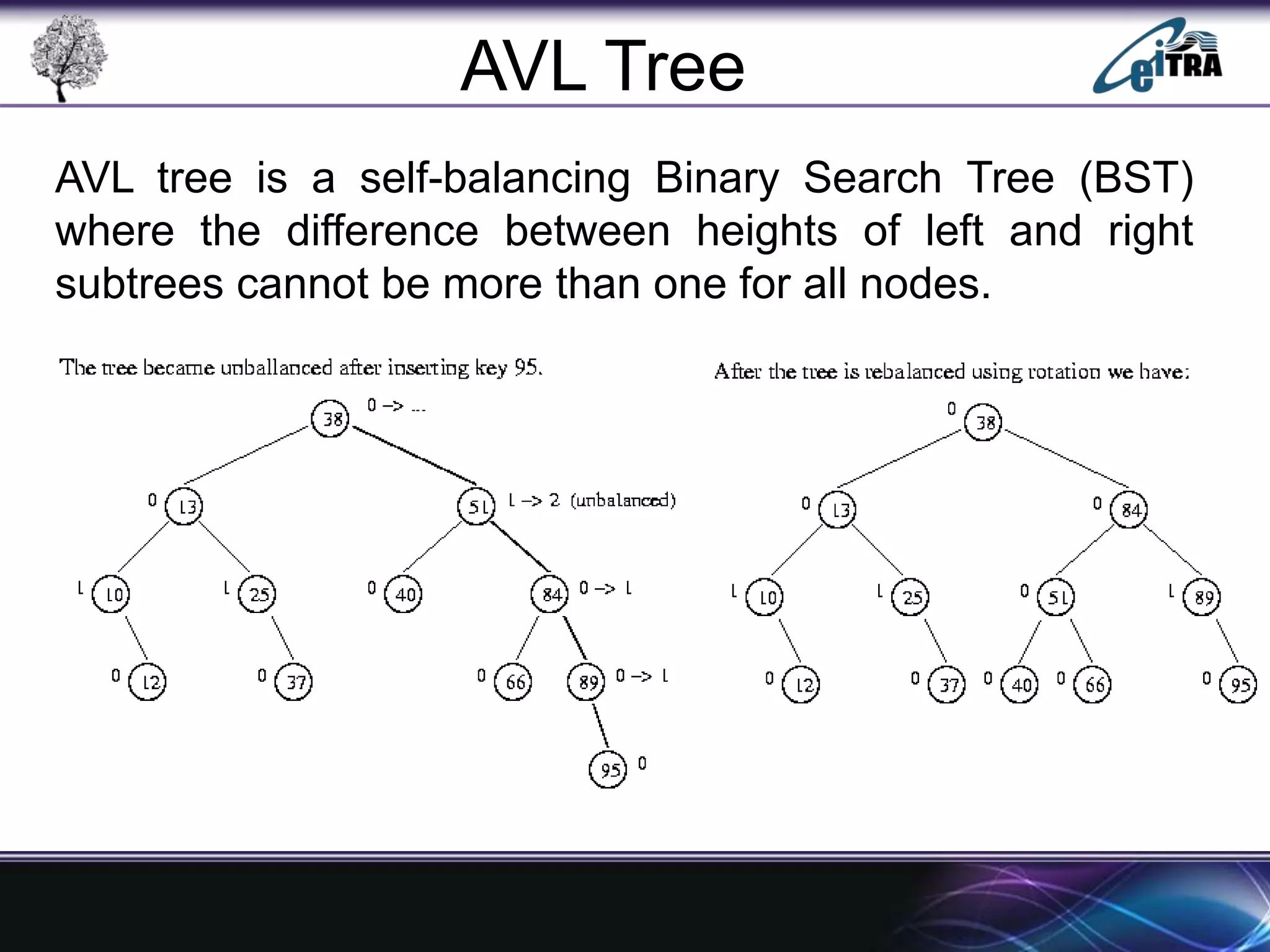
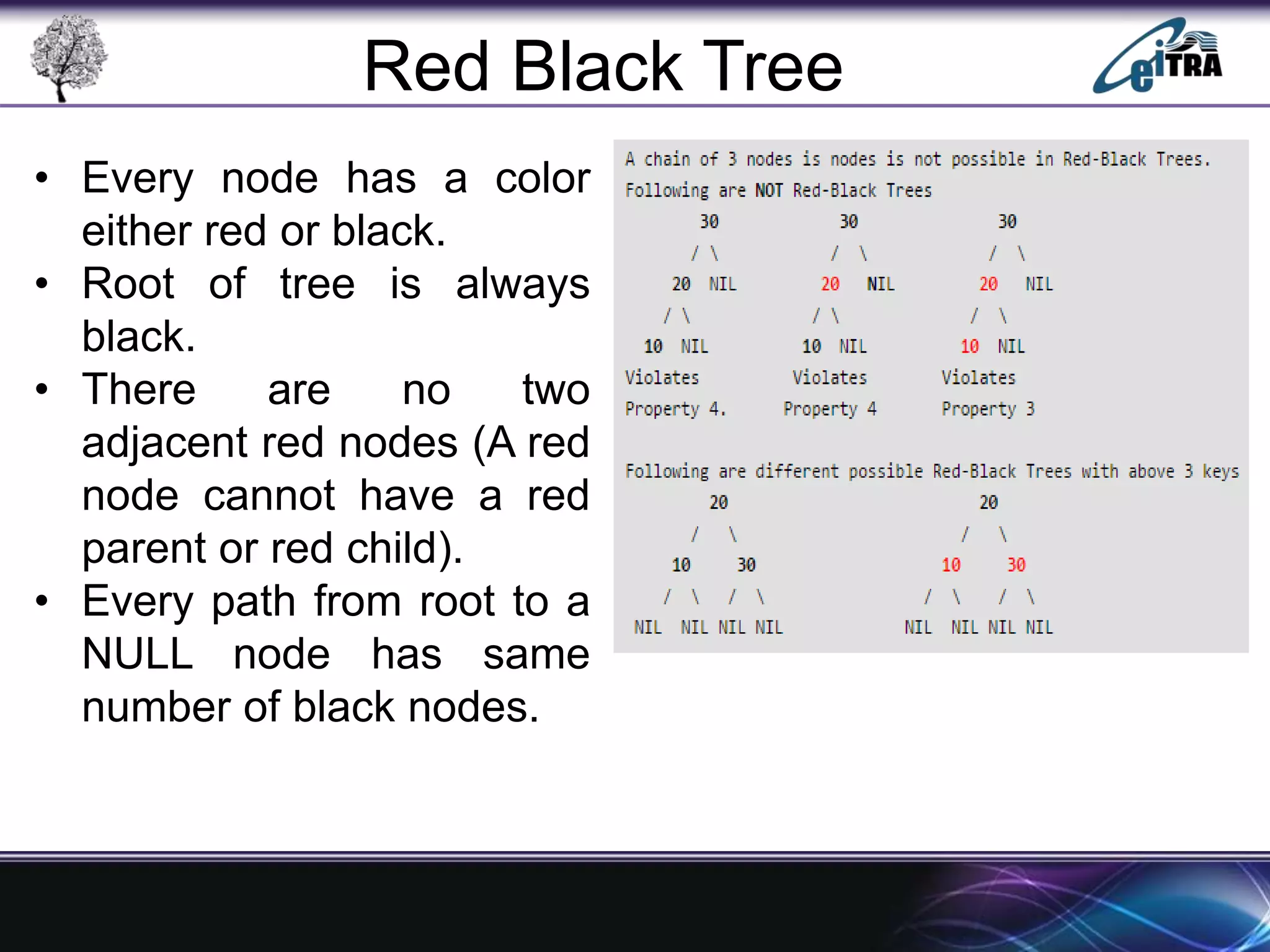
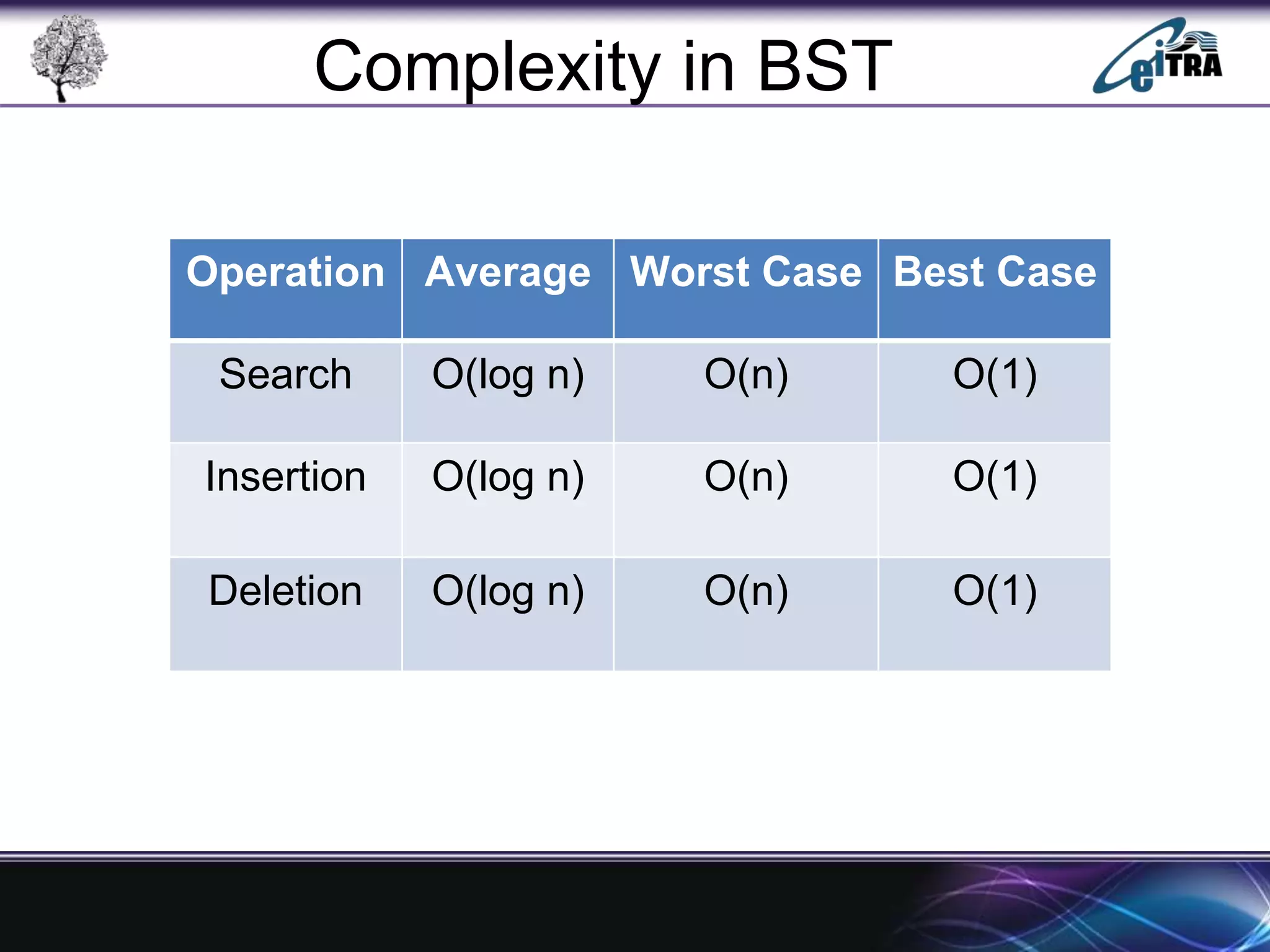
The document provides an overview of binary search trees (BST), detailing their structure, implementation, and core operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal methods. It distinguishes between binary trees and binary search trees, emphasizing the rules that govern node value placements within a BST. Additionally, it discusses complexities involved in BST operations and mentions various types of trees, like red-black and AVL trees.