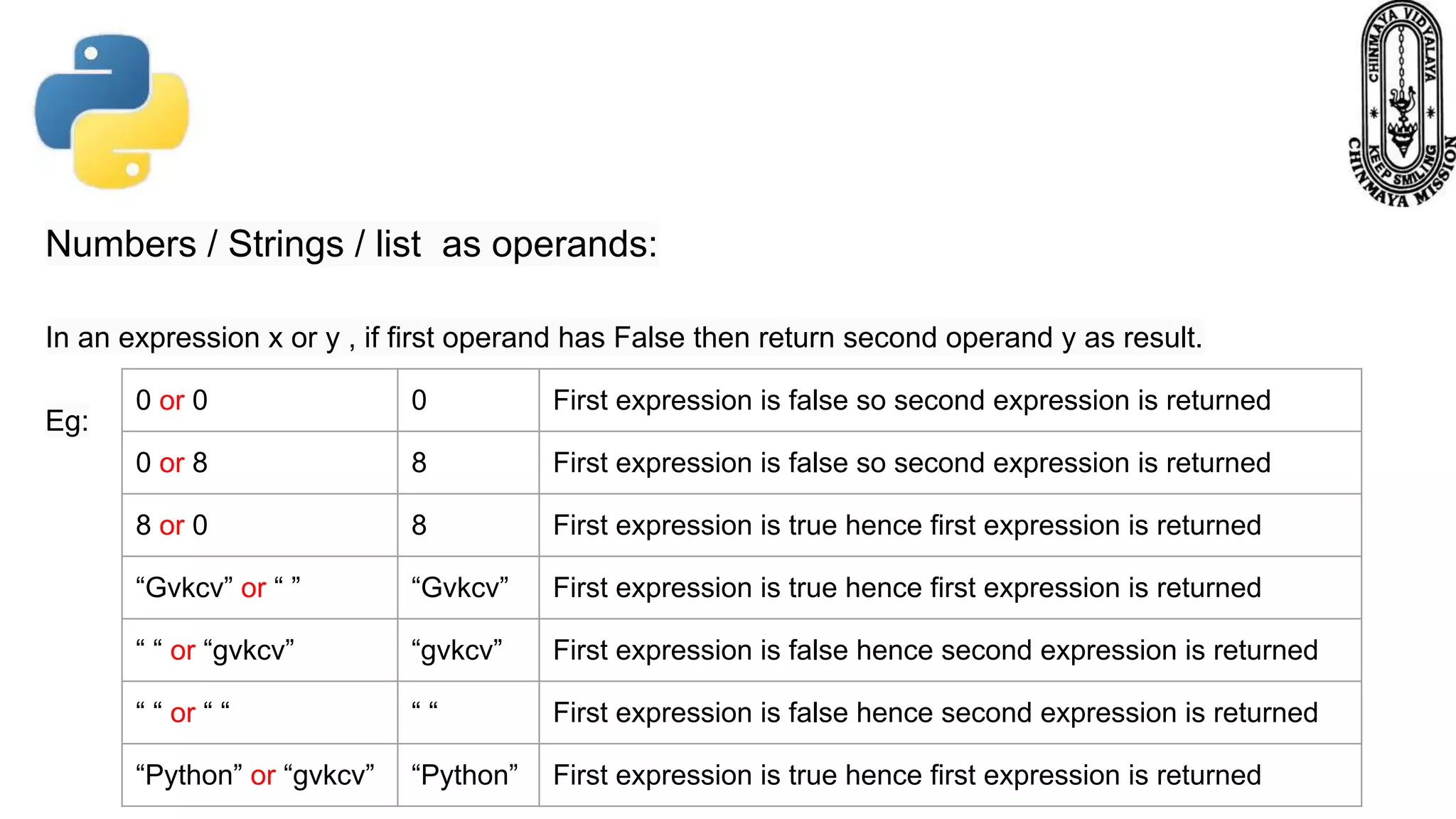
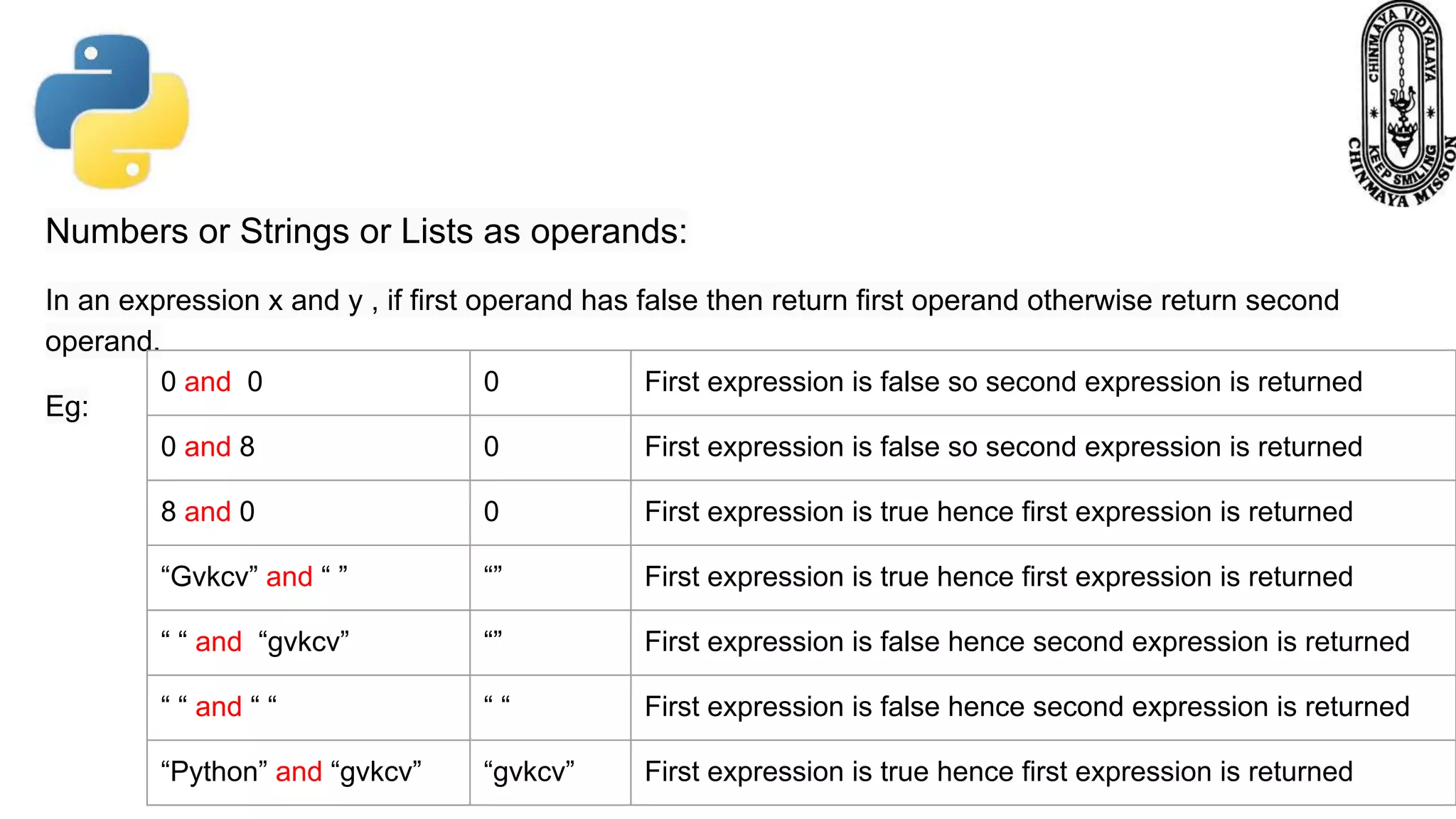
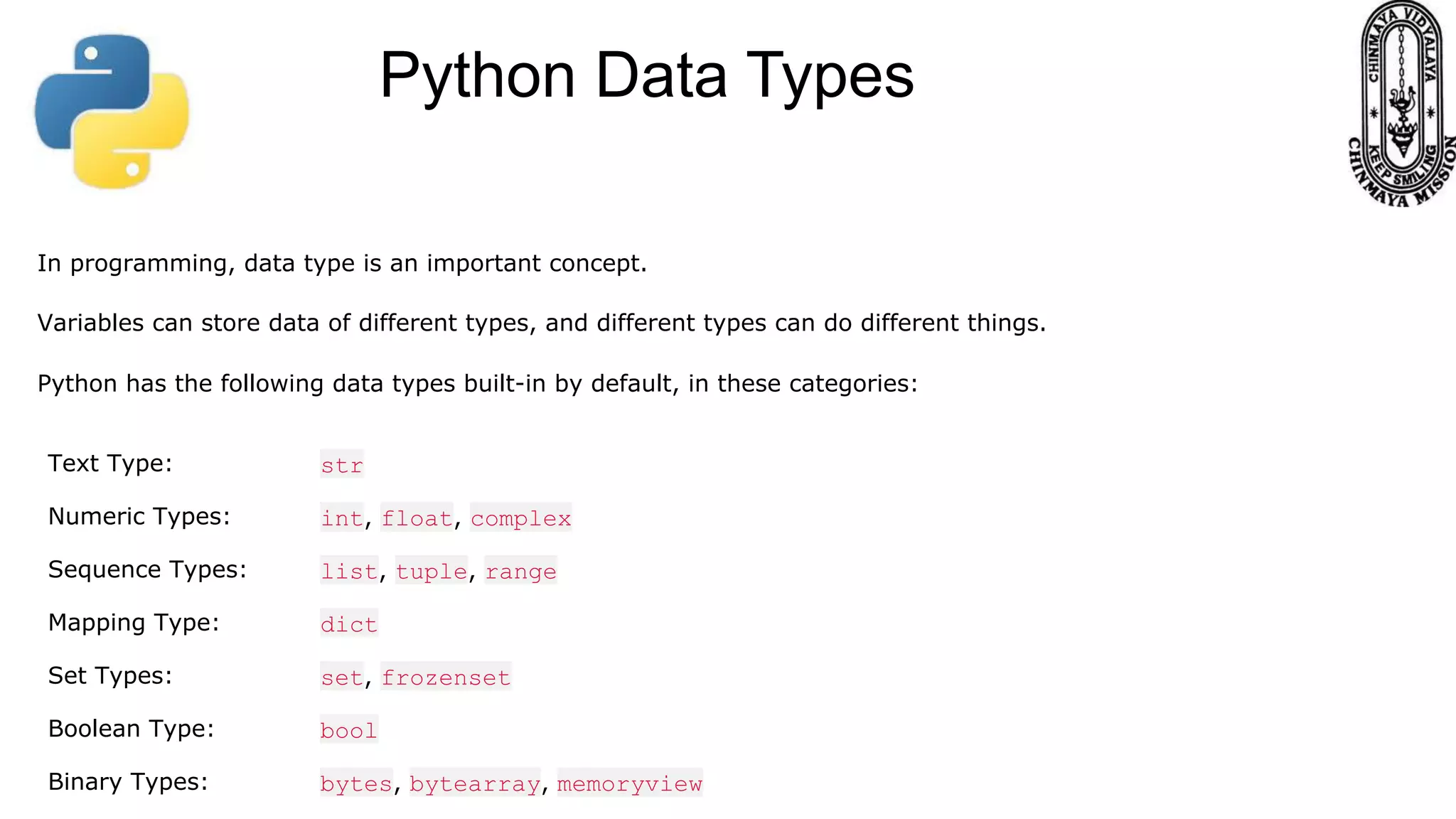
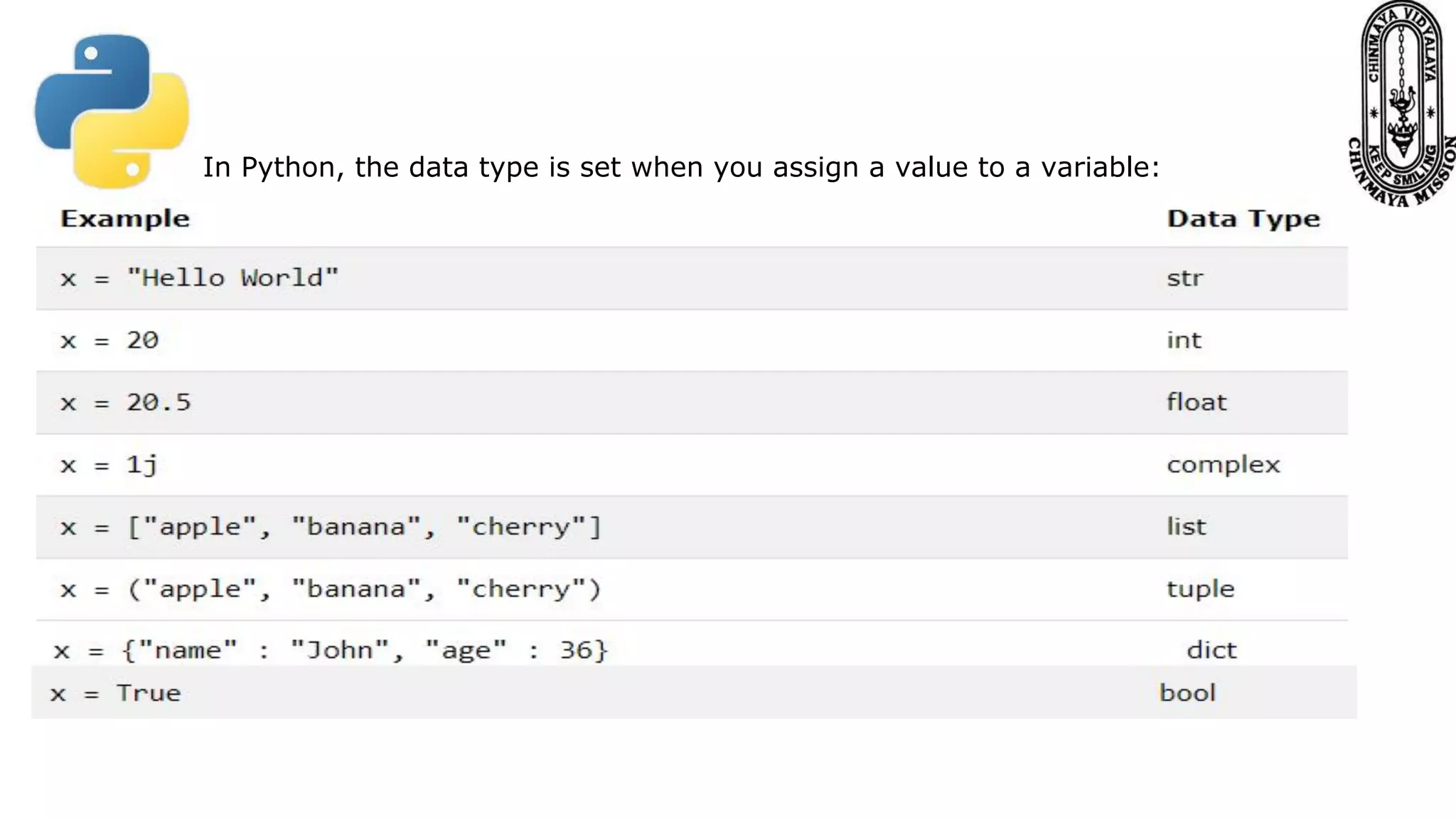
