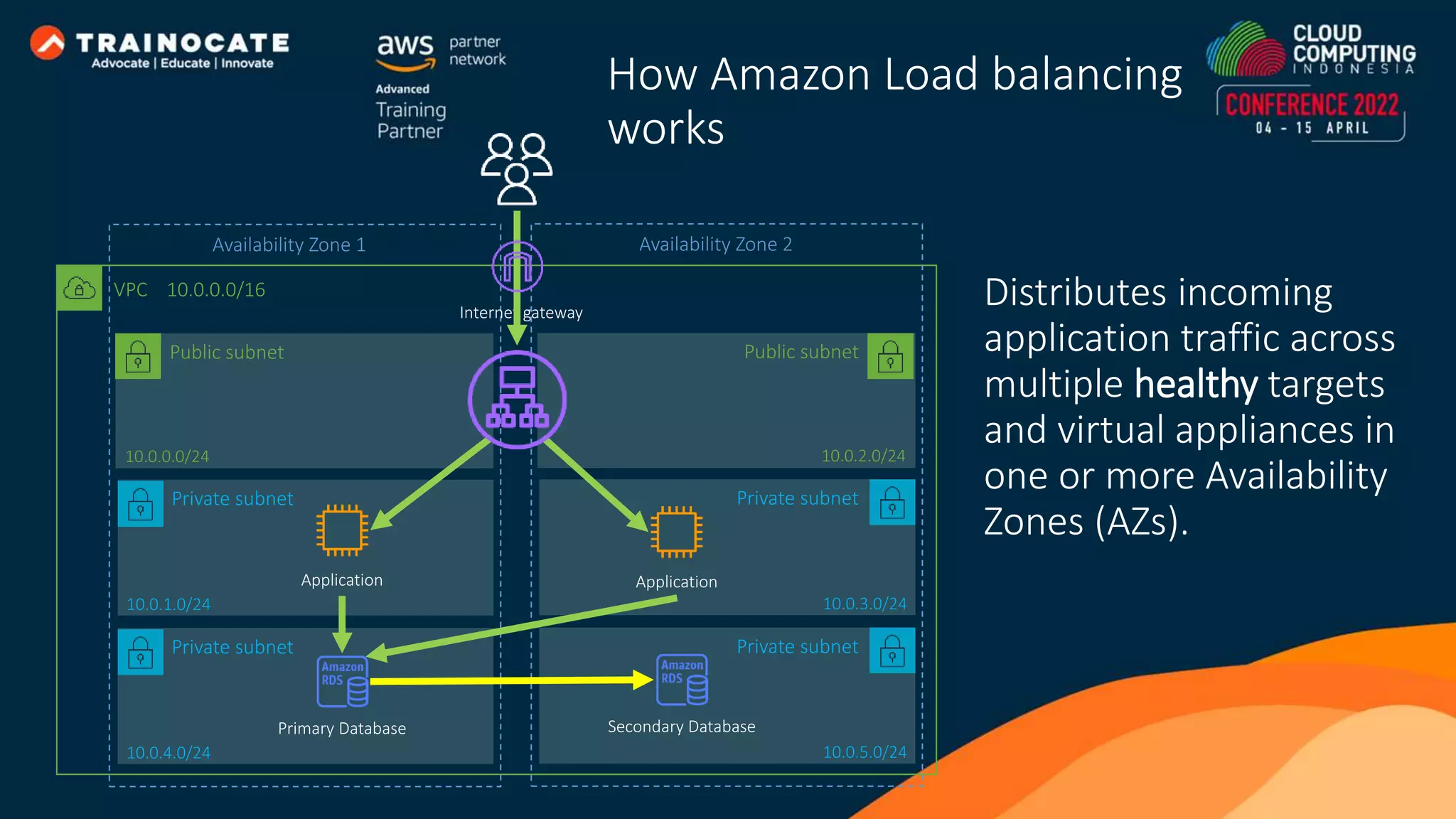
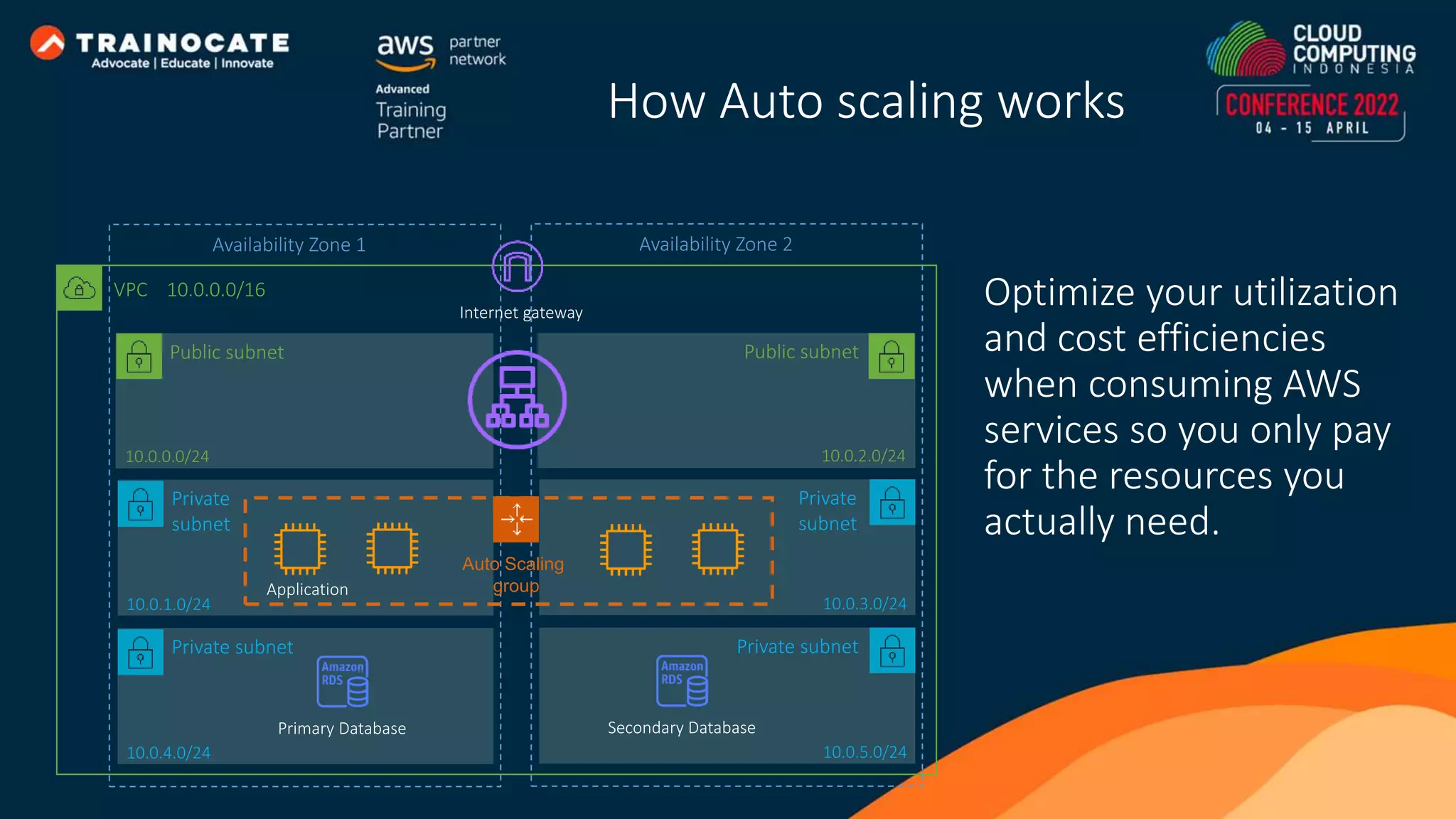
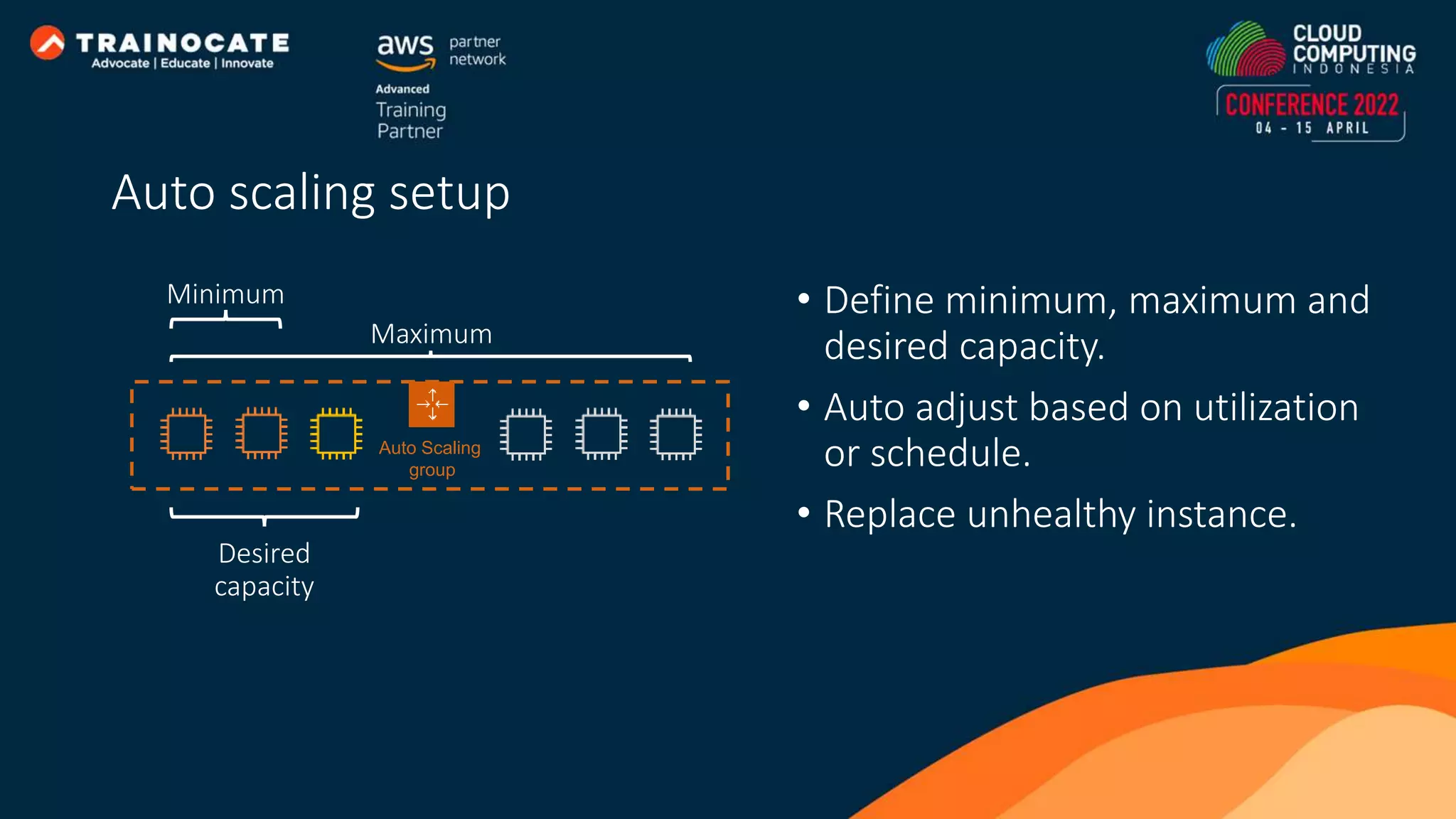
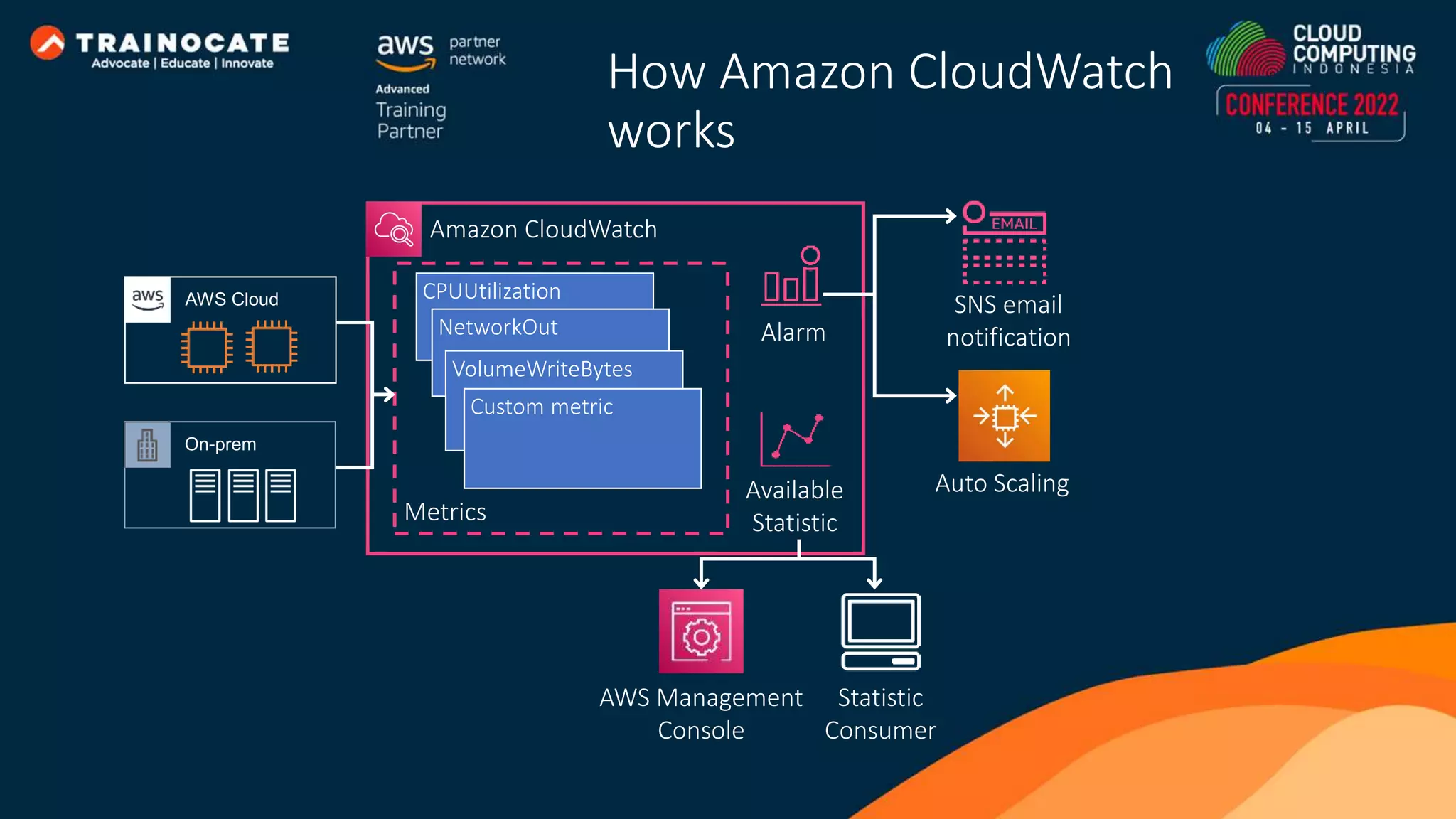
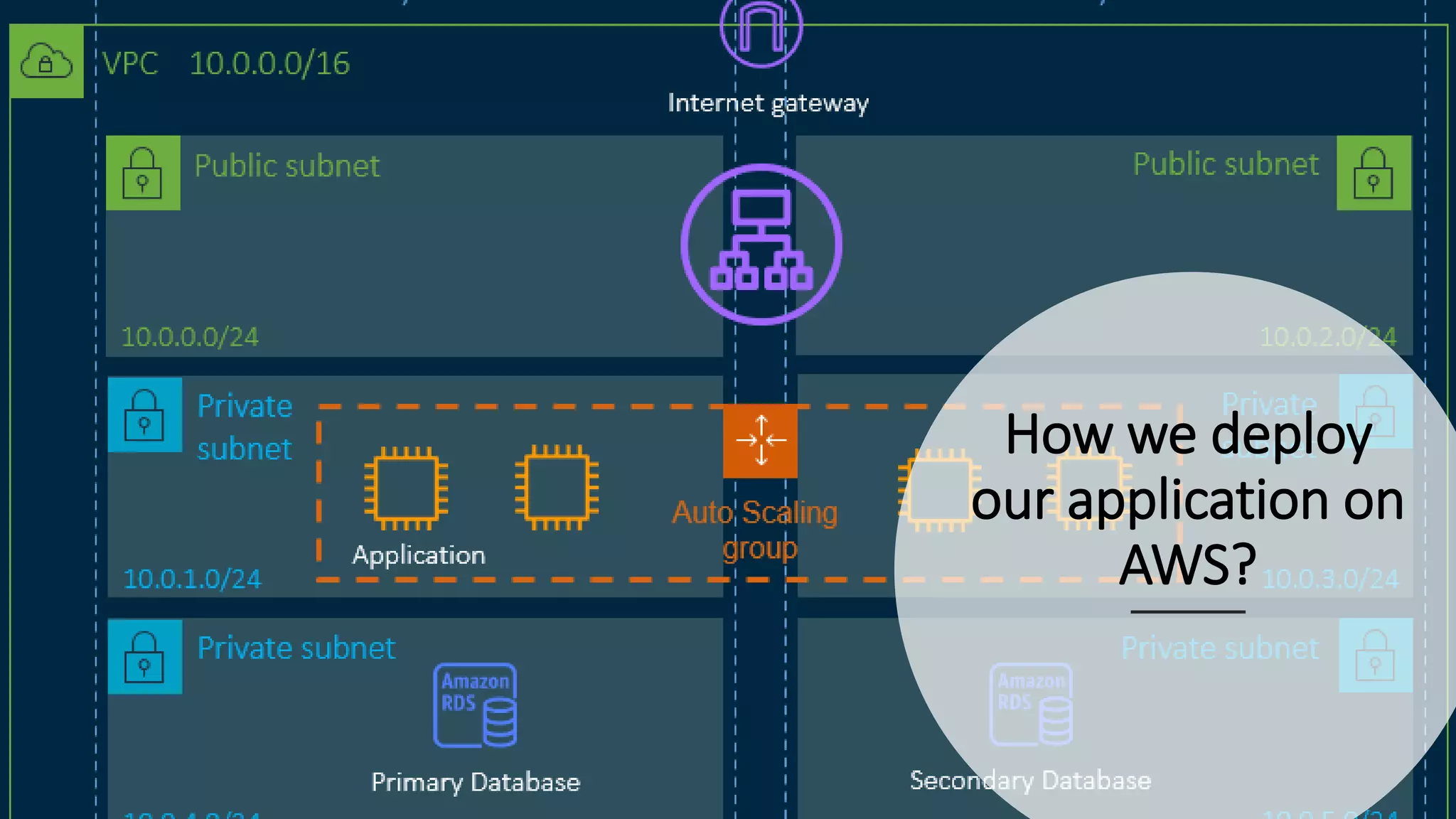
