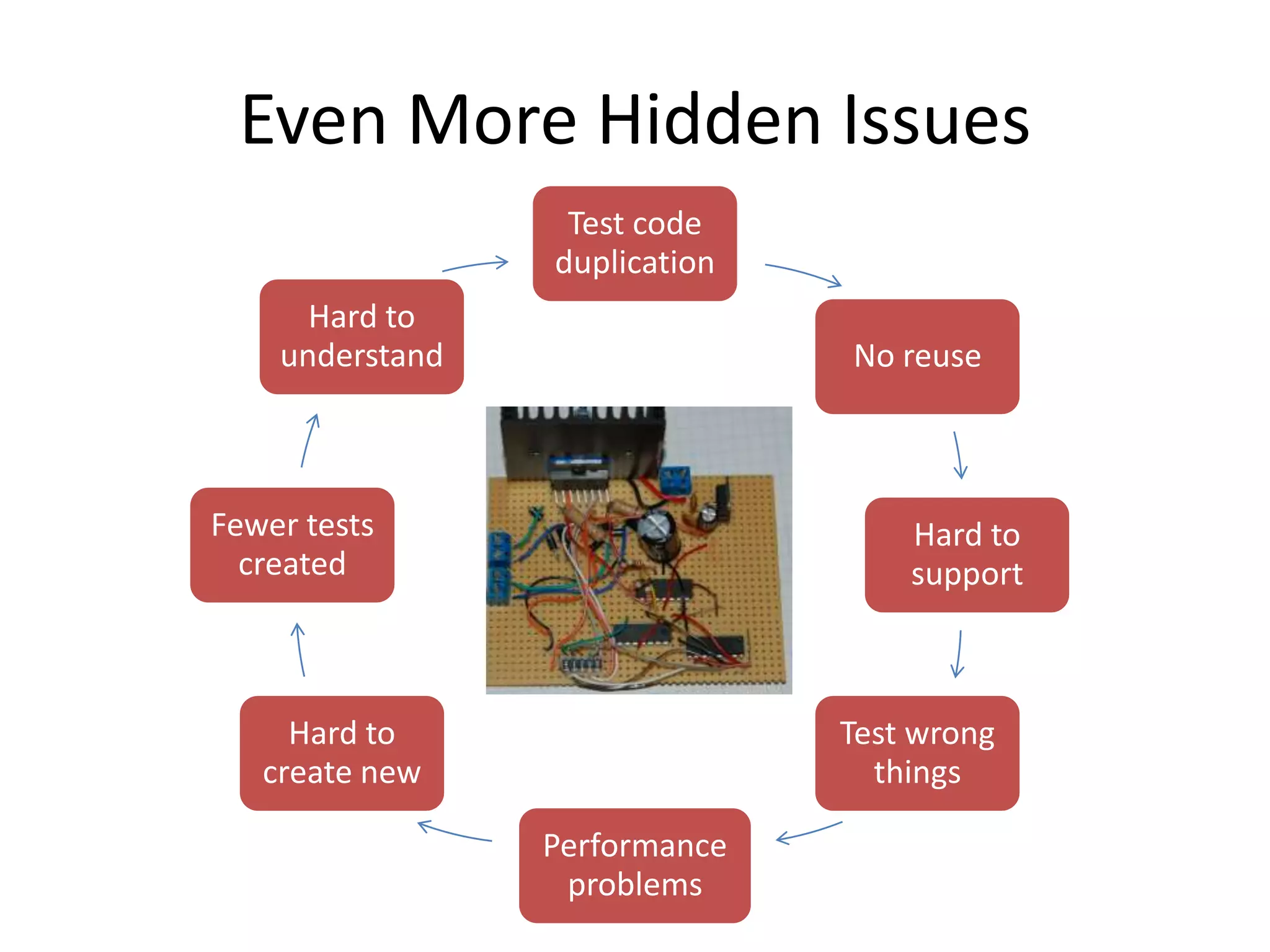
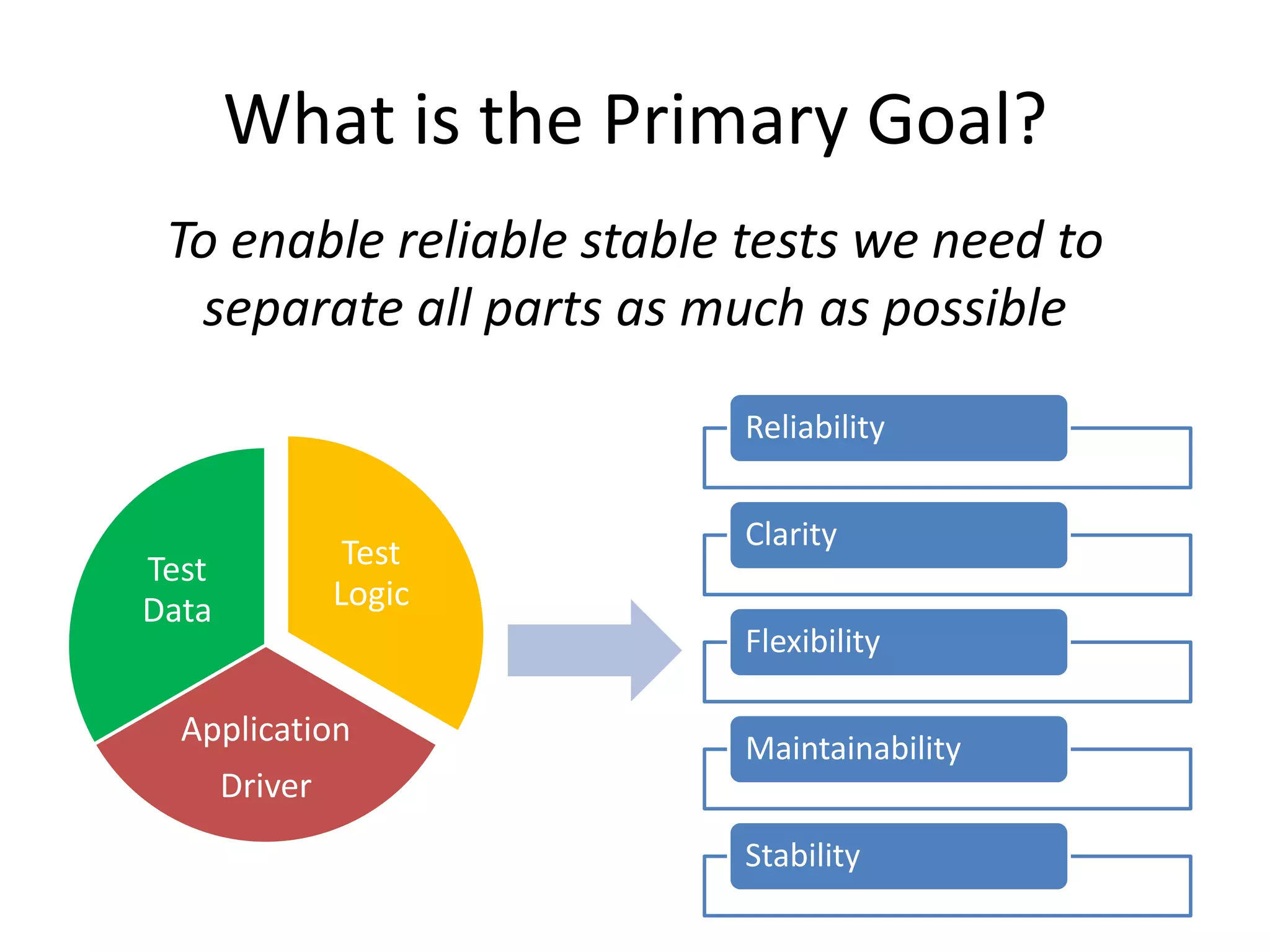
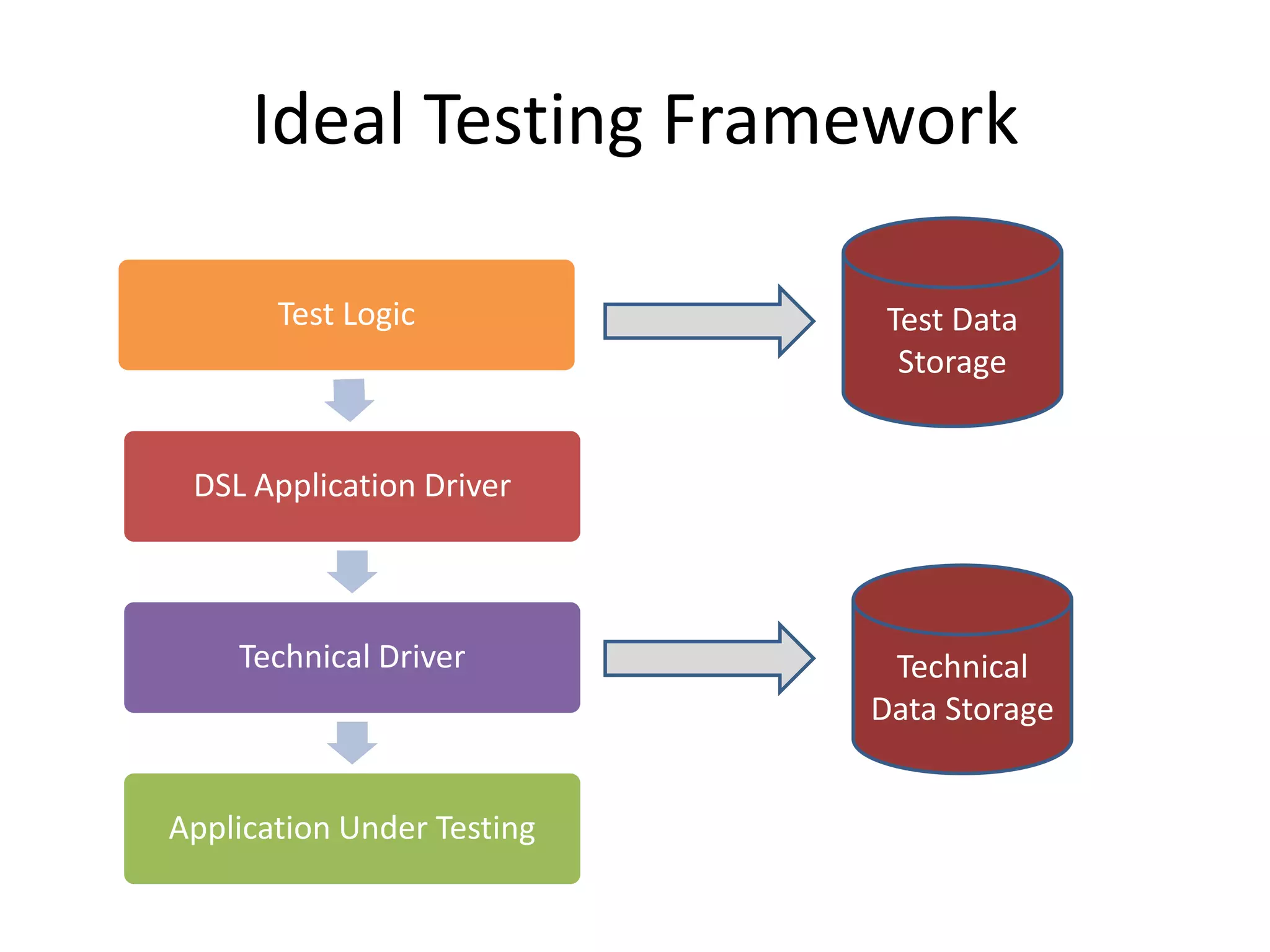
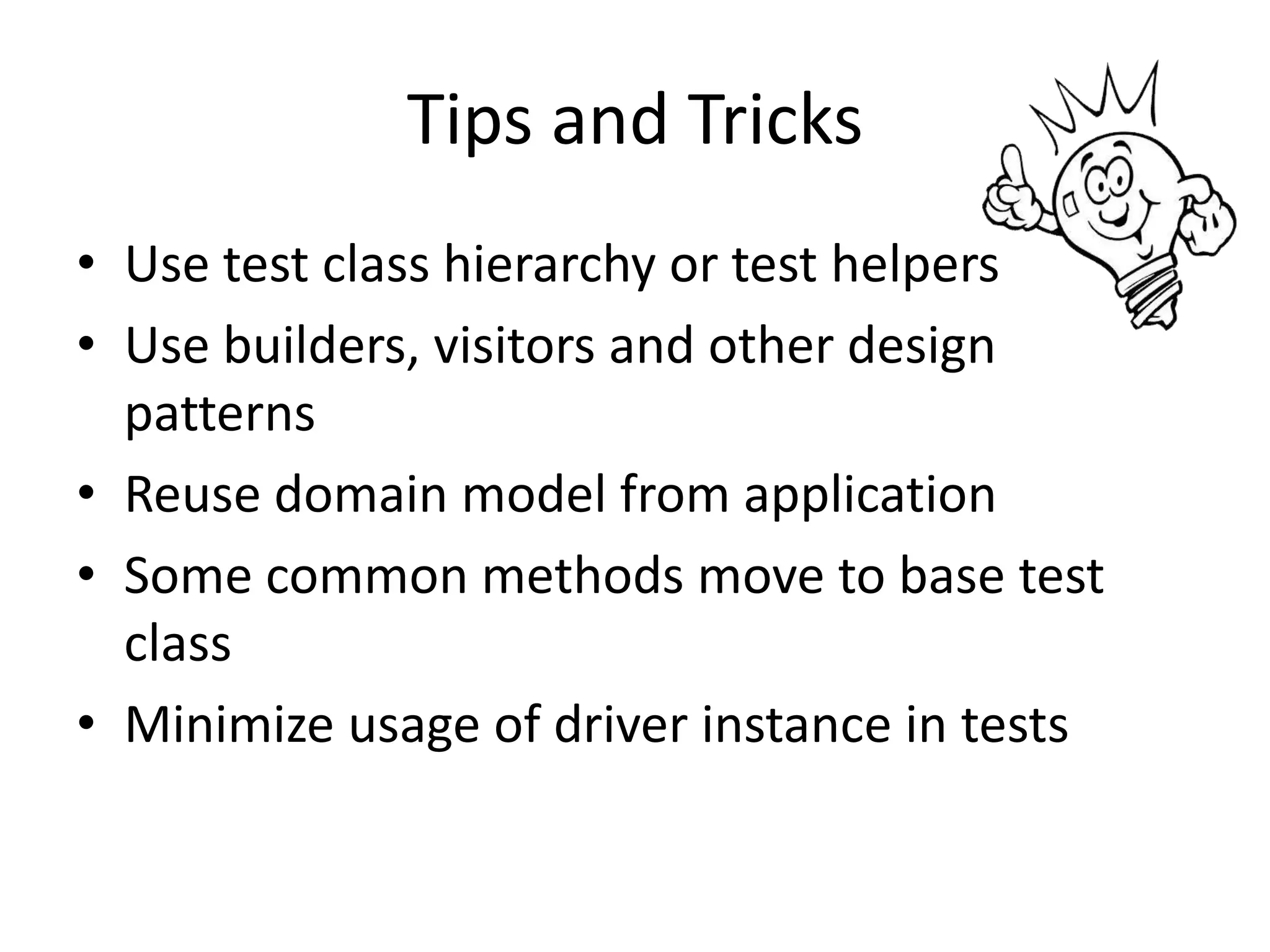
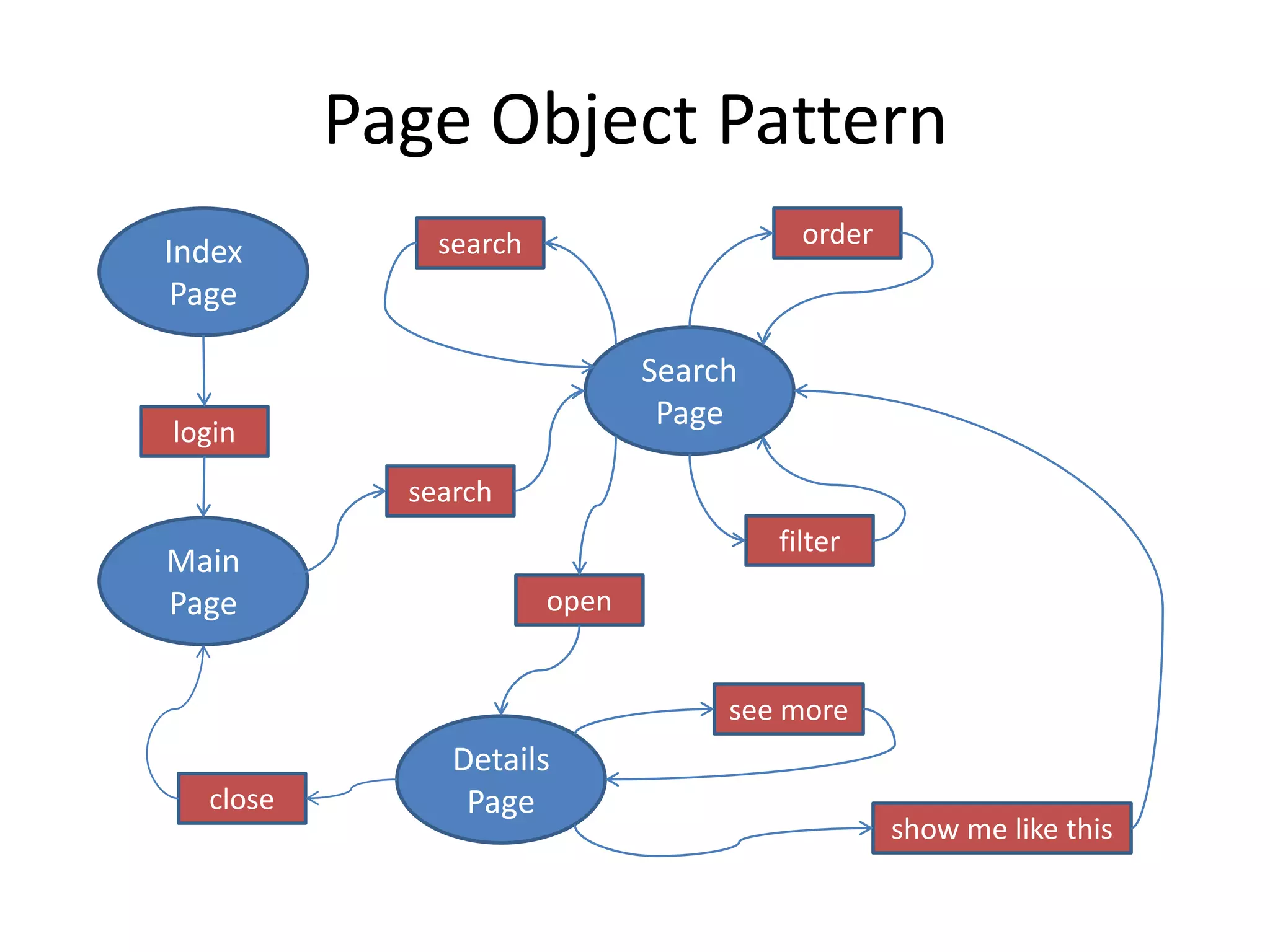
