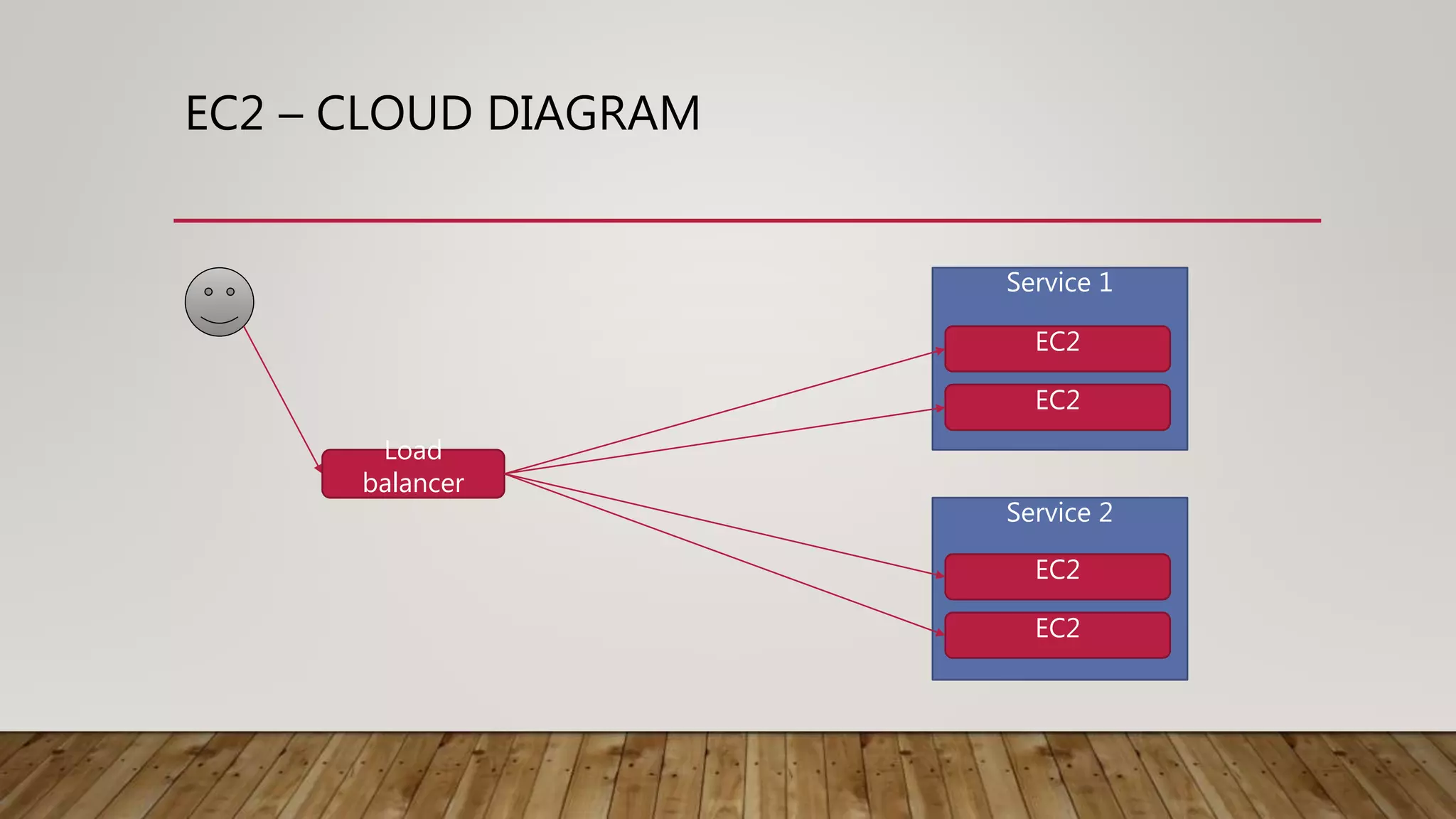
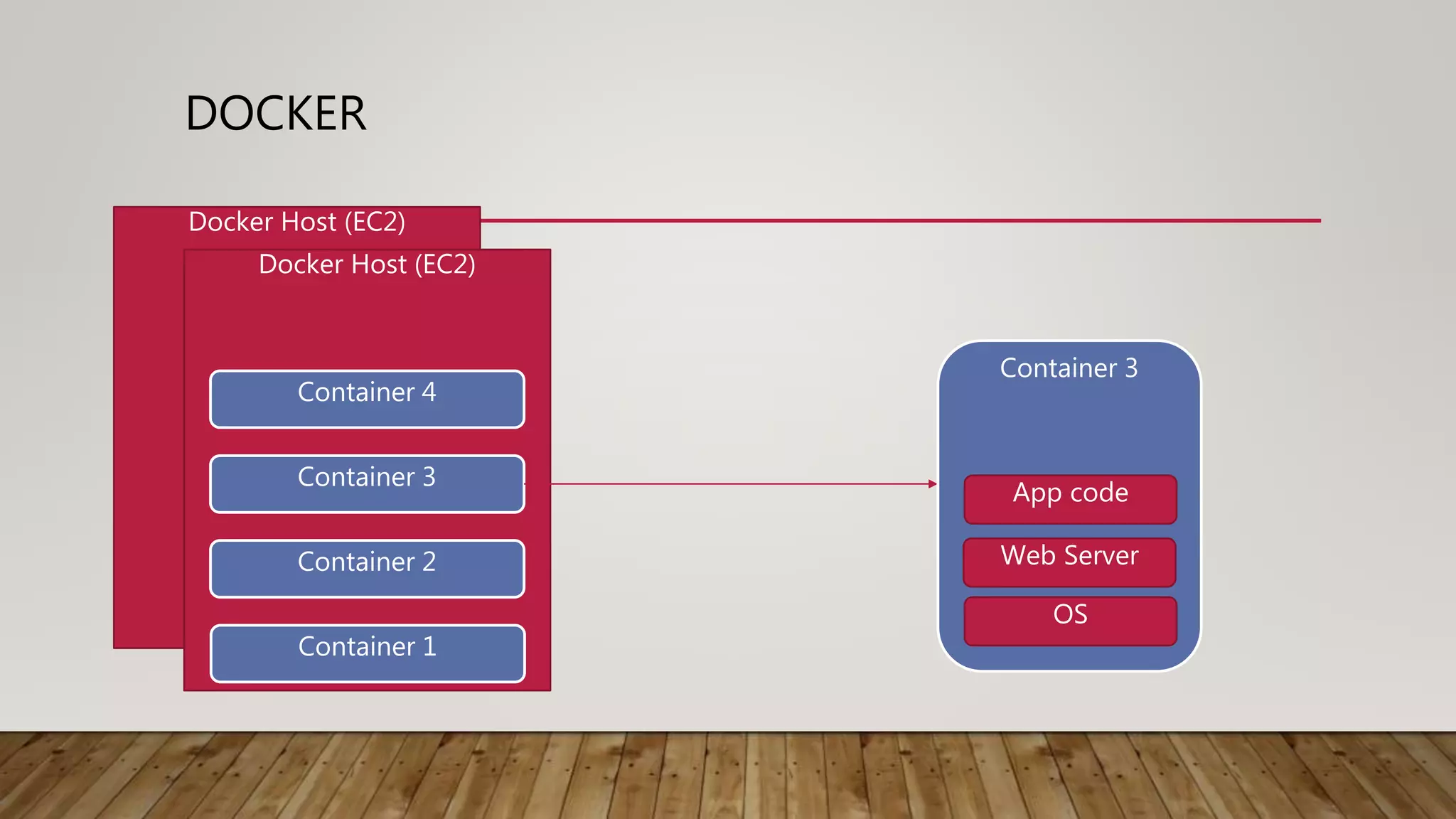
