This study presents an intrusion detection model using a random forest classifier on the NSL-KDD dataset, addressing challenges in cybersecurity caused by big data. The model employs the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) to tackle class imbalances and is evaluated against other models including Support Vector Machine and K-Nearest Neighbors. Results indicate the IDS-RF model achieves superior performance across multiple classification metrics for detecting various attack types.
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 DOI: 10.5121/ijcnc.2024.16605 75 INTRUSION DETECTION MODEL USING MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS ON NSL-KDD DATASET Reem Alshamy and Muhammet Ali Akcayol Department of Computer Science, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey ABSTRACT Big data, generated by various sources such as mobile devices, sensors, and the Internet of Things (IoT), has many characteristics such as volume, velocity, variety, variability, veracity, validity, vulnerability, volatility, visualization, and value. An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is essential for cybersecurity to detect intrusions before or after attacks. Traditional software methods struggle to store, manage, and analyze big data, developing new techniques for effective and rapid intrusion detection in organizations and enterprises. This study introduces the IDS Random Forest (RF) model in binary and multiclass classification for intrusion detection. In this model, we used the Synthetic Minority Oversampling TEchnique (SMOTE) to address class imbalances, and the RF classifier to classify attacks using the Network Security Laboratory (NSL)-KDD dataset. In the experiment, we compared the IDS-RF model with the Support Vector Machine (SVM), k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN), and Logistic Regression (LR) classifiers in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score, and times for training and testing. The experimental results showed that the IDS-RF model achieved high performance in binary and multiclass classification compared to others. In addition, the proposed model also achieved high accuracies for each class (Normal, DoS, Probe, U2R, or R2L) and obtained 98.69%, 99.72%, 98.93%, 95.13%, and 89%, respectively. KEYWORDS Intrusion Detection, Network Security Laboratory (NSL)-KDD dataset, SMOTE, Machine Learning 1. INTRODUCTION Computers and the Internet have become integral components of human life. Cybercrime is rising in a world characterized by connectivity and data dependency, causing significant disruptions to our way of life. Tools such as antivirus software, firewalls, and IDS have been deployed to address these security challenges [1]. An IDS is a device that examines data to identify and detect unauthorized attempts to affect a system or network's security. Traditional methods can be complex and inefficient when dealing with big data, making the system vulnerable to attack. Leveraging big data tools and techniques can reduce the time required for computations. An IDS utilizes three primary methods to detect attacks: 1) Signature-based detection is effective for detecting known attacks but cannot detect new types of attacks. 2) Anomaly-based detection utilizes established profiles to compare user activities and identify odd behaviors; however, it can result in high false-positive rates (FPR). 3) Hybrid-based detection combines multiple methods to address each method's drawbacks while utilizing its strengths. Many researchers have recommended using ML techniques in IDS to reduce FPR and improve IDS accuracy. By leveraging advanced data analysis tools and methodologies, an IDS can enhance the effectiveness and precision of its detection approaches [2, 3].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-1-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 76 The term " big data" refers to an amount of data that stands out for its volume, velocity, and variety. Moreover, the increasing number of attacks worsens these issues. As a result, big data poses challenges, for IDS in identifying and analyzing intrusions and attacks. Dealing with security data from sources is a task for intrusion detection particularly when handling the complexities of big data. The complexity of managing data grows when dealing with issues like having high dimensions of data from various sources or varied data structures. To tackle these challenges effectively an IDS needs to integrate