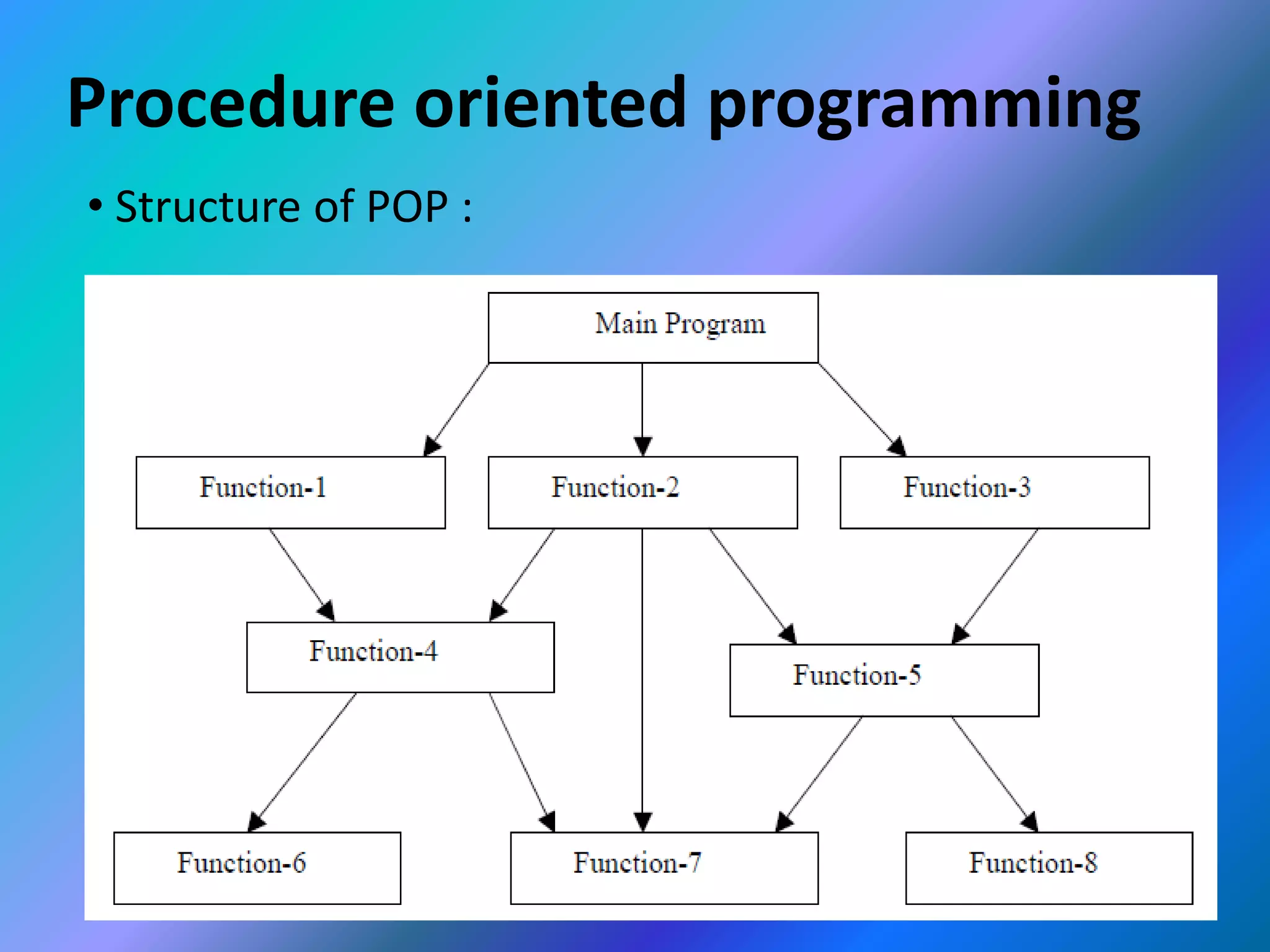
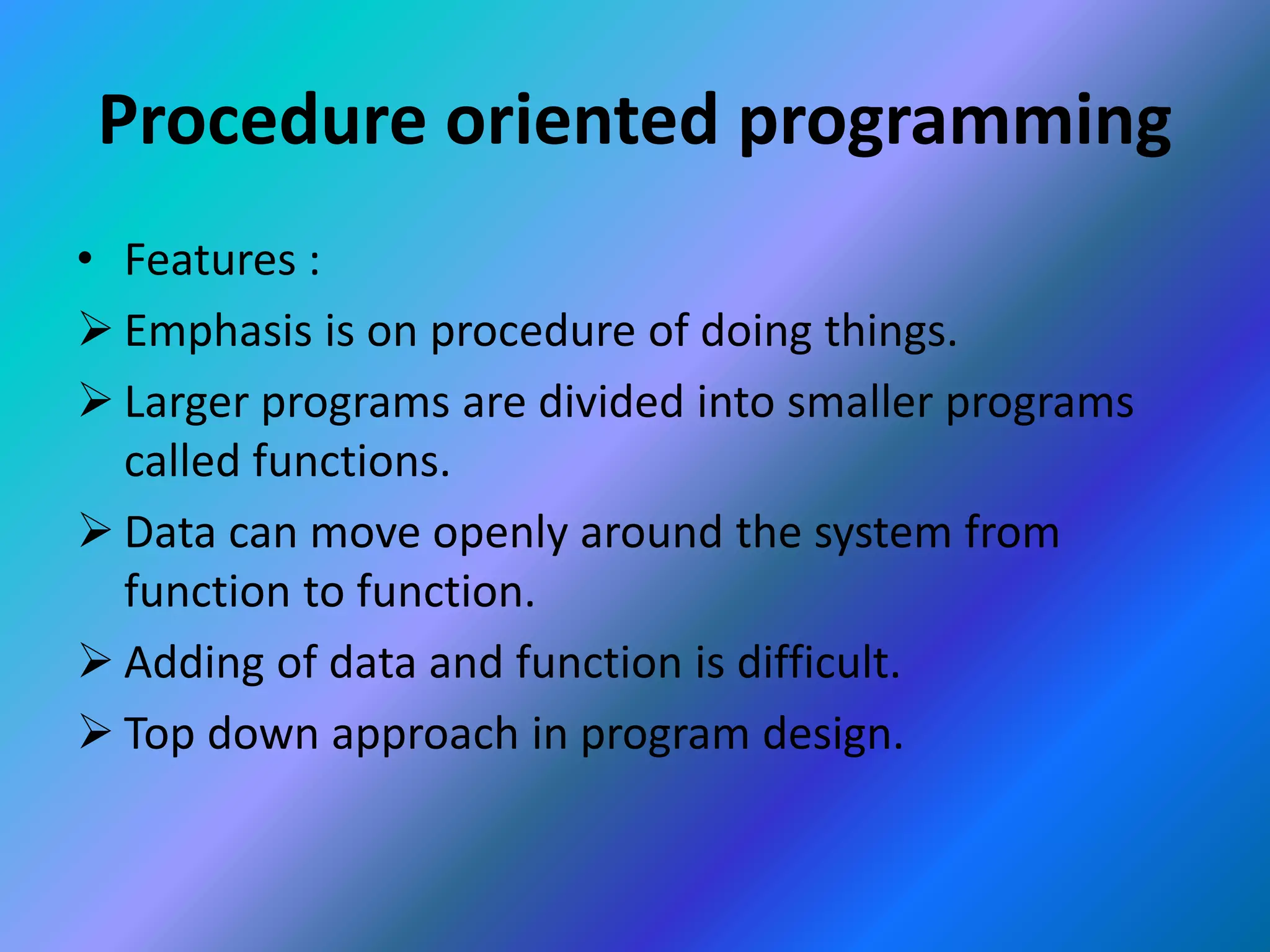
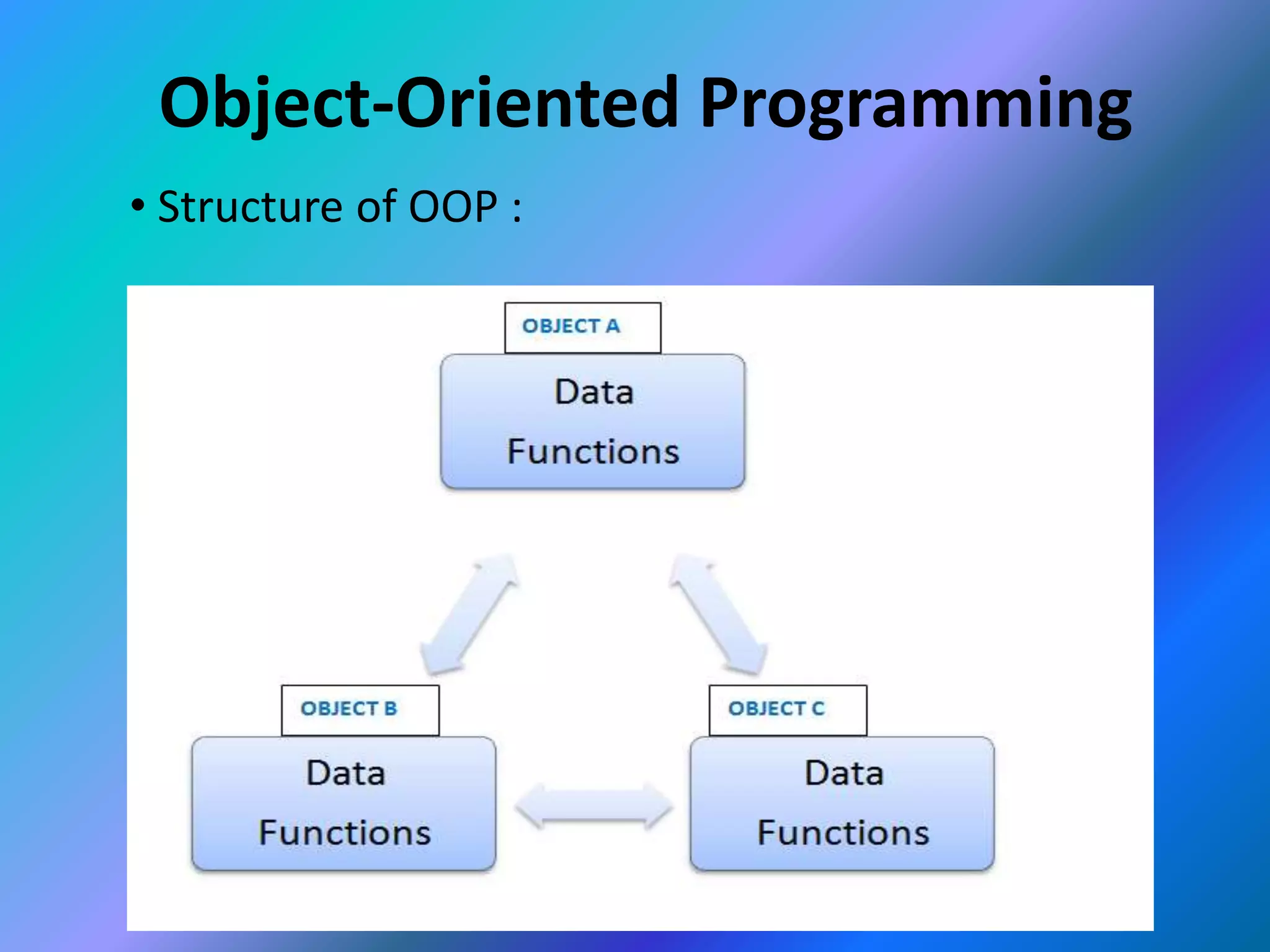
