Embed presentation

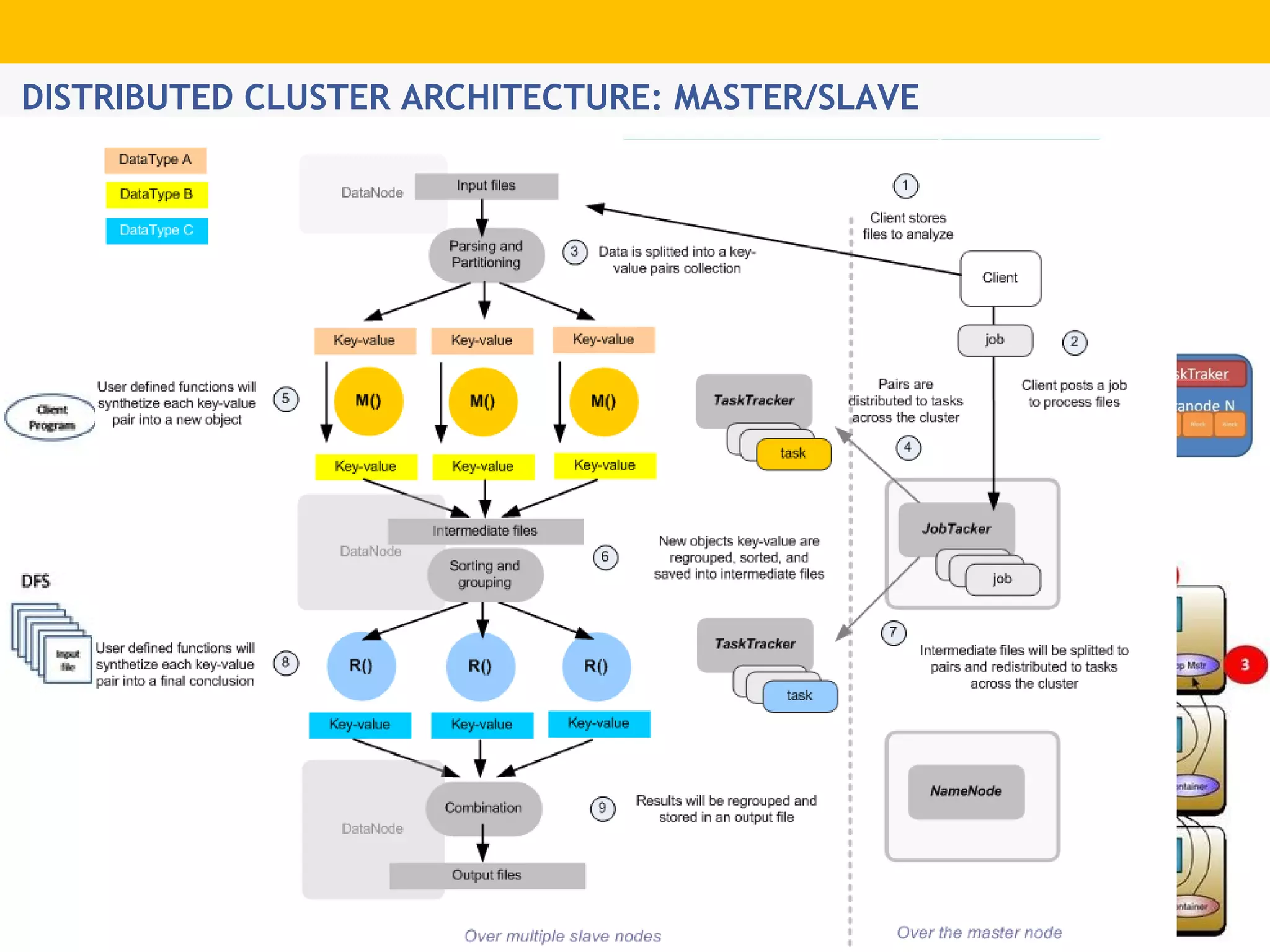
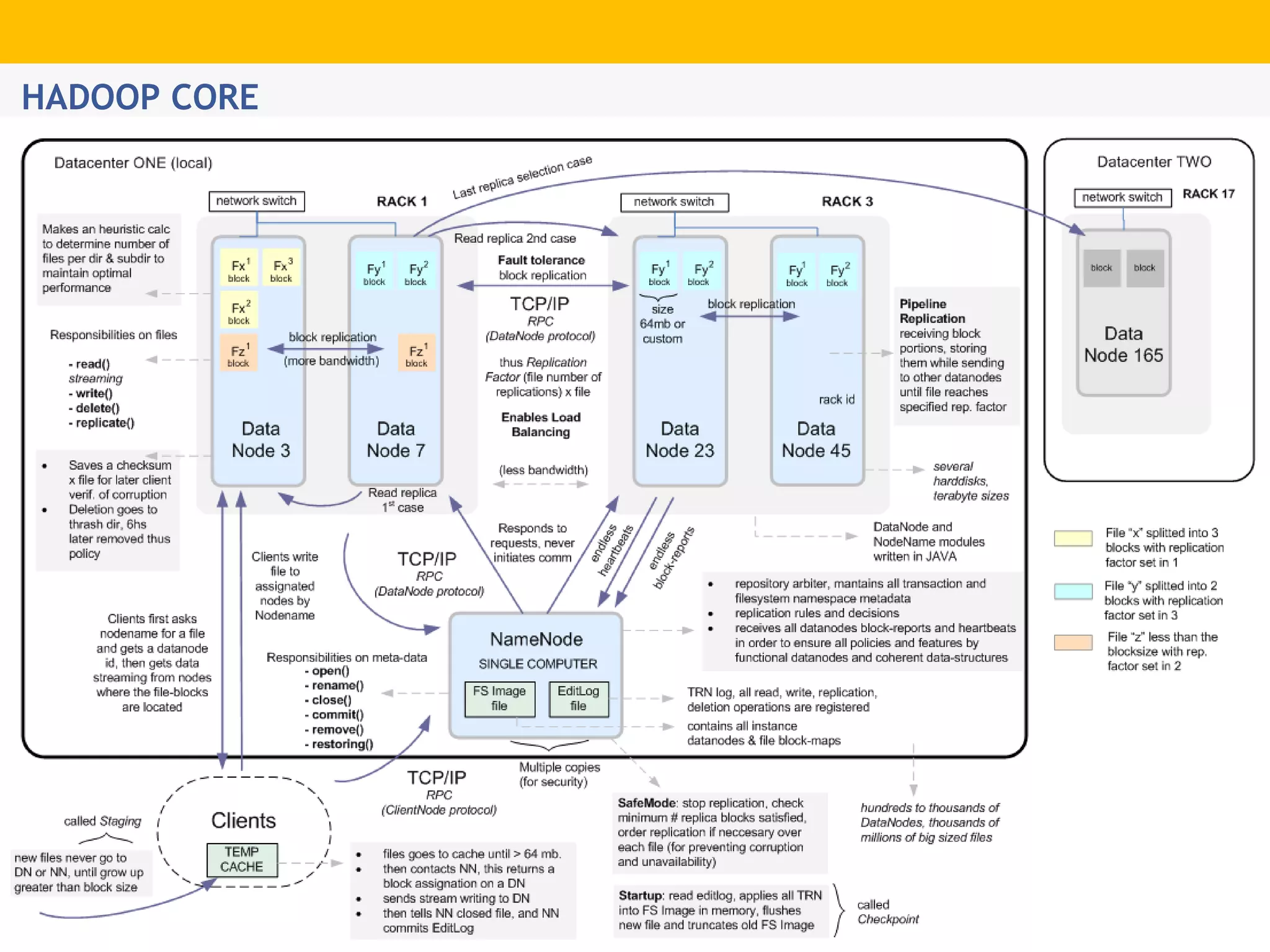
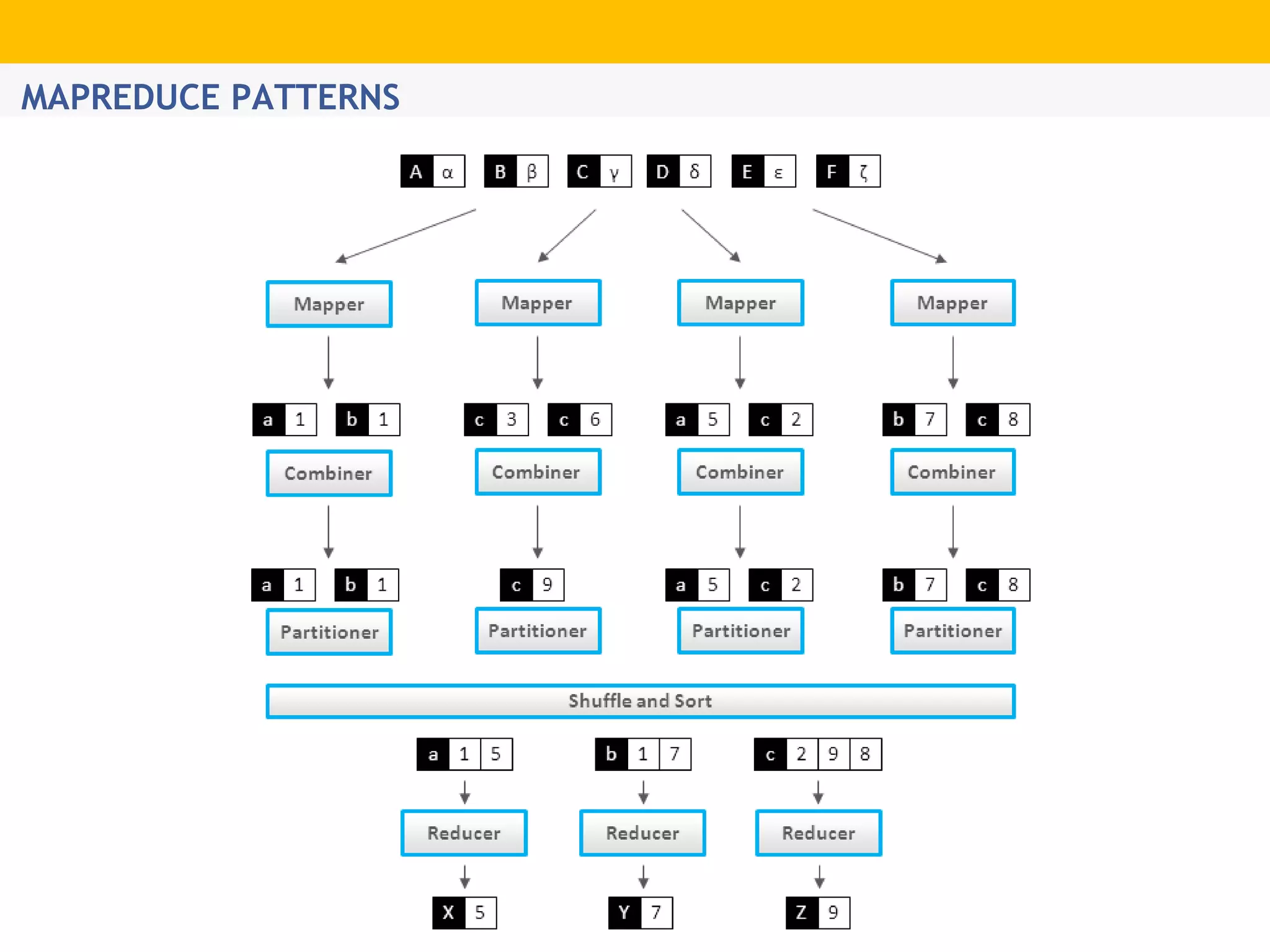