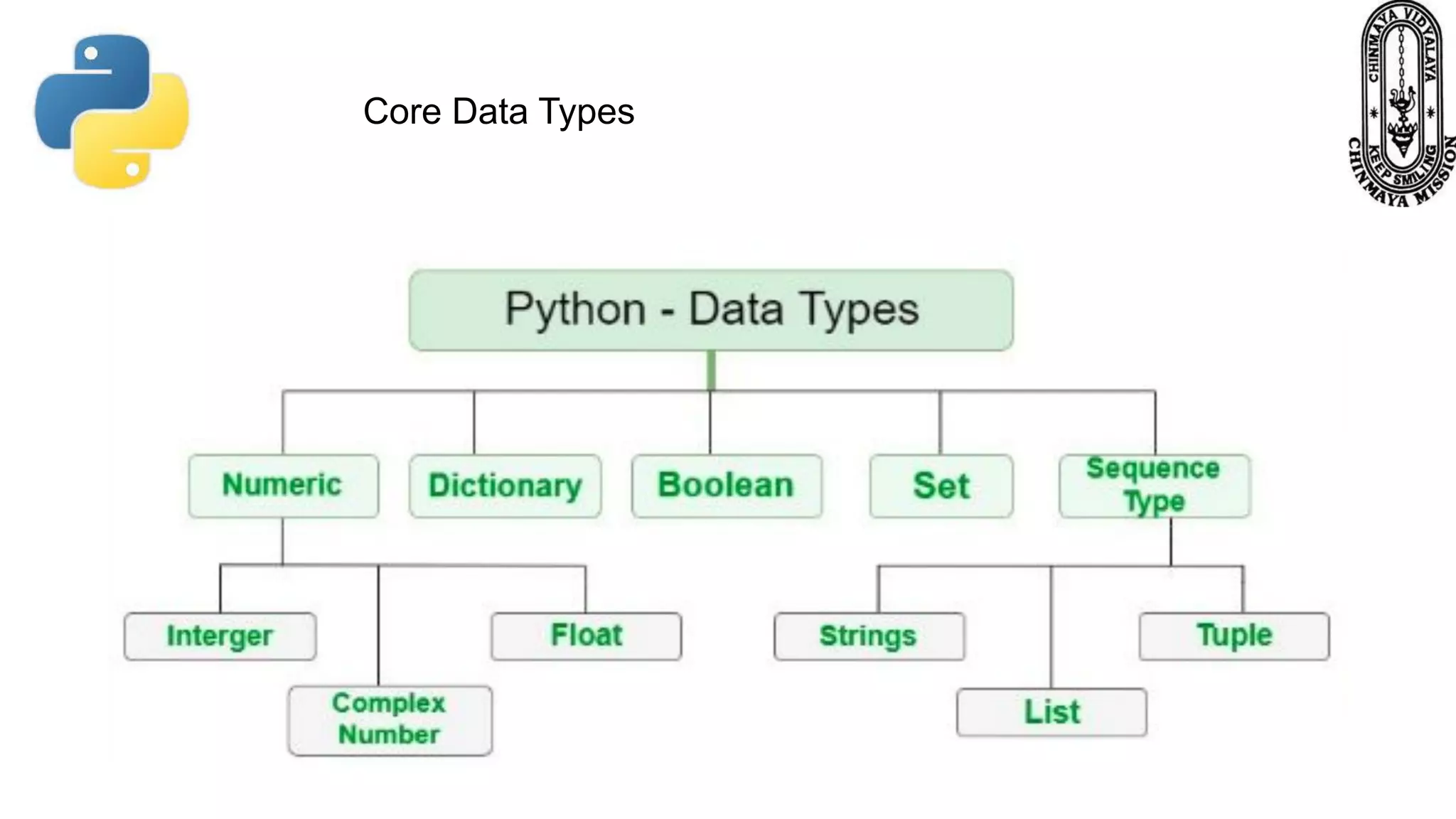
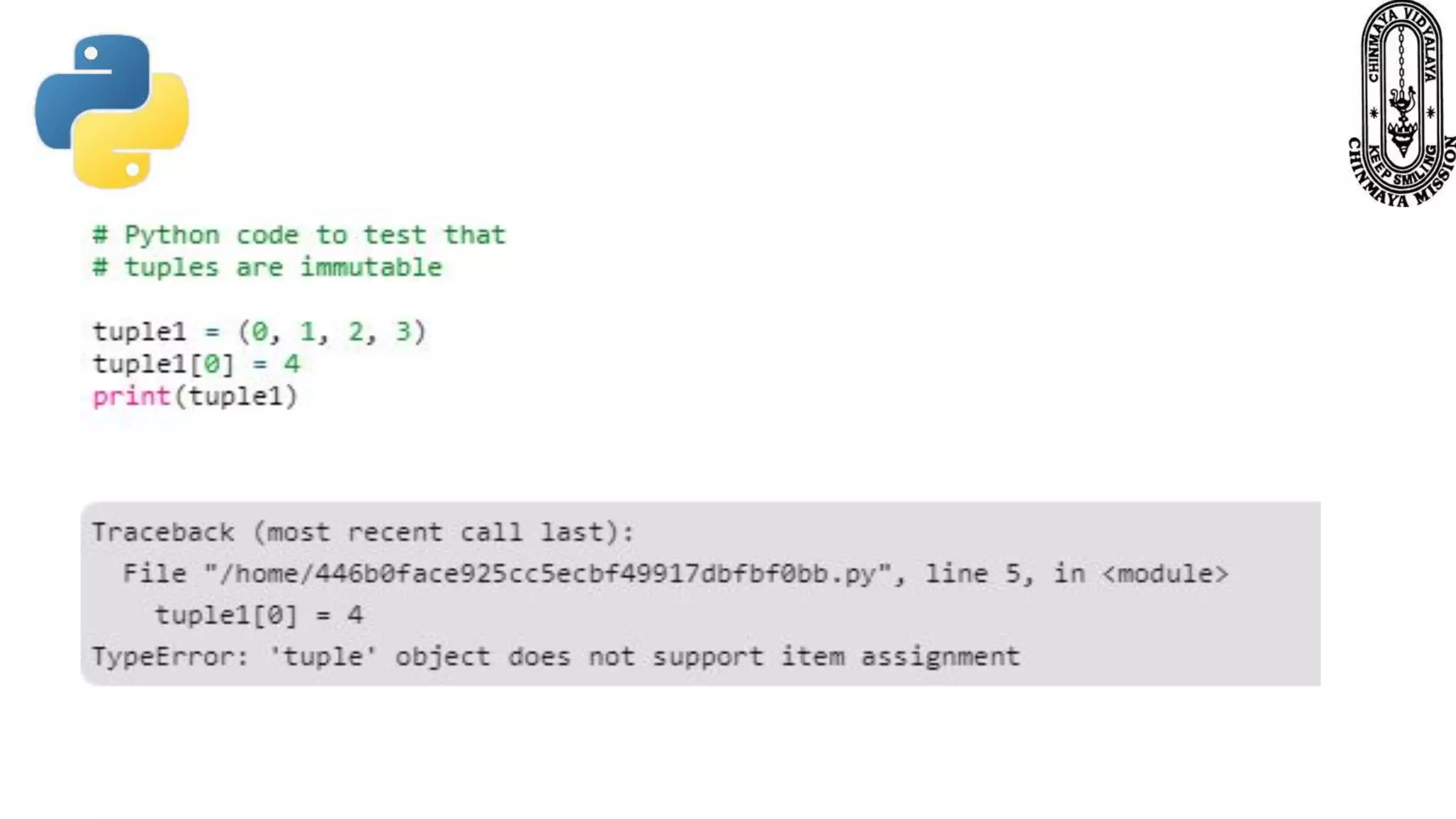
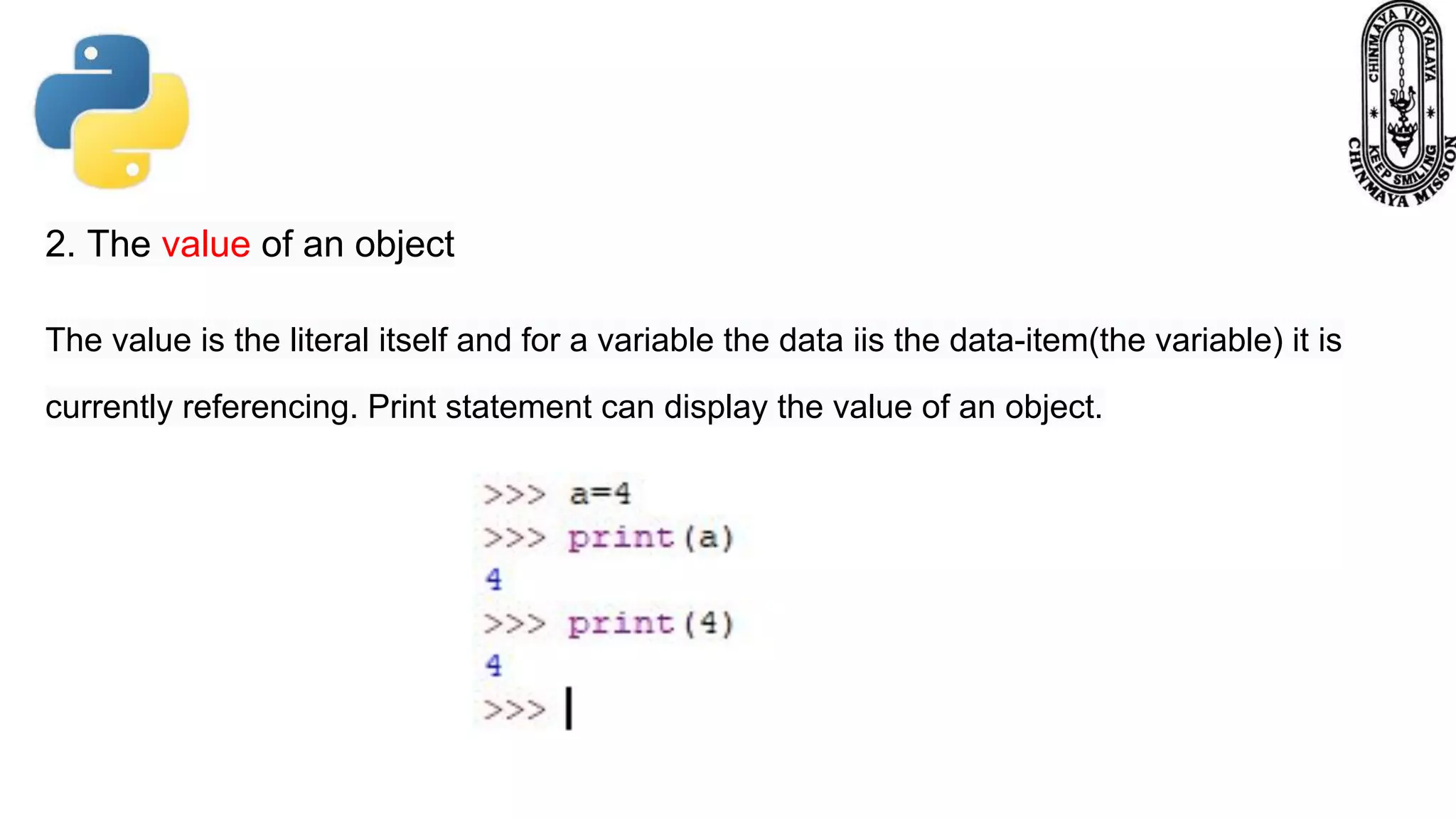
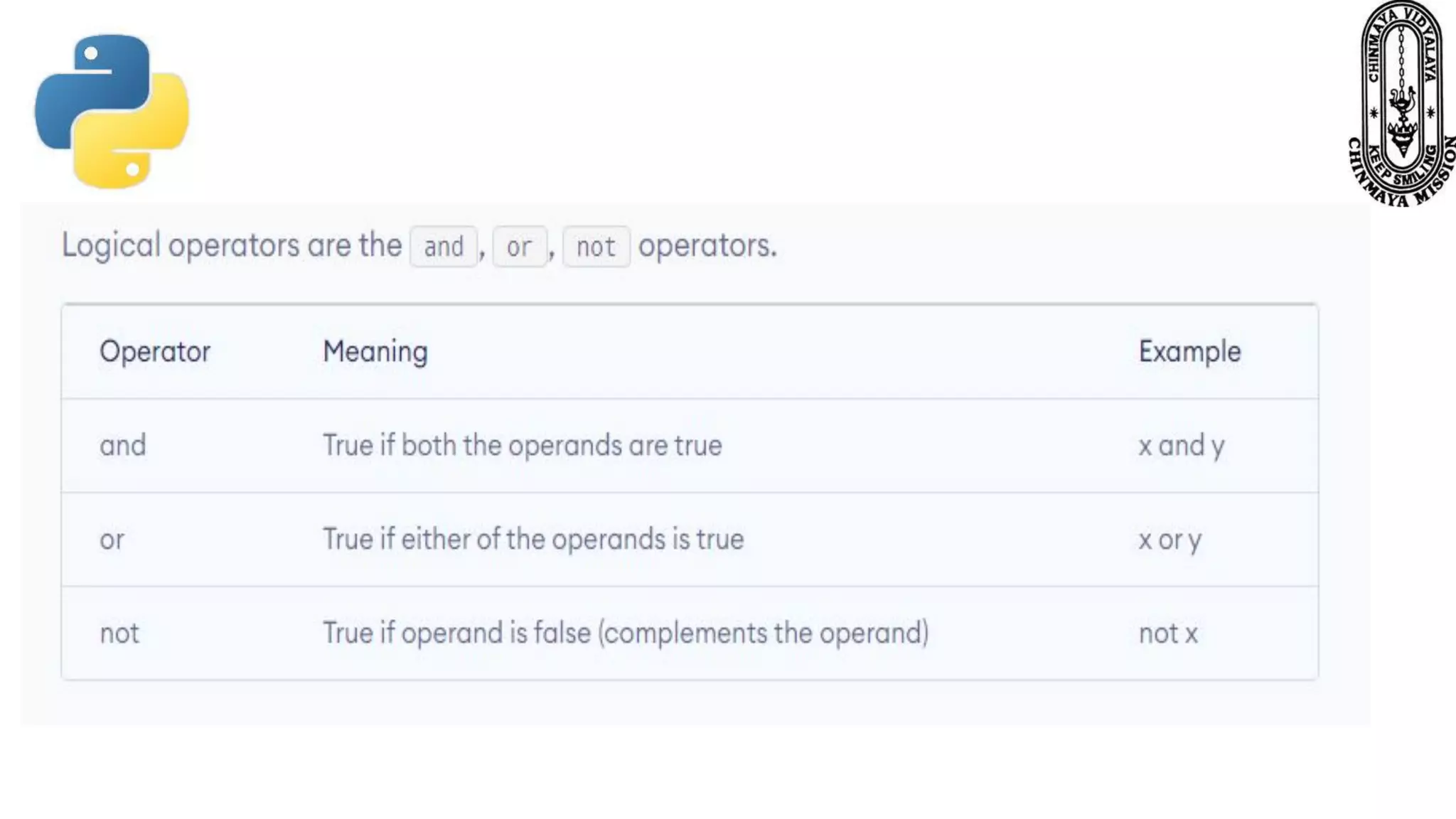