techniques designed for big data environments. Incorporating big data techniques and ML in IDS can help address challenges such, as computational time and speed ultimately contributing to the improvement of more accurate IDS systems [2]. Spark and Hadoop MapReduce are widely recognized examples of frameworks used for processing big data. Spark is a distributed processing system known for its speed. Its flexible architecture supports a range of large-scale workloads including algorithms, batch applications, streaming tasks, and interactive searches. Furthermore, Spark offers an ML library known as MLlib [4]. Numerous research papers have employed ML classifiers to identify intrusions, in settings some of which have integrated techniques, for selecting features to handle amounts of data [5]. Other studies have employed Apache Spark and its MLlib to develop distributed IDS. However, users of the Spark ML library face limitations in applying feature selection methods, as this library only contains the chi-squared selector [6]. Datasets are essential for training and evaluating anomaly-based network IDS. Some studies have used actual data captured from switches and tools designed to simulate attacks to test their systems. However, a major inconvenience is the impossibility of comparing the results with those of other studies because of the differences in the data, which inevitably lead to different outcomes. Consequently, several public network datasets are available for this purpose. The most well-known are DARPA98, ARPA99, KddCup99, NSL-KDD, Kyoto 2006+, UNSW-NB15, and CICIDS2017, which are widely used in numerous studies. However, these datasets typically include a significant number of redundant or missing records and are considered outdated. The landscape of computer networks and their attack patterns has evolved considerably since their creation. To address these challenges, the Communications Security Establishment (CSE) has introduced a new dataset. Since its release, many projects have demonstrated that CSE-CIC-IDS 2018 is more complex than previous datasets, and can be reliably used to evaluate existing and new detection strategies. CSE-CIC-IDS 2018 accurately represents modern network attacks [7, 8]. The remainder of this study is structured as follows: Section 2 presents a review of related works. In the 'Methodology' section, we introduce the IDS-RF model and describe each step of this method. The results of the IDS-RF model and a discussion are presented in Section 4. Comparisons with existing studies are provided in Section 5. Finally, we conclude our work and outline future work in the 'Conclusion' section. 2. RELATED WORKS Many research approaches have been introduced for IDS that apply ML algorithms, feature selection methods, and big data platforms. Different approaches have been proposed for IDS that utilize the benchmark NSL-KDD dataset to improve attack detection. Some researchers have employed traditional techniques, while others have leveraged big data techniques in an IDS, aiming to reduce training and computation time. With the advent of big data, traditional techniques for handling such data have become increasingly complex. In this section, the authors summarize previous works that utilized big data techniques to address classification problems (binary, multi-class, or both) in IDS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-2-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 77 Louati et al. [5] proposed a novel IDS based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) for big data environments. The MARL method leverages decentralized cooperative learning among agents to address the issues presented by the large amount, velocity, and variety of big data. This work contributes significantly to developing advanced IDS that can effectively function within the challenging environments of big data frameworks. Trrad et al. [9] focused on using ML algorithms to categorize network traffic. They specifically examined the NSL-KDD dataset to evaluate how well classifiers, like SVM, k-NN, and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) could detect network activities. Lin et al. [10] introduced the Multi-Feature Extraction Extreme Learning Machine (MFE-ELM) as a method to prevent intrusions in cloud computing environments related to the Internet of Things (IoT). For intrusion detection, the MFE-ELM method employed the NSL-KDD dataset. The results indicate that the proposed algorithm enhances the ability