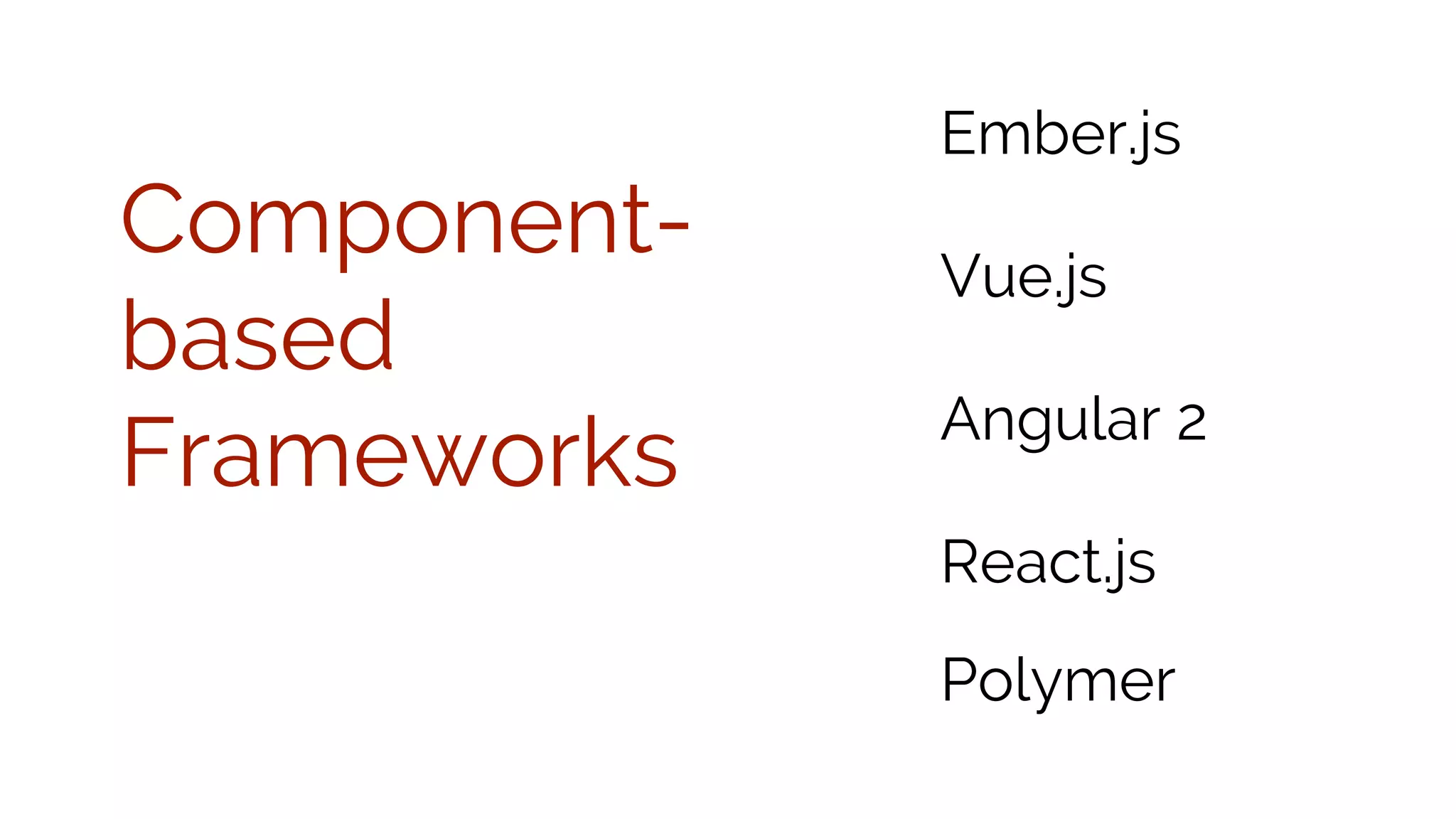
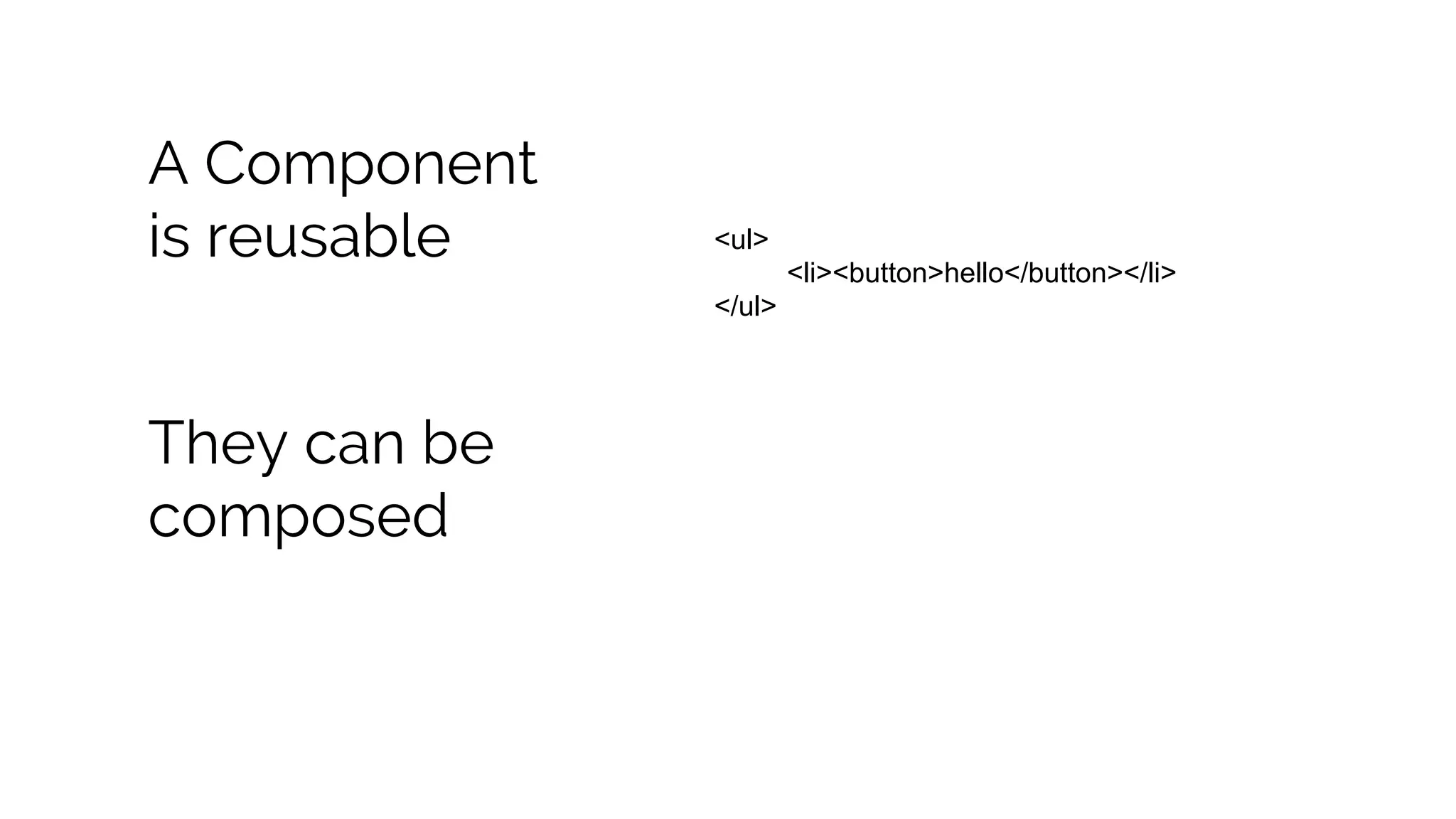
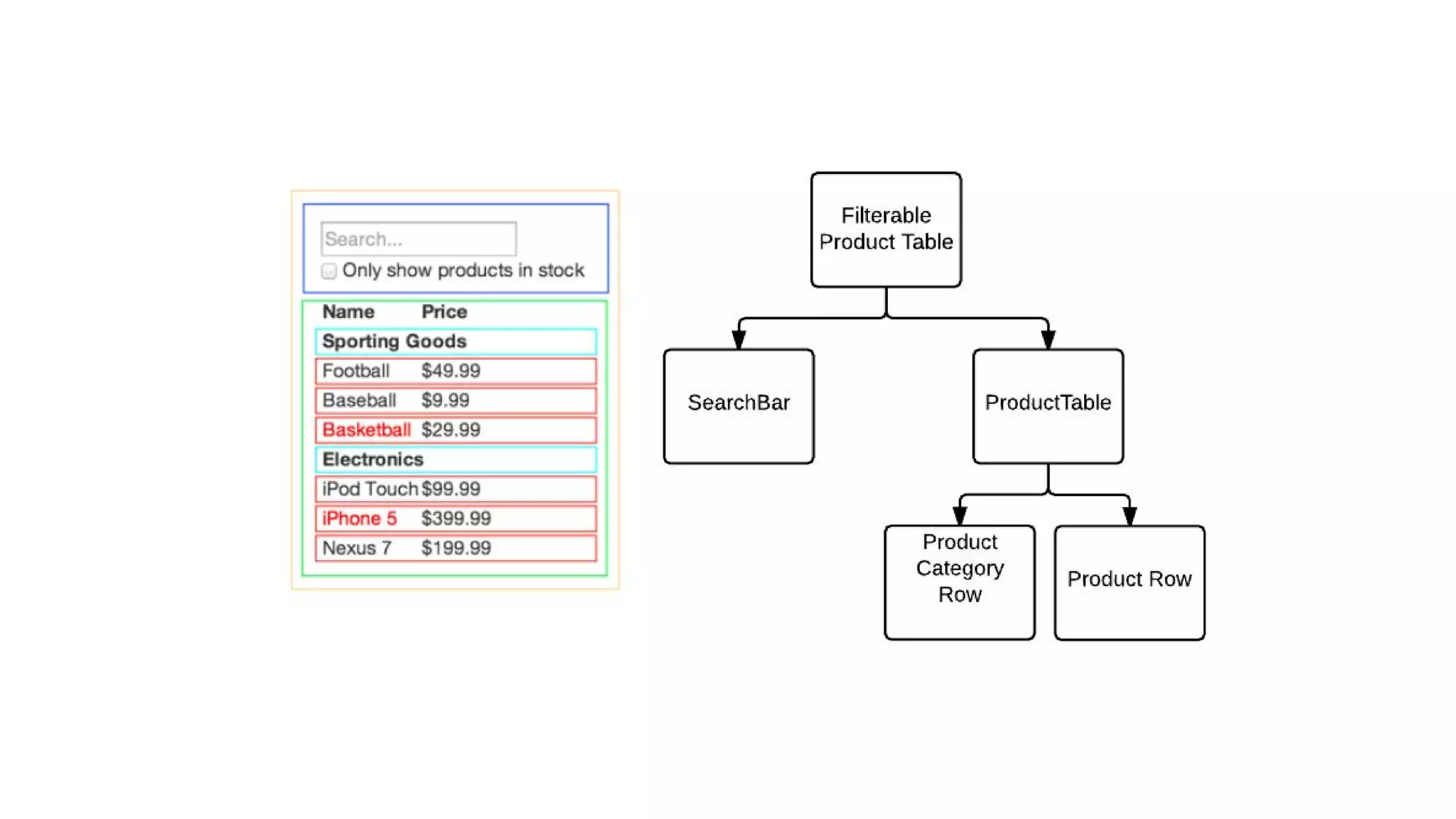
