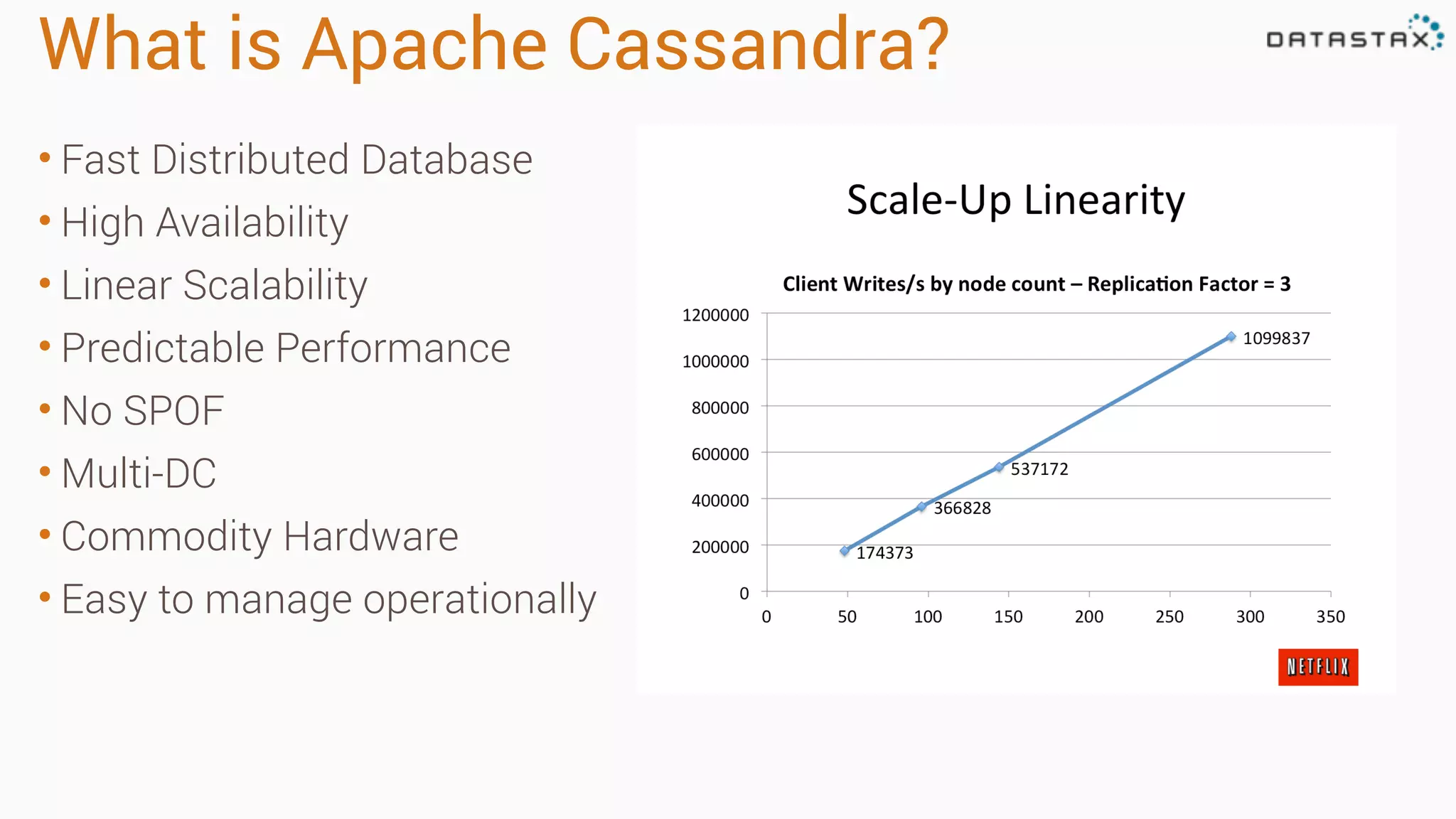
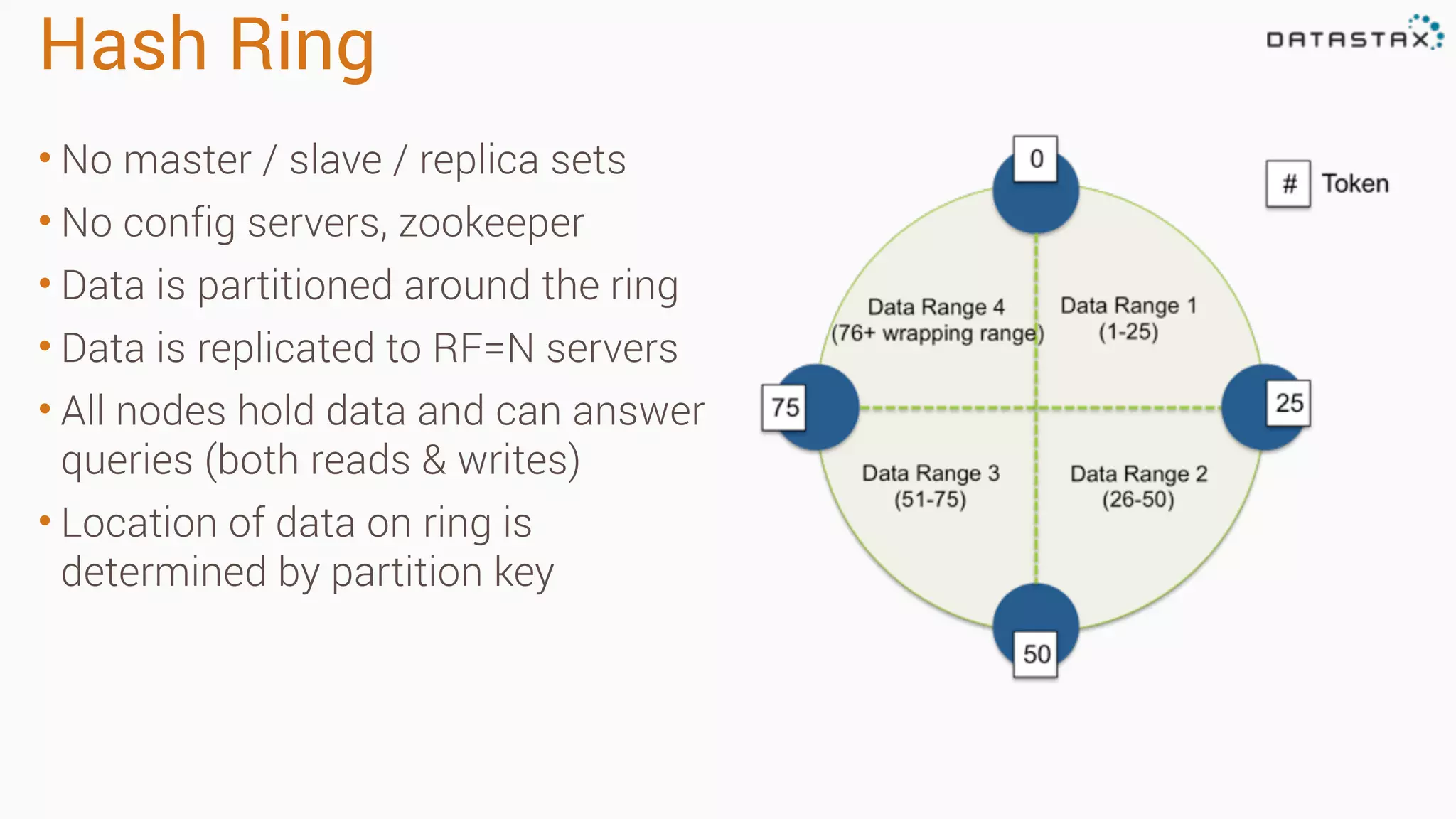
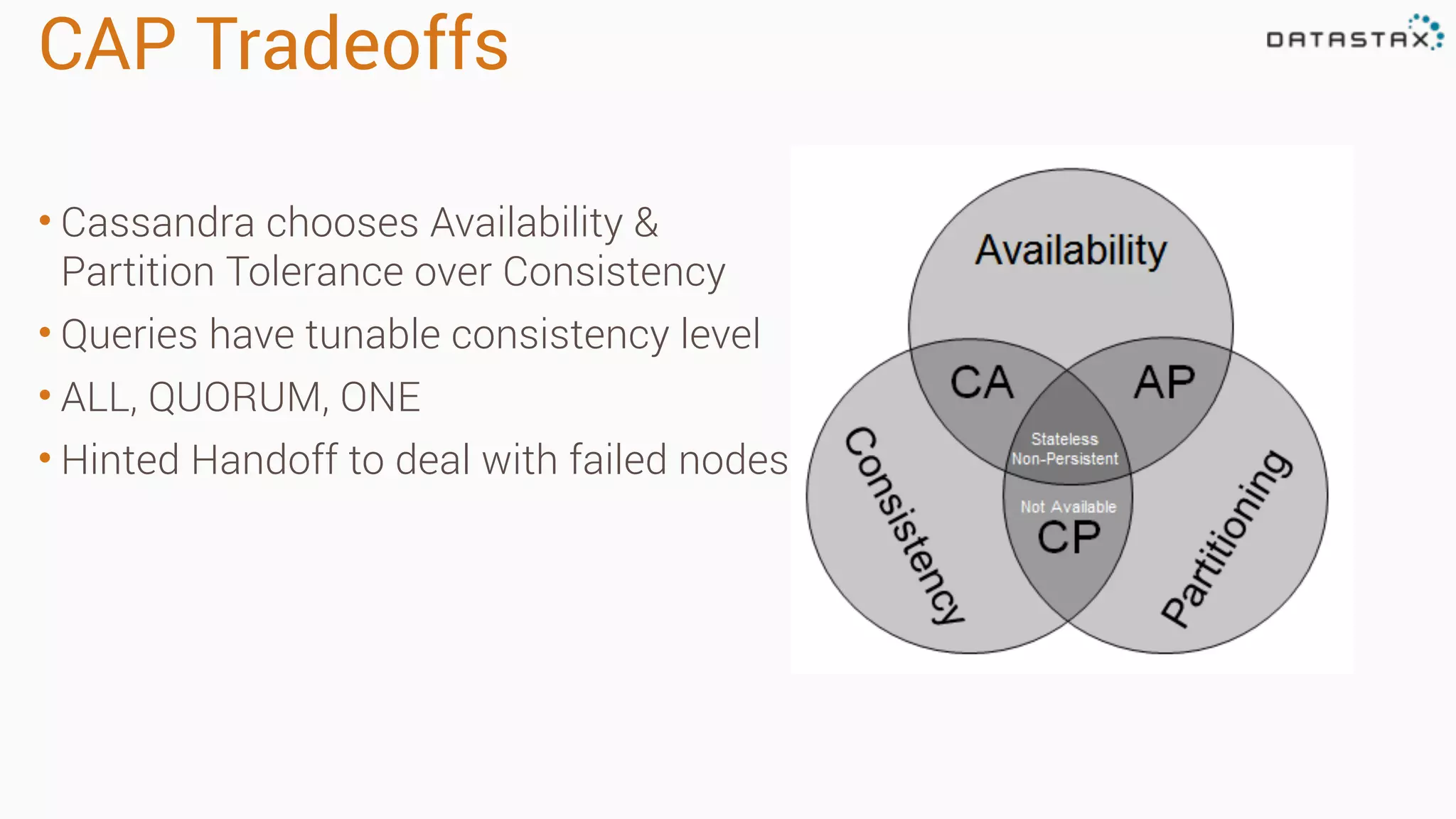
