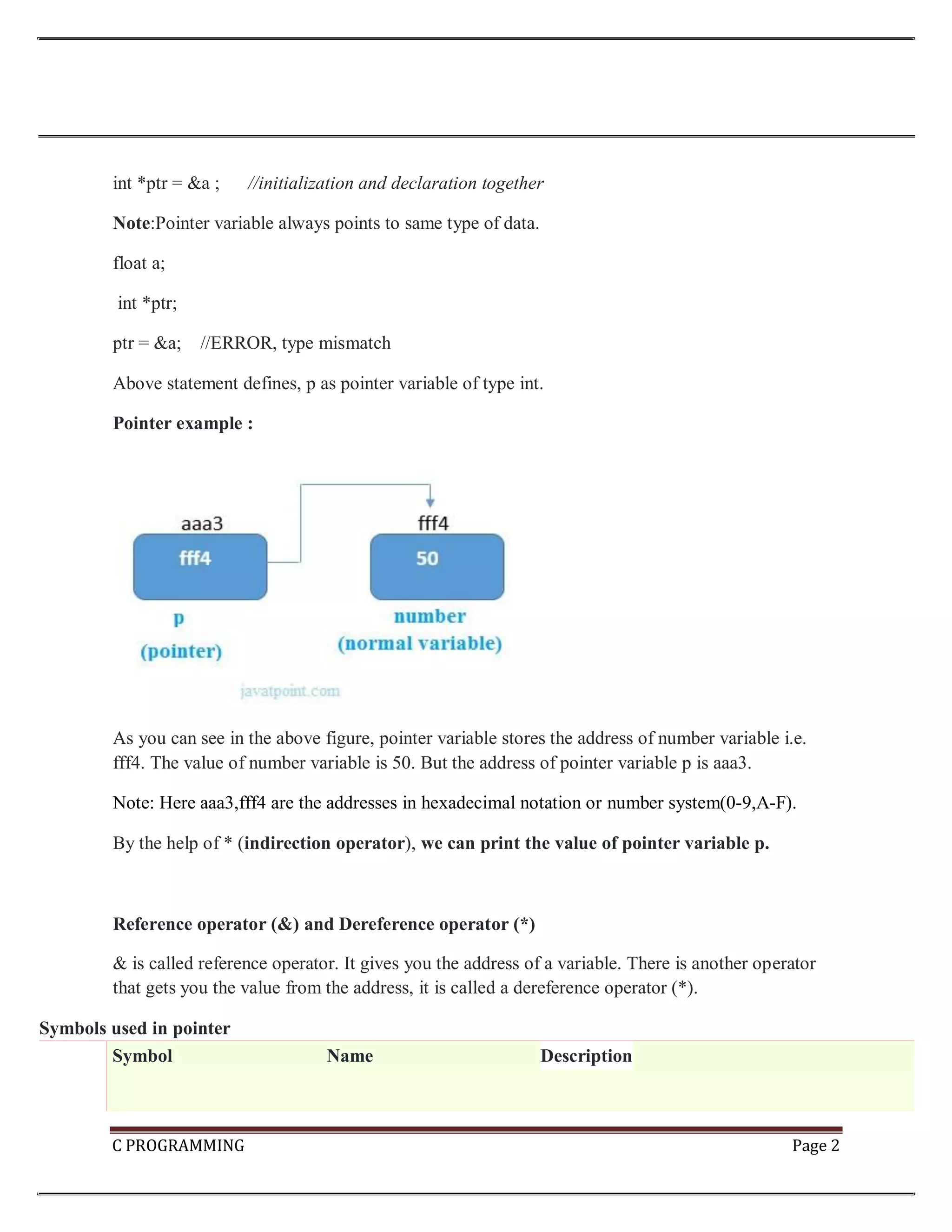
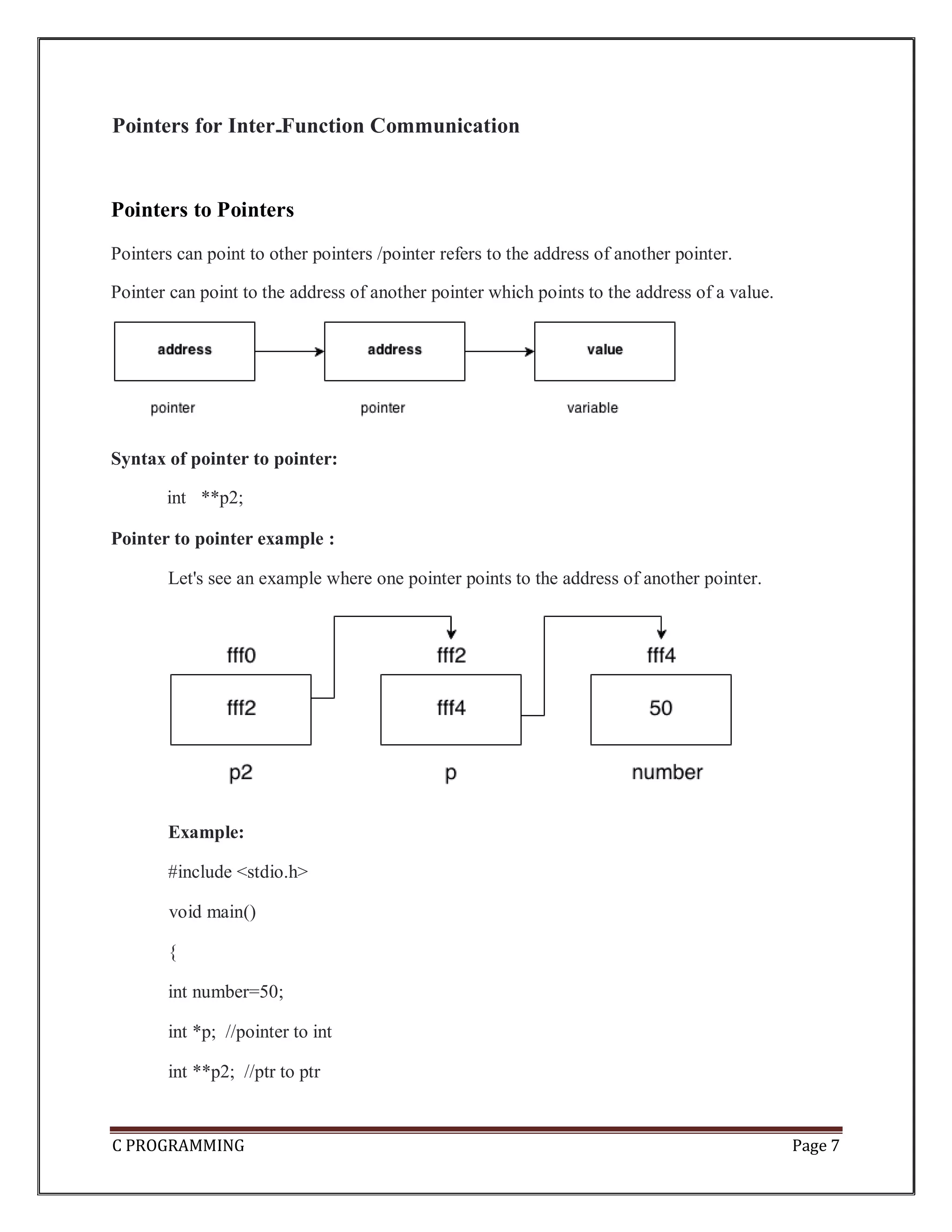
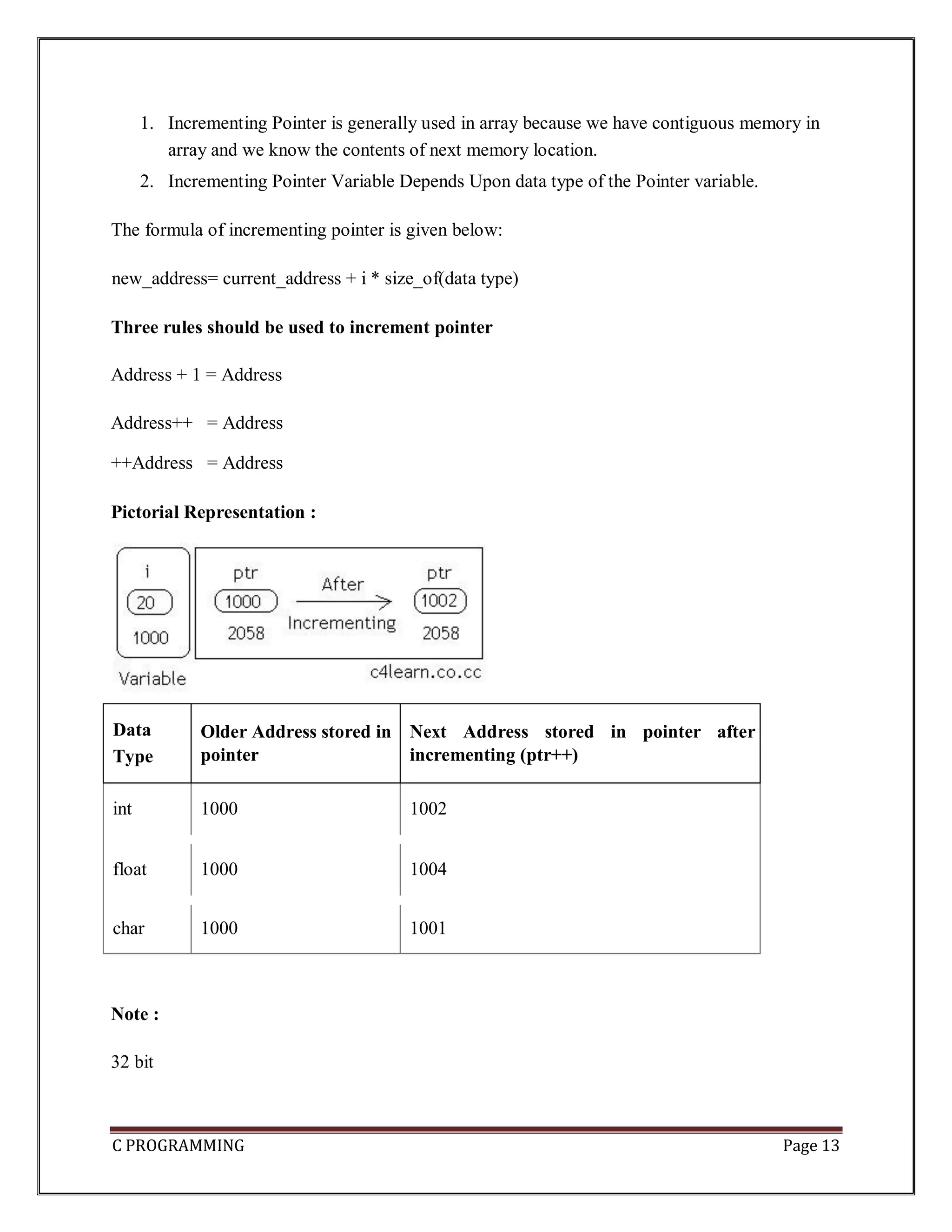
The document provides an introduction to pointers in C programming. Some key points: 1. Pointers store the address of another variable of the same data type. They allow accessing and modifying values using their memory location rather than their name. 2. Pointers are declared with a data type followed by an asterisk, like int *ptr. They must be initialized with the address of a variable using the & operator before being accessed. 3. The dereference operator * accesses the value at the address stored in the pointer. Pointer arithmetic and increment/decrement allow iterating through arrays using pointers. 4. Pointers enable passing by reference in functions and dynamic memory allocation. They are useful for handling arrays





![C PROGRAMMING Page 8 p=&number; //stores the address of number variable p2=&p; printf("Address of number variable is %x n",&number); printf("Address of p variable is %x n",p); printf("Value of *p variable is %d n",*p); printf("Address of p2 variable is %x n",p2); printf("Value of **p2 variable is %d n",**p); } Output Address of number variable is fff4 Address of p variable is fff4 Value of *p variable is 50 Address of p2 variable is fff2 Value of **p variable is 50 Arrays and Pointers: When an array is declared, compiler allocates sufficient amount of memory to contain all the elements of the array. Base address which gives location of the first element is also allocated by the compiler. Suppose we declare an array arr, int arr[5]={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; Assuming that the base address of arr is 1000 and each integer requires two bytes, then five elements will be stored as follows](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-8-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 9 Here variable arr will give the base address, which is a constant pointer pointing to the element, arr[0]. Therefore arr is containing the address of arr[0] i.e 1000. arr is equal to &arr[0] // by default We can declare a pointer of type int to point to the int array arr. int arr[5]={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int *p; p = arr; or p = &arr[0]; //both the statements are equivalent. Now we can access every element of array arr using p++ to move from one element to another. NOTE : You cannot decrement a pointer once incremented. p-- won't work. Pointer to Array we can use a pointer to point to an Array, and then we can use that pointer to access the array. Lets have an example, int i; int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int *p = a; // same as int*p = &a[0] for (i=0; i<5; i++) {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-9-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 