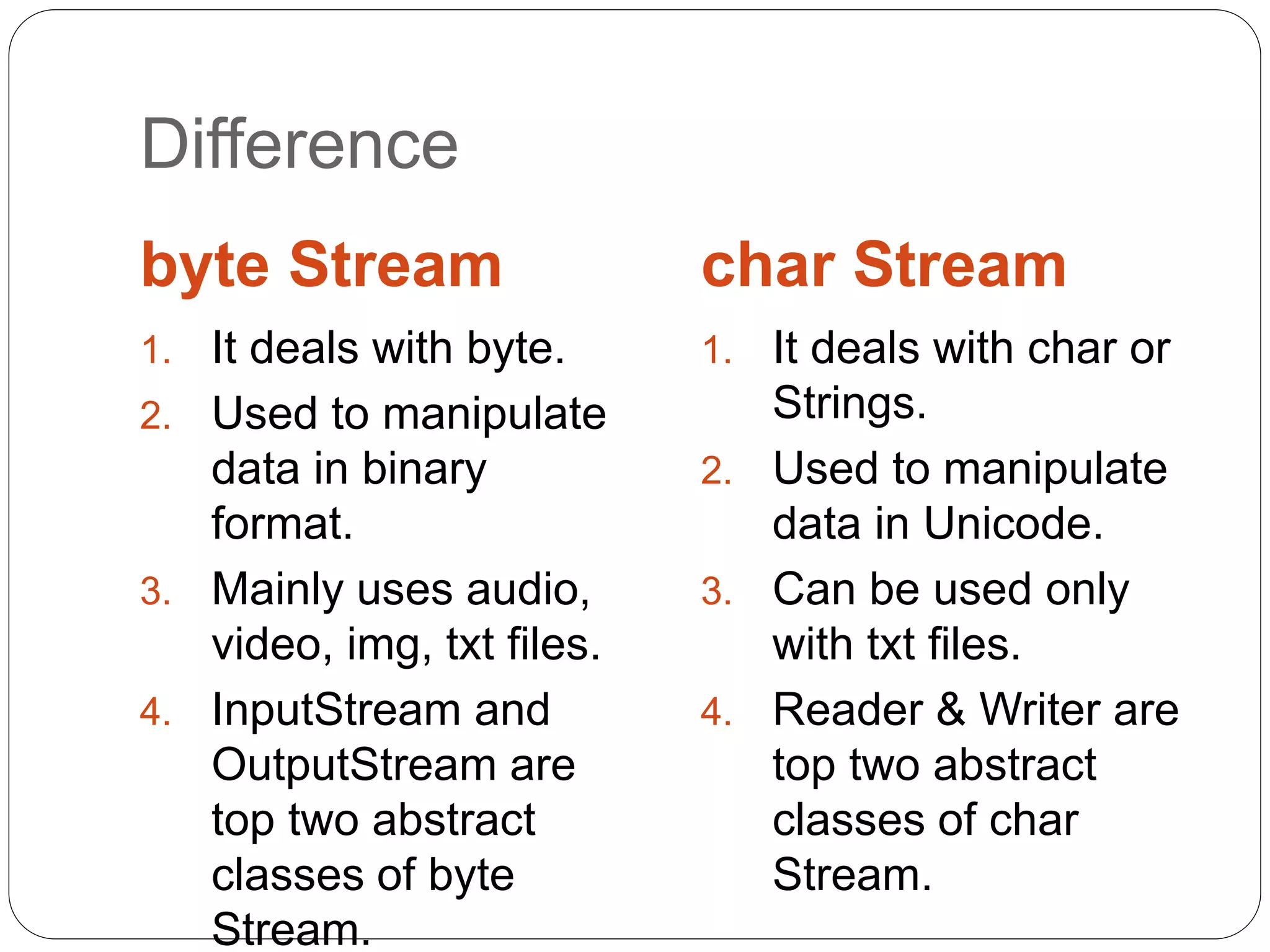
This document discusses input/output streams and files in Java. It describes input streams, which read data from sources like keyboards or files, and output streams, which write data to destinations like monitors or files. It then focuses on reading and writing files using FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, FileReader and FileWriter classes. Constructors and methods of each class are listed, with examples provided of reading and writing files byte-by-byte and character-by-character. The key difference between byte and character streams is also summarized.