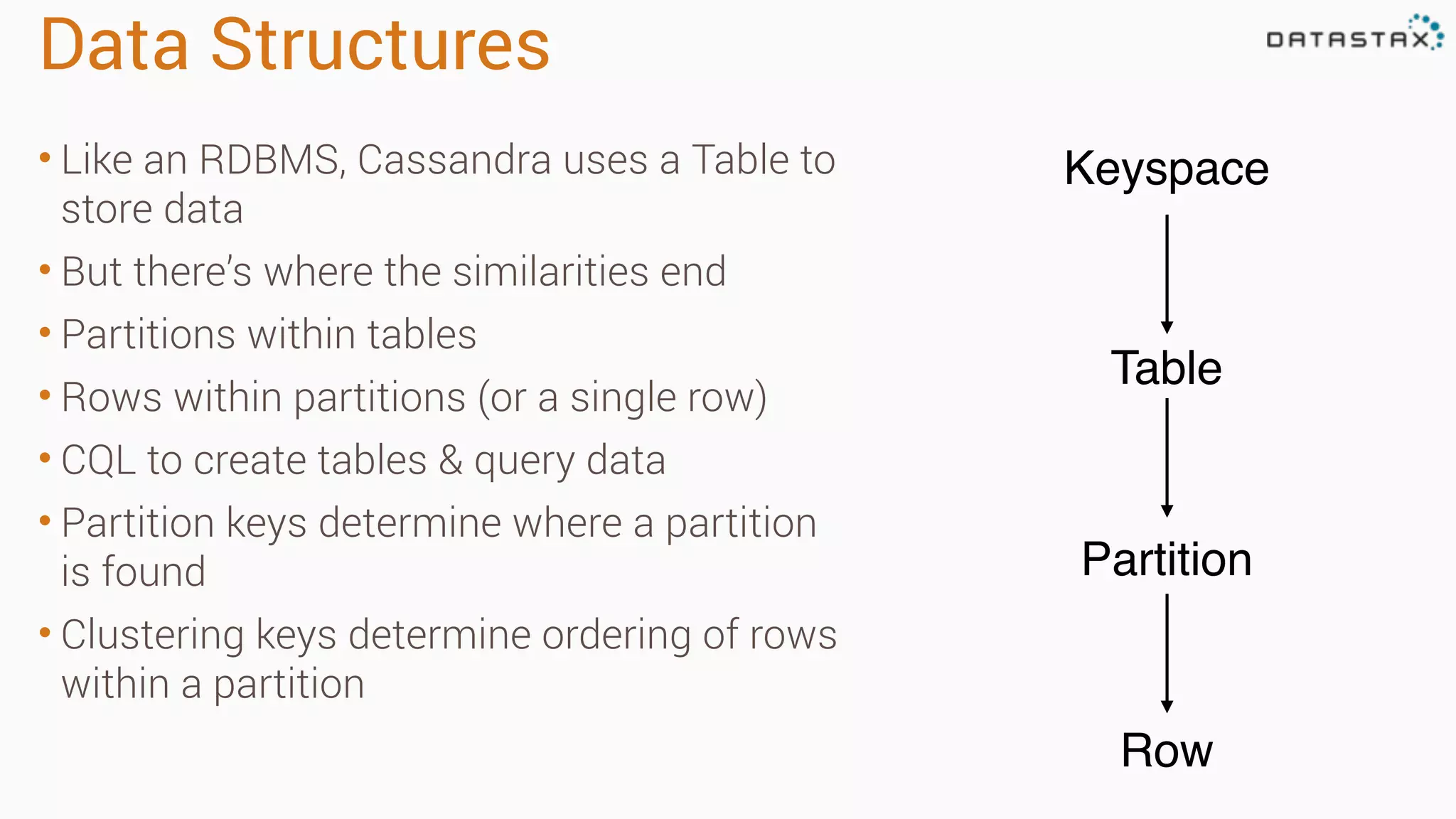
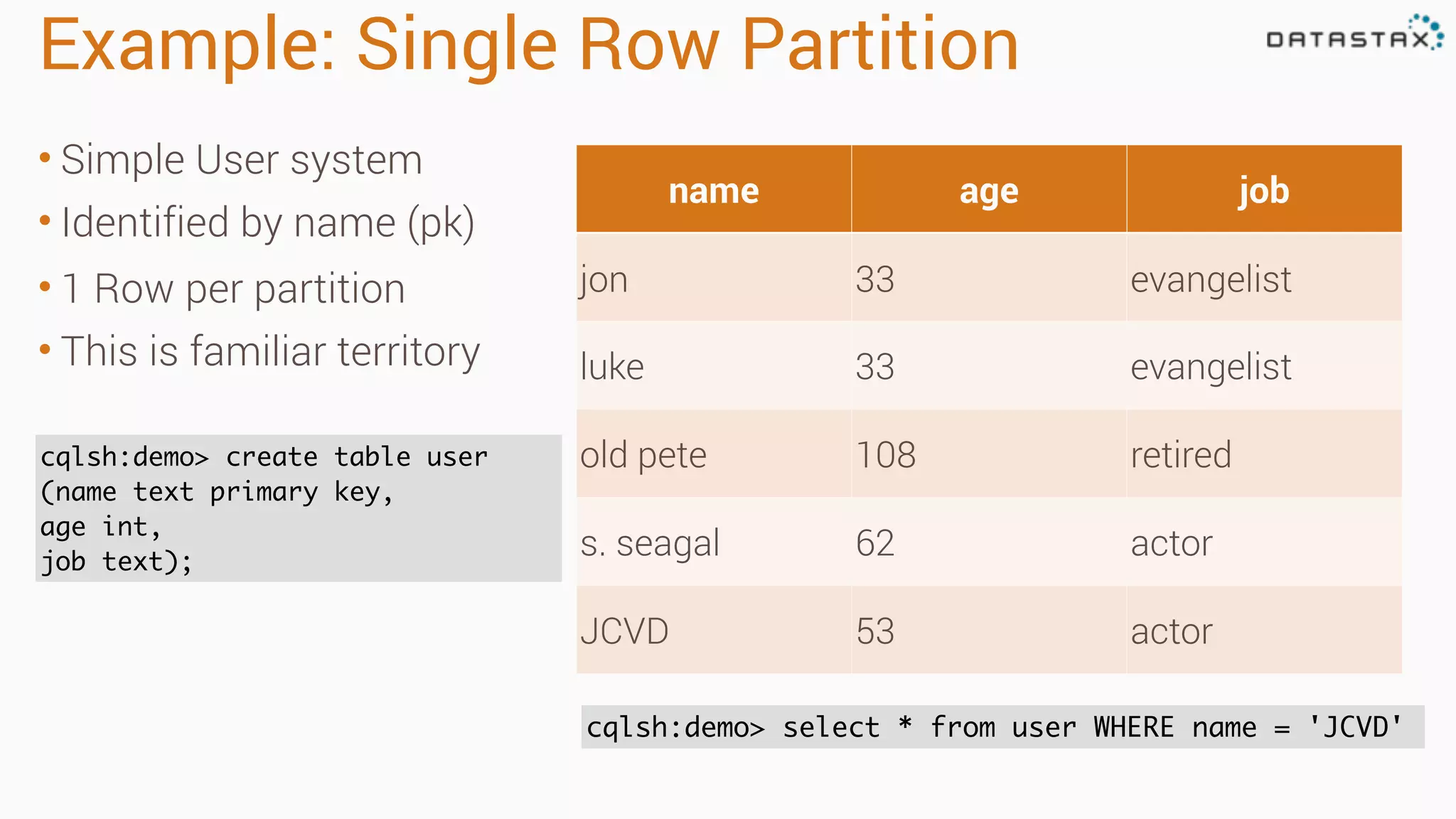