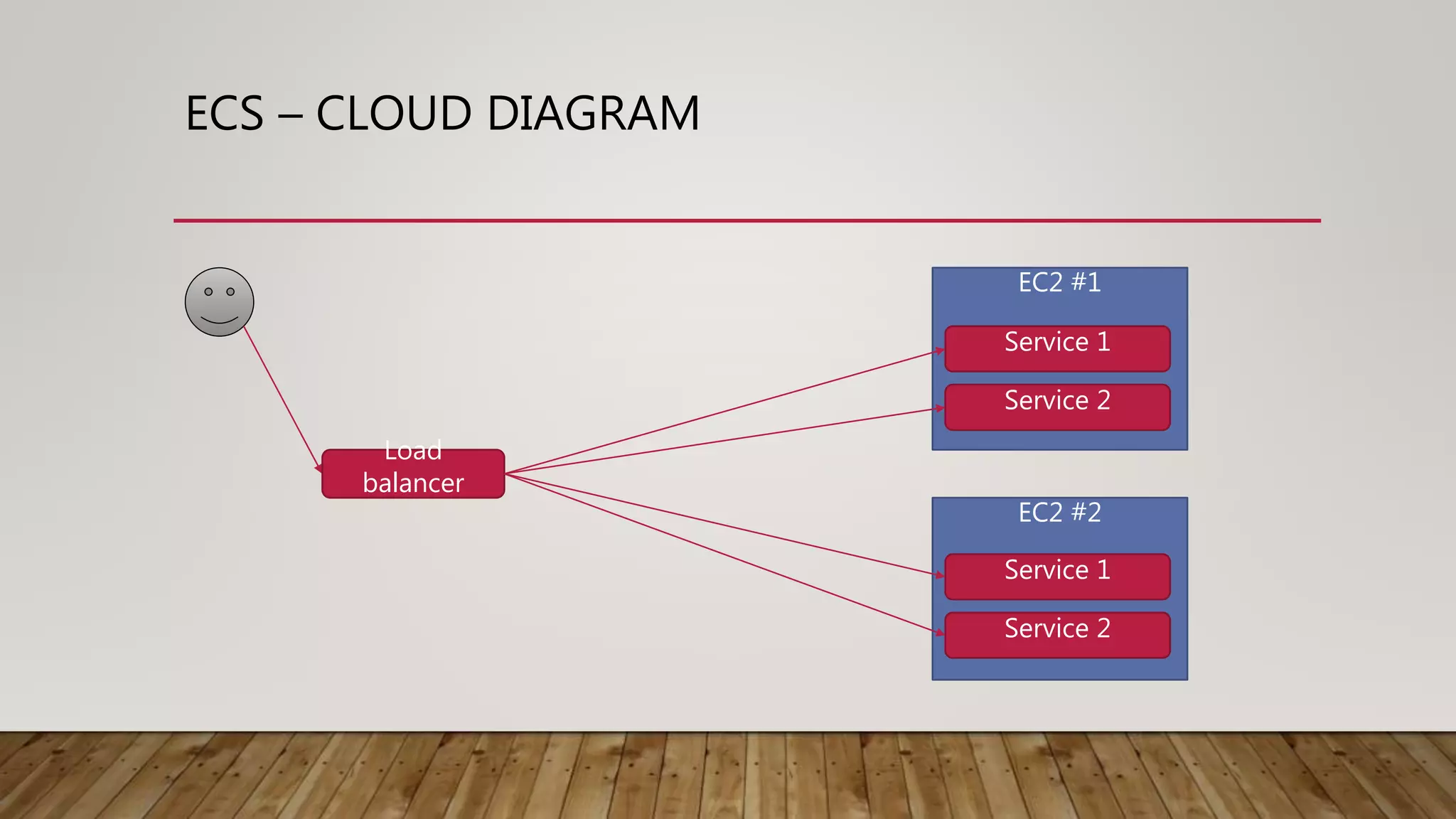
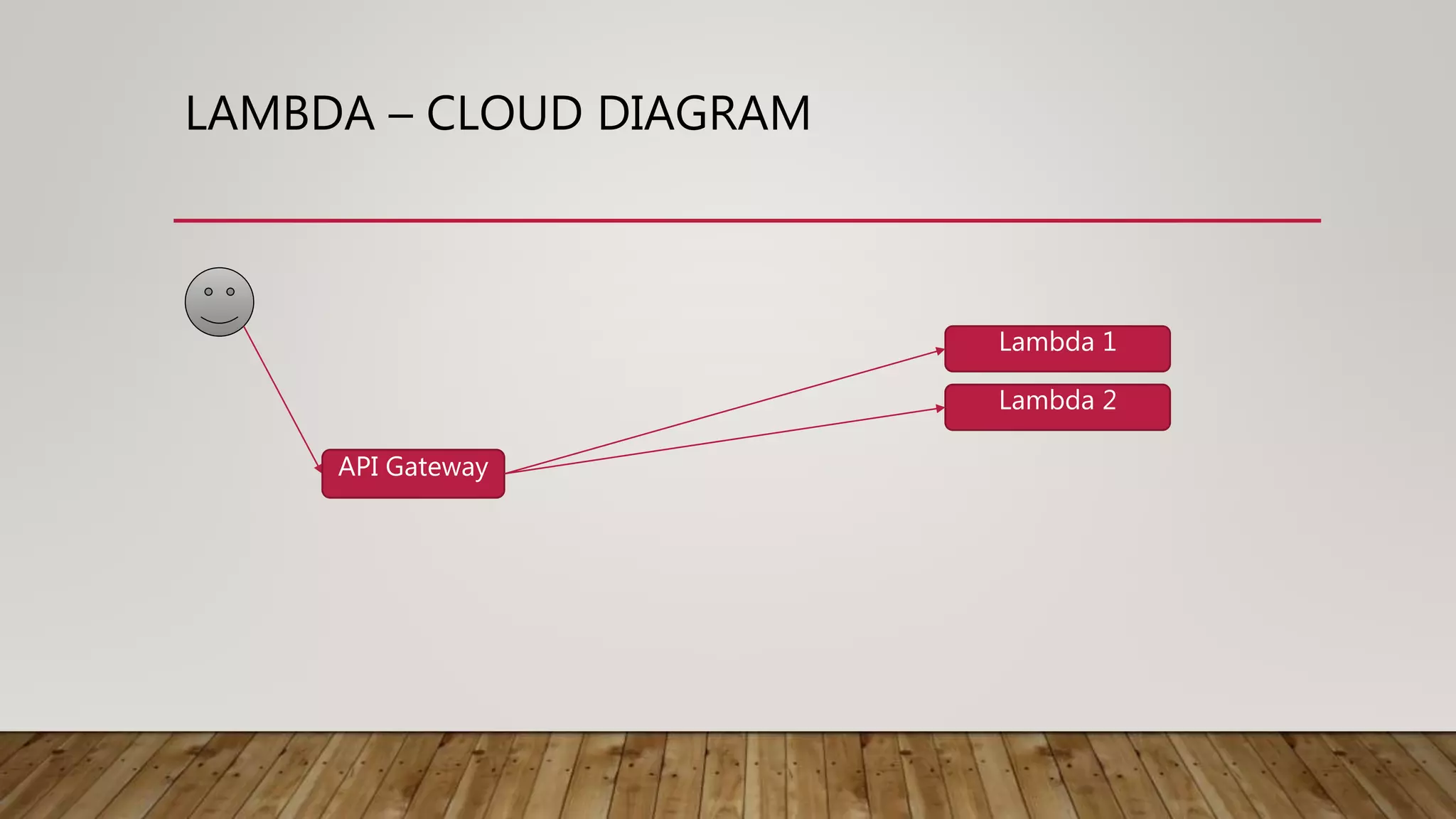
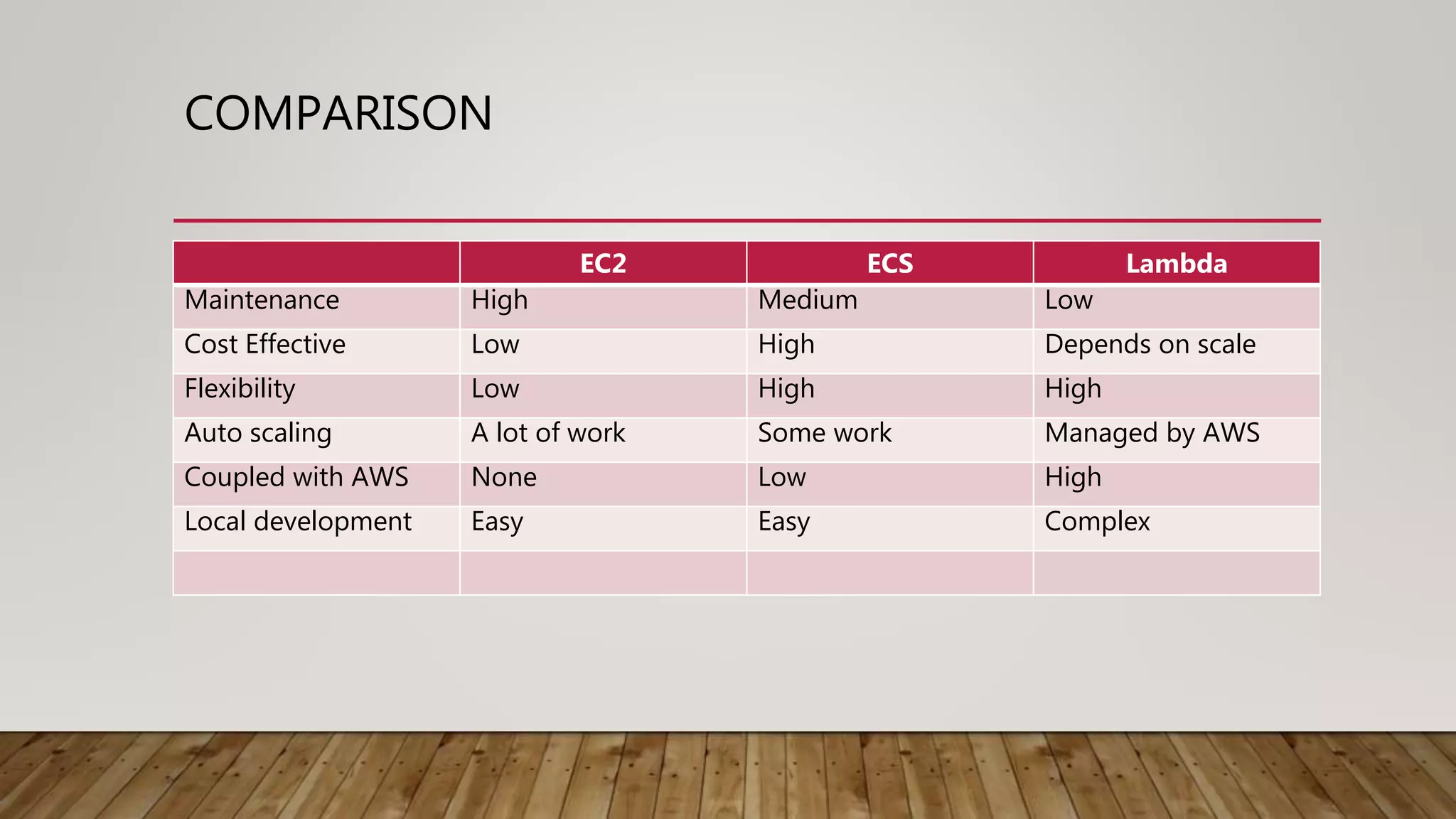