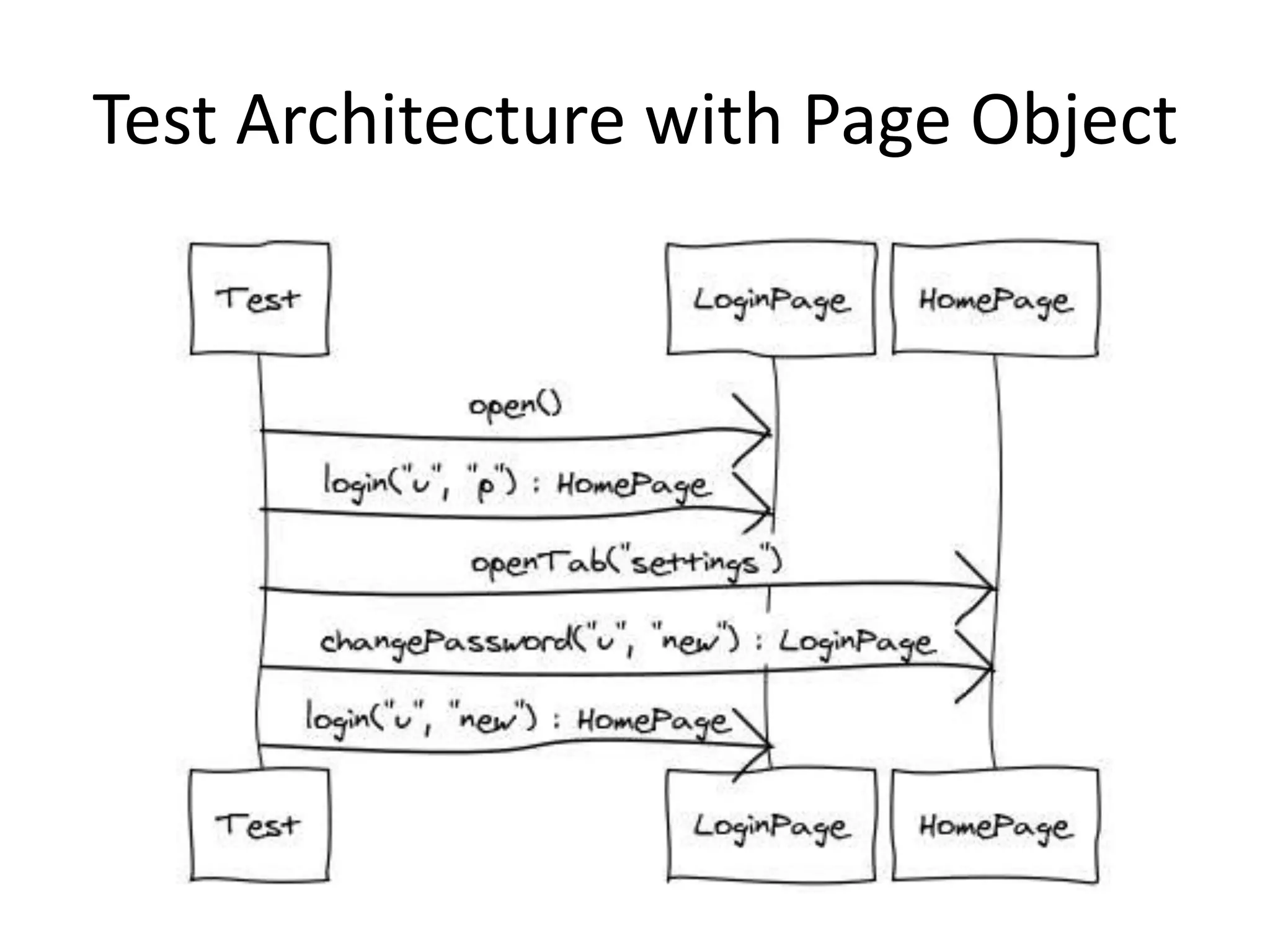
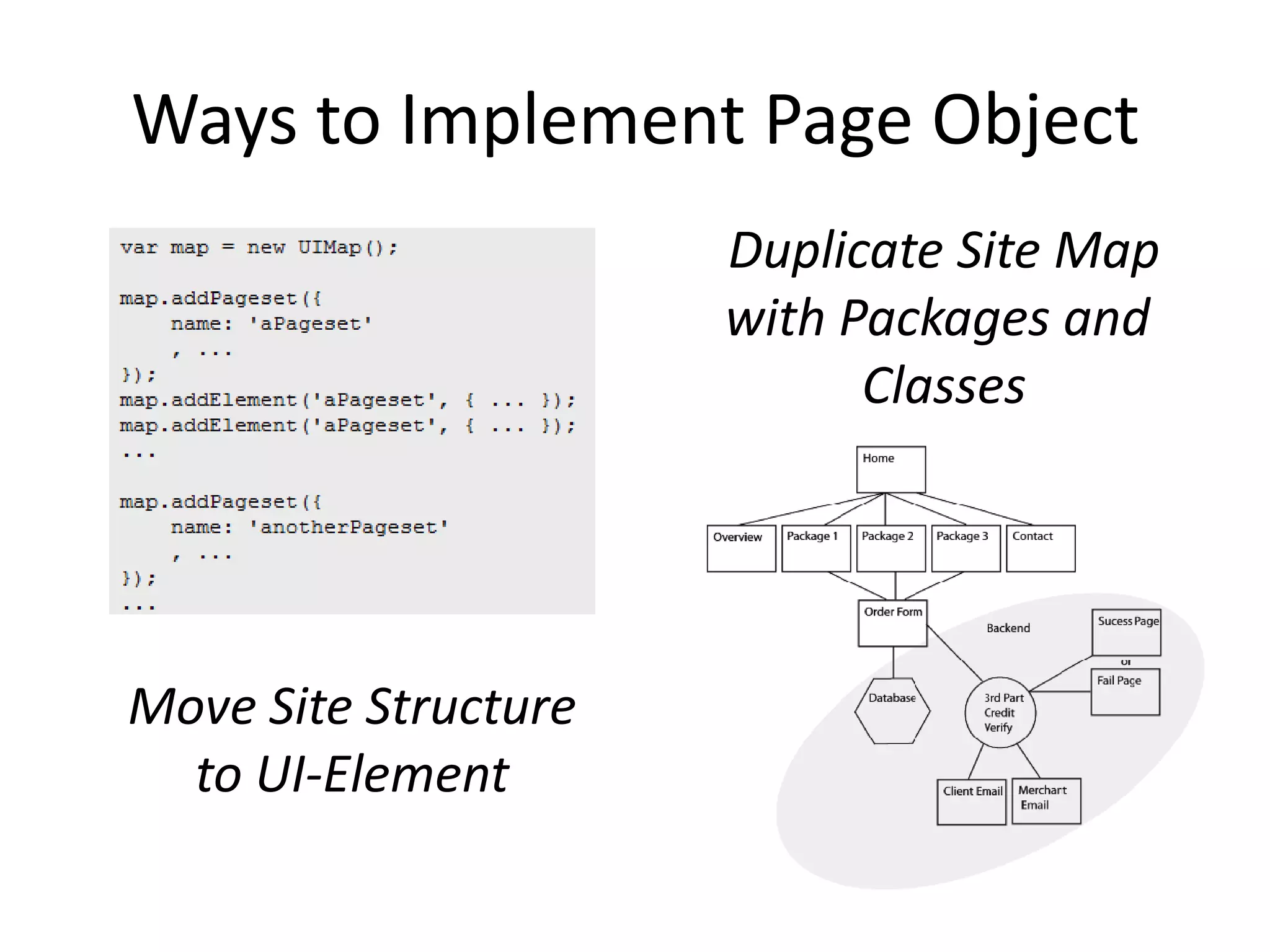
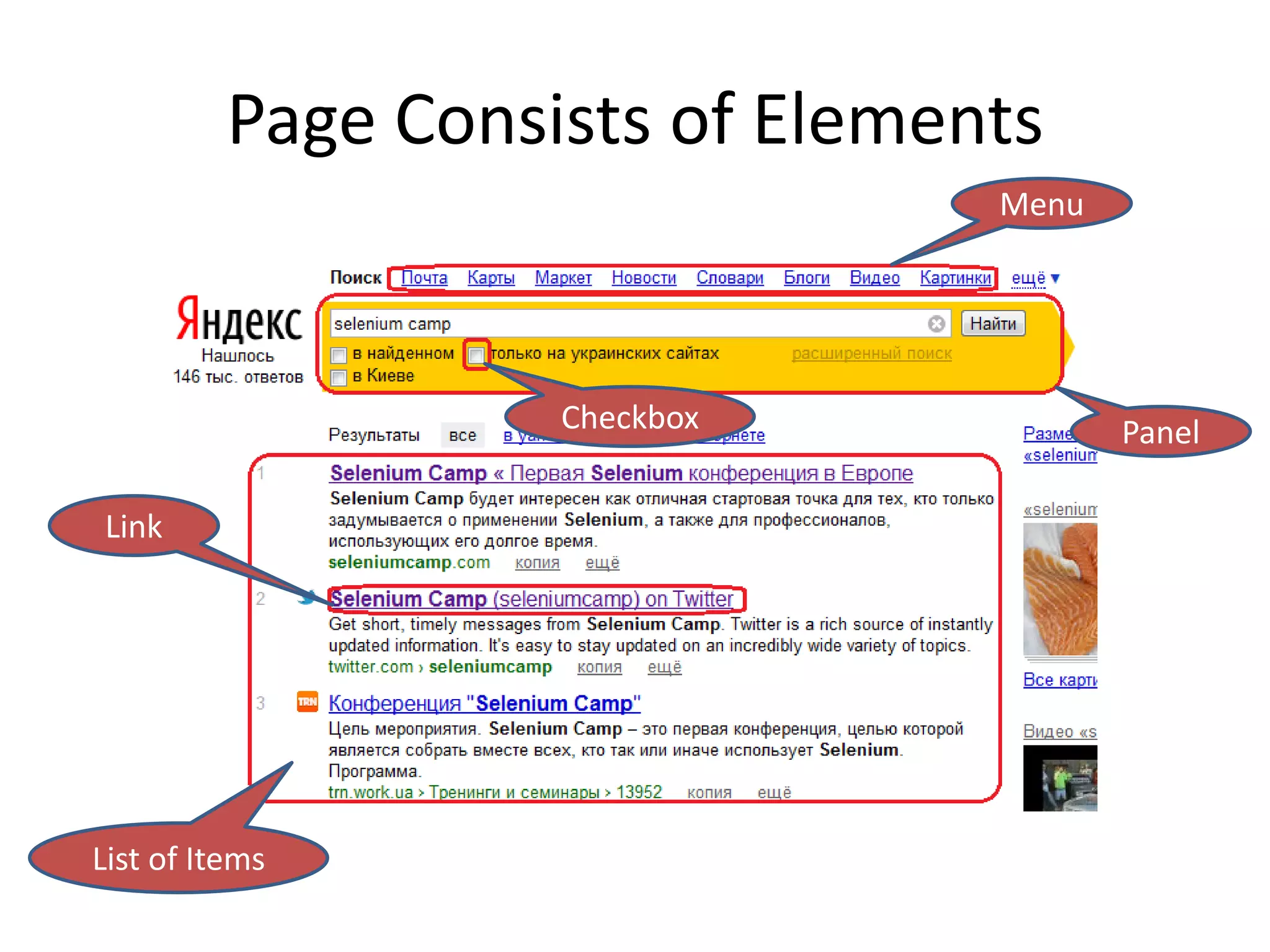
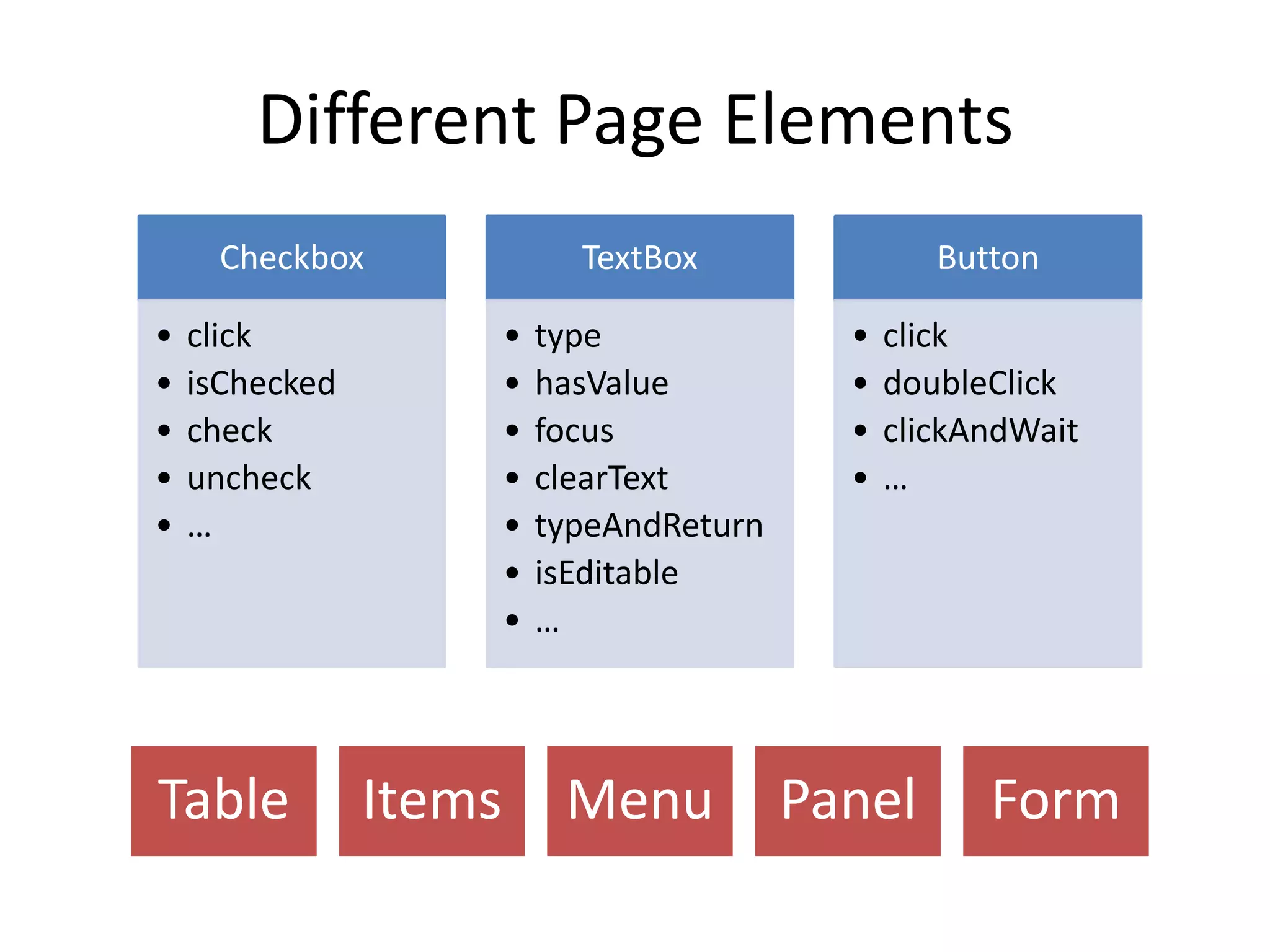
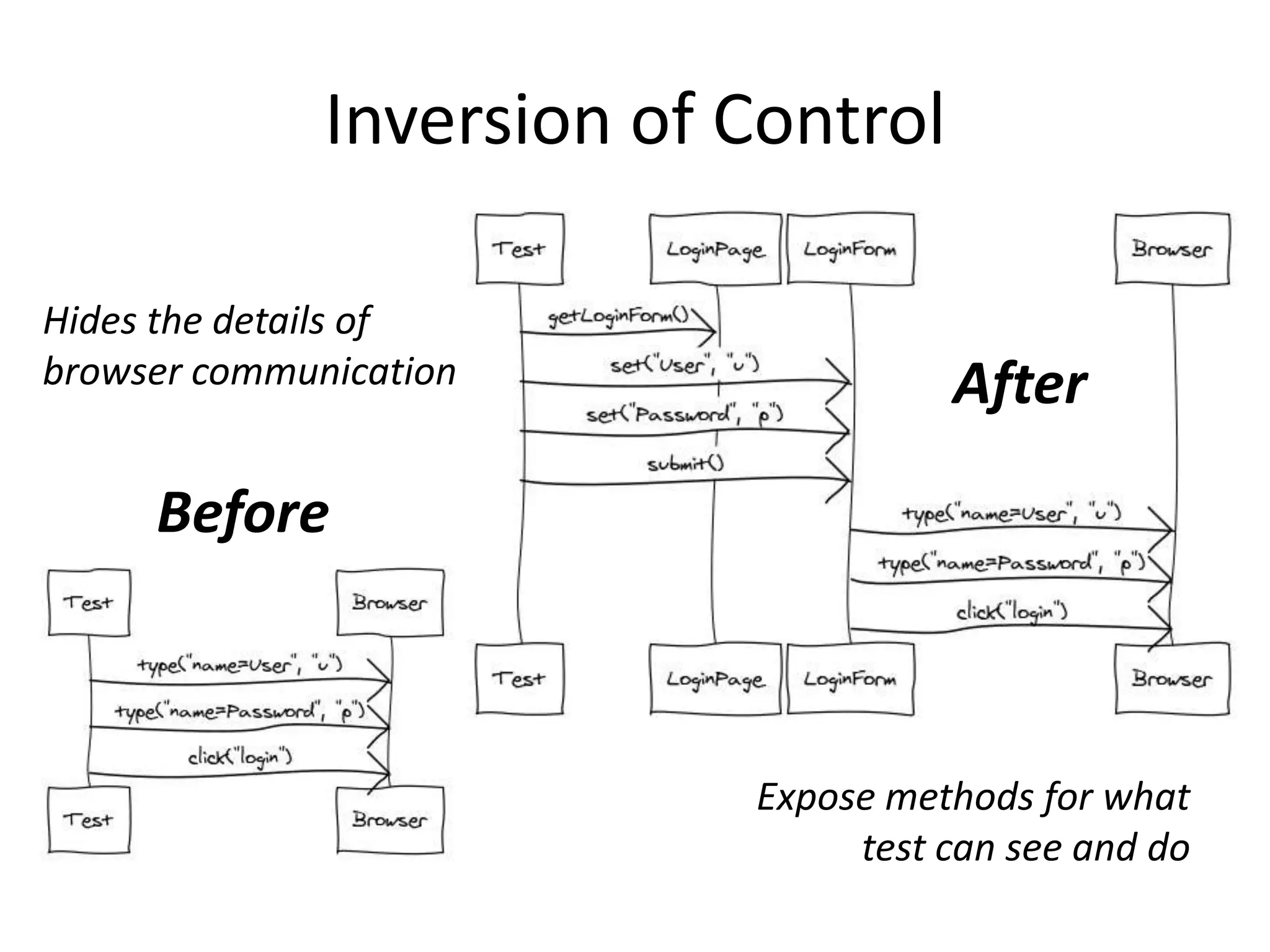
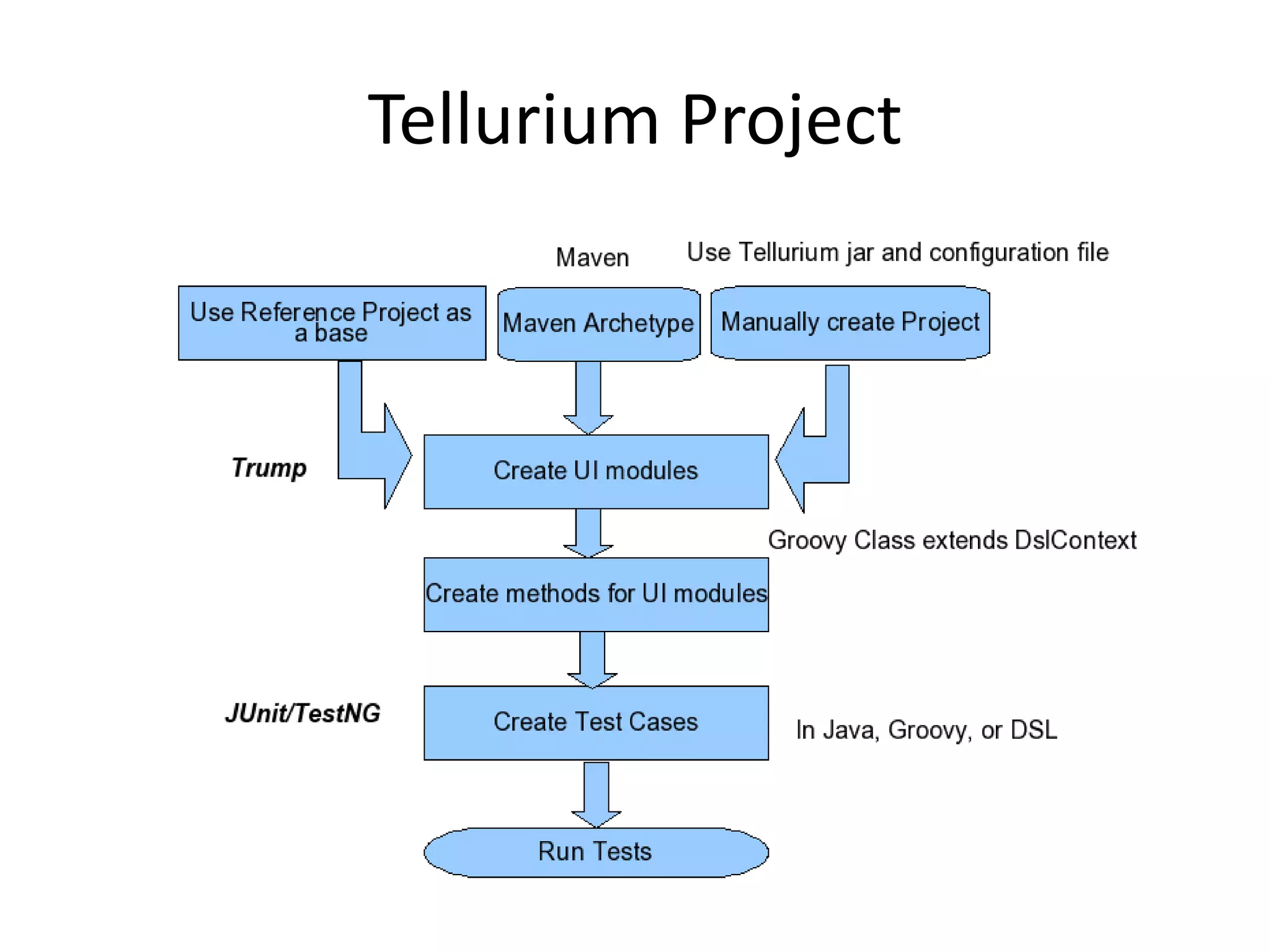