to promptly identify security weaknesses in cloud clusters, facilitating the development of intrusion response strategies. Mari et al. [11] introduced a random forest algorithm that uses learning to enhance feature selection. The algorithm combined three ML models; SVM, LR, and k-NN. Their research showed an enhancement, in detecting and categorizing network intrusions through ML highlighting the importance of feature selection in improving detection accuracy. The study also underlined the potential of these methods for real-time detection and monitoring of cyber-attacks. Türk et al. [12] evaluated intrusion detection capabilities by applying ML and Deep Learning (DL) techniques on two datasets, specifically the University of New South Wales (UNSW)- NB15 and NSL-KDD. They achieved accuracy in classification showcasing the effectiveness of these algorithms, in identifying and categorizing network intrusions. Kalinin et al. [13] investigated Quantum ML (QML) to address challenges, in intrusion detection and improve effectiveness. Their study involved comparing Quantum SVM (QSVM) and Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks (QCNN) as strategies for detecting intrusions. The findings from their experiments showed that intrusion detection based on QML can effectively manage amounts of data inputs with high accuracy and at twice the speed of conventional algorithms. Vibhute et al. [14] developed an ML-based IDS using a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). The study aimed to generate adversarial network traffic instances that might avoid conventional IDS detection. These instances were then used to improve the IDS's ability to detect new and evolving threats. The GAN method not only assessed the durability of the IDS against complex approaches used to avoid detection but also enhanced its capacity to adapt to new attacks, resulting in notable progress in the field of cybersecurity. Abid et al. [15] proposed a real-time, fault-tolerant, distributed, and scalable approach for detecting intrusions in Industrial Control Systems (ICS). Their system employs data fusion techniques to merge streaming datasets into a stream enhancing accuracy and precision. The approach demonstrated performance in binary and multiclass classifications by leveraging Apache Spark Structured Continuous Streaming for real-time data processing along with a Multi- Layer Perceptron Classifier (MLPC). Table 1 provides a comparison of studies focusing on aspects such as algorithms, tools, datasets, and classification problems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-3-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 78 Table 1. The comparison of the related works. In related works, we observed that IDS encounter challenges posed by big data. Researchers have addressed these challenges using two main strategies: employing a complete dataset and applying the proposed approach with Big Data techniques [5]. Table 1 summarizes related works, categorizing them based on the algorithms used for classification, the tools developed for the research, the datasets on which the research was trained and evaluated, and the focus of the classification problems (Binary, Multiclass, or both). 3. METHODOLOGY This section will provide a detailed explanation of the proposed model and the tools that were utilized. Figure 1 shows the IDS-RF model. The IDS-RF model can be summarized in the following steps: 1. Import the NSL-KDD dataset. 2. Conduct data pre-processing. 3. Utilize the SMOTE and RF classifier to train the IDS-RF model on the training dataset. 4. The IDS-RF model is evaluated by applying the RF classifier to the NSL-KDD test dataset. Figure 1. The sequence of steps in the IDS-RF model.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-4-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 79 3.1. Dataset Description The NSL-KDD dataset is among the most widely used datasets for training and evaluating IDS models [16]. This dataset contained 41 features, plus one feature for the target class, including four categorical, four binary, and 33 numerical features. The features in the NSL-KDD dataset are divided into four groups: basic, host, traffic, and content features [17]. The 42 features provide data on five classes of network connections, with each instance classified either as normal or as one of four types of attacks [7, 14]. The attack types in the NSL-KDD dataset can fall into one of the following four main categories: Denial of Service