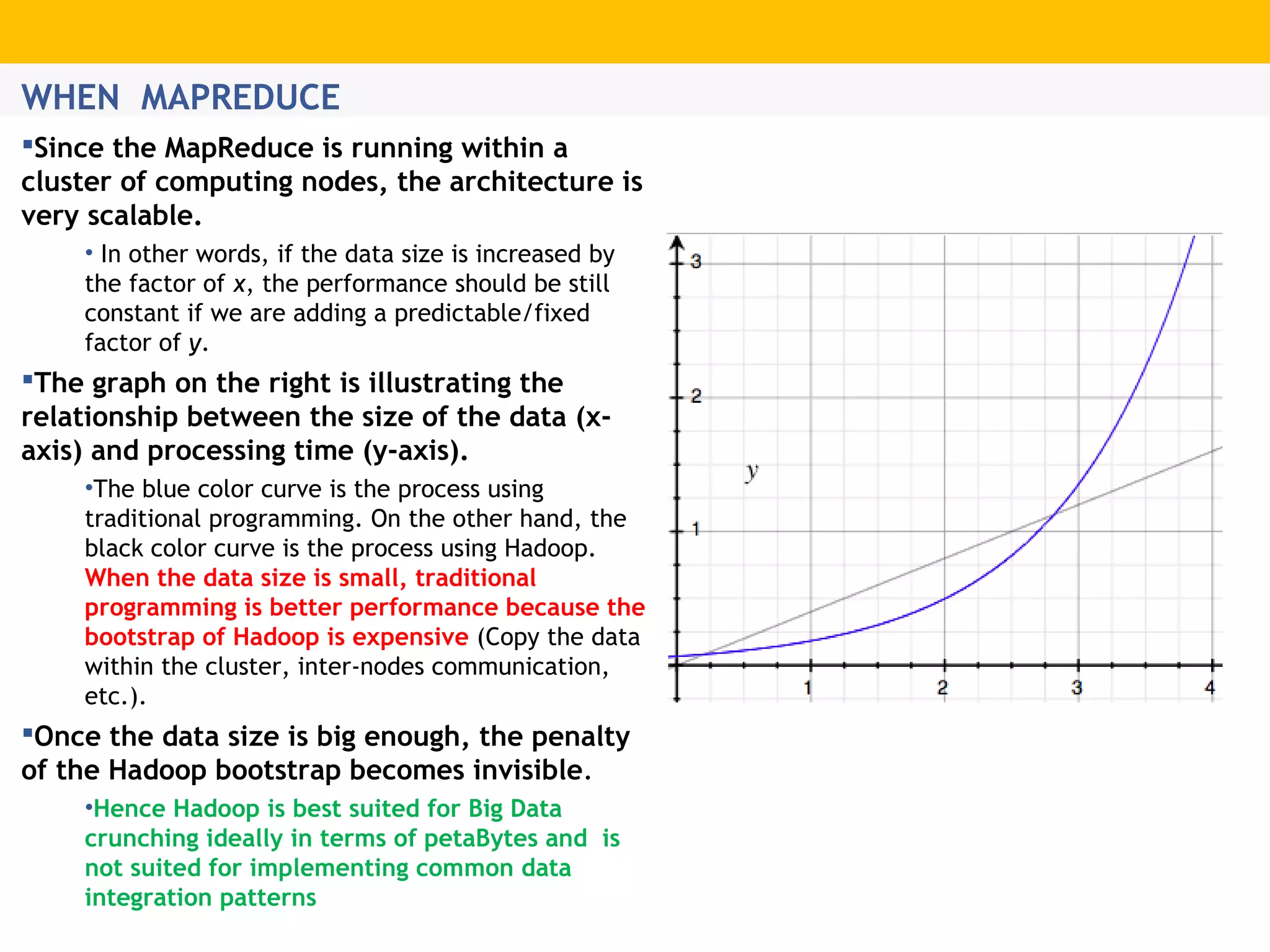
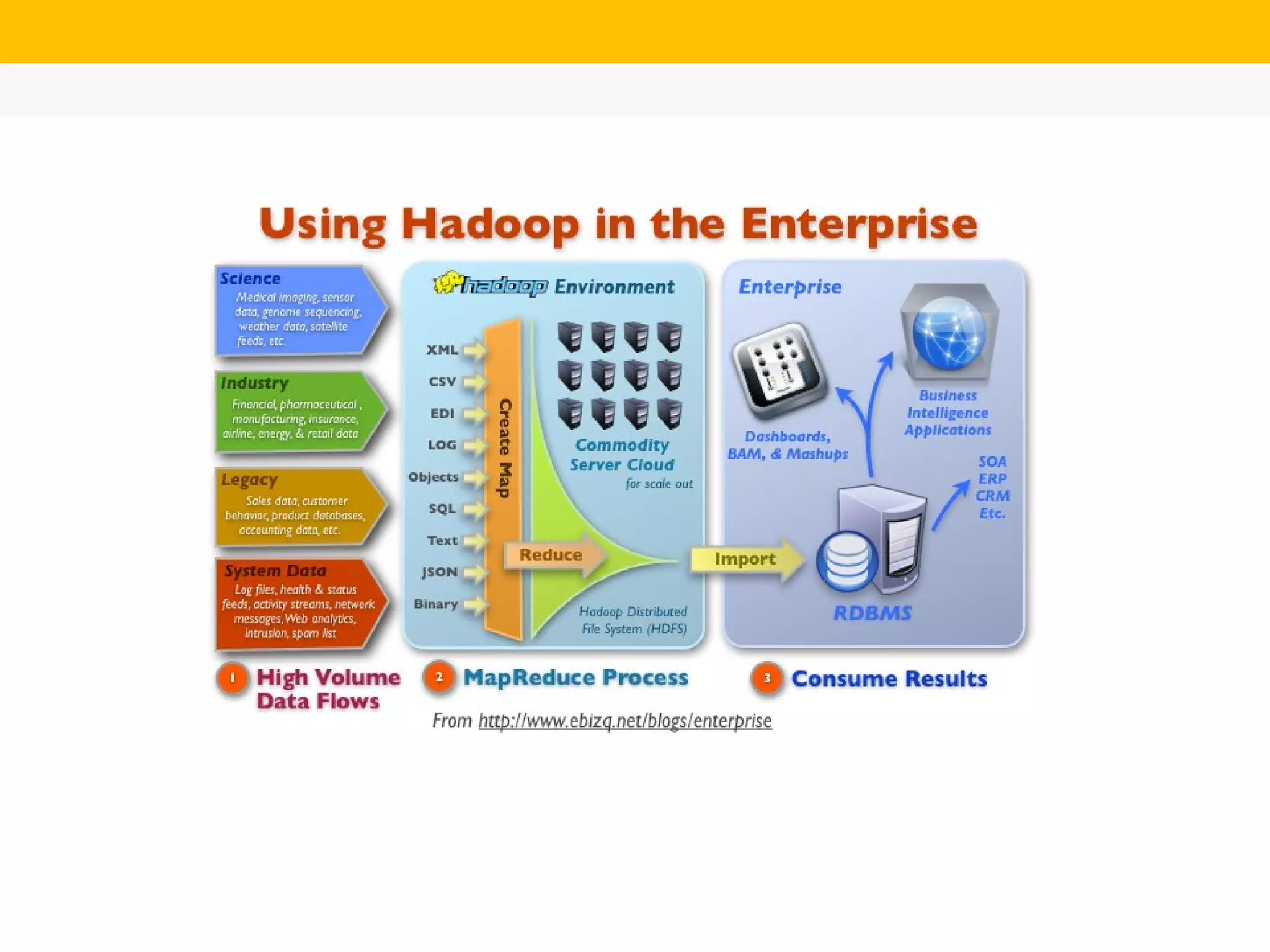
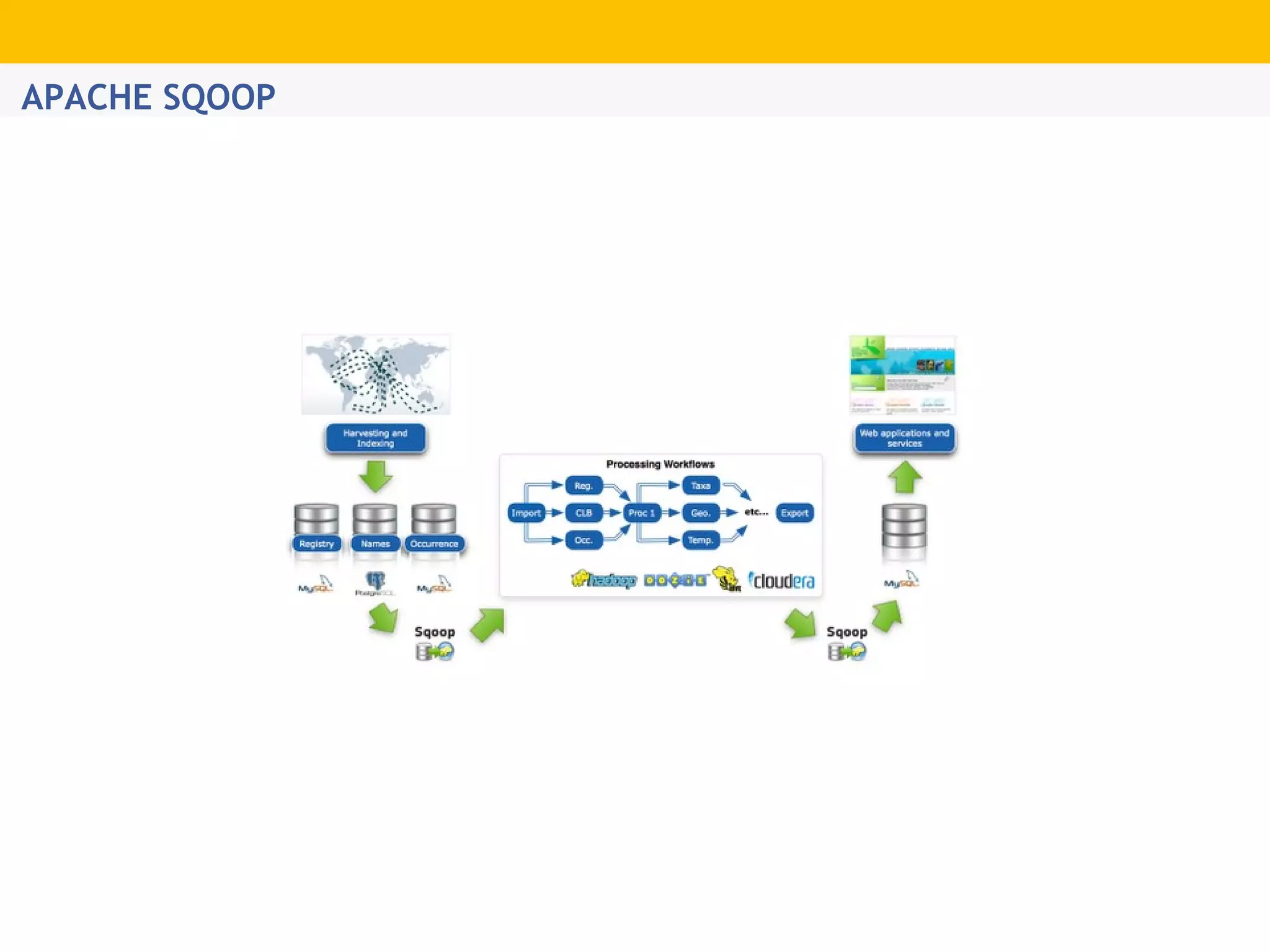
