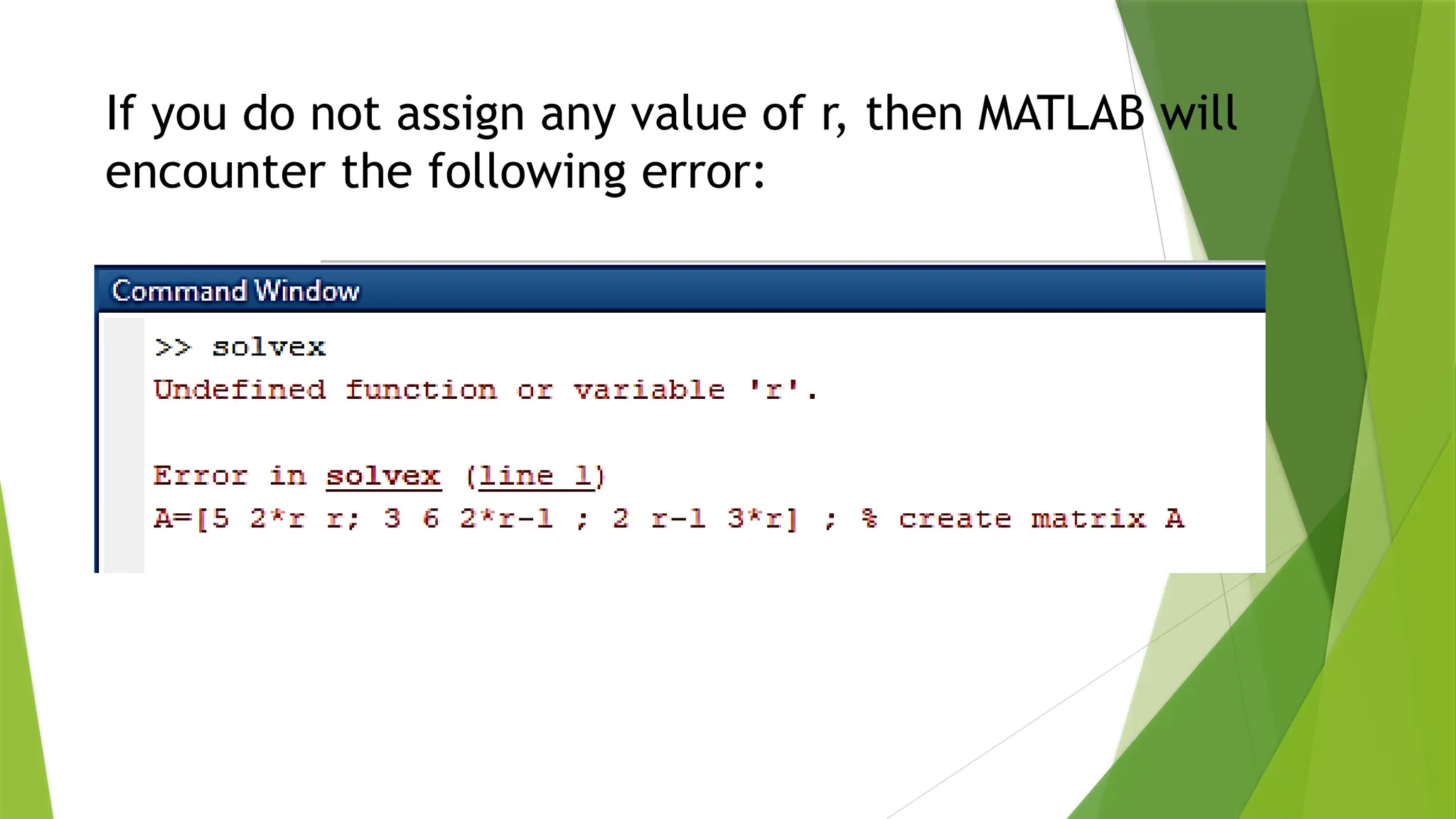
The document discusses MATLAB's extendibility through user-written programs and its ease of use, highlighting its higher-level language features. It details the creation and execution of script files (.m files) and warns against naming script files the same as variables to avoid access issues. An example is provided for writing both a script file and a function file to solve a system of linear equations, along with suggestions for error handling in functions.




![• Example of a script file: Let us write a script file to solve the following system of linear equations: [ 5 2𝑟 𝑟 3 6 2 𝑟 − 1 2 𝑟 − 1 3 𝑟 ][ 𝑥1 𝑥2 𝑥3 ]= [ 2 3 5] • How you create this file, write the commands in it, and save the file depends on the computer you are using. • In any case, you are creating a file called solvex . m, which will be saved on some disk drive in some directory (or folder) .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14-241116201559-f8fae1e4/75/Creating-Functions-file-in-Matrices-Laboratory-using-MATLAB-5-2048.jpg)