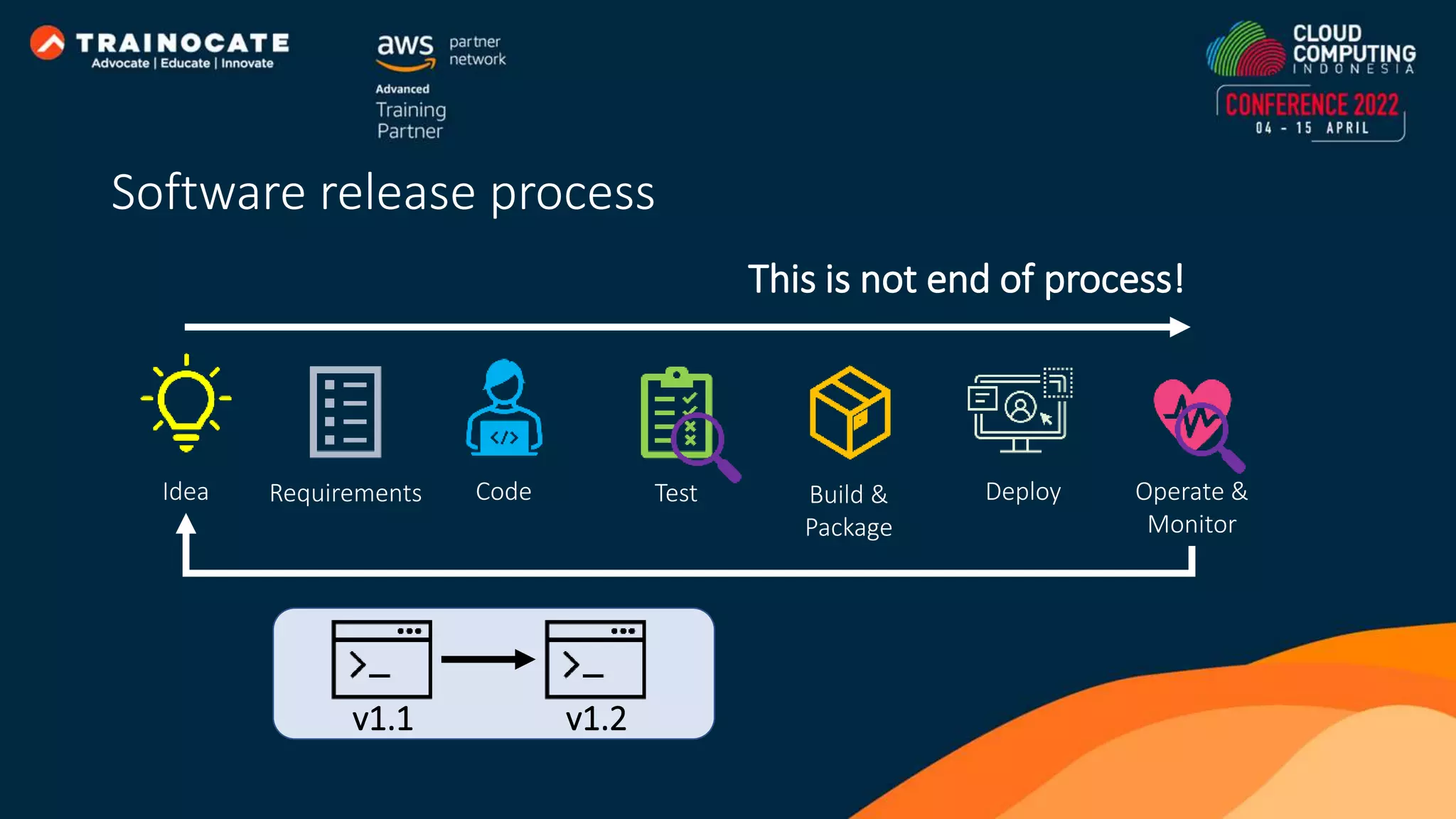
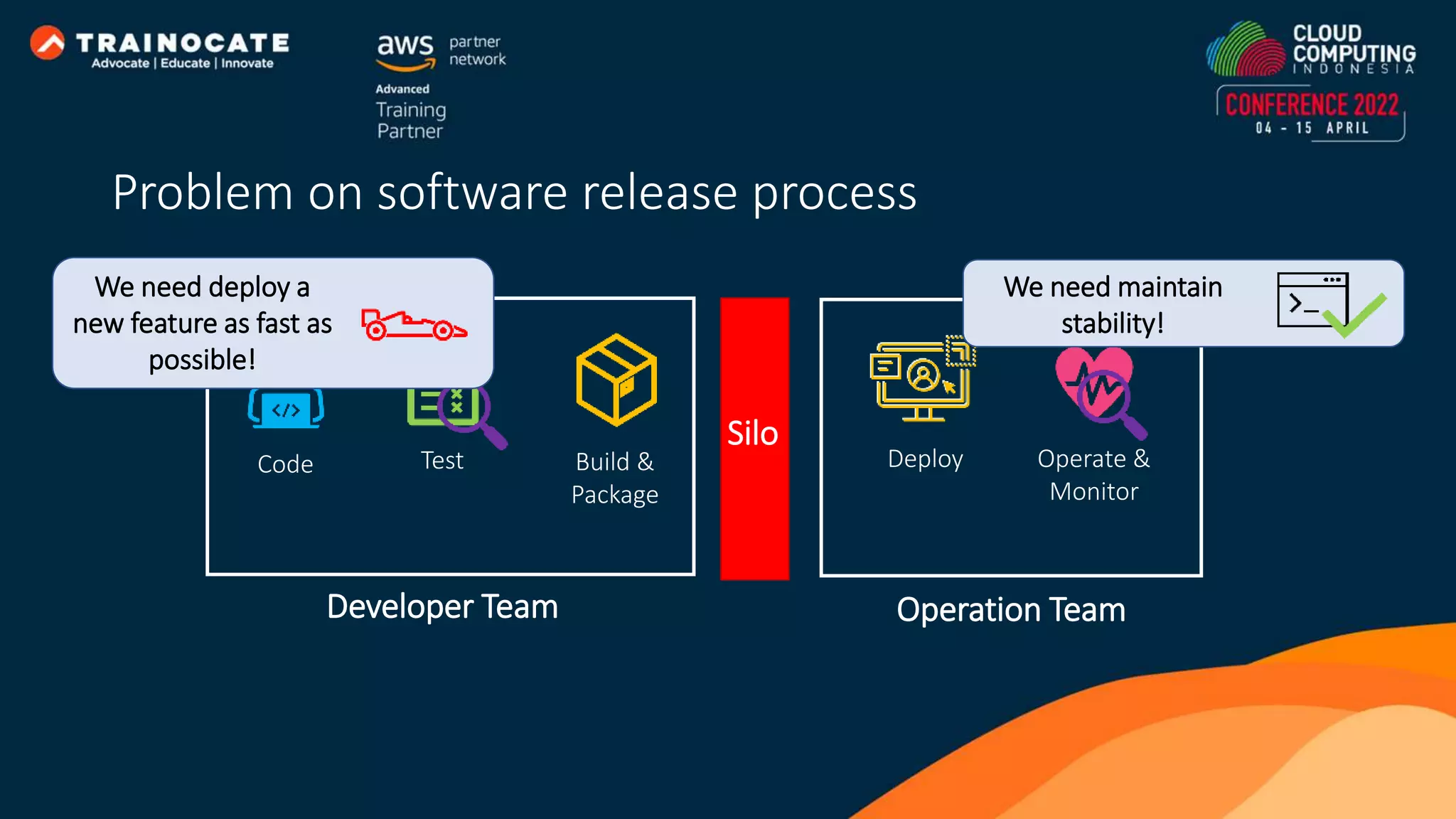
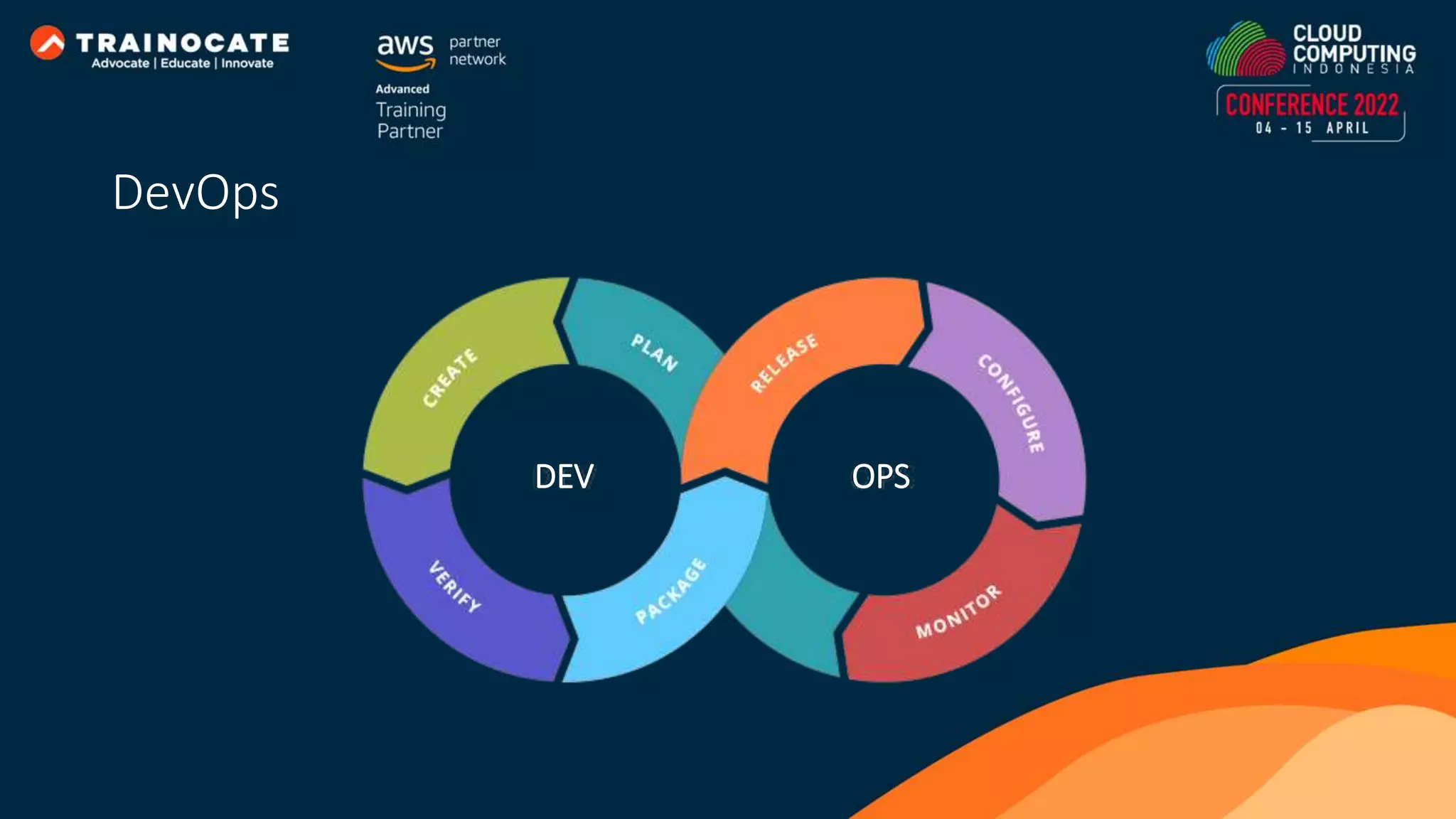
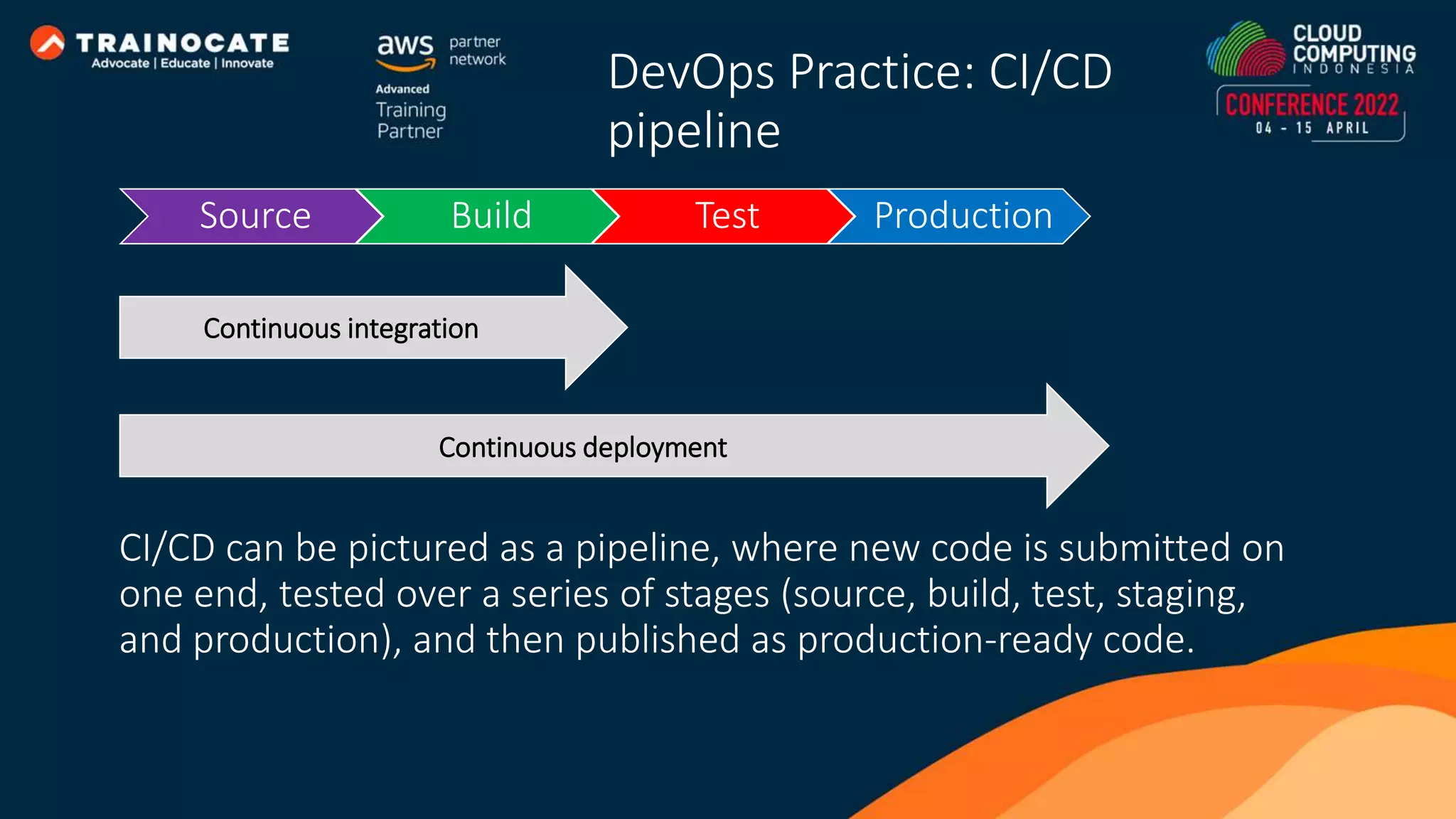
