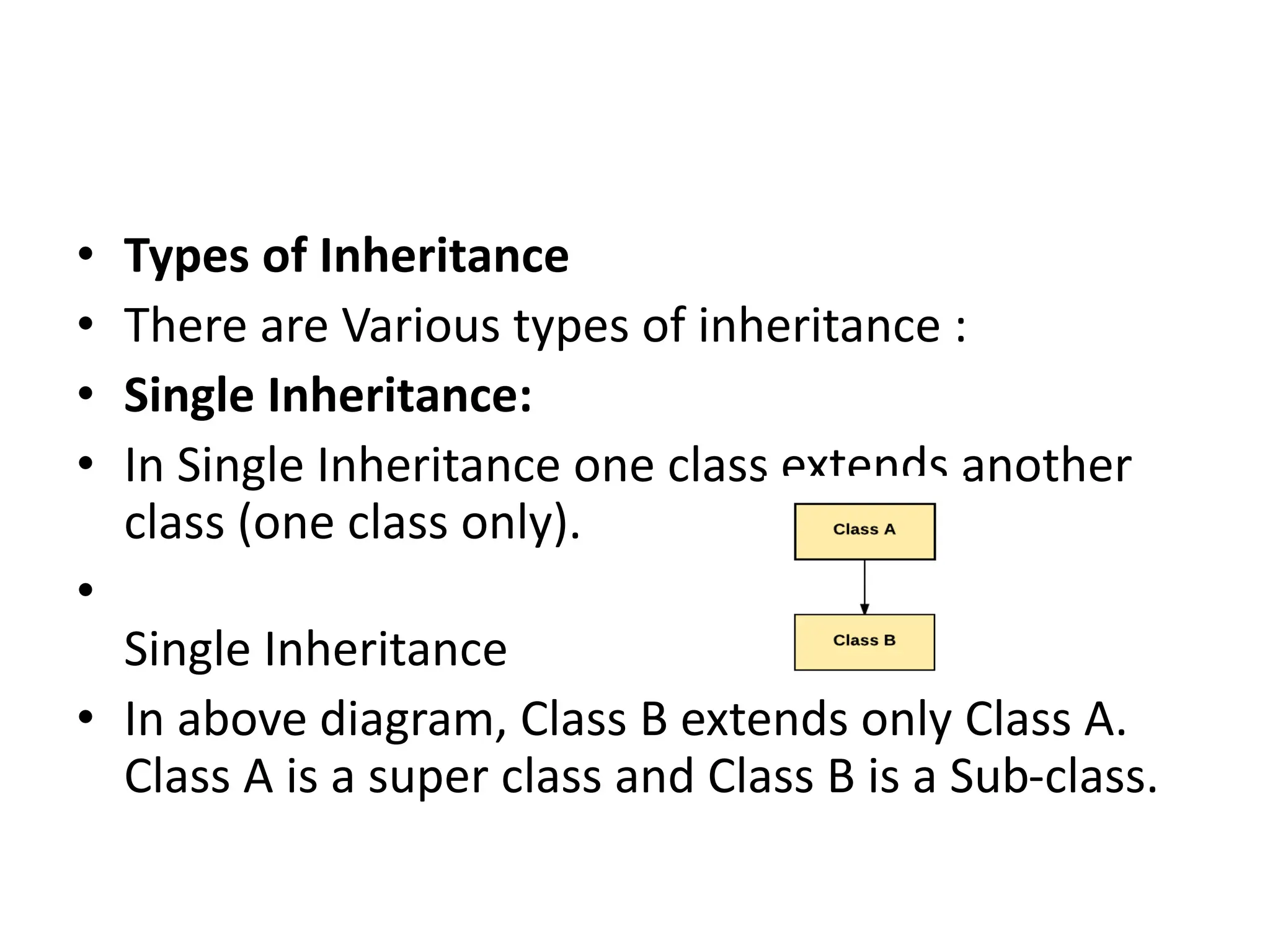
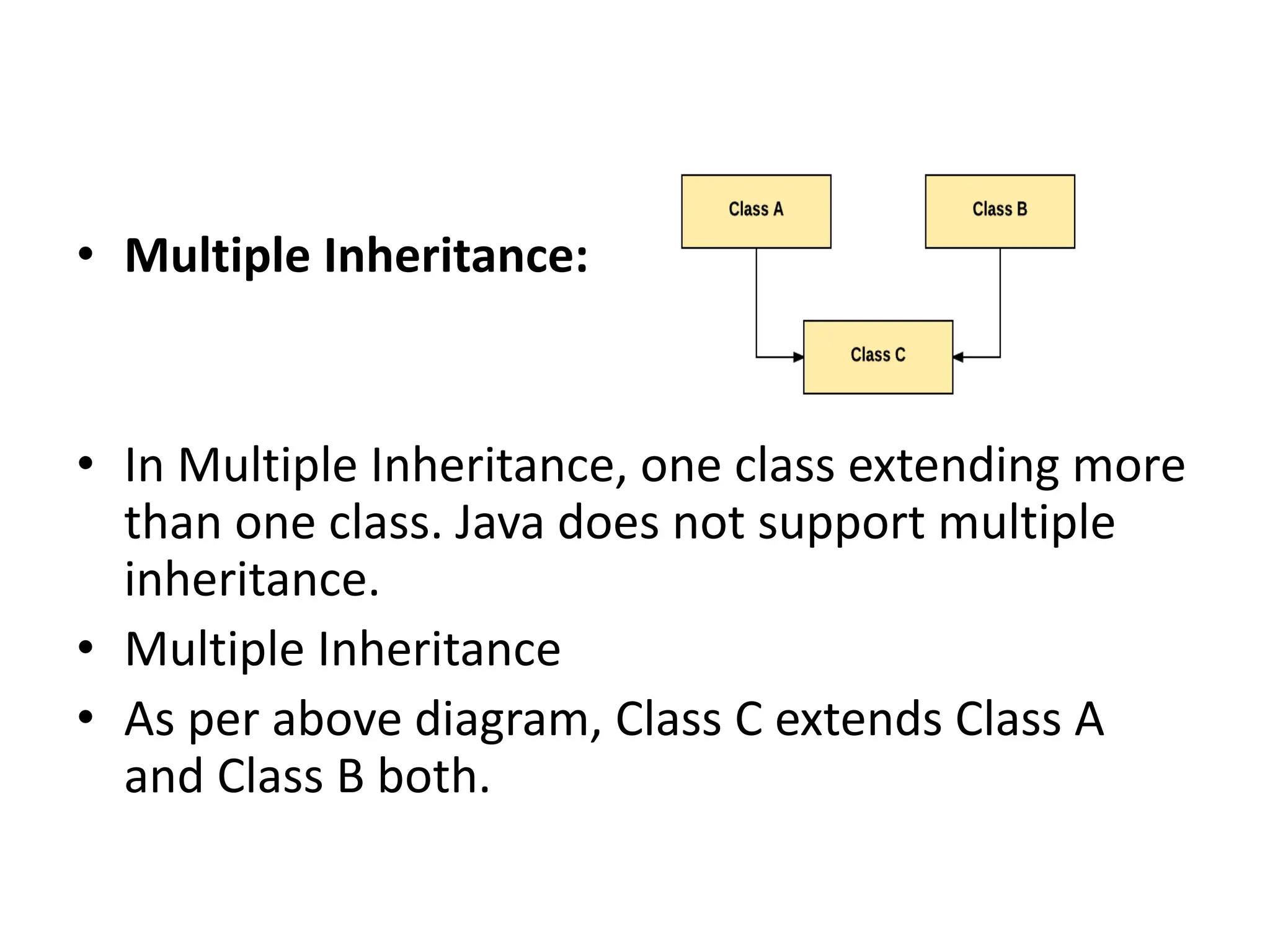
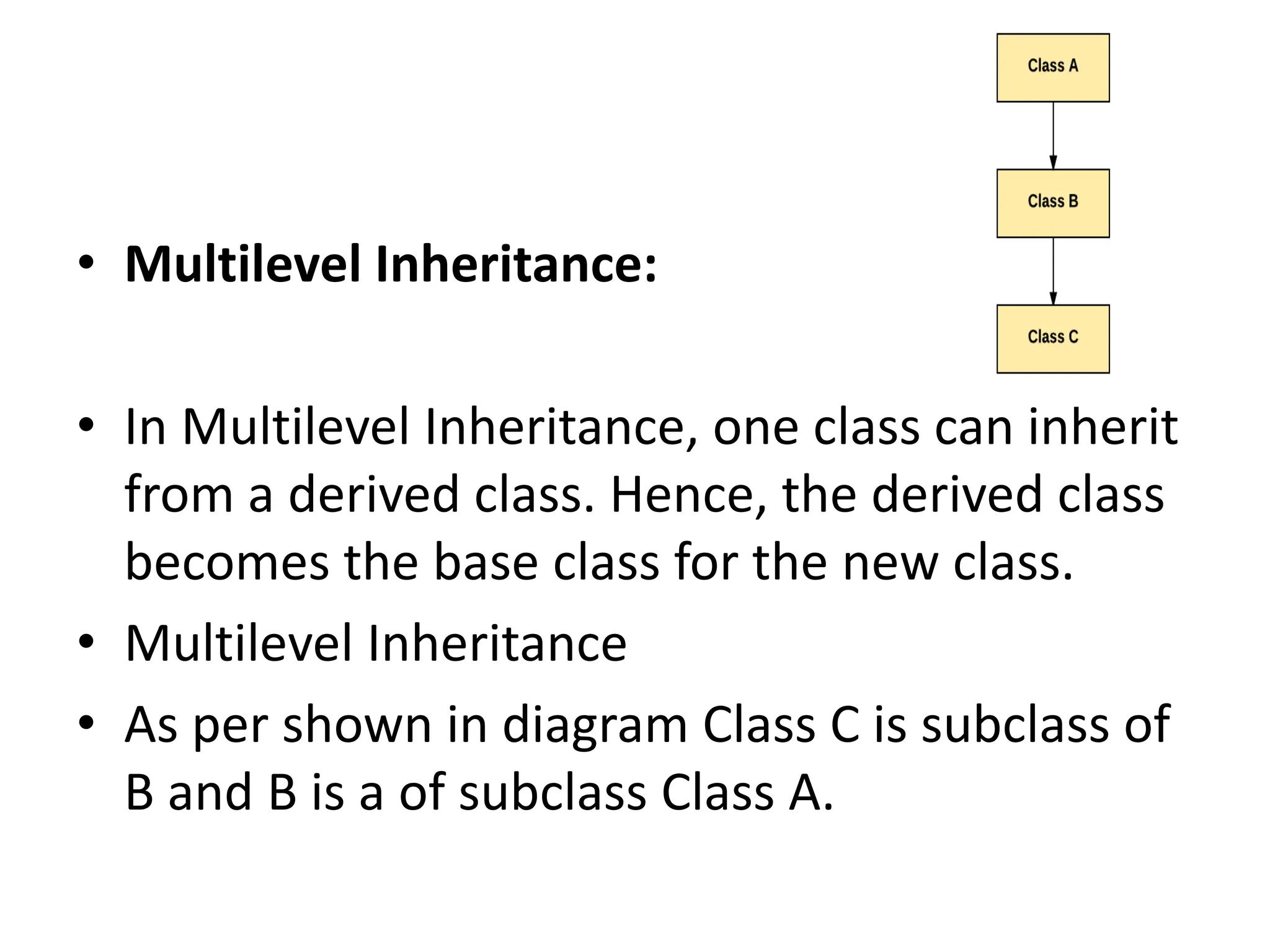