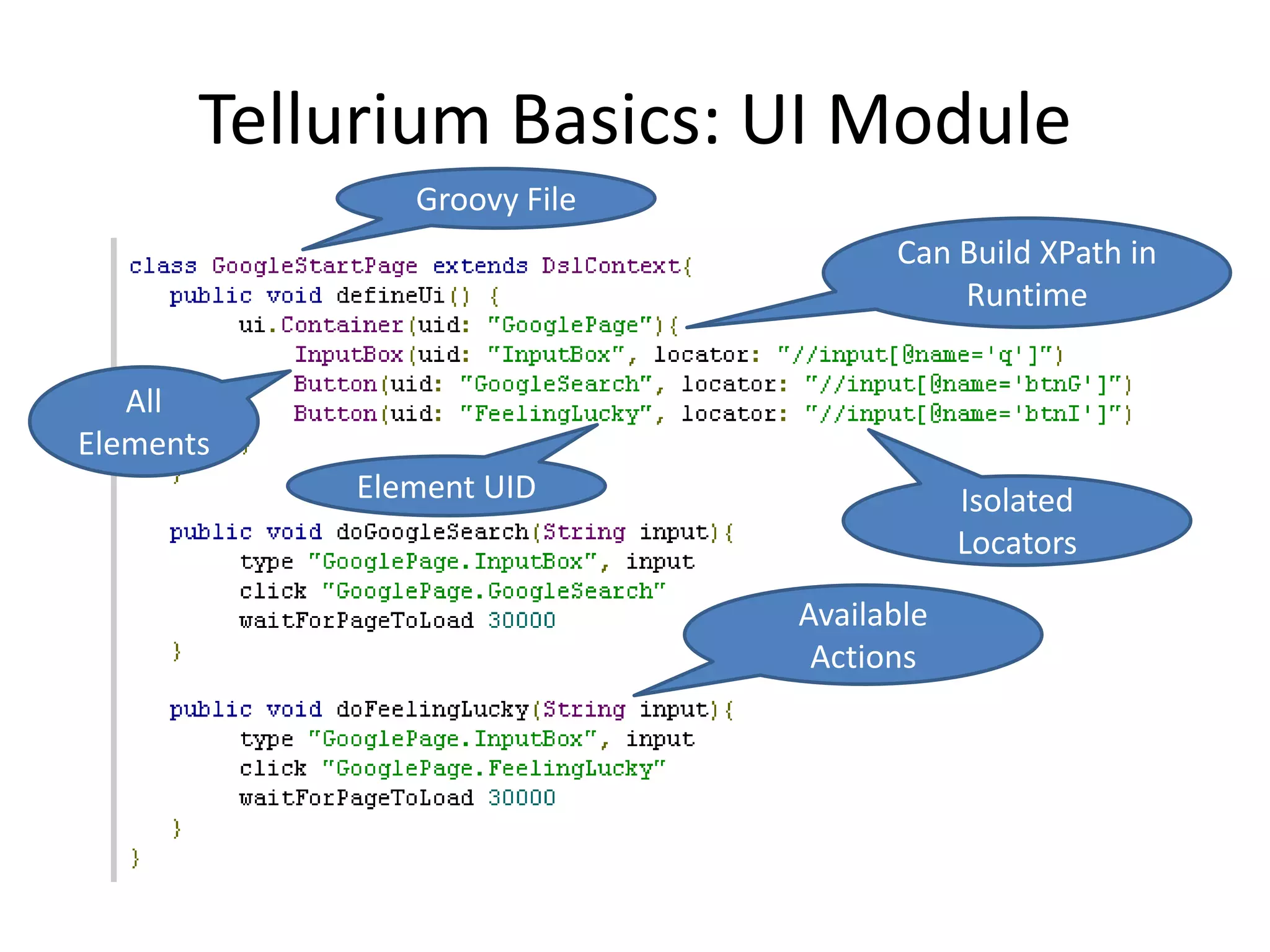
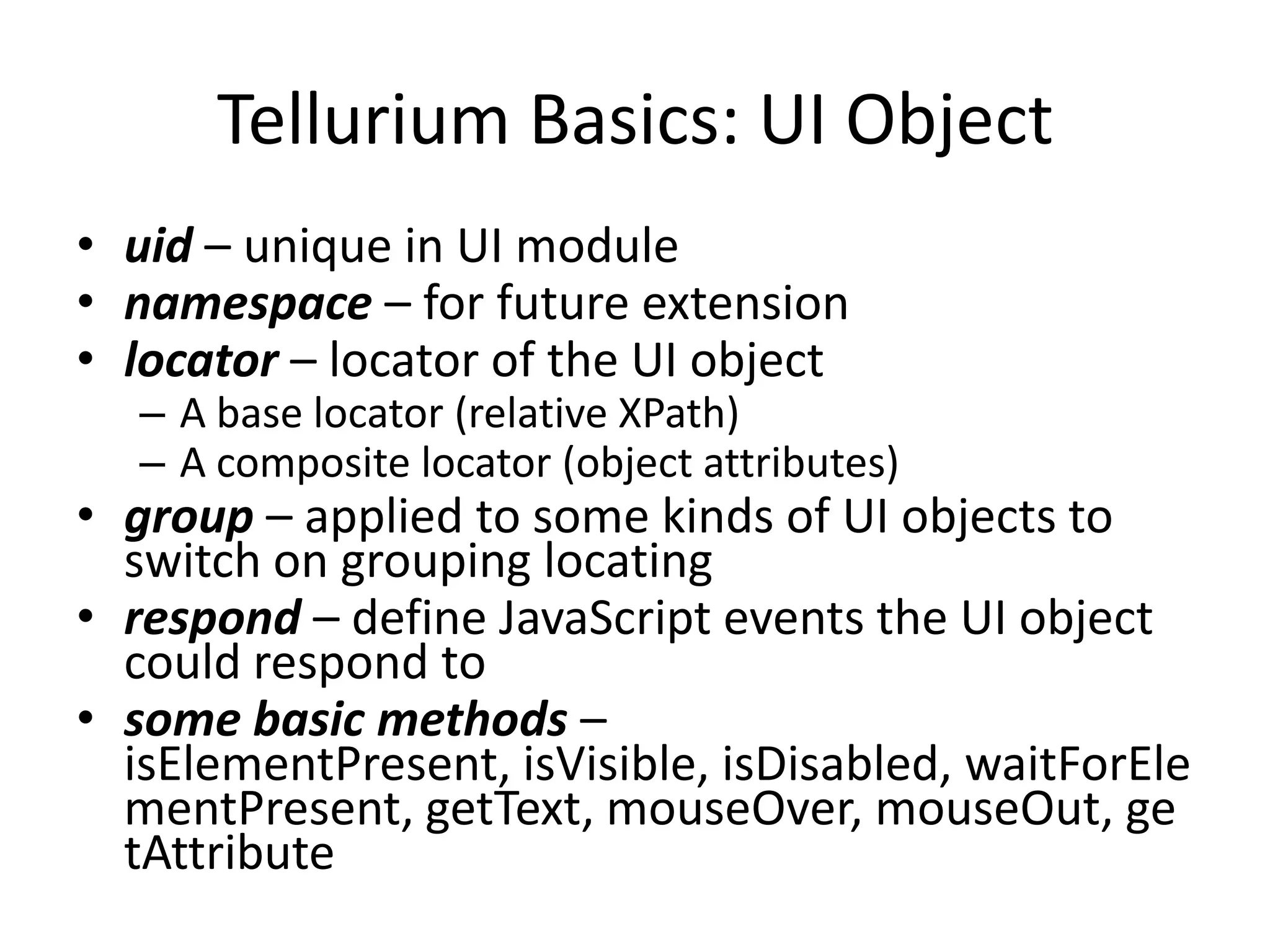
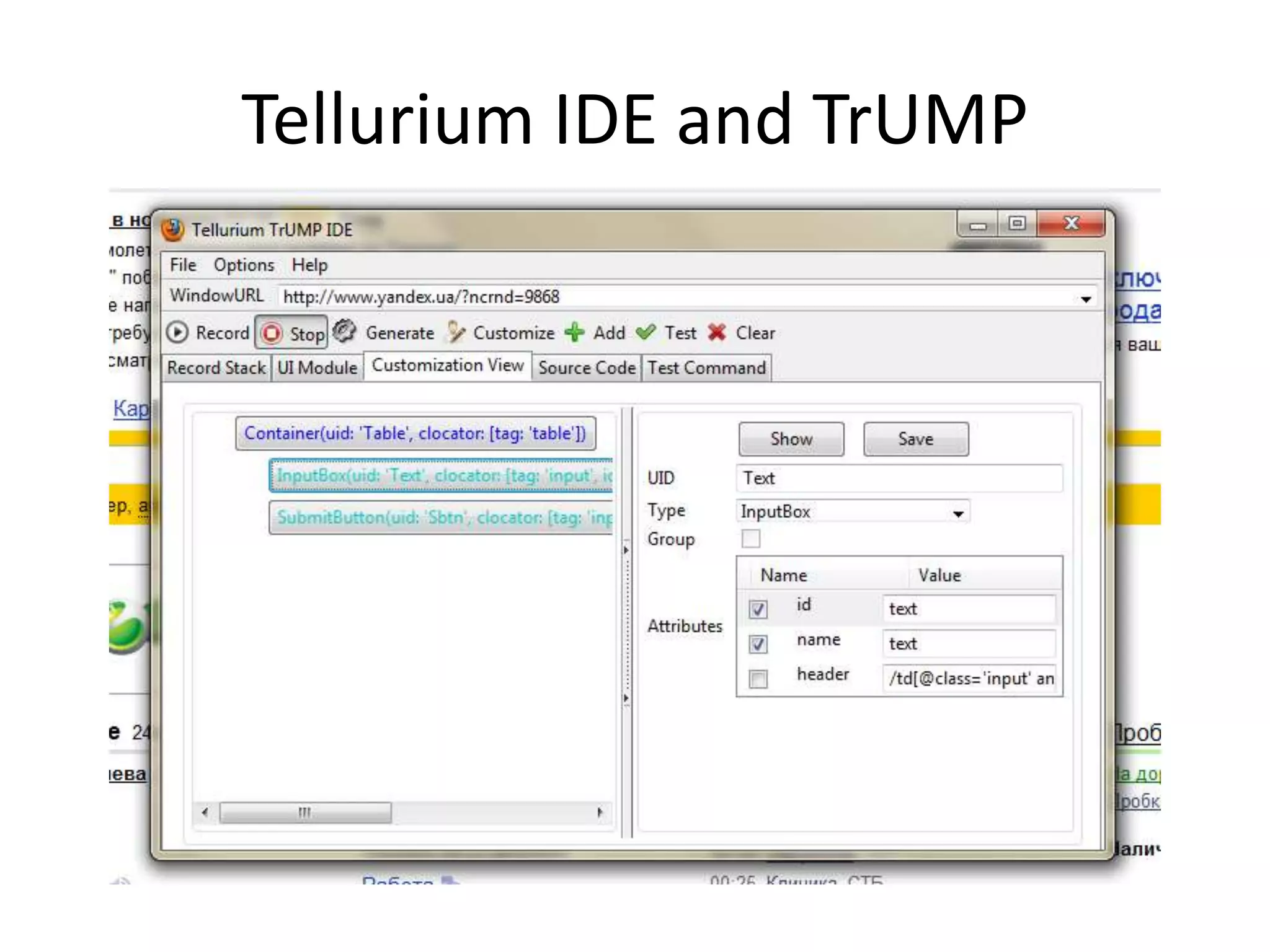
DSL, Page Object and WebDriver patterns help address issues with Selenium tests such as