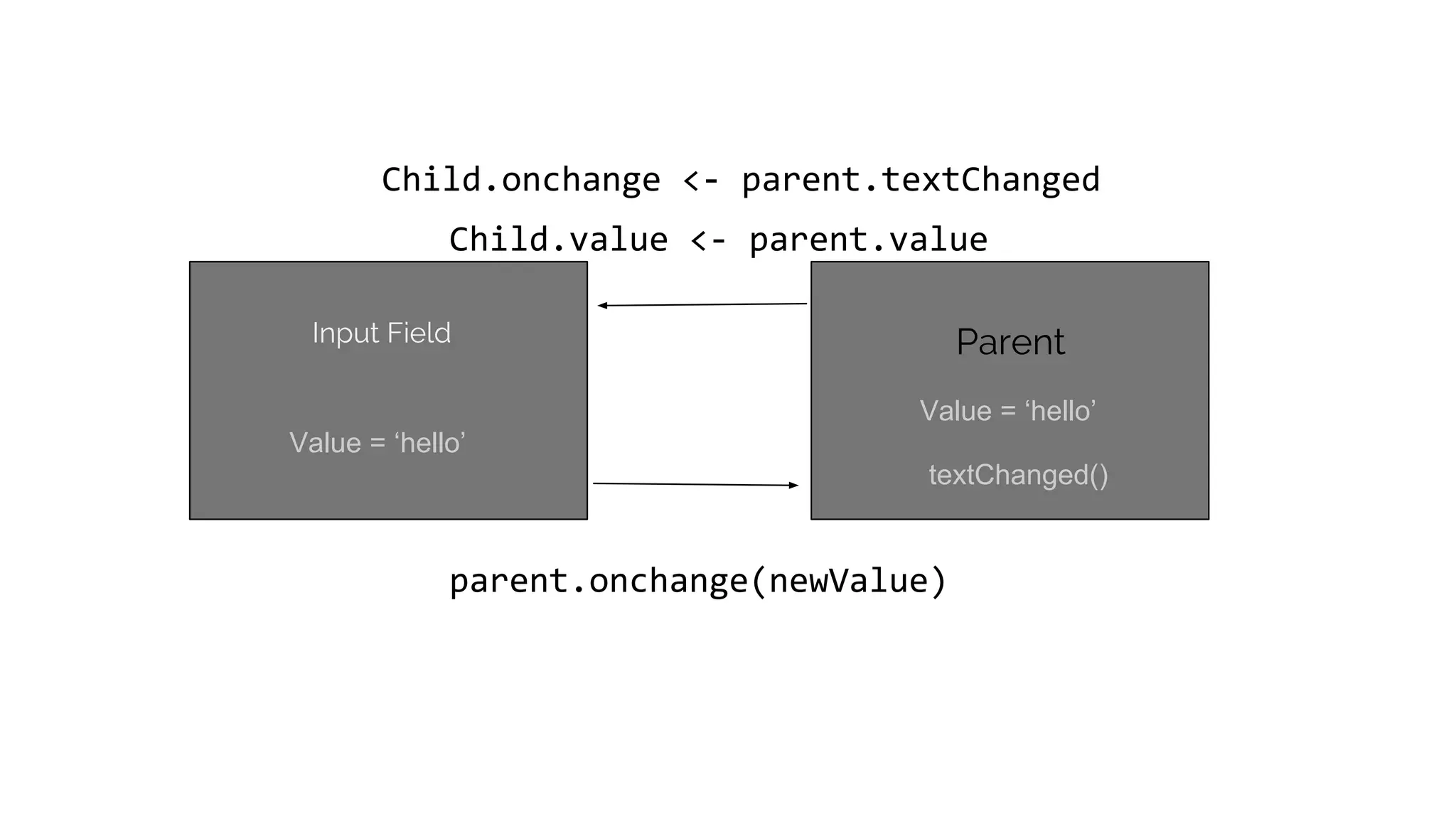
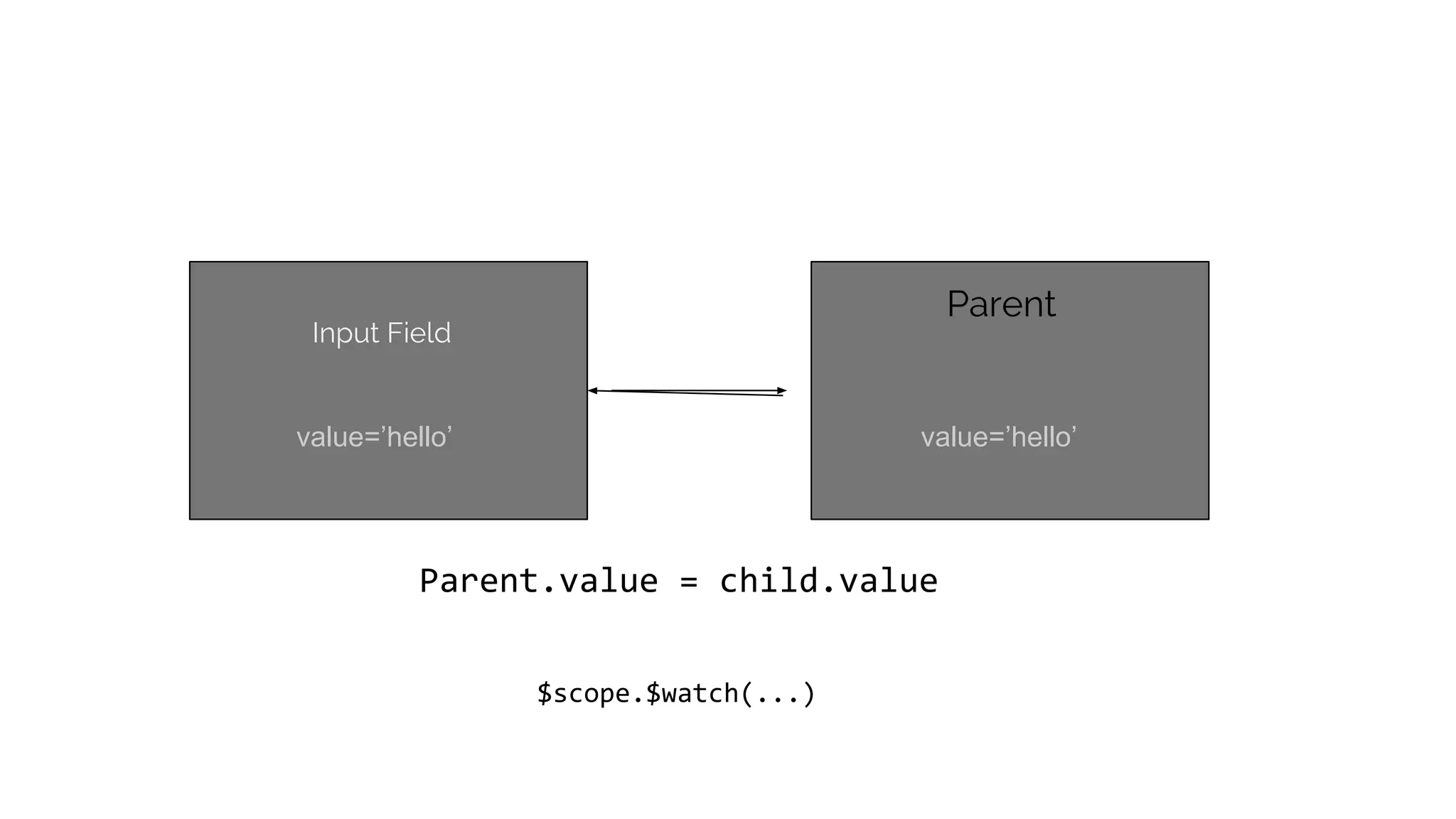
