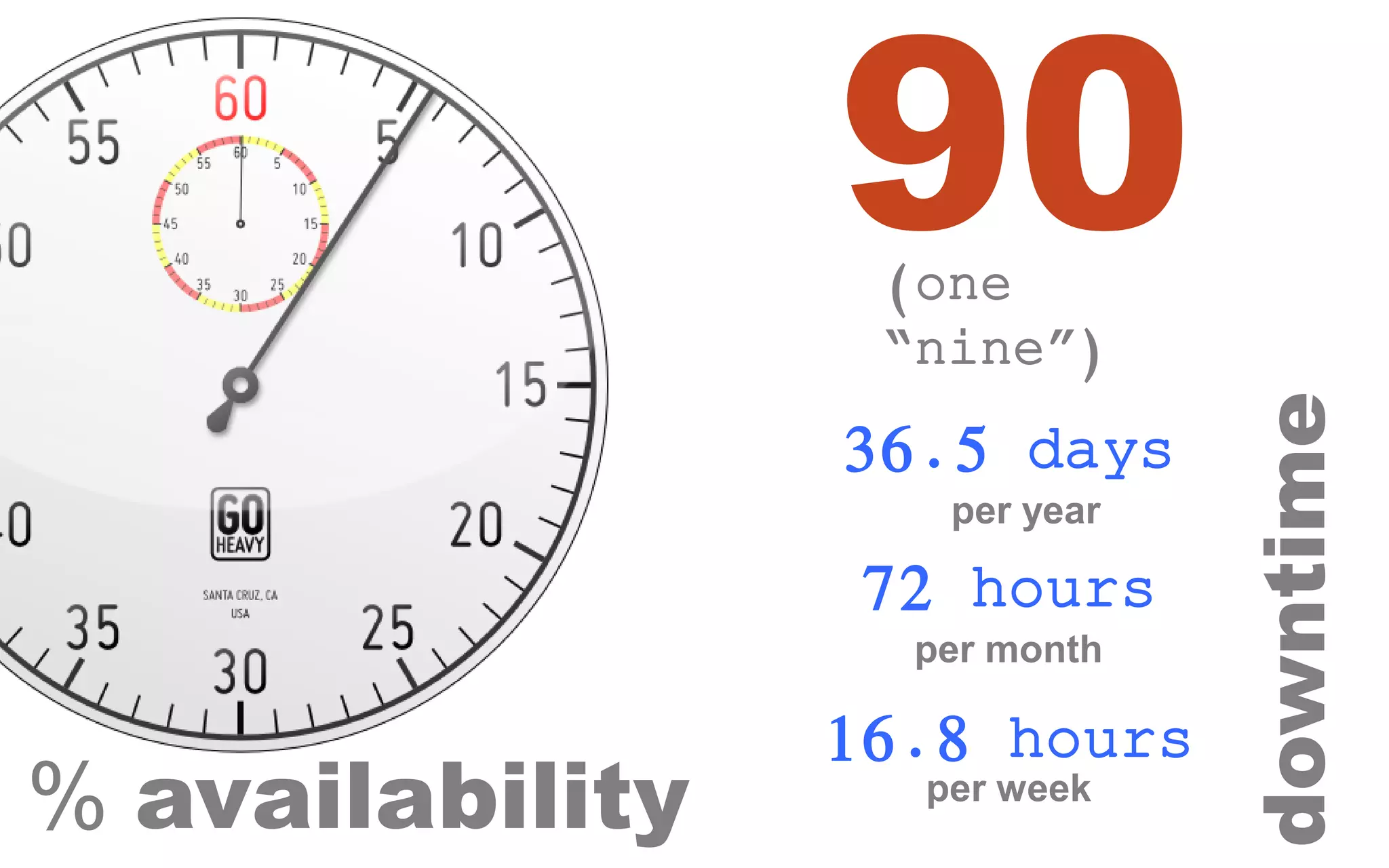
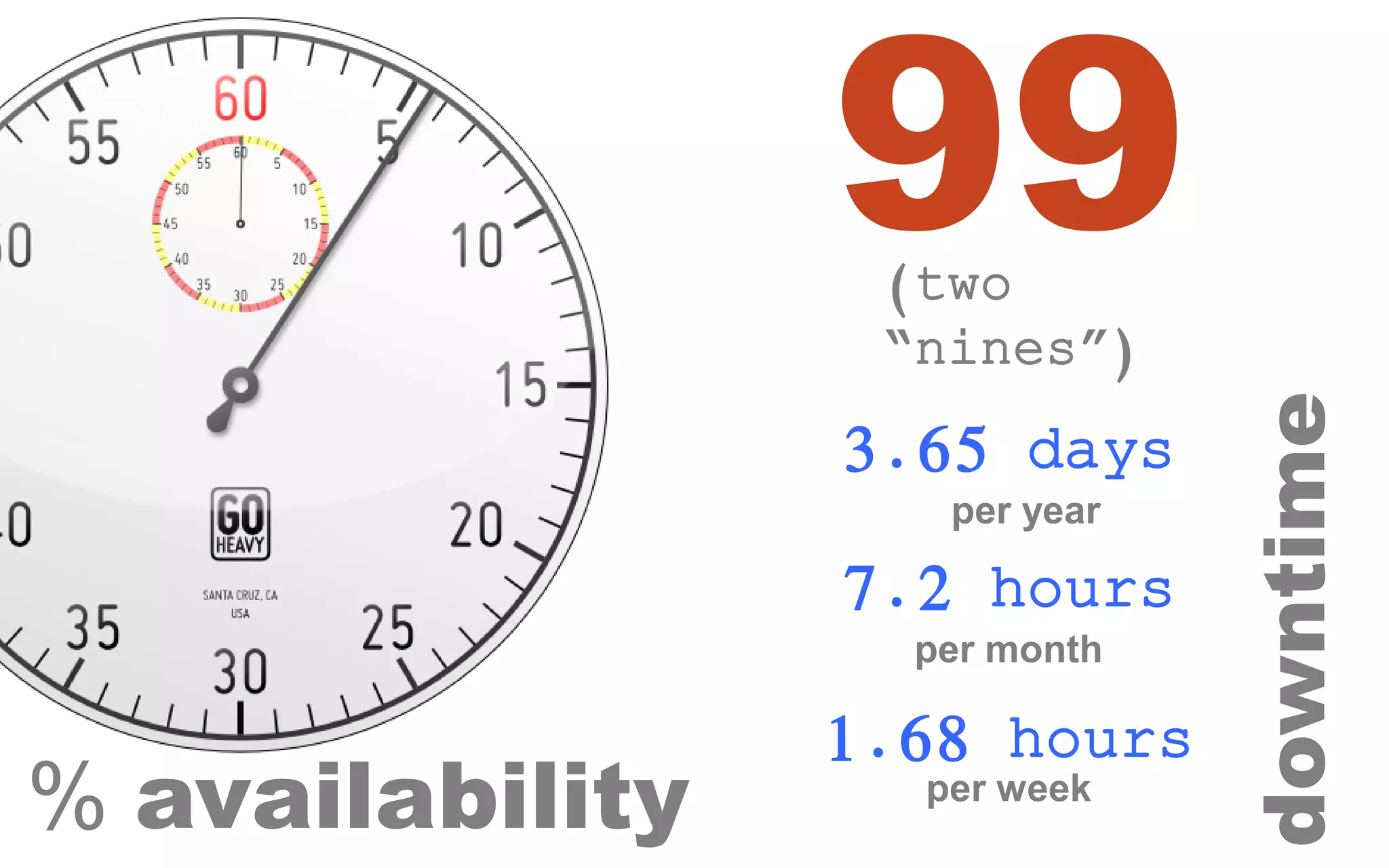
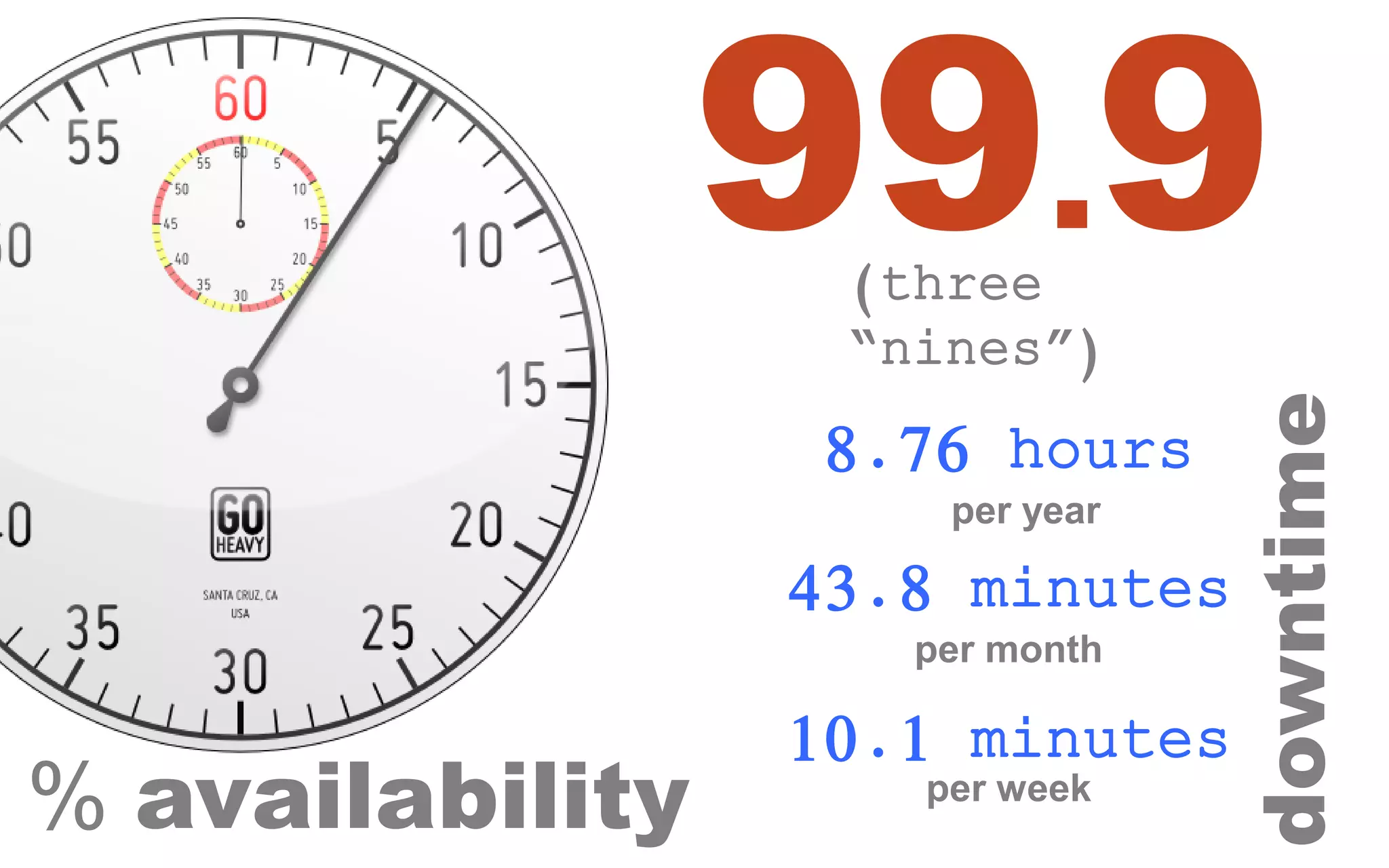