10 printf("%d",*p); p++; } In the above program, the pointer *p will print all the values stored in the array one by one. We can also use the Base address (a in above case) to act as pointer and print all the values. Relation between Arrays and Pointers Consider an array: int arr[4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-10-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 11 In C programming, name of the array always points to address of the first element of an array(Base address). In the above example, arr and & arr[0] points to the address of the first element. &arr[0] is equivalent to arr Since, the addresses of both are the same, the values of arr and &arr[0] are also the same. arr[0] is equivalent to *arr (value of an address of the pointer) Similarly, &arr[1] is equivalent to (arr + 1) AND, arr[1] is equivalent to *(arr + 1). &arr[2] is equivalent to (arr + 2) AND, arr[2] is equivalent to *(arr + 2). &arr[3] is equivalent to (arr + 3) AND, arr[3] is equivalent to *(arr + 3). . . &arr[i] is equivalent to (arr + i) AND, arr[i] is equivalent to *(arr + i). Example: Program to find the sum of six numbers with arrays and pointers #include <stdio.h> int main() { int i, classes[6],sum = 0; printf("Enter 6 numbers:n"); for(i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-11-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 12 // (classes + i) is equivalent to &classes[i] scanf("%d",(classes + i)); // *(classes + i) is equivalent to classes[i] sum += *(classes + i); } printf("Sum = %d", sum); } Output Enter 6 numbers: 2 3 4 5 3 4 Sum = 21 Pointer Arithmetic and Arrays Pointer holds address of a value, so there can be arithmetic operations on the pointer variable. There are four arithmetic operators that can be used on pointers: oIncrement(++) o Decrement(--) oAddition(+) oSubtraction(-) Increment pointer:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-12-2048.jpg)




![C PROGRAMMING Page 18 printf("After subtracting 3: Address of p variable is %u n",p); } Output Address of p variable is 3214864300 After subtracting 3: Address of p variable is 3214864288 Passing an Array to a Function If you want to pass a single-dimension array as an argument in a function, you would have to declare a formal parameter in one of following three ways and all three declaration methods produce similar results because each tells the compiler that an integer pointer is going to be received. Similarly, you can pass multi-dimensional arrays as formal parameters. 1) Formal parameters as a pointer – void myFunction(int *param) { . . . } 2) Formal parameters as a sized array – void myFunction(int param[10]) { . . . } 3) Formal parameters as an unsized array void myFunction(int param[]) { .