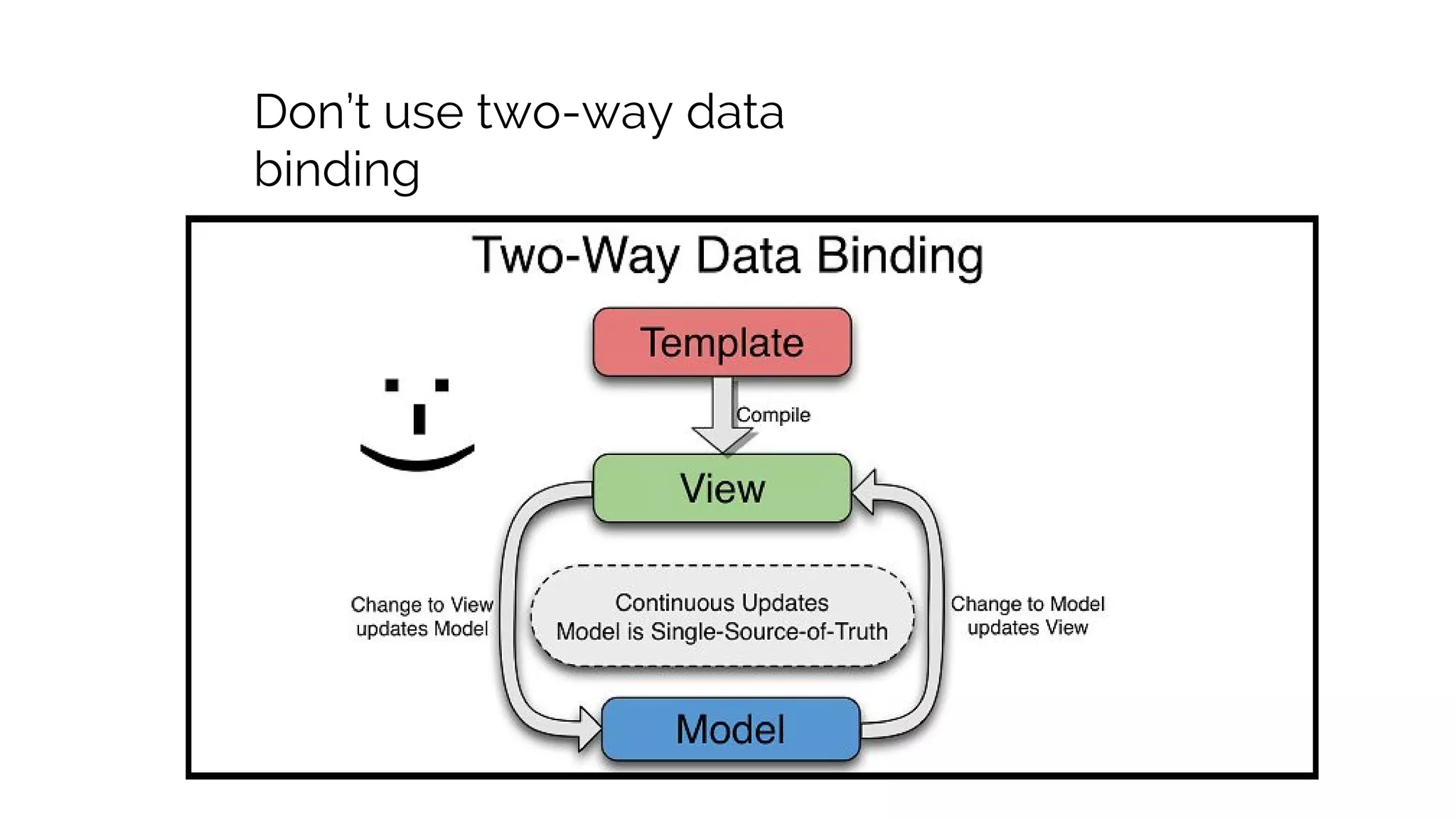
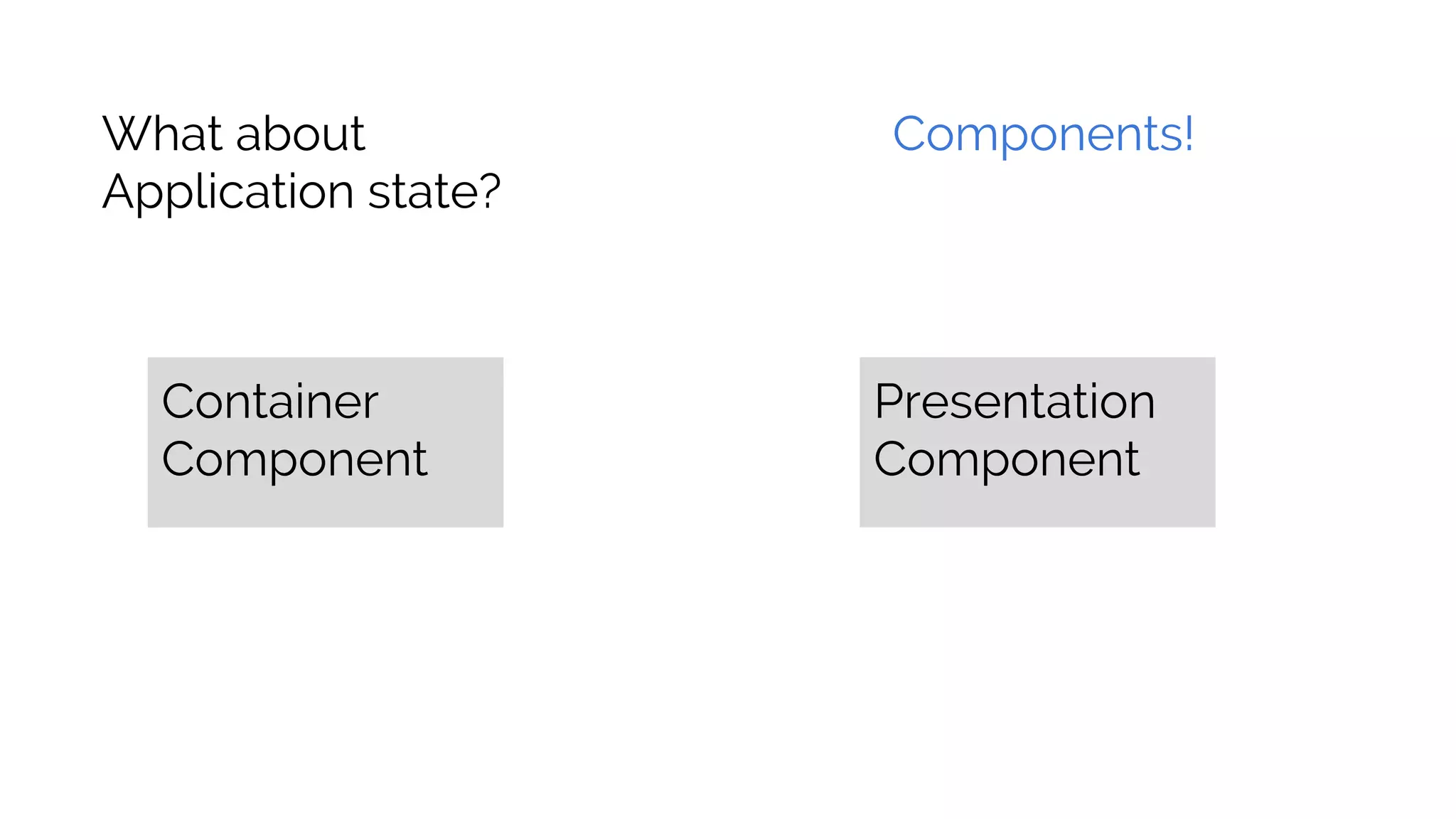
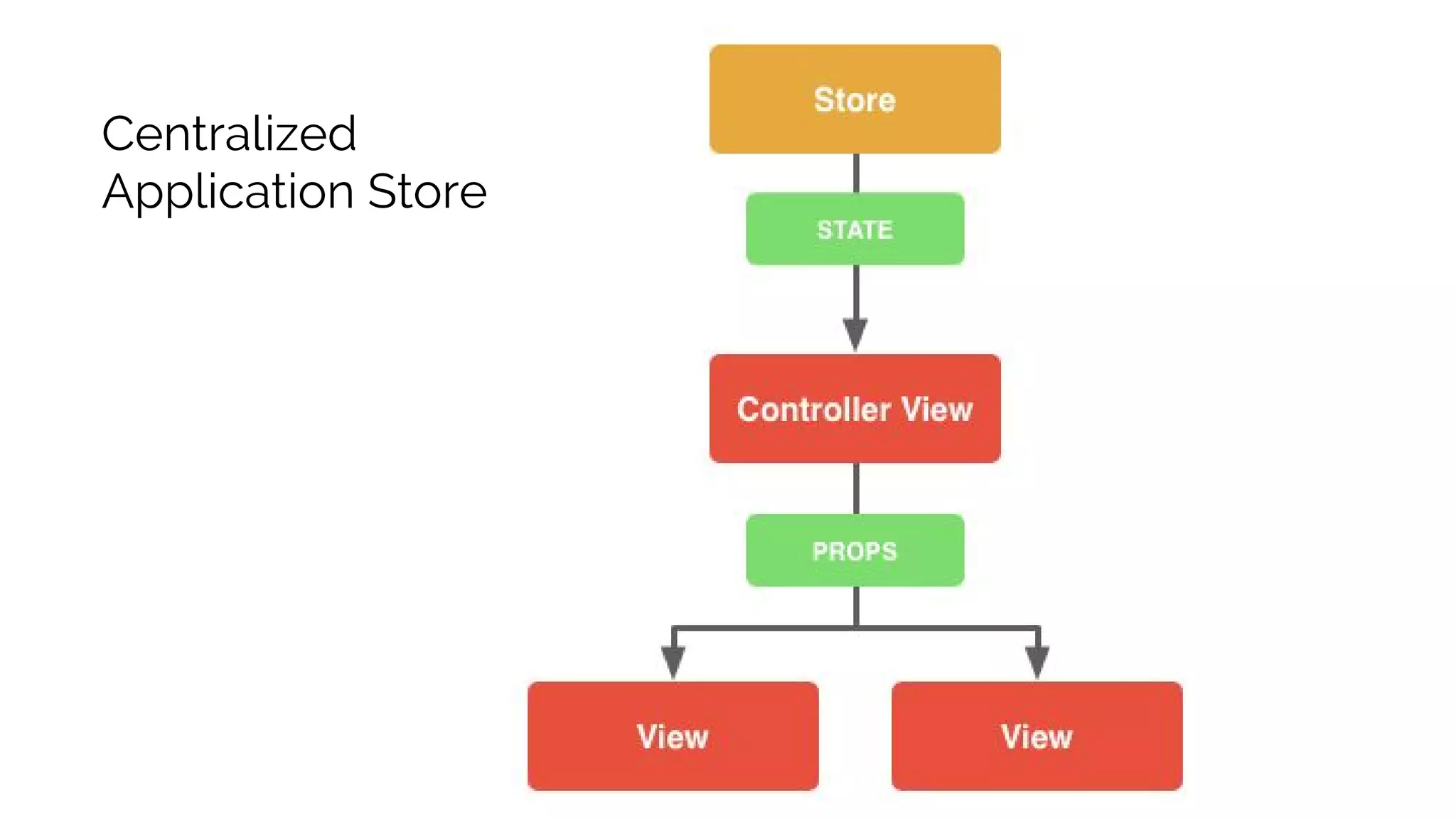
This document discusses component-based frontend architecture and its advantages over traditional MVC frameworks. It outlines some key component-based frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue. Components are self-contained objects that own their own presentation logic, views, and internal state. Components are reusable and can be composed together. The document recommends avoiding two-way data binding between components to reduce coupling. It suggests managing application state centrally rather than within controllers or views.