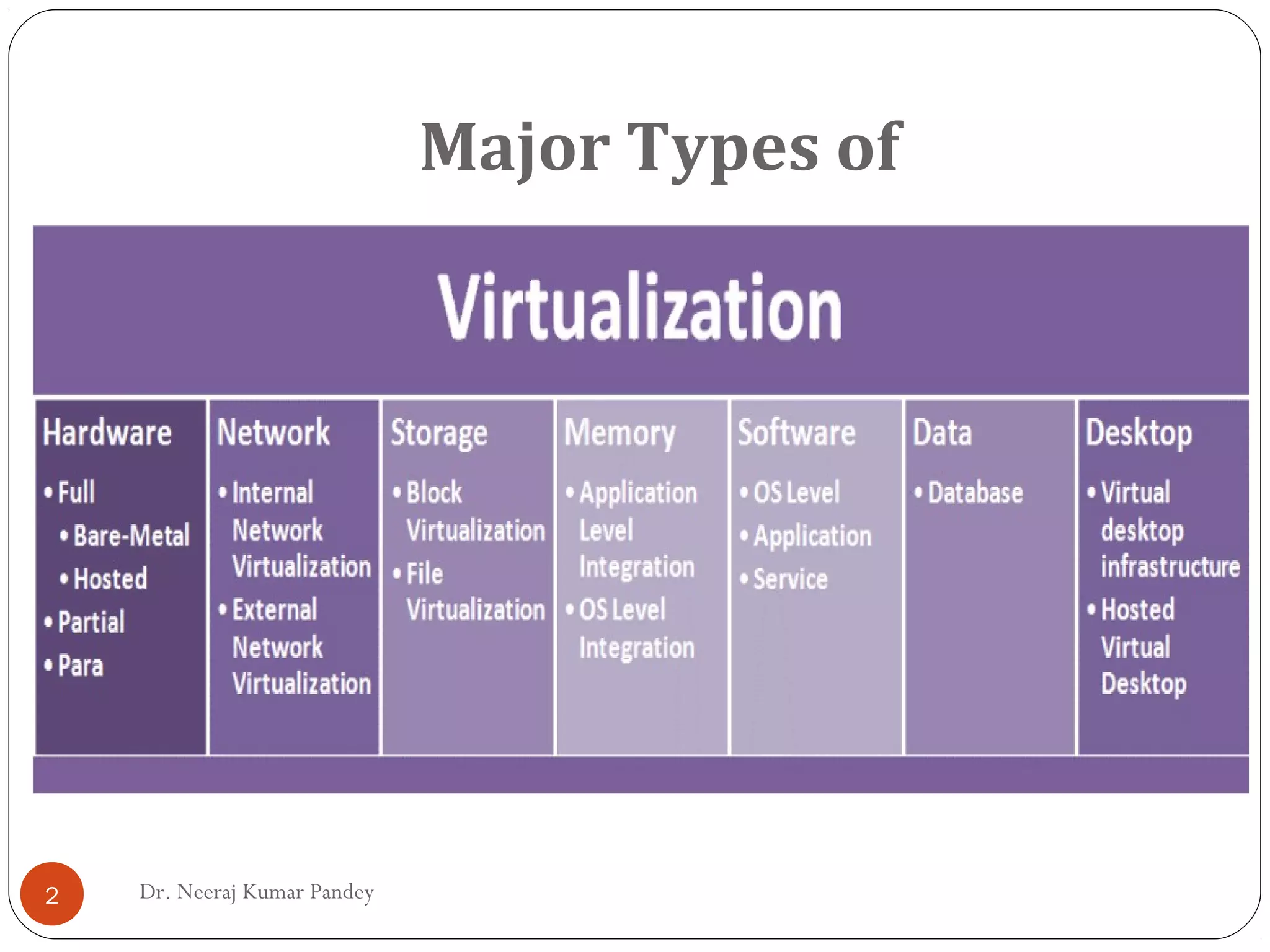
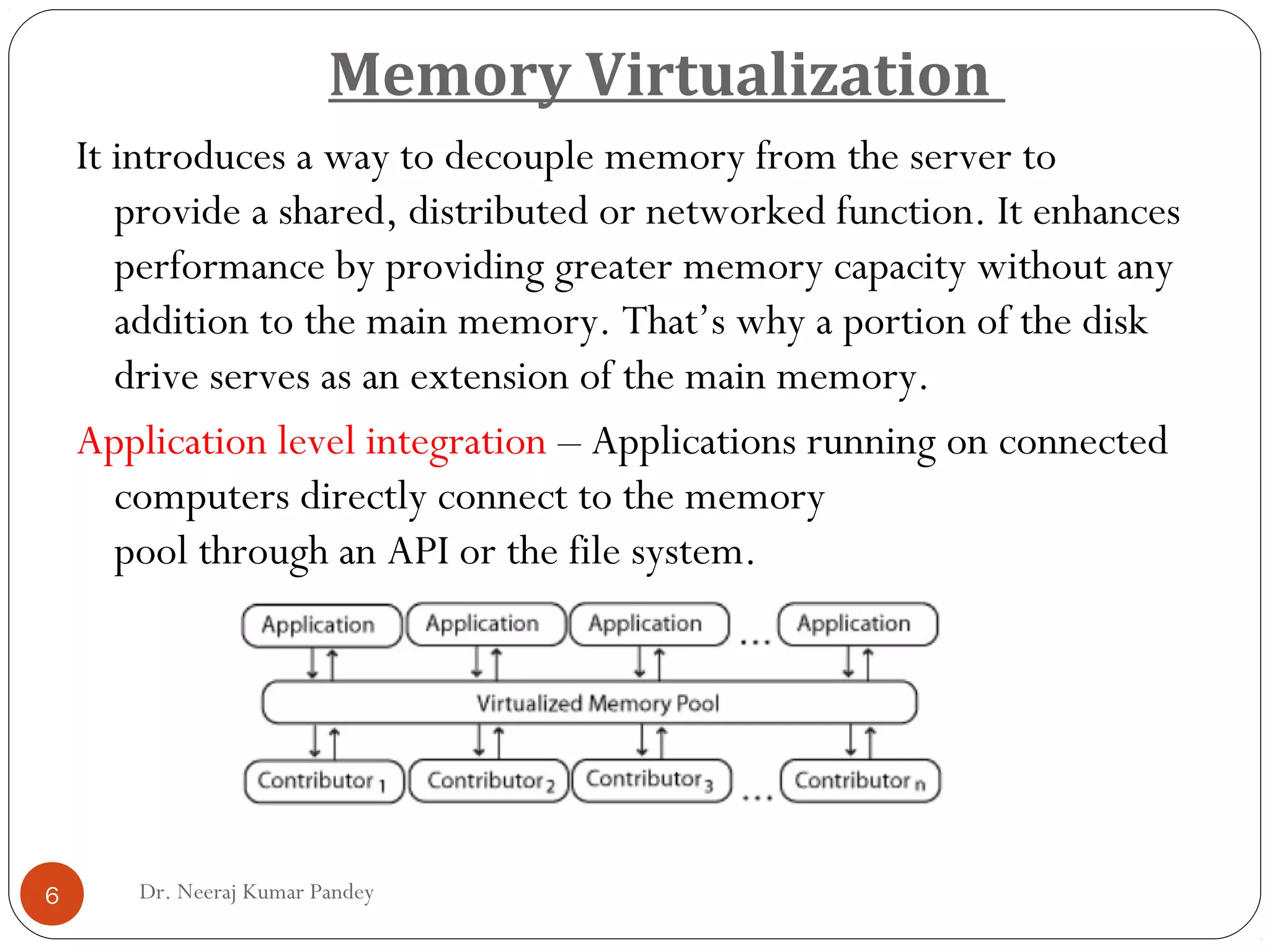
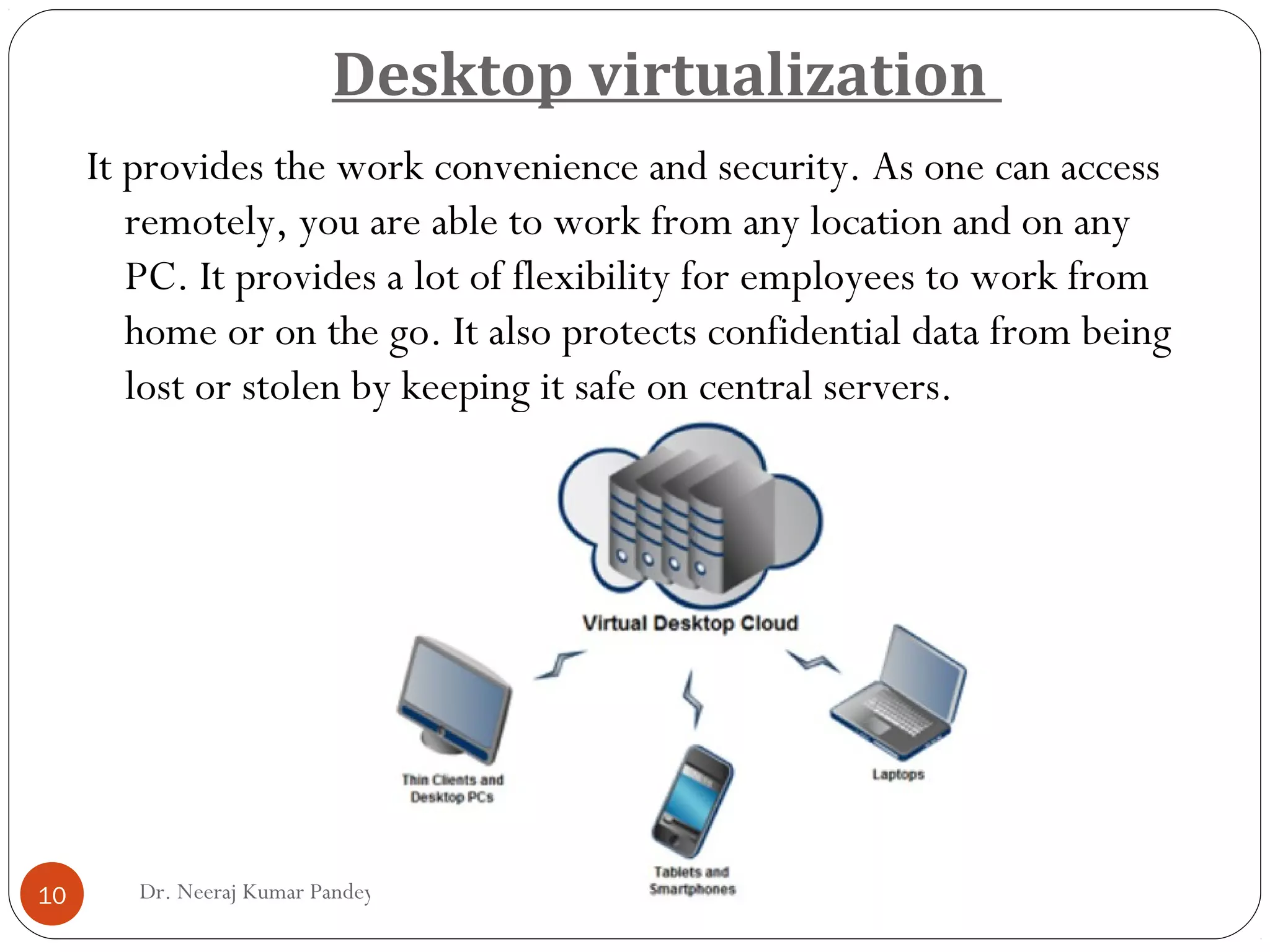
The document discusses different types of virtualization including hardware, network, storage, memory, software, data, and desktop virtualization. Hardware virtualization includes full, para, and partial virtualization. Network virtualization includes internal and external virtualization. Storage virtualization includes block and file virtualization. Memory virtualization enhances performance through shared, distributed, or networked memory that acts as an extension of main memory. Software virtualization allows guest operating systems to run virtually. Data virtualization manipulates data without technical details. Desktop virtualization provides remote access to work from any location for flexibility and data security.