verbosity, lack of expressiveness, fragility, and lack of reuse. The presentation recommends a three step approach: 1. Introduce a DSL to create high-level, readable tests in the language of the application domain. 2. Implement the Page Object pattern to separate test logic from page details through page maps. 3. Divide pages into reusable elements to increase code reuse and simplify page objects. This approach results in reliable, clear, and maintainable tests that better model the application under test.




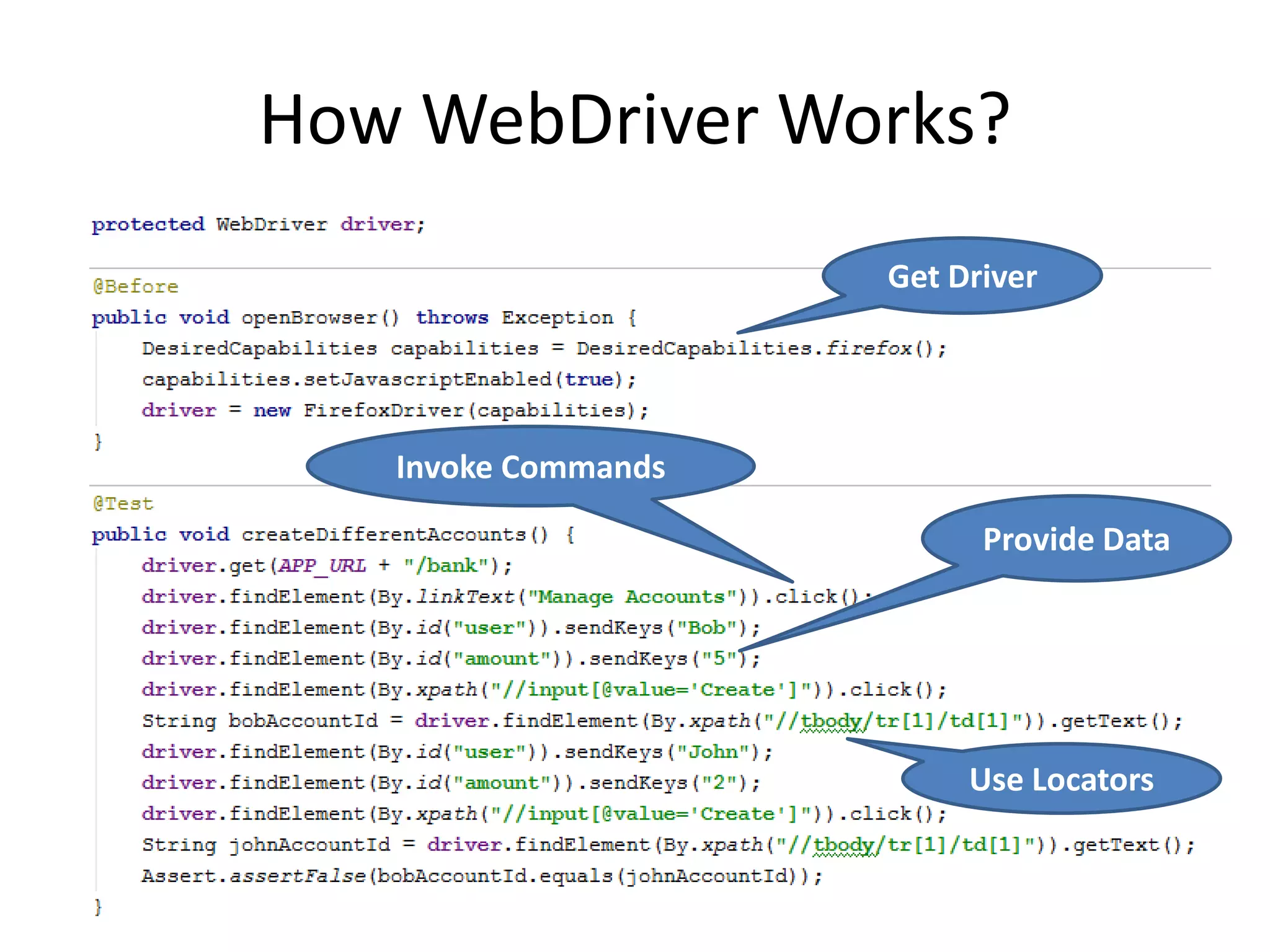

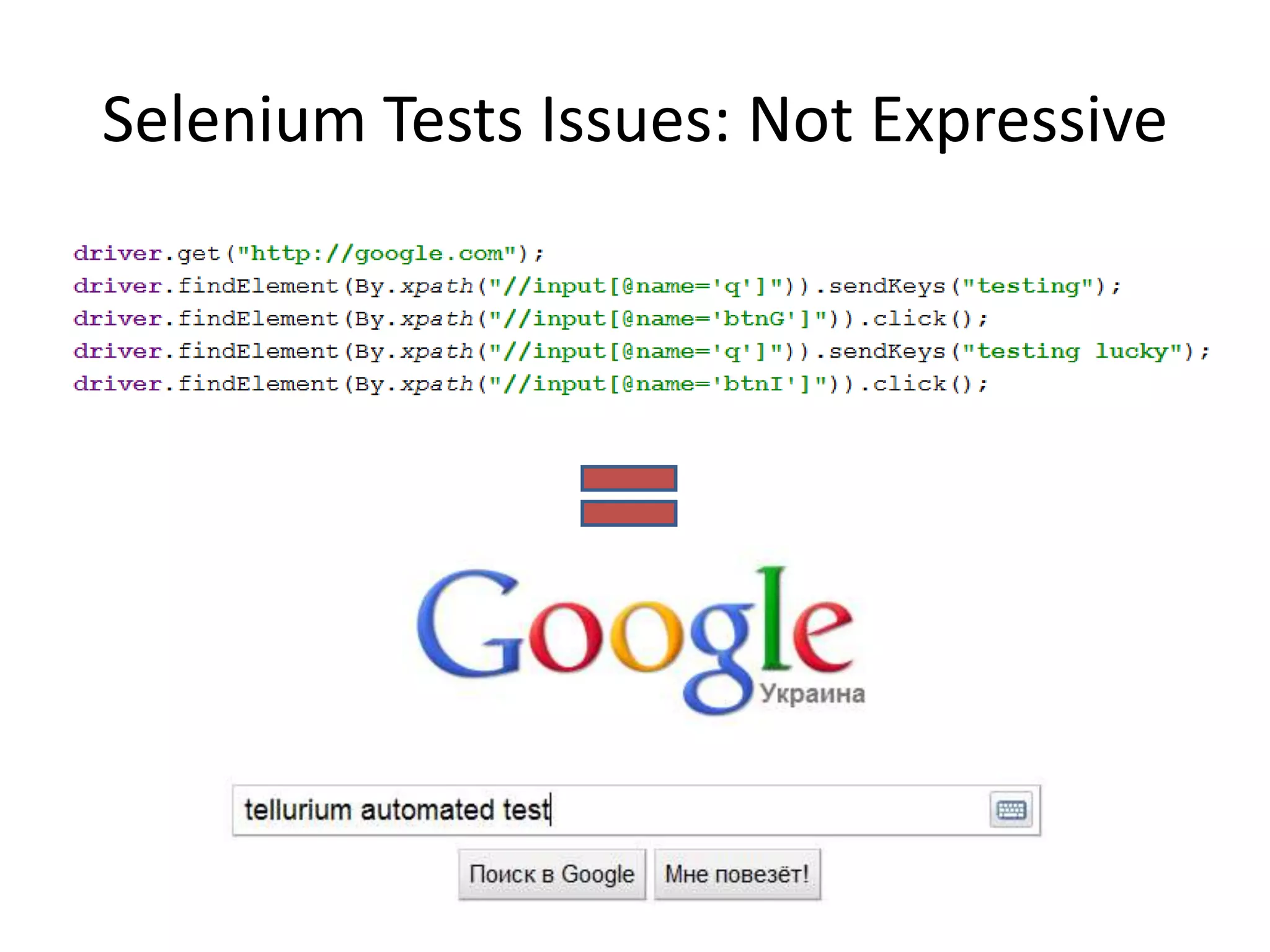
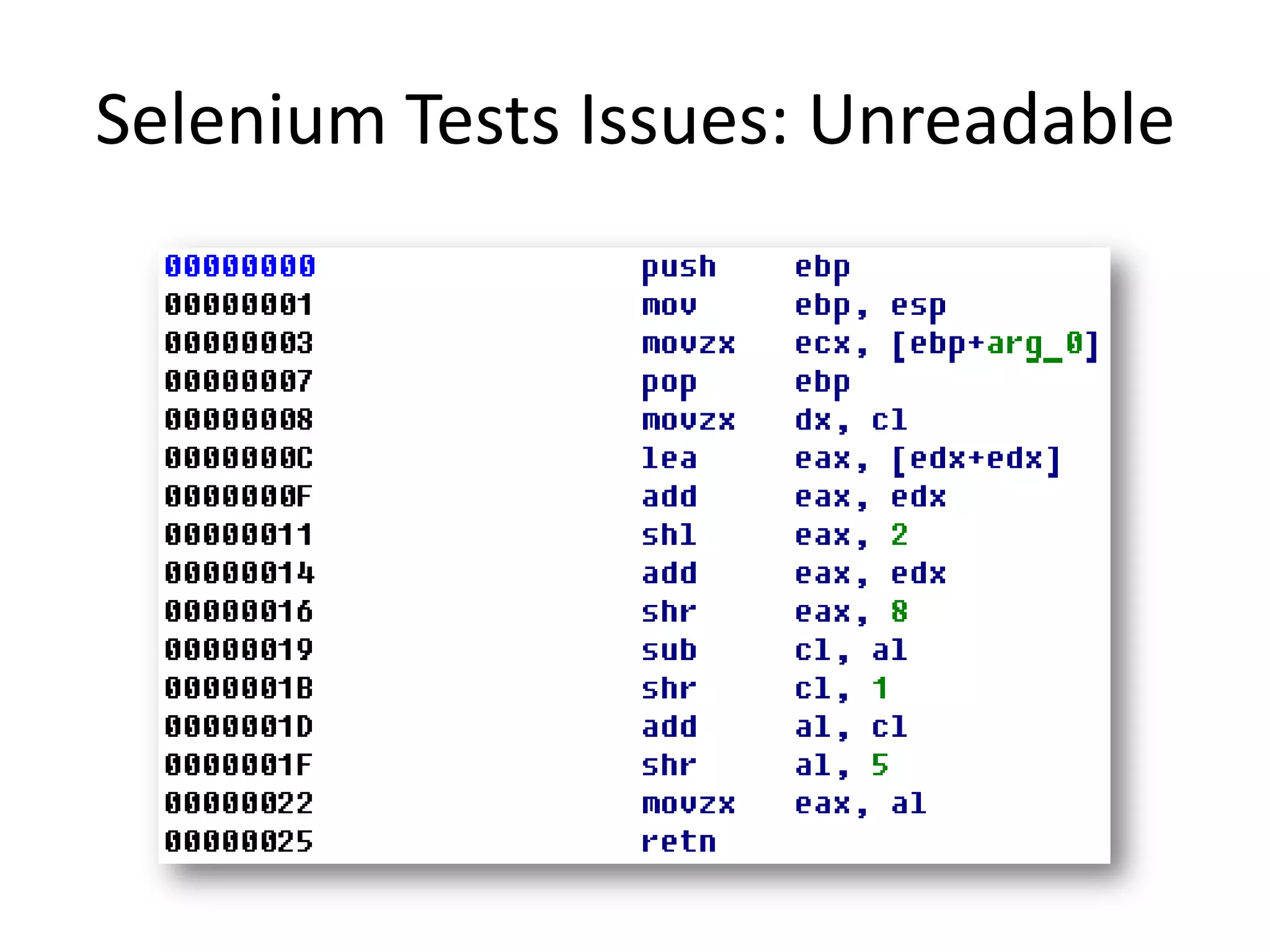
![Selenium Tests Issues: Fragile driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id=(//label[tex t()='Fax']/@for)]")).click(); What is going on here? driver.findElement(By.xpath("//div[@id='App']/div/p[4]/di v[1]/h4[@class='Online']")).getText() Depends too much on page structure!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dslpageobjectandwebdriverthepathtoreliablefunctionaltests-111216025700-phpapp02/75/DSL-Page-Object-WebDriver-10-2048.jpg)