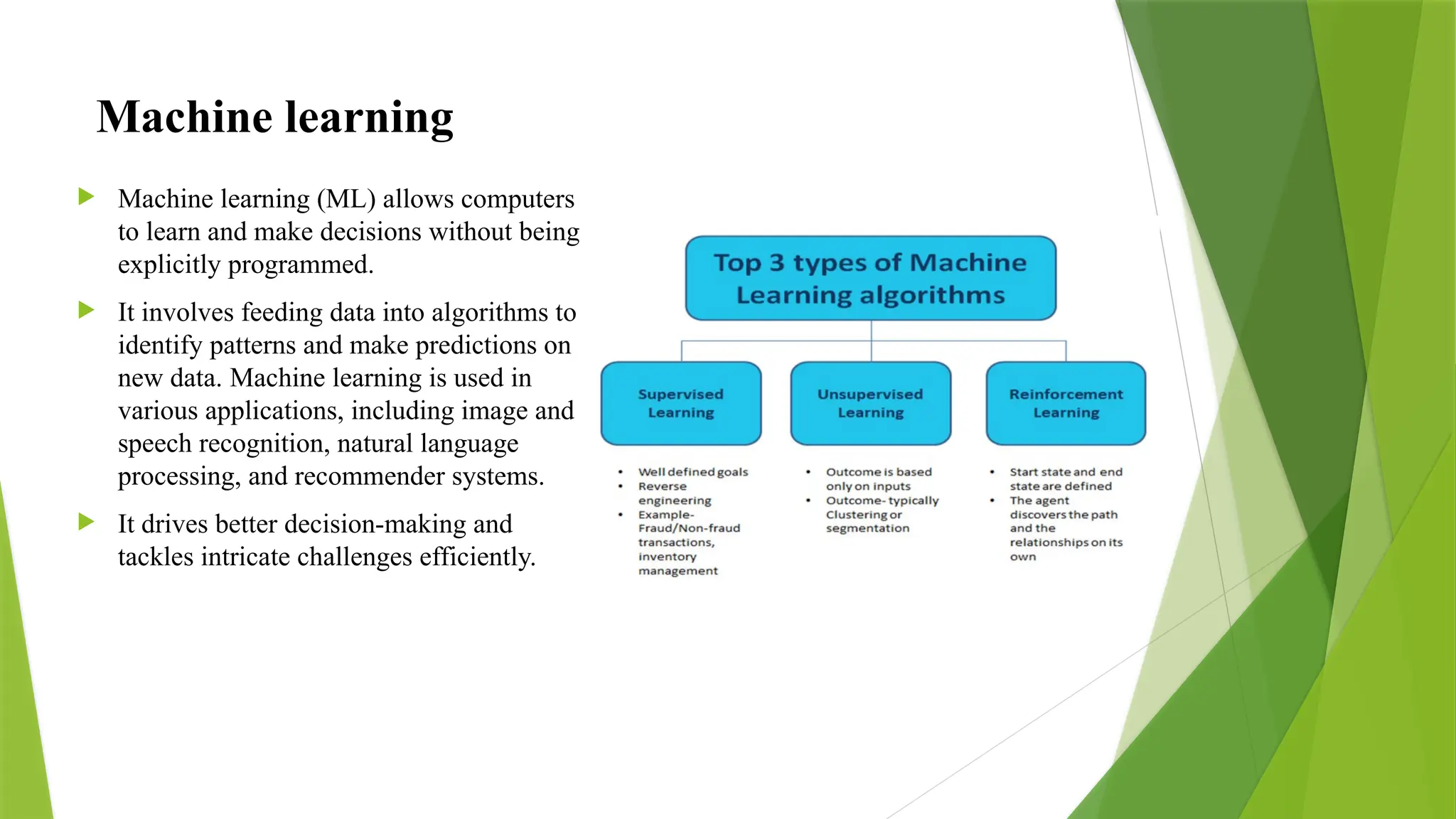
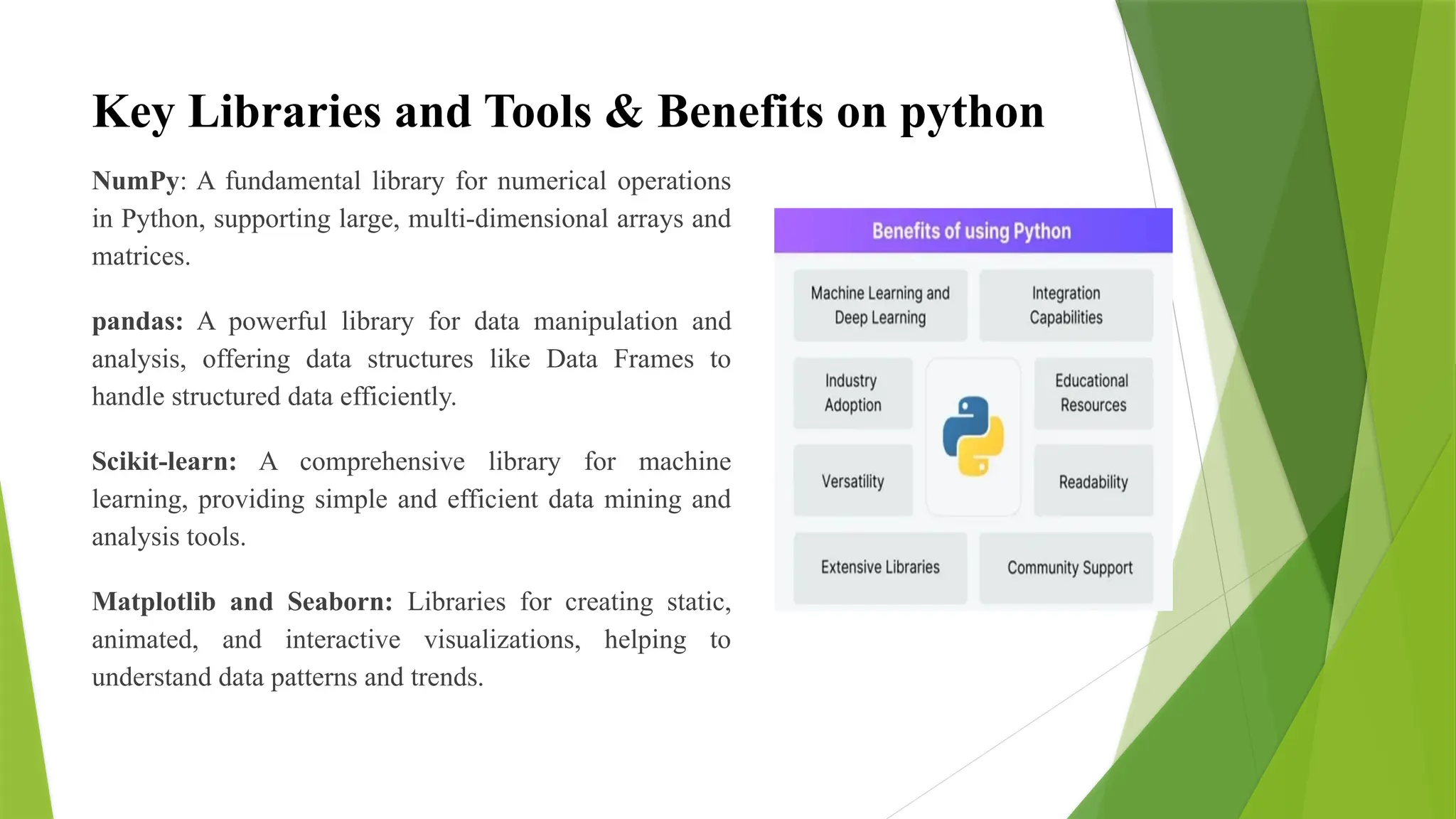
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of Data Science concepts and their practical implementation using Python. It covers the essential stages of a typical data science workflow — from data collection and preprocessing to exploratory data analysis, model building, and result interpretation. The presentation highlights the significance of popular Python libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Scikit-learn, and TensorFlow, showcasing how they empower data scientists to handle real-world data-driven problems efficiently. Through illustrative examples, case studies, and hands-on demonstrations, this presentation aims to equip participants with a strong foundation in applying Python for data analysis, visualization, and machine learning tasks. It also emphasizes best practices in data handling and model evaluation to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions.In the modern, data-driven world, information is being generated at an unprecedented pace. Every click, search, transaction, and interaction contributes to an ever-growing repository of data. From businesses optimizing operations to healthcare systems predicting disease outbreaks and financial firms assessing risks, data is at the core of every significant decision. However, raw data on its own holds limited value. It is the art and science of deriving meaningful insights from this data that fuels innovation and drives impactful decision-making processes. Data Science is the interdisciplinary field that blends statistics, computer science, and domain expertise to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. It involves several stages, including data collection, cleaning, exploration, modeling, and visualization, all aimed at making data-driven predictions and decisions. Among