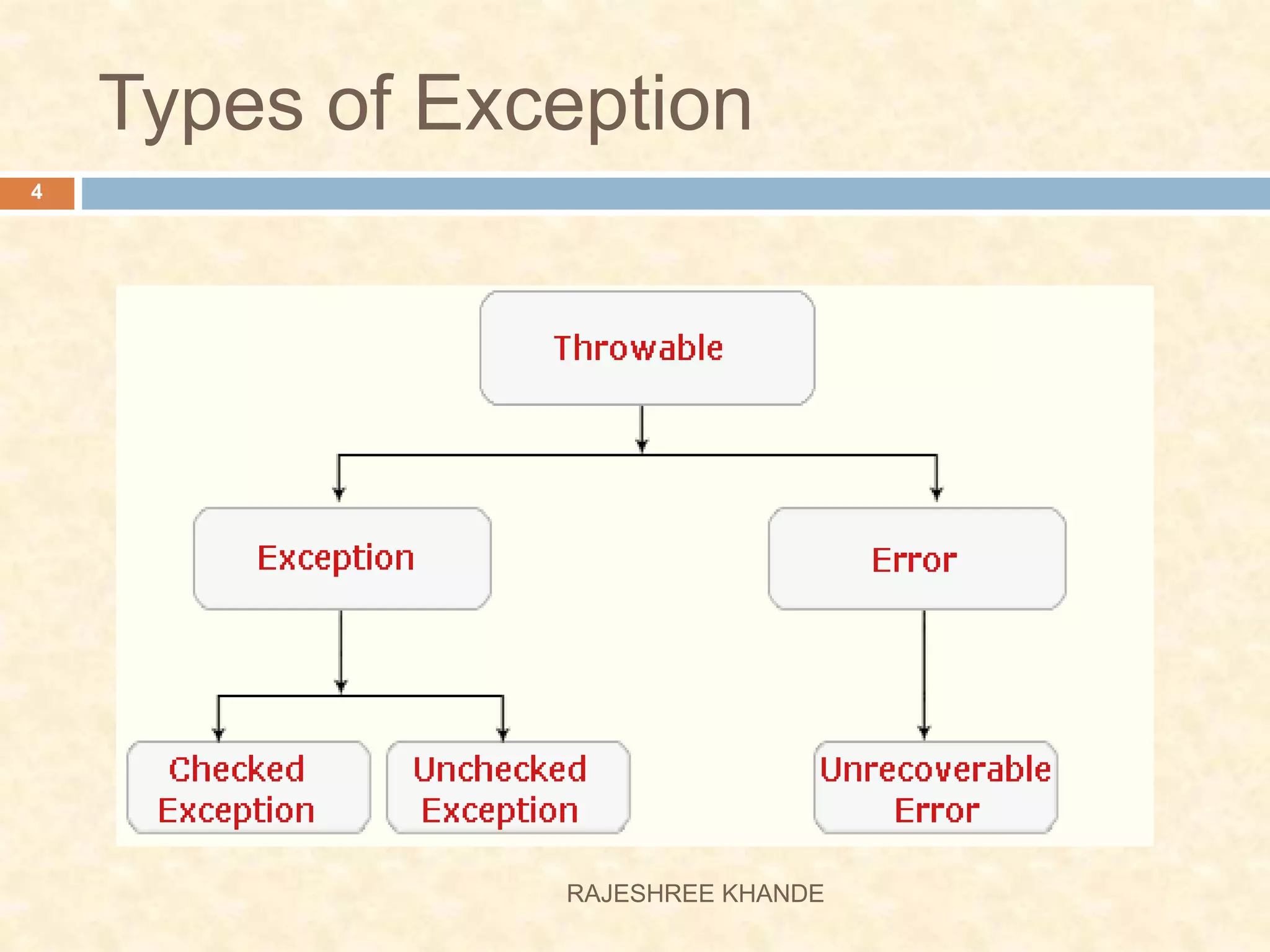
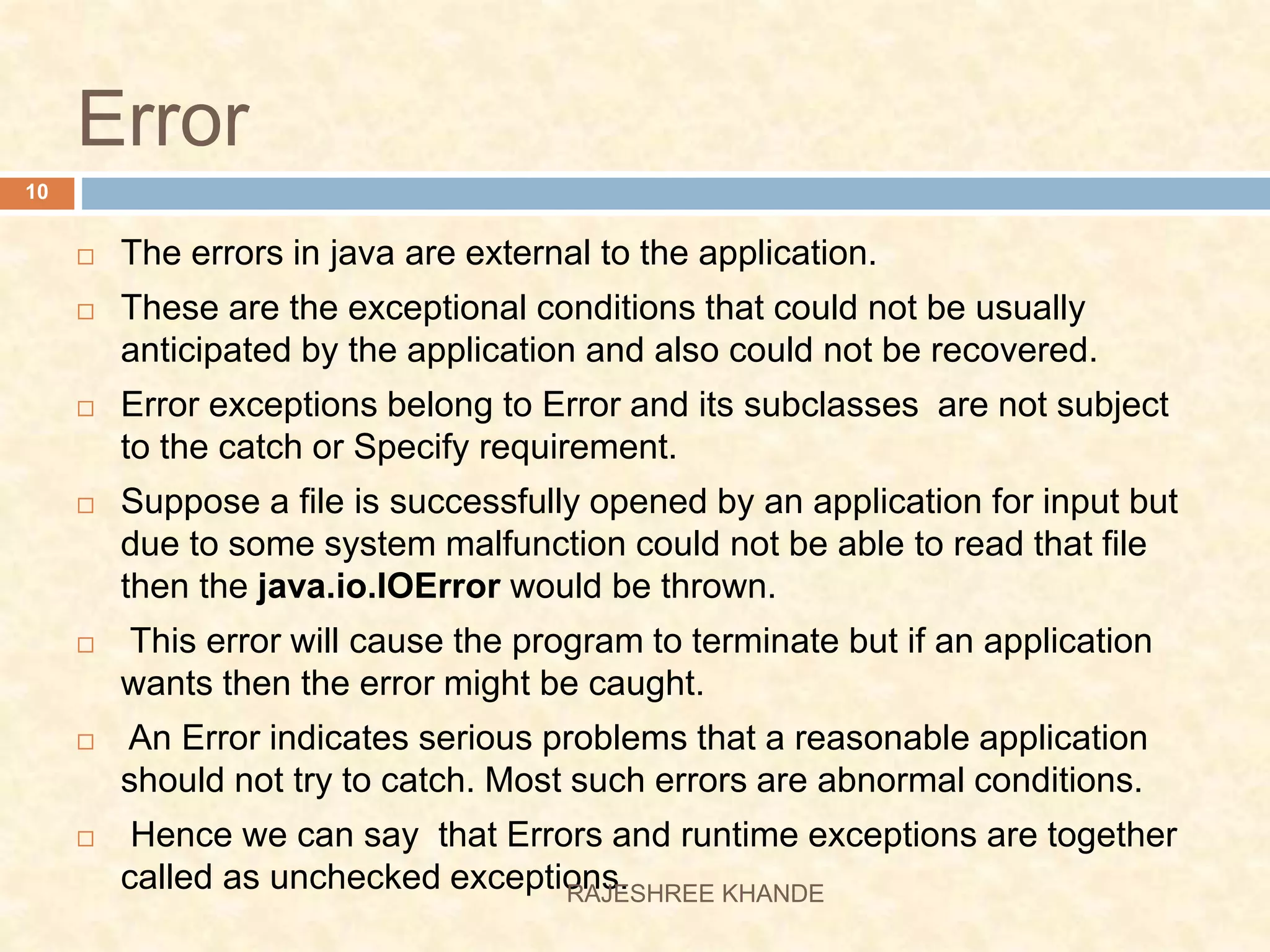
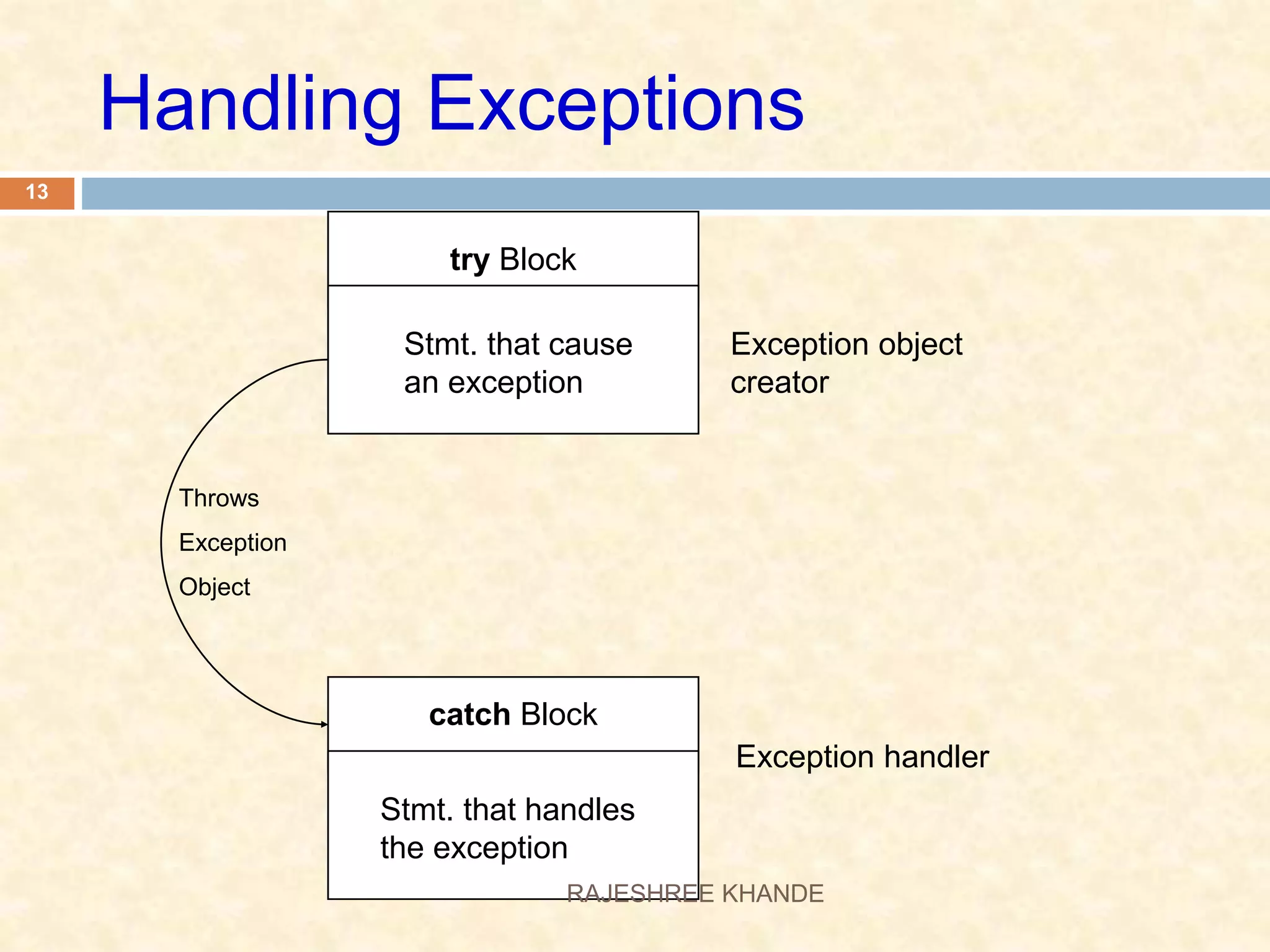