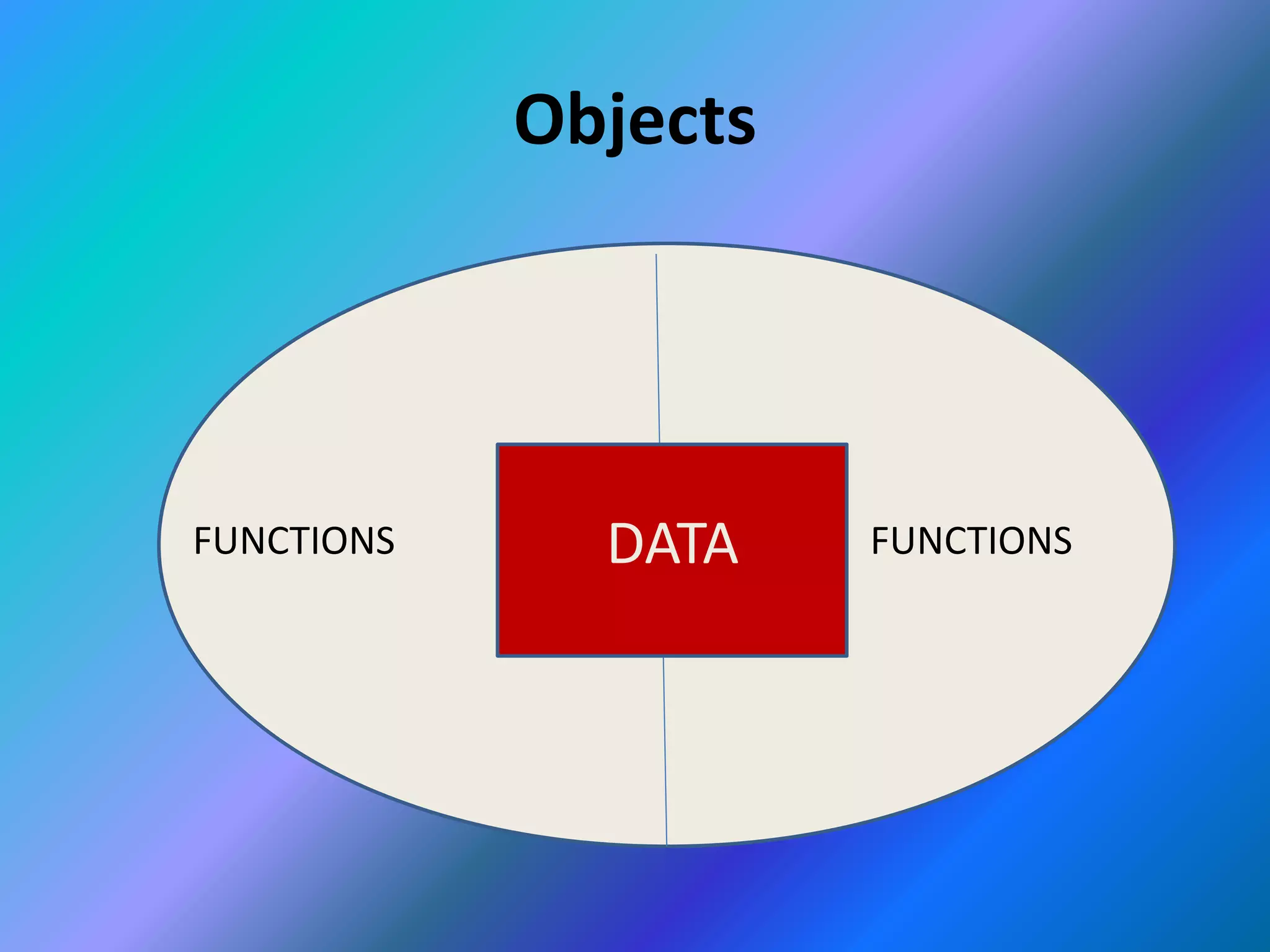
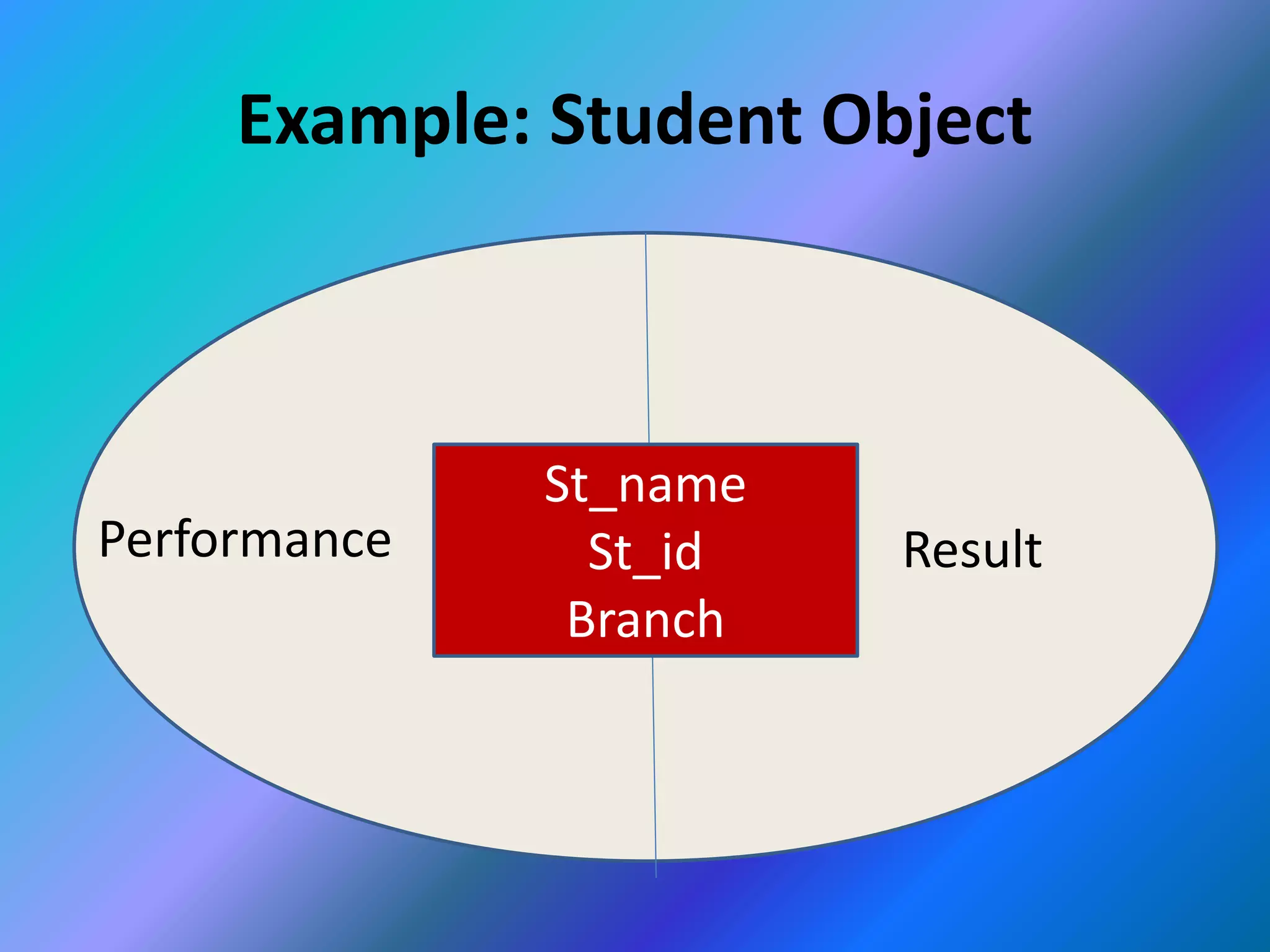
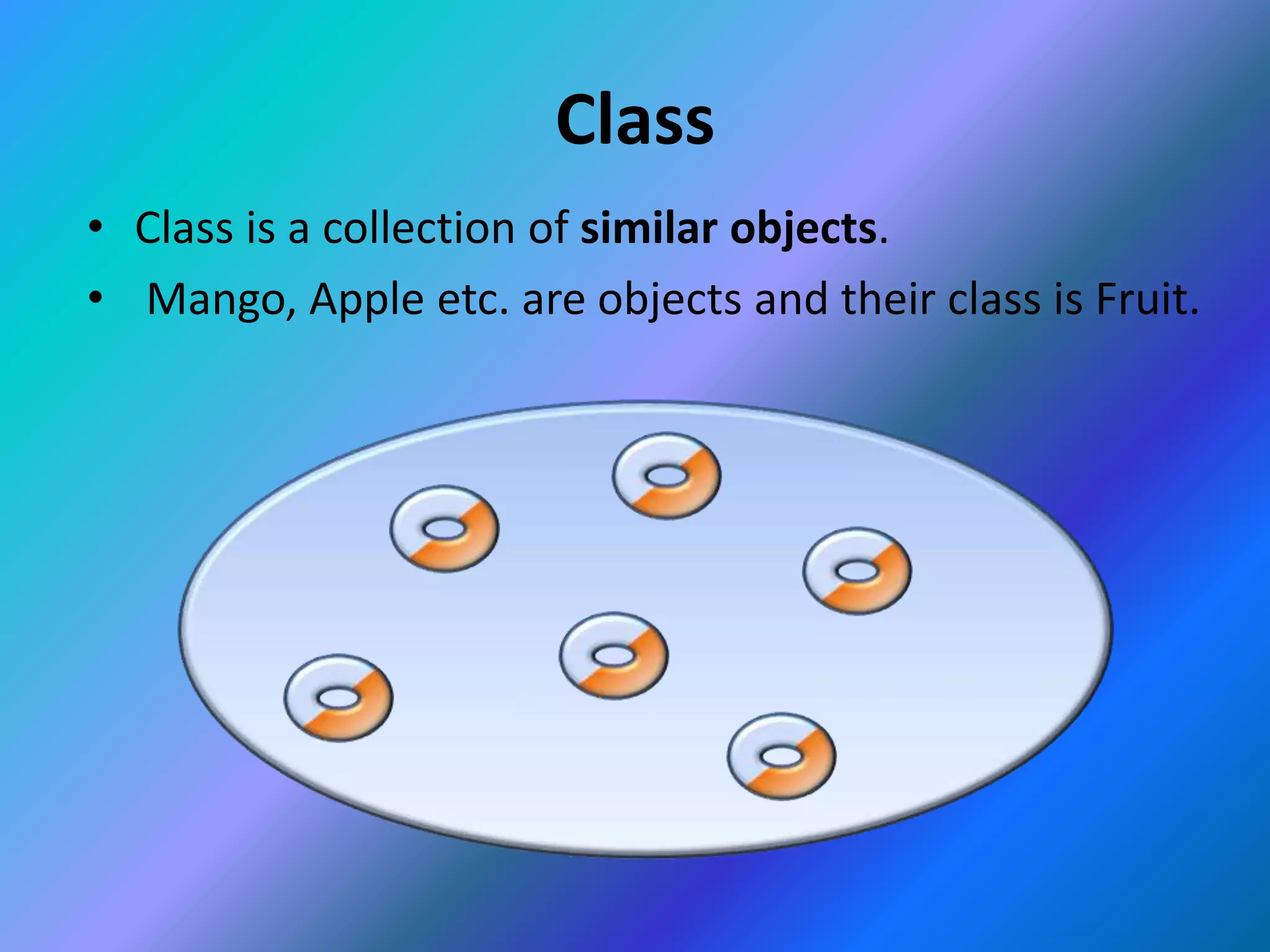