Attack (DoS): The attacker occupies excessive computing or memory resources by performing calculations, thereby denying legitimate users access to the machine. This is achieved by handling more requests so the system can process them logically. Probing Attack: This type of attack occurs when an attacker exploits vulnerabilities to gain local access to the network. Then, the attacker sends packets to the device over the network. Remote to Local Attack (R2L): This attack occurs when an attacker takes advantage of vulnerabilities to gain local network access and begins sending packets to the device over the network. User-to-Root Attack (U2R): An attacker gains root access by exploiting vulnerabilities, potentially allowing the attacker to escalate privileges from a regular user account to root access. The distribution of various attacks on the NSL-KDD dataset is presented in Table 2. Table 2. The Distribution of various attack types in the NSL-KDD dataset [9]. The training dataset consisted of 23 classes, whereas the test dataset included 38. These encompass 21 attacks from the training dataset, 16 novel attacks, and one normal class. The class labels of instances in the dataset were categorized into five main categories: Normal, DoS, Probe, R2L, and U2R. According to the distribution of instances across different attack types, as illustrated in Table 2, the distribution of various types of data is unbalanced. 'Normal' represents the highest percentage of the total data, whereas U2R has the lowest, which may lead to inadequate training and misclassification of data. Attackers often utilize Probe, R2L, and U2R attacks as advanced threats. Therefore, improving the classification accuracy for these types of attacks should be prioritized. 3.2. Dataset Pre-Processing The preprocessing is an essential step that enhances the data quality and aids the extraction of features [18]. This step is essential for developing and training the models. We first need to preprocess the data to derive the value from the dataset and prepare it for the IDS-RF model, Below, we describe the techniques used for data preprocessing:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-5-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 80 3.2.1. Transformation The data performed a transformed into formats that are appropriate for ML algorithms [19]. First, the dataset underwent a process of eliminating features that included zero values. Additionally, we transformed the categorical features within the dataset into numerical features. Second, we employ the one-hot encoder technique to transform categorical features into a one-hot numeric array. We achieve this by identifying the distinct values of each feature and creating corresponding categories. As an illustration, the output of this function can encode the 'protocol_type' feature, which has three separate values (TCP, UDP, and UCMP), as [1,0,0], [0,1,0], and [0,0,1] correspondingly. As a result, this function transformed the initial 41- dimensional NSL-KDD dataset into a format with 122 dimensions. 3.2.2. Standardization In ML, the standardization of datasets is very significant for algorithms that utilize the Euclidean distance. Without standardization, there is a potential risk that features with values in larger ranges may be given undue importance. Because only some features can be represented within the same measurement range, features of varying magnitudes can negatively affect ML algorithms [20]. This issue can be mitigated through standardization, which involves converting data to a common range. Standardization is beneficial because it helps improve the prediction performance of the IDS-RF model. For example, the NSL-KDD dataset encompasses features with a broad spectrum of values. Some features displayed significant discrepancies between their minimum and maximum values, making them incomparable and unsuitable for direct processing. An example is the 'duration' feature, which ranges from a minimum of 0 to a maximum of 58,329, rendering the feature values inconsistent for analysis. To address these challenges within the IDS-RF model, we employ StandardScaler. This tool standardizes features by eliminating the mean and scaling to unit variance using the following formula to achieve data standardization: 𝒛 = 𝒙 − 𝒖 𝒔 𝟏 The equation represents the relationship between the standardized value of a sign (z), the original vector (x), the mean of the vectors (u), and the standard deviation (s). 