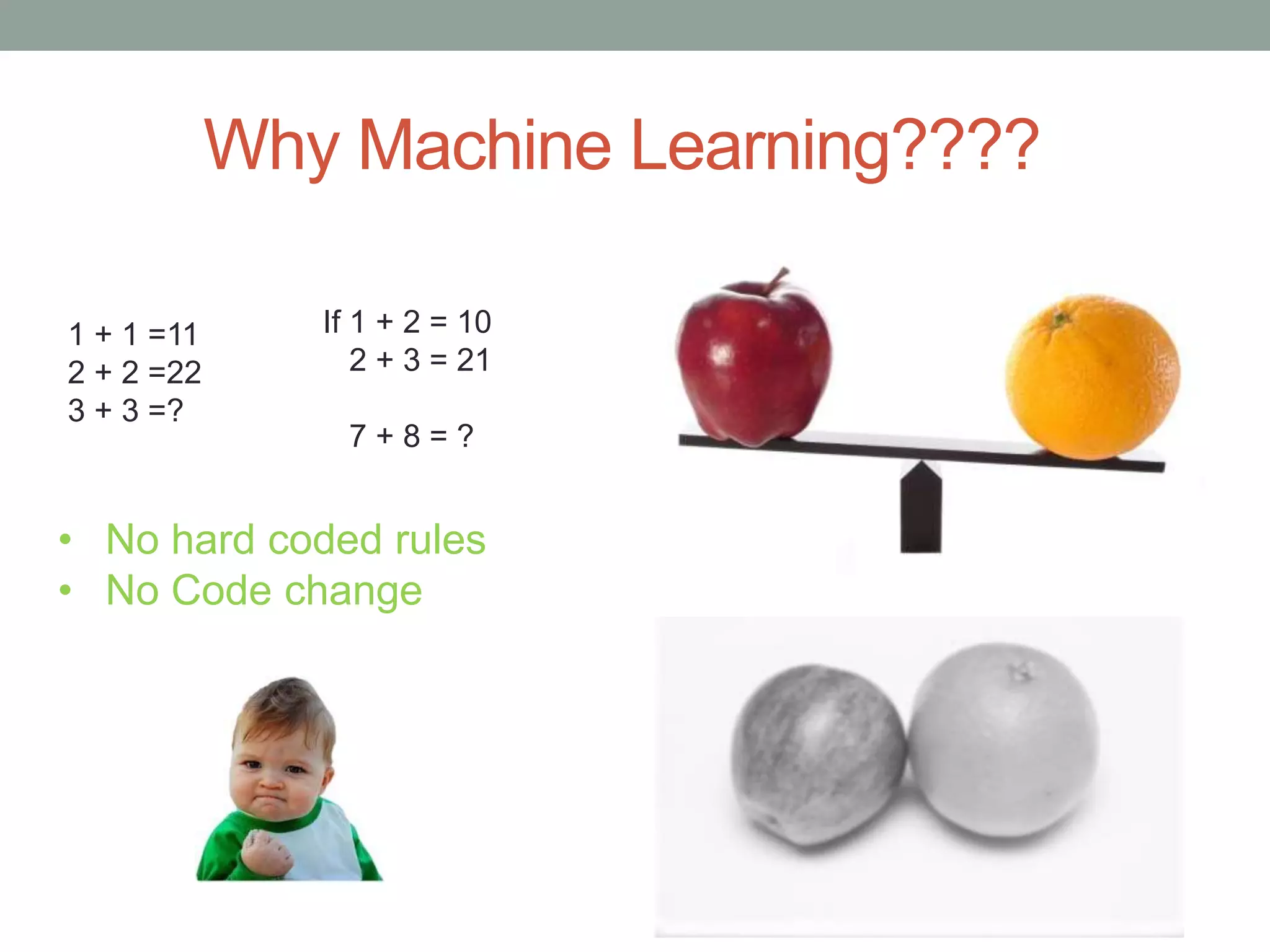
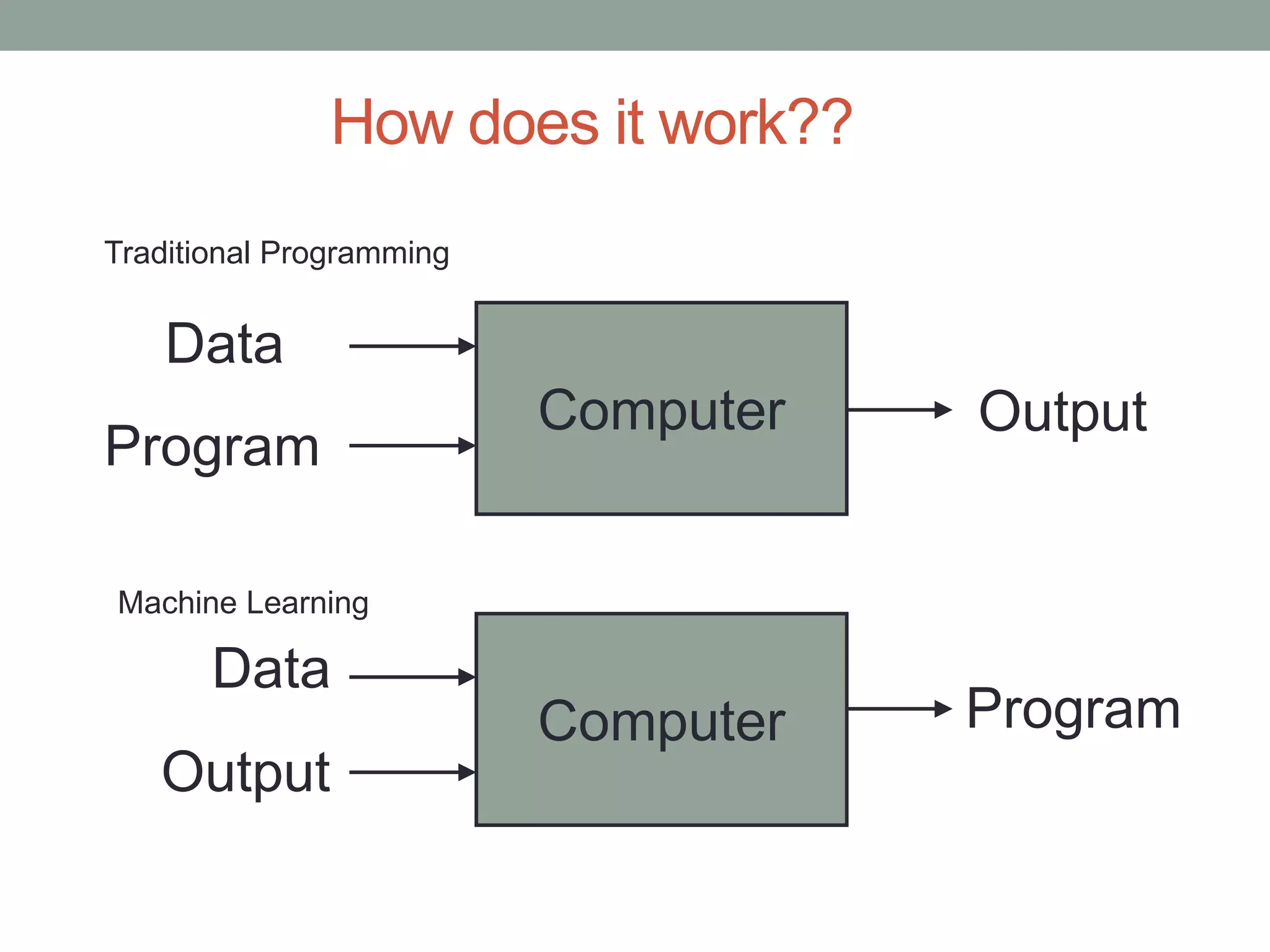
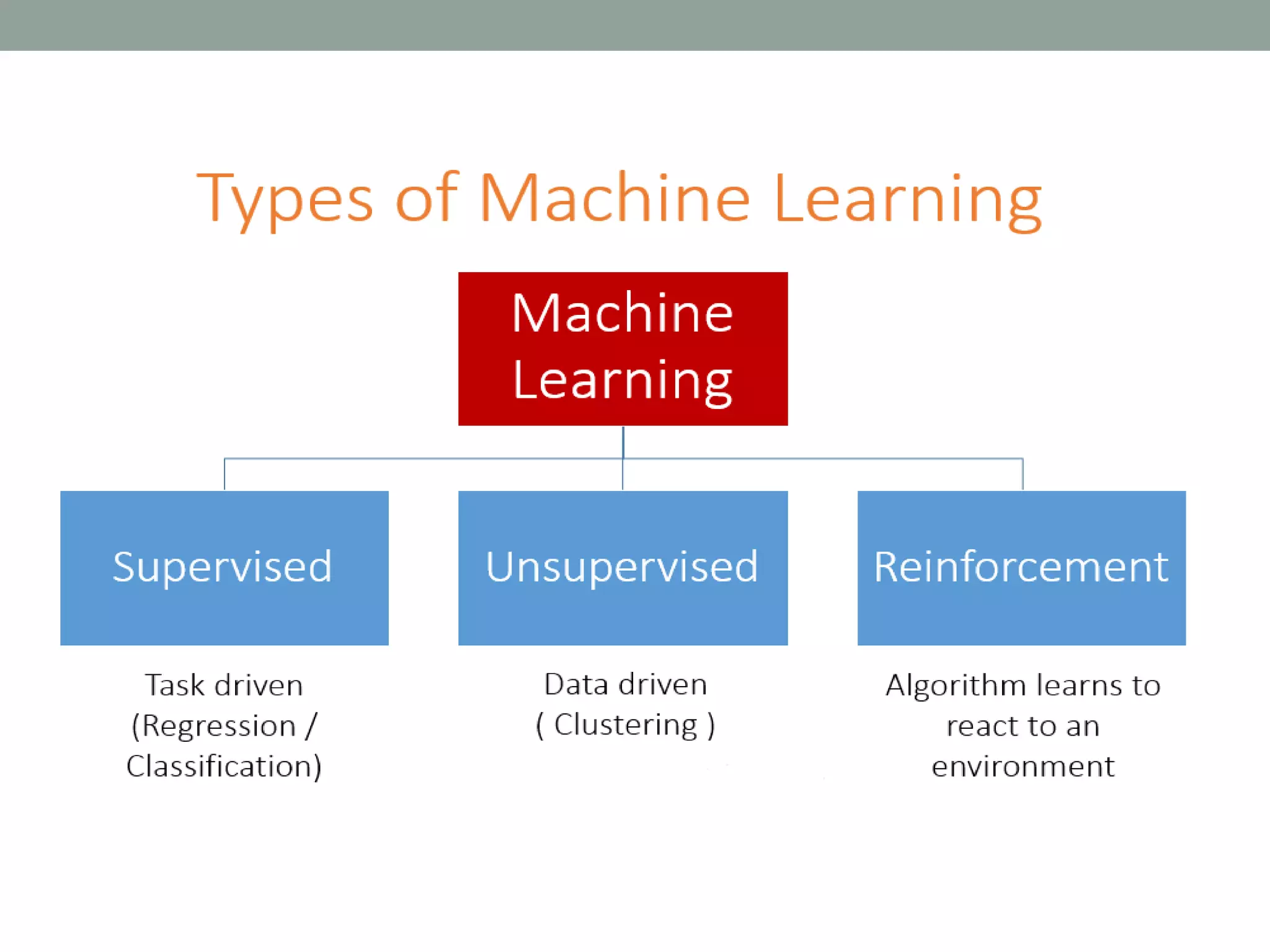