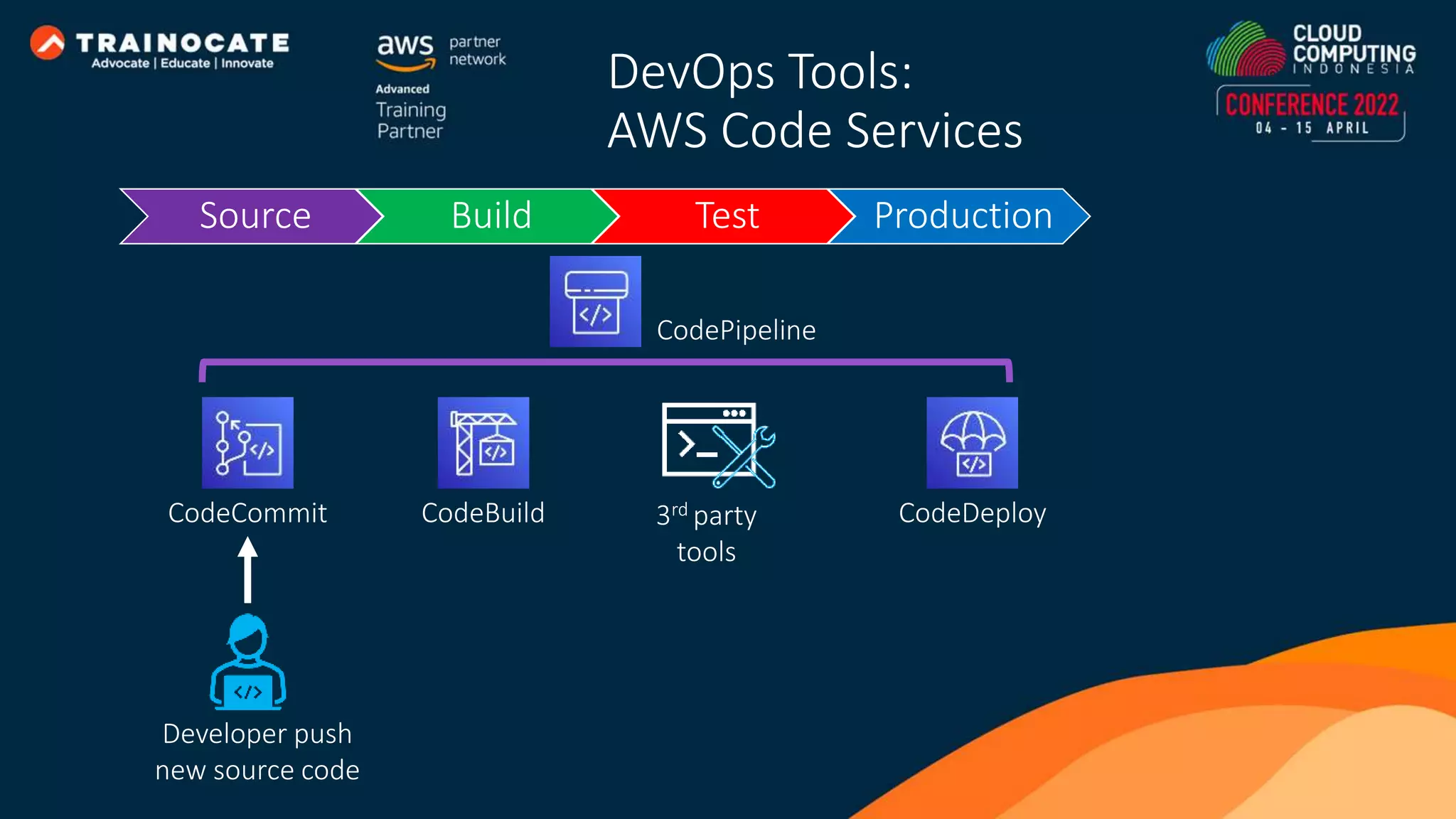
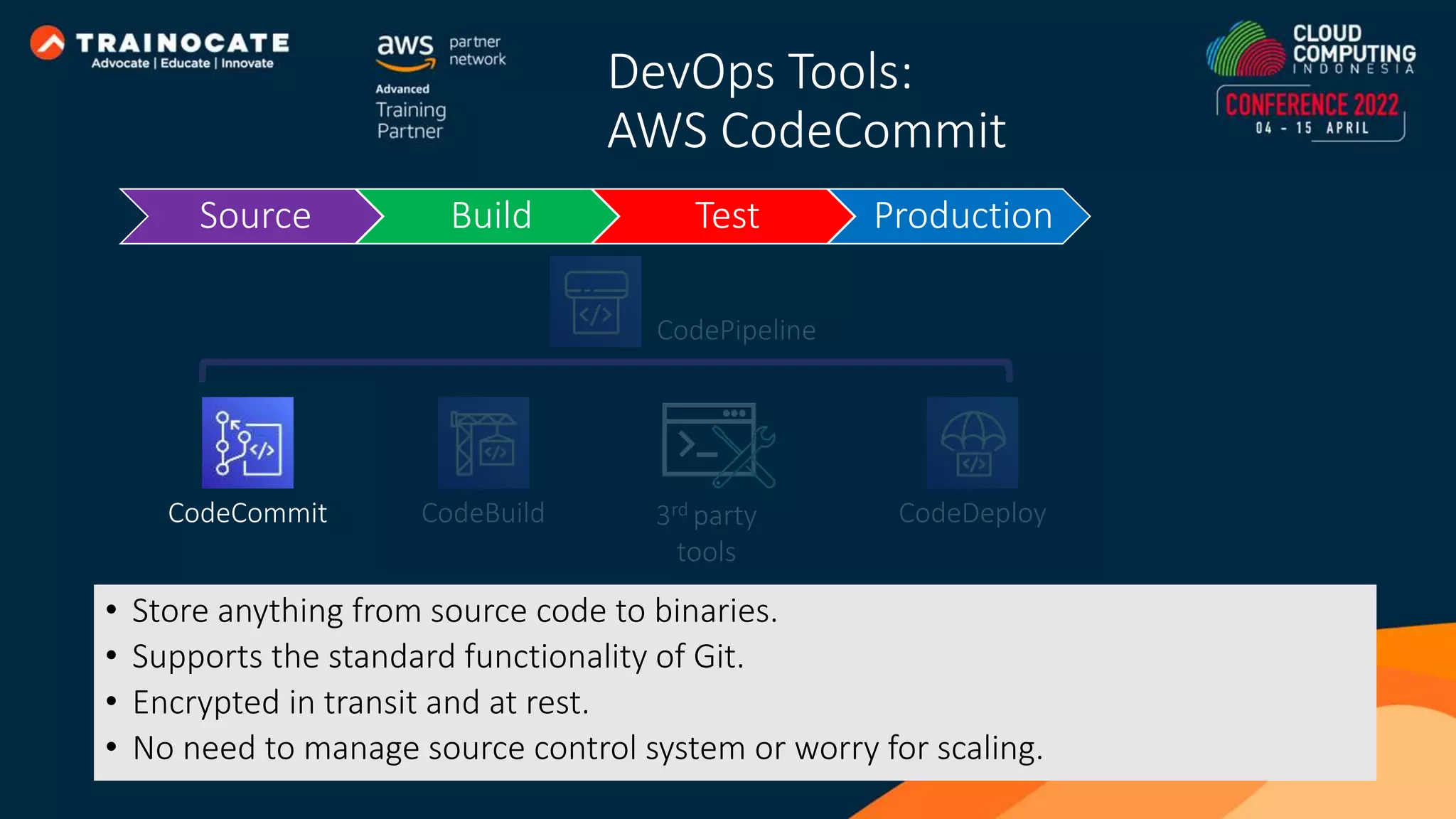
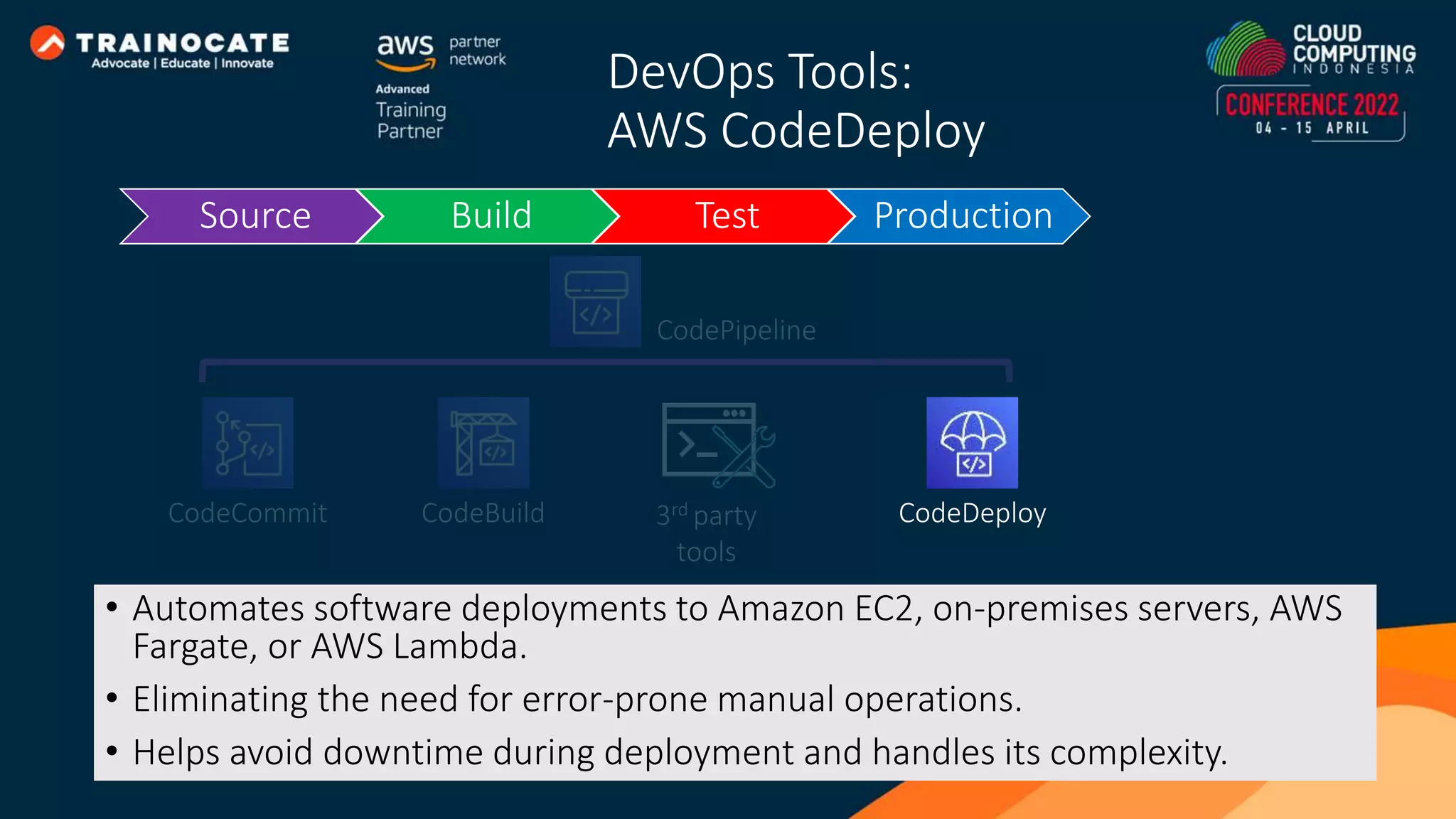
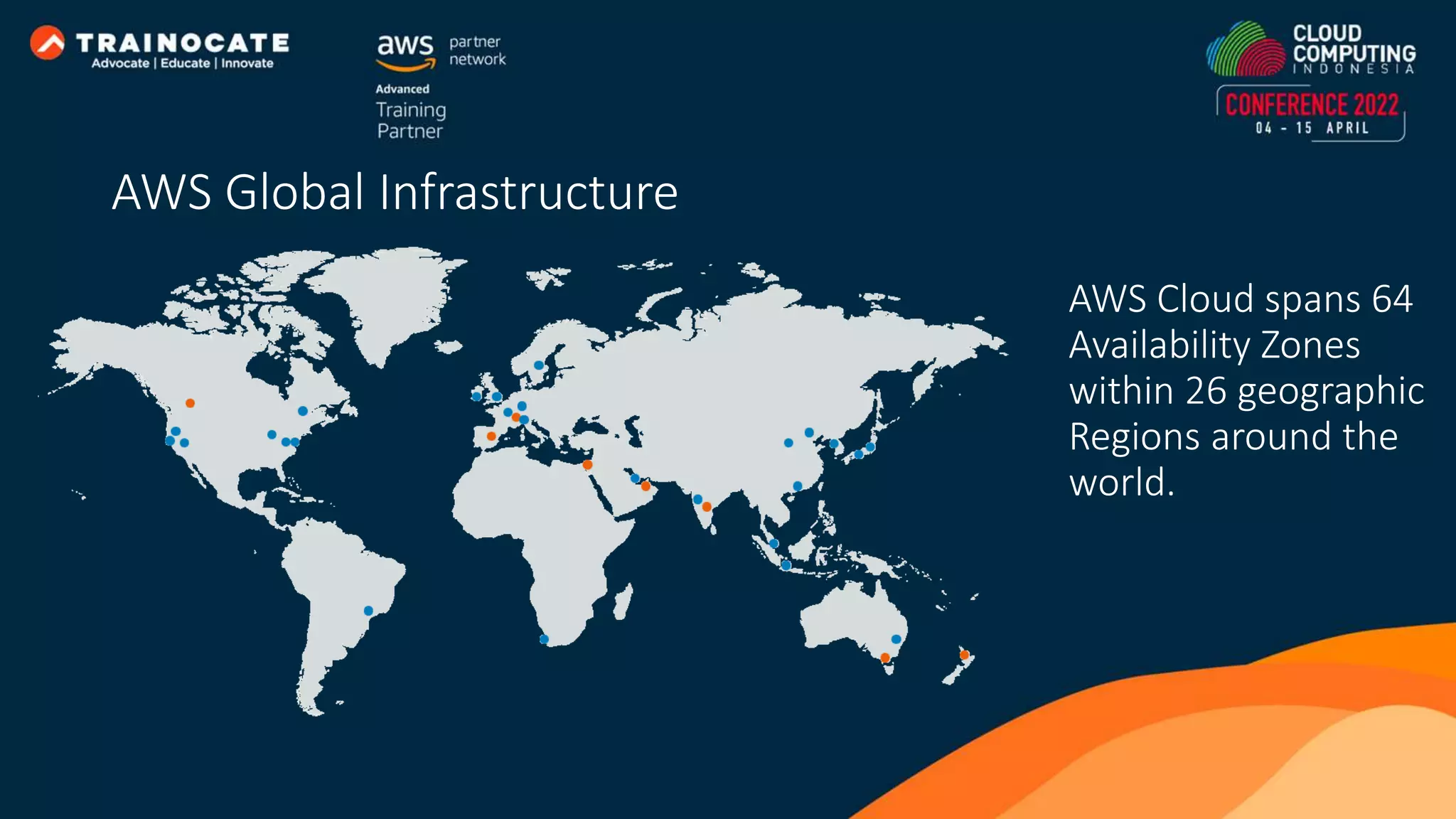
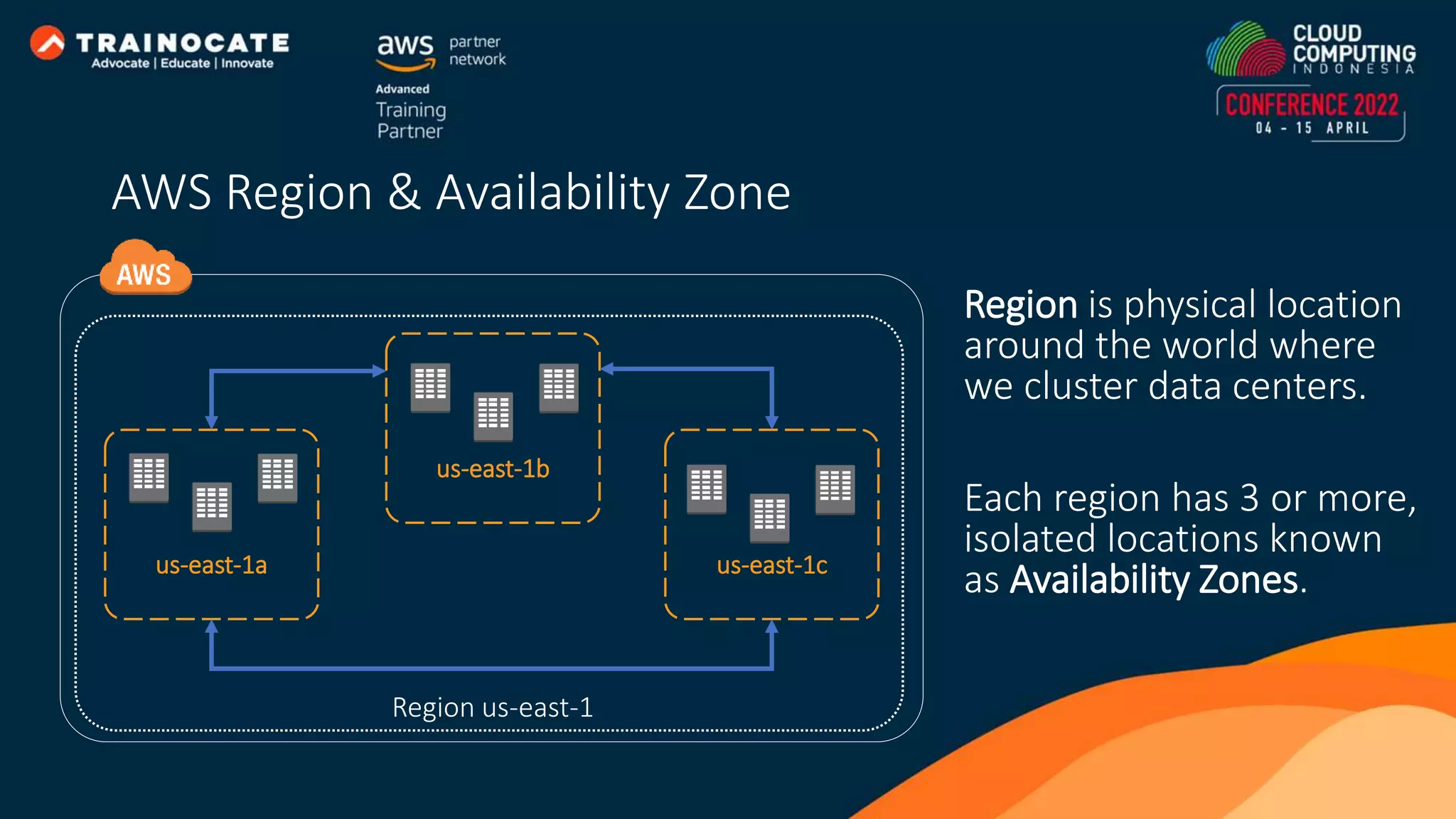
