This document compares the Apriori and Apriori with hashing algorithms for association rule mining. Association rule mining is used to find frequent itemsets and discover relationships between items in transactional databases. The Apriori algorithm uses a bottom-up approach to generate frequent itemsets by joining candidate itemsets of length k with themselves. The Apriori with hashing algorithm improves efficiency by using a hash table to reduce the candidate itemset size. The document finds that Apriori with hashing outperforms the standard Apriori algorithm on large datasets by taking less time to generate frequent itemsets.
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 05 Issue: 01 | Jan-2018 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2018, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 6.171 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 976 Comparative analysis of Apriori and Apriori with hashing algorithm Aesha J Doshi1, Barkha Joshi2 1,2 Department of Computer Engineering , Sardar Vallabhbhai patel Inst. of Tech, Vasad, India ----------------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------------- Abstract: Data mining is a powerful technologytodiscover information within the large amount of the data. It is considered as an important subfield in knowledge management. Research in data mining continuesgrowing in various fields of organization such as Statistics, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Pattern Recognition, business, education, medical, scientific etc. Data mining algorithms are used to retrieval data from large database very efficiently. Association rule mining is used to find the frequent item set from the large database based on the relation. In this paper we are try to compare apriori and apriori with hashing algorithm and try to find which algorithm is better to provide accurate result in less amount of time. Key-word – Association rule, Apriorialgorithm,Apriori with hashing algorithm. INTRODUCTION: Data mining is the computing process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. It is an essential processwhere intelligentmethods are applied to extract data patterns. It is an interdisciplinary subfieldof computerscience. Theoverall goal of the data mining process is to extract information from a data set and transform it into an understandable structure for further use. it involves database and data management aspects, datapreproce- ssin, model and inference considerations,interestingnessmet rics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating. An association rule has two parts, an antecedent (if) and a consequent (then). An antecedent is an item found in the data. A consequent is an item that is found in combination with the antecedent. Association rules are created by analyzing data for frequent if/then patterns and using the criteria support and confidence to identify the most important relationships. Support is an indication of how frequently the items appear in the database. Confidence indicates the number of times the if/ then statements have been found to be true. Apriori uses a "bottom up" approach, where frequent subsets are extended one item at a time (a step known as candidate generation), and groups of candidates are tested against the data. The algorithm terminates when no further successful extensions are found. Apriori also uses “Top down” approach, where maximal candidate item set and search item set used. The not frequent item set is remove from maximal candidate item set and at last final result into maximal candidate item set. Thefrequentitemset generated from maximal candidate item set. Hashing technique is used to improve the efficiency of the apriori algorithm. it work by creating a dictionary (hash table) that stores the candidate item sets as keys, and the number of appearances asthe value. Initialization start with zero and Increment the counter for each item set that you see