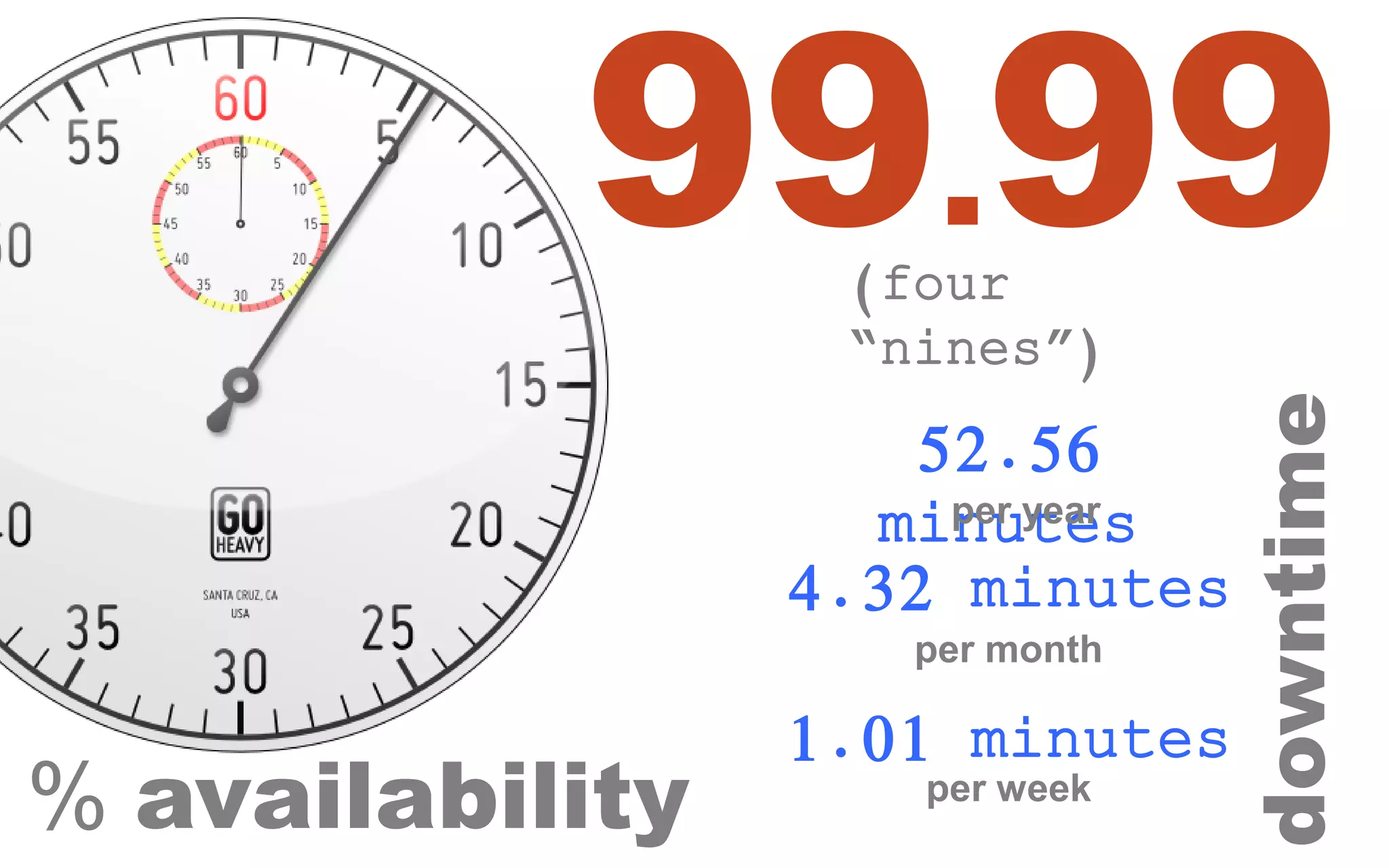
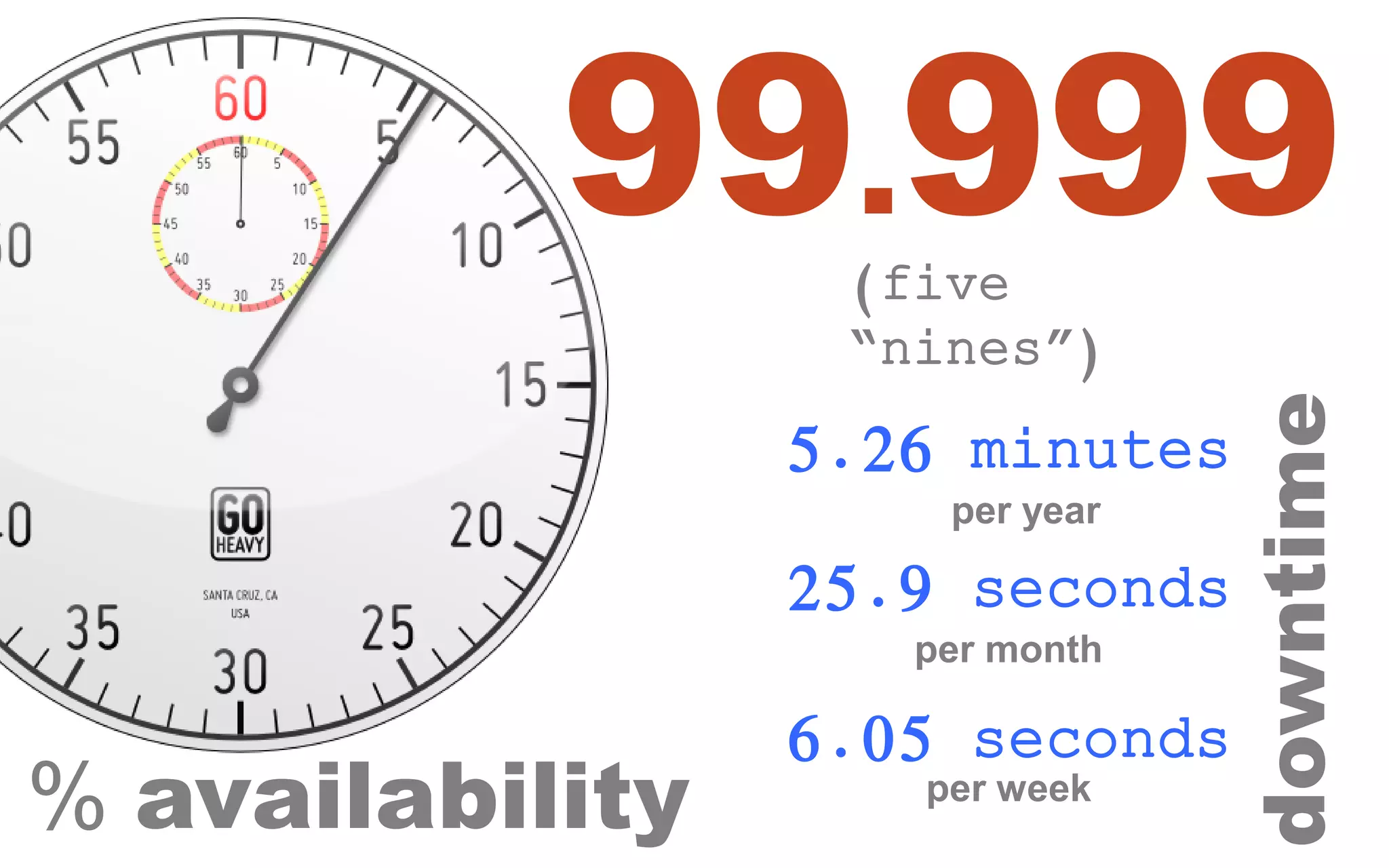
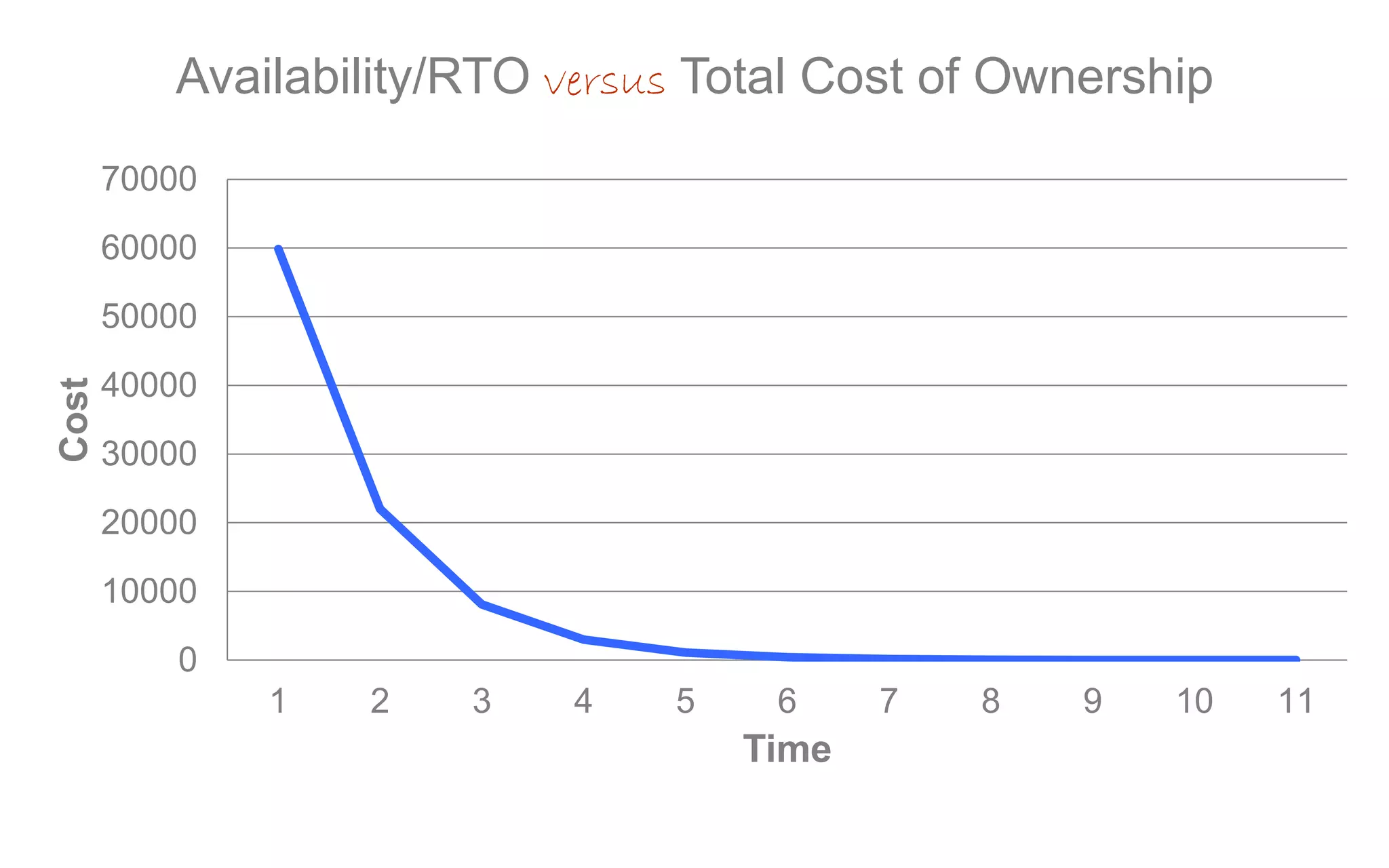
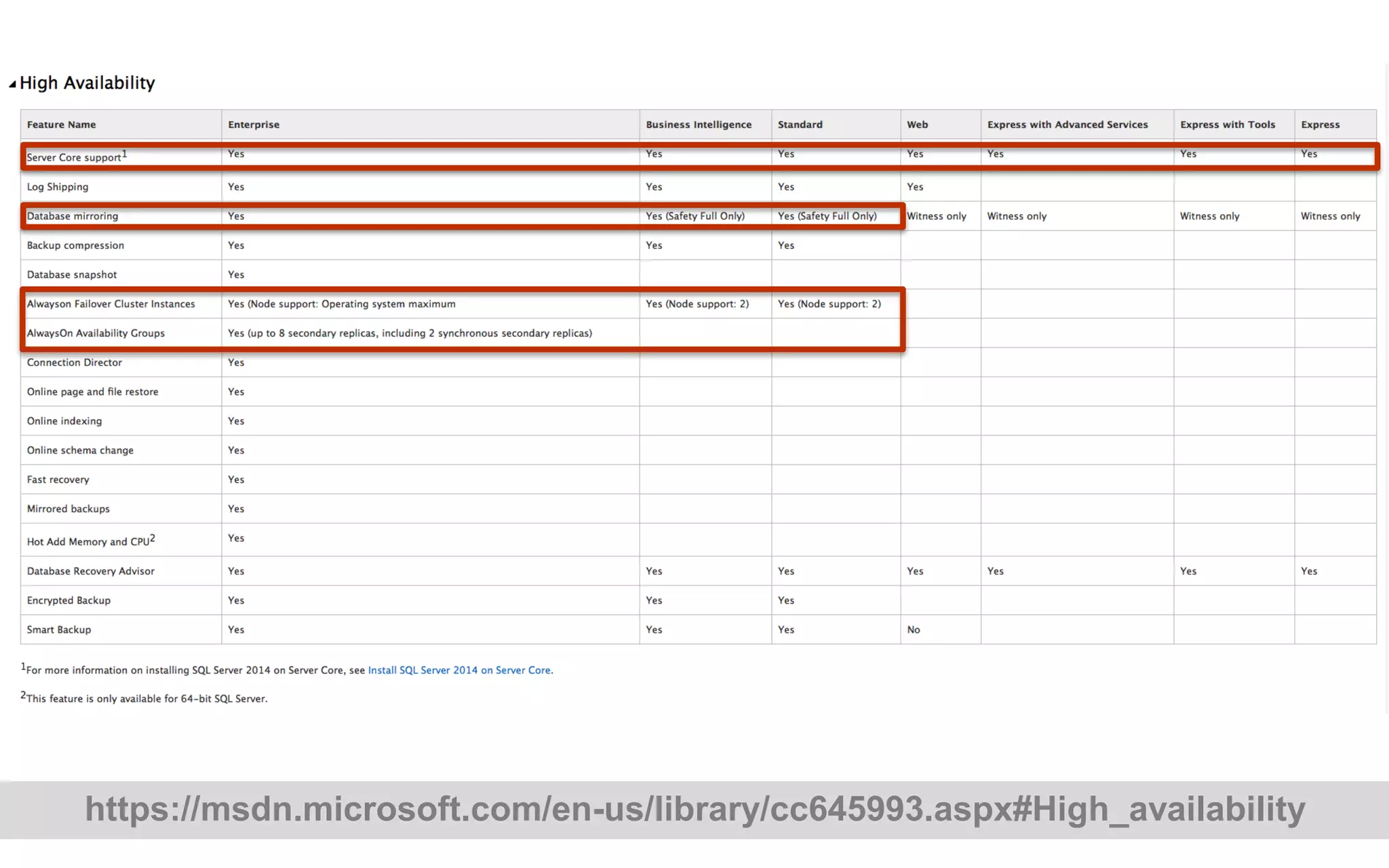
