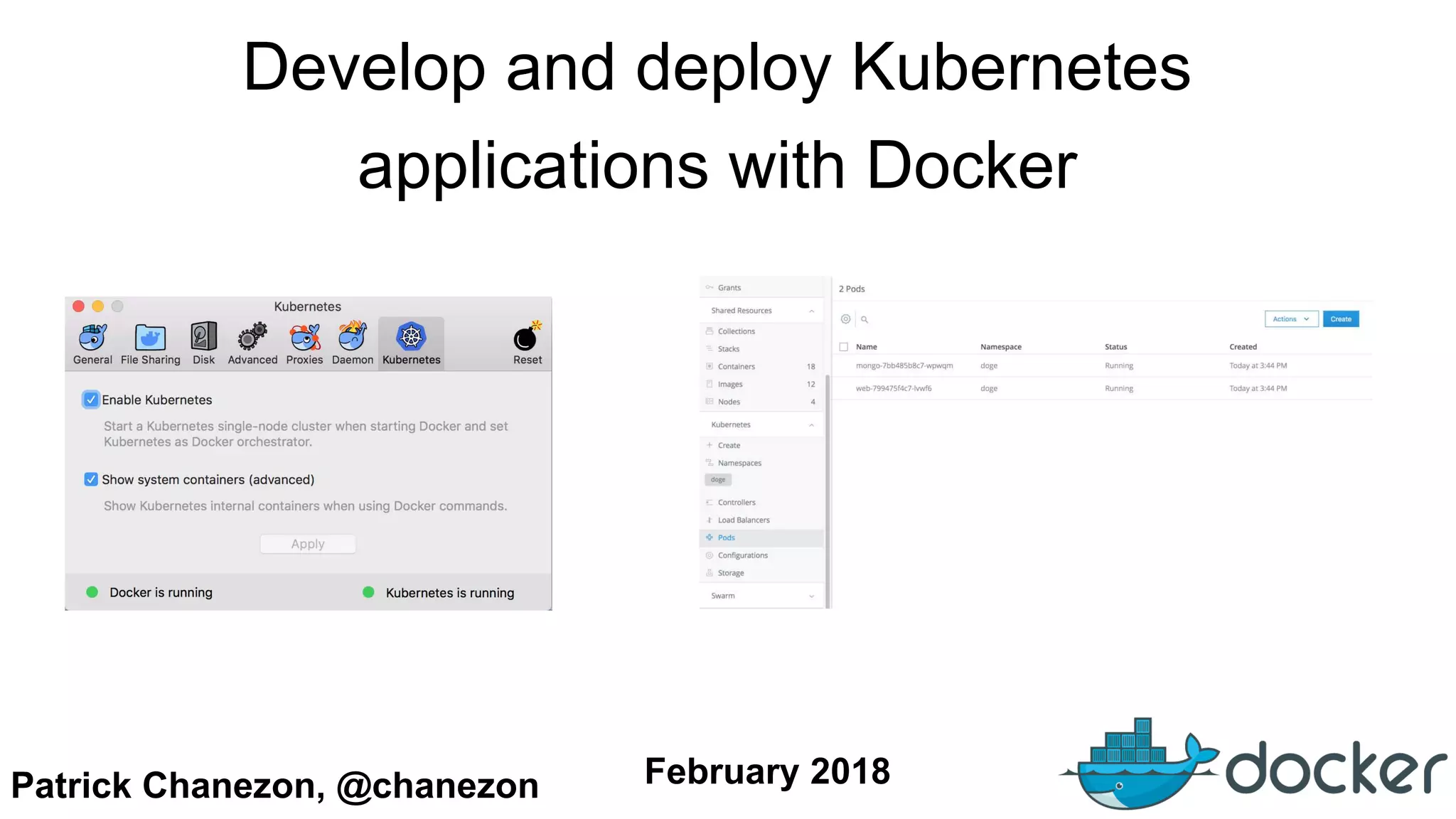
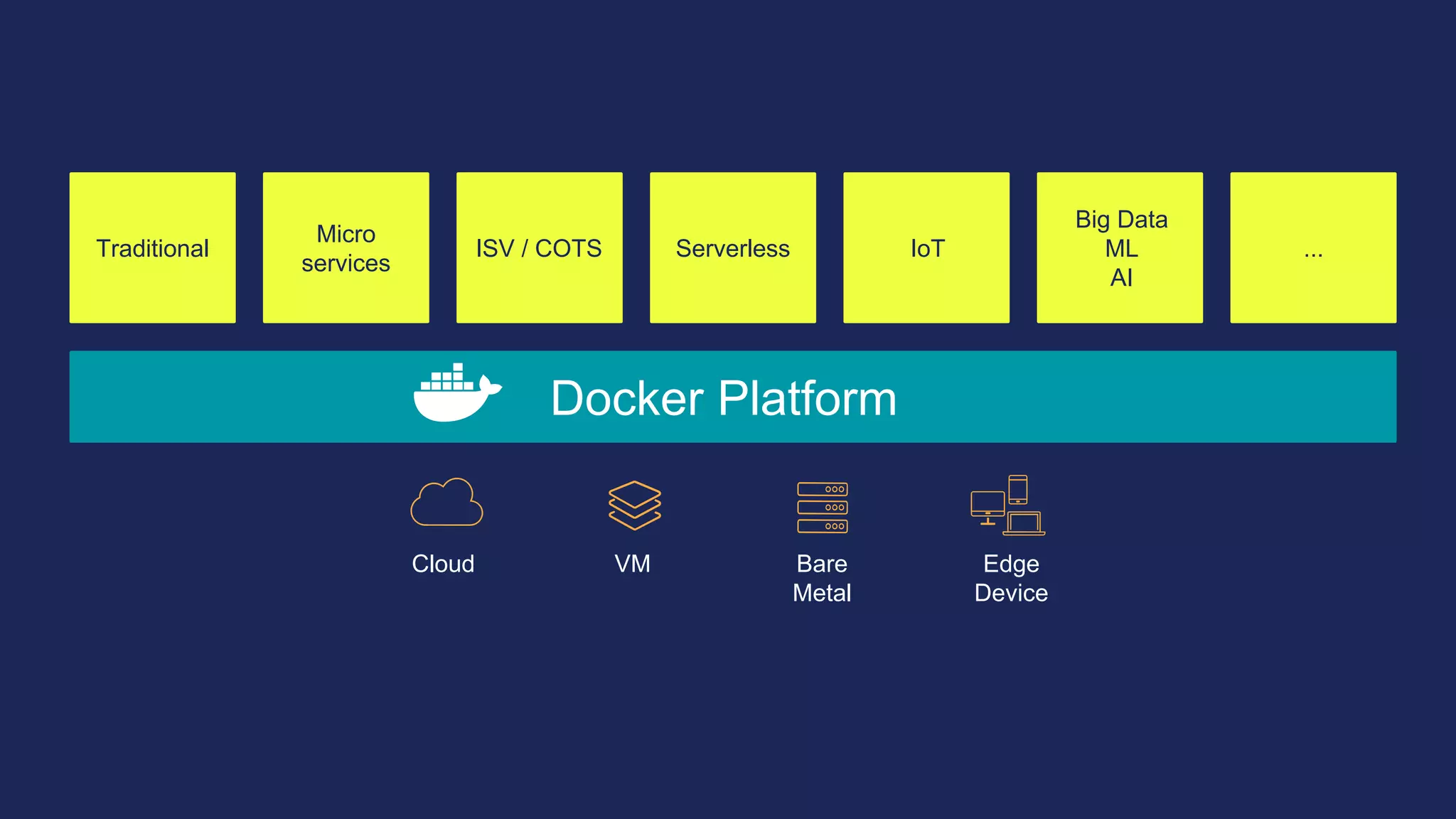
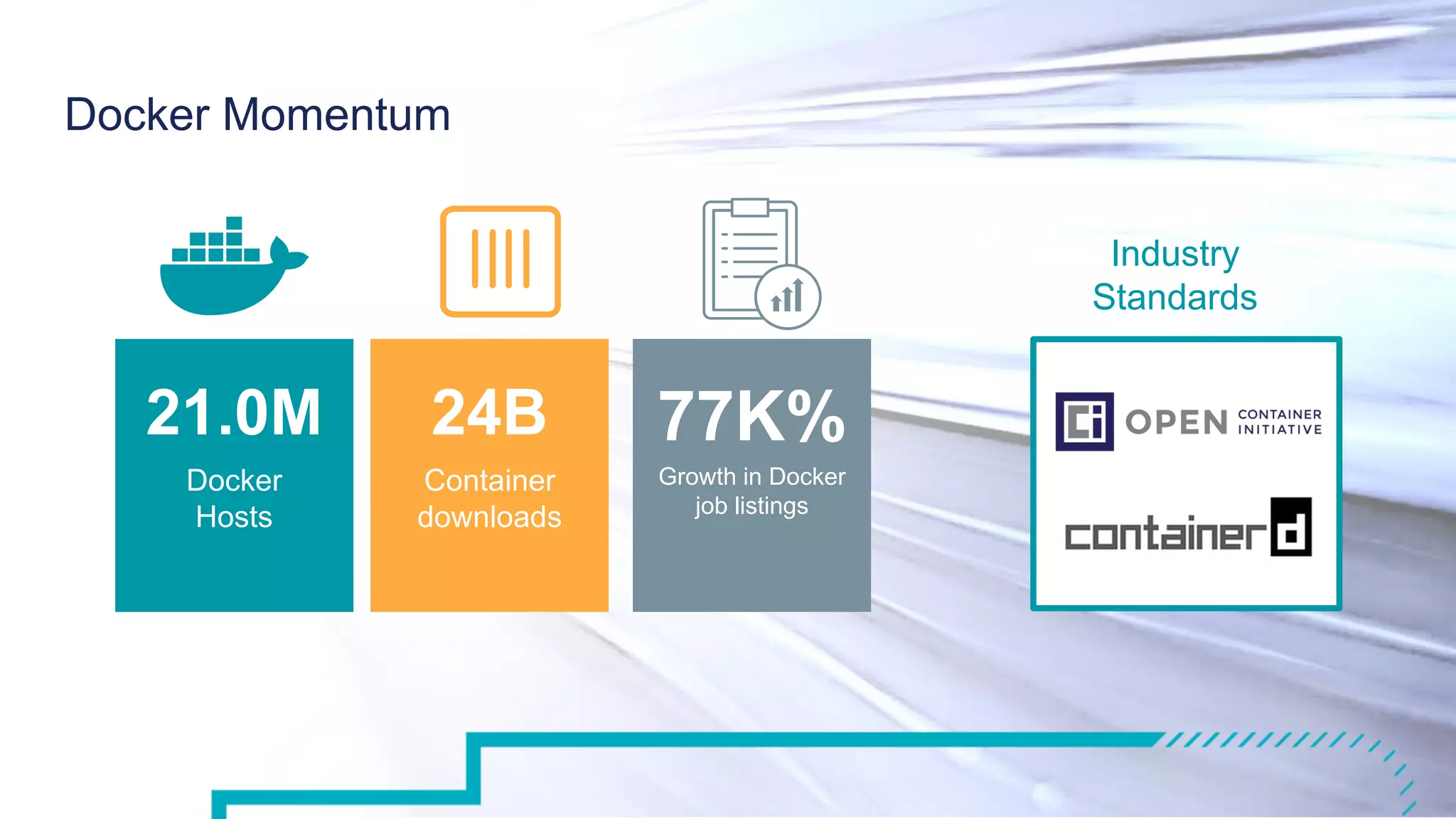
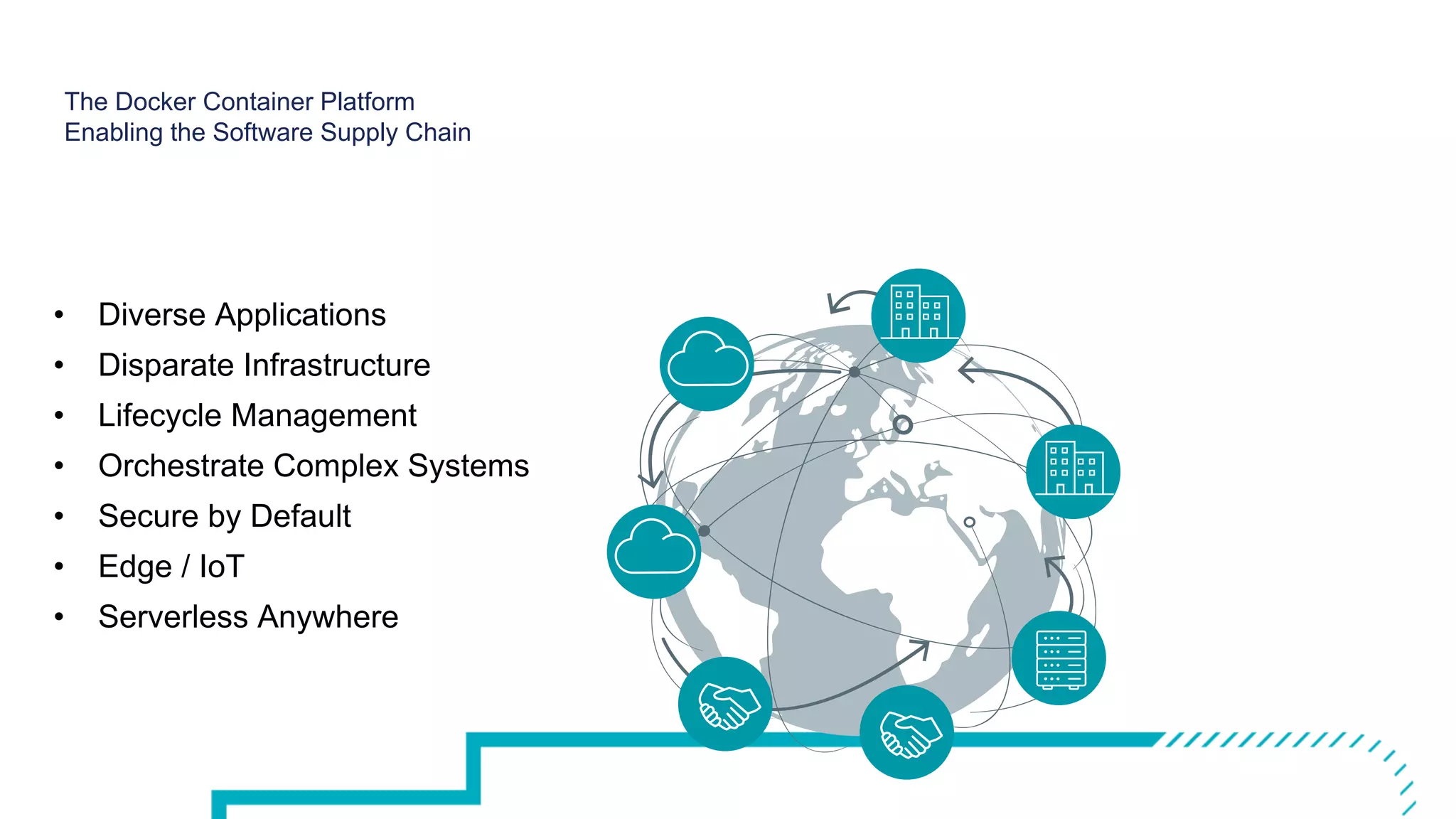