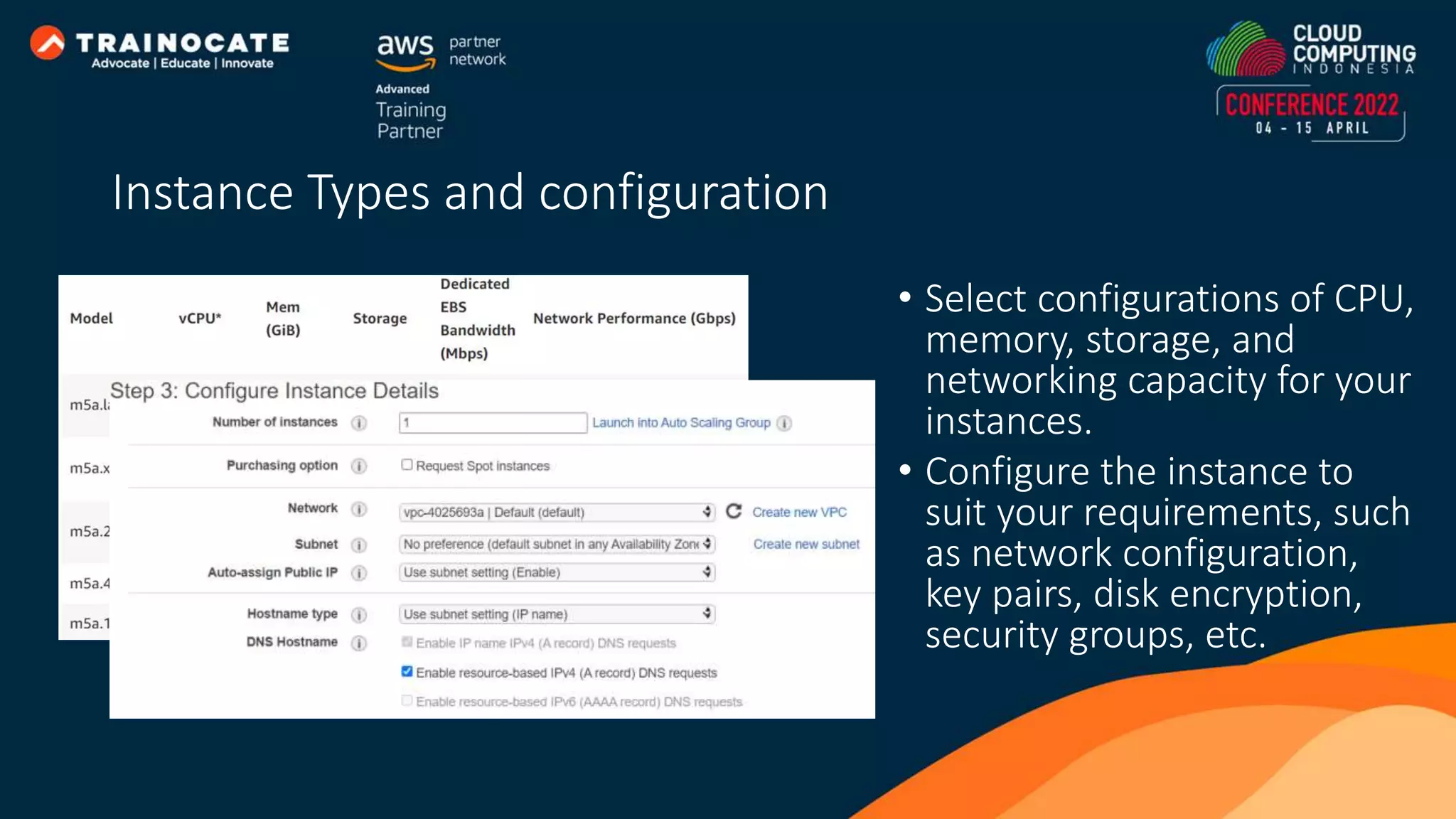
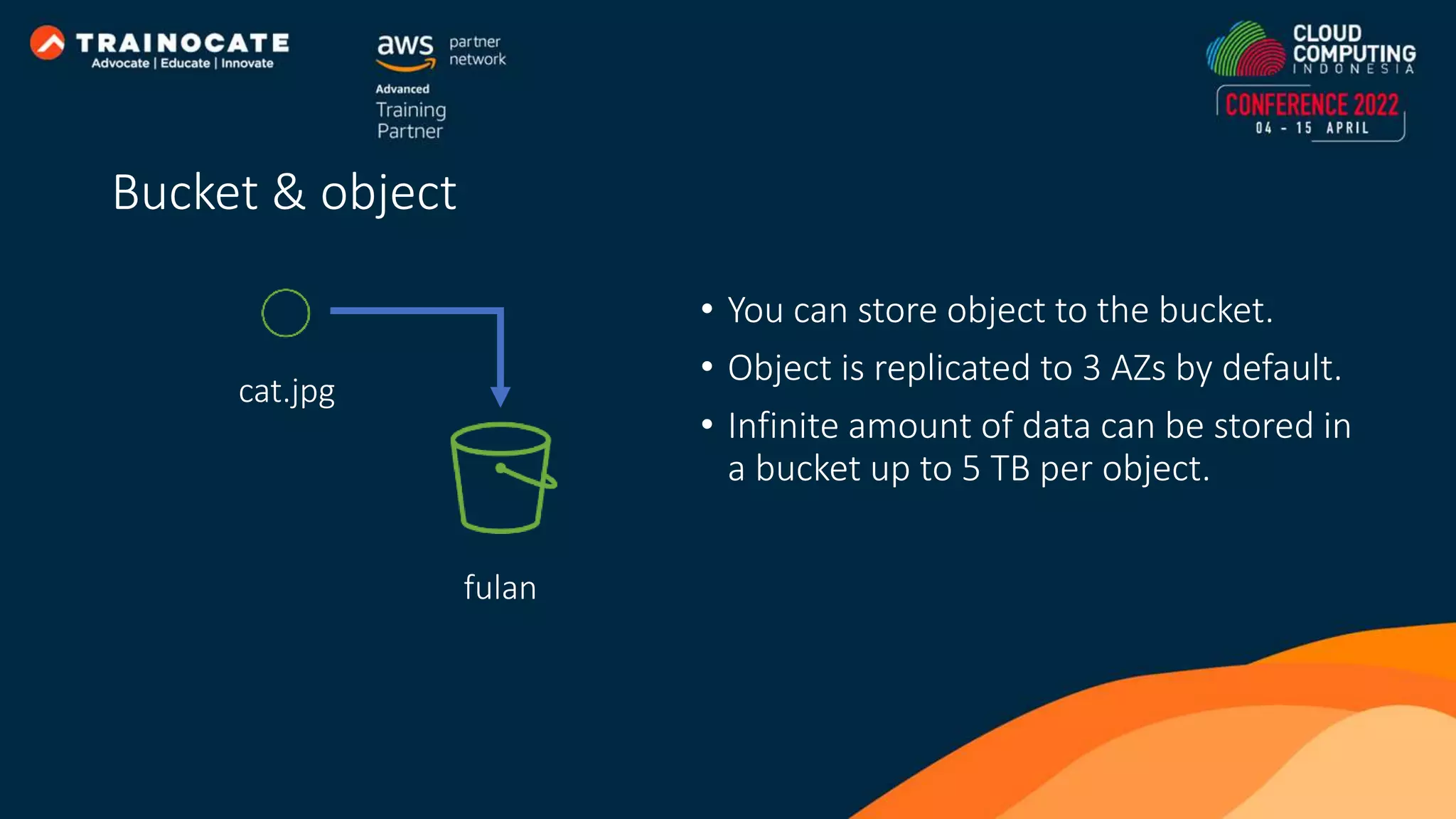
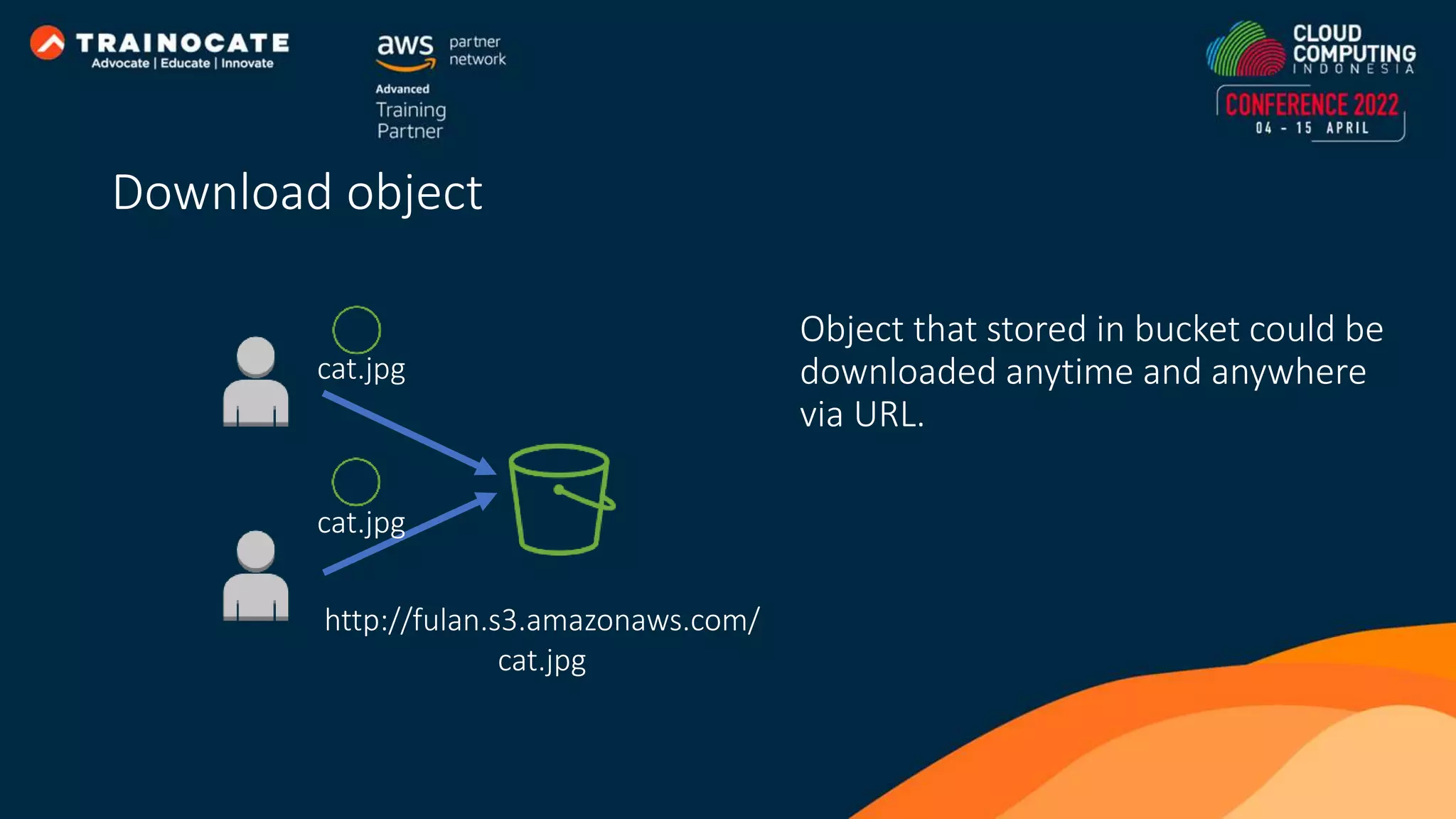
This document discusses how to automate application deployment on AWS using DevOps tools and practices. It provides an overview of cloud computing concepts like AWS services, virtual private clouds, load balancing, and auto scaling. It then explains that DevOps aims to break down silos between development and operations teams through practices like continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. The document outlines how AWS code services like CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, and CodePipeline can be used to automate the application deployment process from source control to production.
















