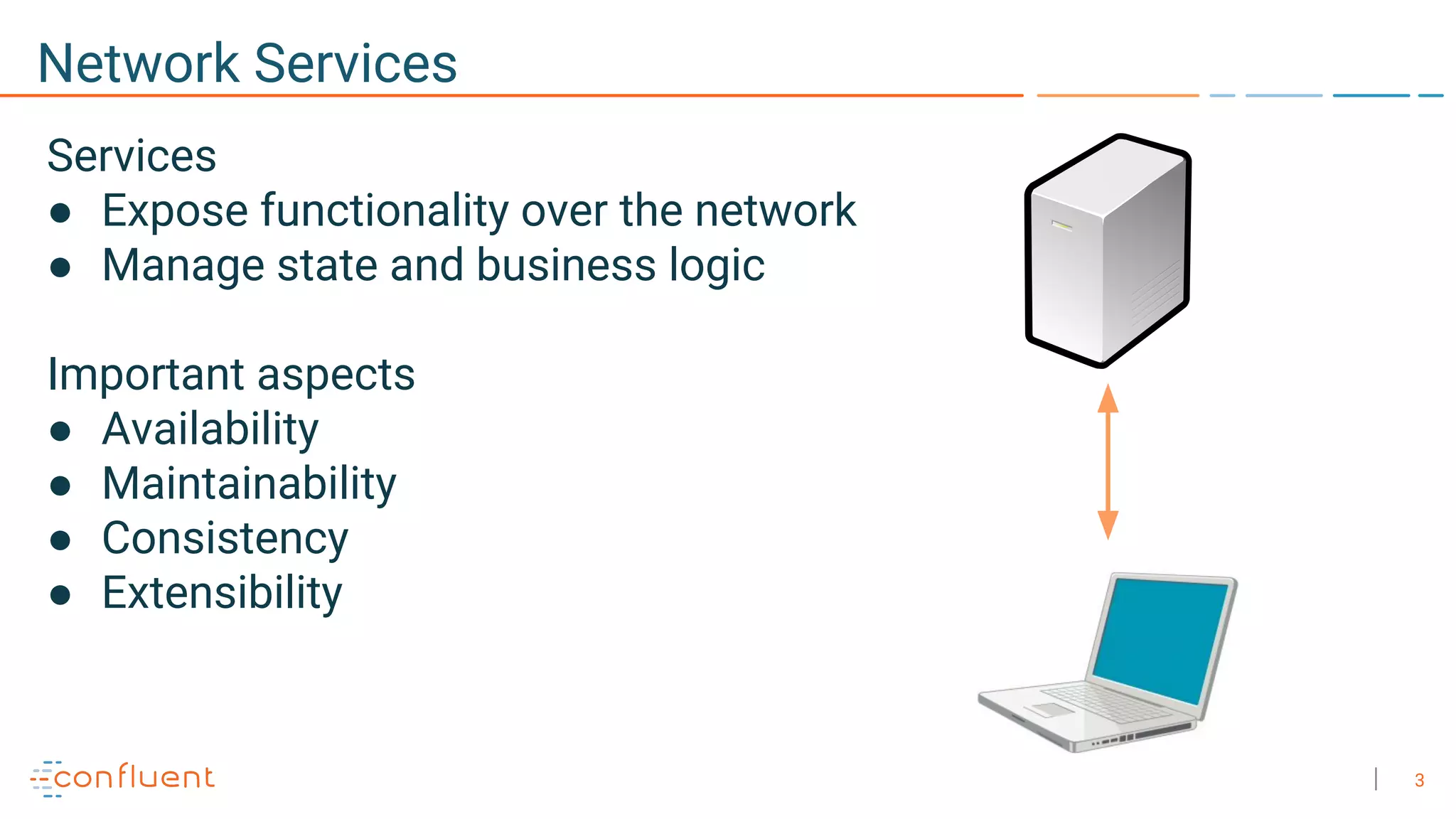
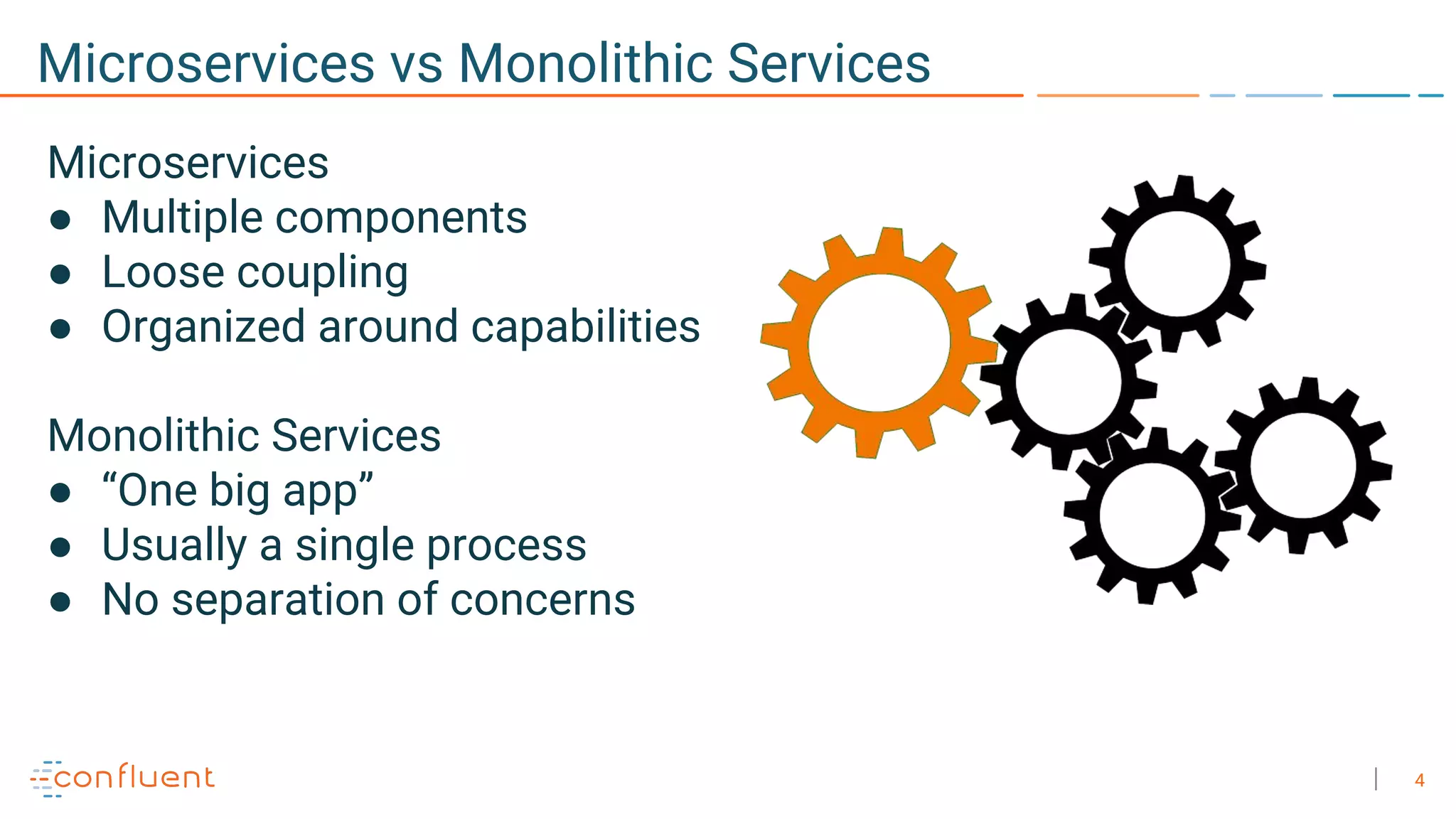
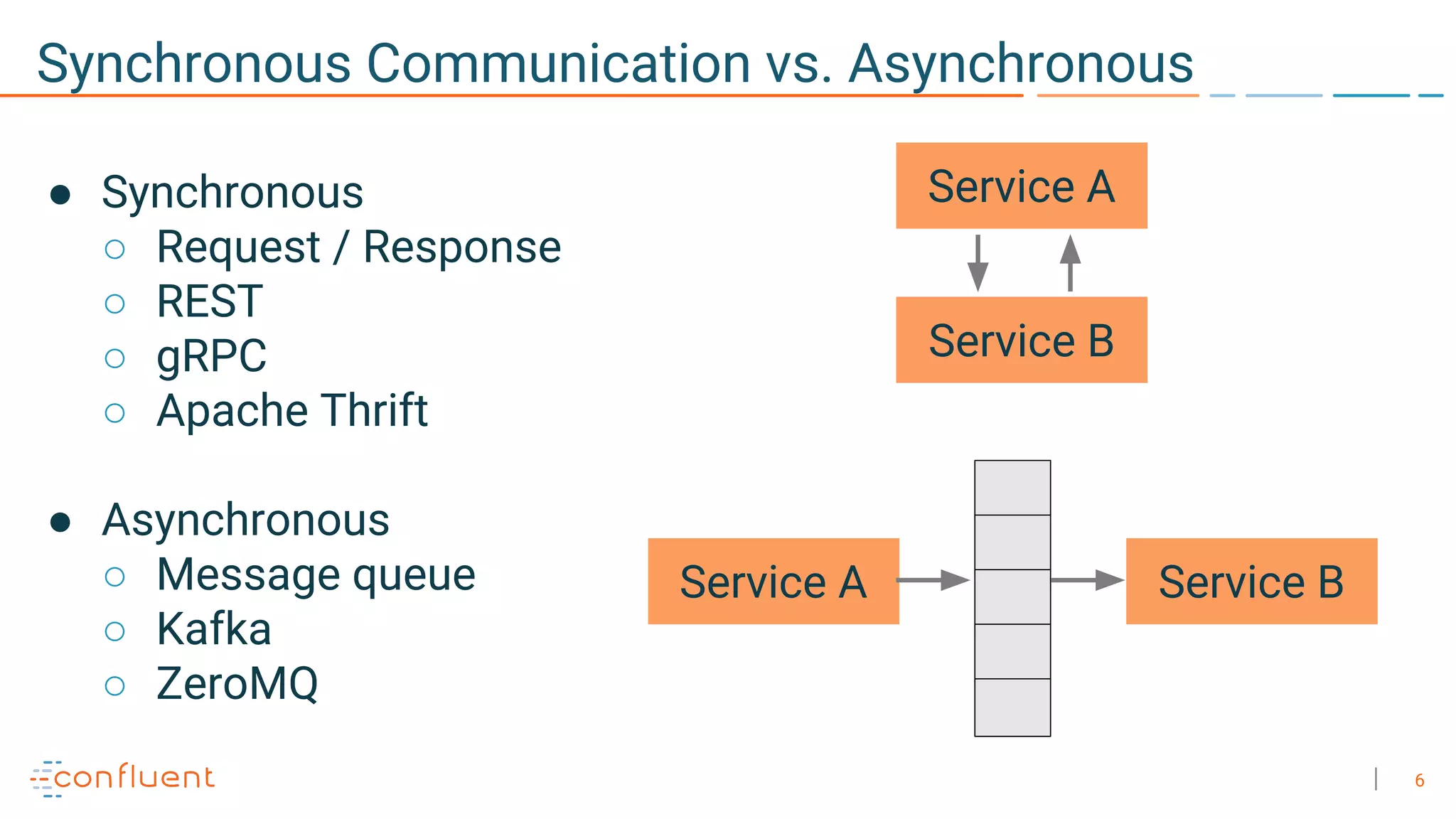