3.3. IDS-RF Model This section presents the SMOTE technique and the RF classifier as a component of the IDS-RF model. 3.3.1. SMOTE The NSL-KDD dataset has a class imbalance issue. When dealing with a dataset that contains a class imbalance, it is preferable to use the SMOTE method to enhance attack detection in the IDS-RF model [21, 22]. SMOTE was developed by Chawla [23]. This method generates synthetic samples in the minority class instead of replacing existing samples, which helps avoid the overfitting problem. The SMOTE algorithm was proposed to overcome the overfitting issue and improve the accuracy. This straightforward cluster-based oversampling technique has gained widespread acceptance in the community [24]. It selects two samples from the minority class and assigns properties between them. The difference in value is calculated for each feature, and then a random value r is generated to lie between 0 and 1. Consequently, the features of the new sample were generated according to the following equation:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-6-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 81 𝒙𝒏𝒊 = 𝒎𝒊𝒏 𝒙𝒋𝒊, 𝒙𝒌𝒊 + |𝒙𝒋𝒊 − 𝒙𝒌𝒊| × 𝒓 (2) Equation (2) calculates the value of xni, which represents the ith feature of the nth new sample. It is determined by taking the minimum value between xji and xki and adding the absolute difference between xji and xki multiplied by the r value. The samples xj and xki are randomly selected from the minority class, and r is a number between 1 and 0. This equation helps generate a set of oversampled values. By employing this method, the two classes were nearly evenly distributed in terms of proportion. This approach effectively preserves the correlation between the characteristics, even when a substantial number of artificially generated samples are included in the dataset. The researchers utilized the SMOTE technique in their tests to attain precise categorization [25]. Figures 2 and 3 demonstrate the distribution of instances for various attacks before and after applying SMOTE to the training dataset in binary and multiclass scenarios. Figure 2. Results of Applying the SMOTE method to the training dataset for binary classification. Figure 3. Results of Applying the SMOTE Method to the training dataset for multiclass classification. 3.3.2. RF Classifier The random forest algorithm is composed of many tree predictors. Each tree makes predictions based on a random vector, which is sampled individually and follows the same distribution across all trees in the forest [26]. Random forests are regarded as an enhanced iteration of bootstrap aggregating (bagging), where the forecasts of many decision trees, developed with bootstrapped data samples that are identically distributed, are aggregated. One drawback of bagging is that the correlations between each pair of variables limit the extent to which the prediction errors can be](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-7-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 82 reduced, even when a large number of trees are aggregated. Random forests enhance the bagging technique by randomly selecting a subset of variables to use for splitting while constructing each decision tree. This helps to reduce the impact of correlations between pairs of variables. To obtain a comprehensive description of the random forest algorithm, please consult the work of Breiman [26]. The number of trees (B) and the number of randomly picked variables utilized for each split in an individual decision tree (m) are two important hyperparameters in constructing random forests. These two parameters are commonly identified using a grid search technique in conjunction with cross-validation [27]. As stated by Breiman [26], the process of building a random forest model involves the following steps: Iterate over the values of b from 1 to B: For b=1 to : (a) Generate a resampled dataset of size N using the bootstrap method from the training data. (b) Construct an RF tree by iteratively performing the following steps for each terminal node of the tree until the minimal node size nmin is reached. 1) Randomly choose m variables from the complete set of variables. 2) Choose the most optimal variable from the options provided. 3) Partition the node into two sub-regions. Print the collection of trees { }i, i=1, 2,…, . For a regression problem, given a new input x, the corresponding prediction can be written as: (3) Figure 4 illustrates the steps described above. Figure 4. Random Forest Architecture [27].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-8-2048.jpg)