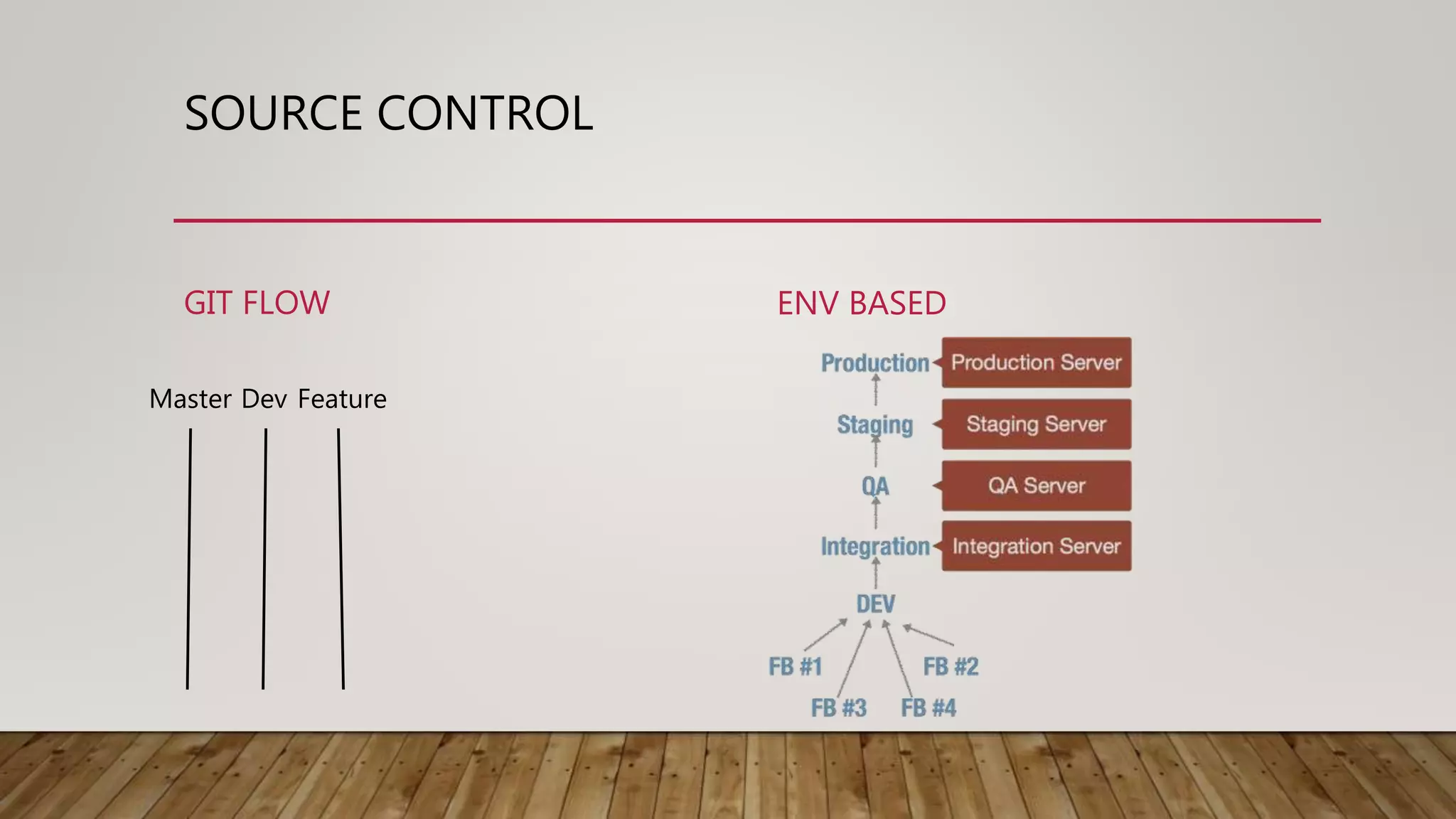
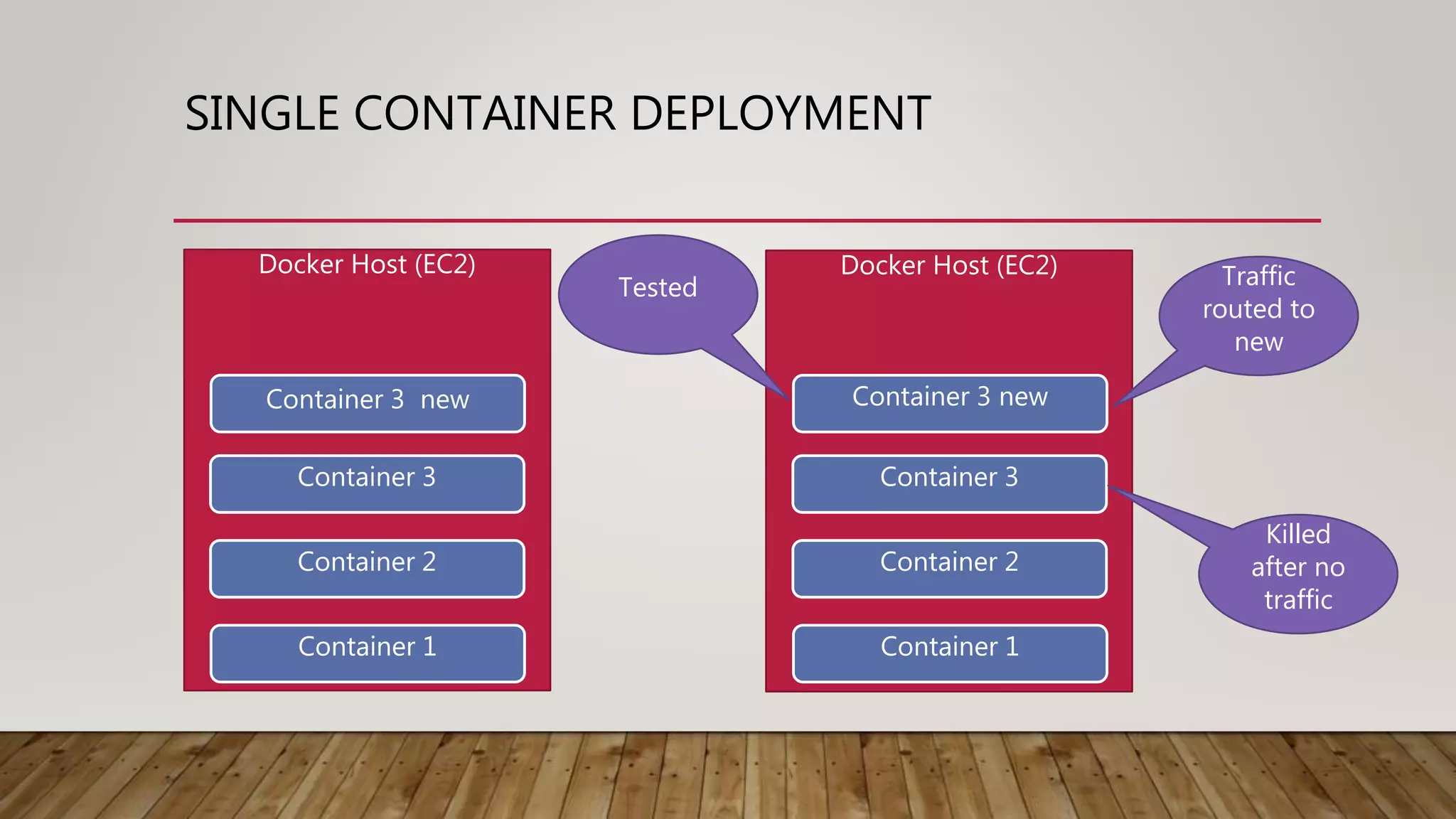