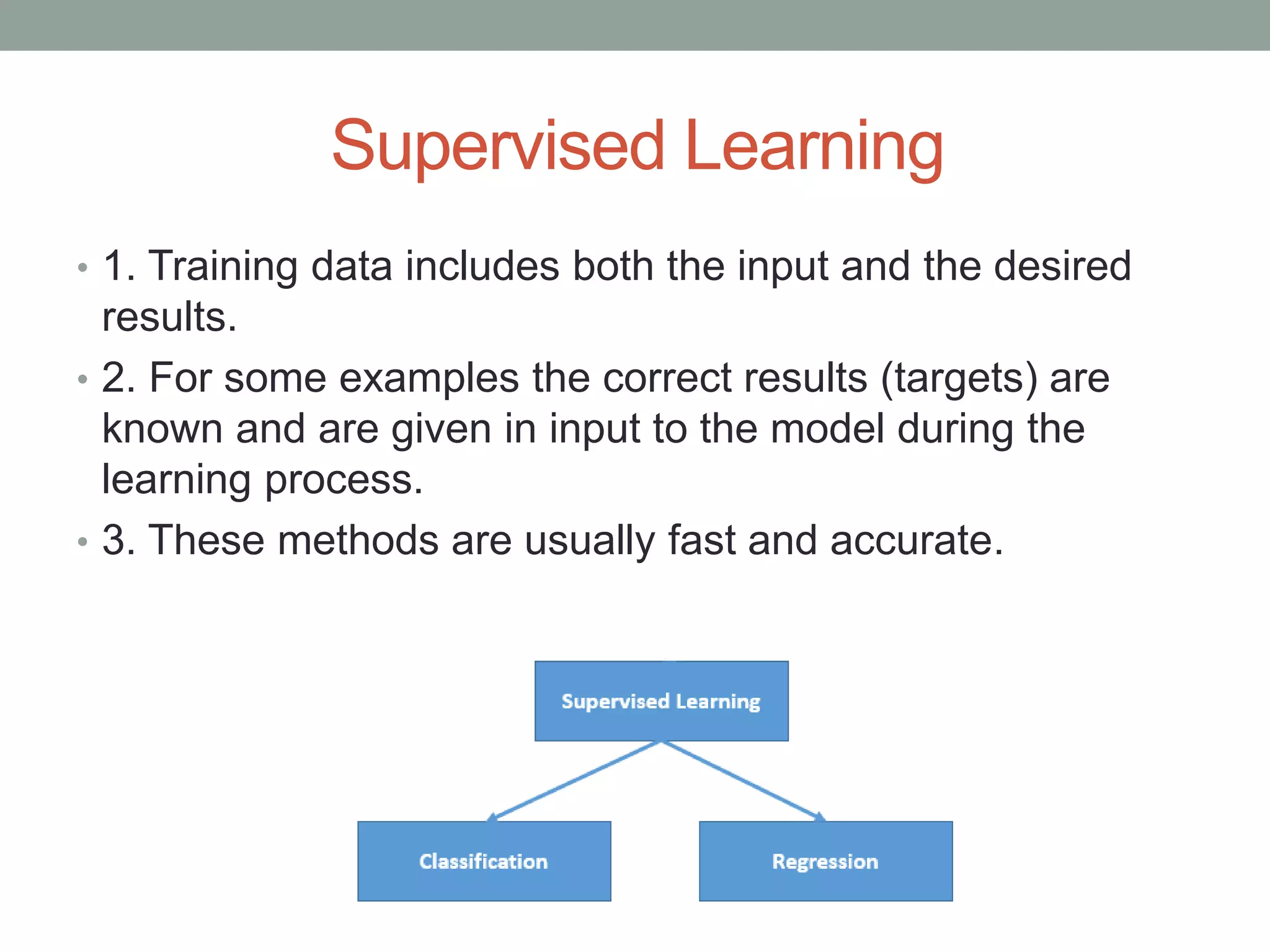
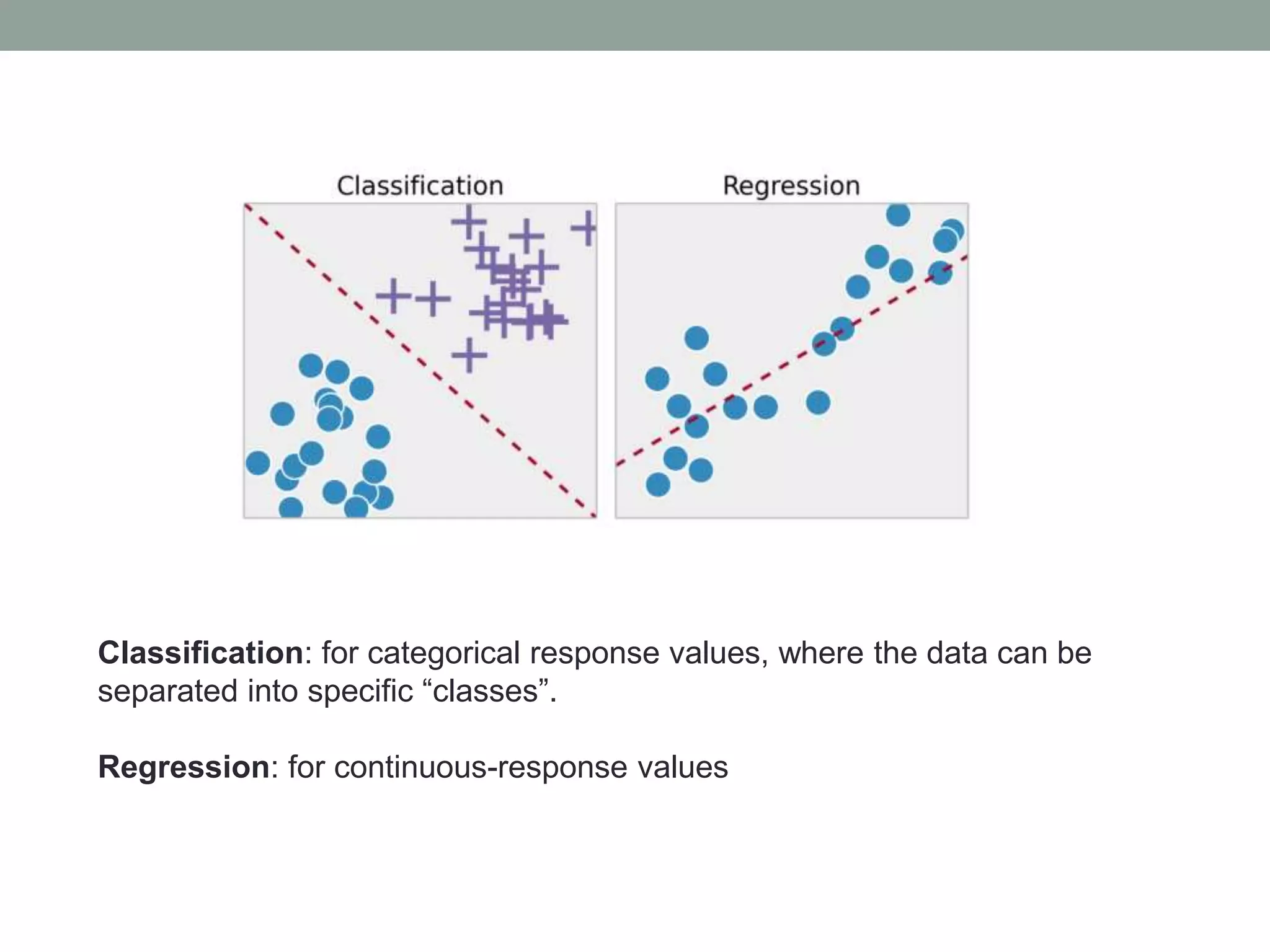
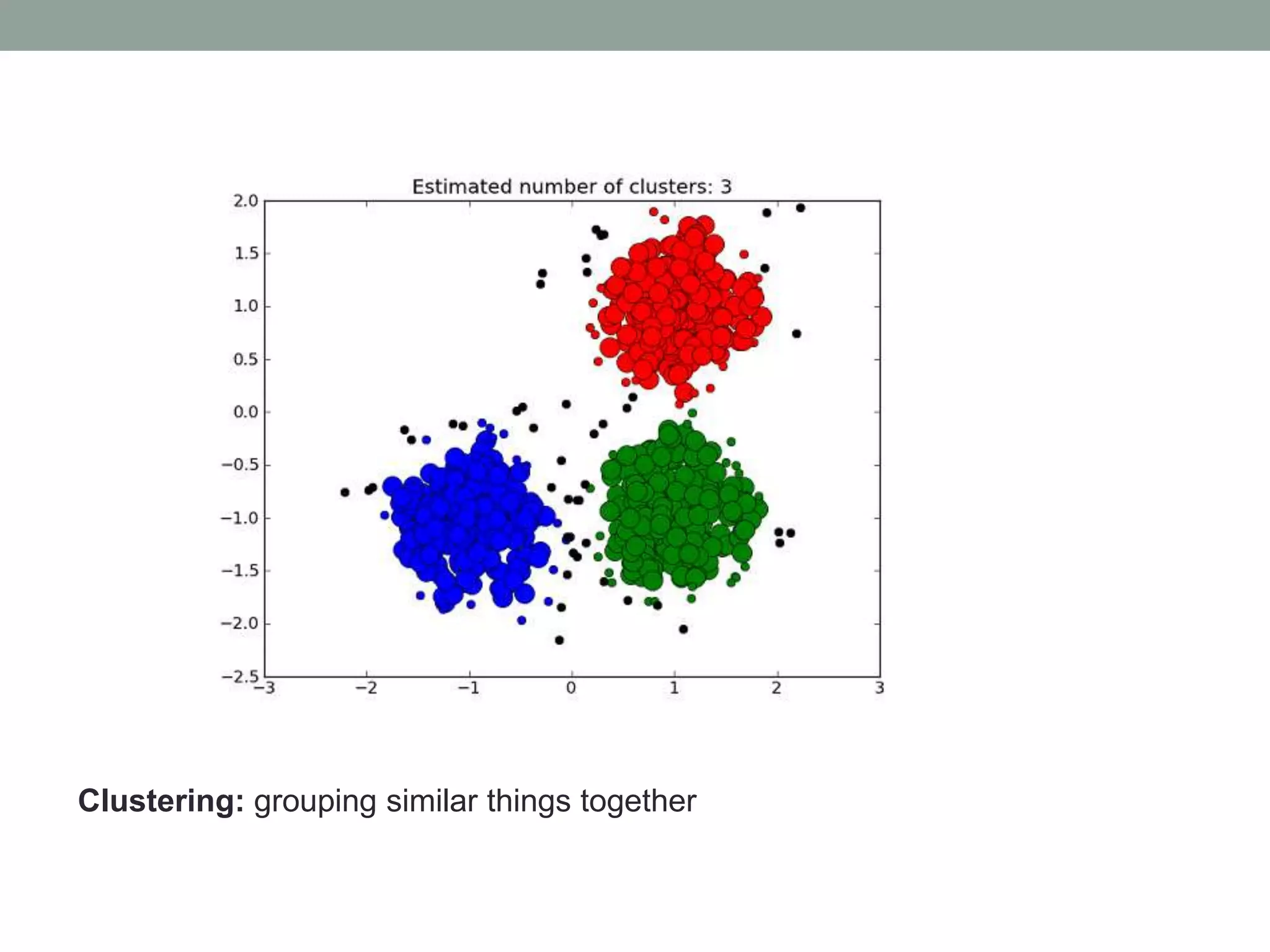