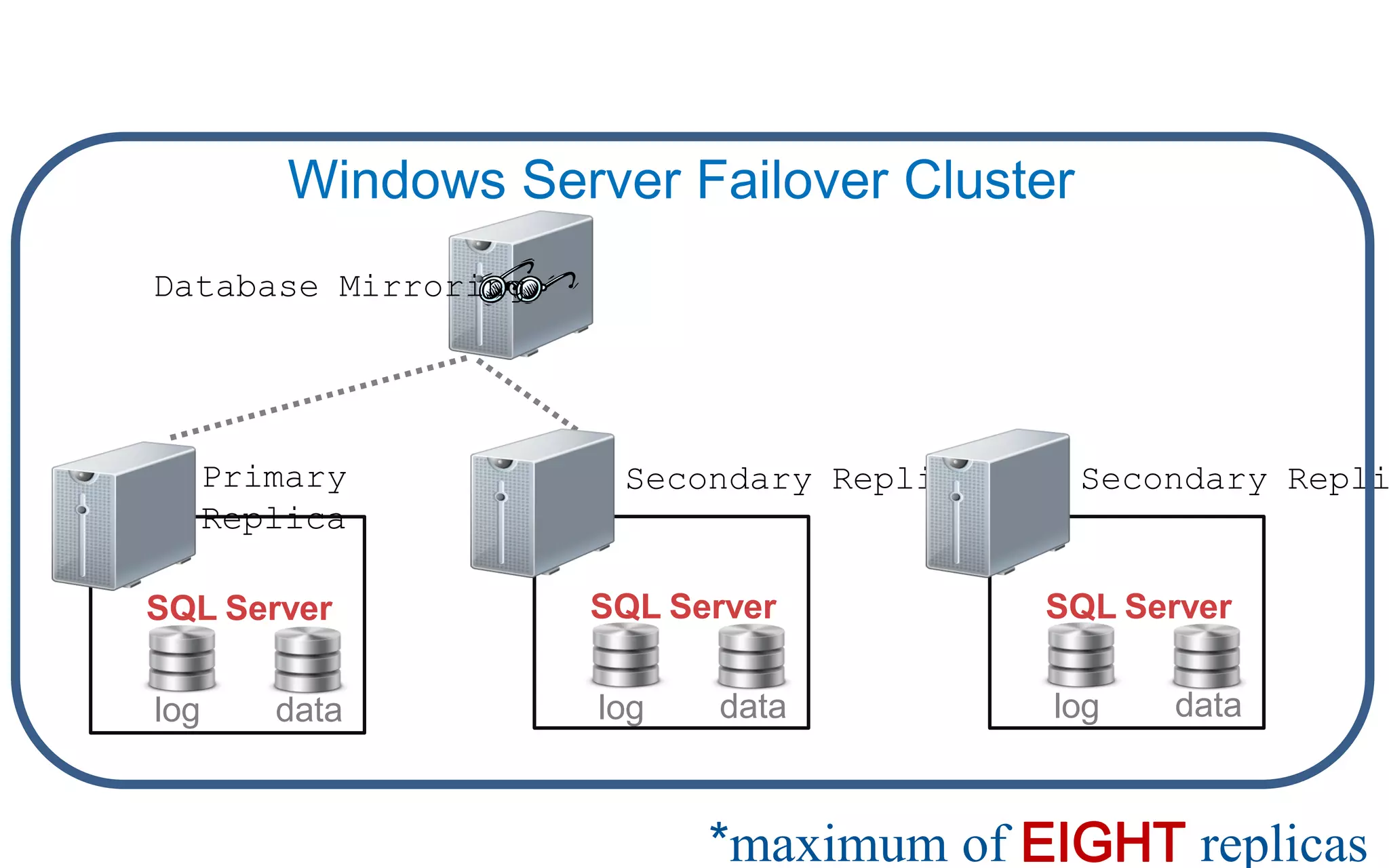
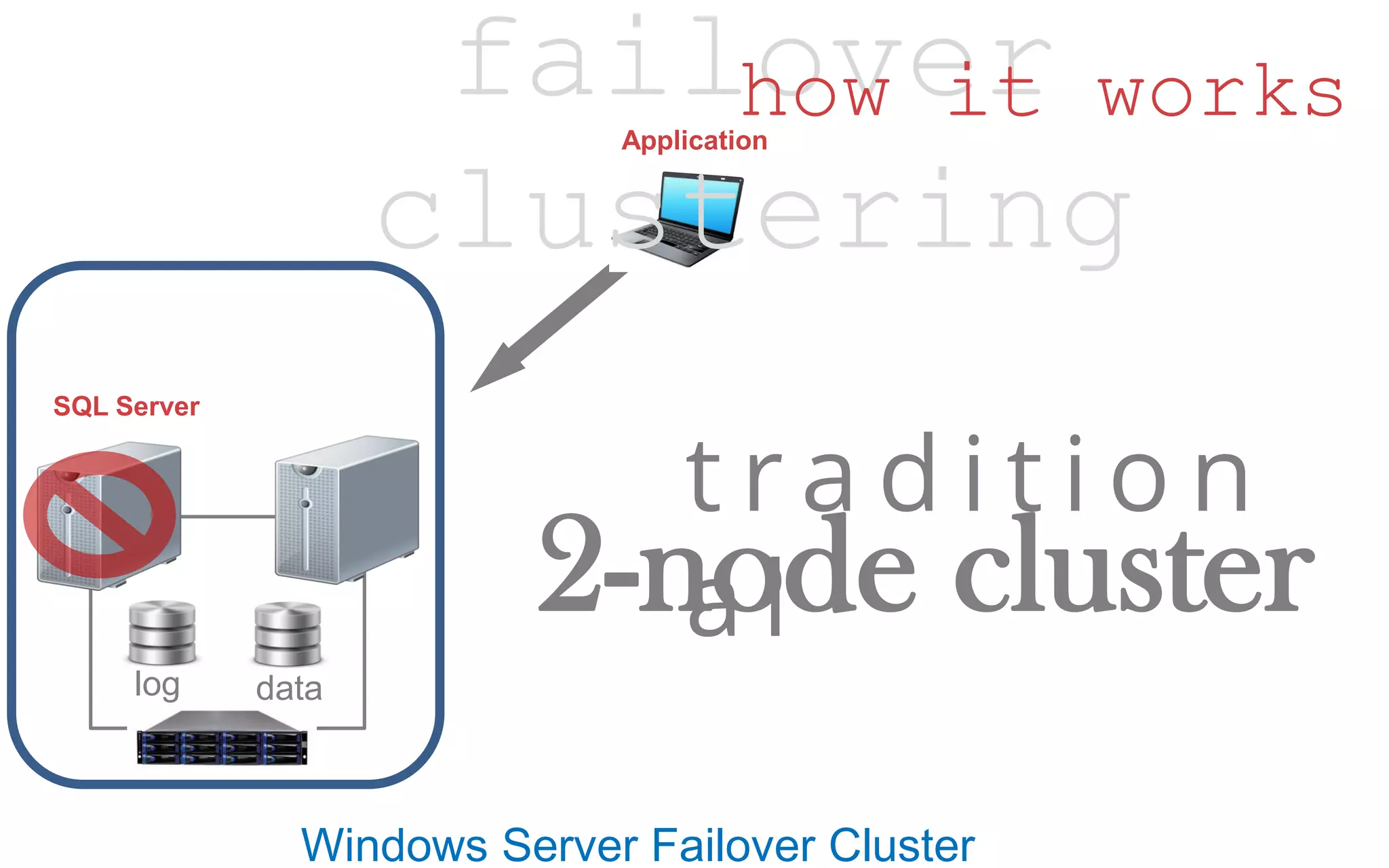
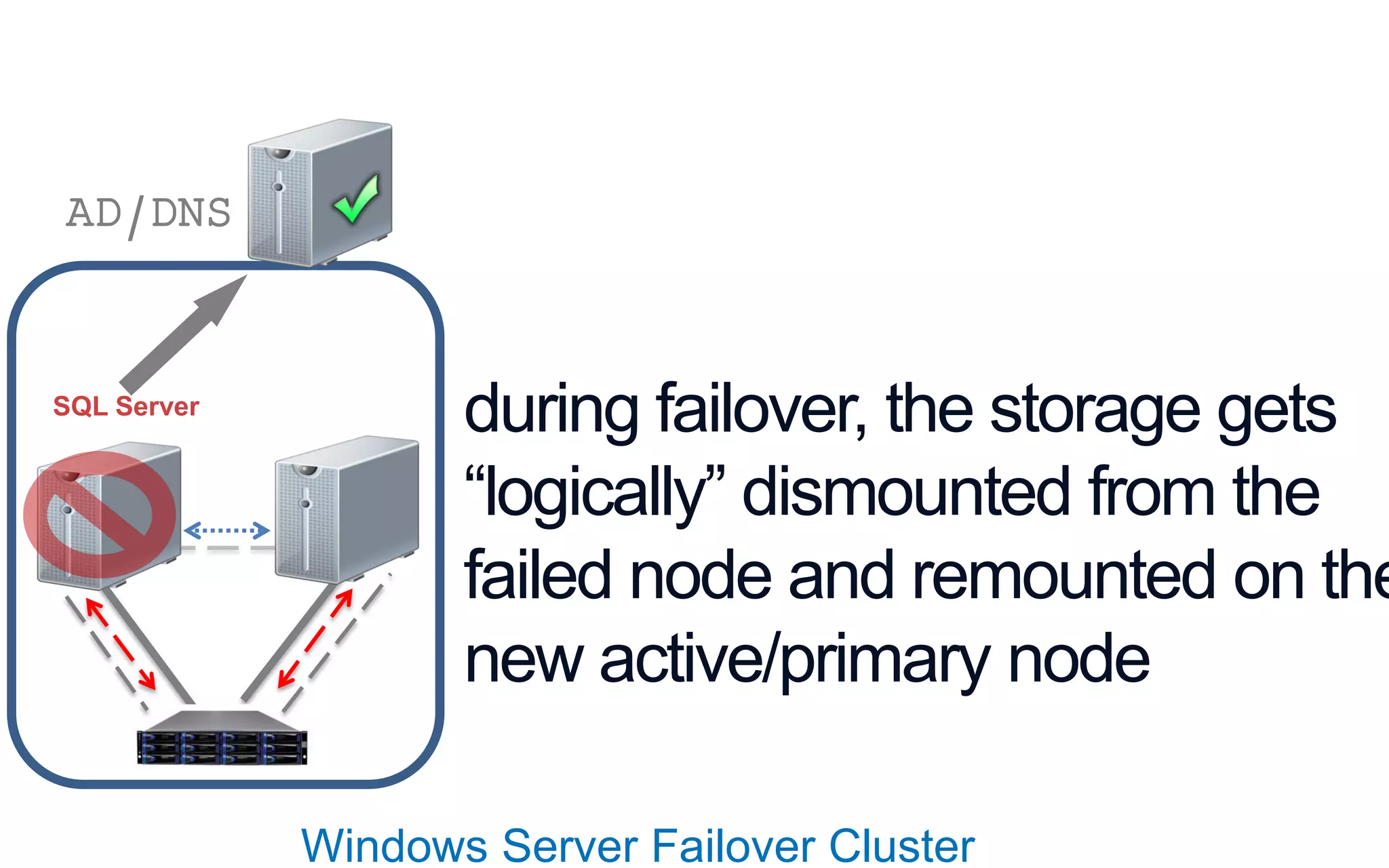