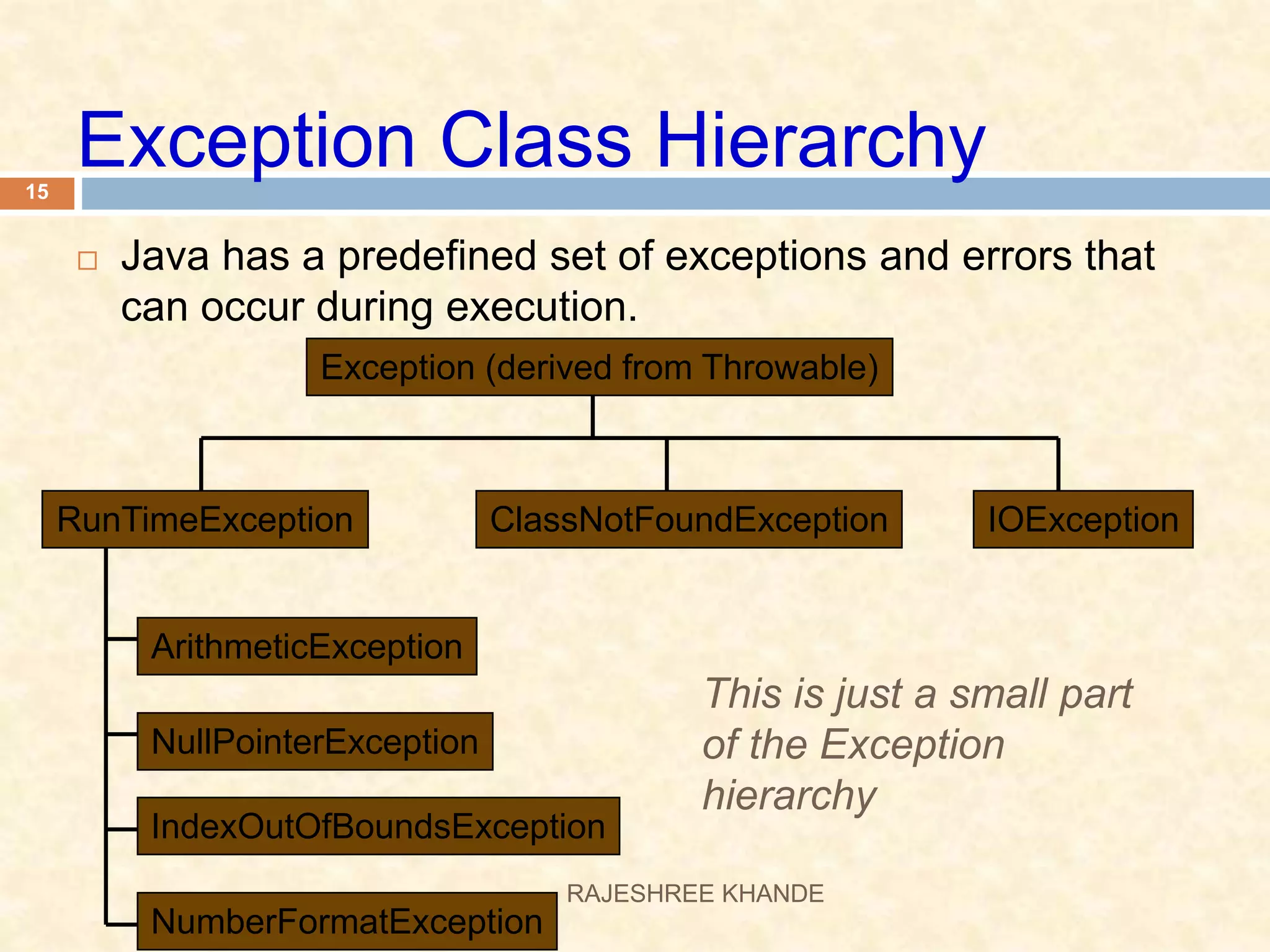
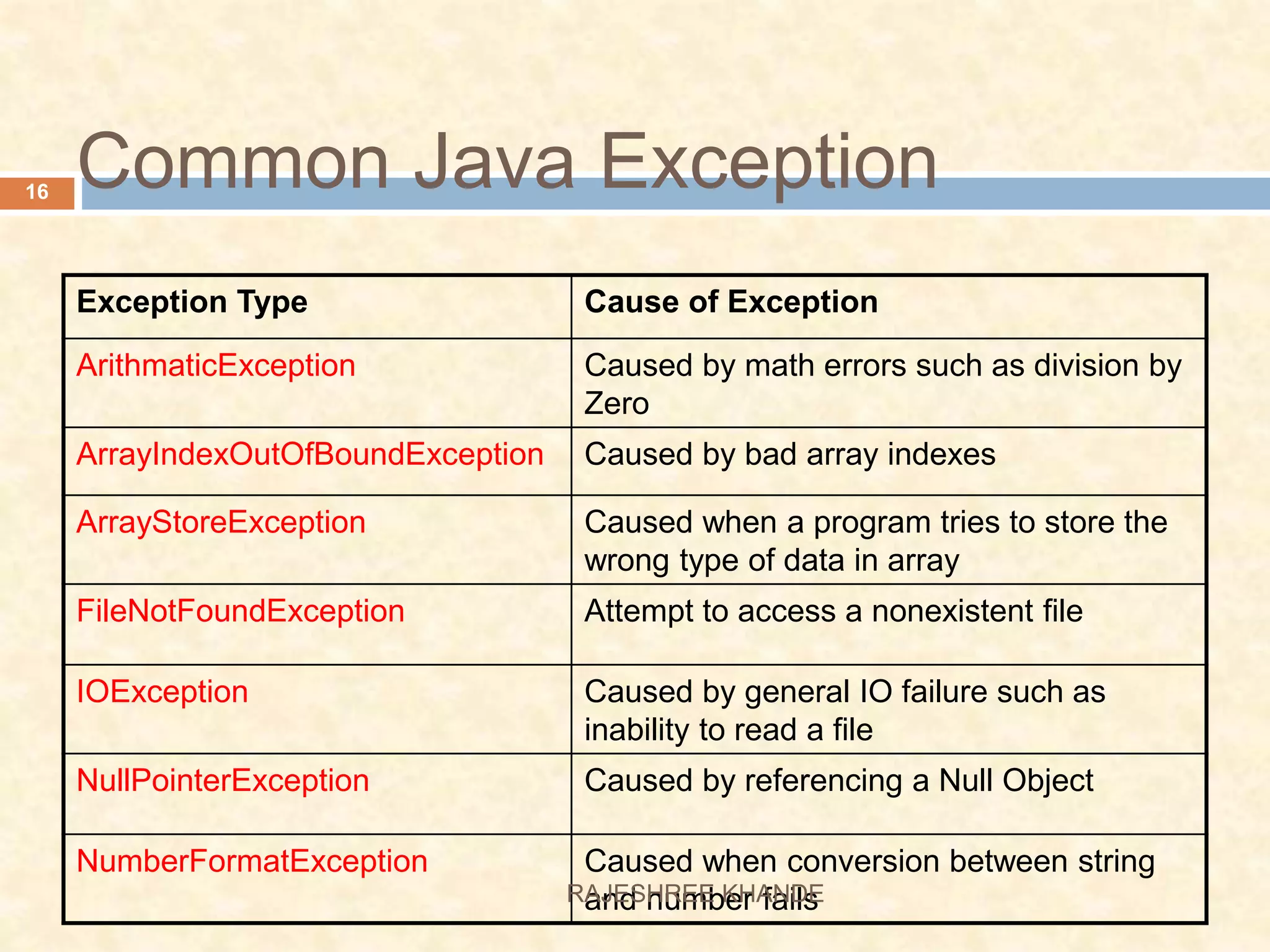