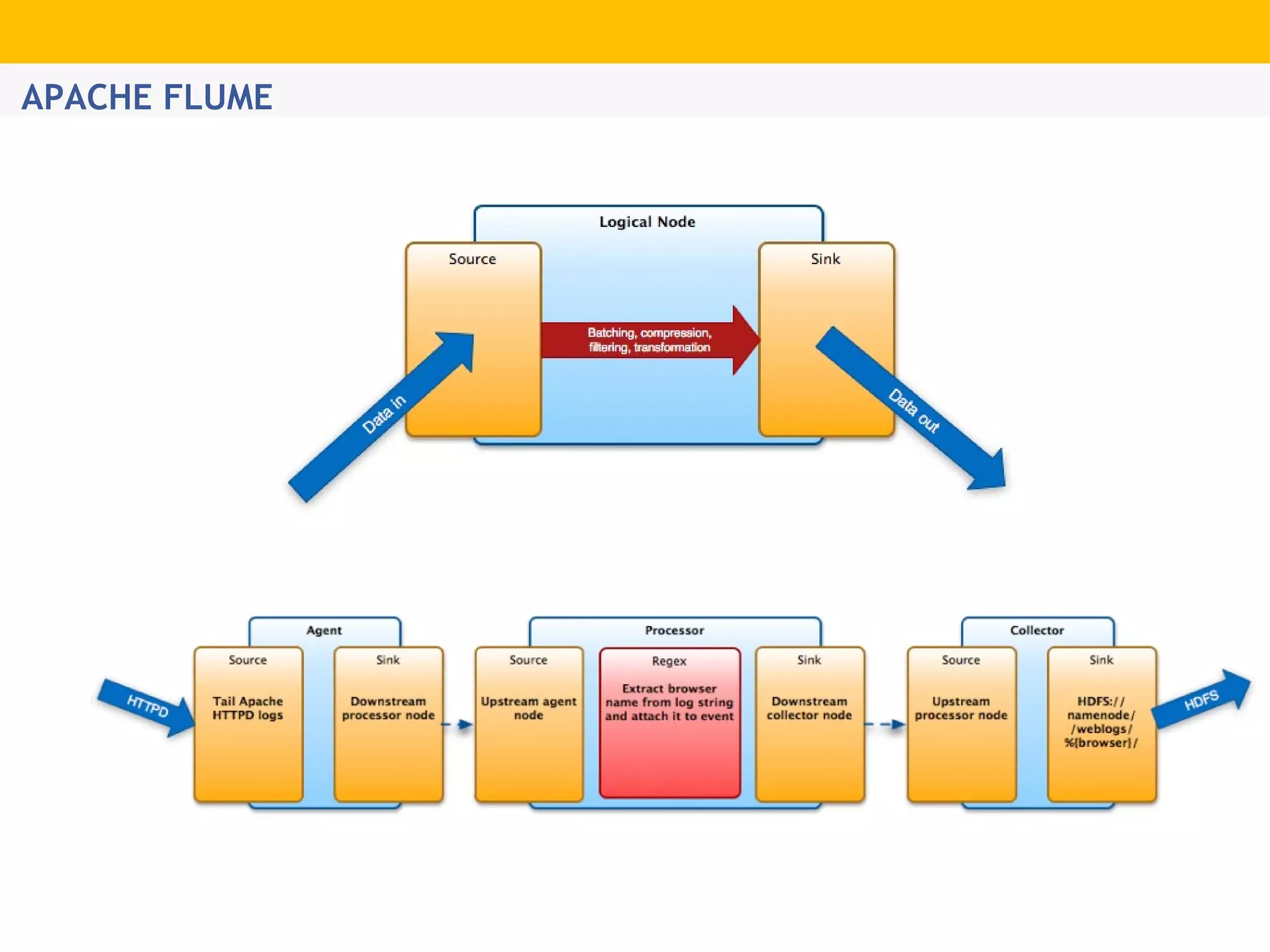
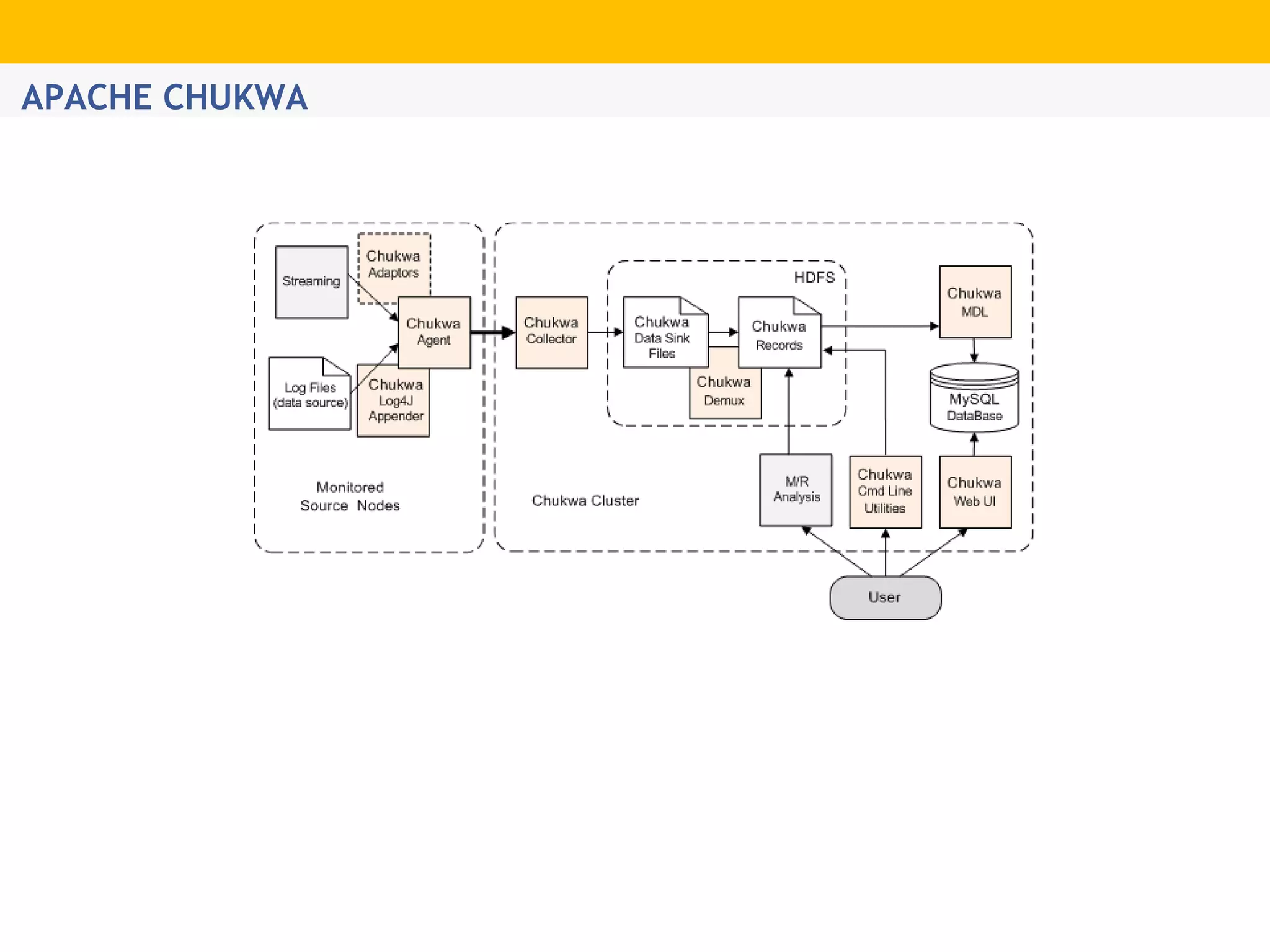
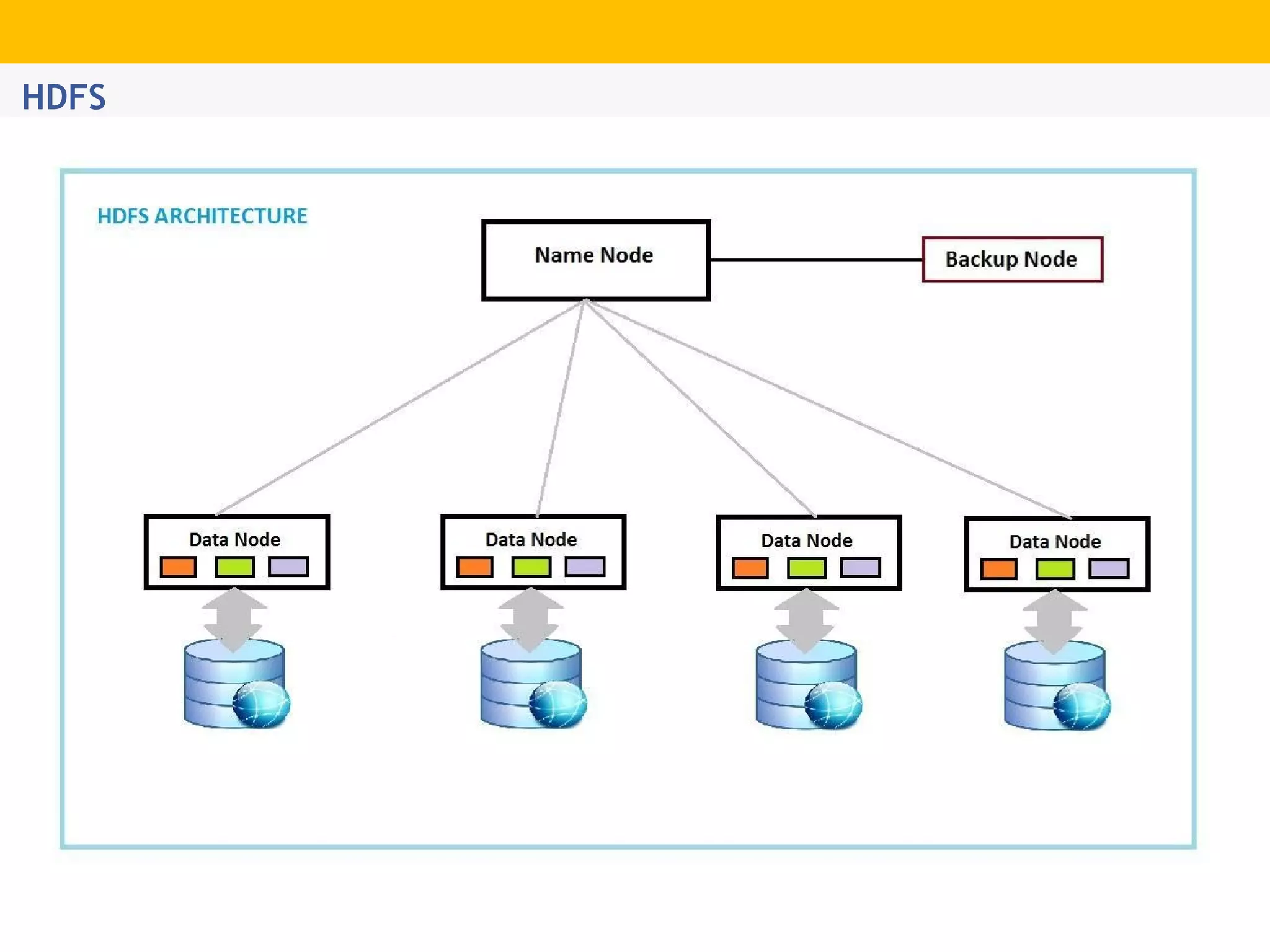
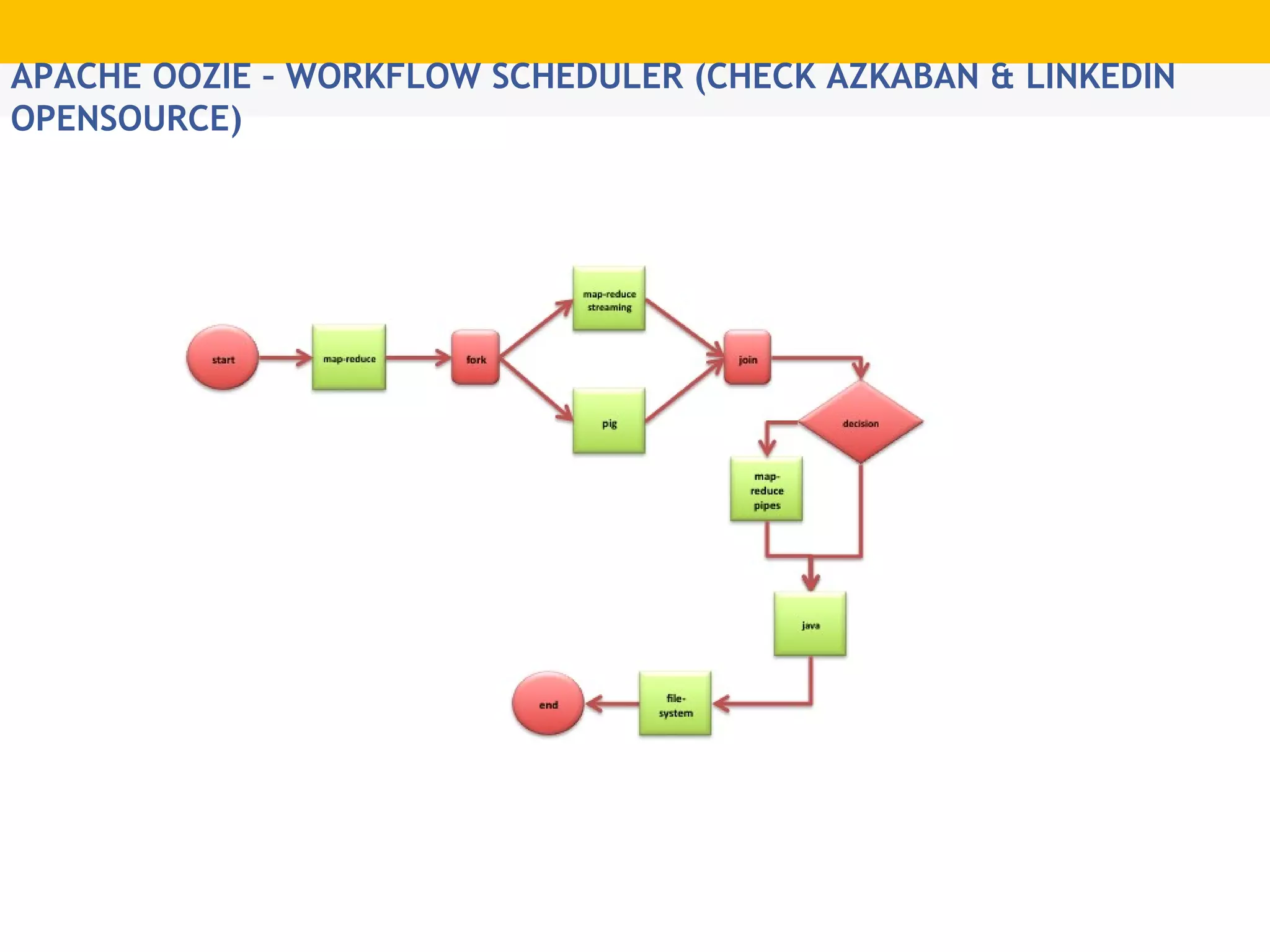