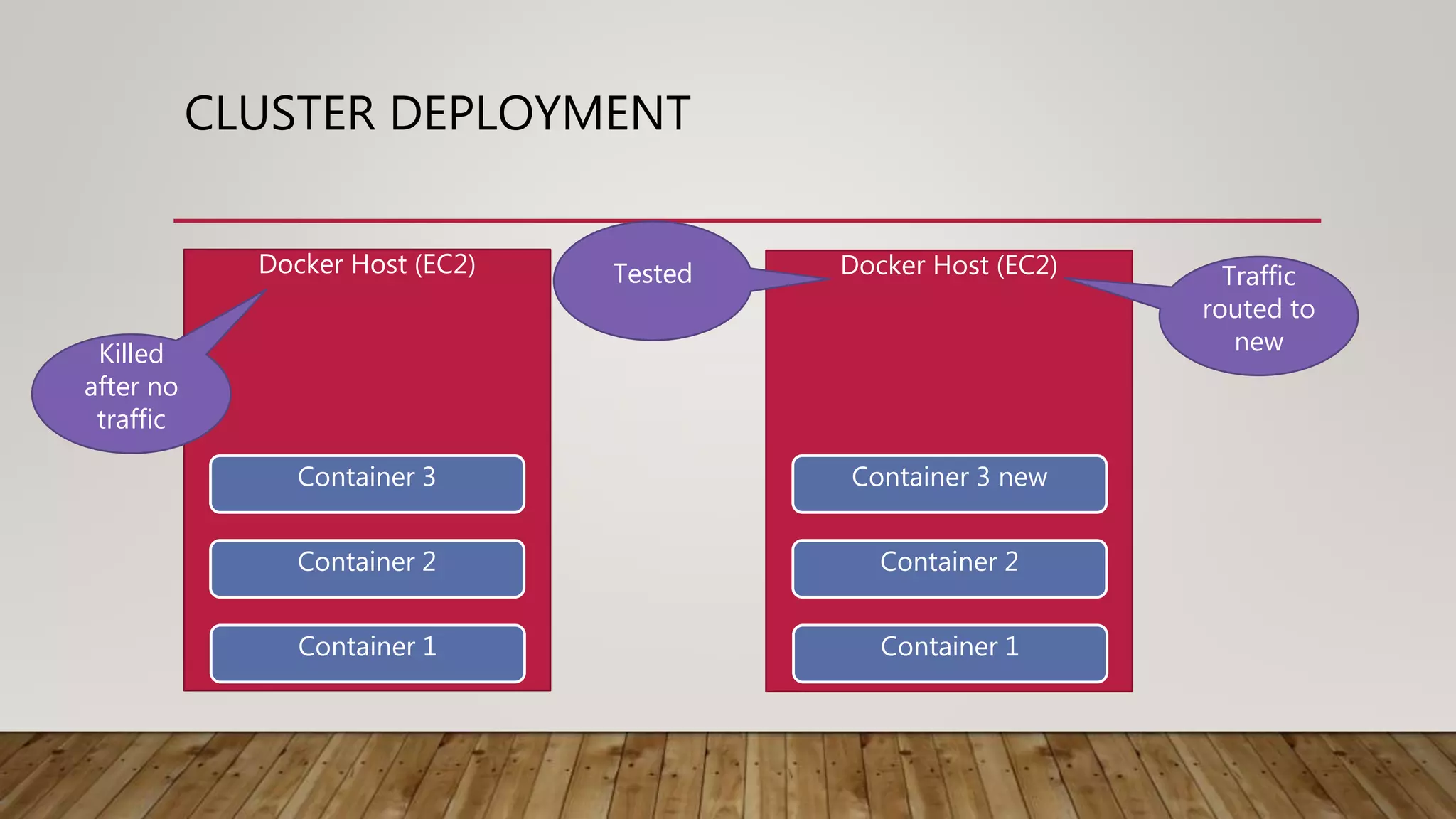
This document discusses deploying microservices on AWS. It begins by explaining what microservices are and then discusses hosting options on AWS including EC2, ECS, and Lambda. ECS is identified as the preferred option since it allows hosting containers with Docker. The document then covers deployment aspects like using source control with Git for multiple environments, building and testing code, deploying single services or entire clusters, live testing, and monitoring with alerts.