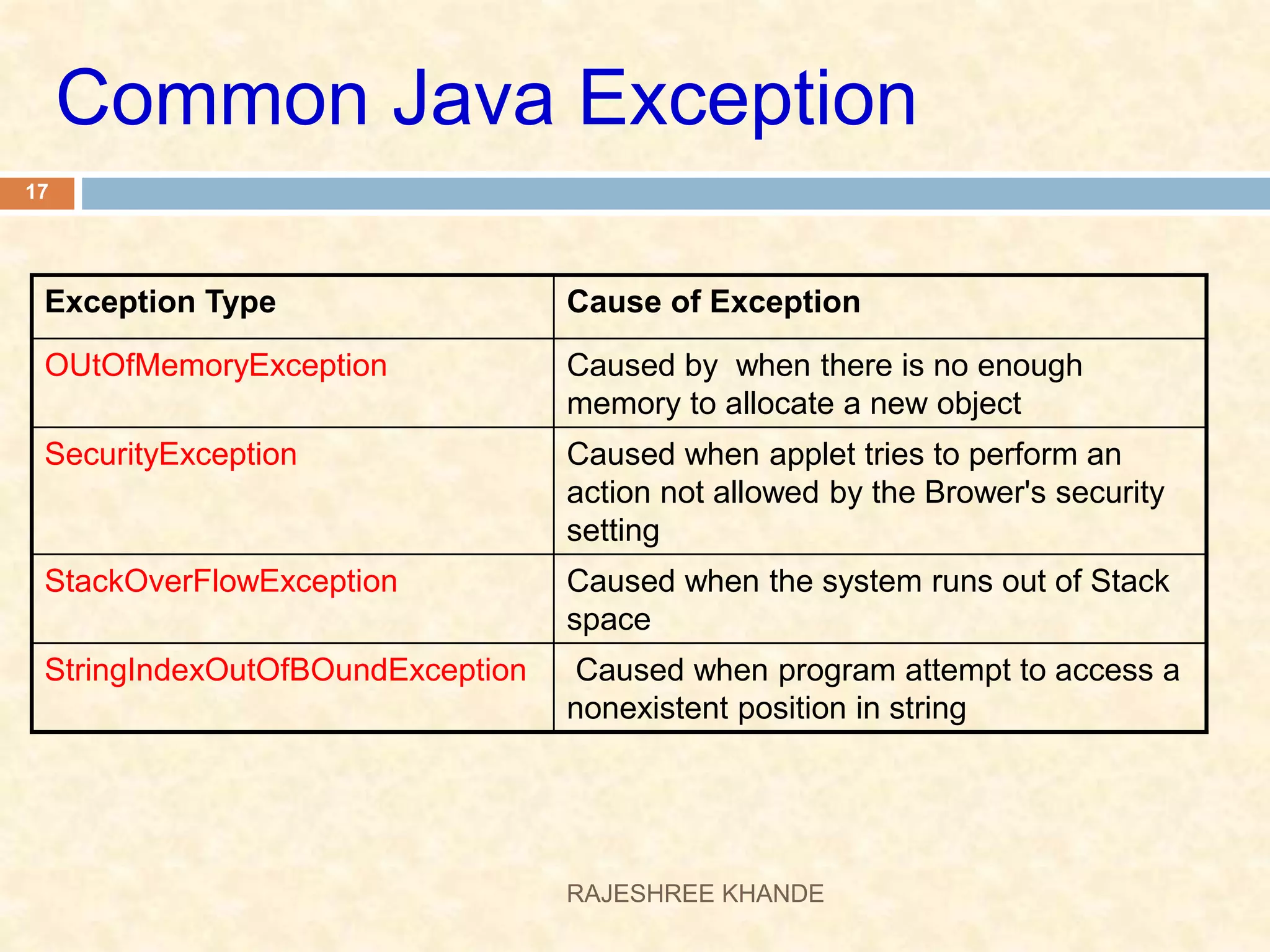
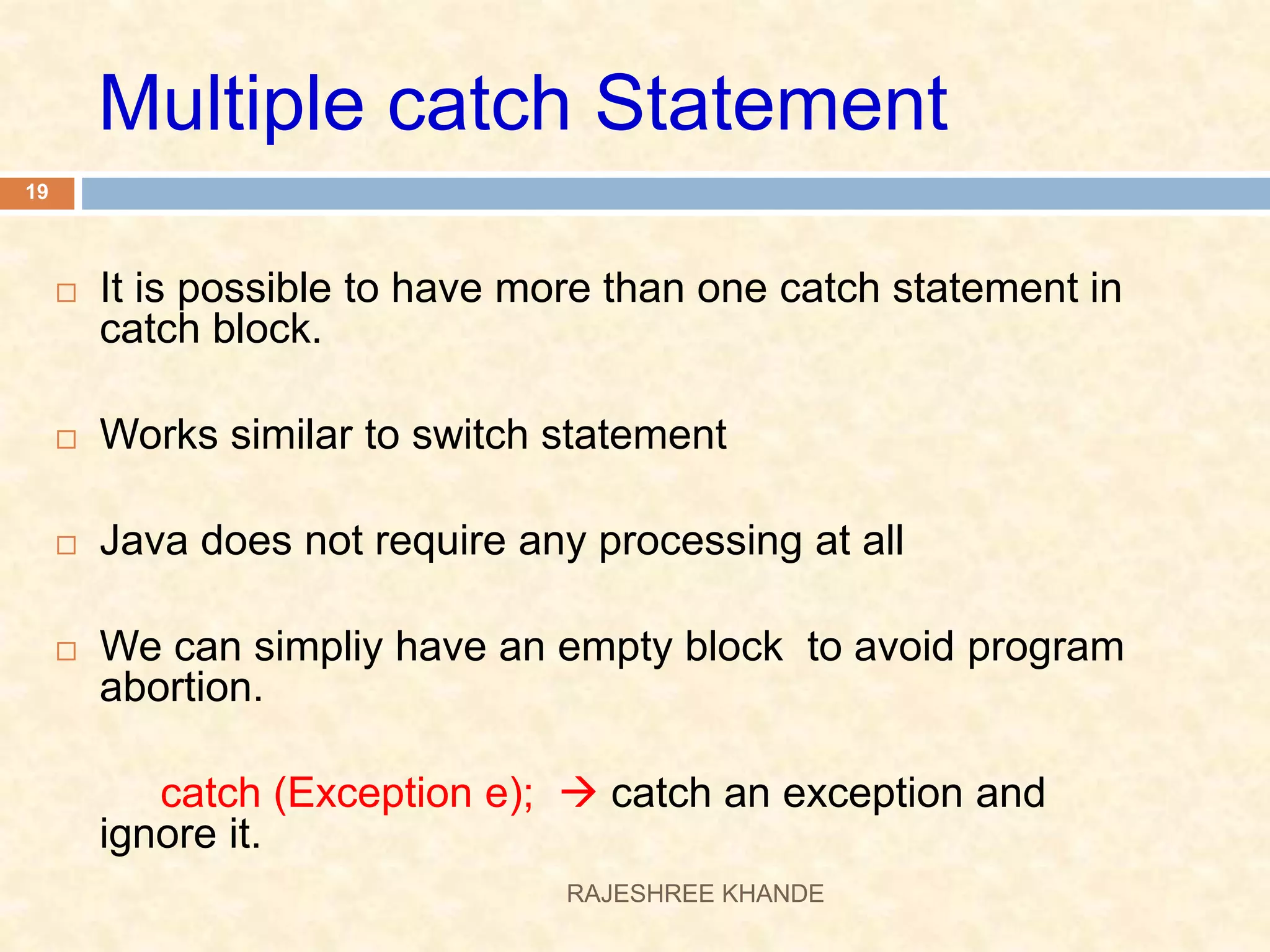
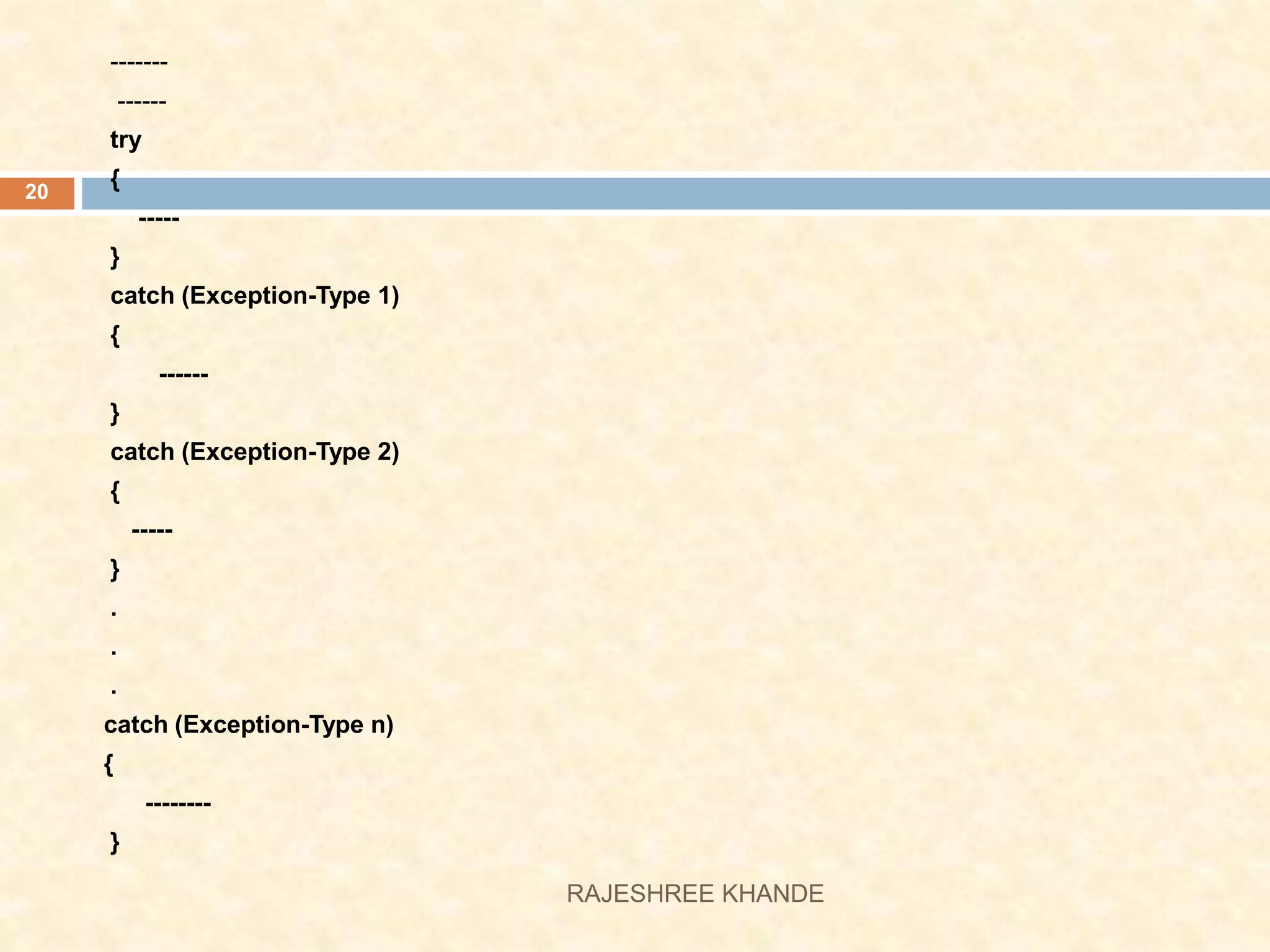