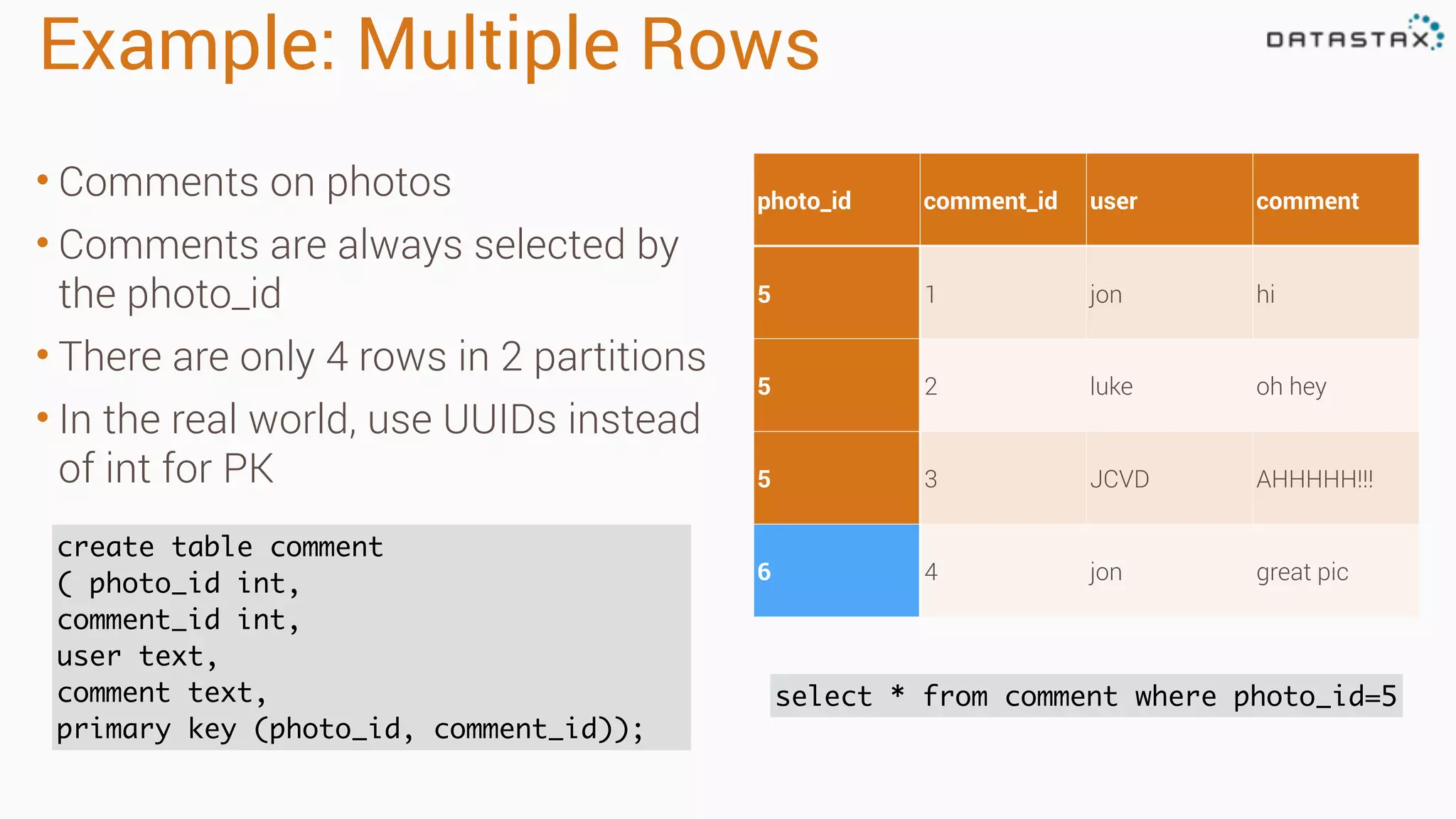
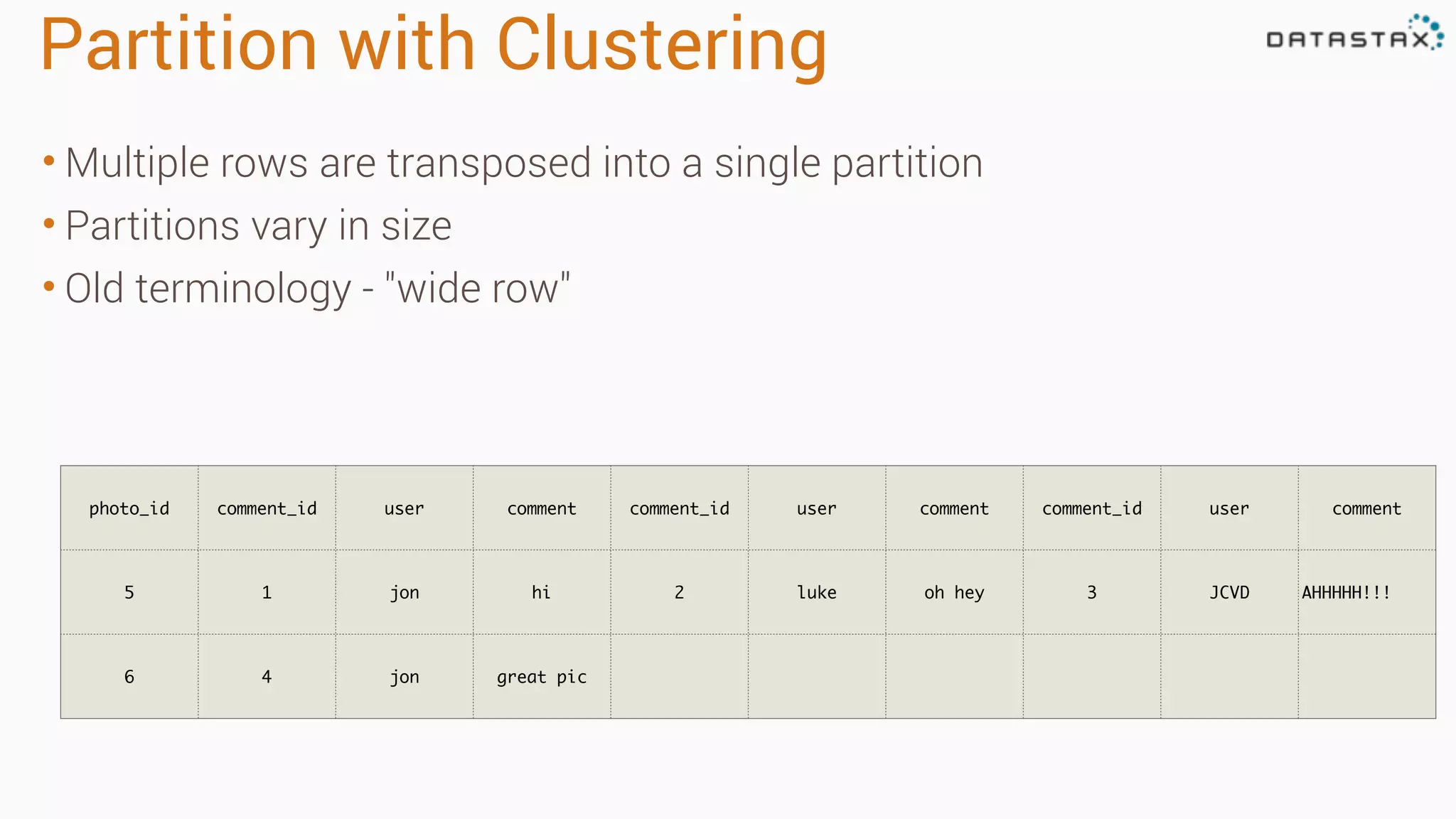
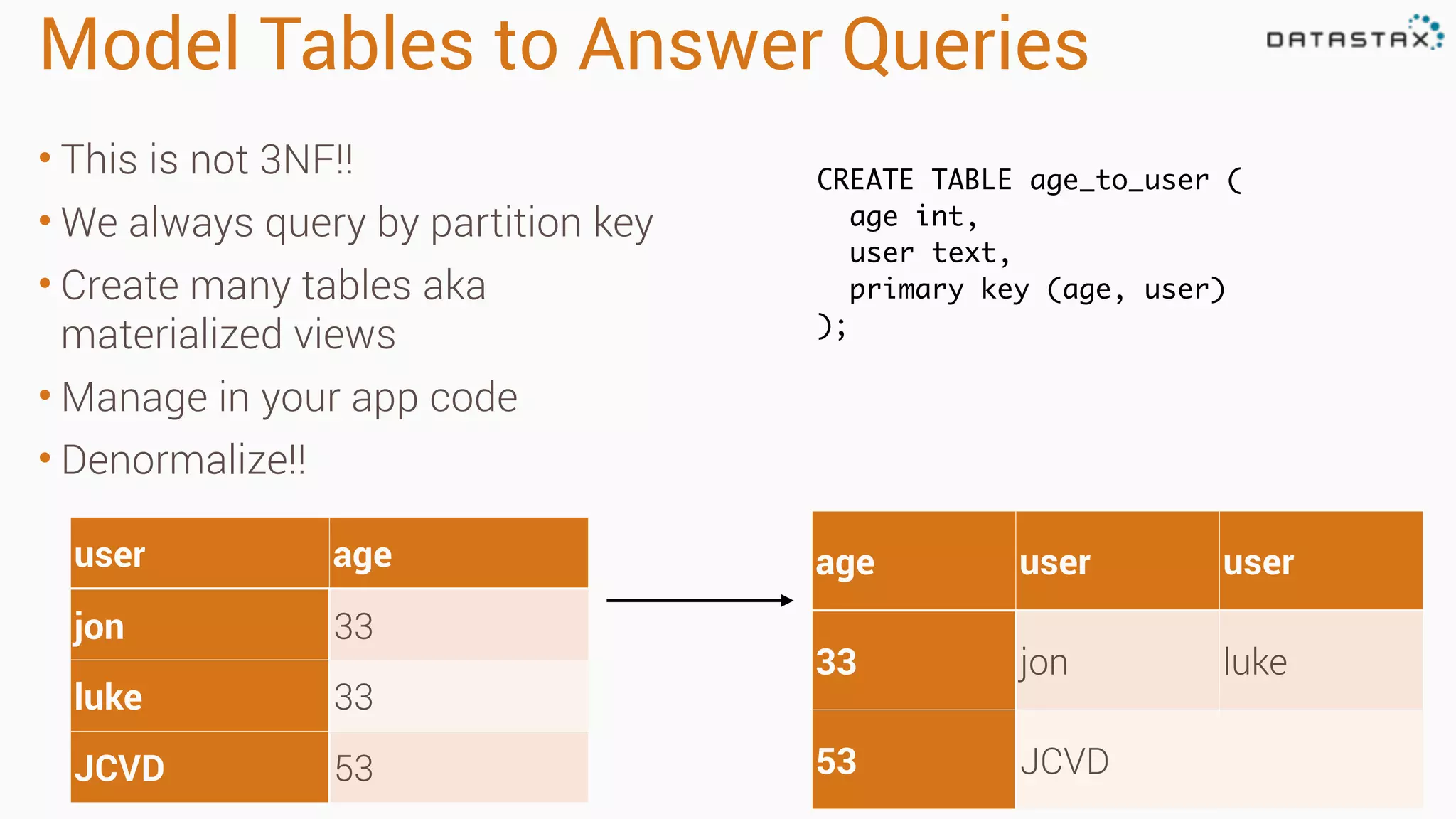