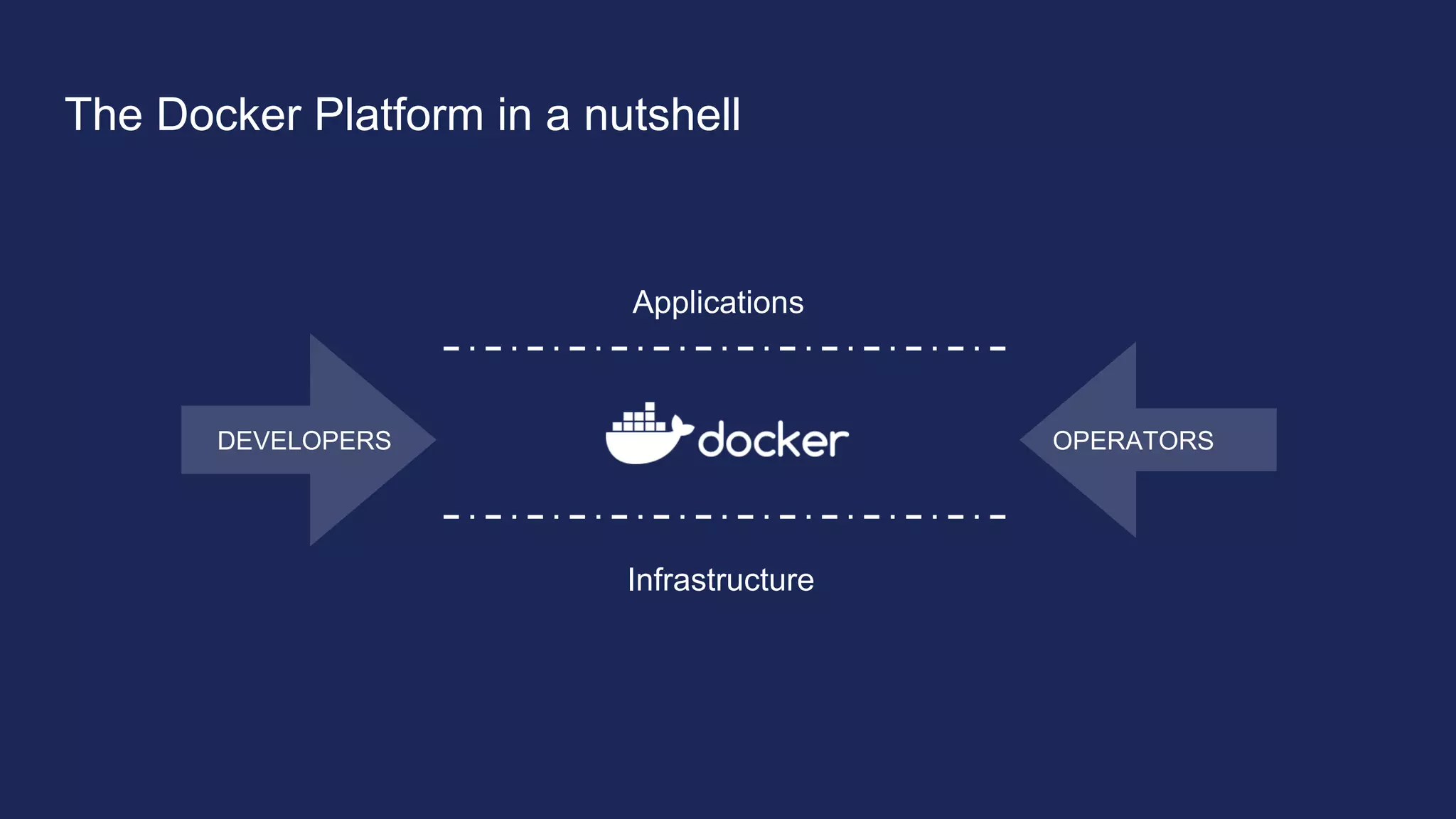
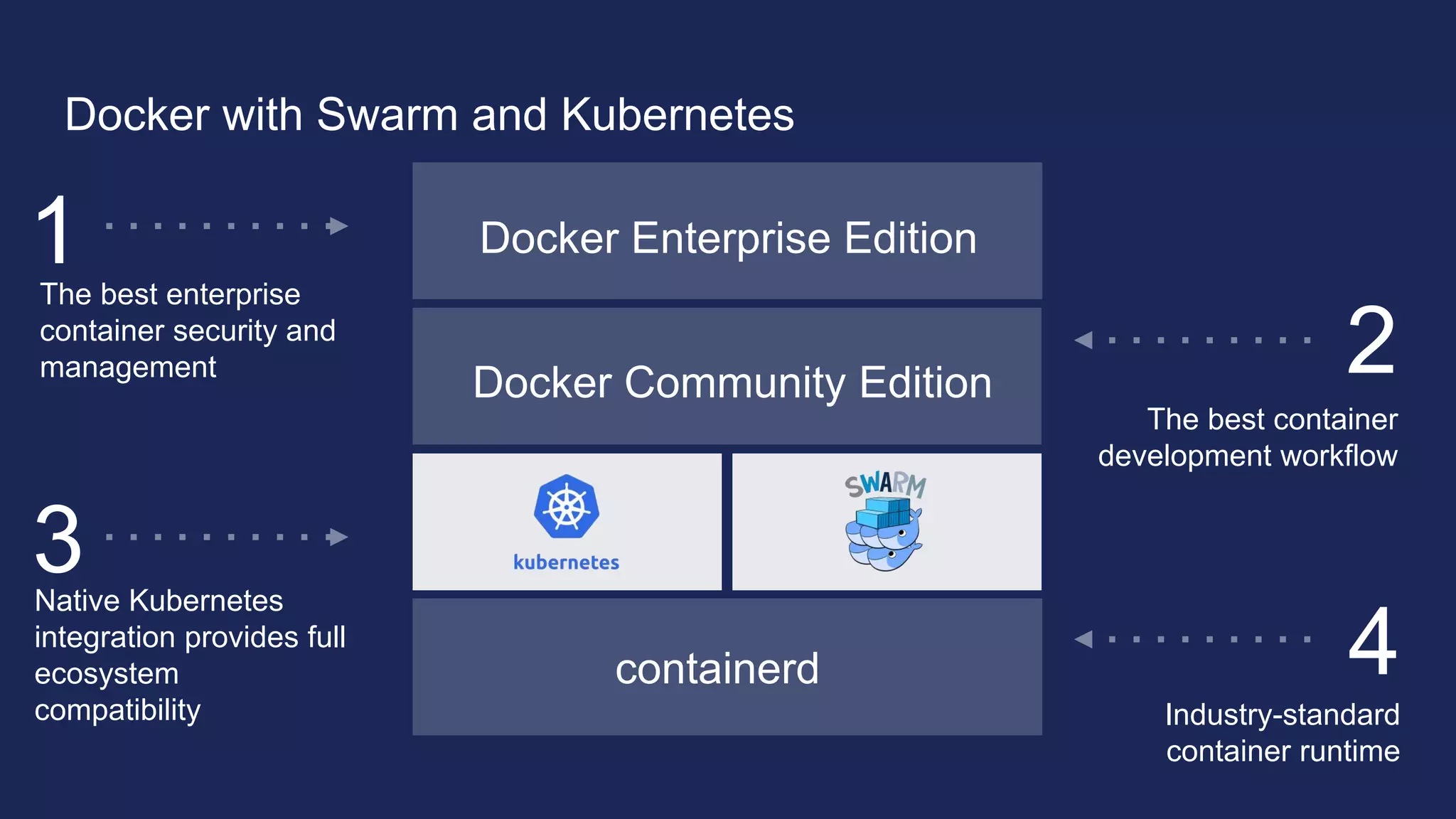
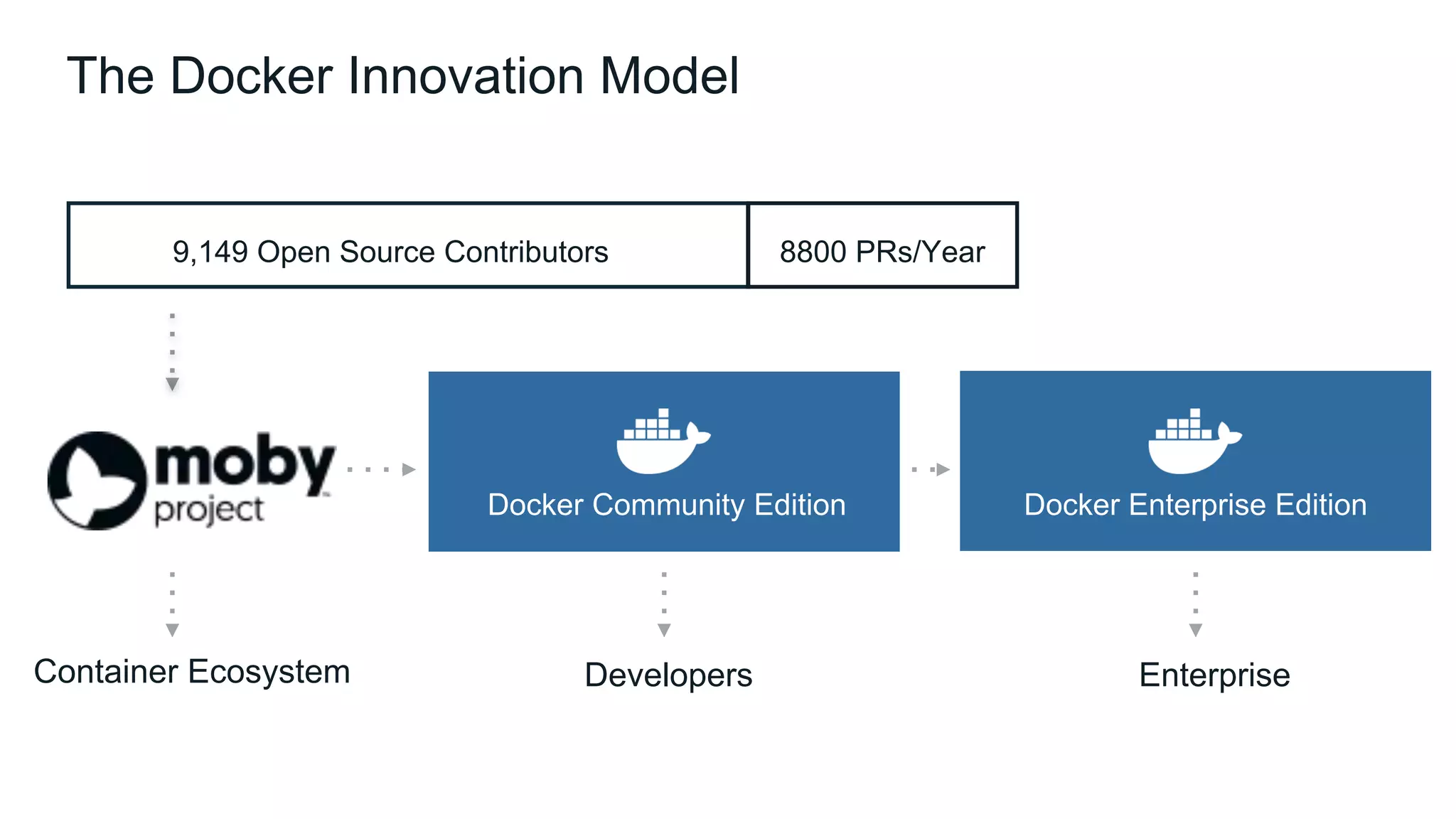
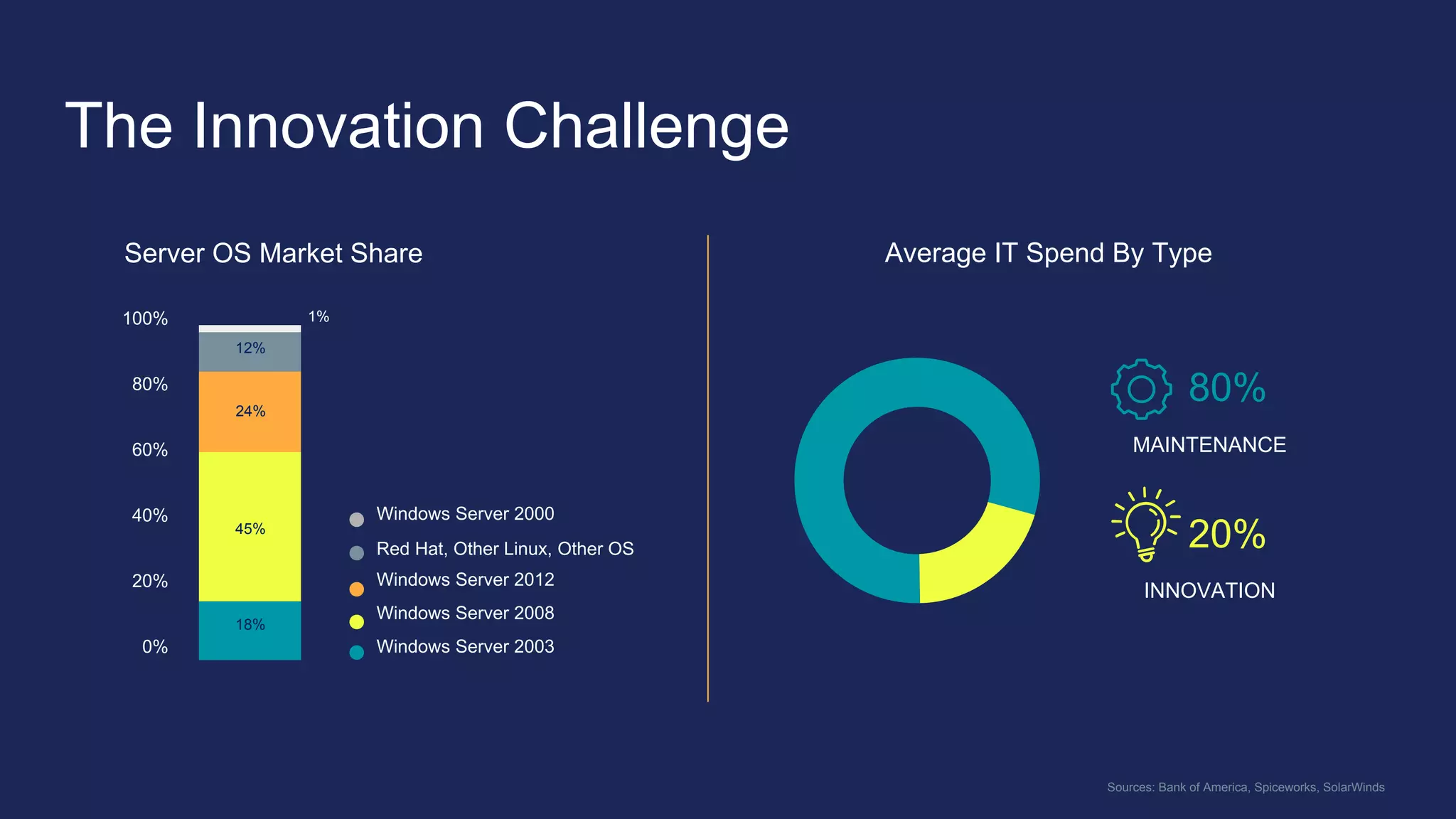
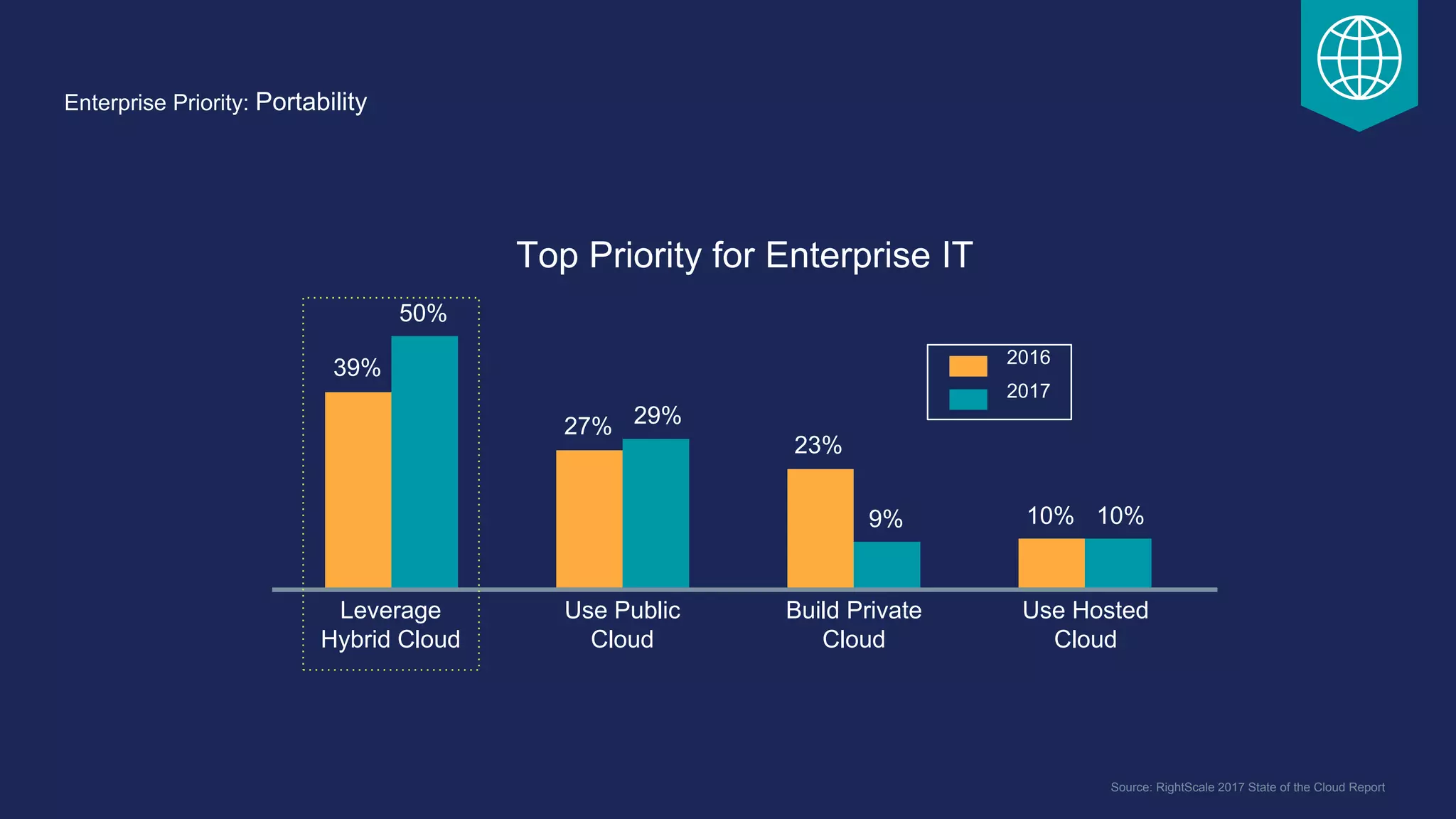