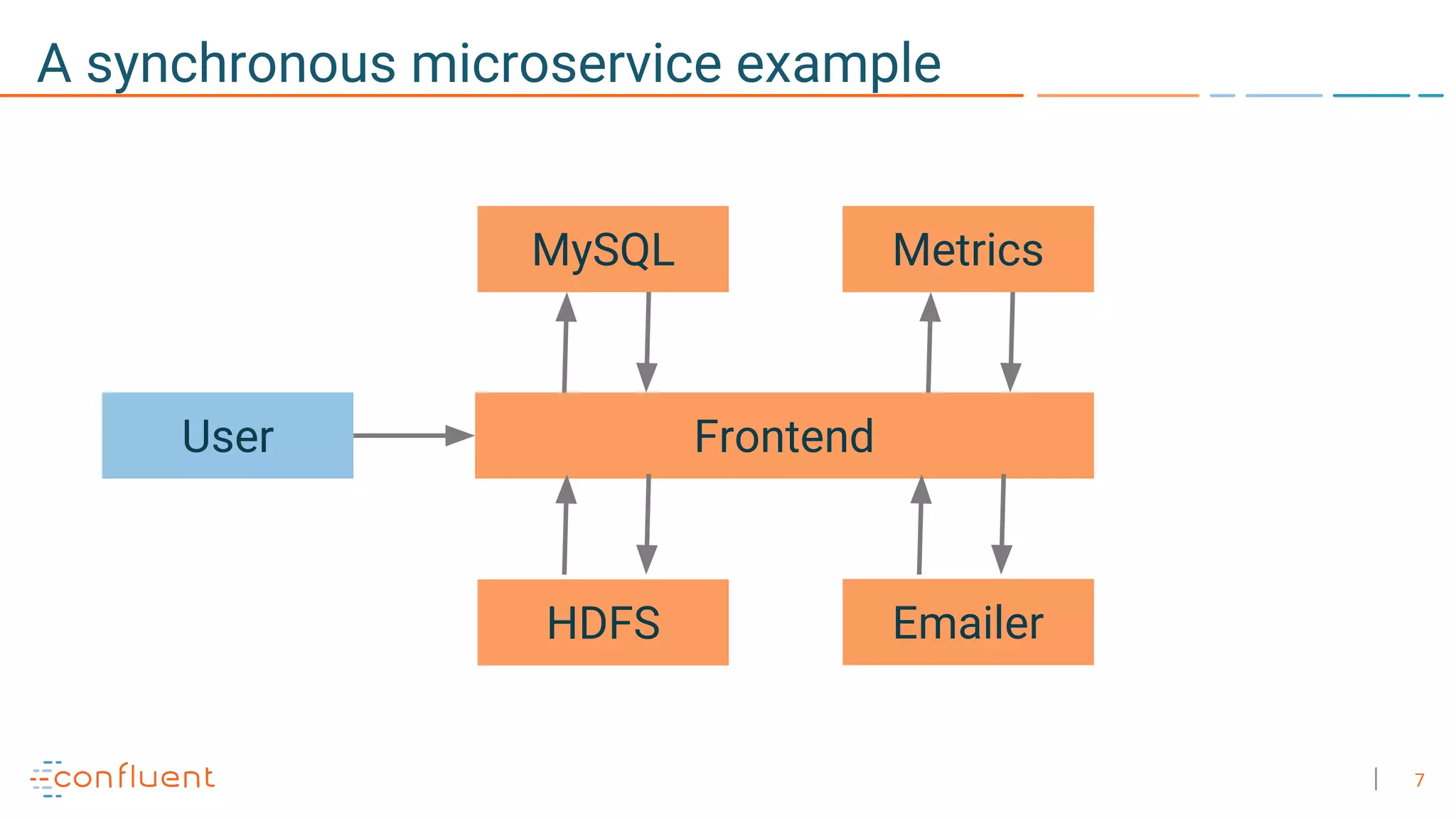
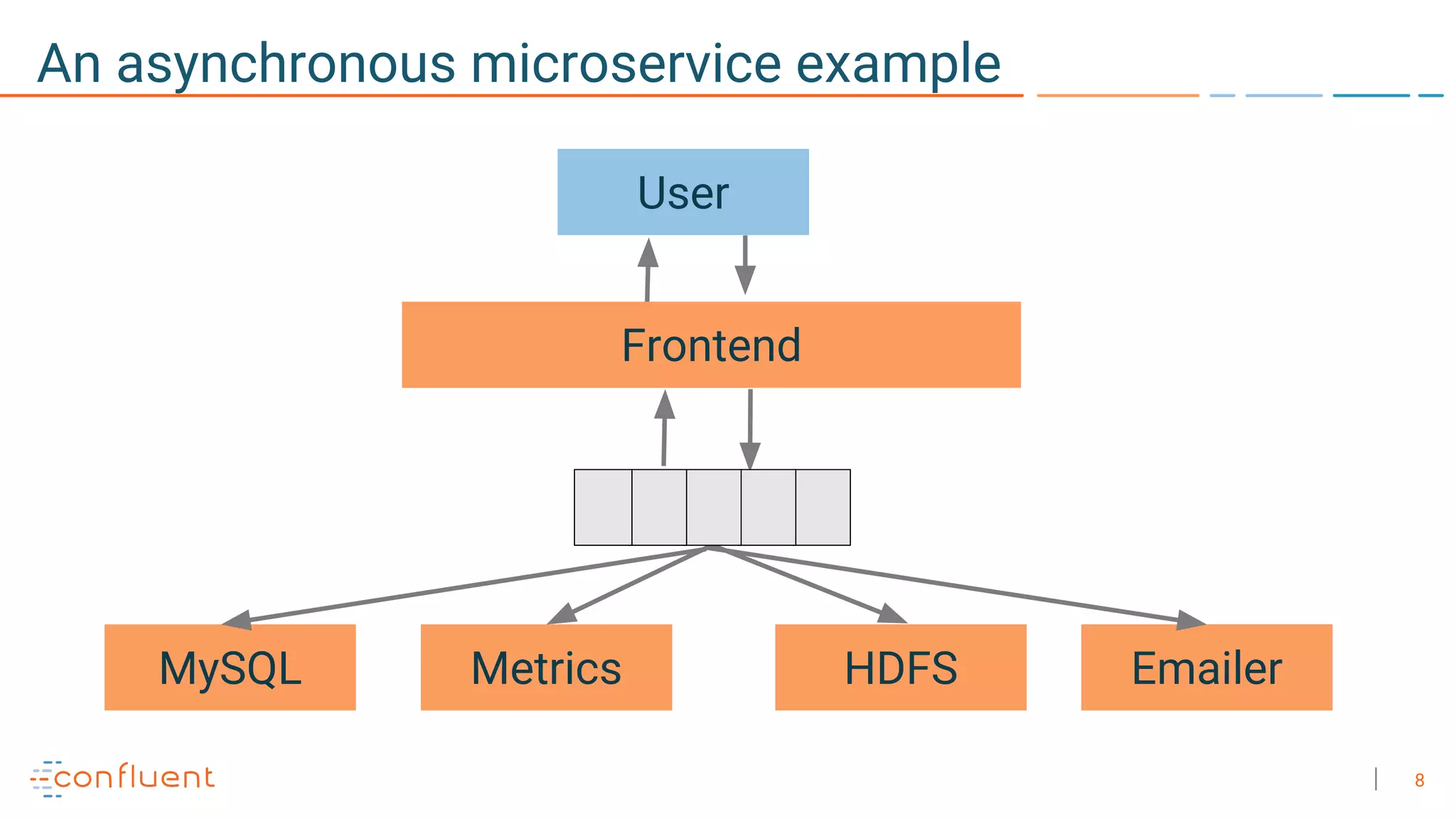
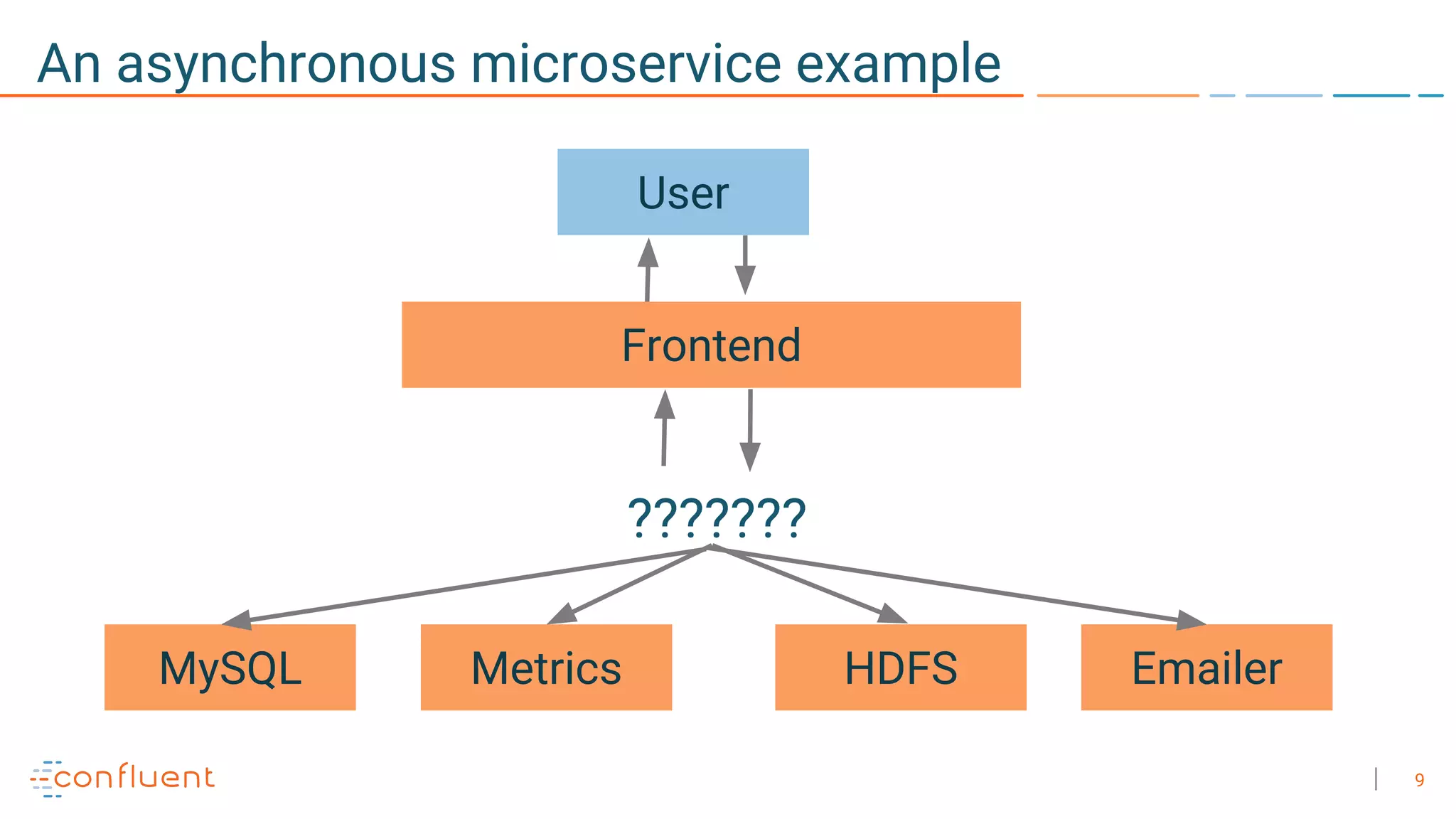
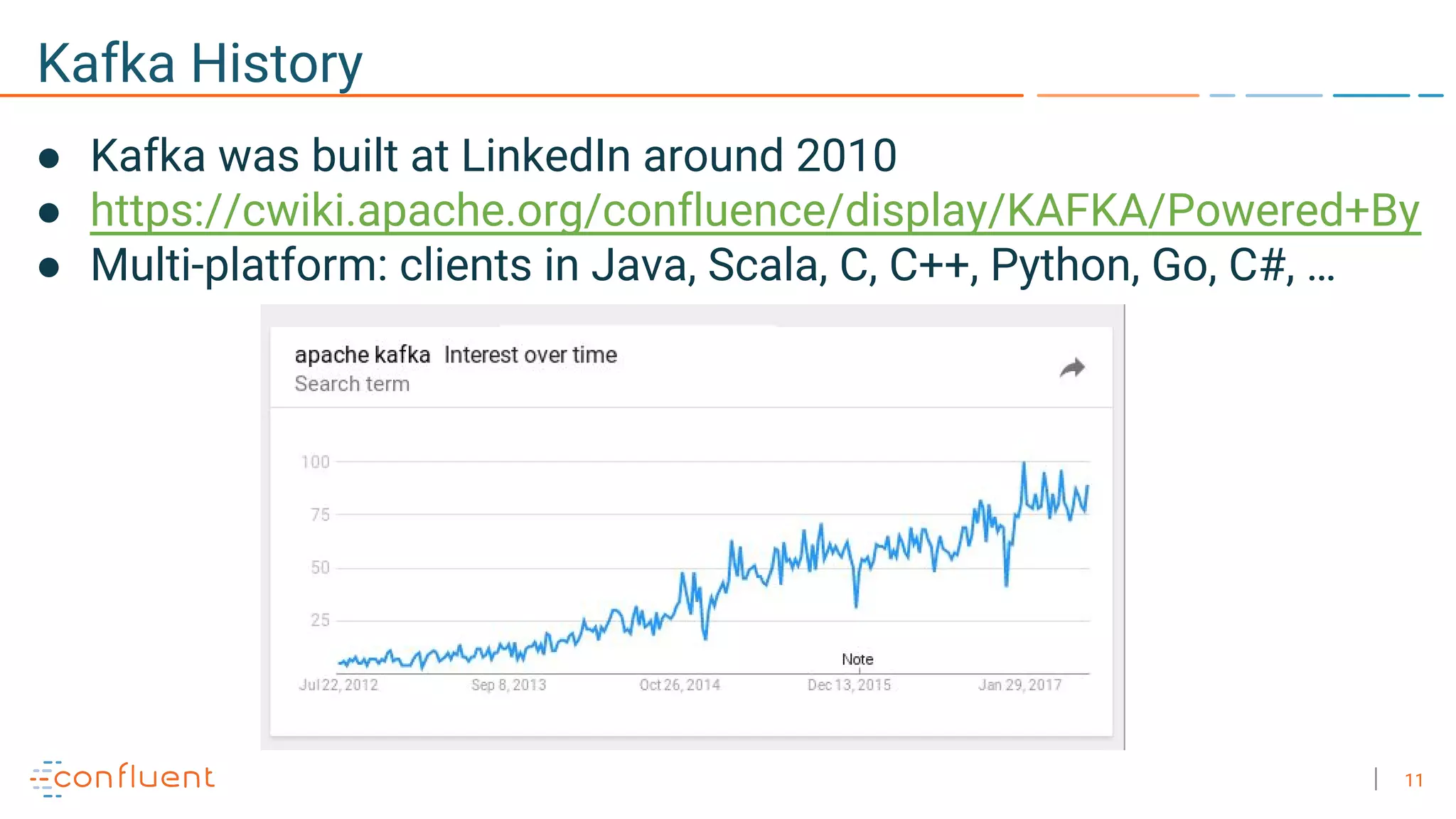