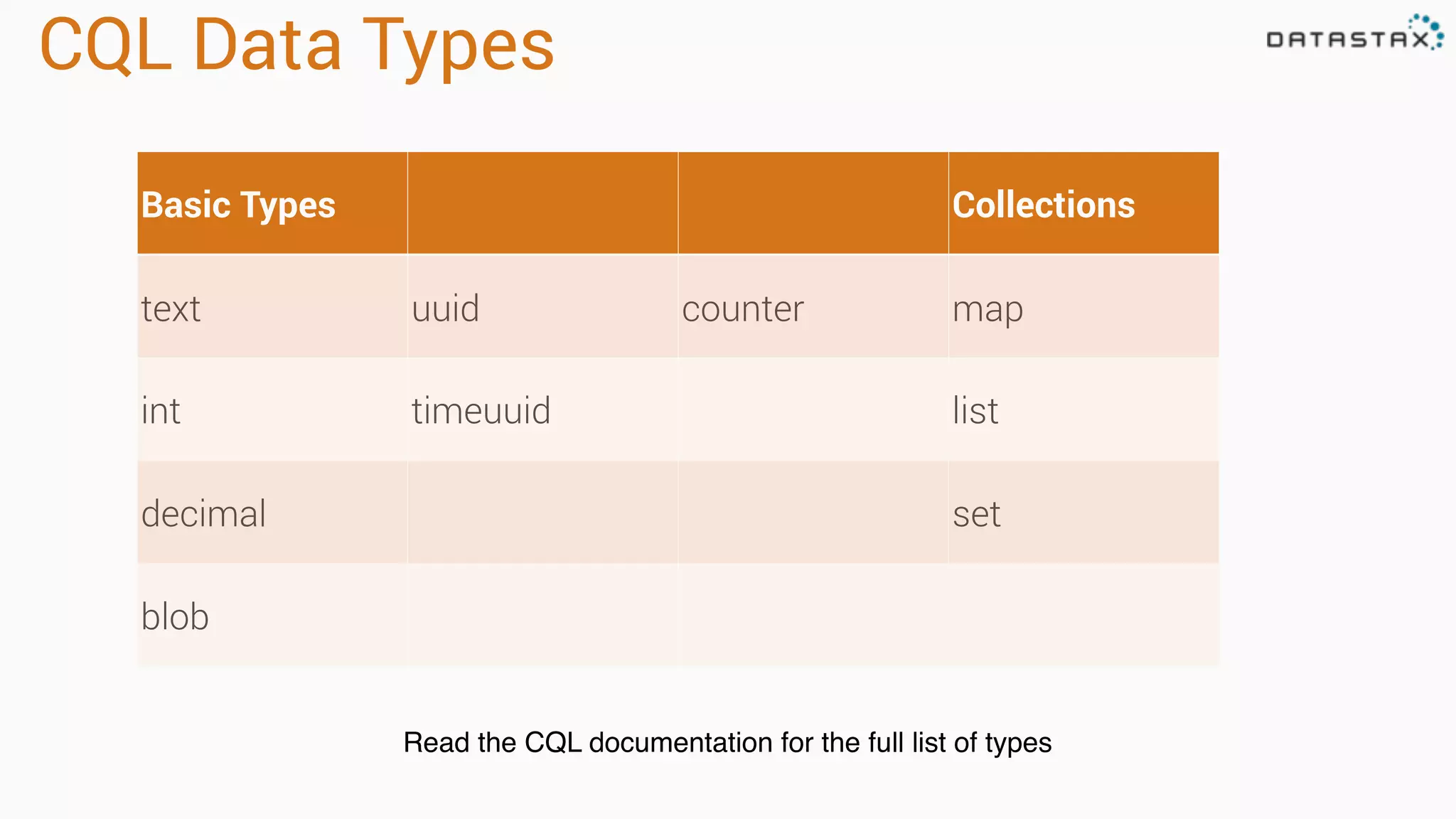
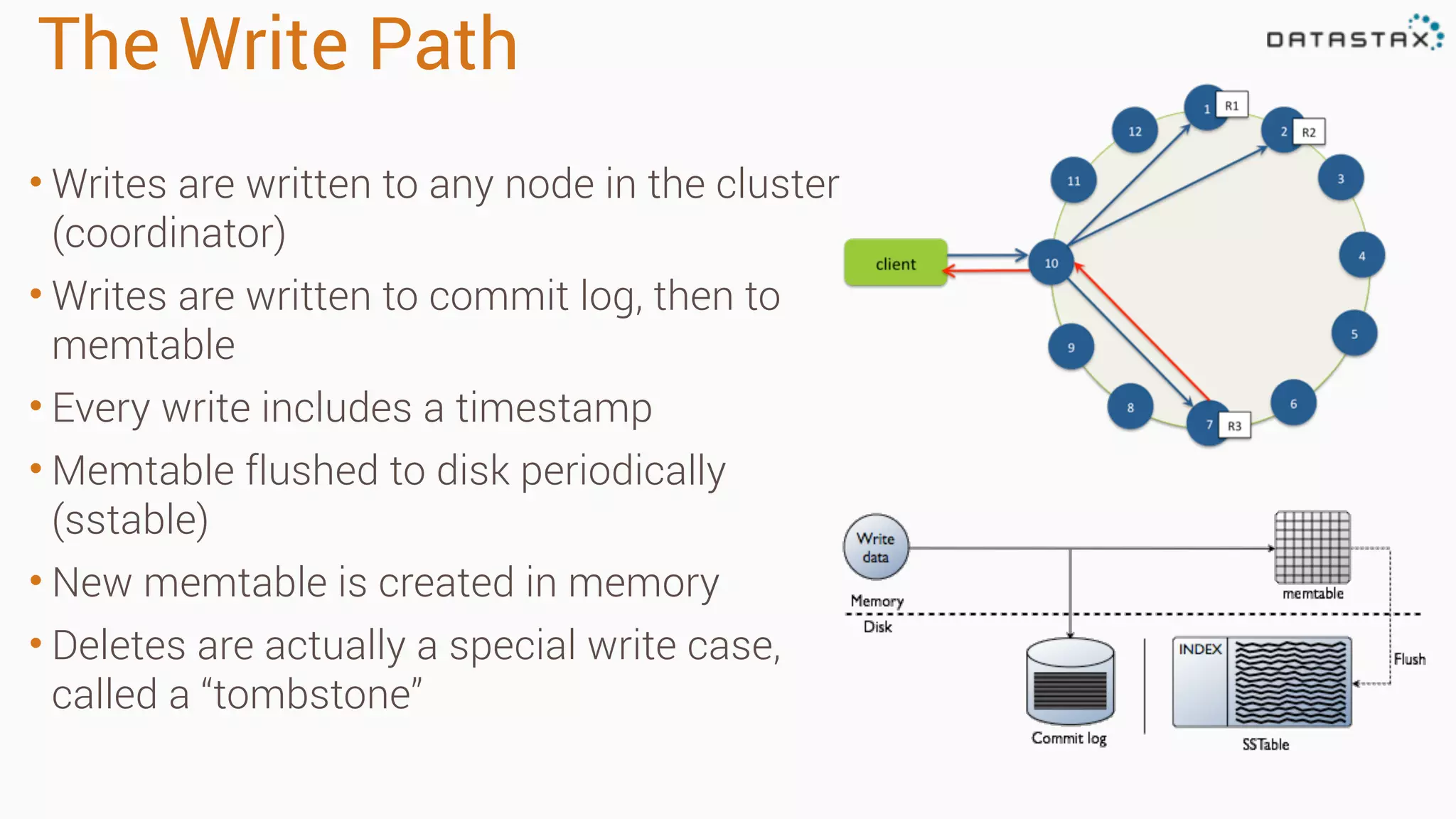
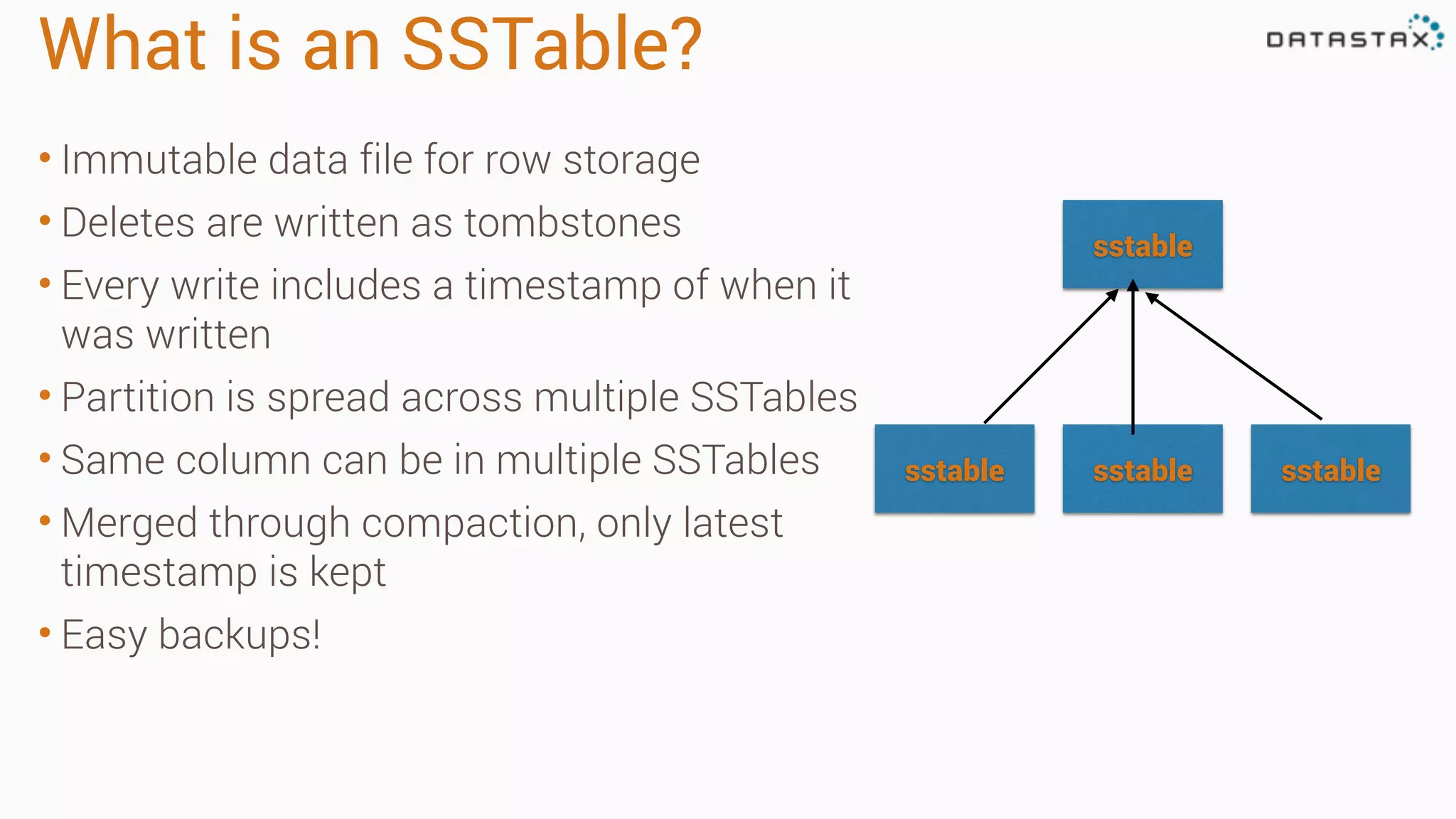