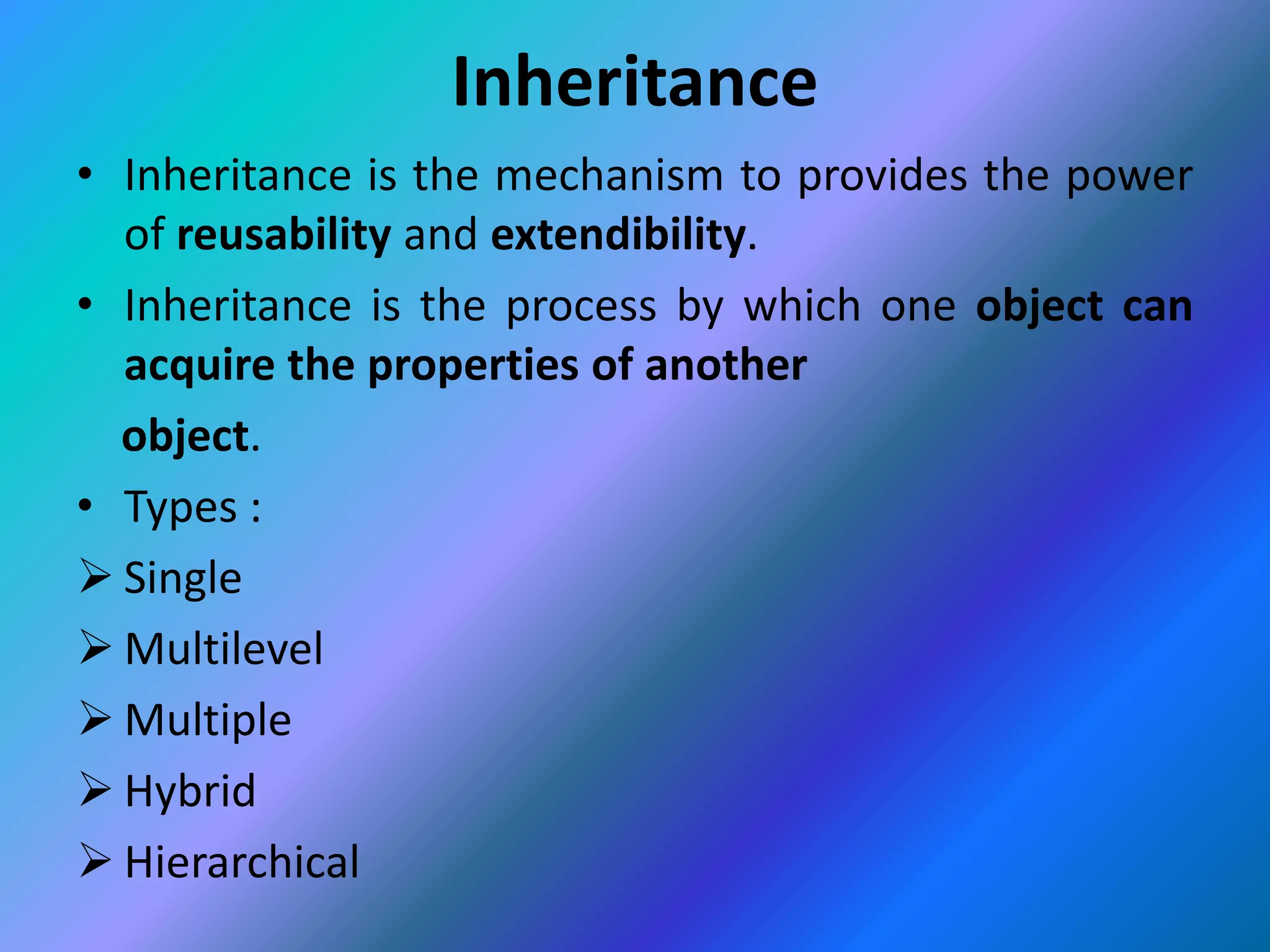
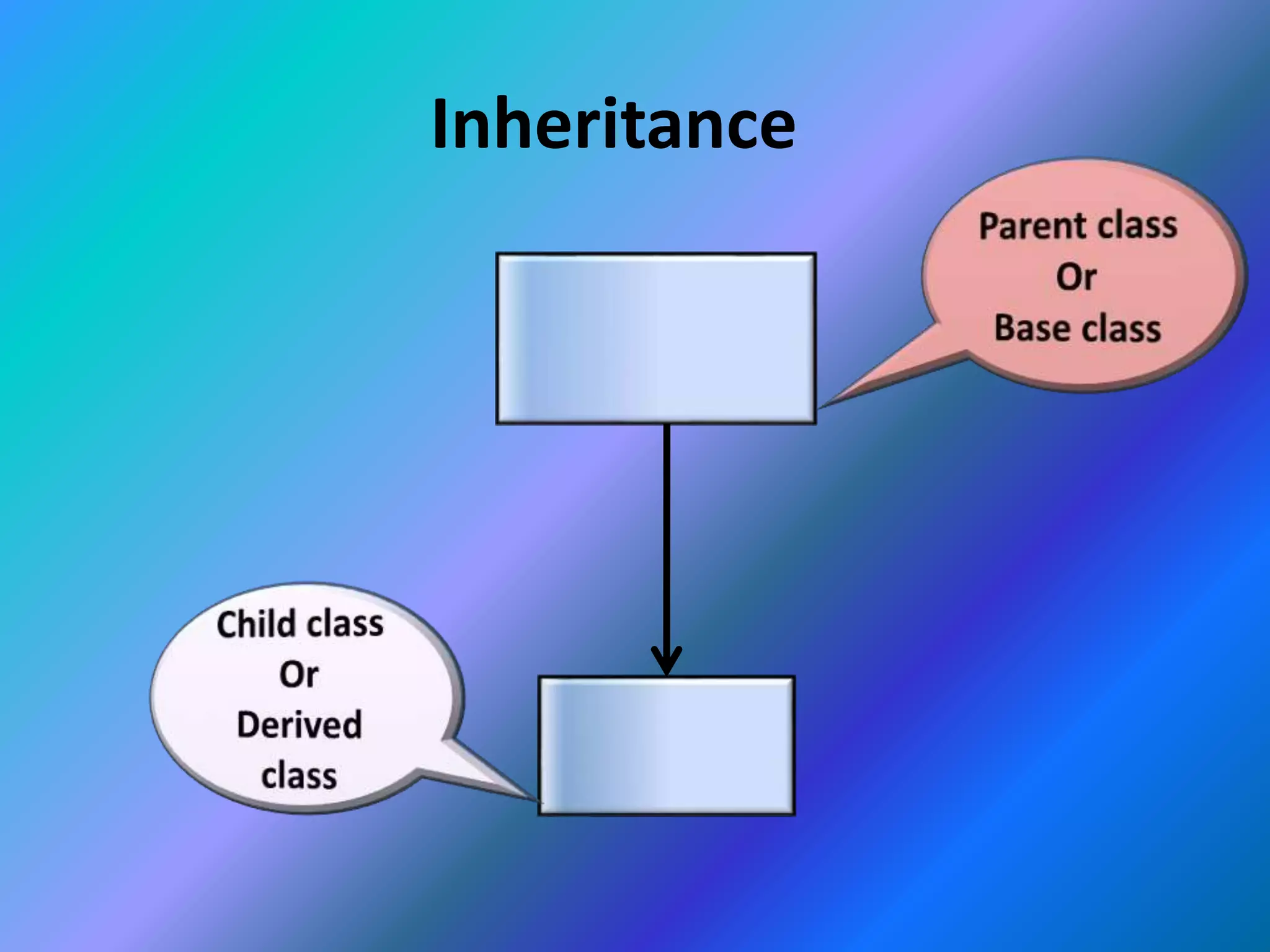
This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming (OOP). It discusses the differences between procedural programming and OOP, defining OOP as a methodology that associates data structures with operators. The core concepts of OOP are defined as objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and message passing. Objects are instances of classes that package both data and methods. Encapsulation binds data and methods within an object, while inheritance allows classes to acquire properties from other classes in a hierarchy. Polymorphism enables different implementations through message passing between objects.