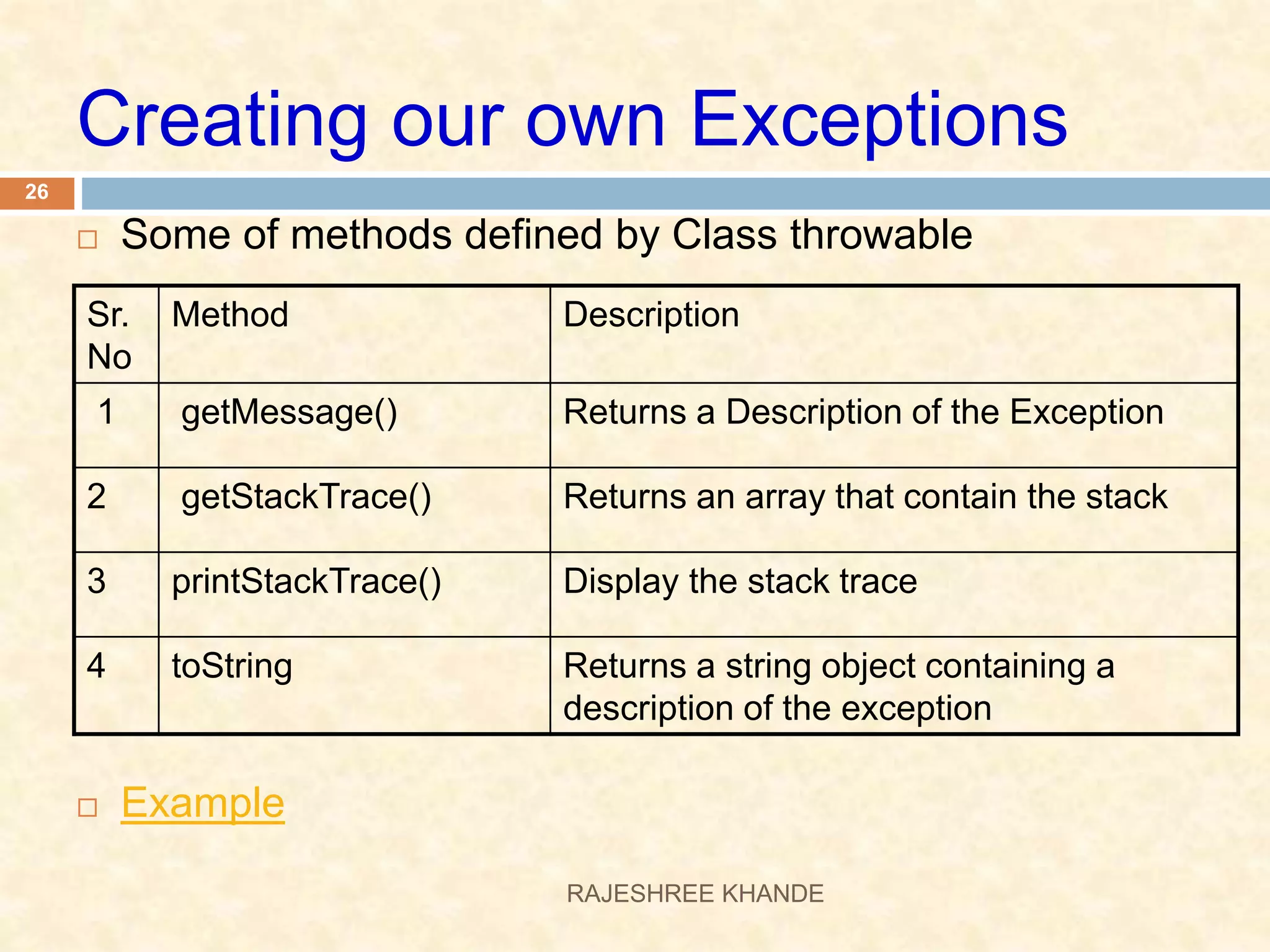
This document discusses exception handling in Java. It defines exceptions as errors that occur during program execution and disrupt normal flow. Exceptions are represented as objects that can be thrown and caught. There are two main types of exceptions - checked exceptions which must be handled, and unchecked exceptions which occur due to bugs and do not need to be handled. The try, catch, and finally keywords are used to handle exceptions. Custom exceptions can also be created by extending the Exception class.