in the data. Association rule Association rule is important aspect of data mining.Itisused to discover frequent pattern, Association, Connection or on the other hand casual structures among sets of products in value-based databases and other data stores. The volume of information is expanding significantly as the information produced by day by day exercises. Subsequently, mining association rules from bulky data in DB is best interested area for many industries. The strategies for finding association rules from the information have generally centered around recognizing connections between things, which demonstrate customer behavior[4]. For some applications, it is hard to discover strongrelationshipamong information things at low or on the other hand crude levels of abstraction because of the deficiency of information at those levels. The Strong association can foundathighlevelof abstraction represent sensible knowledge[1]. Suppose I={I1, I2, I3….. In } be the set of items. Let D is set of database transaction where each transaction T isset ofitem. Each transaction has identifier TID. Now A is the set of item in particular transaction. There are two important measuresof association rulethatis support and confidence. Support(S): It can be define as it is probability or percentage of transaction in D that contain A B or in other word we can say that it is ratio of occurrences of items and total num of transactions. Support (AB)= P(A B) S (A B) = Amount of transaction A & B Total Transaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v5i1206-180317112230/75/IRJET-Comparative-Analysis-of-Apriori-and-Apriori-with-Hashing-Algorithm-1-2048.jpg)

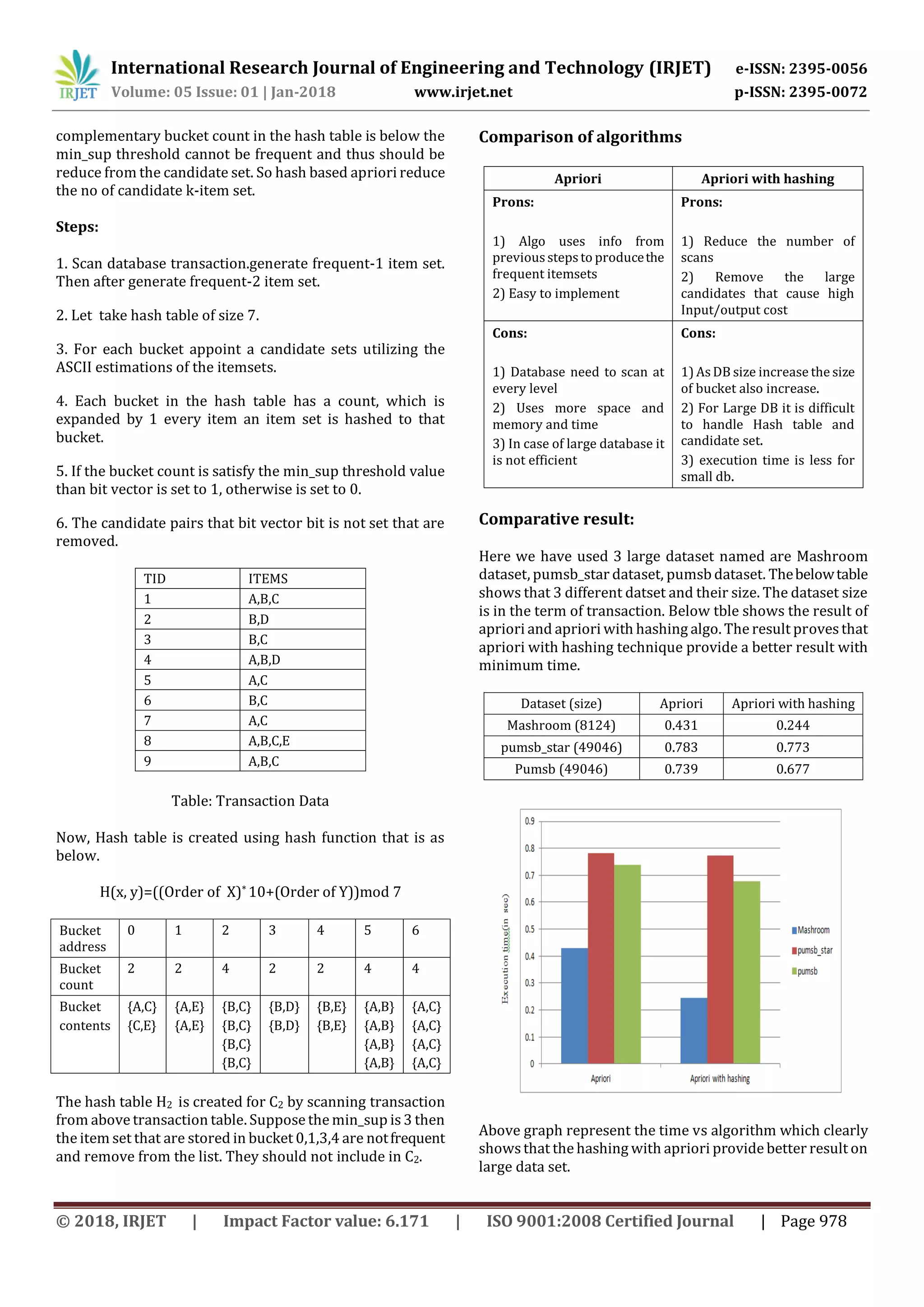
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 05 Issue: 01 | Jan-2018 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2018, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 6.171 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 979 Conclusion: Above result proves that the apriori with hashing provide better results in less amount of time as compare to apriori. We try to reduce more time with accurate result using map reduce concept. References: [1] Han J, Kamber M. Data Mining : ConceptsandTechniques. Higher Education Press,2001.. [2] Warnia Nengsih “A Comparative Study On MarketBasket Analysis And Apriori Association Technique” Politeknik Caltex Riau –Indonesia 2015 IEEE [3] Sudhanshu Shekhar Bisoyi; Pragnyaban Mishra; S. N. Mishra”Weighted frequent multi partitioned itemset mining of market-basket data using MapReduce on YARN framework”-2016 IEEE [4] Surbhi K. Solanki, Jalpa T. Patel”Survey on association rule”,(2015),212 – 216 [5] Zhang Chunsheng ,Li Yan “The Visual Mining Method of Apriori Association Rule Based on Natural Language”-2016 IEEE. [6] Thanmayee, H R Manjunath Prasad “Revamped Market- Basket Analysis UsingIn-MemoryComputationFramework”- 2017 IEEE. [7] Ashish Shah “Association Rule Mining with Modified Apriori Algorithm using Top down Approach”-2016 IEEE. [8] O. Yahya, O. Hegazy, Ehab Ezat. “An Efficient Implementation of Apriori Algorithm Based on Hadoop- Mapreduce Model.”, Proc. of the International Journal of Reviews in Computing. (2012). Vol. 12: 59–67. [9] T. Karthikeyan and N. Ravikumar, “A Survey on Association Rule Mining,” International Journalof Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (IJARCCE), pp. 5223-5227, 2014. [10] Abhijit Sarkar, Apurba Paul, Sainik Kumar Mahata, DeepakKumar, Modified Apriori Algorithm to find out Association Rules using Tree based Approach. [11] Kaushal vyas,Shipa sherasiya “ Modified apriori algorithm using hash based technique”.IJARIIE-ISSN(O)- 2395-4396. [12] Rupali, Gaurav gupta“Apriori Based Algorithms And Their Comparisons”. ISSN: 2278-0181 [13] http://fimi.ua.ac.be/data/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v5i1206-180317112230/75/IRJET-Comparative-Analysis-of-Apriori-and-Apriori-with-Hashing-Algorithm-4-2048.jpg)