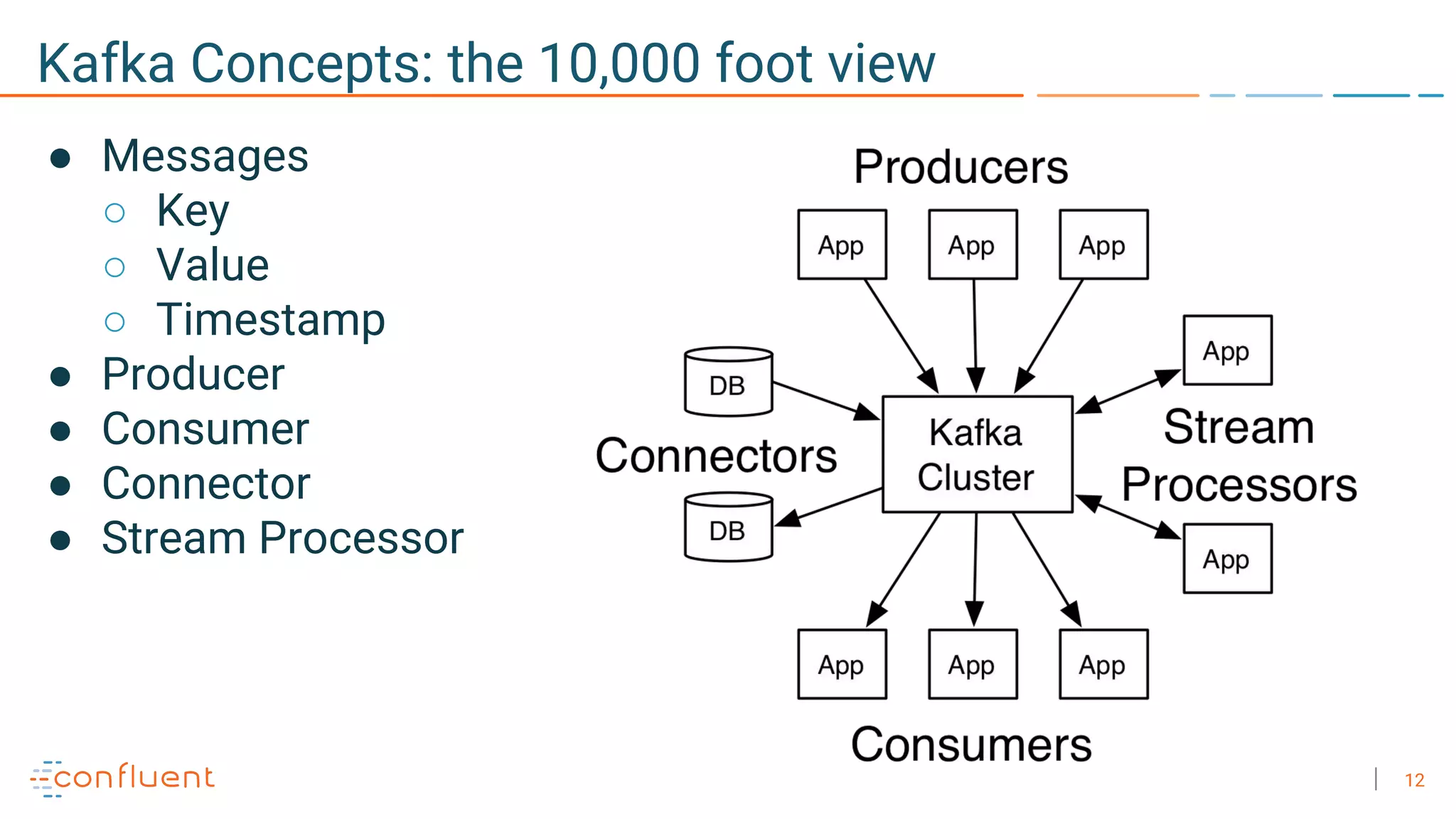
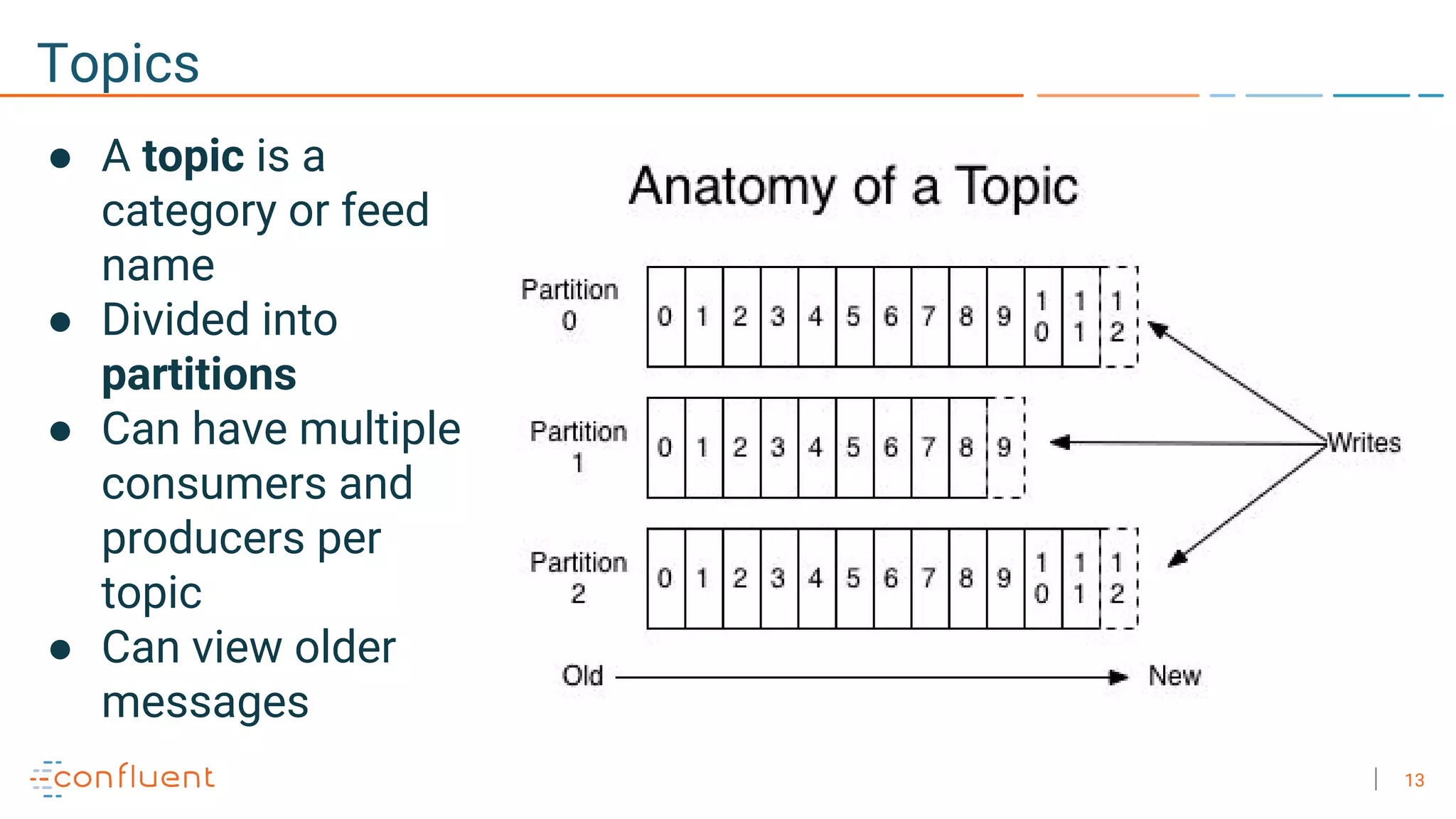
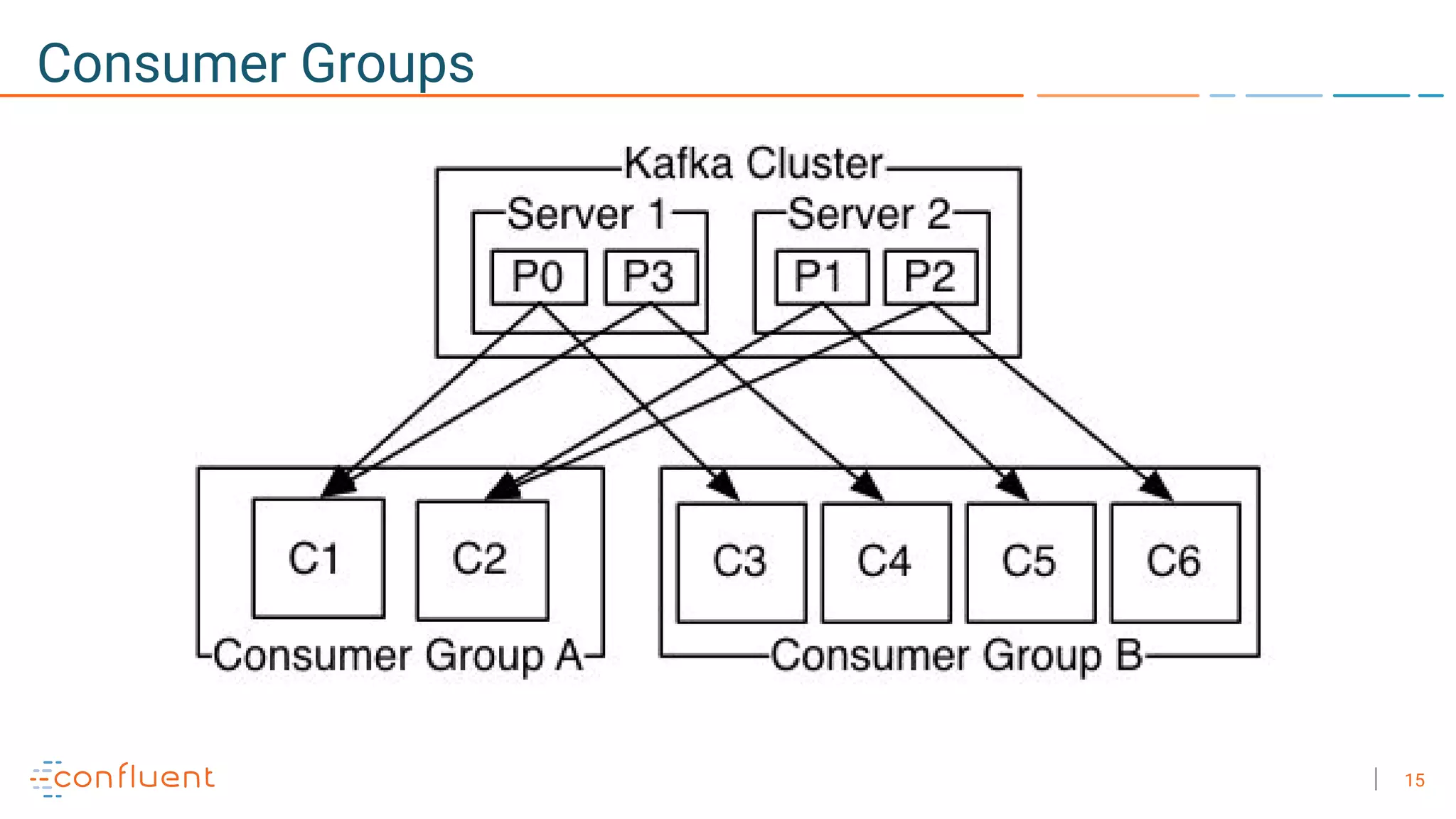