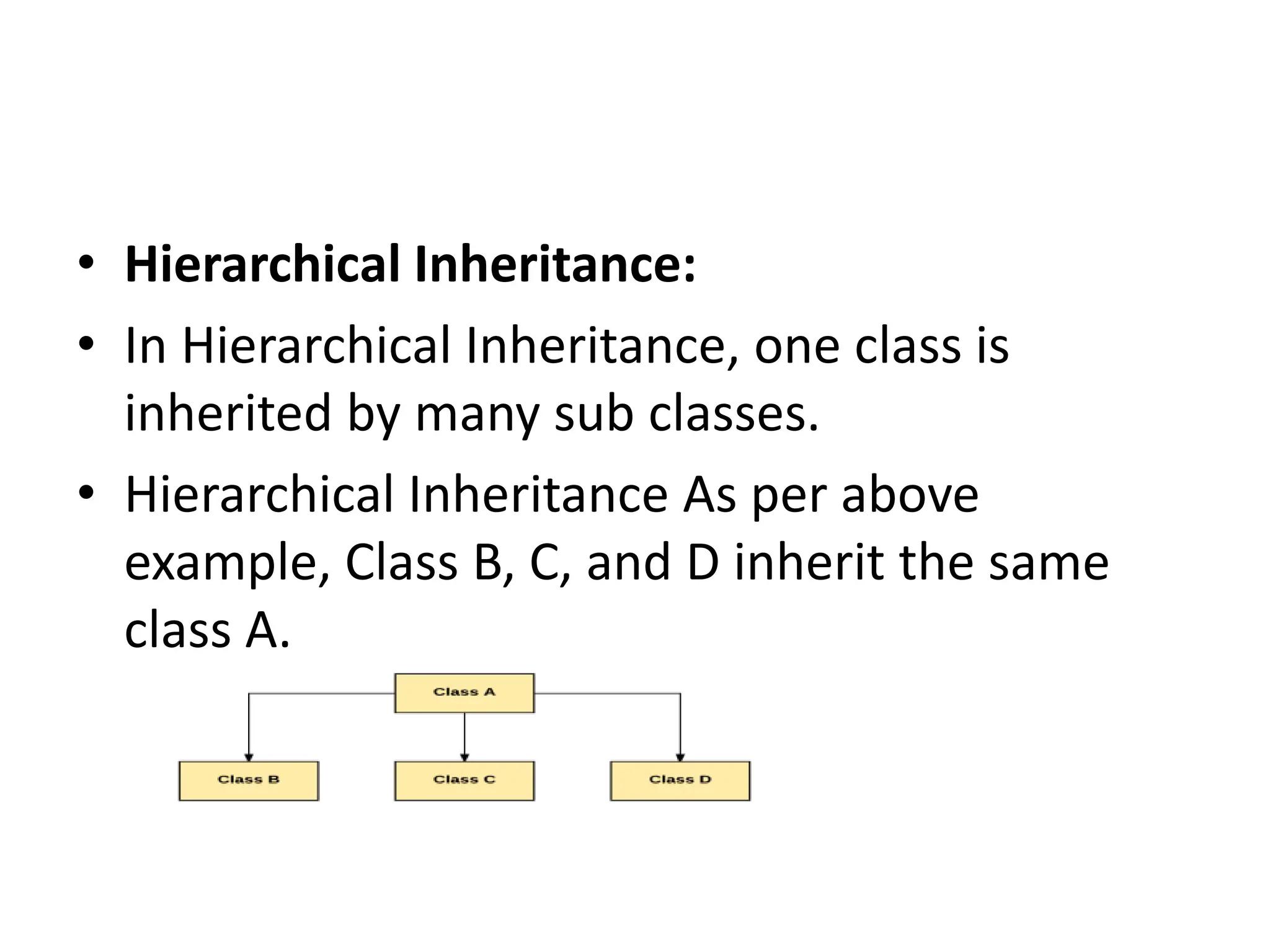
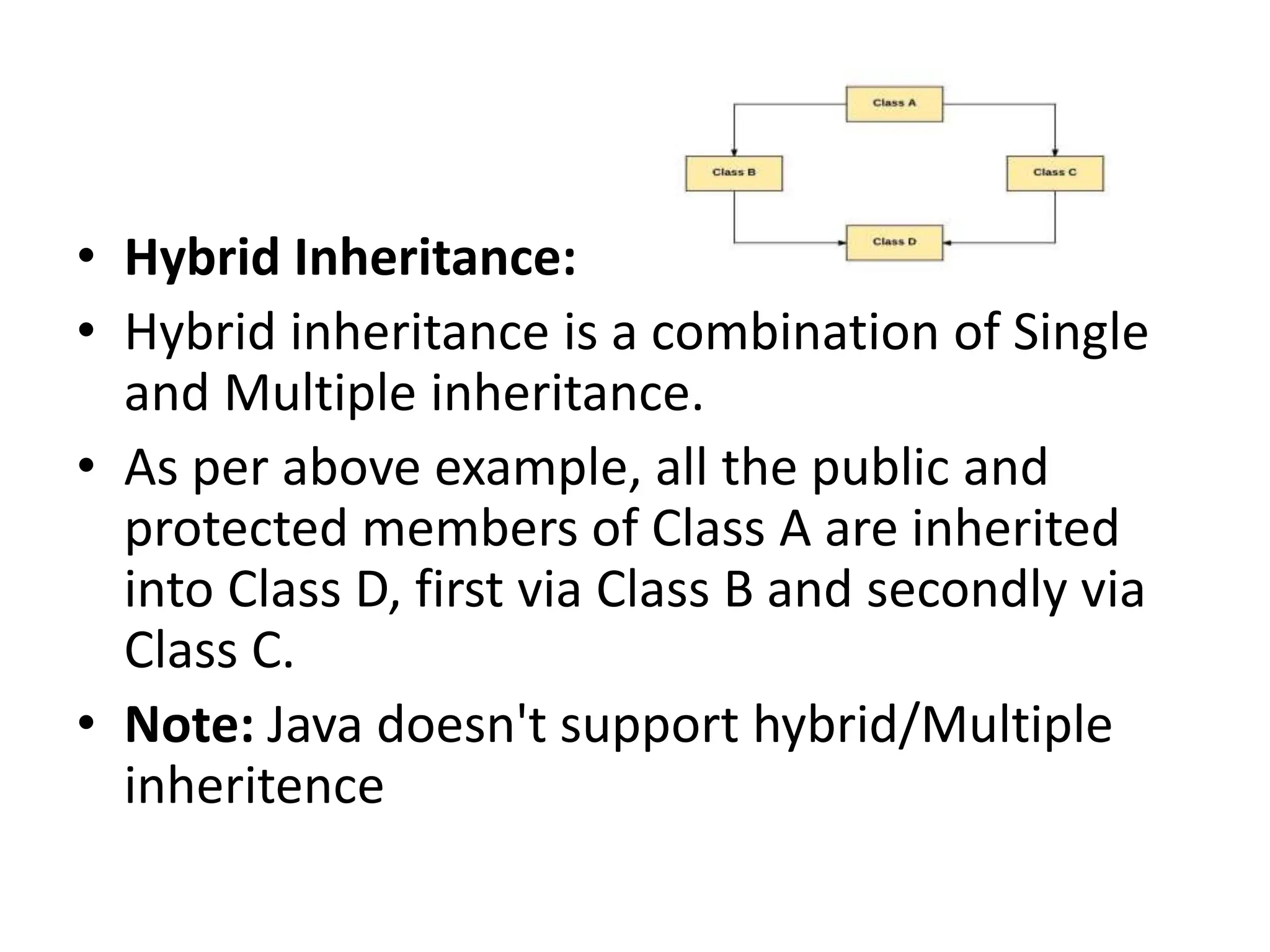
Inheritance is a mechanism where one class acquires the properties and behaviors of another class. In Java, inheritance allows classes to reuse fields and methods from the parent class. The key types of inheritance in Java are single inheritance, multilevel inheritance, hierarchical inheritance, and method overriding which enables runtime polymorphism. The super keyword refers to the parent class, and the final keyword can restrict classes, methods, and variables from being overridden or redefined.