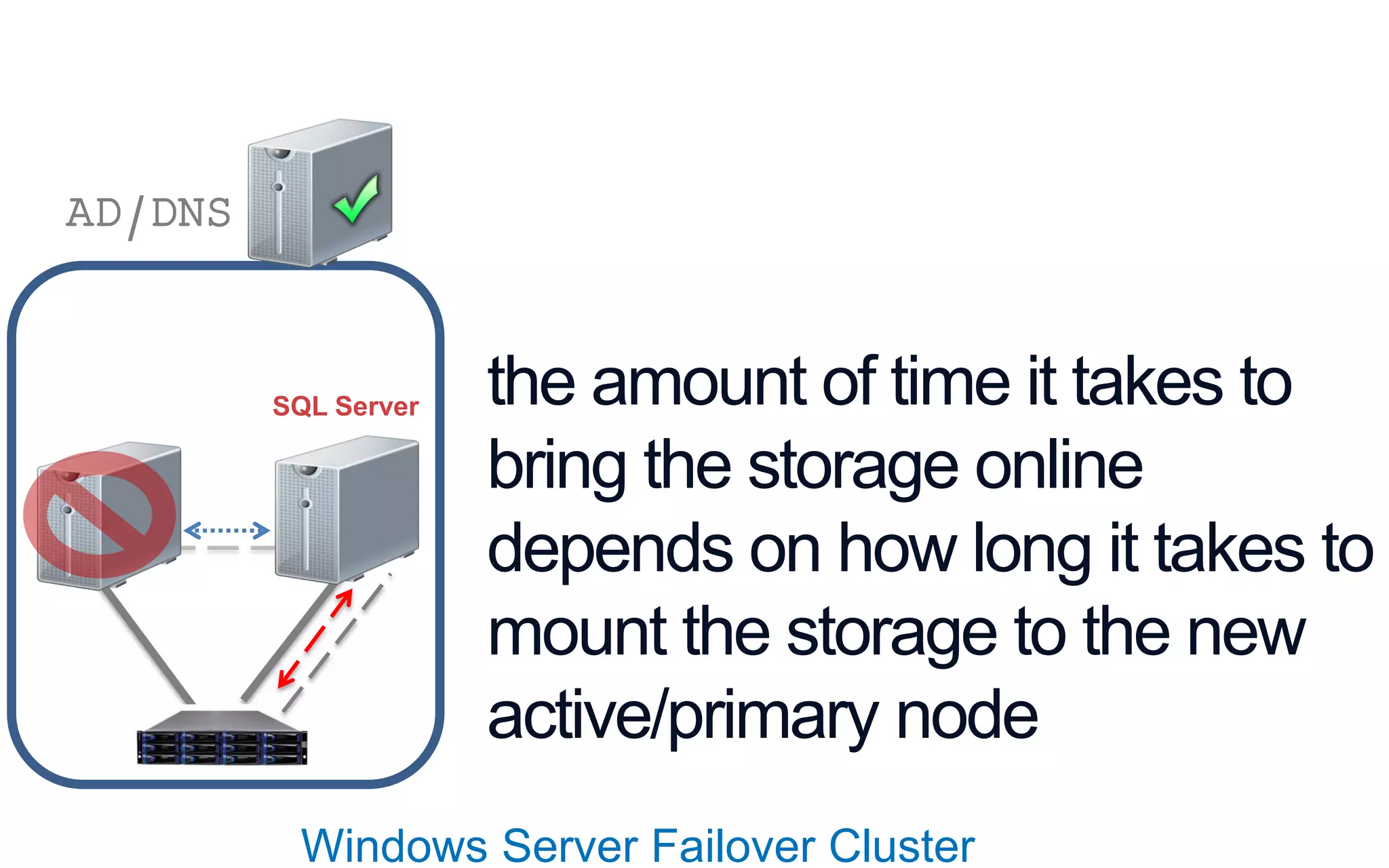
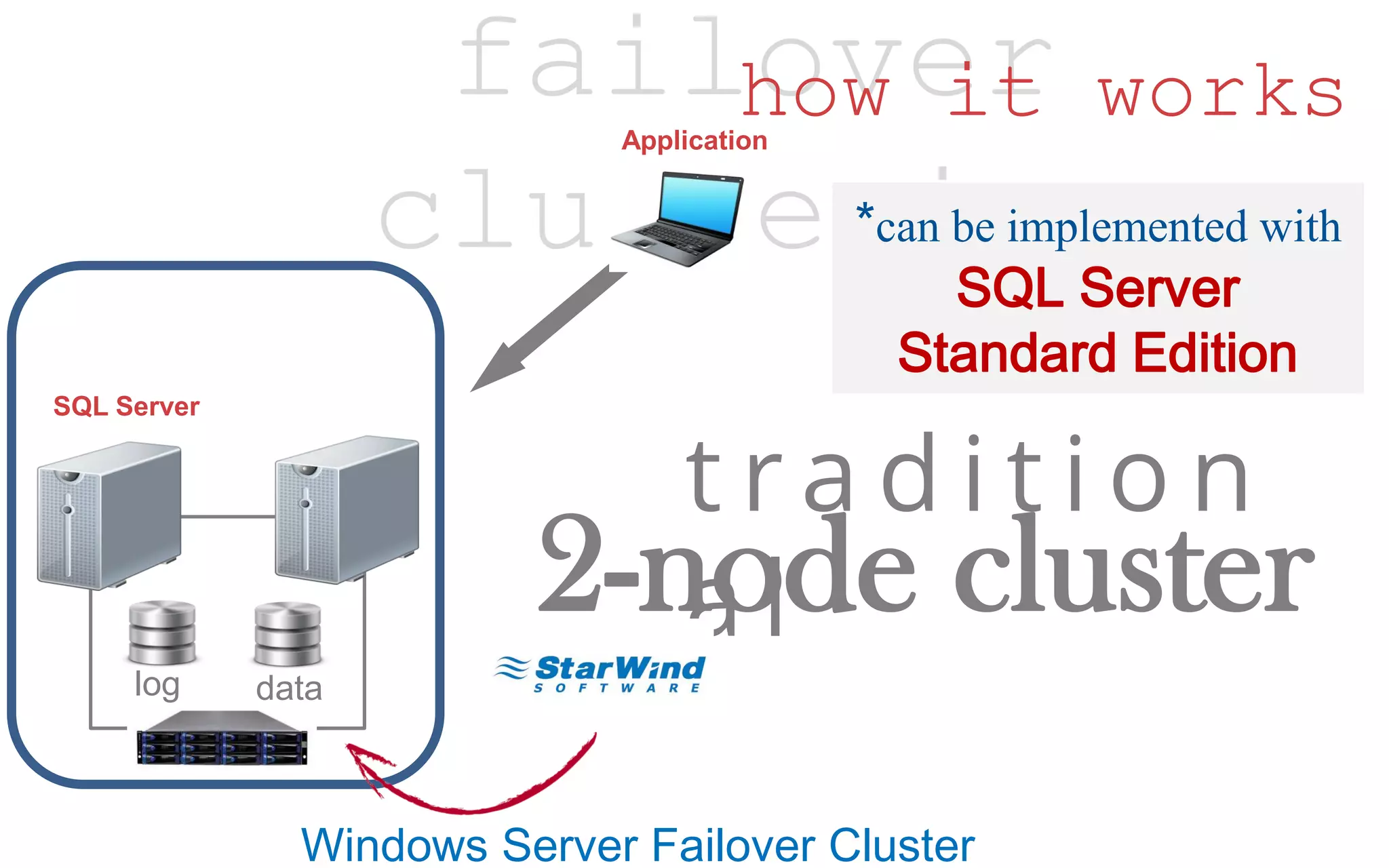
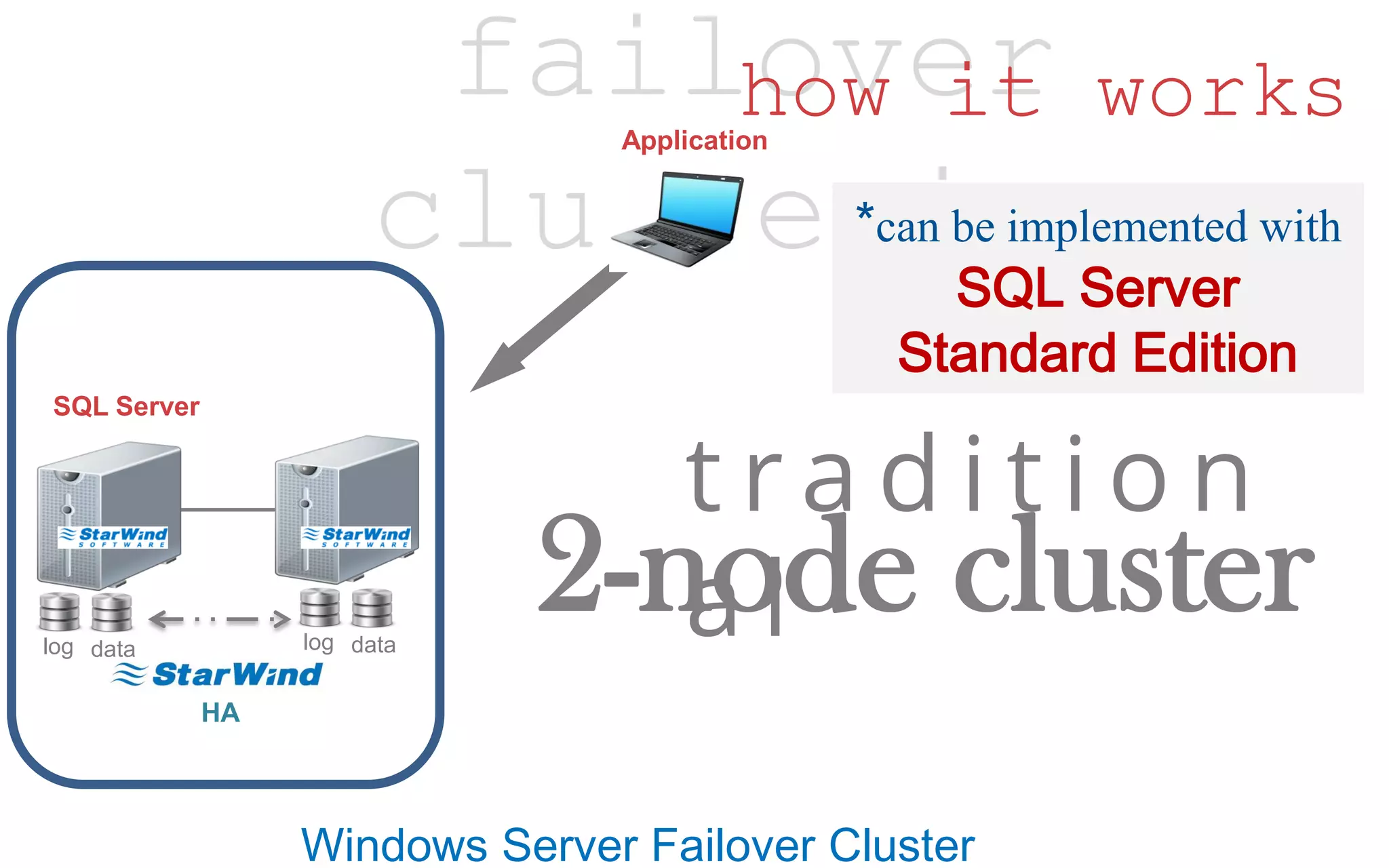