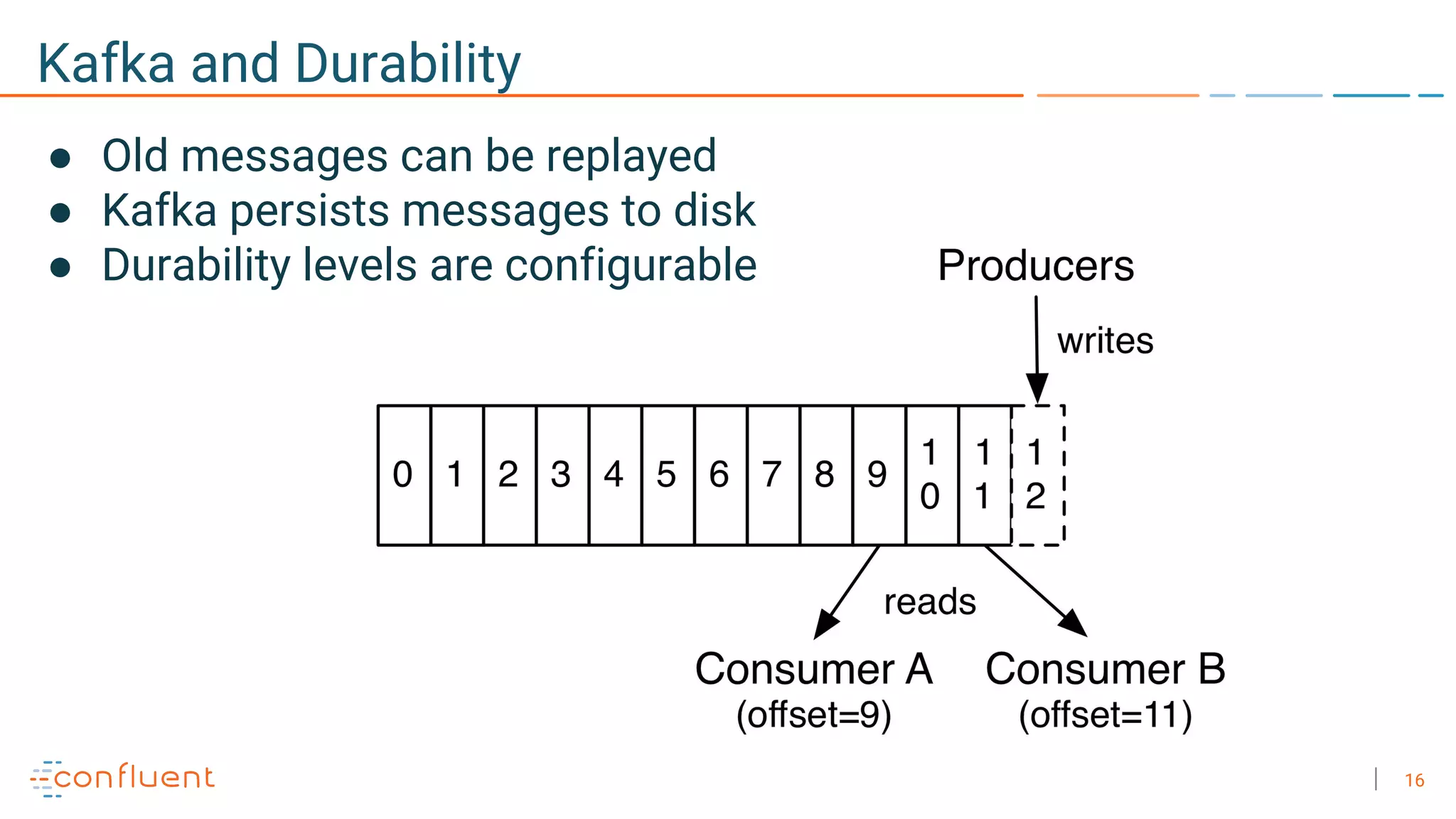
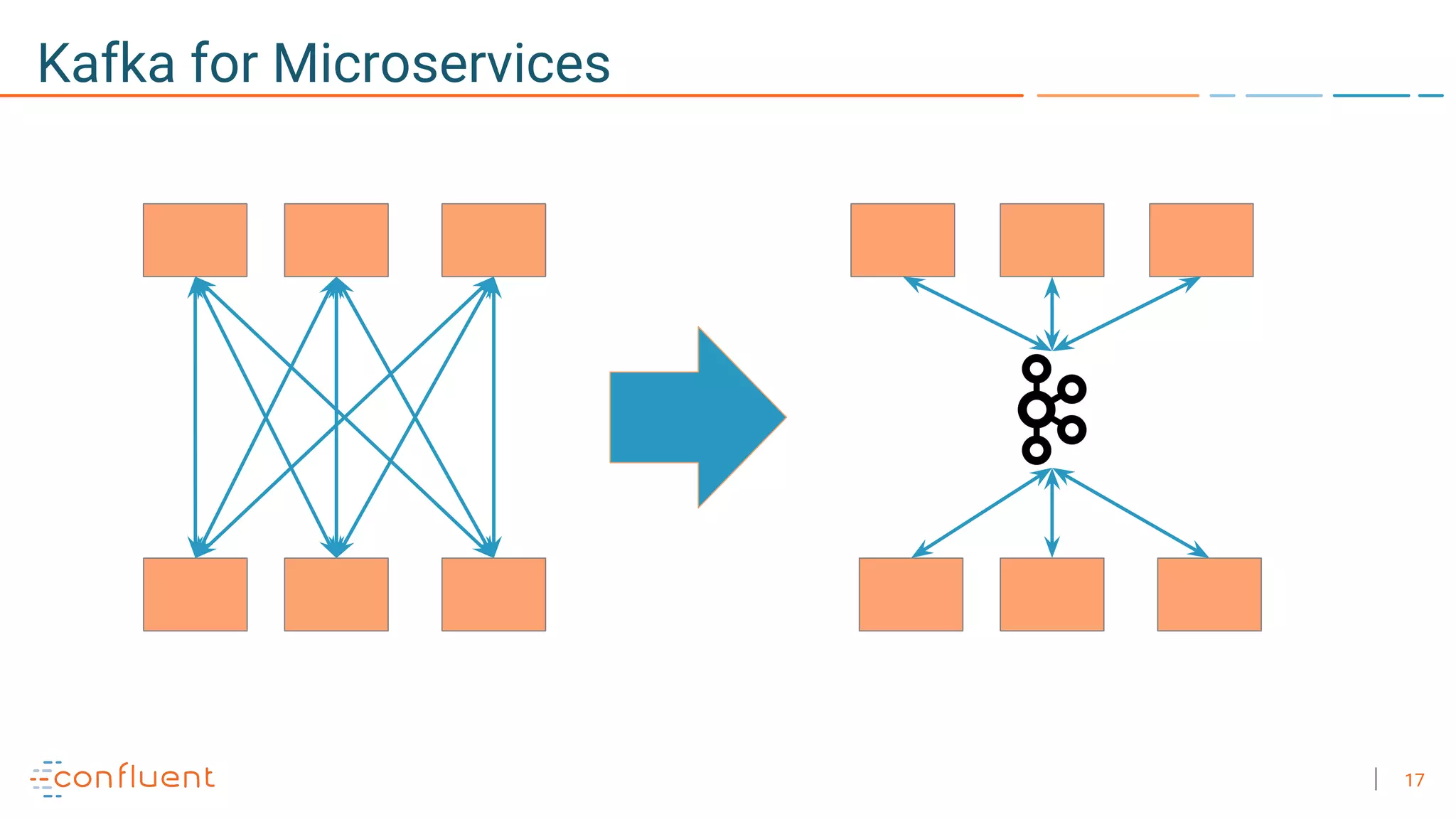
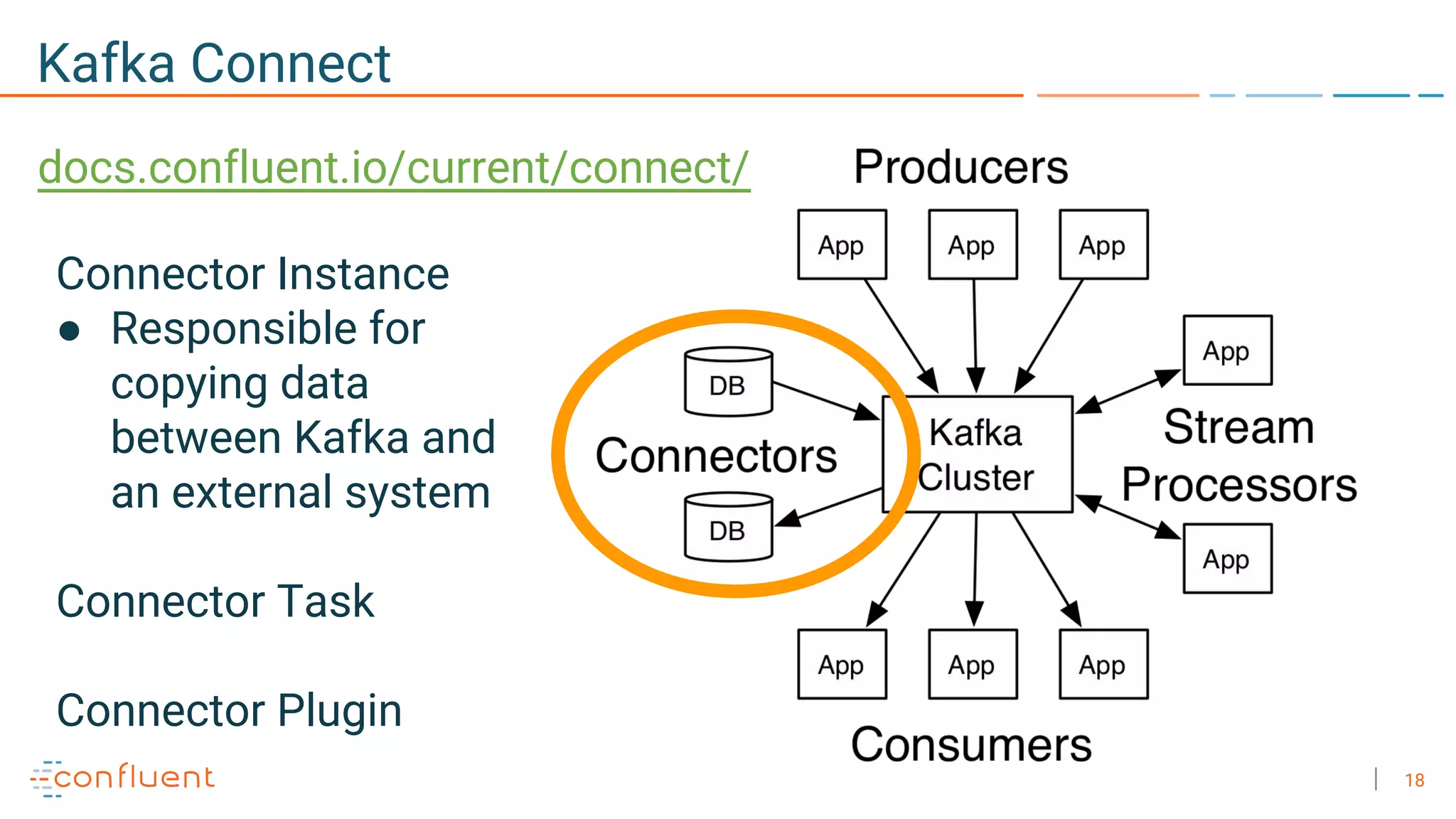