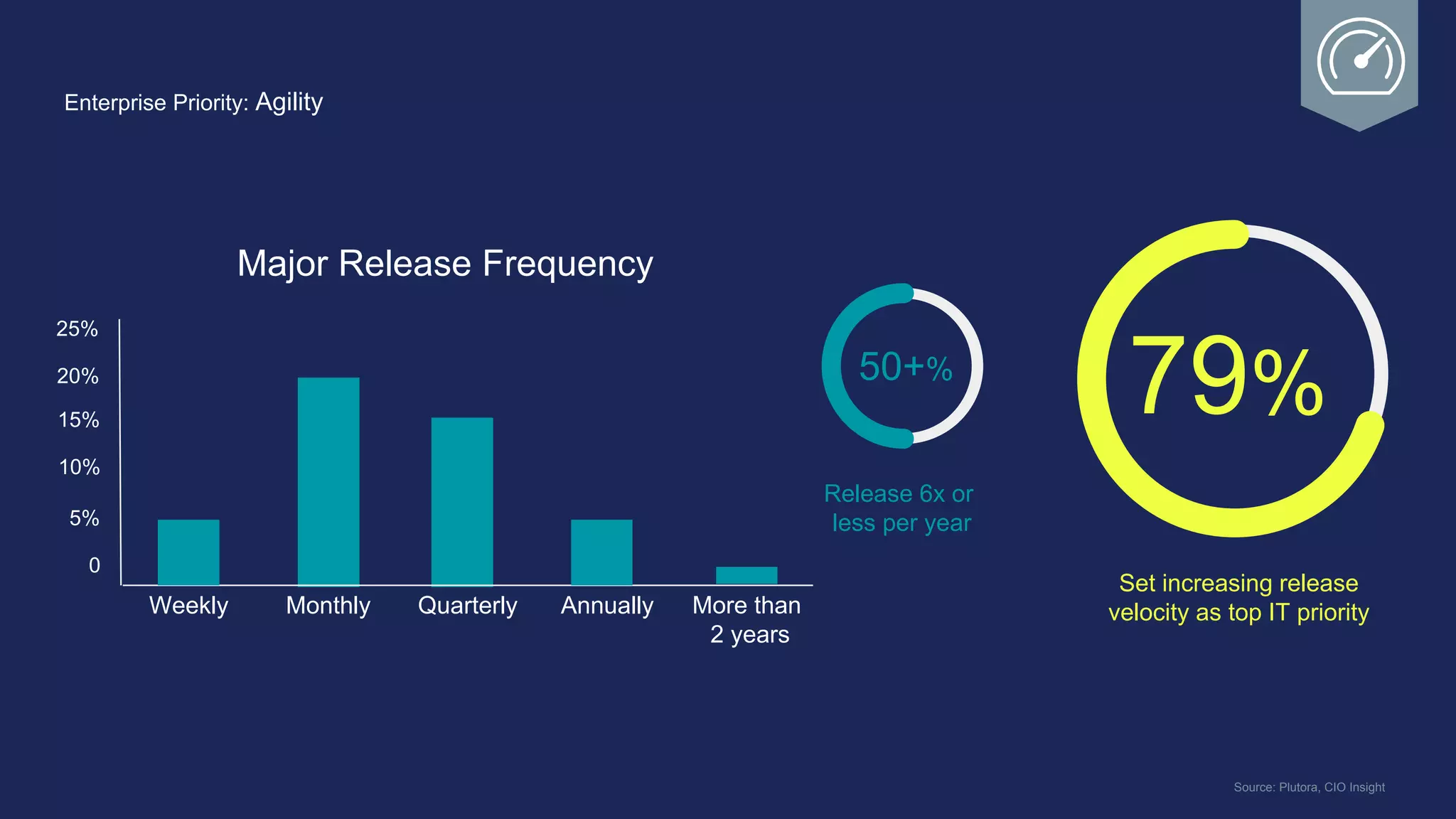
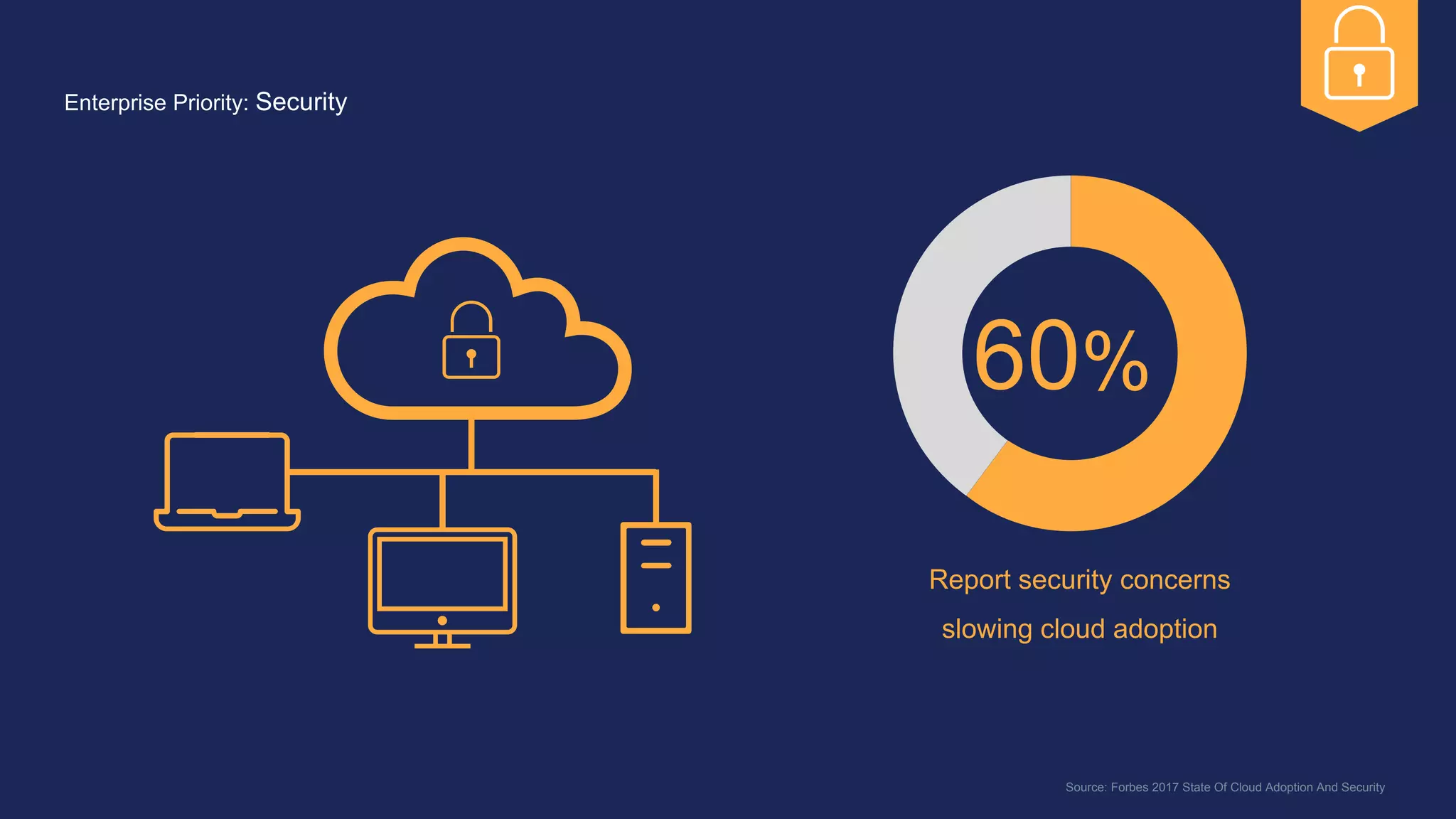
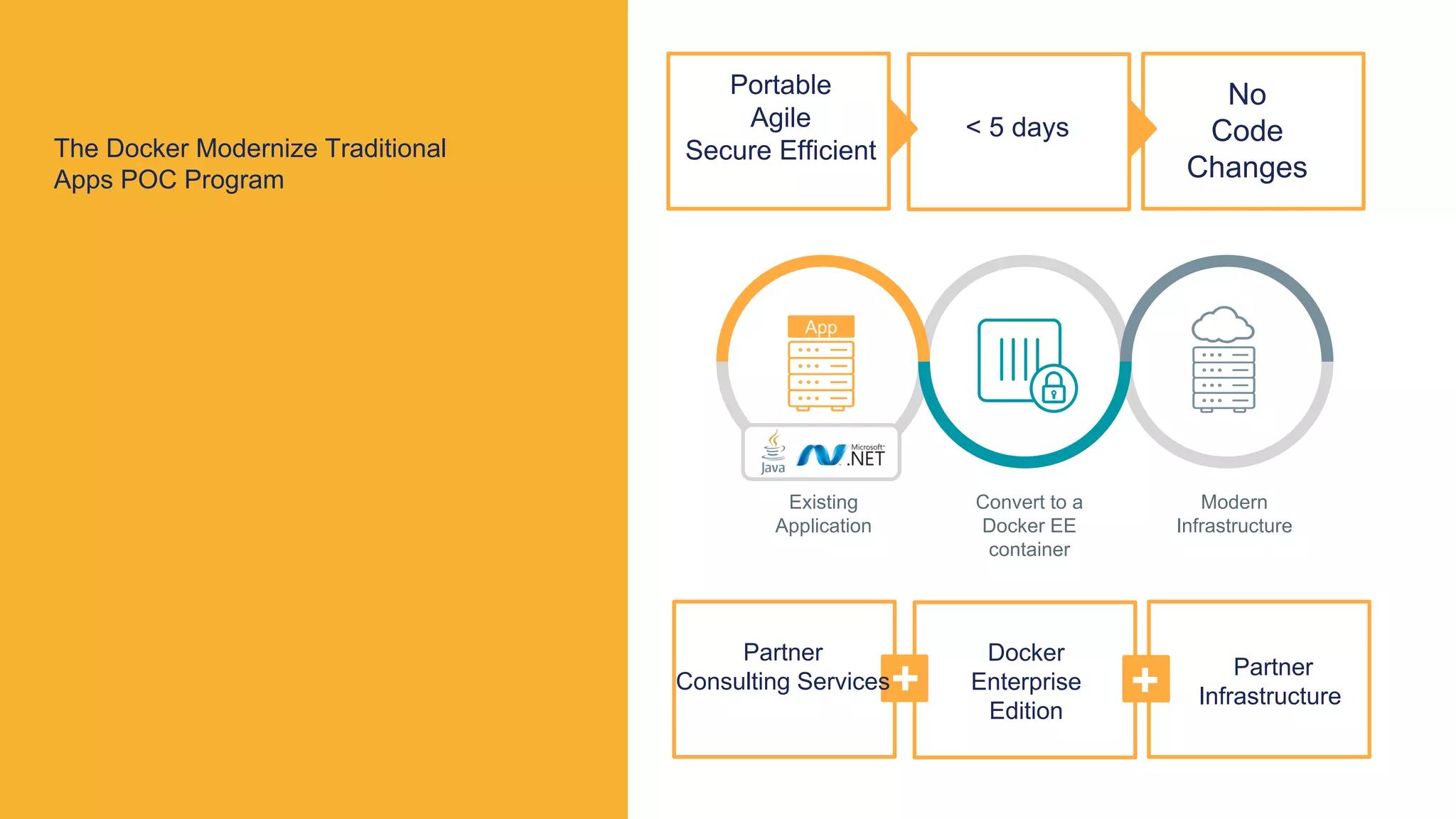
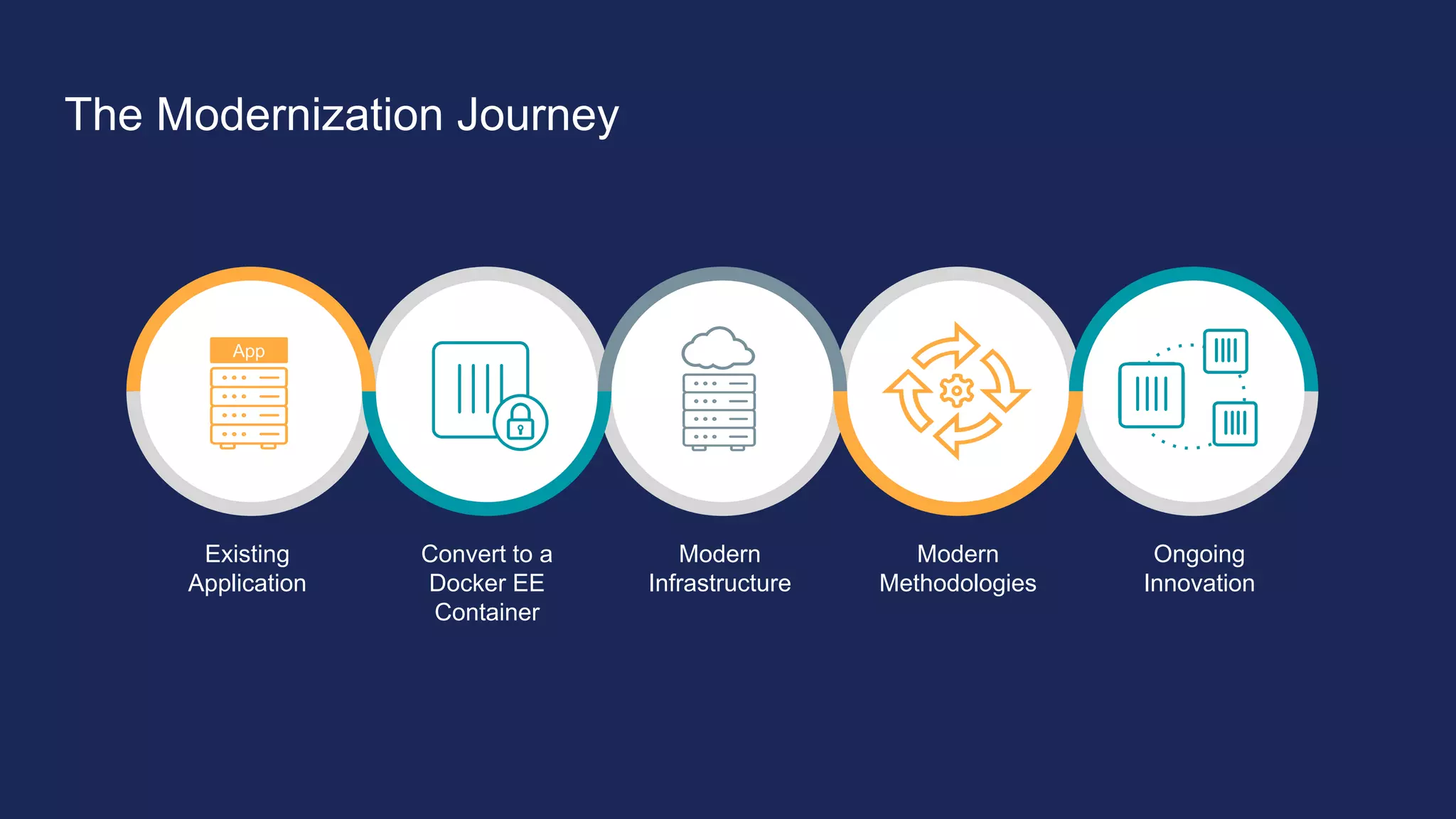