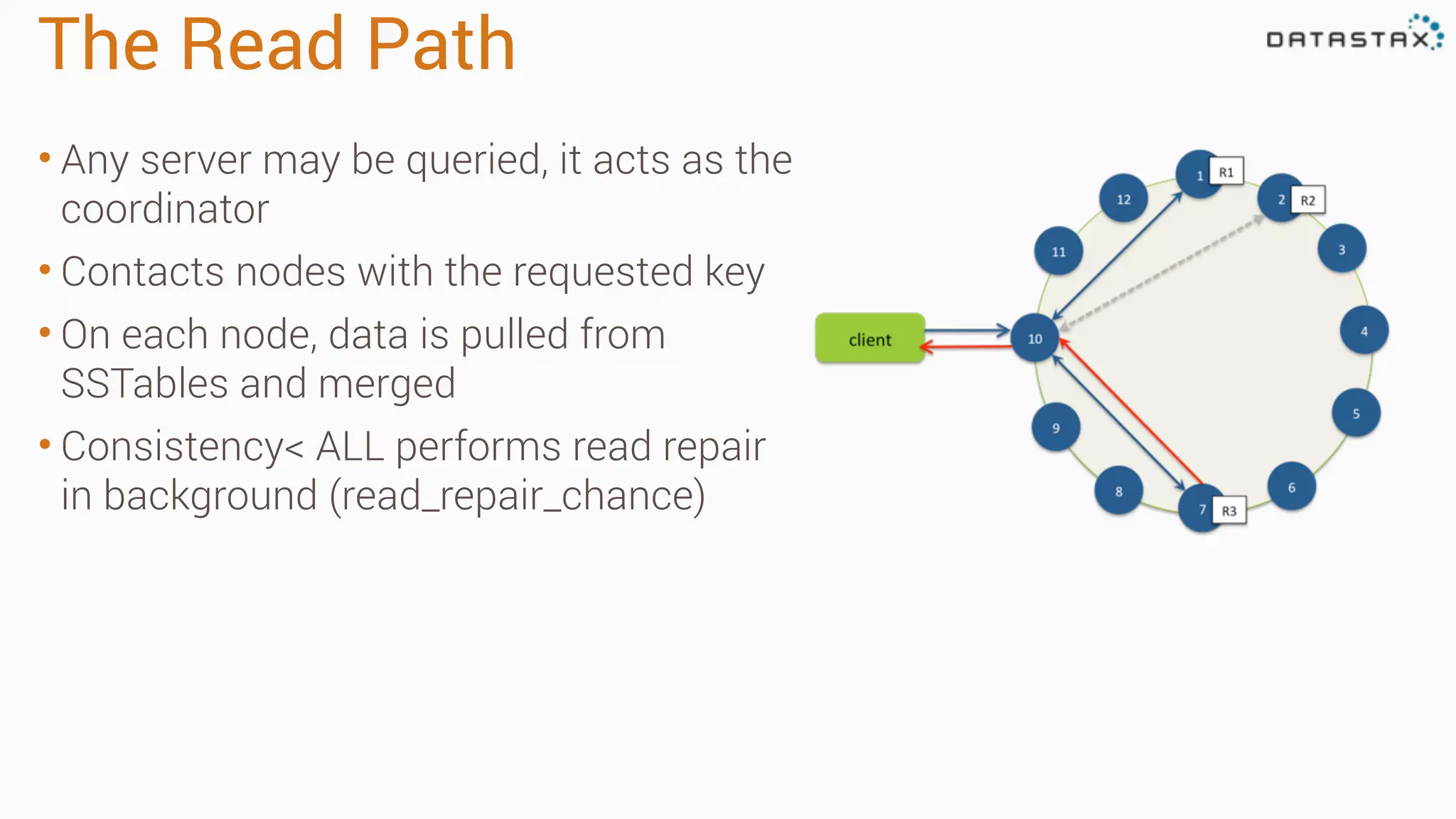
Apache Cassandra is a fast, distributed database designed for high availability and linear scalability, allowing for predictable performance without single points of failure. It utilizes a unique data modeling approach that leverages partitions and clustering keys, enabling tunable consistency levels for queries. Additionally, it integrates with Apache Spark for advanced analytics and real-time processing.