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-18-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 19 . . } Example1: pass an entire array to a function argument #include <stdio.h> /* function declaration */ double getAverage(int arr[], int size); int main () { /* an int array with 5 elements */ int balance[5] = {1000, 2, 3, 17, 50}; double avg; /* pass pointer to the array as an argument */ avg = getAverage( balance, 5 ) ; /* output the returned value */ printf( "Average value is: %f ", avg ); } double getAverage(int arr[], int size) { int i; double avg; double sum = 0; for (i = 0; i < size; ++i) { sum += arr[i]; } avg = sum / size; return avg; } Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-19-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 20 Average value is: 214.400000 Example2: pass an entire array to a function argument #include <stdio.h> myfuncn( int *var1, int var2) { for(int x=0; x<var2; x++) { printf("Value of var_arr[%d] is: %d n", x, *var1); /*increment pointer for next element fetch*/ var1++; } } int main() { int var_arr[] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77}; myfuncn(&var_arr, 7); return 0; } Output Value of var_arr[0] is: 11 Value of var_arr[1] is: 22 Value of var_arr[2] is: 33 Value of var_arr[3] is: 44 Value of var_arr[4] is: 55 Value of var_arr[5] is: 66 Value of var_arr[6] is: 77 Example: Call by value method #include <stdio.h> disp( char ch) { printf("%c ", ch); } main() {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-20-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 21 char arr[] = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'I', 'j'}; for (int x=0; x<=10; x++) { /* I‟m passing each element one by one using subscript*/ disp (arr[x]); } } Output: a b c d e f g h i j In this method of calling a function, the actual arguments gets copied into formal arguments. In this example actual argument(or parameter) is arr[x] and formal parameter is ch. Example: Call by reference method: Using pointers #include <stdio.h> disp( int *num) { printf("%d ", *num); } int main() { int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}; for (int i=0; i<=10; i++) { /* I‟m passing element‟s address*/ disp (&arr[i]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-21-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 22 } } Output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Array of Pointers An array of pointers would be an array that holds memory locations. An array of pointers is an indexed set of variables in which the variables are pointers (a reference to a location in memory). Syntax: data_type * variable_name Example int *ptr[10]; Array alpha[] Pointer a alpha[0] *a alpha[1] *(a+1) alpha[2] *(a+2) alpha[3] *(a+3) alpha[n] *(a+n) Example1: #include <stdio.h>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-22-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 23 const