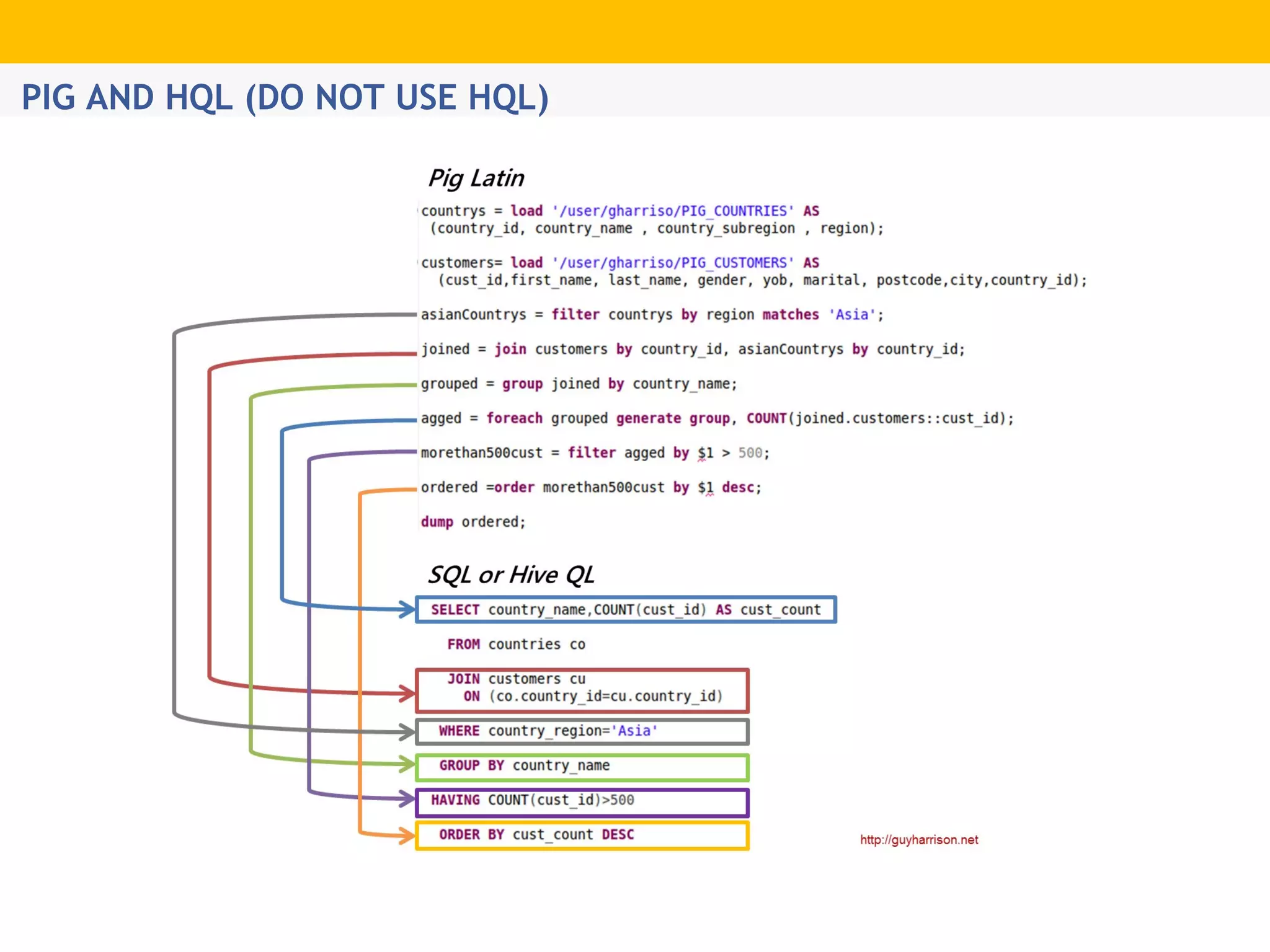
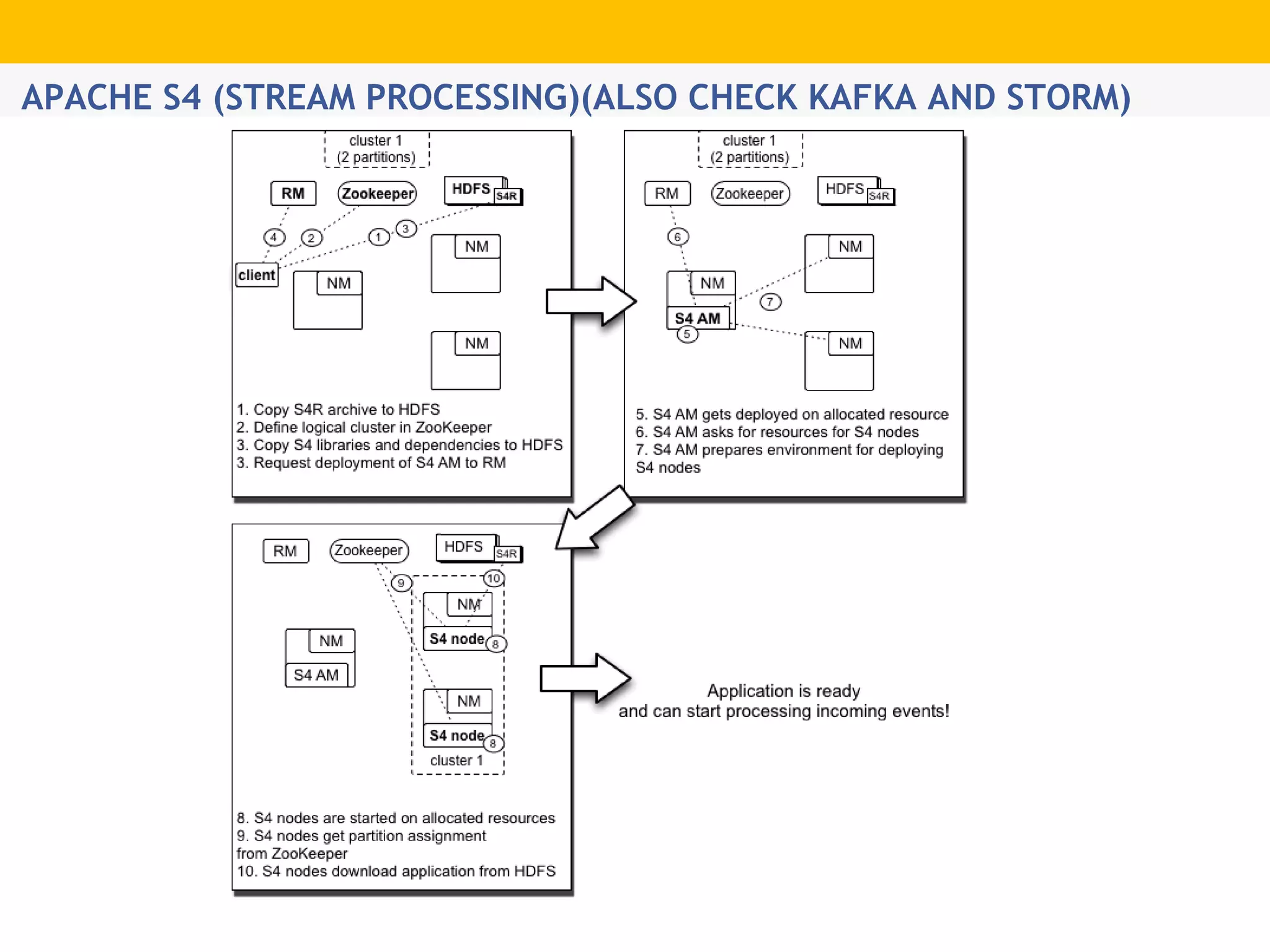
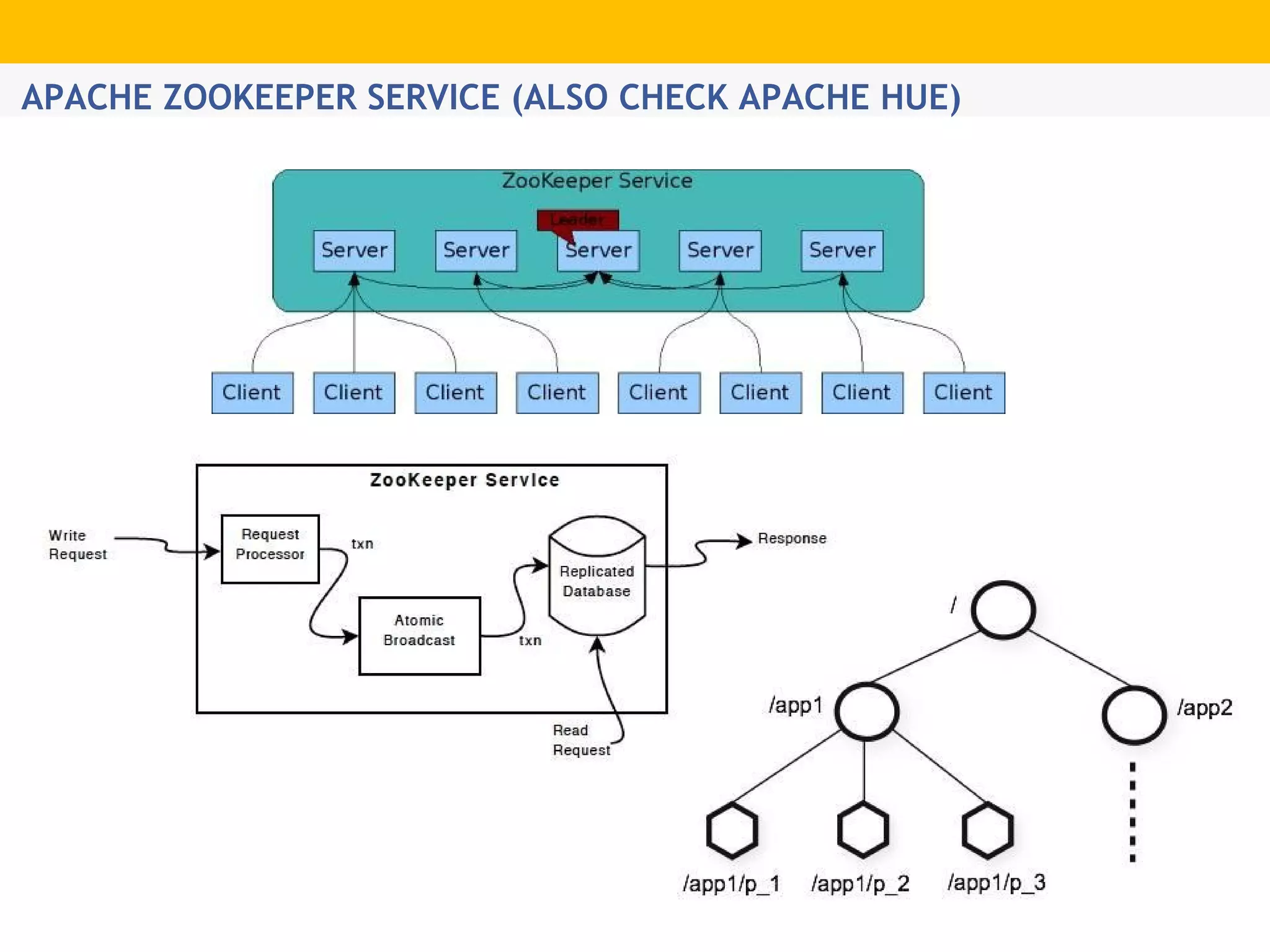