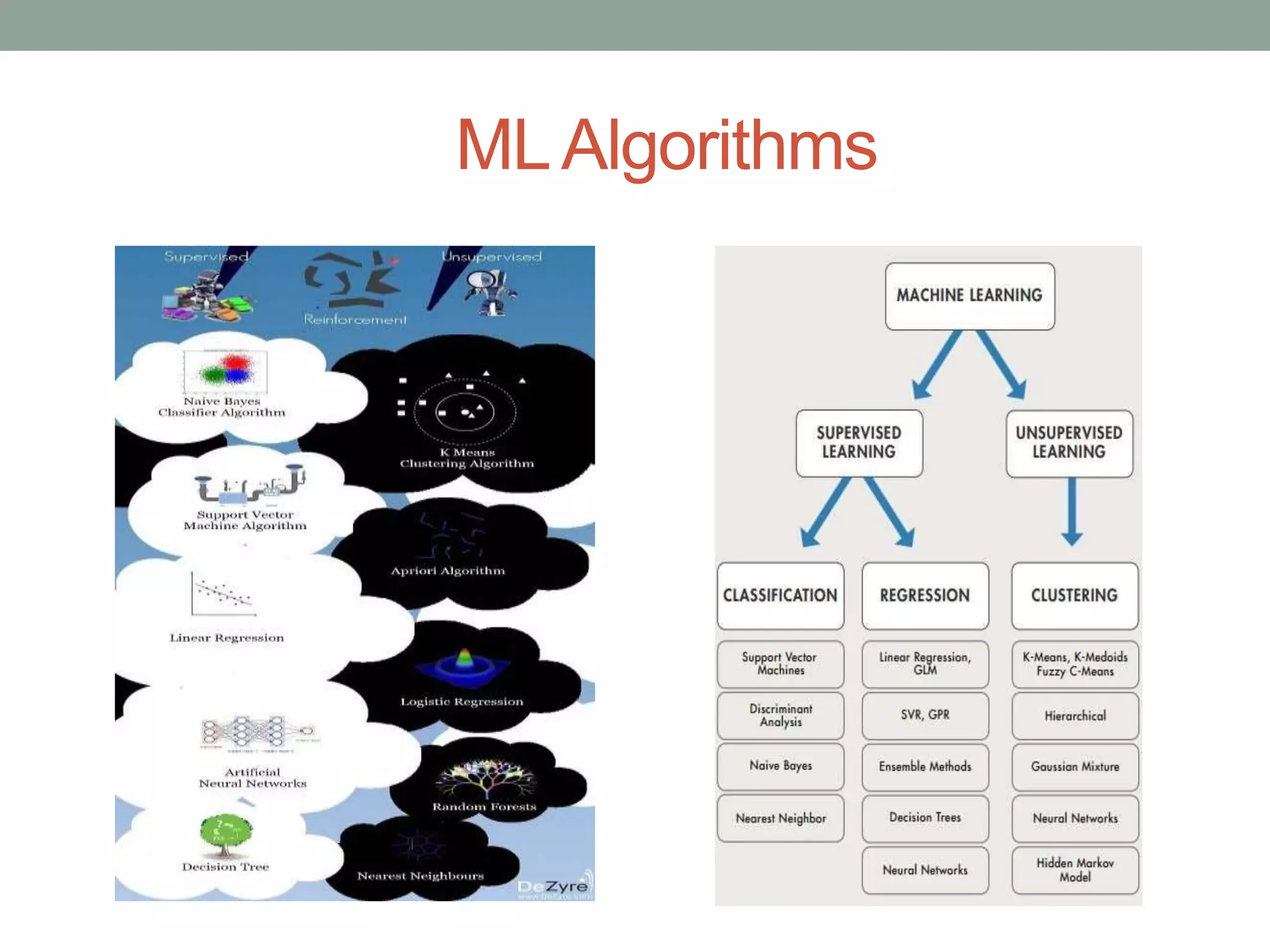
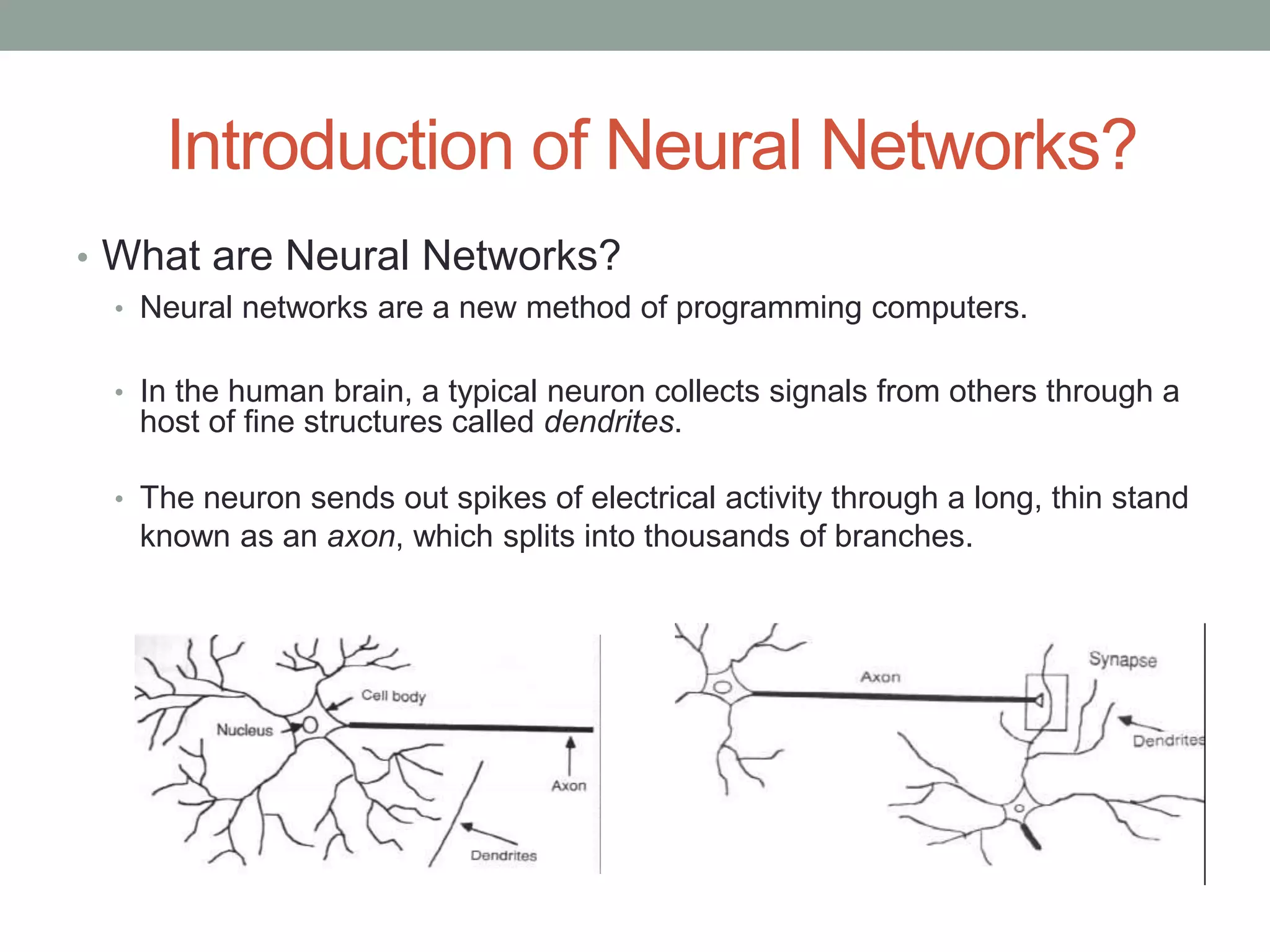
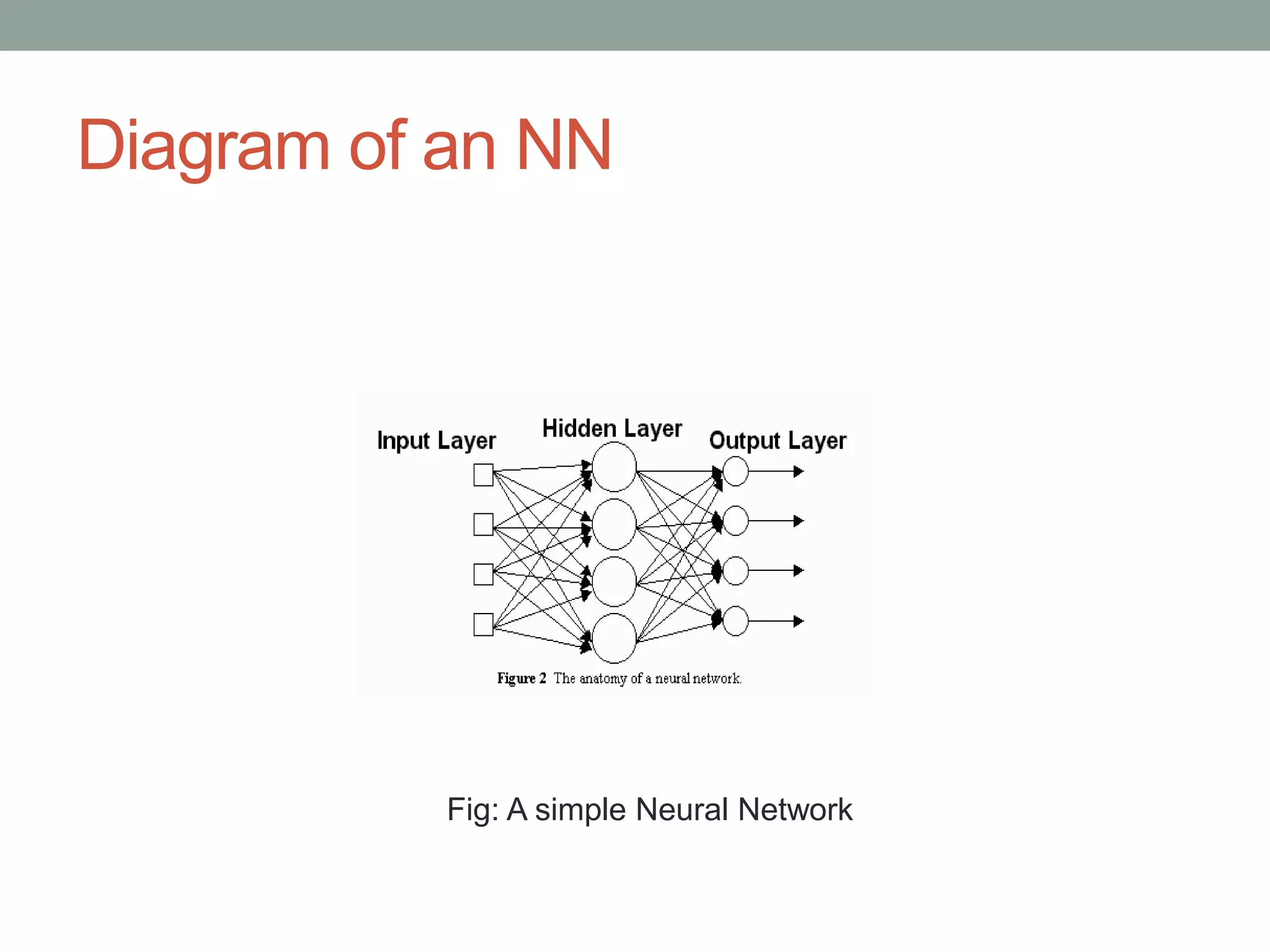
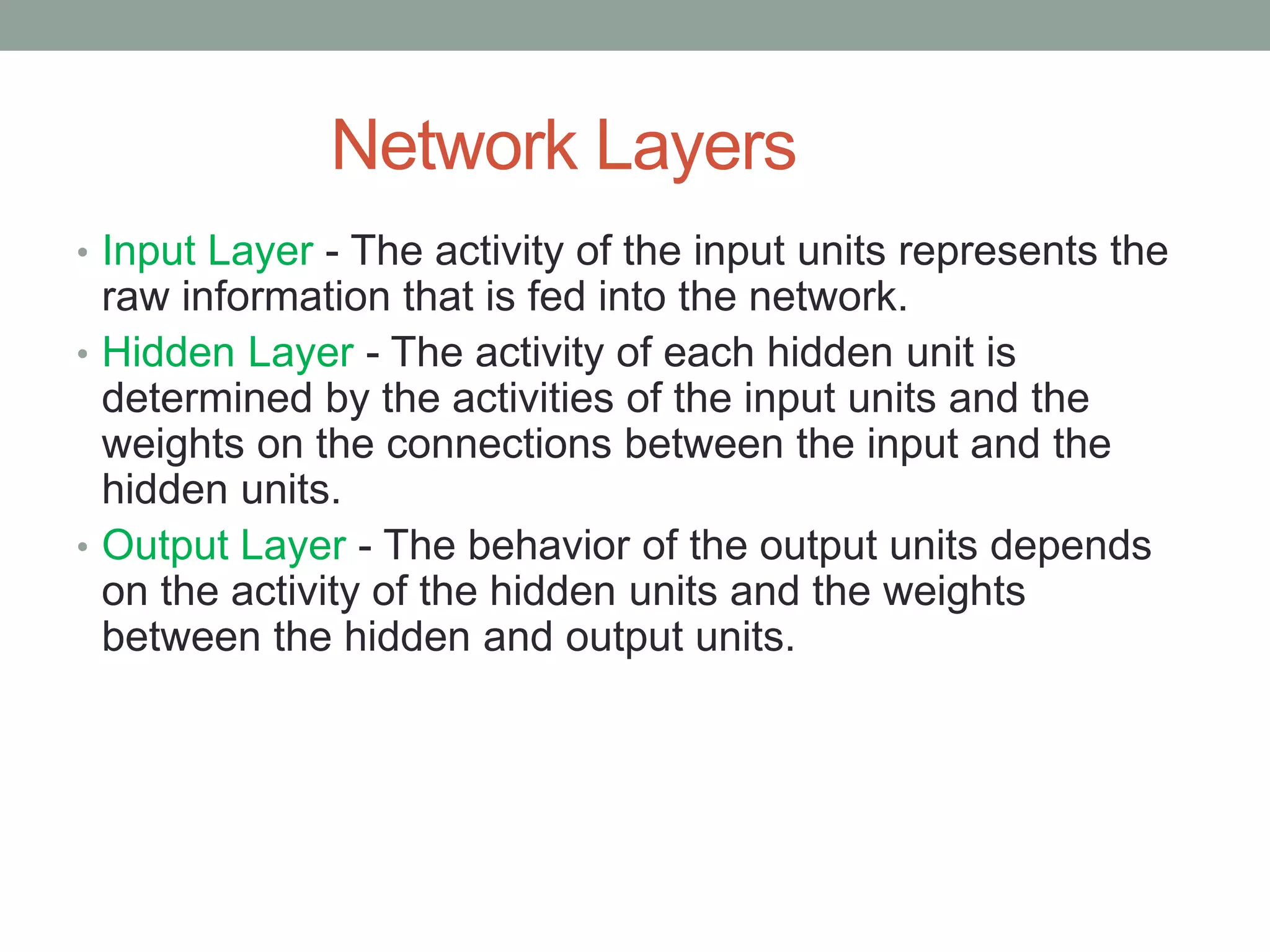
