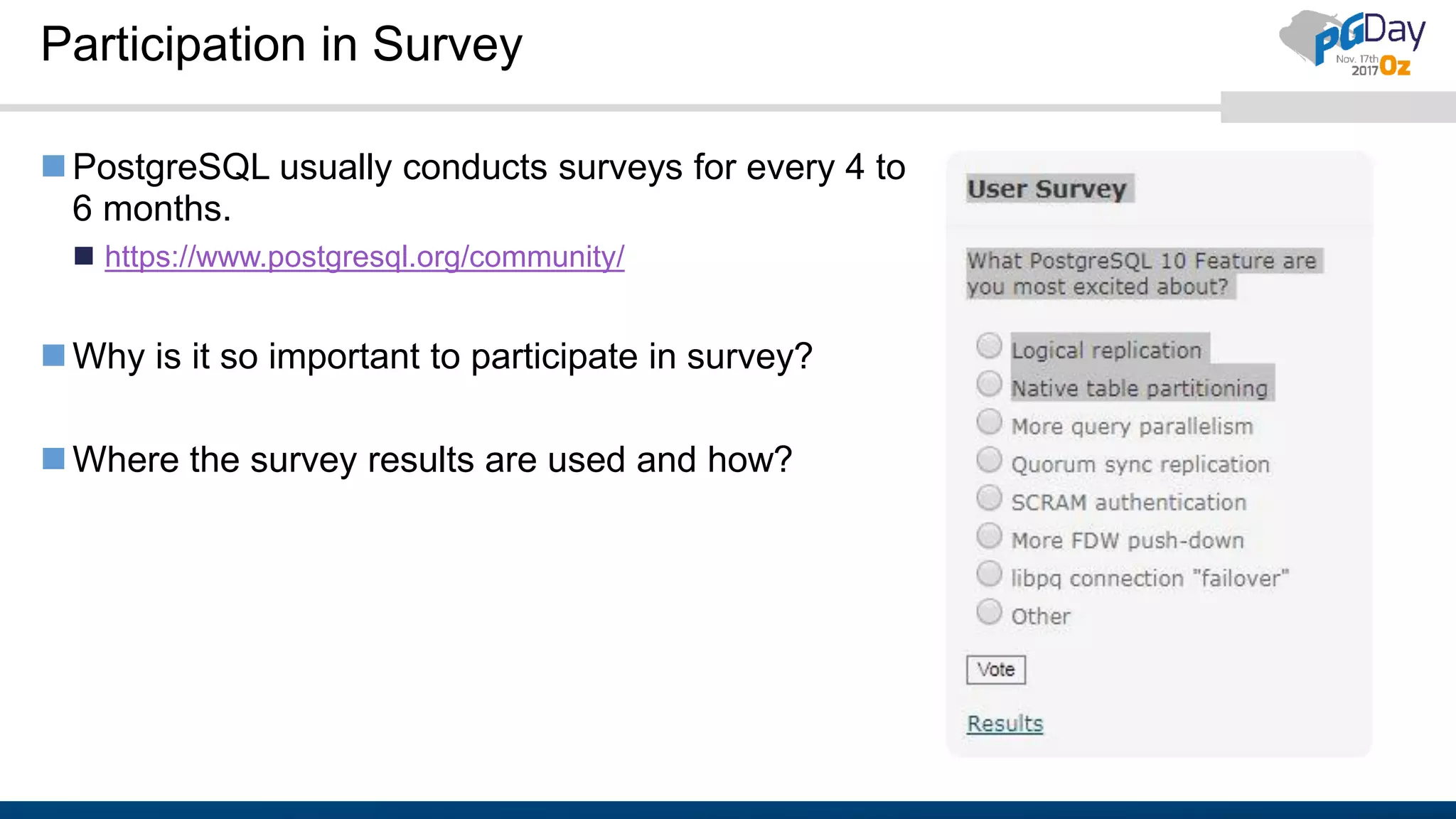
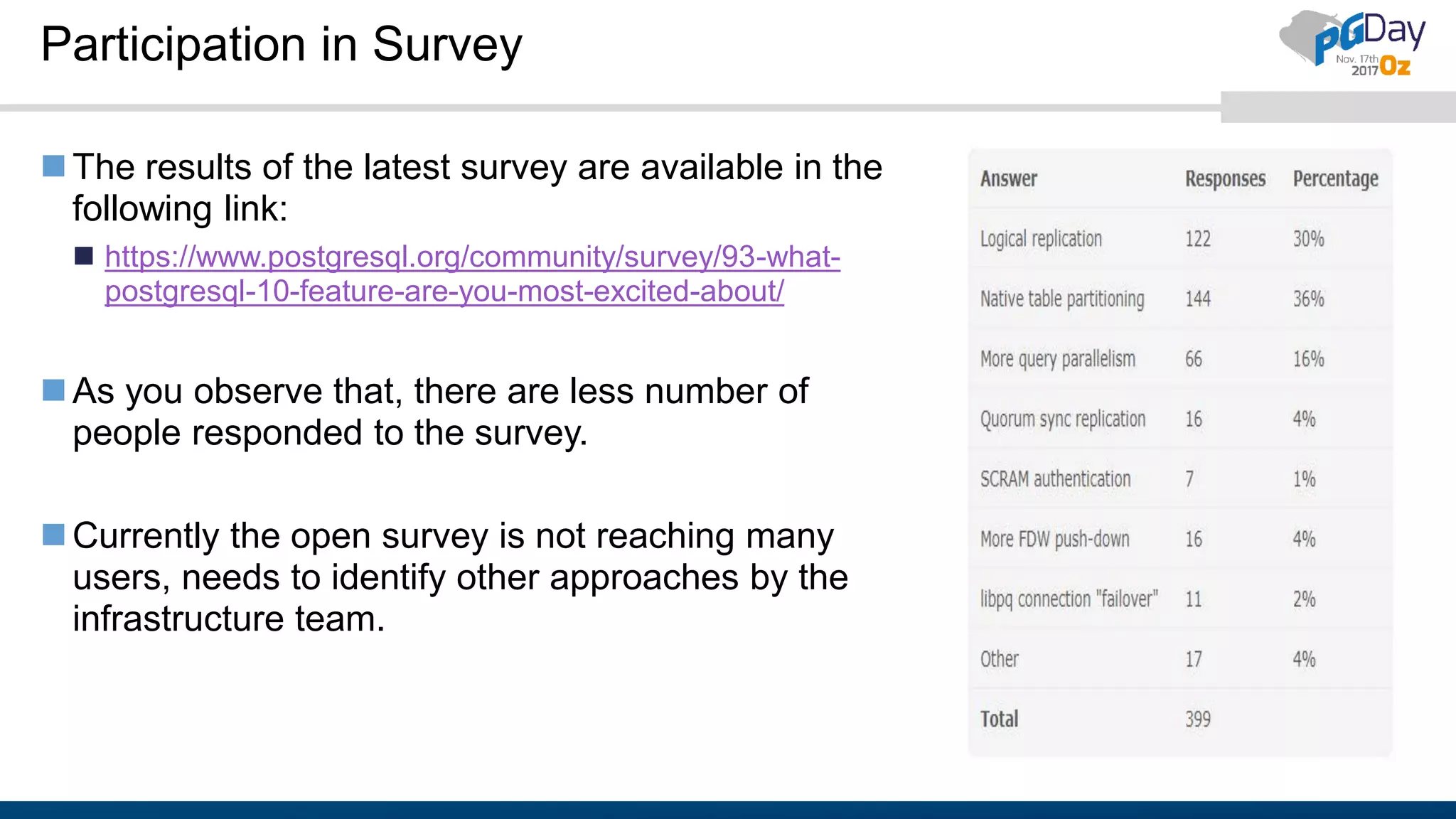
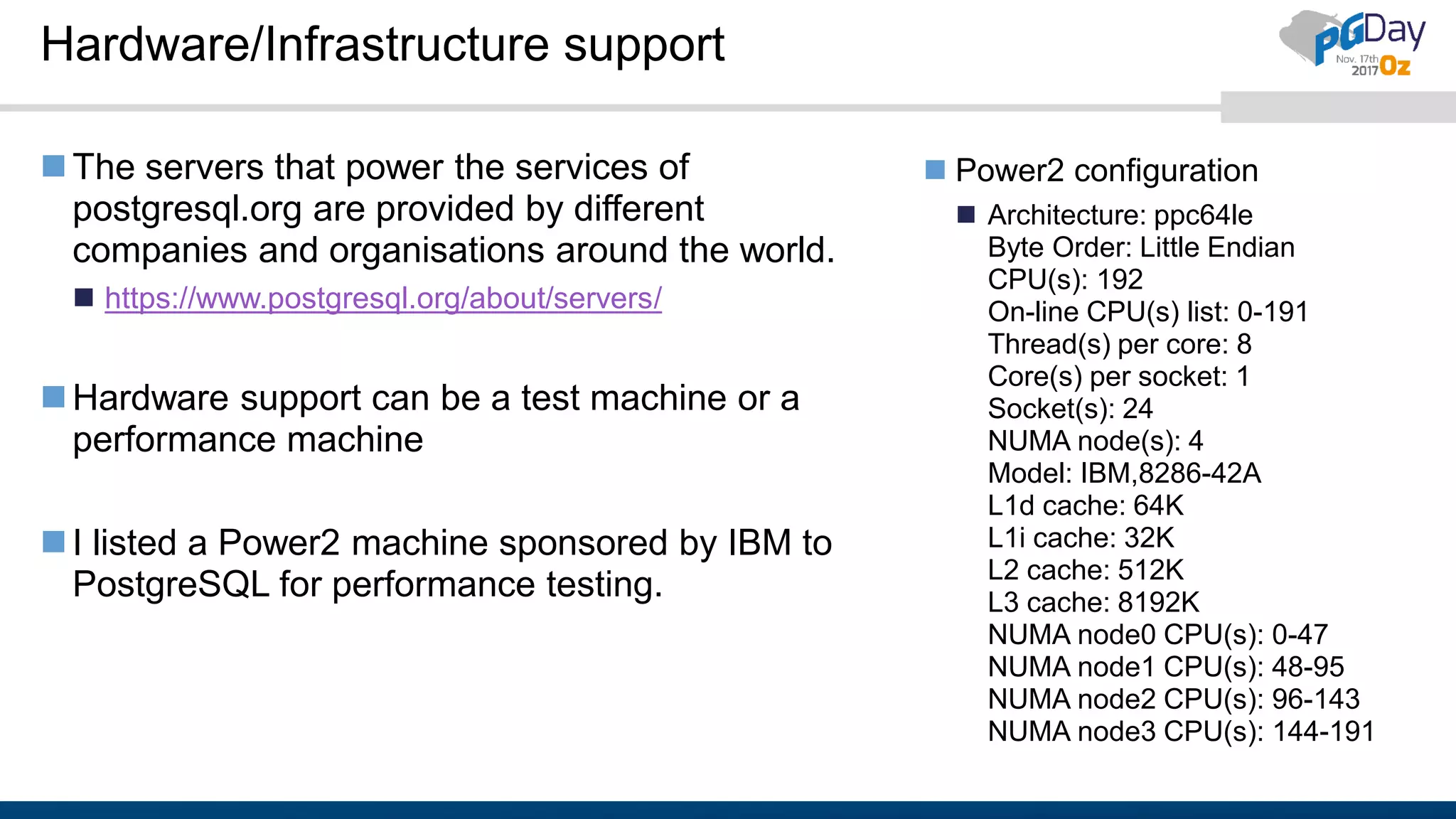
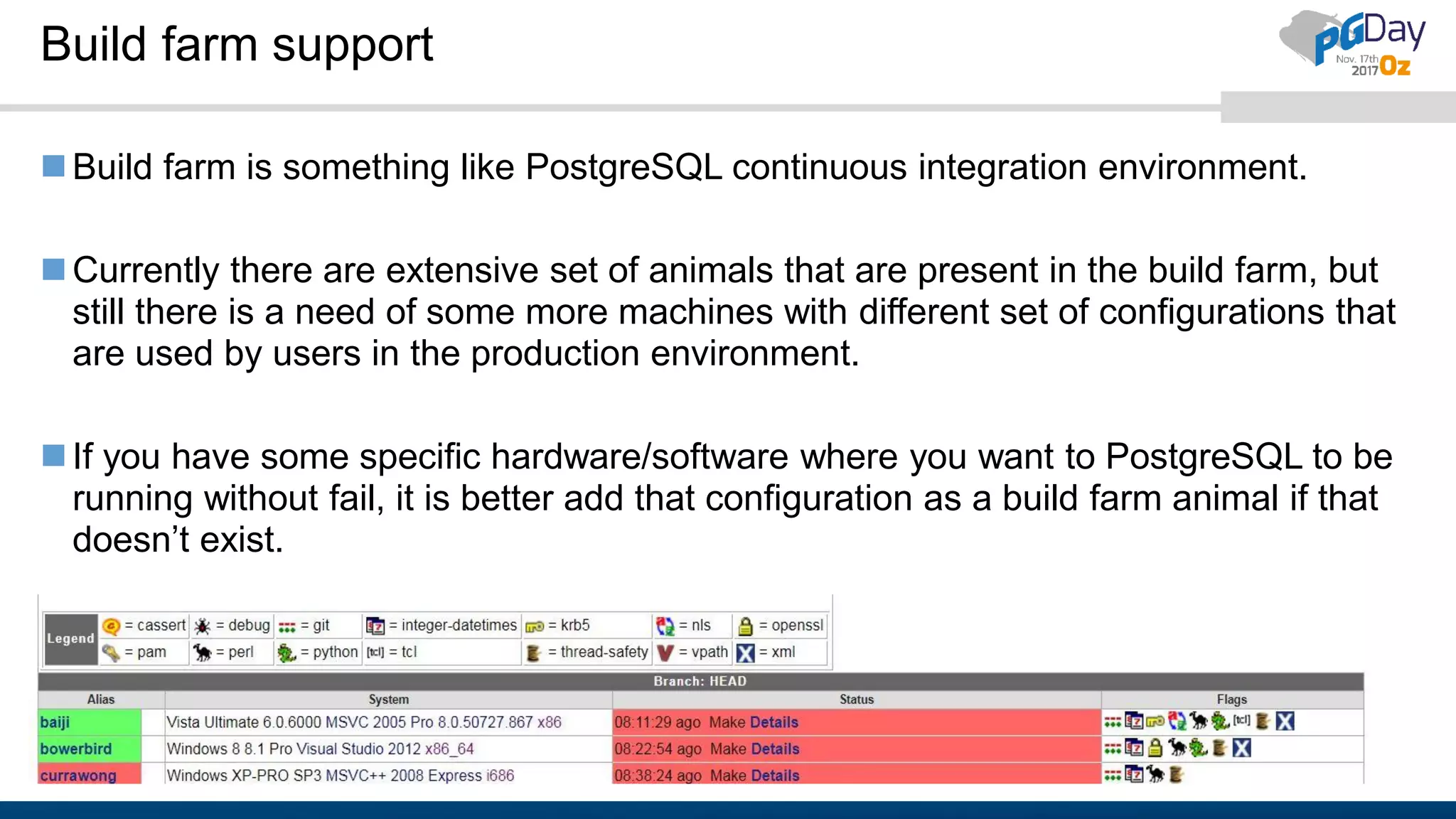
The document outlines the need for contributions to the PostgreSQL community, highlighting its status as a leading open-source database and the various methods through which individuals and companies can contribute, such as donations, documentation, and bug reporting. It discusses the benefits of contributing, including recognition as a contributor or sponsor, and encourages participation in events and surveys to strengthen community engagement. Additionally, the document provides resources and links for potential contributors to access further information and facilitate their involvement.