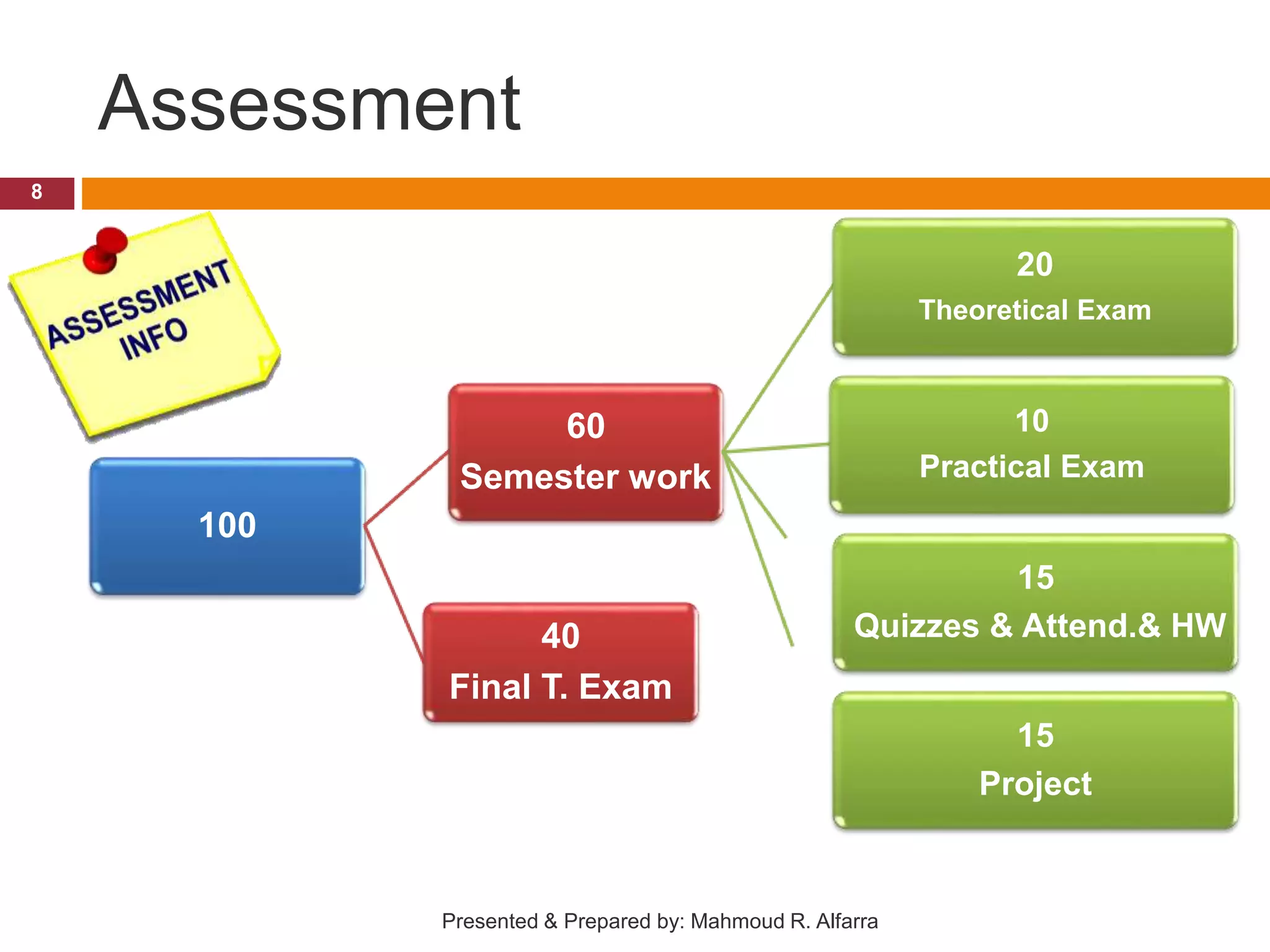
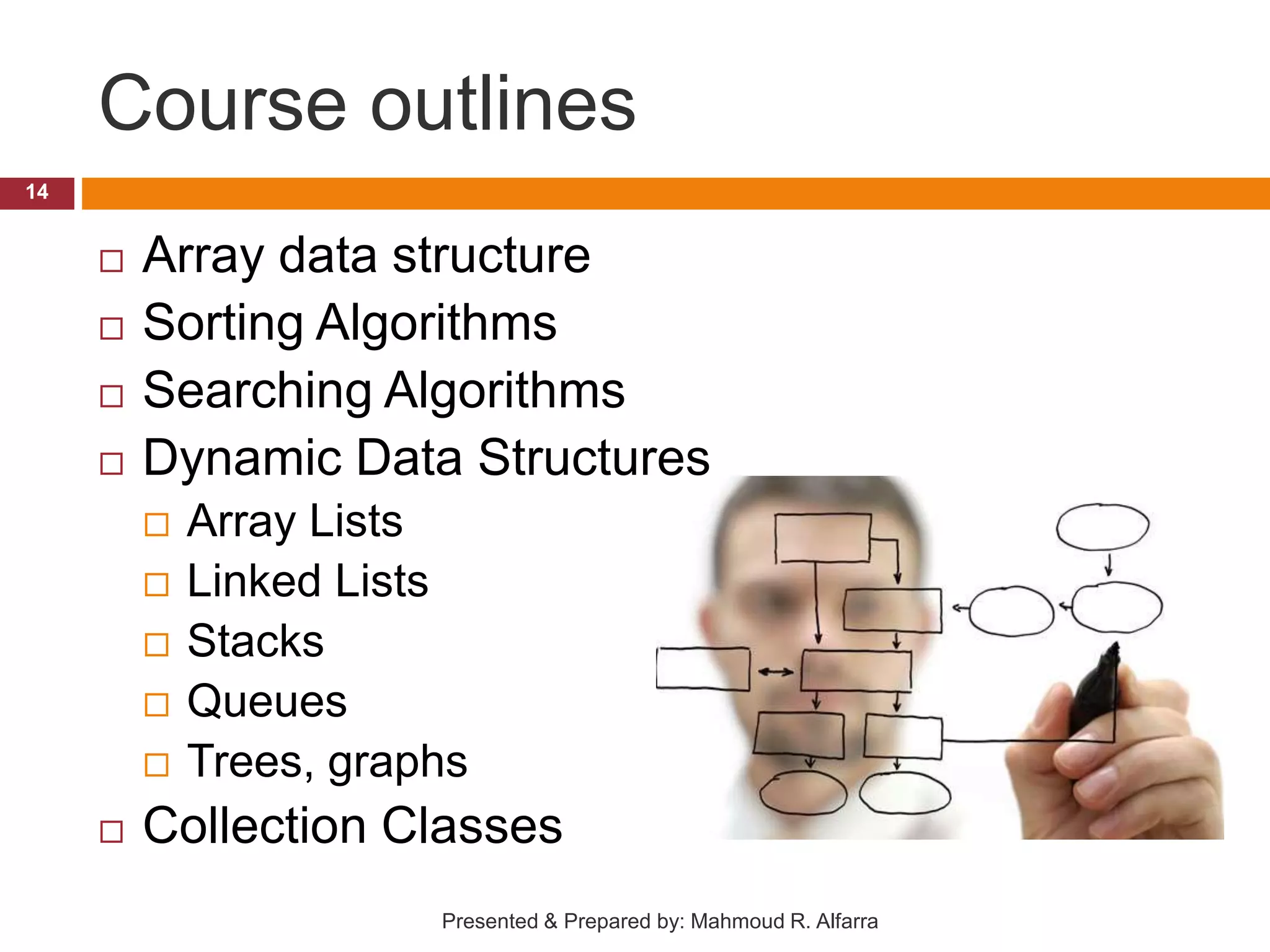
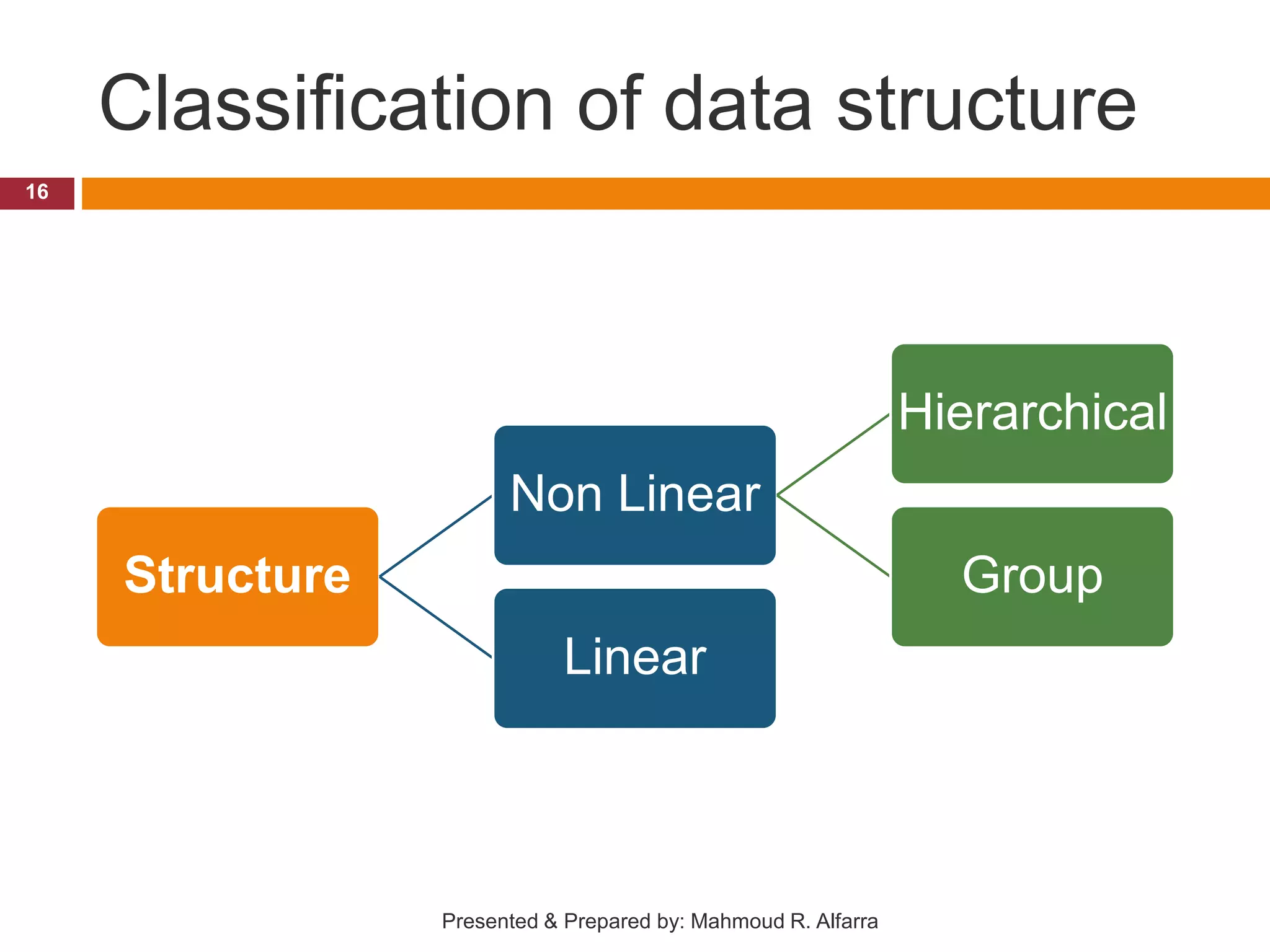
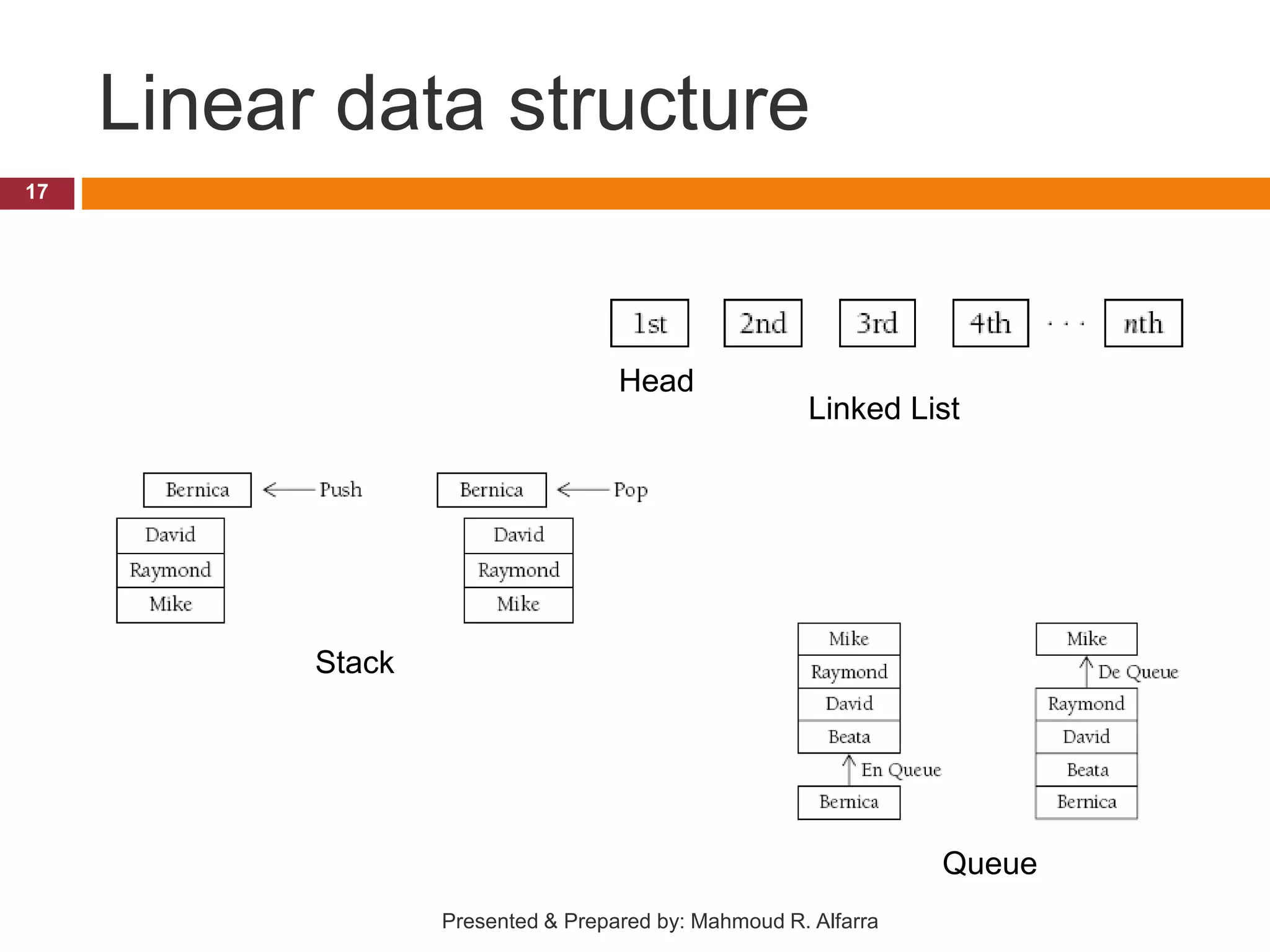
