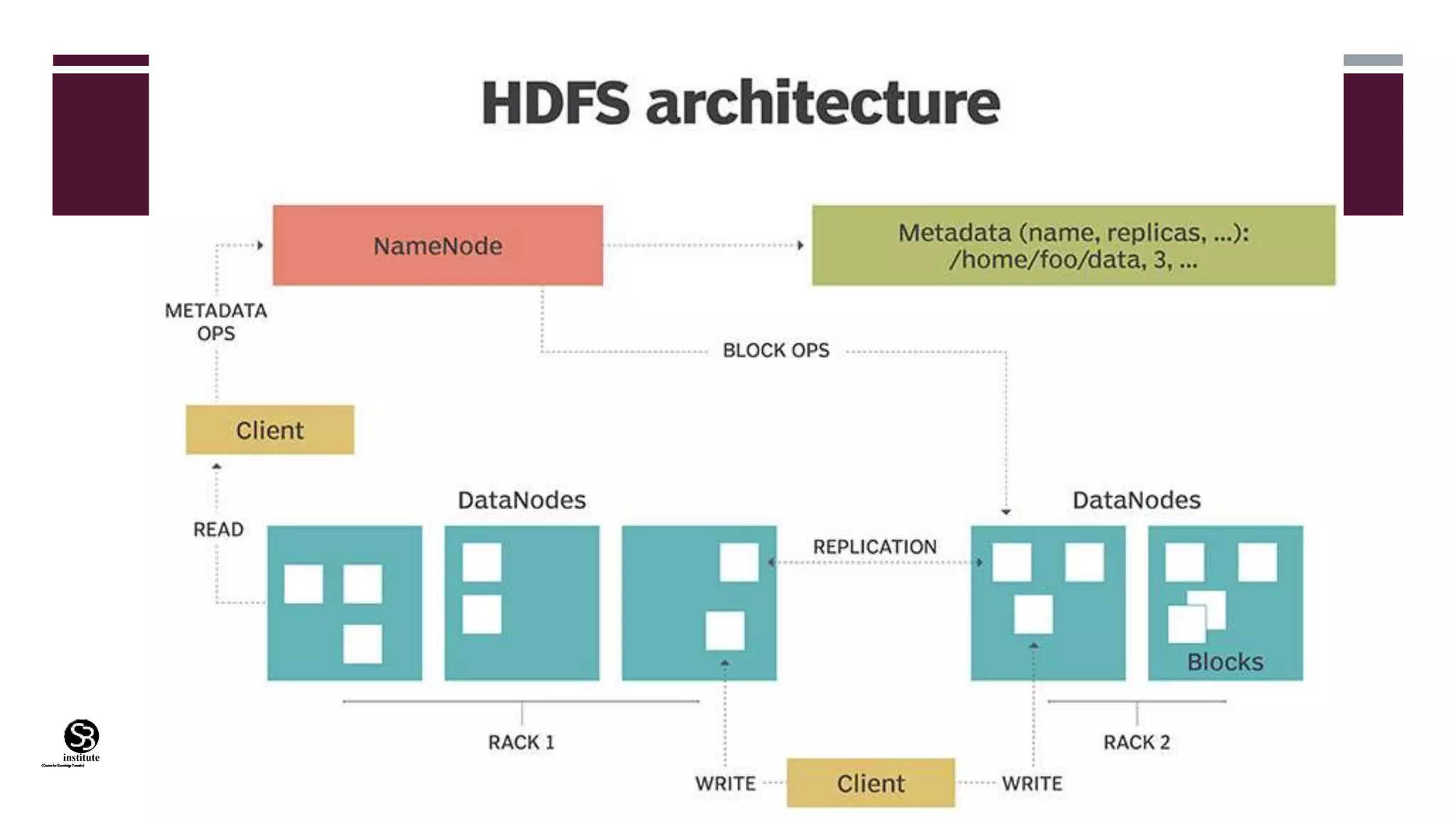
The document outlines the design and operation of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), highlighting its architecture, features, and benefits for managing large data sets. HDFS uses a namenode and datanode structure for high-performance data access and provides fault tolerance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for big data applications. It also emphasizes the importance of data replication to ensure availability and resilience against hardware failures.