![Constructors, Methods Of FileOutputStream CONSTRUCTORS: FileOutputStream(String fname); FileOutputStream(File F); FileOutputStream(String fname, boolean app); METHODS: void write(int n); //write(n); //n is the byte to be written void write(byte []b); // writes the array contents to file.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-7-2048.jpg)
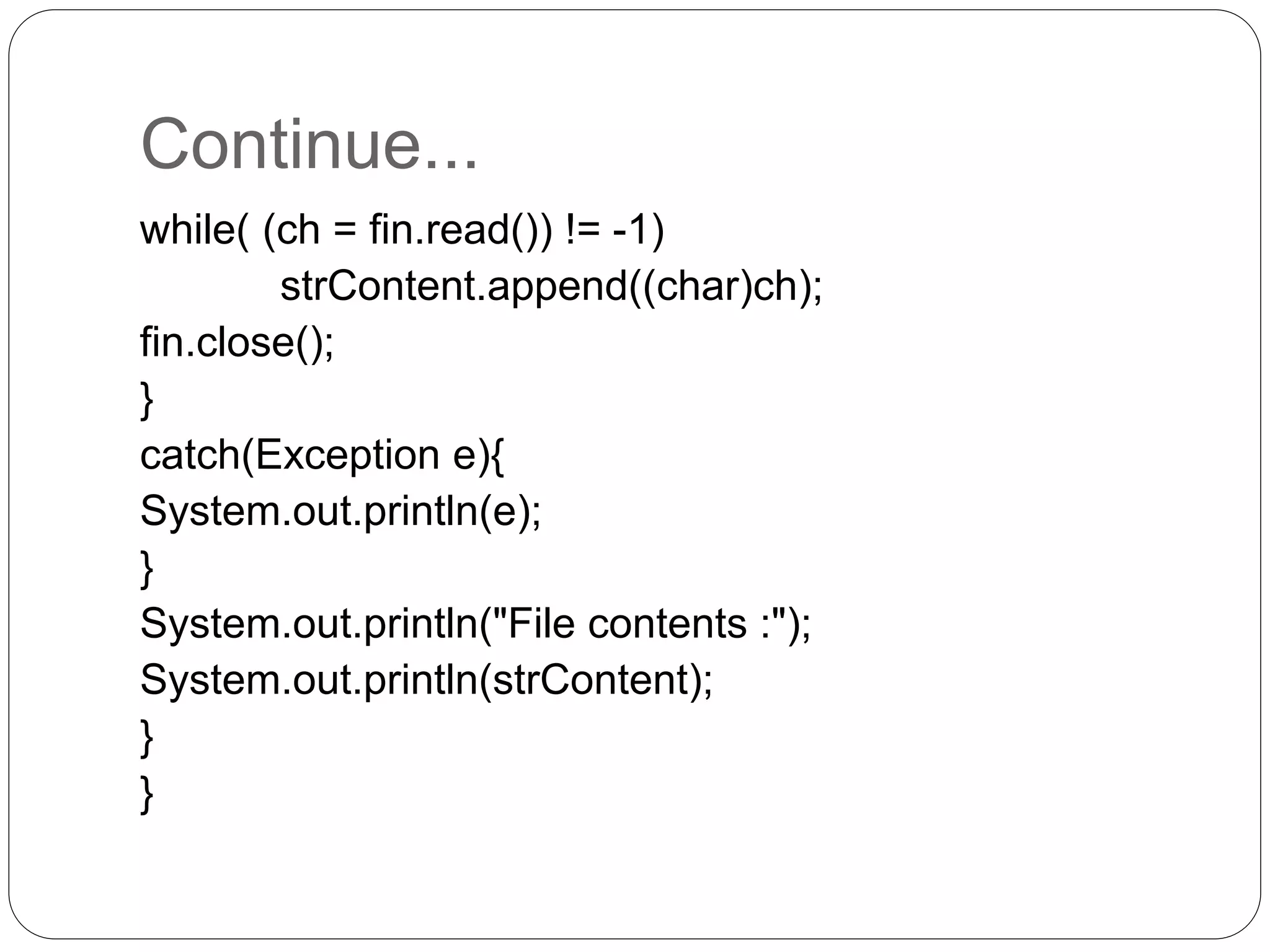
![Example: FileInputStream import java.io.*; public class ReadStringFromFile { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("C://FileIO//ReadString.txt"); int ch; StringBuffer strContent = new StringBuffer(""); FileInputStream fin = null; try { fin = new FileInputStream(file);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-8-2048.jpg)
![Example: FileOutputStream import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class FileOutputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { byte[] b = {65,66,67,68,69}; int i=0; char c; try{ FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("C://test.txt"); fos.write(b);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-10-2048.jpg)

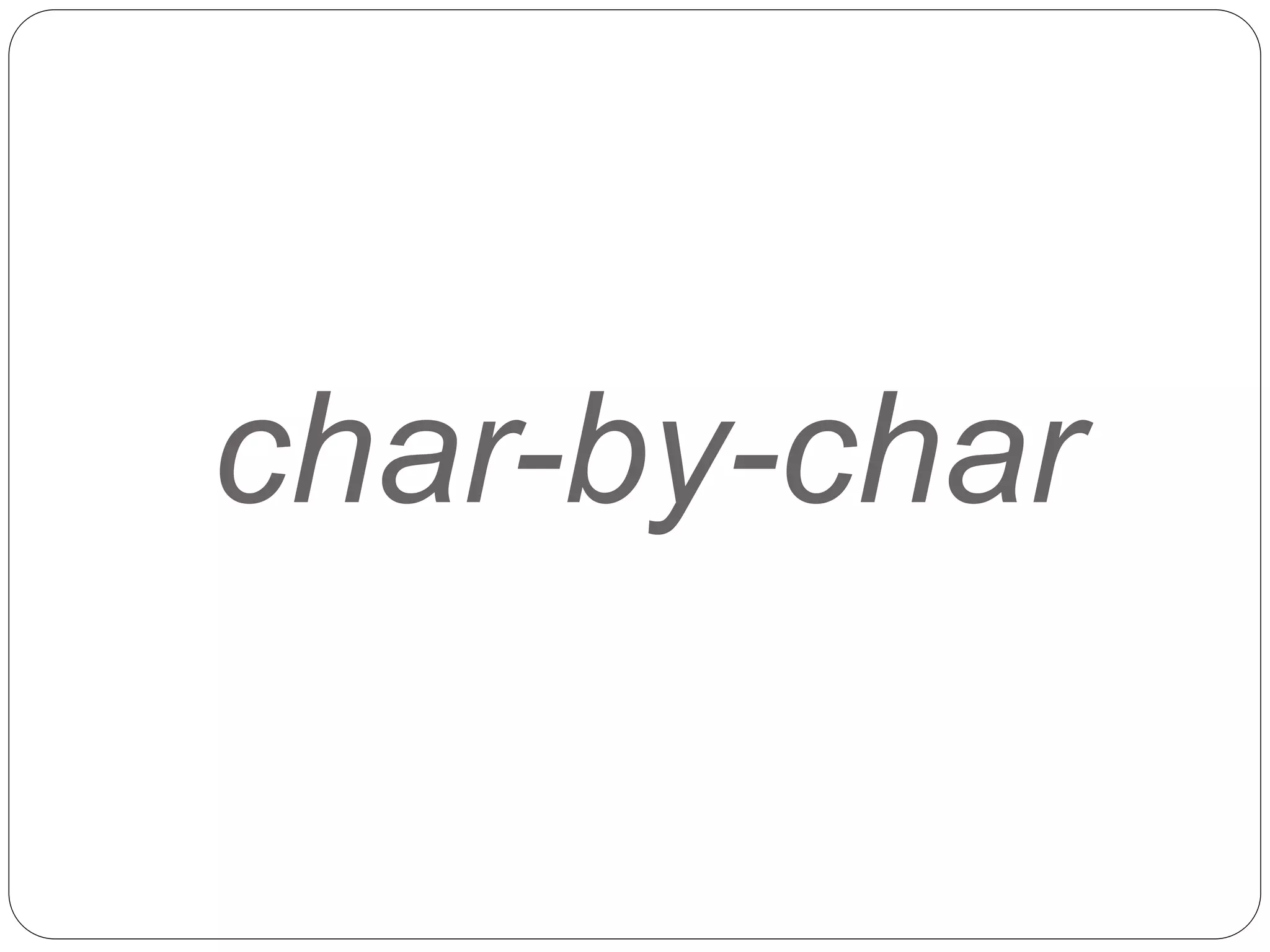
![Constructors, Methods Of FileReader CONSTRUCTORS: FileReader(String fname); FileReader(File F); FileReader(String fold, String fname); METHODS: int read(); // n= fis.read(); // n is the char read. int read(char [] c, int offset, int len); // reads character into an array and returns the number of chars read.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-13-2048.jpg)
![Constructors, Methods Of FileWriter CONSTRUCTORS: FileWriter(String fname); FileWriter(File F); FileWriter(String fold, String fname); METHODS: void write(String n); // write(n); //n is the String to be written to file. public void write(char [] c, int offset, int len); // Writes a portion of an array of characters starting from offset and with a length of len. public void write(String s, int offset, int len);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-14-2048.jpg)
![Example: FileReader import java.io.*; public class FileRead { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { File file = new File("Hello1.txt"); file.createNewFile(); //returns true if file is created FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file); fw.write("Thisn isn ann examplen"); fw.flush(); fw.close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-15-2048.jpg)
![Continue... FileReader fr = new FileReader(file); char [] a = new char[50]; fr.read(a); //reads content to array for(char c : a) System.out.print(c); fr.close(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-16-2048.jpg)
![Example: FileReader using BufferedReader import java.io.*; public class Reader { public static void main(String[]args) throws IOException{ FileReader fr = new FileReader("C:/test.txt"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in); while (br.readLine() != null) { System.out.println(br.readLine()); } fr.close(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-17-2048.jpg)
![Example: FileWriter • import java.io.*; class Simple{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("abc.txt"); fw.write(“Hello World"); fw.close(); } catch(Exception e) {System.out.println(e);} System.out.println(“Success"); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-18-2048.jpg)
![ import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class BufferedWriterDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File f = new File("java2learn.txt"); System.out.println(f.exists()); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f)); char[] ch1 = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd' }; bw.write(ch1); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandstreams-170901152228/75/Files-and-streams-In-Java-19-2048.jpg)