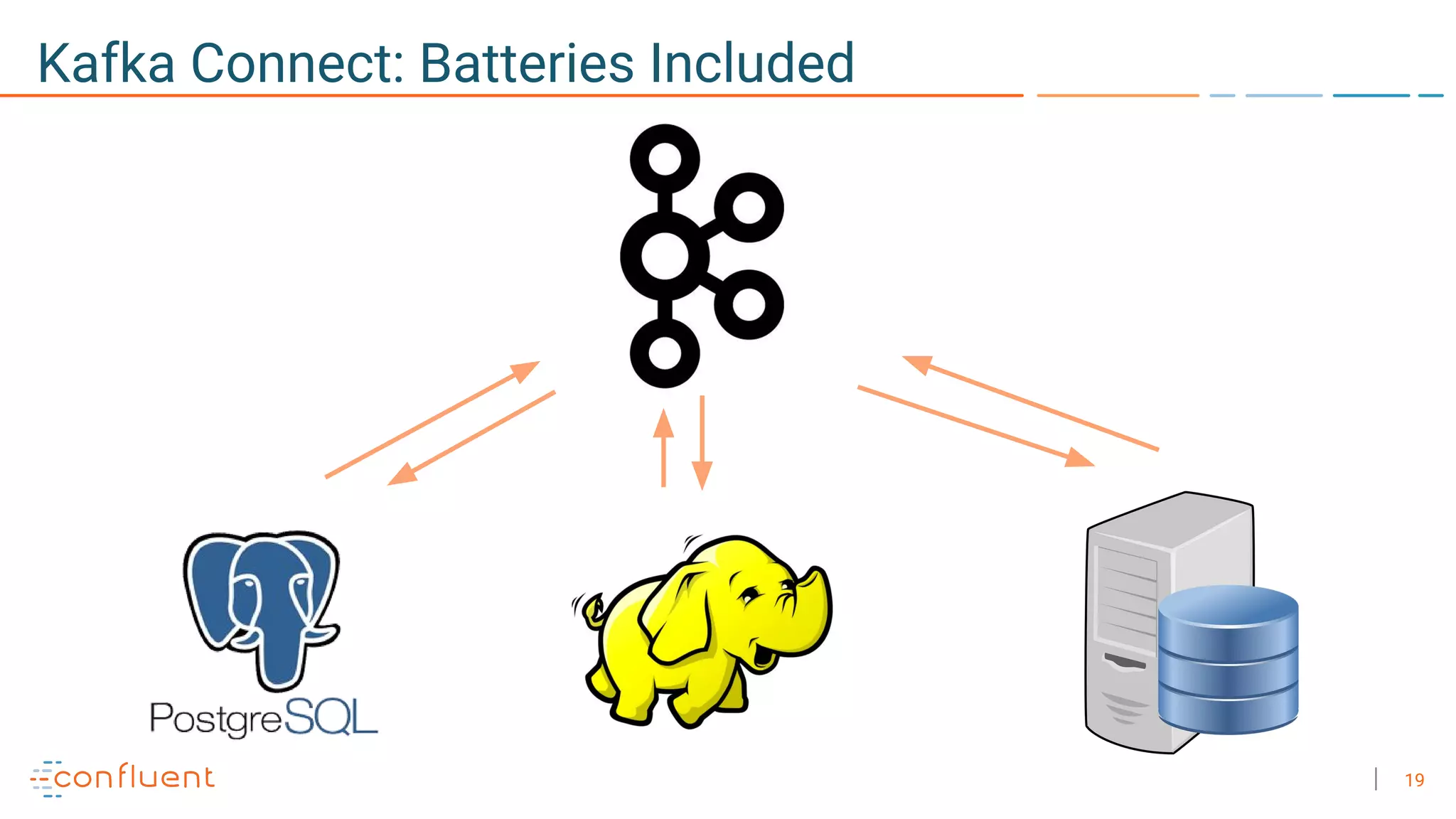
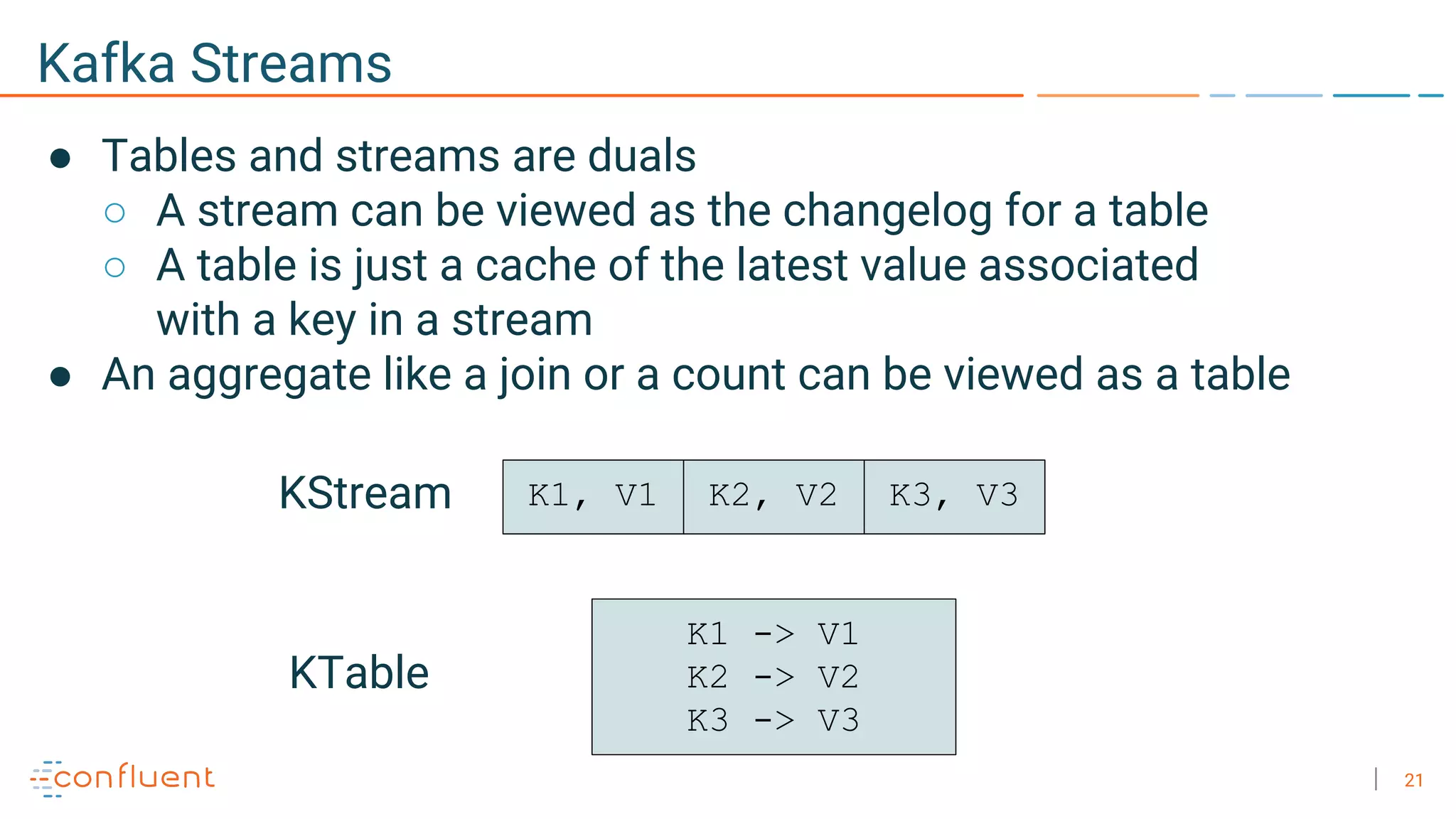
The document discusses the advantages of microservices over monolithic architectures, highlighting aspects like loose coupling and easier scaling. It introduces Apache Kafka as a distributed streaming platform that facilitates data publishing and subscription in real-time for microservices. The content covers Kafka concepts, including topics, durability, and stream processing, emphasizing its reliability and versatility in supporting microservices.