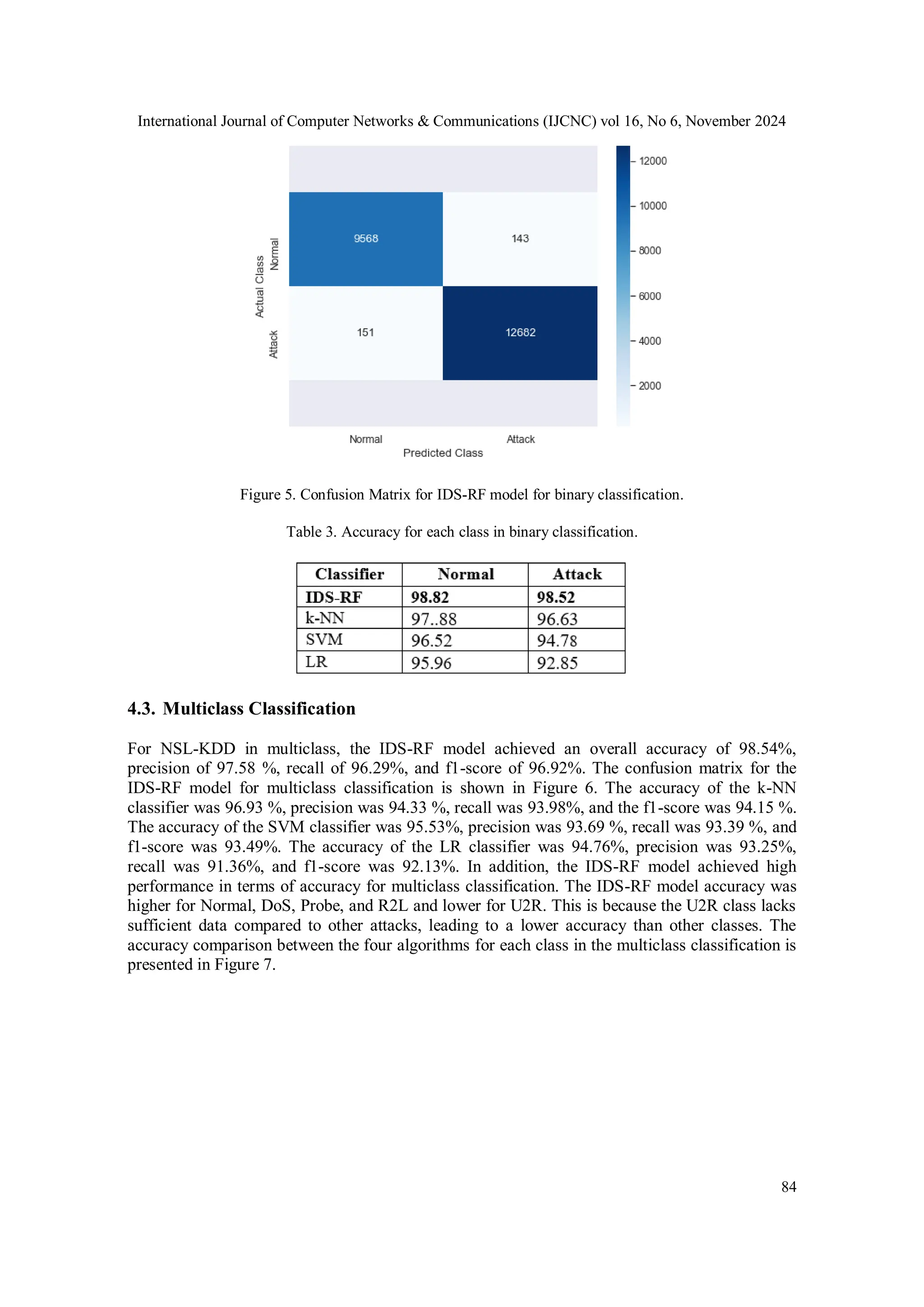
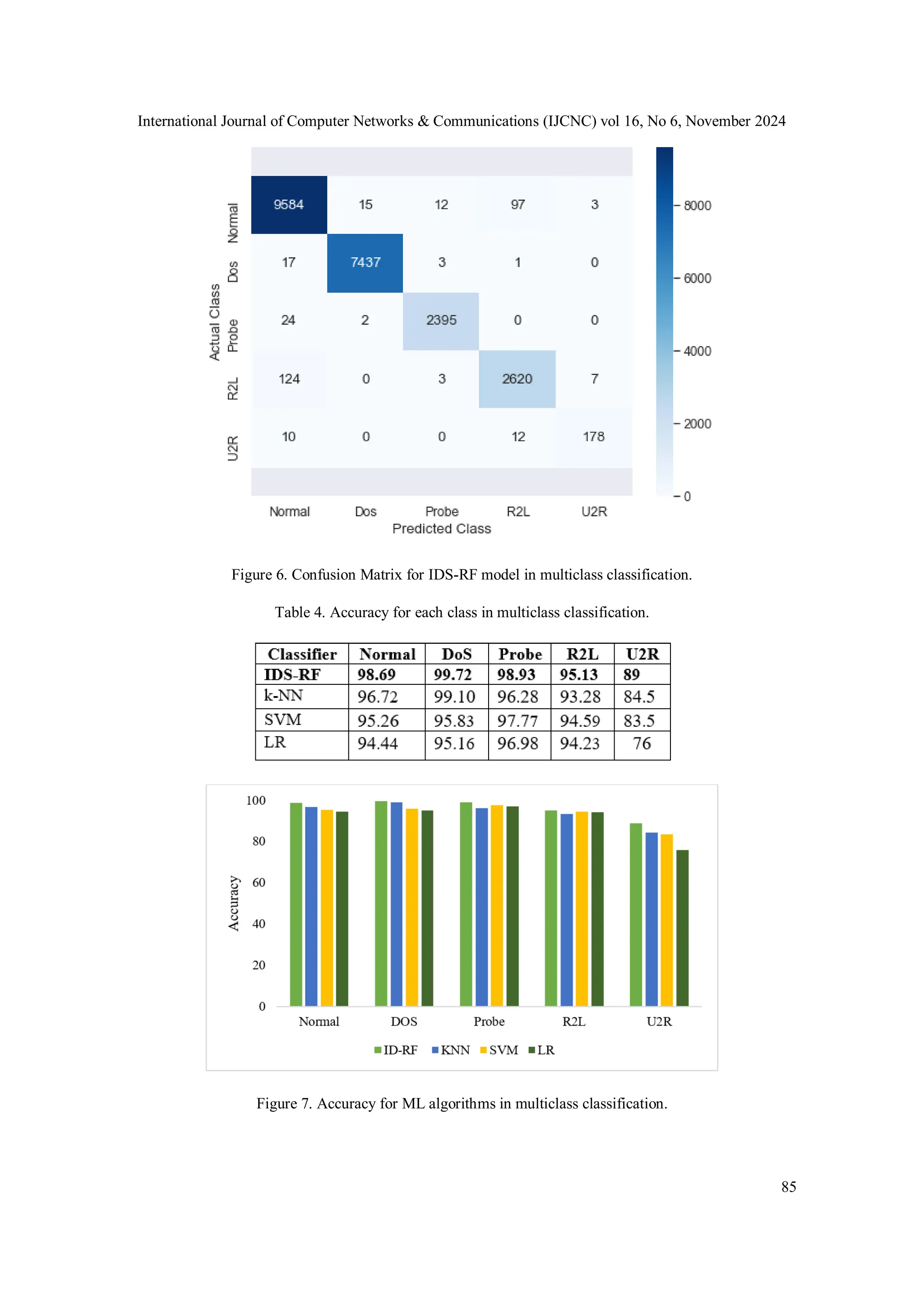
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 83 4. RESULTS ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Evaluation Metrics Some of the performance metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of the IDS-RF model involve accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score, and prediction time for binary and multiclass classification. Accuracy is a metric that measures the proportion of correct predictions made by the IDS-RF model when applied to a test dataset. Precision is a measure of the accuracy of a positive prediction. Recall, or the true positive rate, is the measure of the number of true positives predicted out of all positives in the dataset. The f1-score measures the accuracy of a model based on its recall and precision. The metrics mentioned above have definitions in Eqs. (4), (5), (6), and (7). where TP is True Positive, FN is False Negative, FP is False Positive, and TN is True Negative. TP indicates the number of records correctly detected as a normal class, FN indicates the number of records not correctly detected as an attack class, FP indicates the number of records not correctly detected as a normal class, and TN indicates the number of records correctly detected as an attack class. 4.2. Binary Classification The IDS-RF model achieved an accuracy of 98.67% for binary classification on the NSL-KDD dataset. Precision was 98.68%, recall was 98.67%, and f1-score was 98.67%. The confusion matrix for the IDS-RF model in the binary classification is shown in Figure 5. In addition, we assessed the performance of the ML algorithms k-NN, SVM, and LR, focusing on accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. These algorithms were chosen because of their extensive application and proven efficacy in IDS [17]. The accuracy of the k-NN classifier was 97.34%, the precision was 97.32%, the recall was 97.26%, and the f1-score was 97.29%. The accuracy of the SVM classifier was 95.77%, the precision was 95.72%, the recall was 95.65%, and the f1-score was 95.69%. The accuracy of the LR classifier was 94.62%, precision was 94.61%, recall was 94.41%, and f1-score was 94.50%. A comparison of the accuracy values between the four algorithms for each class (normal and attack) is presented in Table 3. The results in Table 3 highlight the superior performance of the IDS-RF model in terms of accuracy for binary and multiclass classification.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-9-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 86 In IDS, analyzing big data requires high real-time performance, which requires not only high evaluation metrics but also minimal detection times to ensure the efficiency of network security applications. To demonstrate the superiority of the IDS-RF model, researchers measured its training and prediction times for binary and multiclass classification and compared these metrics with other ML algorithms. The findings revealed that our proposed model significantly reduced training and prediction times. Table 5 compares the training and prediction times between the proposed IDS-RF model and the other classifiers for binary and multiclass classification. Table 5. Training and testing times for IDS-RF model with other classifiers. IDS-RF consistently outperformed the other algorithms in all metrics, establishing it as the most effective option for the classification task in this study. These impressive results were achieved by integrating the RF classifier with the SMOTE method, which was applied to the training data for binary classification, as illustrated in Table 3. The superiority of the IDS-RF model is mainly due to its flexibility and adeptness in identifying correlations between features, rendering it an ideal choice for this task. In addition, RF consistently shows excellent performance, even when handling large datasets. Moreover, the preprocessing stages yielded a dataset comprising 134,686 instances for binary classification and 202,305 for multiclass classification. Utilizing Anaconda capabilities [28], our system achieved an exceptional processing rate of 22,544 instances in just 6 s for binary classification and 41.762 s for multiclass classification (as shown in Table 5). This rapid processing rate significantly boosts the intrusion detection capabilities, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the system. The results highlight the efficiency and reliability of the proposed system classification. 