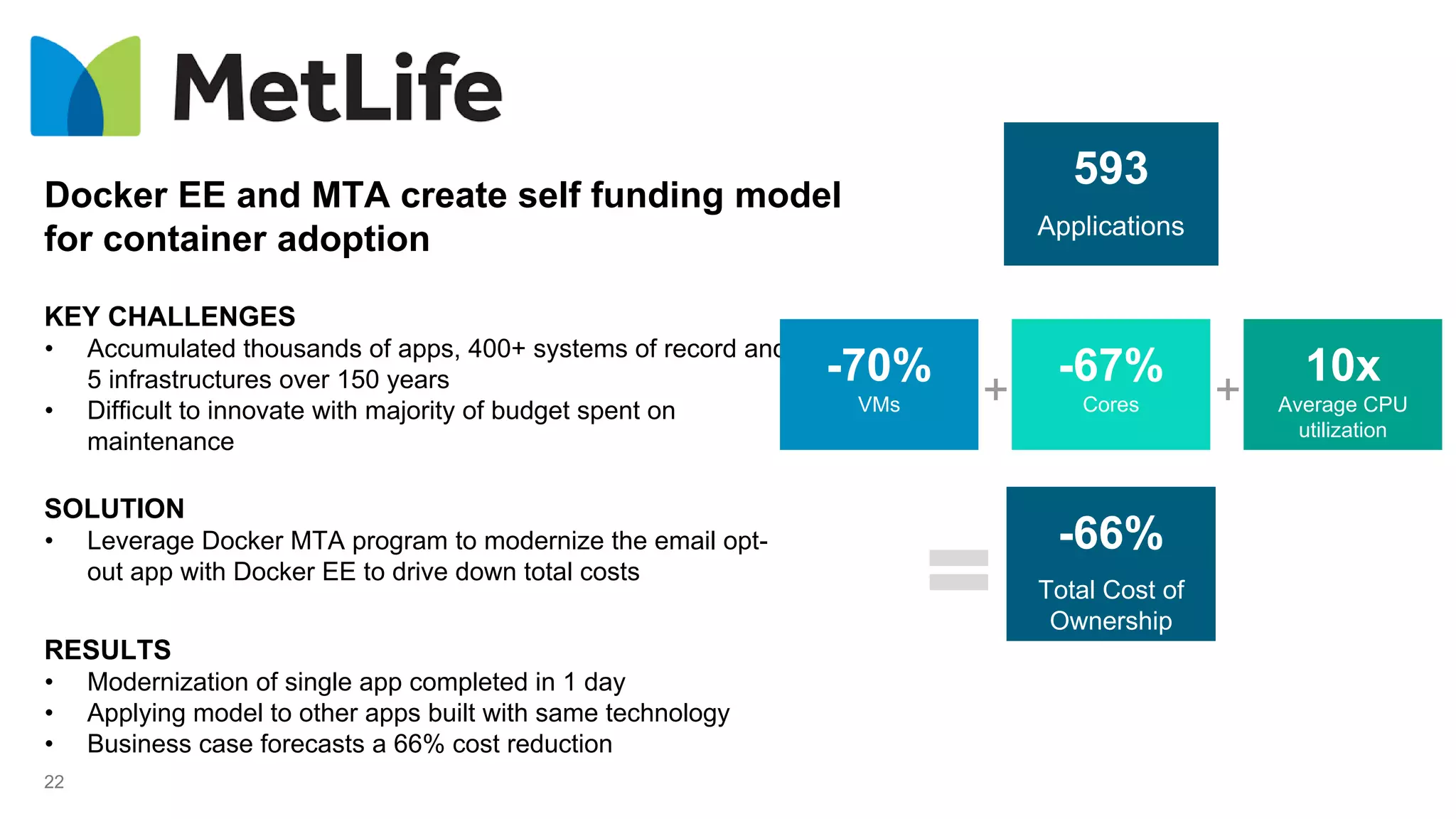
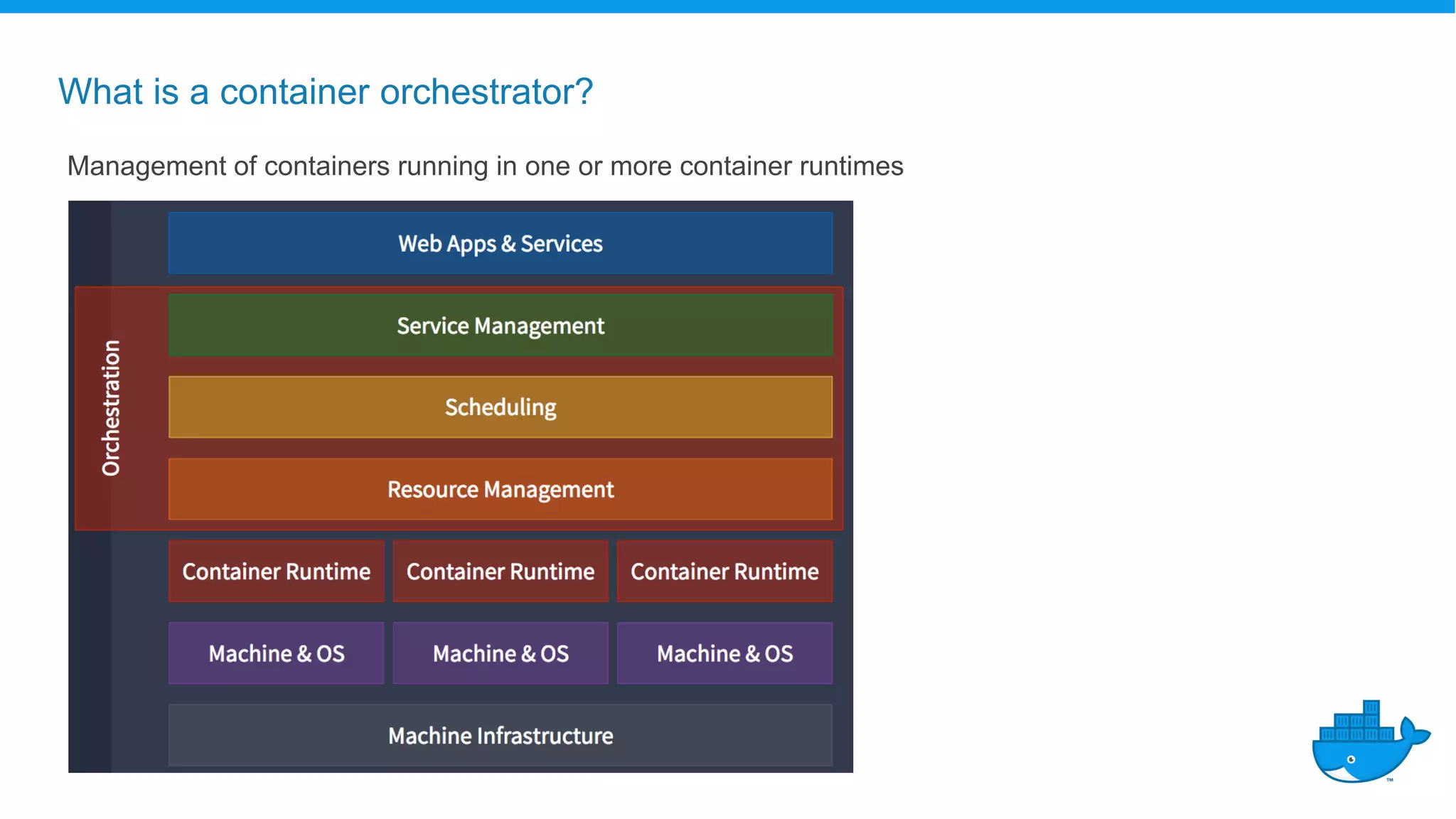
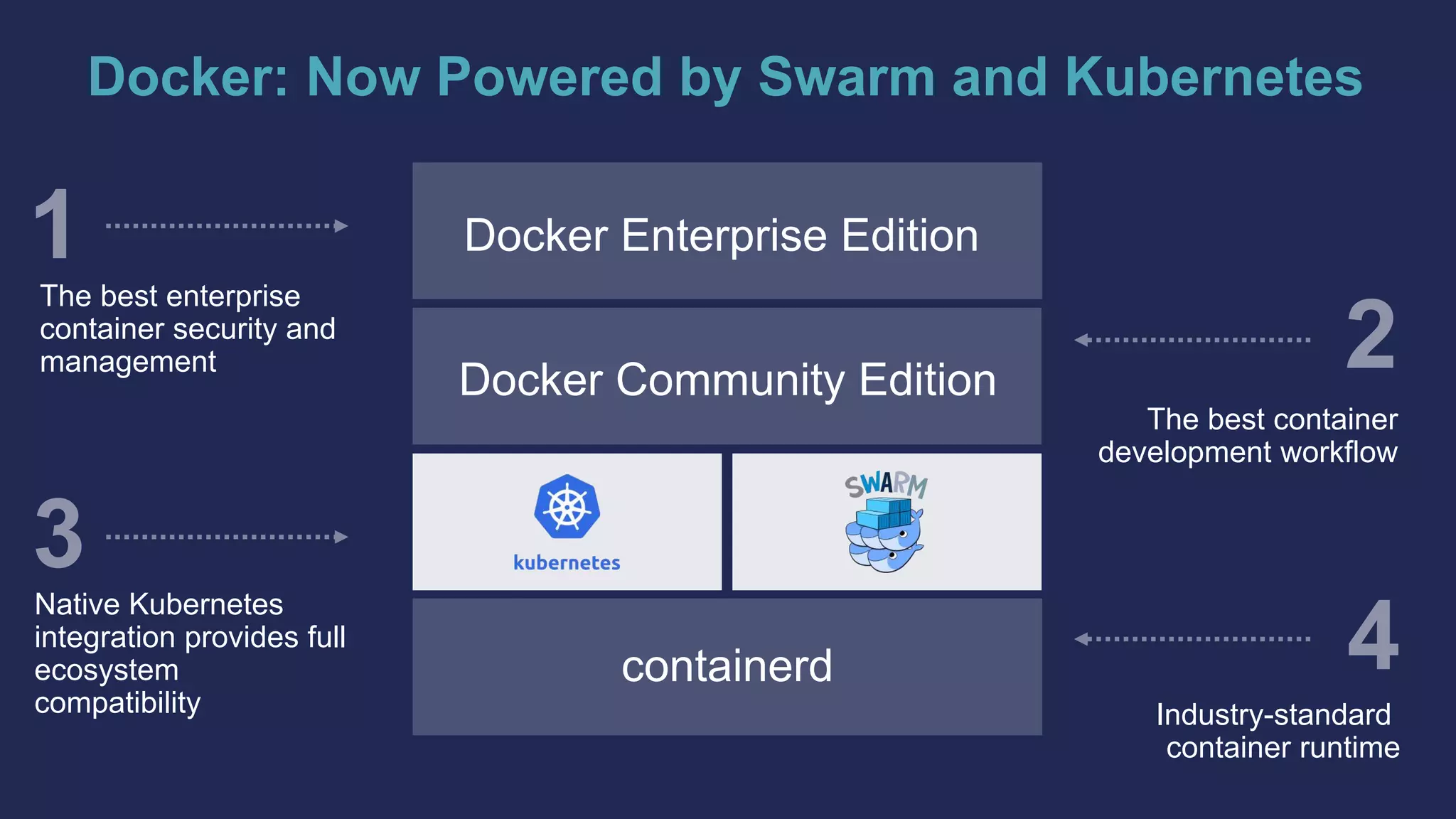
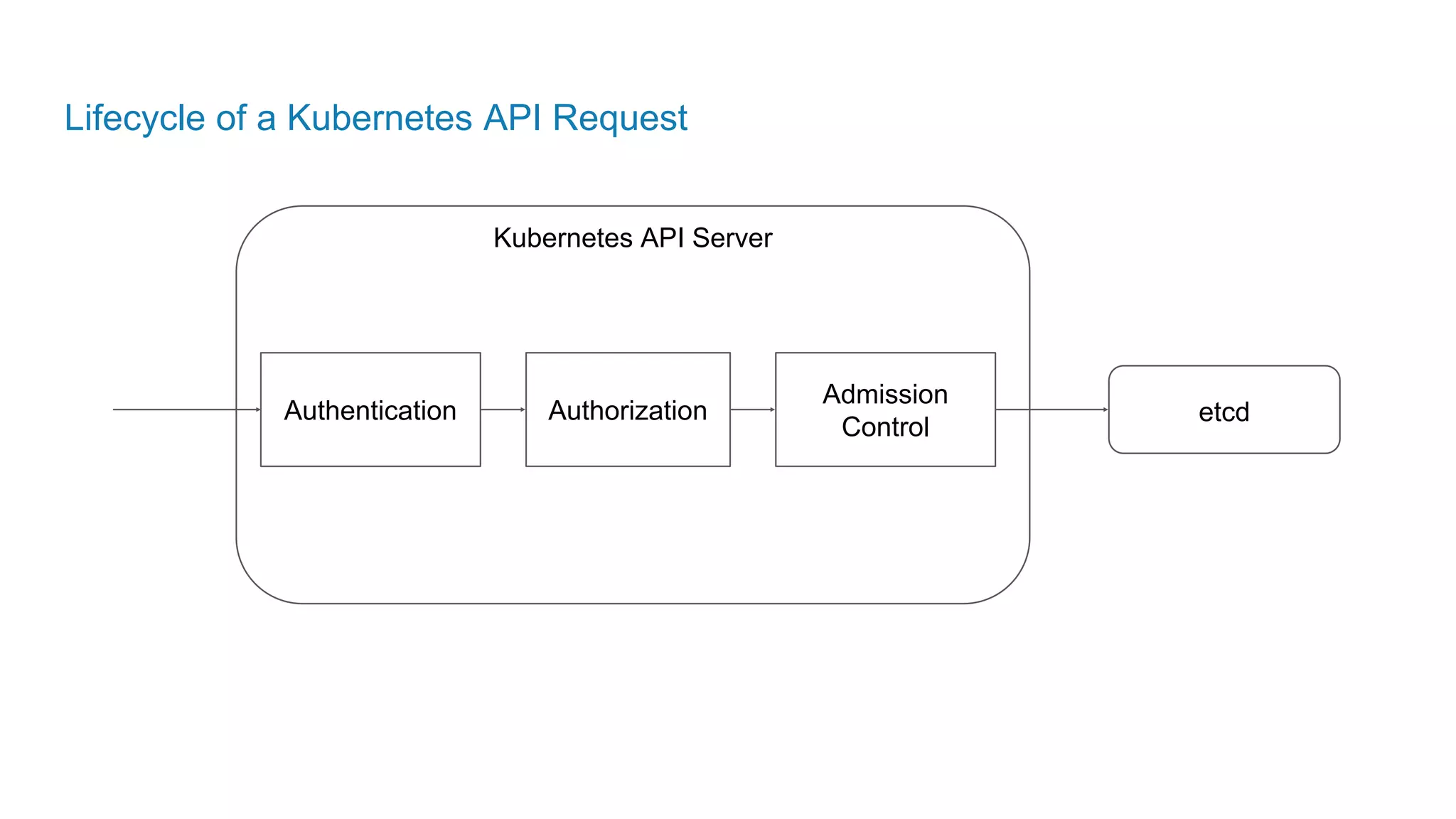