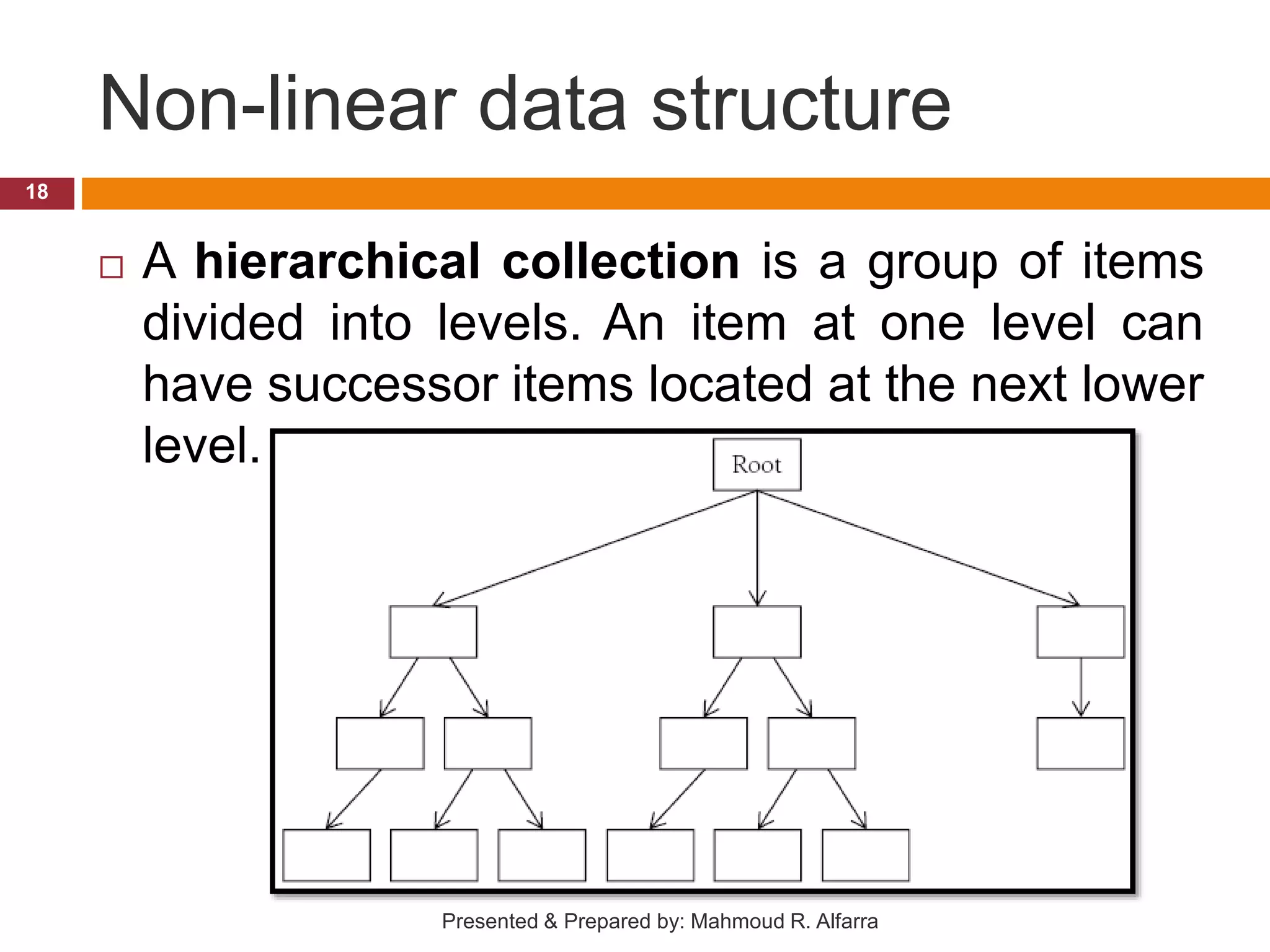
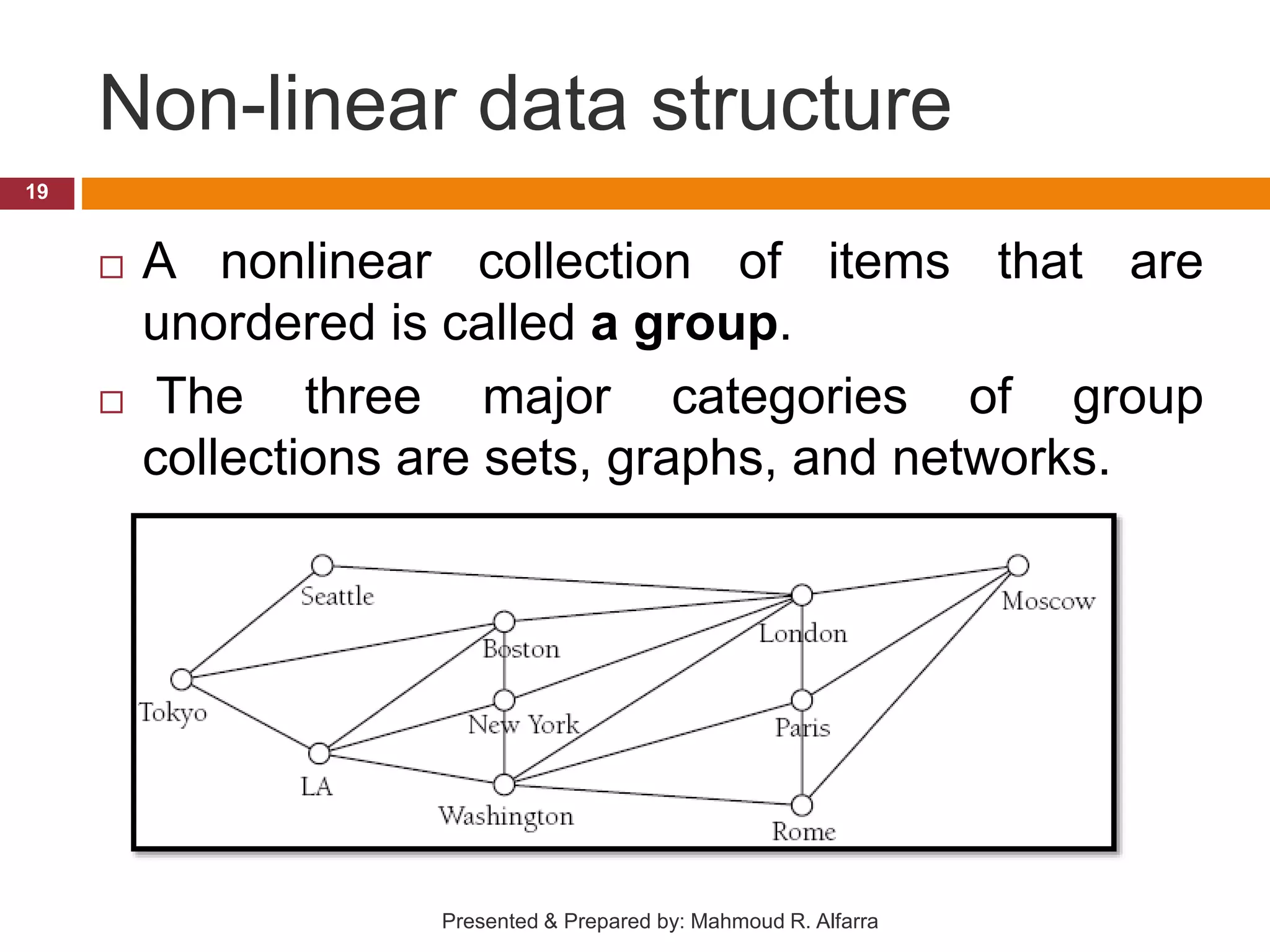
This document provides an introduction and outline for a course on data structures. It introduces the lecturer, Mahmoud Rafeek Alfarra, and lists his qualifications. It outlines the course objectives, resources, guidelines, assessment, and schedule. Key topics that will be covered include arrays, sorting and searching algorithms, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees and graphs. The document provides classifications of different types of data structures such as linear vs nonlinear, static vs dynamic memory allocation. It concludes with information about how students can be successful in the course.