5. COMPARISON WITH EXISTING WORKS The importance of the strategy presented in the IDS-RF model is compared with existing studies. Some previous studies focused on ML and DL algorithms and achieved satisfactory results. In this section, we focus on studies that use the same dataset used in our model to train and test the IDS-RF model. Although the NSL-KDD dataset we used does not cover modern attacks, researchers still use it widely. In addition, when comparing the IDS-RF model with previous studies that used the NSL-KDD dataset for binary and multiclass classification, the IDS-RF model consistently demonstrated high performance and speed in attack detection across all metrics evaluated. The accuracy of the k-NN model in [14] was 98.24% when using the ensemble learning-enabled RF algorithm for feature selection. In [11], correlation-based feature selection achieved an accuracy of 91.33% through k-NN, less than that achieved in our study. Based on our findings, the IDS-RF model suggested in this work outperforms the models used in previous studies [5, 9, 10, 12] in terms of accuracy, training, and testing times. To enhance the performance of the IDS-RF model, we recommend its implementation in Apache Spark, a cluster computing platform designed for high-speed processing [11]. Table 6 shows the significance of the current study compared to recent studies in binary and multiclass classification.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-12-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 87 Table 6. Comparison results with other studies in binary and multiclass classification. 6. CONCLUSIONS This study introduces an IDS-RF model developed by researchers to detect intrusions using the NSL-KDD dataset. The classification process for big data is complicated in an IDS because of its high dimensionality. The proposed model leveraged the Anaconda platform to process and analyze big data rapidly. In the proposed model, researchers utilized the SMOTE technique to handle a dataset and utilized Random Forest (RF) for binary and multiclass classification. The experimental results showed that the model achieved high accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score, and speed for binary and multiclass classification compared with the k-NN, SVM, and LR algorithms. The proposed model achieved an overall accuracy of 98.67% for binary classification and 98.54% for multiclass classification. The proposed model also achieved high testing accuracies for Normal (98.69%), DoS (99.72%), Probe (98.93%), R2L (95.13%), and U2R (89%) even though the accuracy of the U2R class was lower compared with other attacks because the number of instances in this class is small. In addition, the proposed model achieved high accuracy, which is remarkable for binary and multiclass classification compared to existing models. In future work, we plan to apply the IDS-RF model on more modern datasets to detect intrusions and reduce computation time using the Apache Spark environment. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We would like to thank all authors for their contributions and the success of this manuscript and all editors and anonymous reviewers of this manuscript. REFERENCES [1] F. Bannat Wala and M. J. a. e.-p. Kiran, "5G Network Security Practices: An Overview and Survey," p. arXiv: 2401.14350, 2024. [2] S. M. Othman, N. T. Alsohybe, F. M. Ba-Alwi, A. T. J. I. J. o. C.-S. Zahary, and D. Forensics, "Survey on intrusion detection system types," vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 444-463, 2018. [3] A. Touzene, A. Al Farsi, N. J. I. J. o. C. N. Al Zeidi, and Communications, "HIGH PERFORMANCE NMF BASED INTRUSION DETECTION SYSTEM FOR BIG DATA IOT TRAFFIC," vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 43-58, 2024. [4] X. Sun, L. Zhao, J. Chen, Y. Cai, D. Wu, and J. Z. J. E. A. o. A. I. Huang, "Non-MapReduce computing for intelligent big data analysis," vol. 129, p. 107648, 2024. [5] F. Louati, F. B. Ktata, and I. J. C. C. Amous, "Big-IDS: a decentralized multi agent reinforcement learning approach for distributed intrusion detection in big data networks," pp. 1-19, 2024. [6] K. Pramilarani and P. V. J. A. S. C. Kumari, "Cost based Random Forest Classifier for Intrusion Detection System in Internet of Things," vol. 151, p. 111125, 2024.