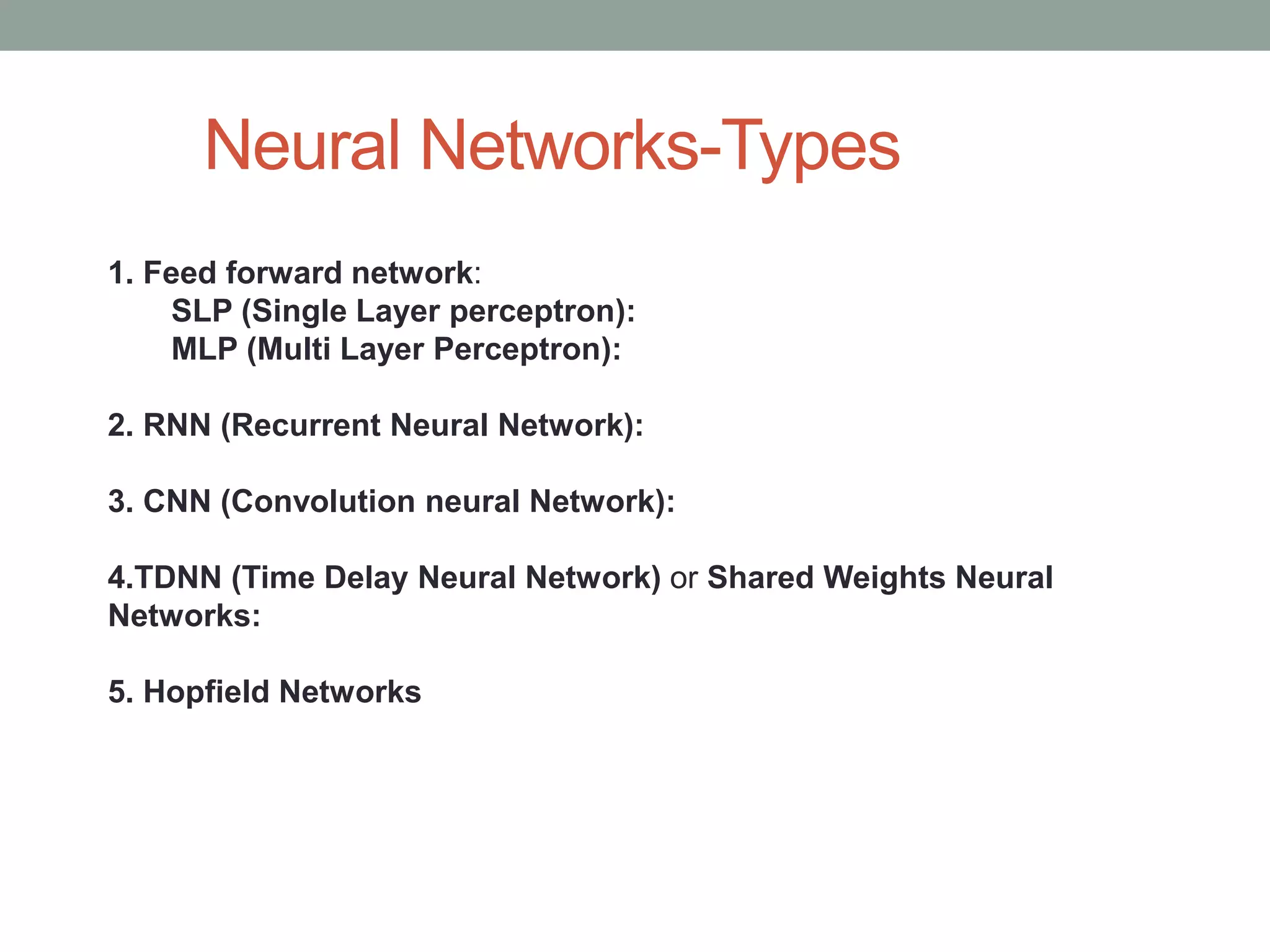
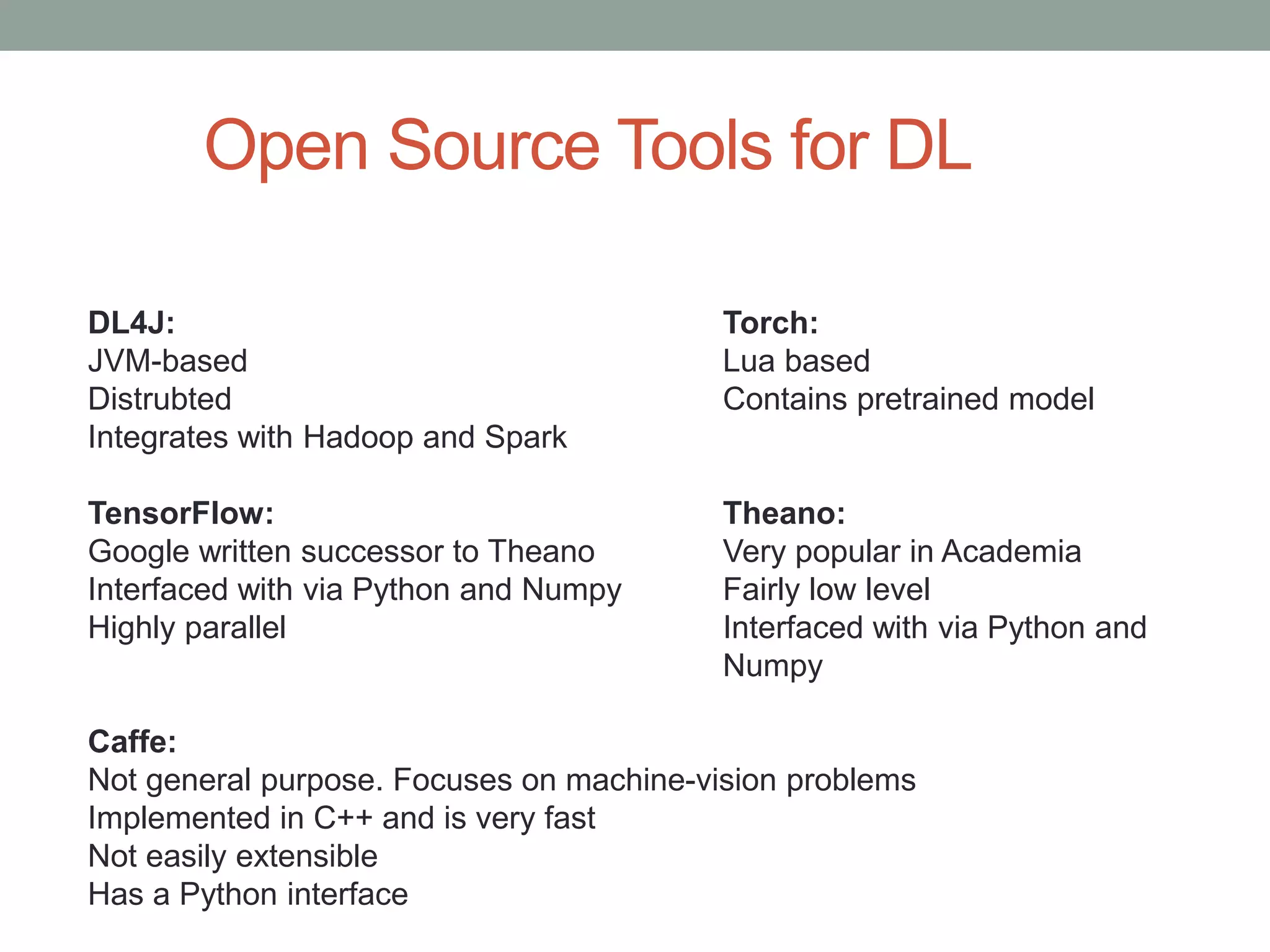
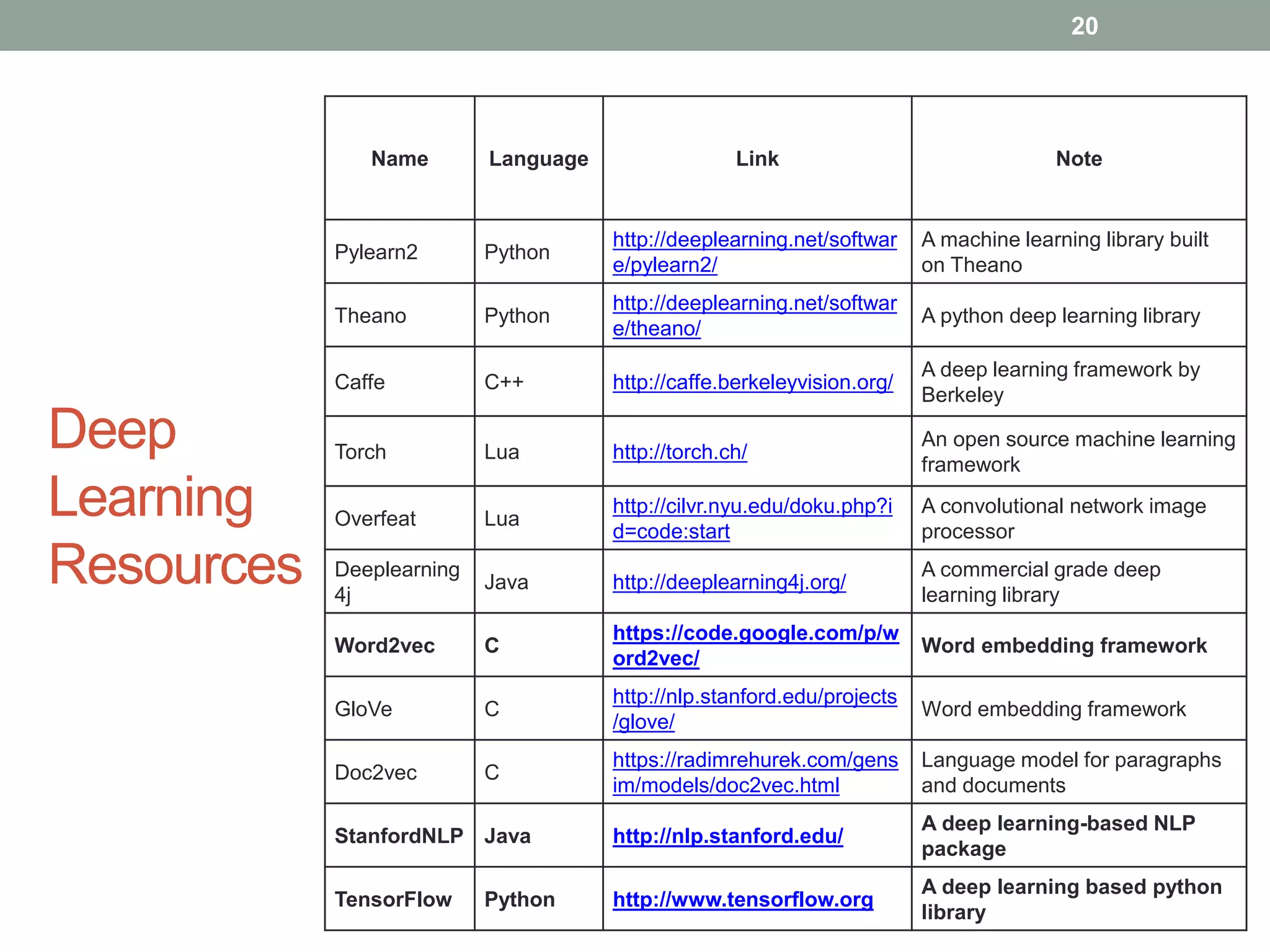
The document provides an overview of machine learning and deep learning, detailing definitions, types of learning (supervised and unsupervised), and the concept of neural networks. It includes information on various algorithms, applications across different domains, and a list of open-source tools available for deep learning development. Key topics discussed include neural network architecture, learning methods, and examples of real-world applications such as spam filtering and recommendation engines.