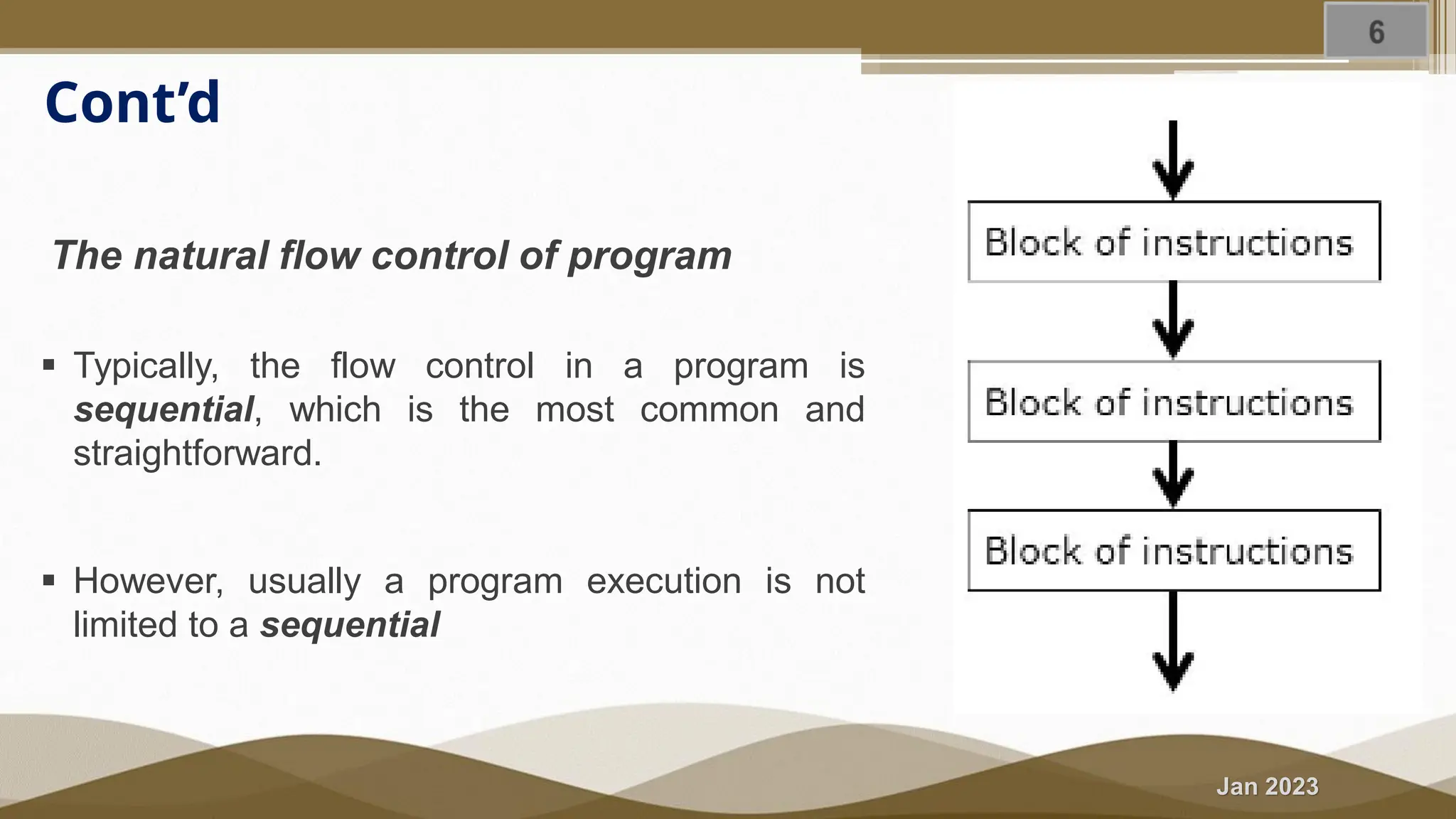
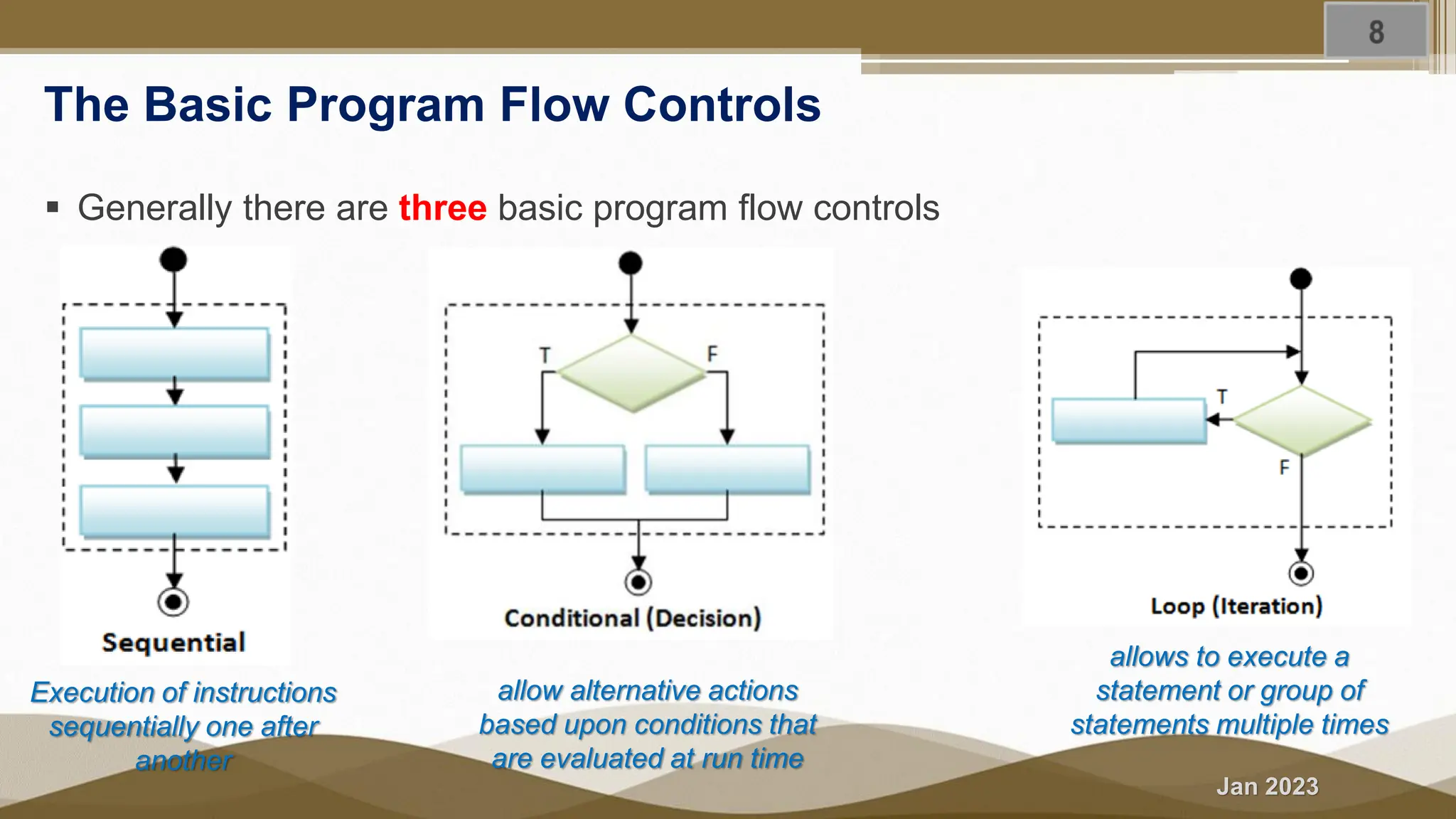
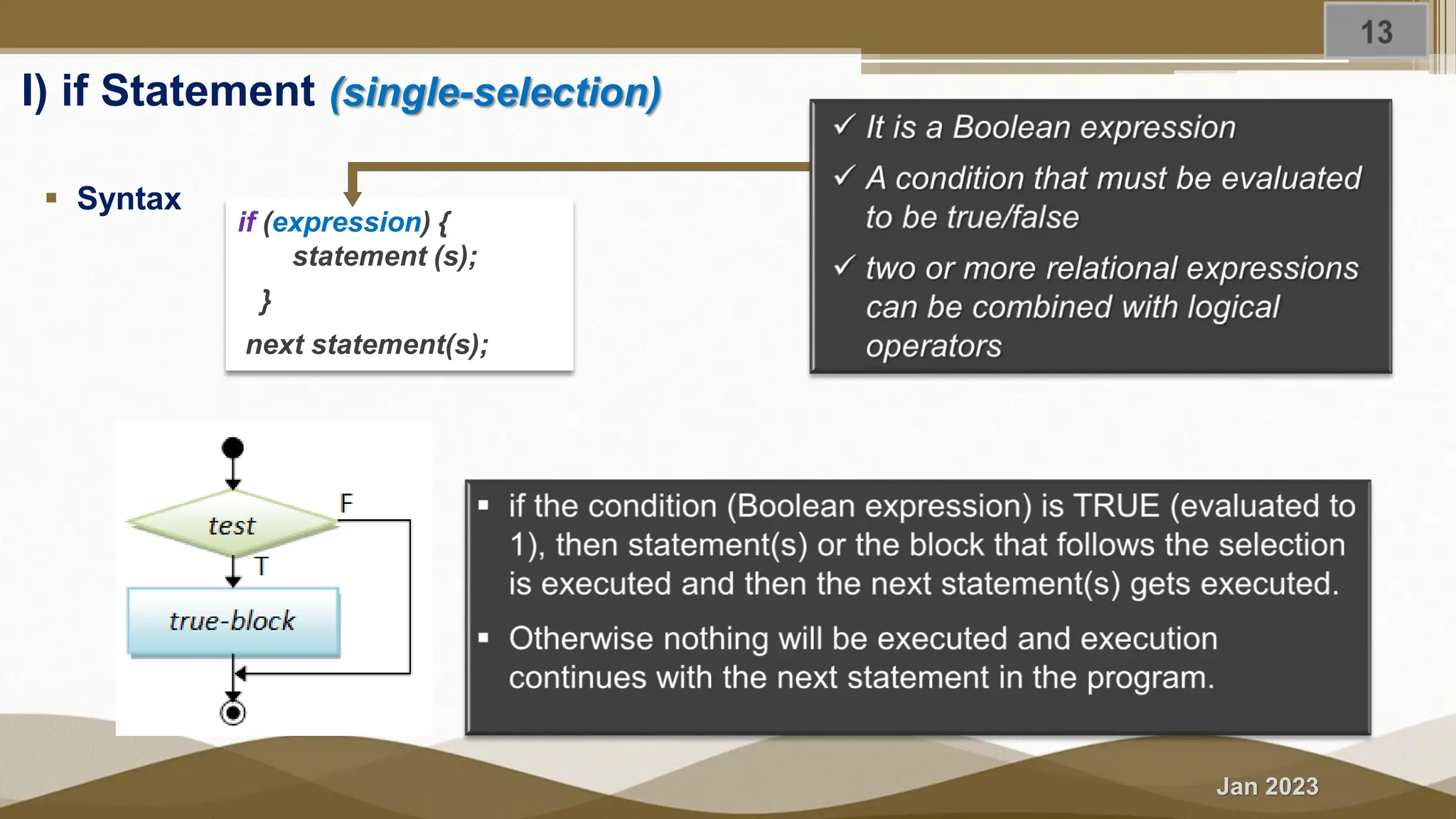
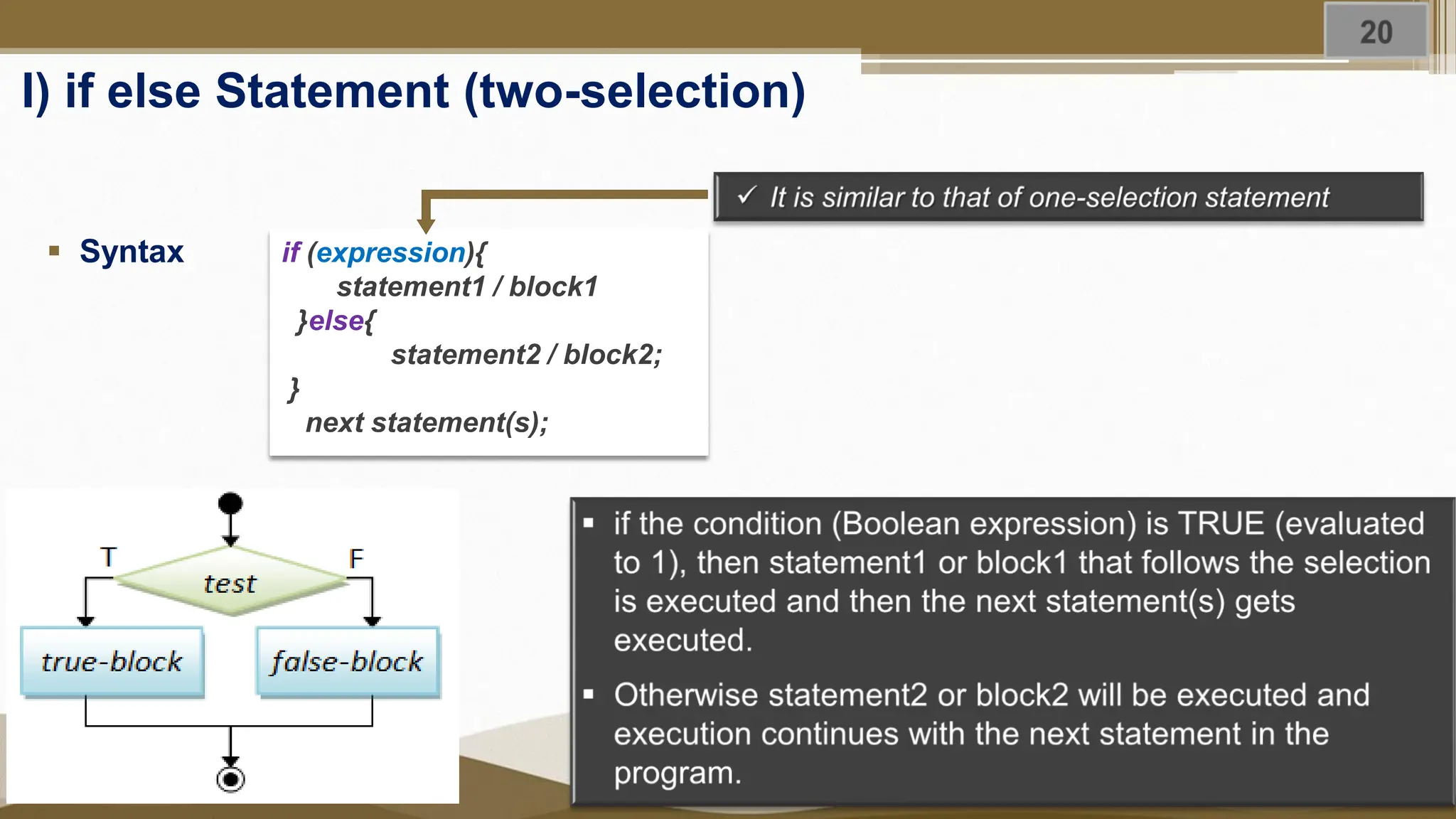
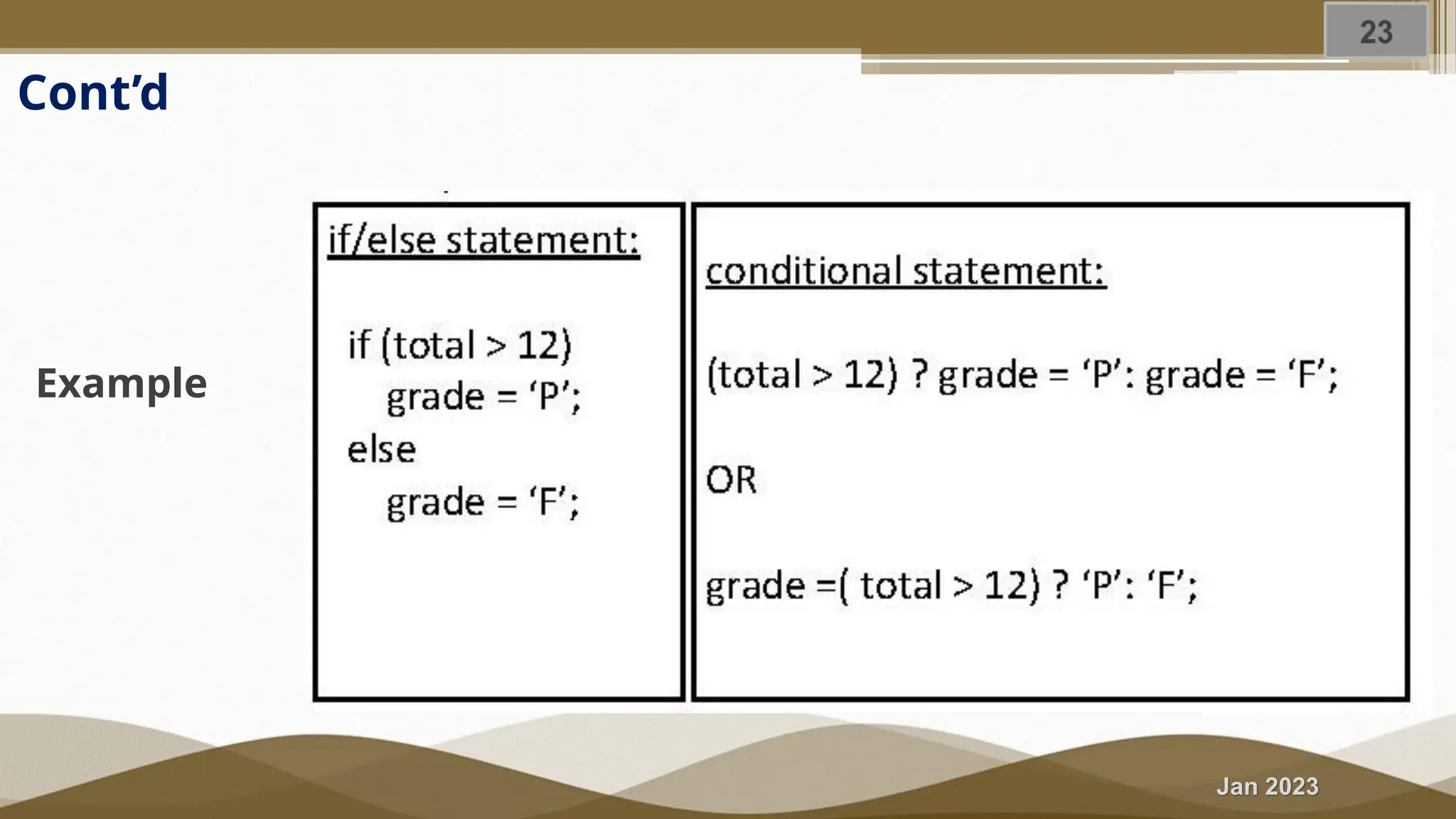
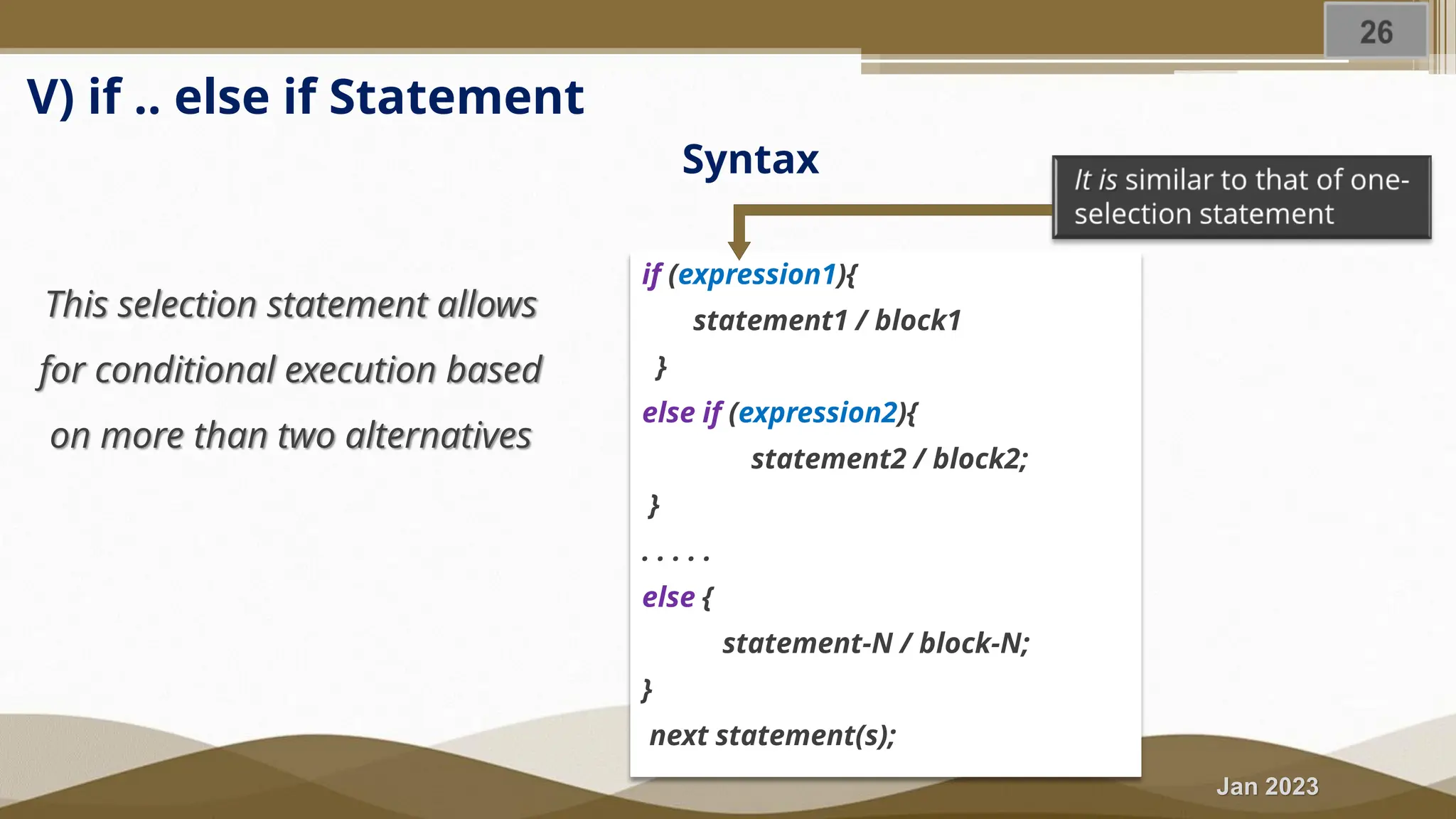
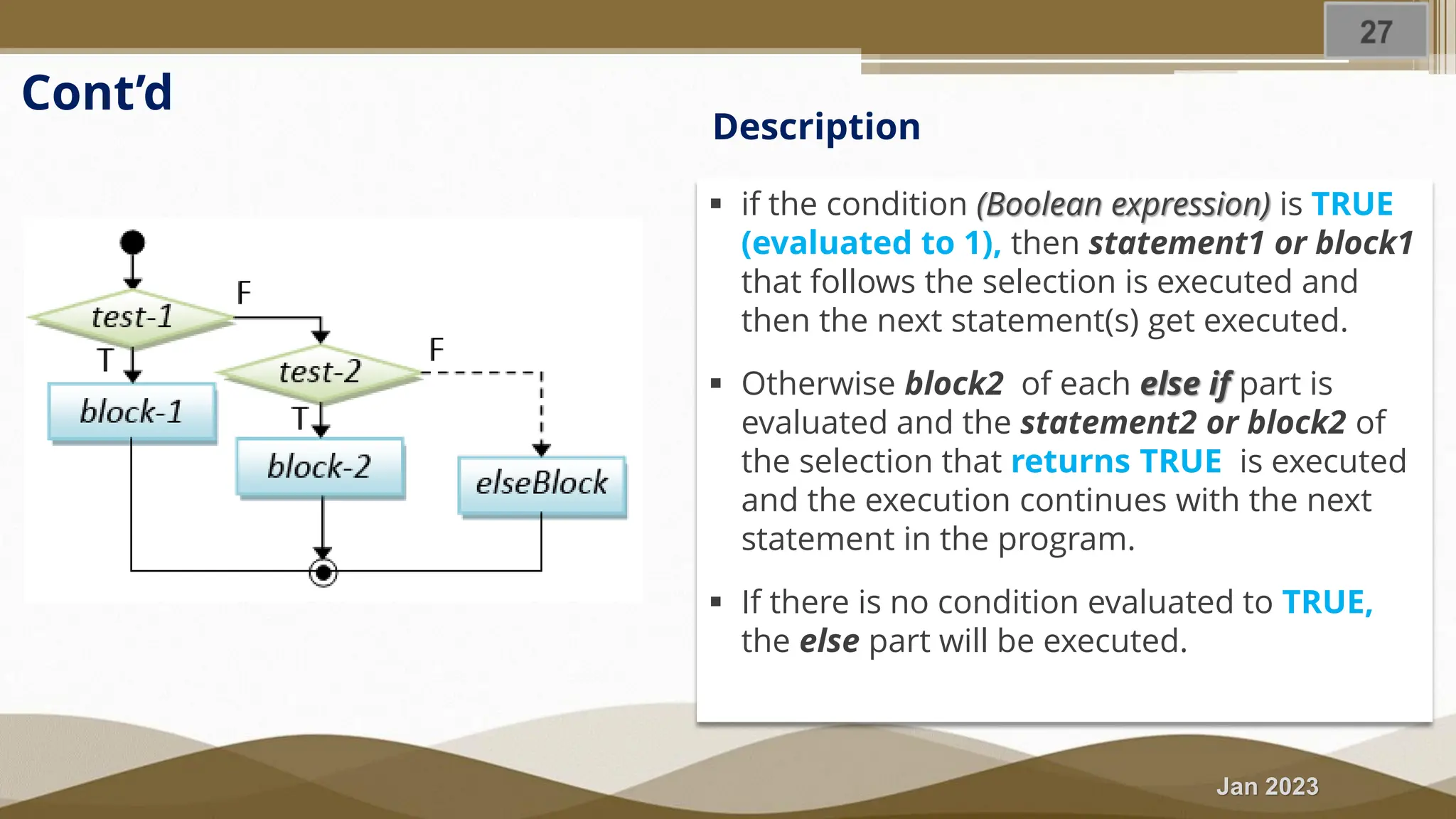
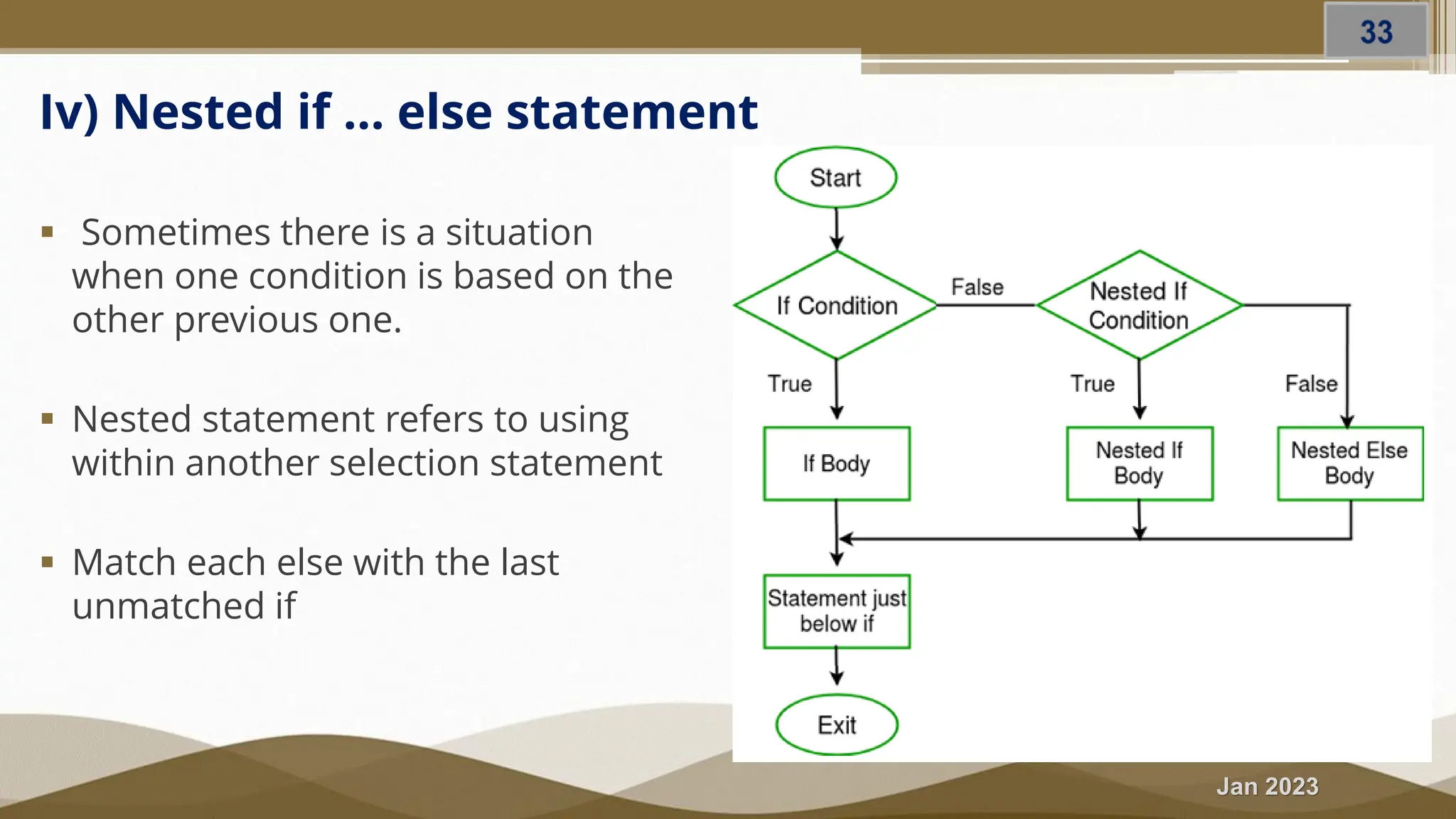
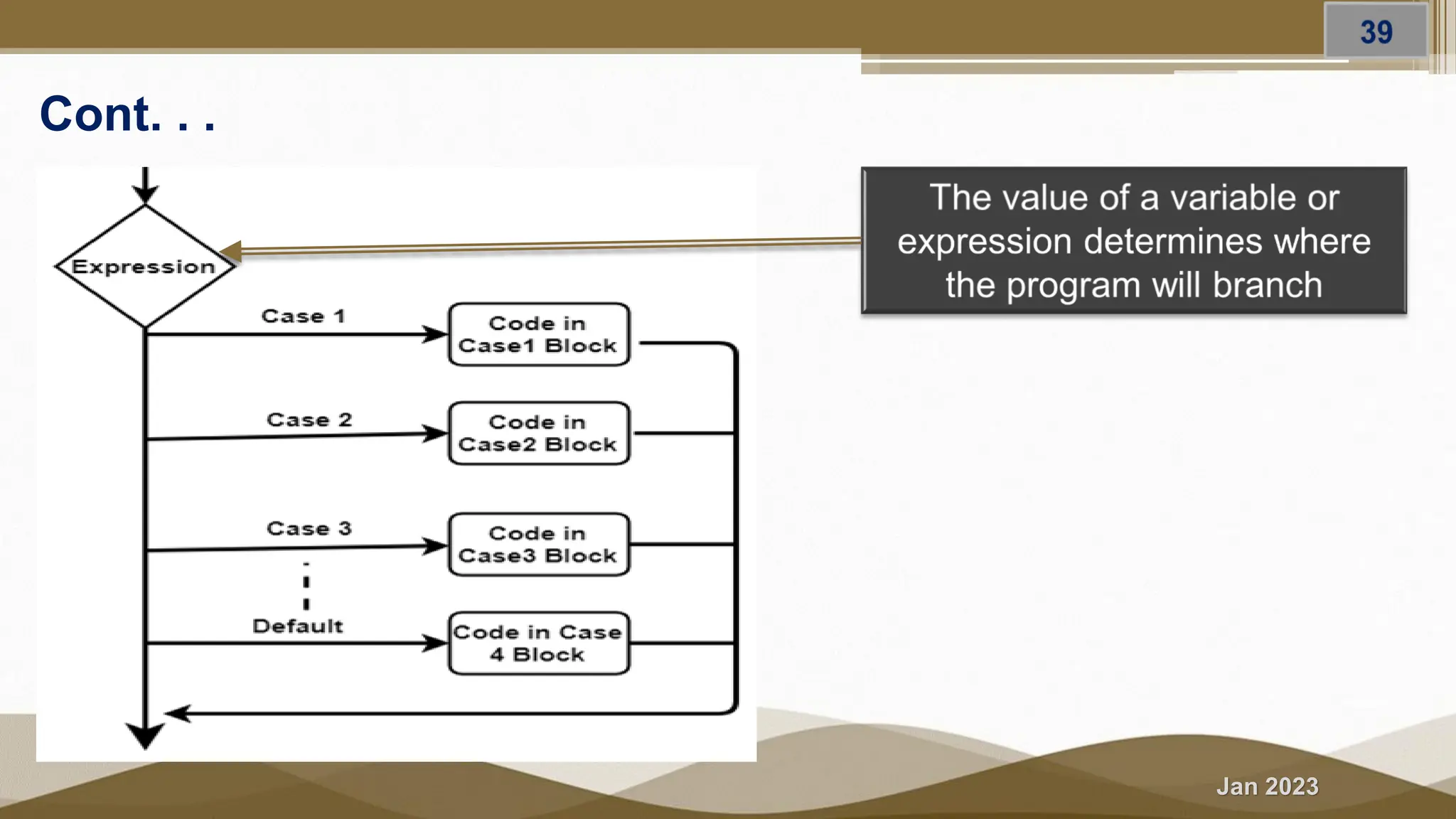