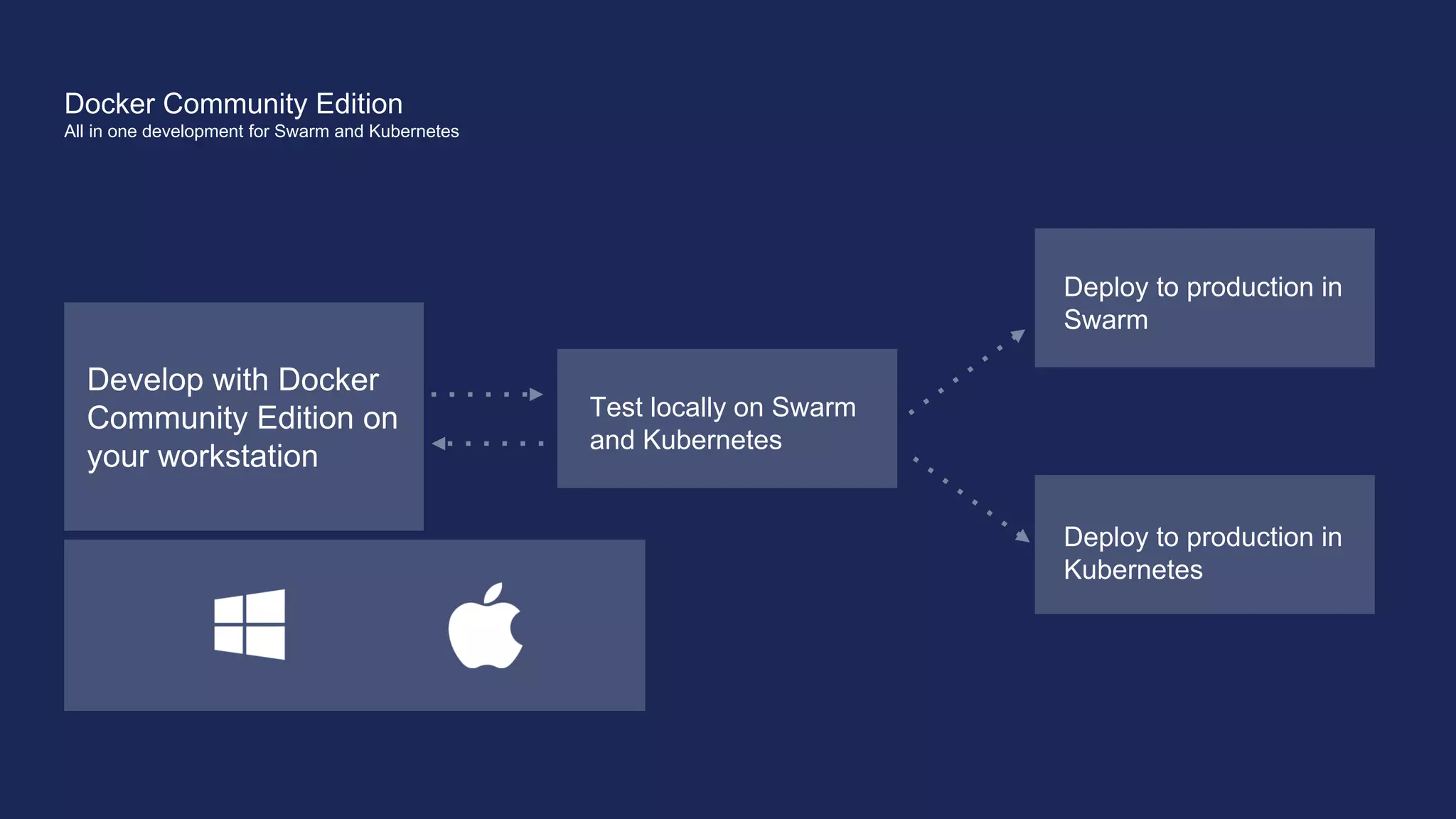
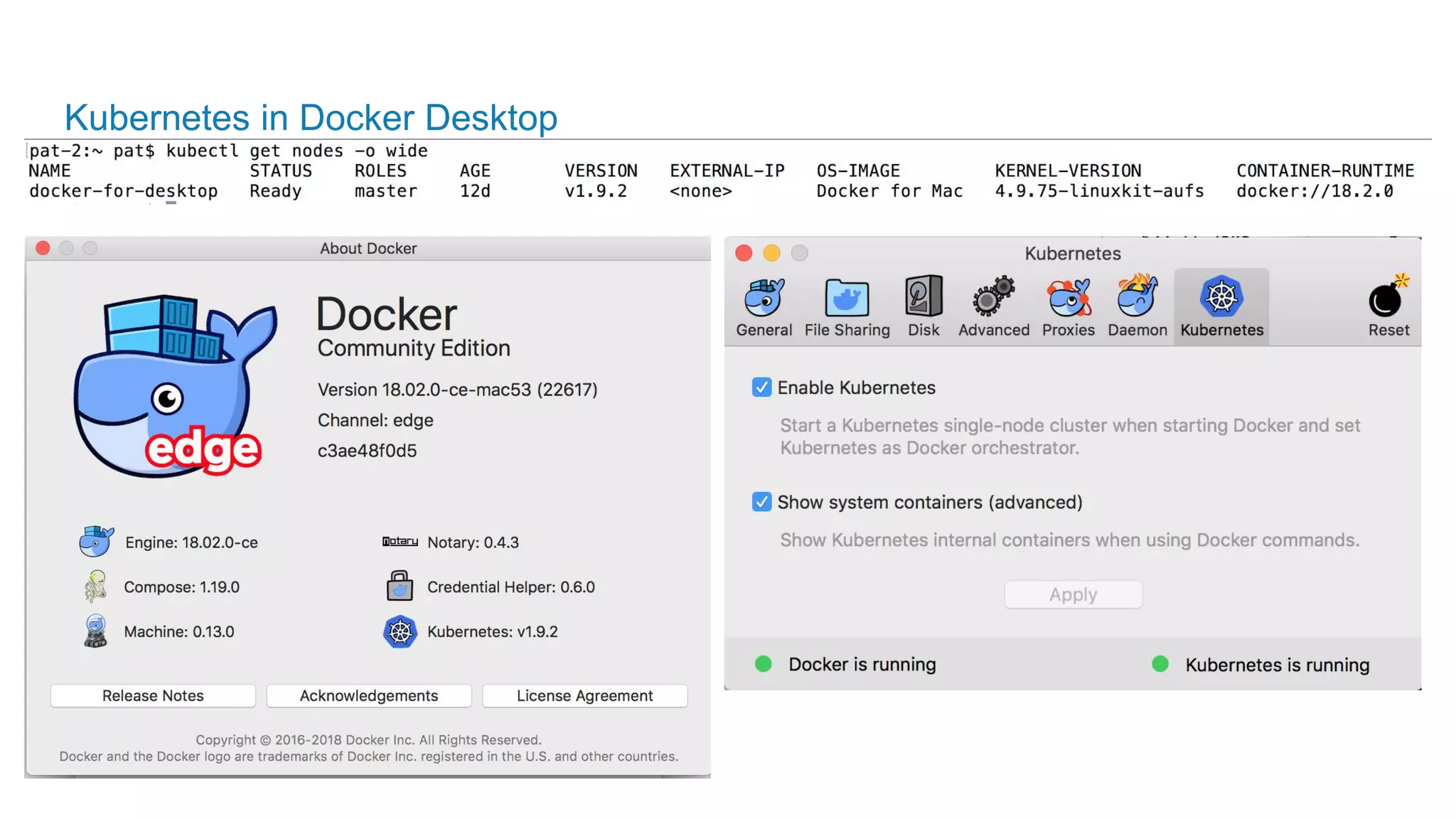
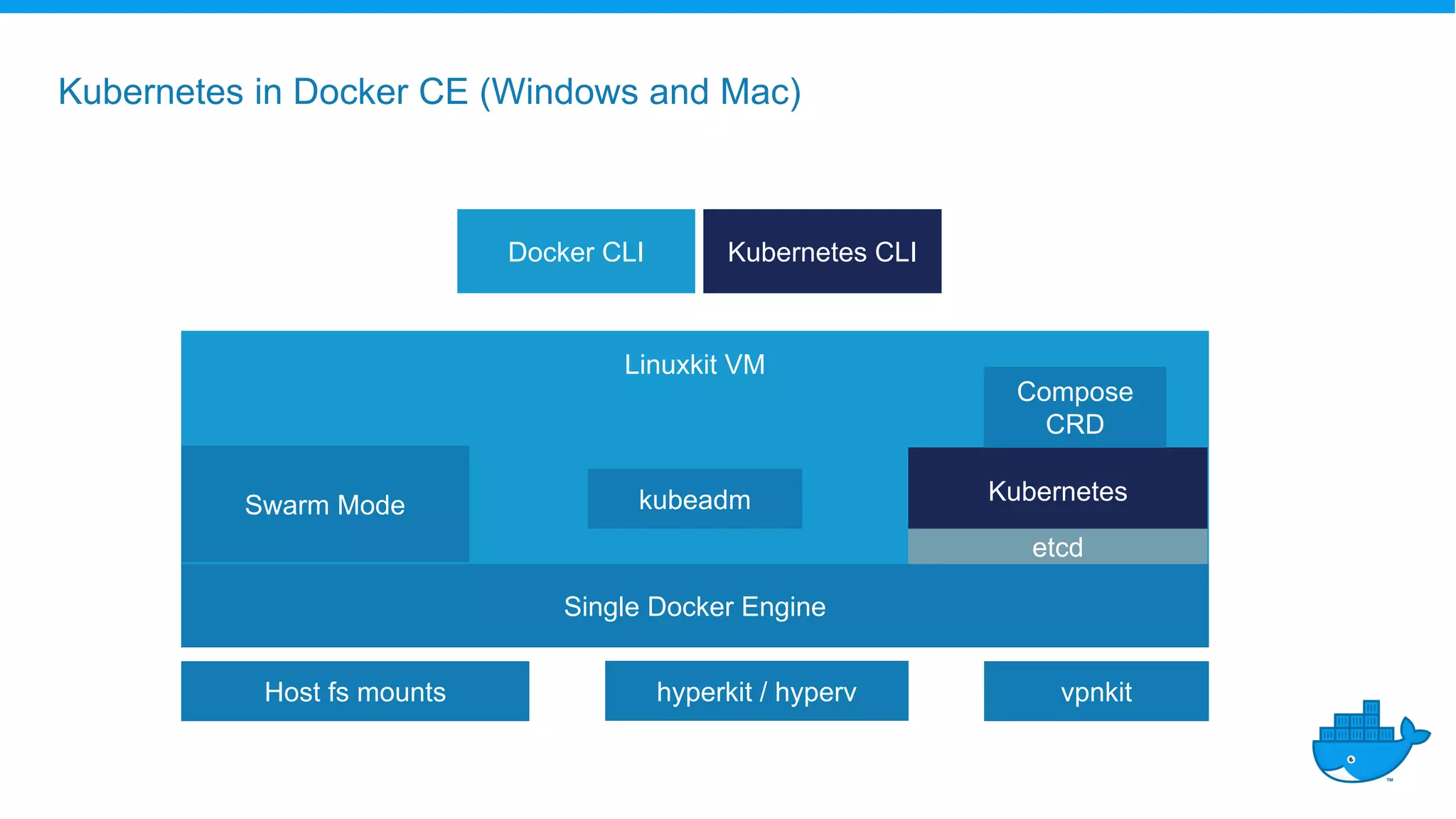
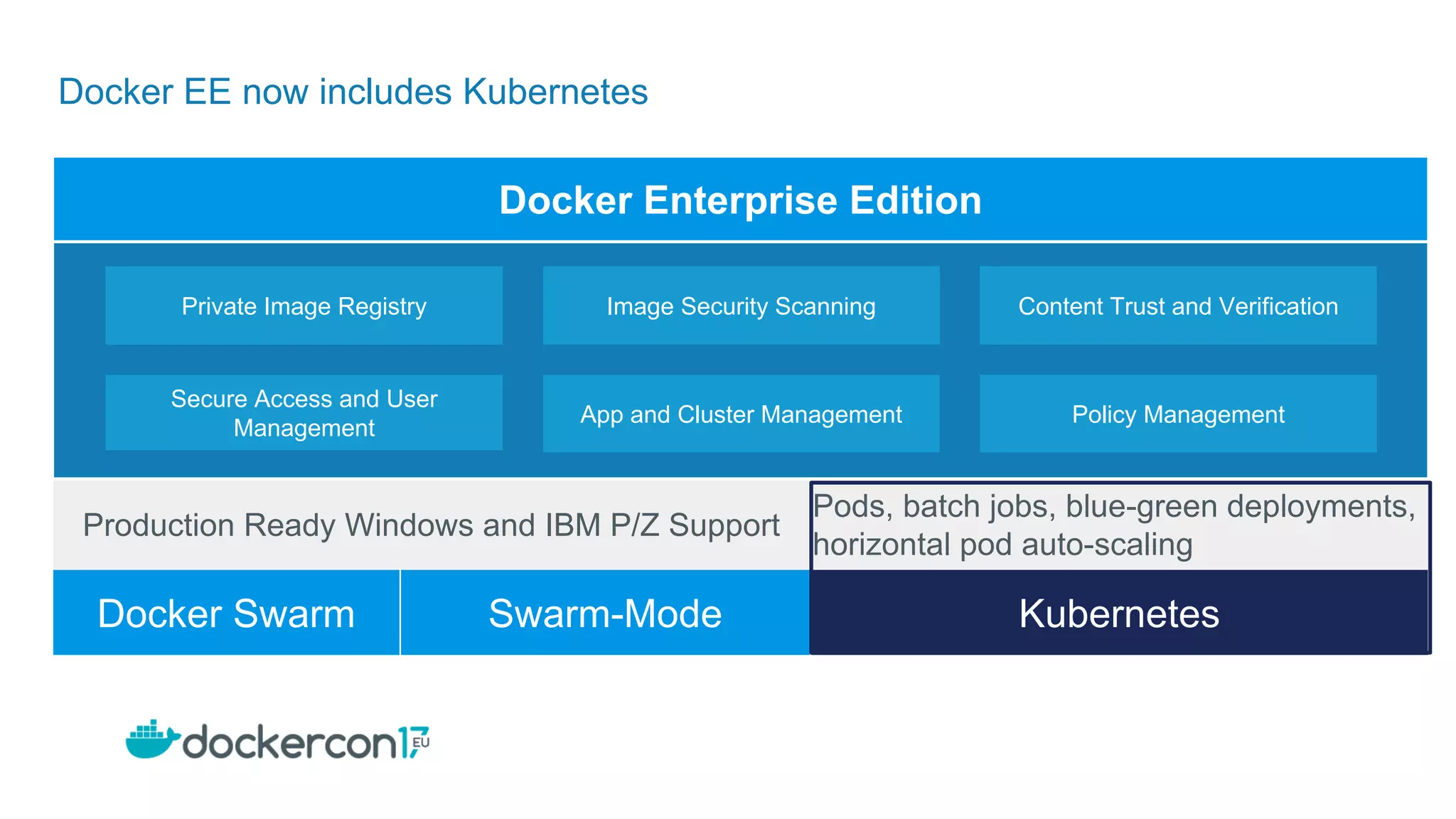
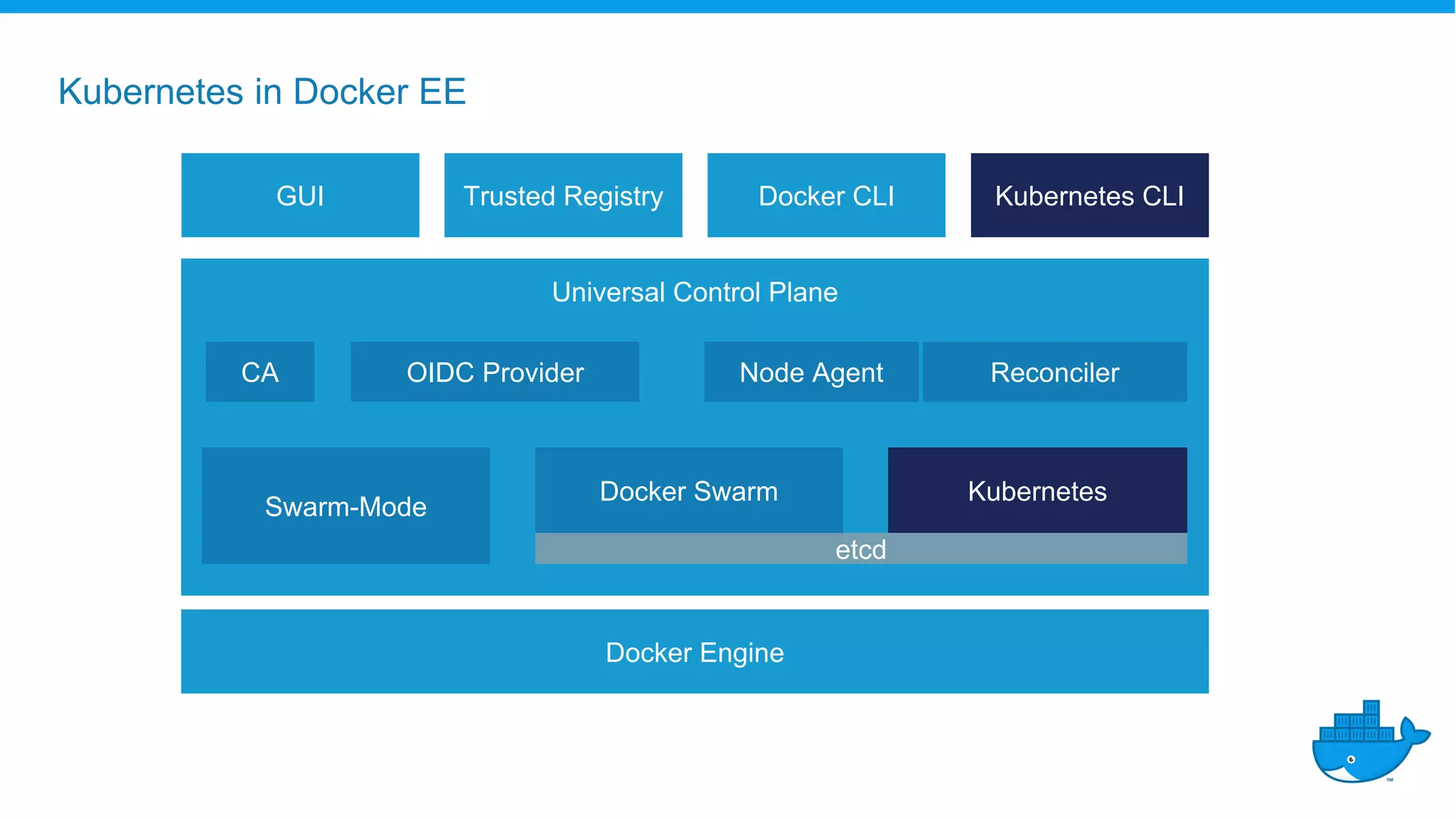