![• class Employee{ • double salary=40000; • } • class Programmer extends Employee{ • int bonus=10000; • } • • class Main{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • Programmer p=new Programmer(); • System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary); • System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus); • } • } • https://compiler.javatpoint.com/opr/online-java-compiler.jsp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
![IS-A relationship : Single inheritance • class Animal{ • void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");} • } • class Dog extends Animal{ • void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");} • } • class Main{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • Dog d=new Dog(); • d.bark(); • d.eat(); • }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![IS-A relationship : Multilevel Inheritance • class Animal{ • void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");} • } • class Dog extends Animal{ • void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");} • } • class BabyDog extends Dog{ • void weep(){System.out.println("weeping...");} • } • class Main{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • BabyDog d=new BabyDog(); • d.weep(); • d.bark(); • d.eat(); • }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![Has-A inheritance • class Operation{ • int square(int n){ • return n*n; • } • } • • class Circle{ • Operation op;//aggregation • double pi=3.14; • • double area(int radius){ • op=new Operation(); • int rsquare=op.square(radius);//code reusability (i.e. delegates the method call). • return pi*rsquare; • } • • • • public static void main(String args[]){ • Circle c=new Circle(); • double result=c.area(5); • System.out.println(result); • } • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-14-2048.jpg)


![• class Vehicle{ • //defining a method • void run(){System.out.println("Vehicle is running");} • } • //Creating a child class • class Bike2 extends Vehicle{ • //defining the same method as in the parent class • void run(){System.out.println("Bike is running safely");} • • public static void main(String args[]){ • Bike2 obj = new Bike2();//creating object • obj.run();//calling method • } • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-17-2048.jpg)

![super is used to refer immediate parent class instance variable. • class Animal{ • String color="white"; • } • class Dog extends Animal{ • String color="black"; • void printColor(){ • System.out.println(color);//prints color of Dog class • System.out.println(super.color);//prints color of Animal class • } • } • class TestSuper1{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • Dog d=new Dog(); • d.printColor(); • }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-19-2048.jpg)
![super can be used to invoke parent class method • class Animal{ • void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");} • } • class Dog extends Animal{ • void eat(){System.out.println("eating bread...");} • void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");} • void work(){ • super.eat(); • bark(); • } • } • class TestSuper2{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • Dog d=new Dog(); • d.work(); • }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-20-2048.jpg)
![super is used to invoke parent class constructor • class Animal{ • Animal(){System.out.println("animal is created");} • } • class Dog extends Animal{ • Dog(){ • super(); • System.out.println("dog is created"); • } • } • class TestSuper3{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • Dog d=new Dog(); • }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-21-2048.jpg)

![Java Runtime Polymorphism • class Bike{ • void run(){System.out.println("running");} • } • class Splendor extends Bike{ • void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 60km"); } • • public static void main(String args[]){ • Bike b = new Splendor();//upcasting • b.run(); • } • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![• class Shape{ • void draw(){System.out.println("drawing...");} • } • class Rectangle extends Shape{ • void draw(){System.out.println("drawing rectangle...");} • } • class Circle extends Shape{ • void draw(){System.out.println("drawing circle...");} • } • class Triangle extends Shape{ • void draw(){System.out.println("drawing triangle...");} • } • class TestPolymorphism2{ • public static void main(String args[]){ • Shape s; • s=new Rectangle(); • s.draw(); • s=new Circle(); • s.draw(); • s=new Triangle(); • s.draw(); • } • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-inheritance-240220094736-2d2a8cef/75/Java-Inheritance_multiple_inheritance-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