The document discusses selection statements in C++ programming. It covers one-way selection using if statements, two-way selection using if-else statements, and multiple selections using else-if statements and switch statements. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating employee salary and determining whether a number is even, odd, positive or negative. Exercises are included to write programs to find the largest of three numbers, assign grades based on marks, and calculate BMI. Nested if-else statements and when to use different selection statements are also explained.
































![Jan 2023 Exercise 4.5 Problem description Write a basic calculator program that reads an operator and numbers from the user and prints the result. [Hint: switch-case statement) Purpose: ✓ To demonstrate the use case of the switch-case statements Outcome: ✓ You able to write a menu-based program using switch-case statements Solution [LET’S DO TOGETHER] ➢ Perform an Analysis of the problem ➢ Design the program on paper ➢ Write the program.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch-4a-flowofcontrolselectionstatements-240320043425-3169a7db/75/Fundamentals-of-Computer-Programming-Flow-of-Control-I-42-2048.jpg)






![Jan 2023 Reading Resources/Materials eBooks ▪ Chapter 5 & 6: Diane Zak; An Introduction to Programming with C++ [8th Edition], 2016 Cengage Learning ▪ Chapter 4: Gary J. Bronson; C++ For Engineers and Scientists [3rd edition], Course Technology, Cengage Learning, 2010 ▪ Chapter 2 (section 2.4): Walter Savitch; Problem Solving With C++ [10th edition], University of California, San Diego, 2018 ▪ Chapter 4: P. Deitel , H. Deitel; C++ how to program, [10th, Global Edition] (2017)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch-4a-flowofcontrolselectionstatements-240320043425-3169a7db/75/Fundamentals-of-Computer-Programming-Flow-of-Control-I-49-2048.jpg)
![Jan 2023 Reading Resources/Materials eBooks – looping statements ▪ Chapter 7 & 8: Diane Zak; An Introduction to Programming with C++ [8th Edition], 2016 Cengage Learning ▪ Chapter 5: Gary J. Bronson; C++ For Engineers and Scientists [3rd edition], Course Technology, Cengage Learning, 2010 ▪ Chapter 2 (section 2.4): Walter Savitch; Problem Solving With C++ [10th edition], University of California, San Diego, 2018 ▪ Chapter 4 & 5: P. Deitel , H. Deitel; C++ how to program, [10th, Global Ed.] (2017)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch-4a-flowofcontrolselectionstatements-240320043425-3169a7db/75/Fundamentals-of-Computer-Programming-Flow-of-Control-I-50-2048.jpg)