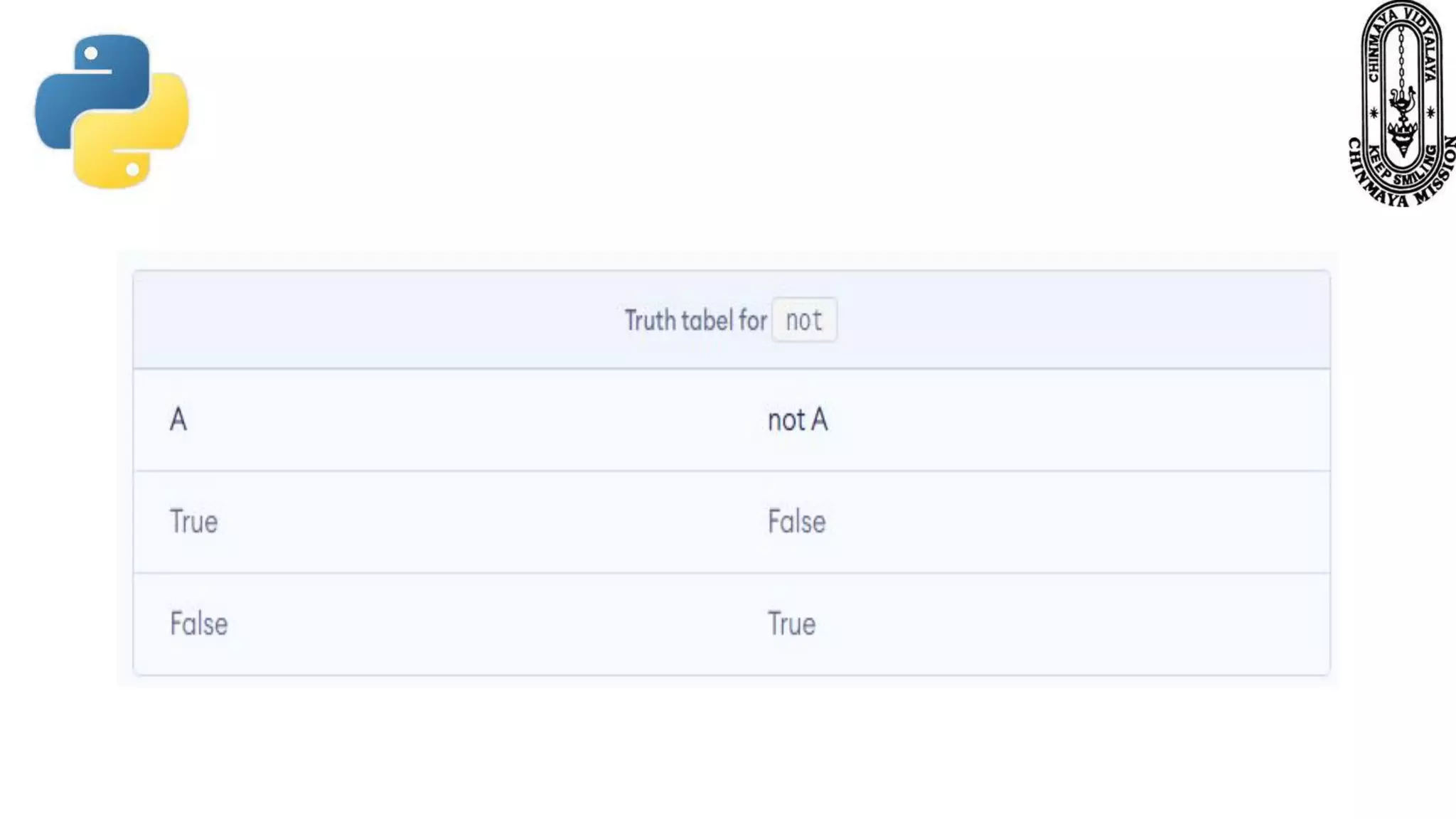
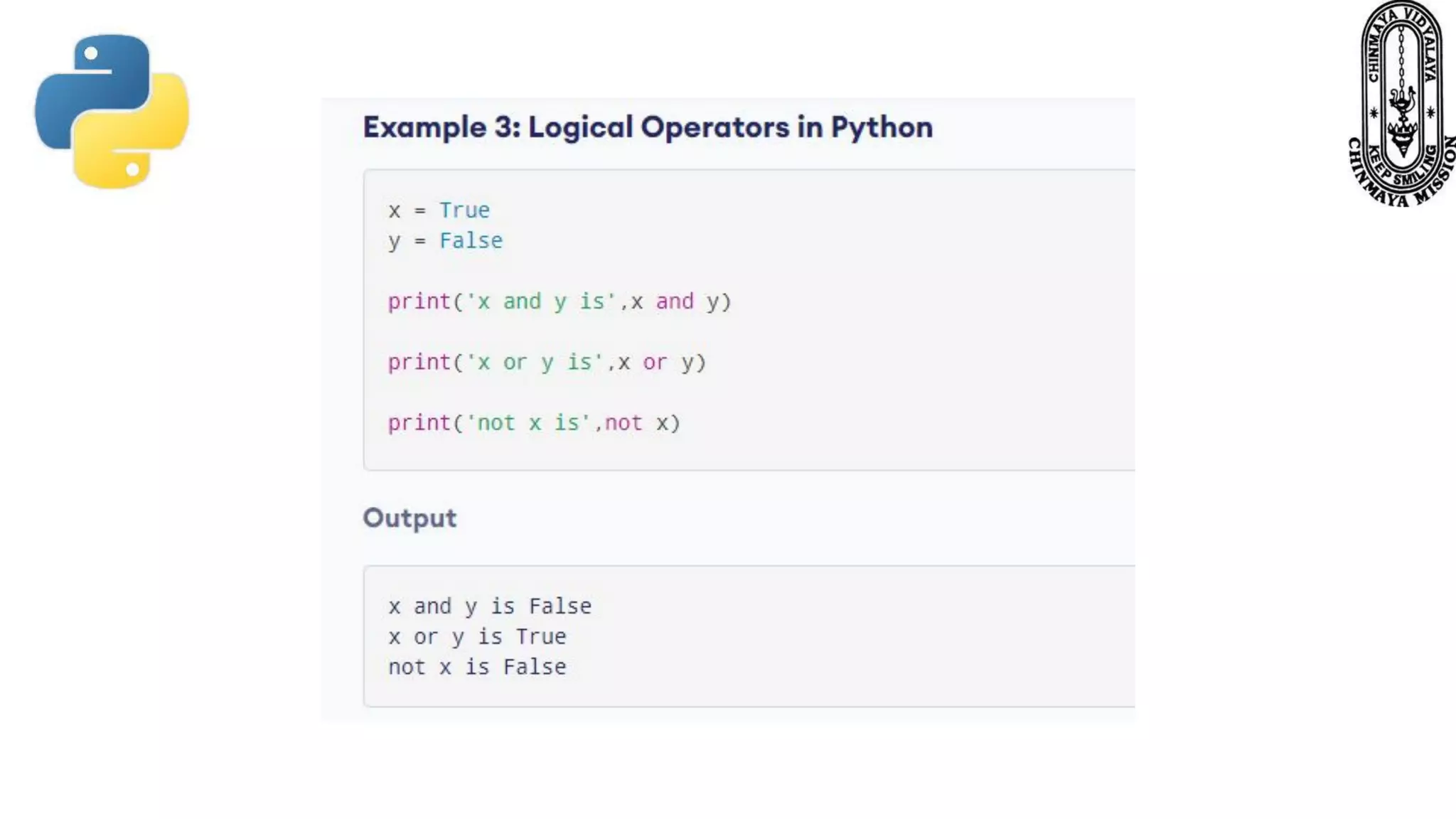
This document provides information about various Python data types including text, numeric, sequence, mapping, set, boolean, and binary types. It discusses how variables can store different data types in Python. It also covers numeric types like integers, floats, and complexes. Strings are described as arrays of characters that can be indexed and sliced. Boolean values and operators like or, and, and not are explained. The document contrasts mutable and immutable objects in Python.
















![Truth Value Testing Value with truth value as false Values with truth value as truth None All the other values are considered true False (Boolean value False) Zero for any numeric type,for example 0,0.0,0j Any empty sequence eg:( ),[ ], Any empty mapping eg: { } www.gvkcv.in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datahandling-200906045519/75/Data-handling-CBSE-PYTHON-CLASS-11-31-2048.jpg)