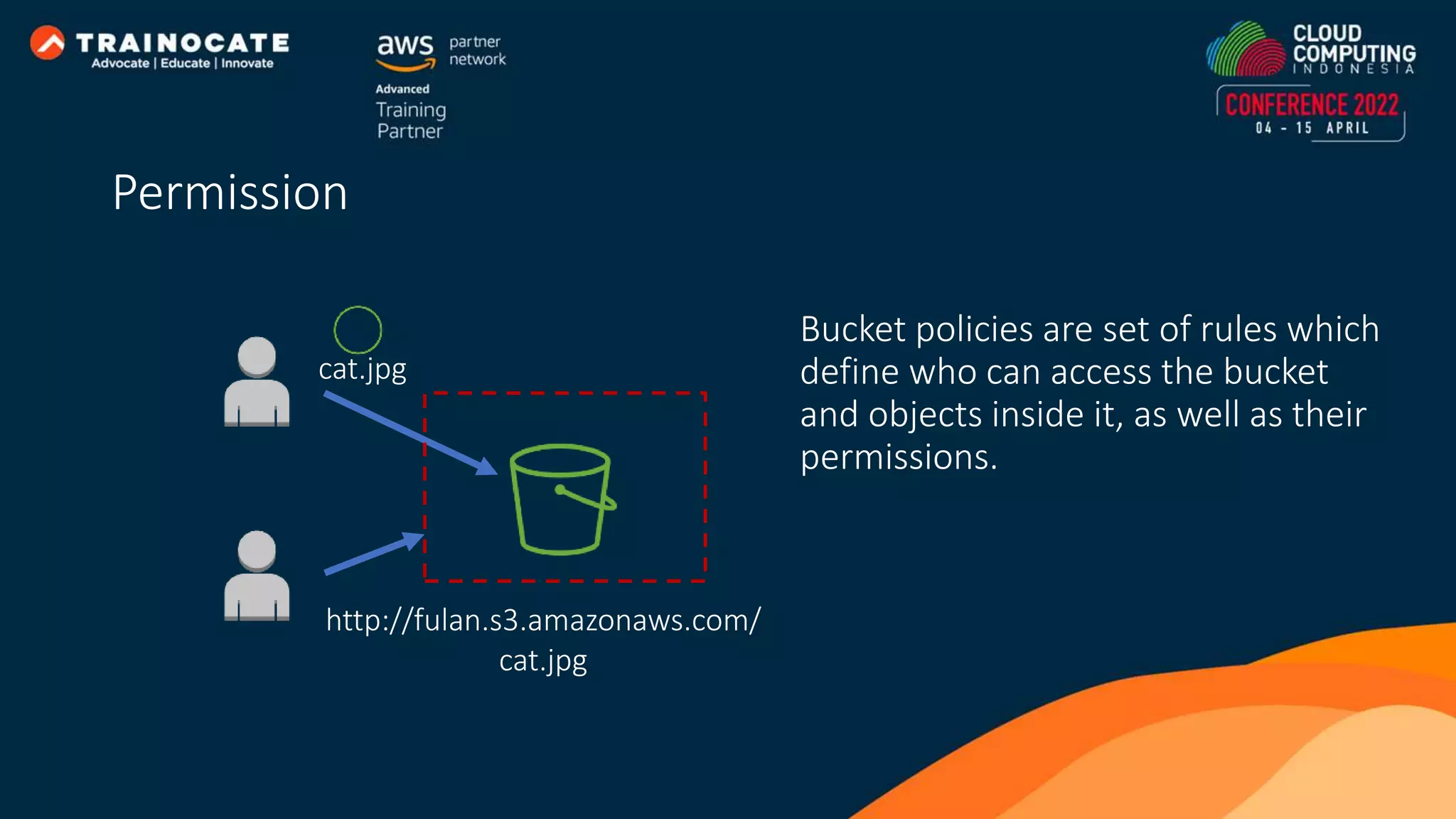

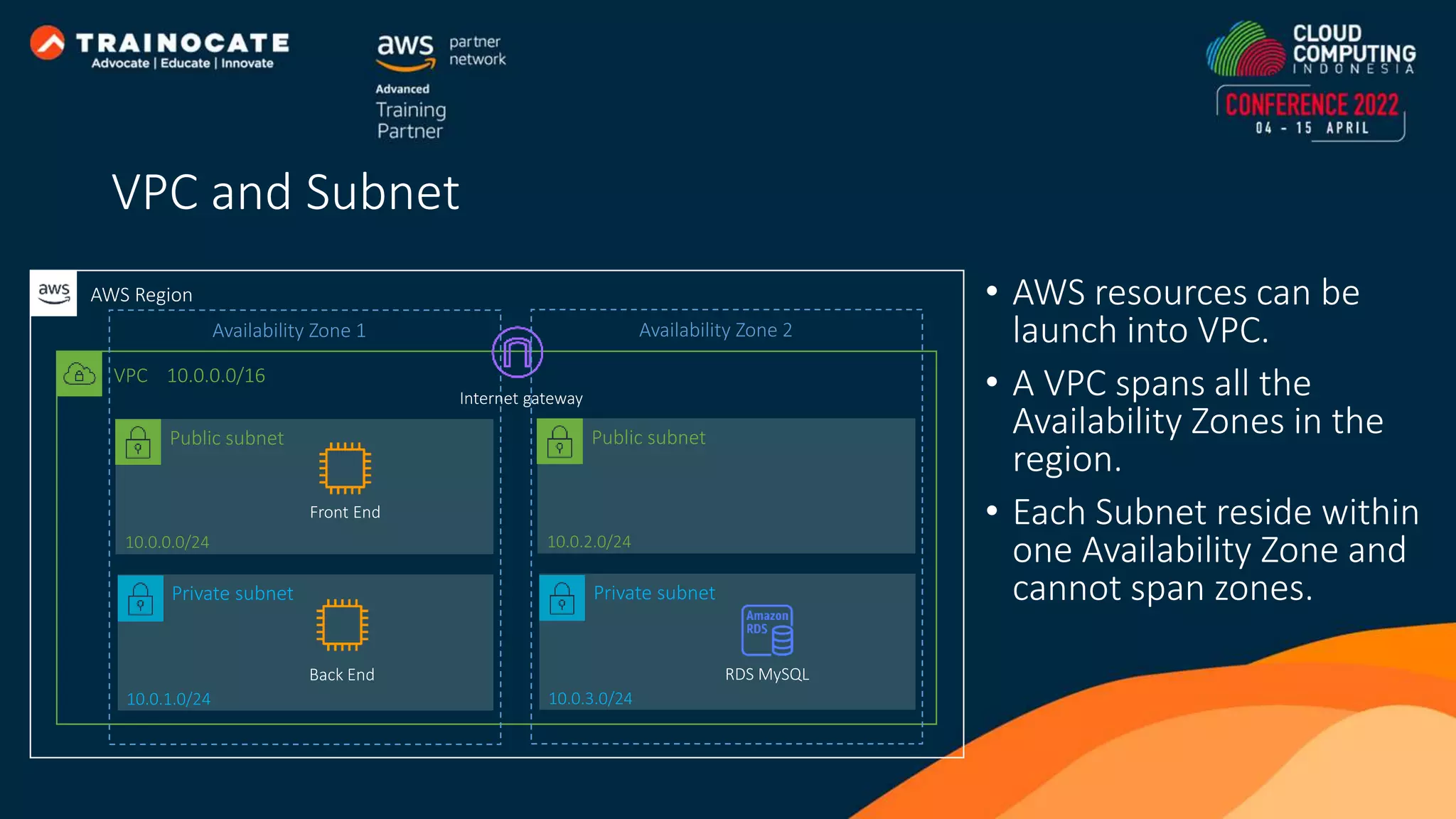
![Network ACLs act as a firewall for associated subnets, controlling both inbound and outbound traffic at the subnet level. Security groups act as a firewall for associated instances, controlling both inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level. 10.0.0.0/24 Website [1] Deny ALL – 12.12.12.12/32 [2] Allow HTTP(80) - 0.0.0.0/0 Allow HTTP (80) - 0.0.0.0/0 12.12.12.12 11.11.11.11 Network ACL and Security Group](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howeasytoautomateapplicationdeploymentonaws-221223063434-58b86df9/75/How-Easy-to-Automate-Application-Deployment-on-AWS-27-2048.jpg)