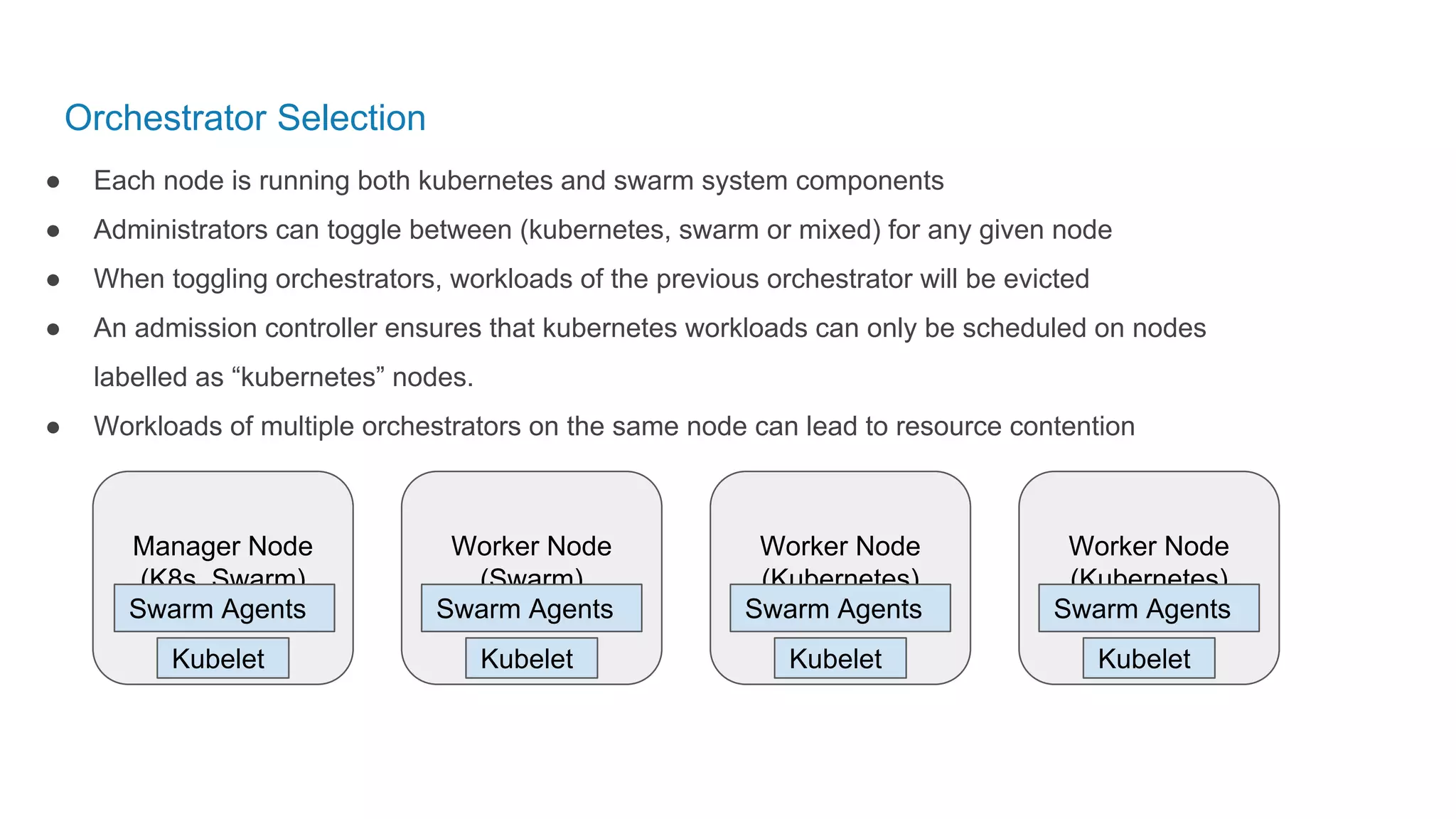
The document outlines the development and deployment of Kubernetes applications using Docker, highlighting its core principles of independence, openness, and simplicity. It discusses modernizing traditional applications with Docker's container platform, emphasizing efficiency gains and cost reductions. Additionally, it provides insights into the integration of Kubernetes within Docker and architectural details of Docker Enterprise Edition for enhanced security and management.