the many programming languages available for data science, Python has emerged as one of the most popular and powerful tools due to its simplicity, flexibility, and the vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks tailored for data-related tasks. This presentation titled "Data Science with Python" serves as an introductory yet comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental concepts of data science and how Python acts as an effective medium for performing data-centric tasks. It encompasses theoretical explanations, practical implementations, and real-world examples to ensure a well-rounded learning experience. Objectives of the Presentation The primary objective of this presentation is to introduce the audience to the realm of data science while focusing on the practical application of Python as a tool for performing data analysis, visualization, and machine learning. The specific goals include: To provide a clear understanding of what data science is and its significance in modern industries. To introduce the standard workflow followed in data science projects. To familiarize the audience with Python’s libraries and frameworks that facilitate datasci
![DATA SCIENCE USING PYTHON Under the guidance of Dr. M. Krishna Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering GAYATRI VIDYA PARISHAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING FOR WOMEN (A) [Approved by AICTE NEW DELHI, Affiliated to Andhra University] [Accredited by National Board of Accreditation (NBA) for B.Tech. CSE, ECE & IT – Valid from 2019-22 and 2022- 25] [Accredited by National Board of Accreditation (NBA) for B.Tech. EEE – Valid from 2023-24 and 2025-26] Kommadi , Madhurawada, Visakhapatnam–530048 2024–2025](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facet-copy-250416191510-b7bdc839/75/data-science-with-python-internship-ppt-1-2048.jpg)