int MAX = 3; int main () { int var[] = {10, 100, 200}; int i, *ptr[MAX]; for ( i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { ptr[i] = &var[i]; /* assign the address of integer. */ } for ( i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { printf("Value of var[%d] = %dn", i, *ptr[i] ); } } Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-23-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 24 Value of var[0] = 10 Value of var[1] = 100 Value of var[2] = 200 Example2: #include <stdio.h> main() { int *array[3]; int x = 10, y = 20: int z = 30,i; array[0] = &x; array[1] = &y; array[2] = &z; for (i=0; i< 3; i++) { printf("The value of %d= %d ,address is %ut n", i, *(array[i]), array[i]); } } Output Example3: #include <stdio.h> const int MAX =4; int main ()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-24-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 25 { char *names[] = { "Zara Ali", "Hina Ali", "Nuha Ali", "Sara Ali" }; int i = 0; for ( i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { printf("Value of names[%d] = %sn", i, names[i] ); } } Output: Value of names[0] = Zara Ali Value of names[1] = Hina Ali Value of names[2] = Nuha Ali Value of names[3] = Sara Ali Example4: #include <stdio.h> int main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-25-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 26 { char *fruit[] = { "watermelon", "banana", "pear", "apple", "coconut", "grape", "blueberry" }; int x; for(x=0;x<7;x++) puts(fruit[x]); } Pointers to Void and Pointers to Functions Pointers to Void A pointer variable declared using a particular data type cannot hold the location address of variables of other data types. It is invalid and will result in a compilation error. Ex:- char *ptr; int var1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-26-2048.jpg)












![C PROGRAMMING Page 40 It is possible to pass some values from the command line to your C programs when they are executed. These values are called command line arguments and many times they are important for your program especially when you want to control your program from outside instead of hard coding those values inside the code. The arguments passed from command line are called command line arguments. These arguments are handled by main() function. To support command line argument, you need to change the structure of main() function Syntax: int main(int argc, char *argv[] ) Here, argc counts the number of arguments. It counts the file name as the first argument. The argv[] contains the total number of arguments. The first argument is the file name always. Example1 #include <stdio.h> int main( int argc, char *argv[] ) { if( argc == 2 ) { printf("The argument supplied is %sn", argv[1]); } else if( argc > 2 ) { printf("Too many arguments supplied.n"); } else { printf("One argument expected.n"); } } Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-40-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 41 Example2 #include <stdio.h> void main(int argc, char *argv[] ) { printf("Program name is: %sn", argv[0]); if(argc <2) { printf("No argument passed through command line.n"); } else { printf("First argument is: %sn", argv[1]); } } Output program.exe hello Program name is: program First argument is: hello Note But if you pass many arguments within double quote, all arguments will be treated as a single argument only. Example ./program "hello c how r u" Program name is: program First argument is: hello c how r u You can write your program to print all the arguments. In this program, we are printing only argv[1], that is why it is printing only one argument. Example3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-41-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 42 #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int i; clrscr(); printf("Total number of arguments: %d",argc); for(i=0;i< argc;i++) { printf("n %d argument: %s",i,argv[i]); getch(); } } Output C:/TC/BIN>TCC mycmd.c C:/TC/BIN>mycmd 10 20 Number of Arguments: 3 0 arguments c:/tc/bin/mycmd.exe 1 arguments: 10 2 arguments: 20 Note: In above output we passed two arguments but is show "Number of Arguments: 3" because argc take Number of arguments in the command line including program name. So here two arguments and one program name (mycmd.exe) total 3 arguments.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-42-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 43 Example4: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main(int argc, char* argv[]) { clrscr(); printf("n Program name : %s n", argv[0]); printf("1st arg : %s n", argv[1]); printf("2nd arg : %s n", argv[2]); printf("3rd arg : %s n", argv[3]); printf("4th arg : %s n", argv[4]); printf("5th arg : %s n", argv[5]); getch(); } Output C:/TC/BIN>TCC mycmd.c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-43-2048.jpg)
![C PROGRAMMING Page 44 C:/TC/BIN>mycmd this is a program Program name : c:/tc/bin/mycmd.c 1st arg : this 2nd arg : is 3rd arg : a 4th arg : program 5th arg : (null) Explanation: In the above example. argc = 5 argv[0] = "mycmd" argv[1] = "this" argv[2] = "is" argv[3] = "a" argv[4] = "program" argv[5] = NULL Why command line arguments program not directly run form TC IDE Command line arguments related programs are not execute directly from TC IDE because arguments cannot be passed. Edit Command Line Argument Program To Edit the Command Line Argument Program use edit Command. Syntax C:/cprogram>edit mycmd.c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/easyunderstandingofpointersinclanguage-230413093011-166a389f/75/EASY-UNDERSTANDING-OF-POINTERS-IN-C-LANGUAGE-pdf-44-2048.jpg)