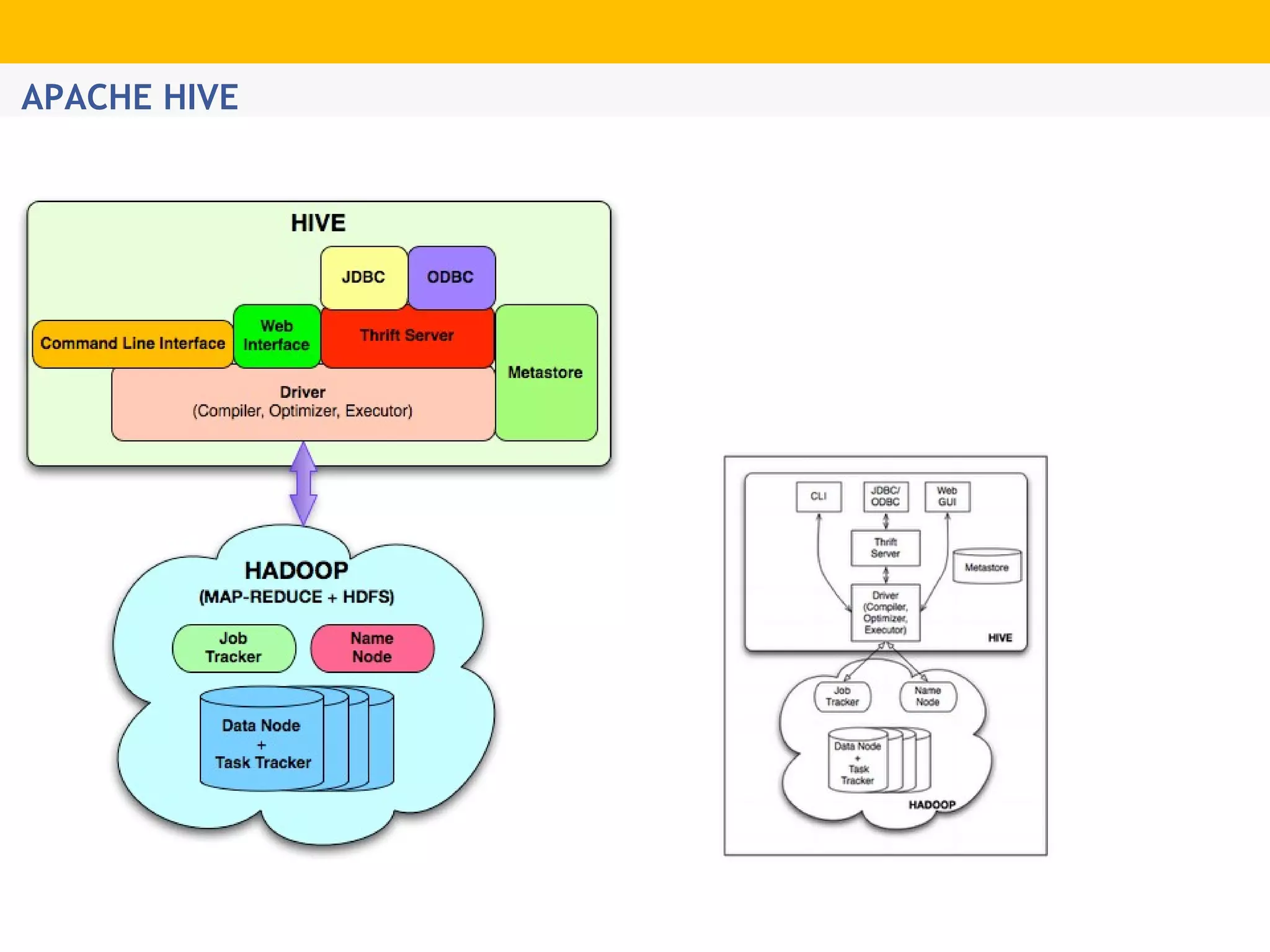
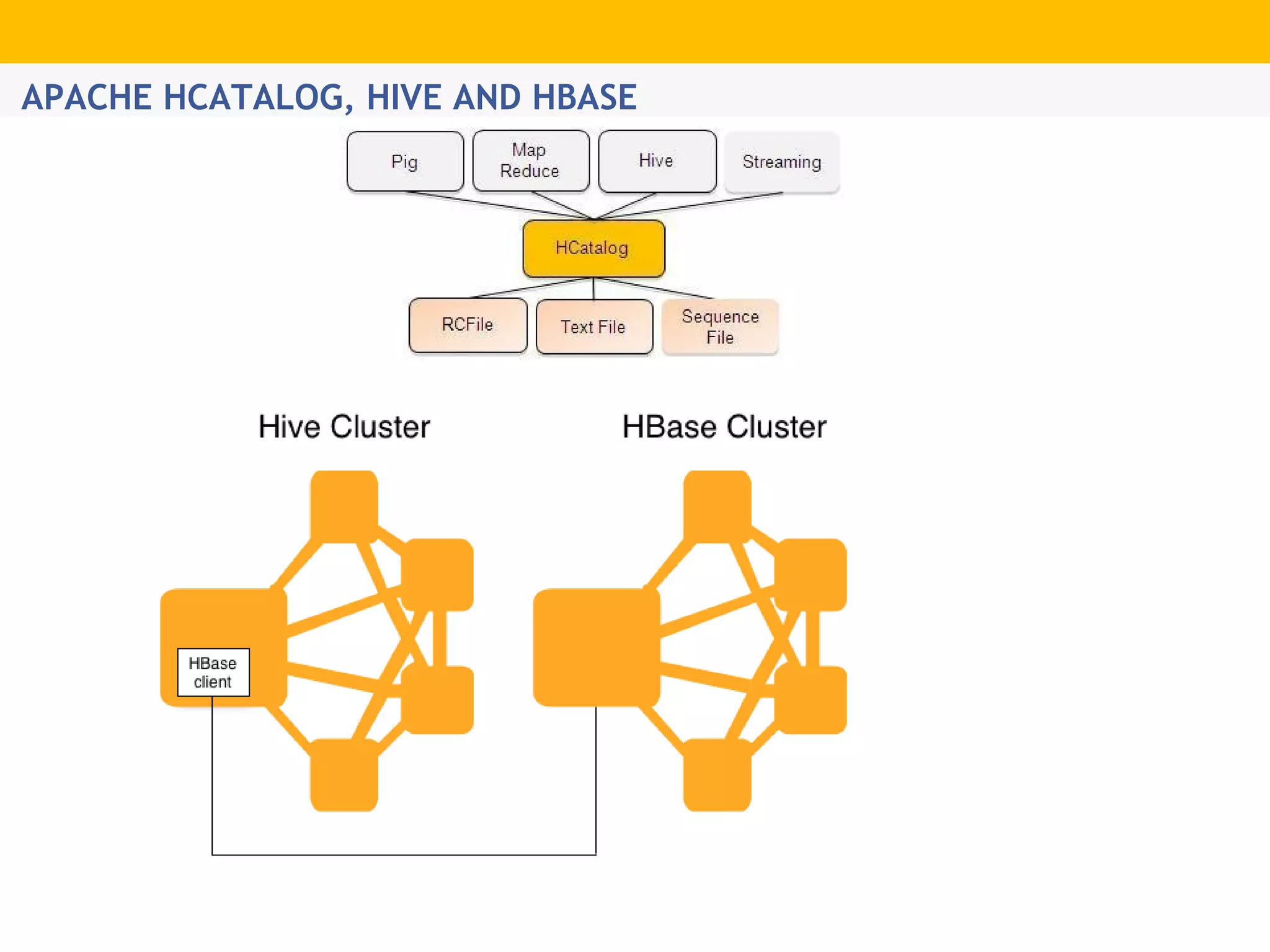

The document provides an overview of Hadoop's distributed cluster architecture, emphasizing its scalability through MapReduce patterns. It contrasts the performance of traditional programming with Hadoop's bootstrap processes, noting that Hadoop excels in handling large datasets, particularly in the petabyte range. Additionally, it mentions various associated Apache projects like Sqoop, Flume, Oozie, Hive, and others that enhance Hadoop's capabilities.















