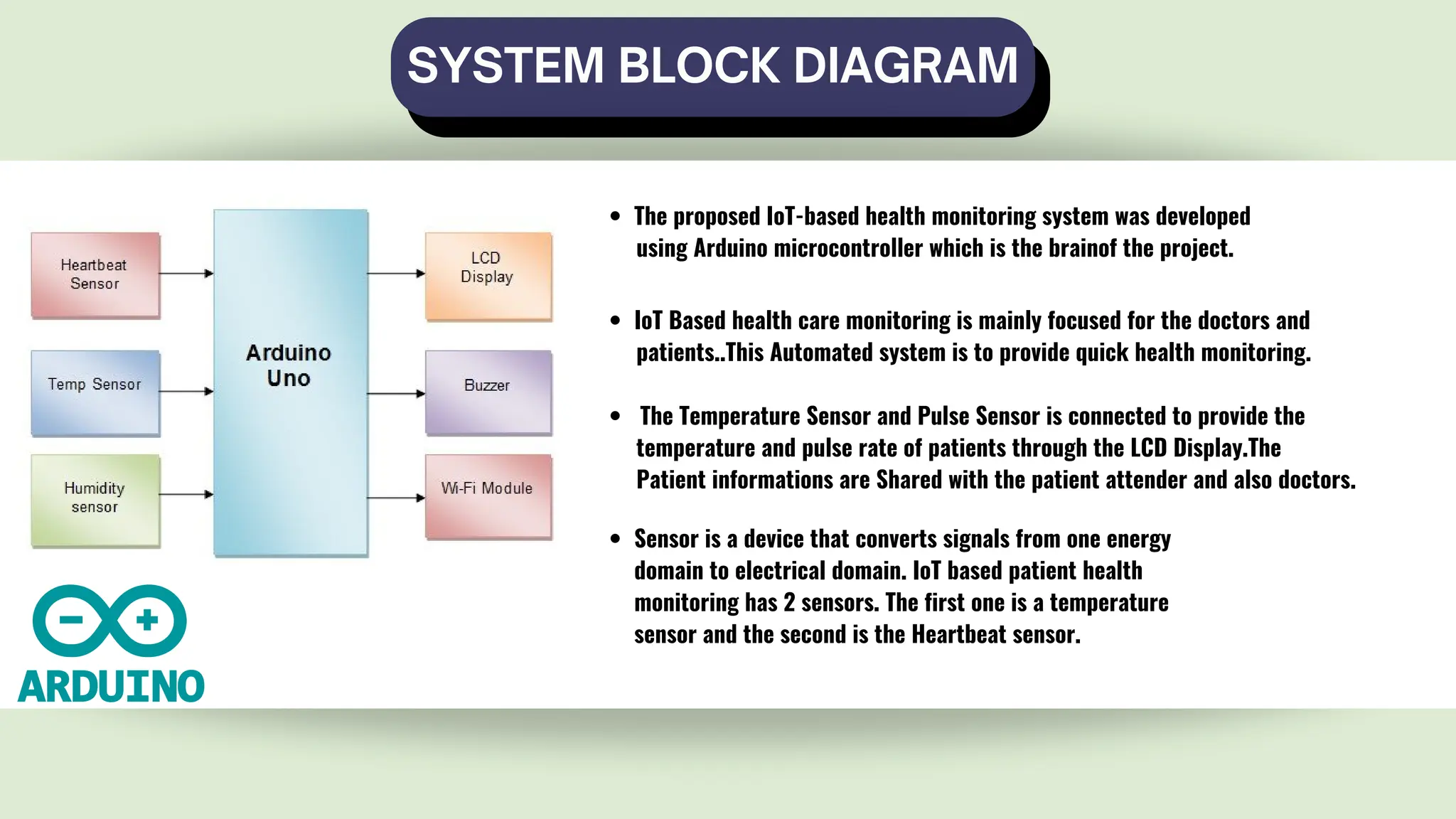
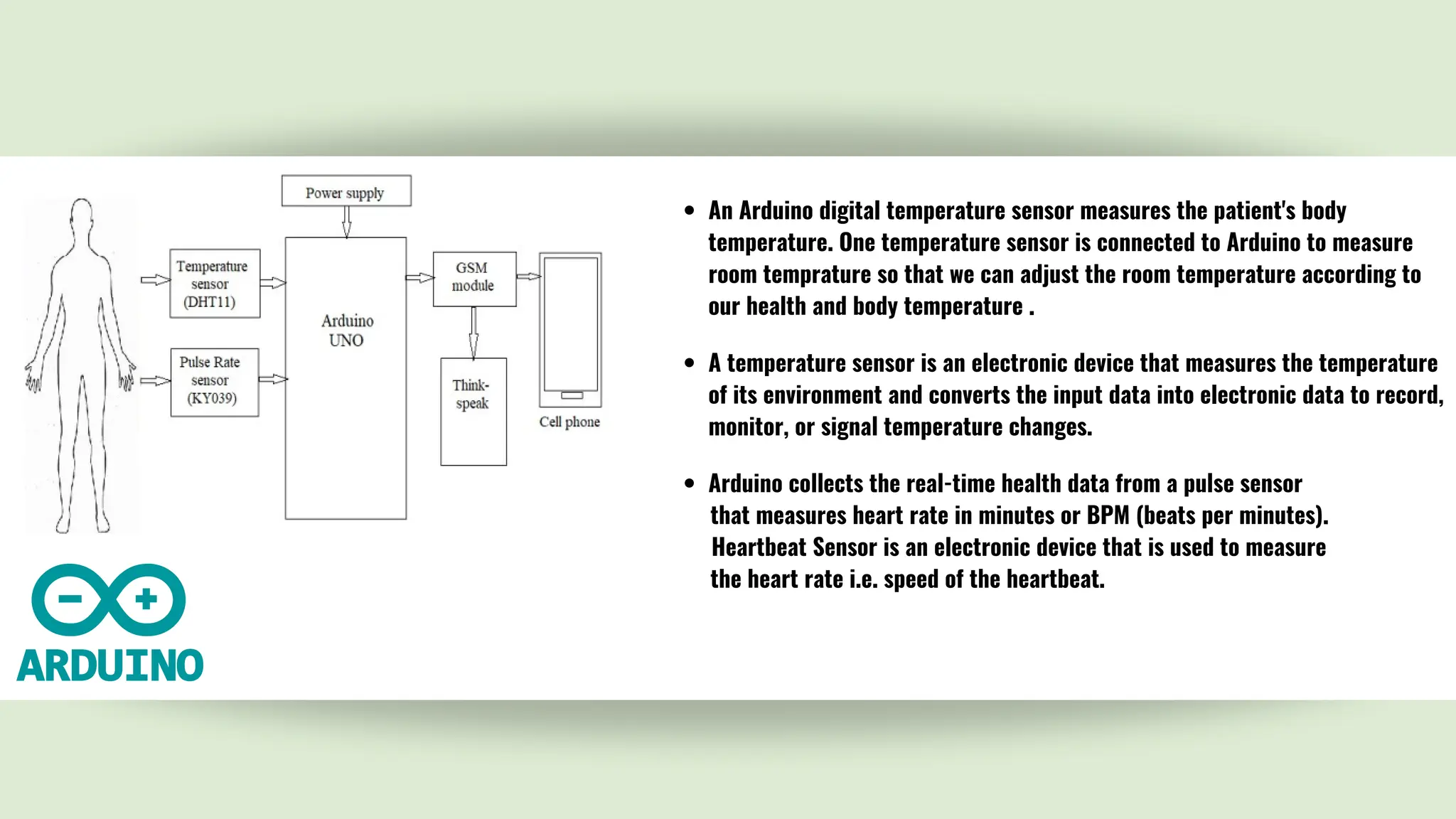
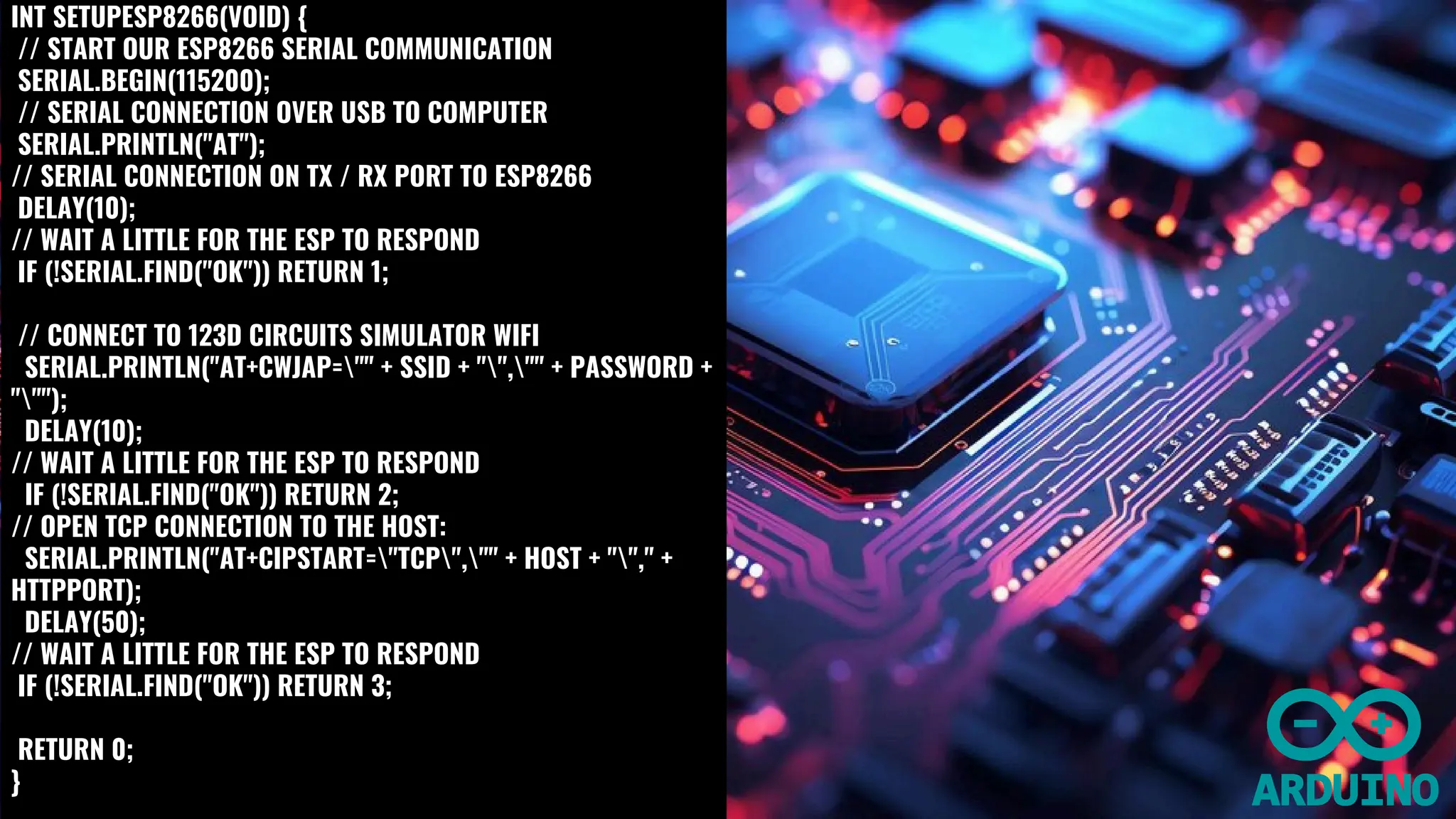
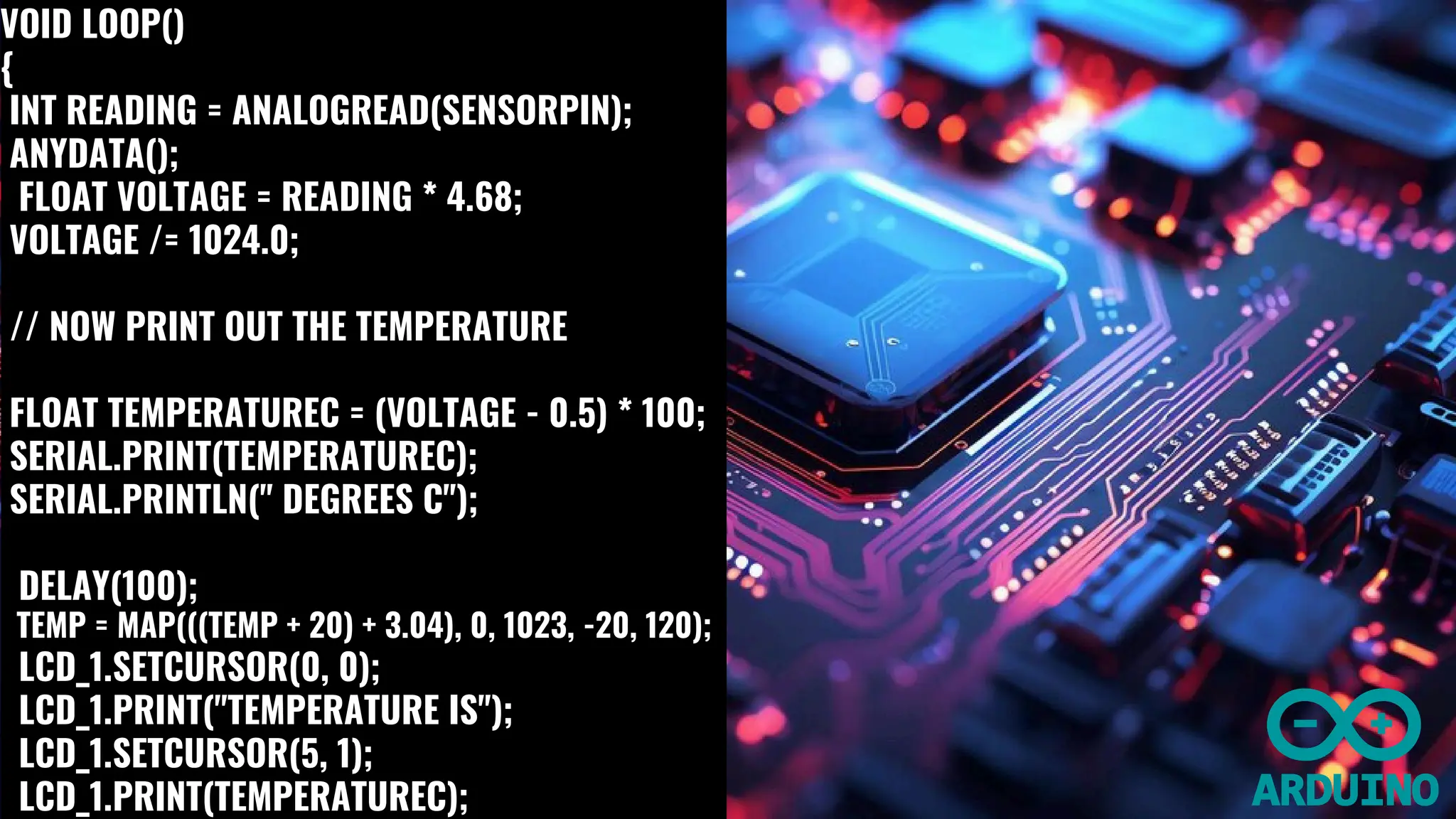
The document outlines the development of an IoT-based patient health monitoring system utilizing Arduino, enabling remote monitoring of vital signs like temperature and pulse for patients, especially the elderly and those in quarantine. The system employs various sensors to collect real-time health data, which is then shared with healthcare providers, enhancing patient care and enabling better management of health monitoring. The proposed solution aims to improve the healthcare monitoring system, making it efficient for use in emergency situations.