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-13-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) vol 16, No 6, November 2024 88 [7] M. Ghurab, G. Gaphari, F. Alshami, R. Alshamy, and S. J. A. J. o. R. i. C. S. Othman, "A detailed analysis of benchmark datasets for network intrusion detection system," vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 14-33, 2021. [8] M. Ghurab, R. Alshamy, S. J. I. J. o. S. R. Othman, and E. Development, "Performance Evaluation for Attack Detection in Intrusion Detection System," vol. 4, no. 5, 2021. [9] Trrad, "Applying Deep Learning Techniques for Network Traffic Classification: A Comparison Study on the NSL-KDD Dataset," 2024. [10] H. Lin, Q. Xue, J. Feng, and D. Bai, "Internet of things intrusion detection model and algorithm based on cloud computing and multi-feature extraction extreme learning machine," Digital Communications and Networks, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 111-124, 2023. [11] A.-G. Mari, D. Zinca, and V. J. S. Dobrota, "Development of a Machine-Learning Intrusion Detection System and Testing of Its Performance Using a Generative Adversarial Network," vol. 23, no. 3, p. 1315, 2023. [12] F. J. B. E. Ü. F. B. D. Türk, "Analysis of intrusion detection systems in UNSW-NB15 and NSL- KDD datasets with machine learning algorithms," vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 465-477, 2023. [13] M. Kalinin and V. Krundyshev, "Security intrusion detection using quantum machine learning techniques," Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 125-136, 2023. [14] A. D. Vibhute, C. H. Patil, A. V. Mane, and K. V. J. P. C. S. Kale, "Towards Detection of Network Anomalies using Machine Learning Algorithms on the NSL-KDD Benchmark Datasets," vol. 233, pp. 960-969, 2024. [15] A. Abid, F. Jemili, and O. Korbaa, "Real-time data fusion for intrusion detection in industrial control systems based on cloud computing and big data techniques," Cluster Computing, pp. 1-22, 2023. [16] R. Alshamy, M. J. J. o. C. S. Ghurab, and Engineering, "A review of big data in network intrusion detection system: Challenges, approaches, datasets, and tools," vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 62-74, 2020. [17] NSL-KDD dataset. Accessed at Jan. 01, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/nsl.html [18] M. A. Bouke, A. Abdullah, K. Cengiz, and S. J. P. C. S. Akleylek, "Application of BukaGini algorithm for enhanced feature interaction analysis in intrusion detection systems," vol. 10, p. e2043, 2024. [19] K. C. Santos, R. S. Miani, F. J. J. o. N. de Oliveira Silva, and S. Management, "Evaluating the Impact of Data Preprocessing Techniques on the Performance of Intrusion Detection Systems," vol. 32, no. 2, p. 36, 2024. [20] M. A. Talukder, S. Sharmin, M. A. Uddin, M. M. Islam, and S. J. I. J. o. I. S. Aryal, "MLSTL-WSN: machine learning-based intrusion detection using SMOTETomek in WSNs," pp. 1-20, 2024. [21] W. A. Ali, M. Roccotelli, G. Boggia, and M. P. J. I. S. J. A. G. P. Fanti, "Intrusion detection system for vehicular ad hoc network attacks based on machine learning techniques," pp. 1-19, 2024. [22] R. Alshamy, M. Ghurab, S. Othman, and F. Alshami, "Intrusion detection model for imbalanced dataset using SMOTE and random forest algorithm," in Advances in Cyber Security: Third International Conference, ACeS 2021, Penang, Malaysia, August 24–25, 2021, Revised Selected Papers 3, 2021, pp. 361-378: Springer. [23] N. V. Chawla, K. W. Bowyer, L. O. Hall, and W. P. J. J. o. a. i. r. Kegelmeyer, "SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique," vol. 16, pp. 321-357, 2002. [24] J. S. Aguilar-Ruiz and M. J. S. R. Michalak, "Classification performance assessment for imbalanced multiclass data," vol. 14, no. 1, p. 10759, 2024. [25] A. Kumar, D. Singh, R. J. M. T. Shankar Yadav, and Applications, "Class overlap handling methods in imbalanced domain: A comprehensive survey," pp. 1-48, 2024. [26] L. J. M. l. Breiman, "Random forests," vol. 45, pp. 5-32, 2001. [27] H. Gong, Y. Sun, W. Hu, P. A. Polaczyk, and B. Huang, "Investigating impacts of asphalt mixture properties on pavement performance using LTPP data through random forests," Construction and Building Materials, vol. 204, pp. 203-212, 2019. [28] Anaconda platform. Accessed at Jan. 01, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.anaconda.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16624cnc05-250102122315-0f8867eb/75/Intrusion-Detection-Model-using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-on-NSL-KDD-Dataset-14-2048.jpg)