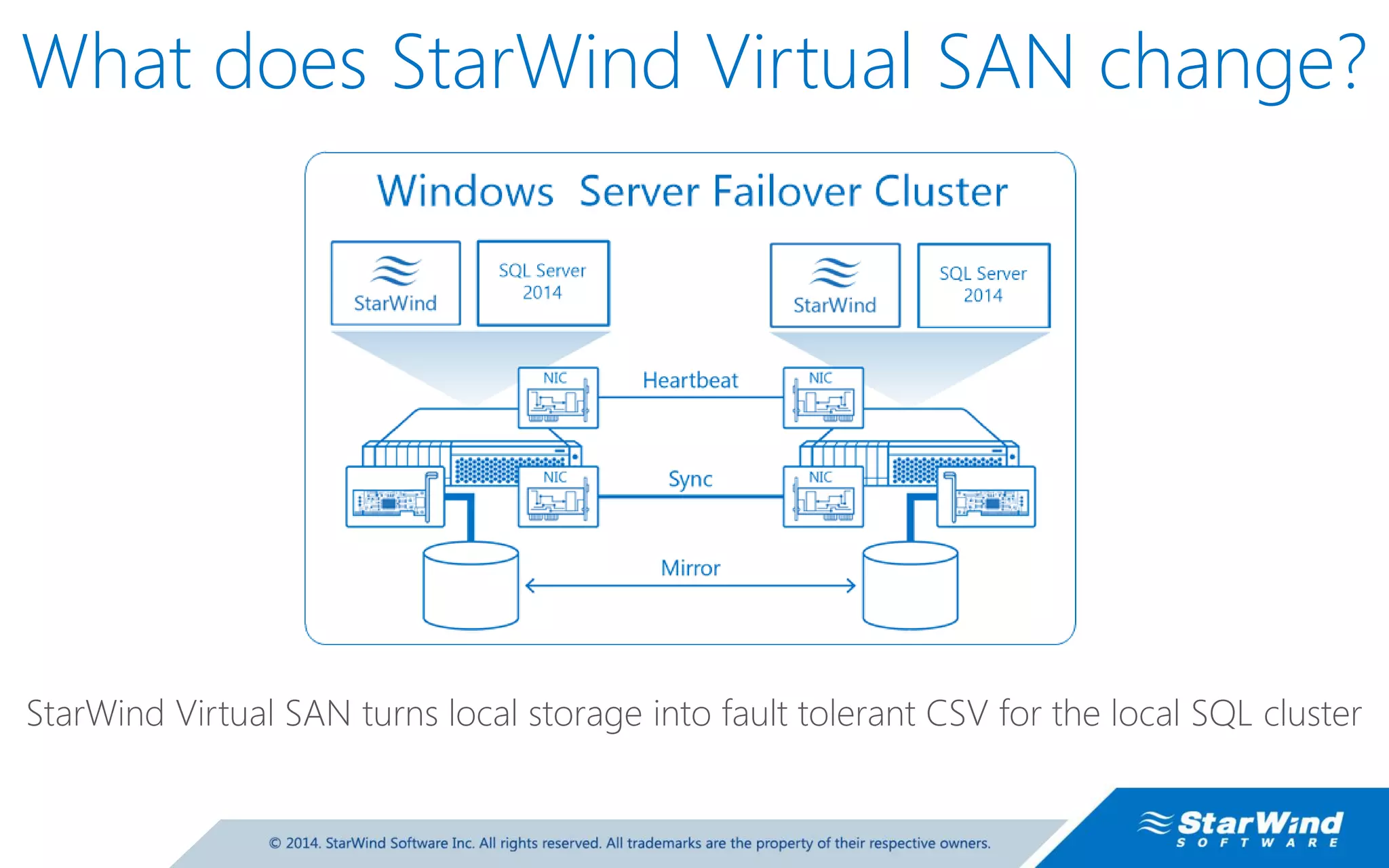
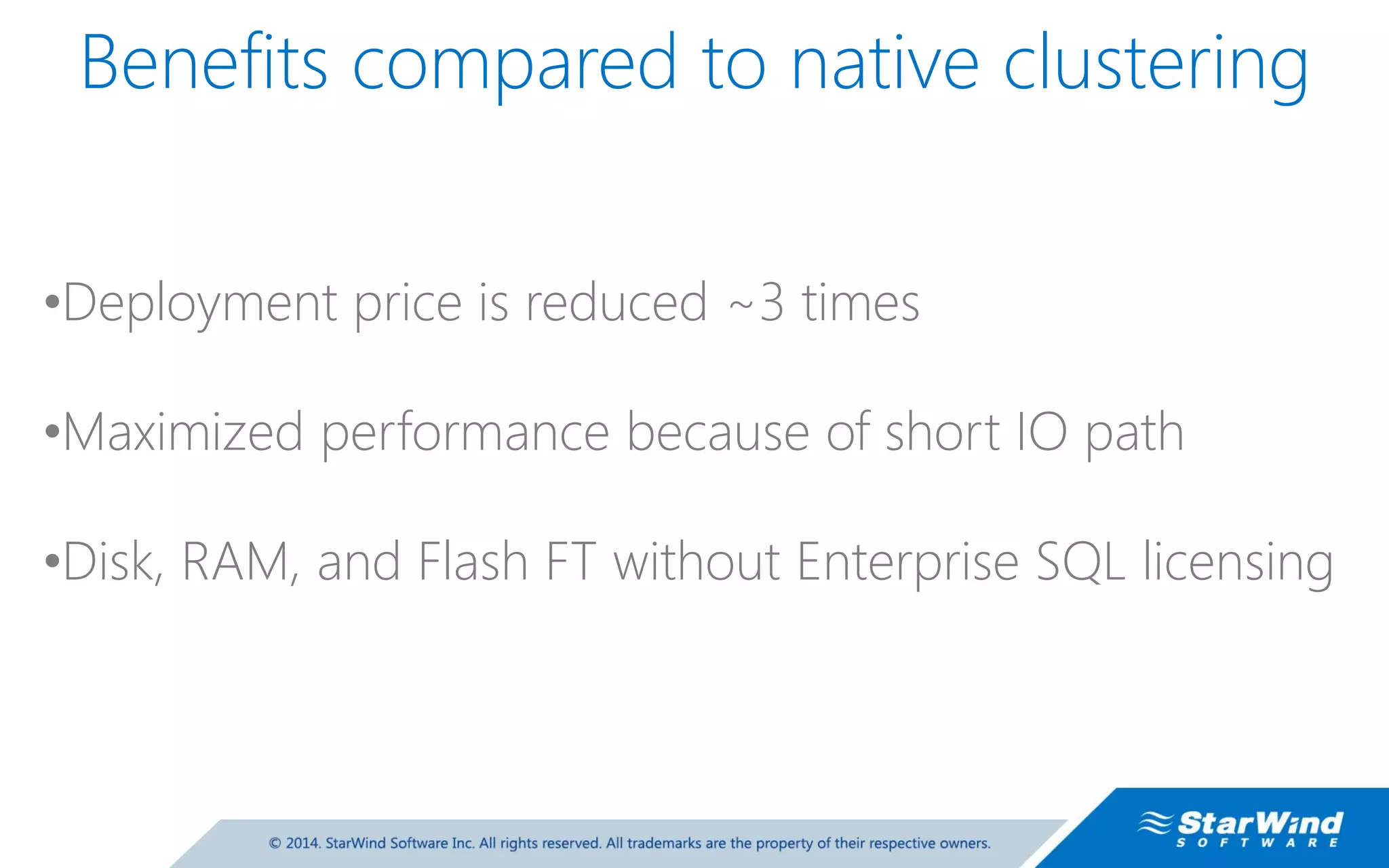
The document discusses high availability (HA) in SQL Server databases, emphasizing the significance of continuous uptime versus mere operational status. It covers various availability percentages and their corresponding downtime, highlighting solutions like AlwaysOn Availability Groups and Failover Clustering to enhance resilience. Additionally, it introduces Starwind Virtual SAN as a cost-effective way to create fault-tolerant Cluster Shared Volumes by leveraging local storage.