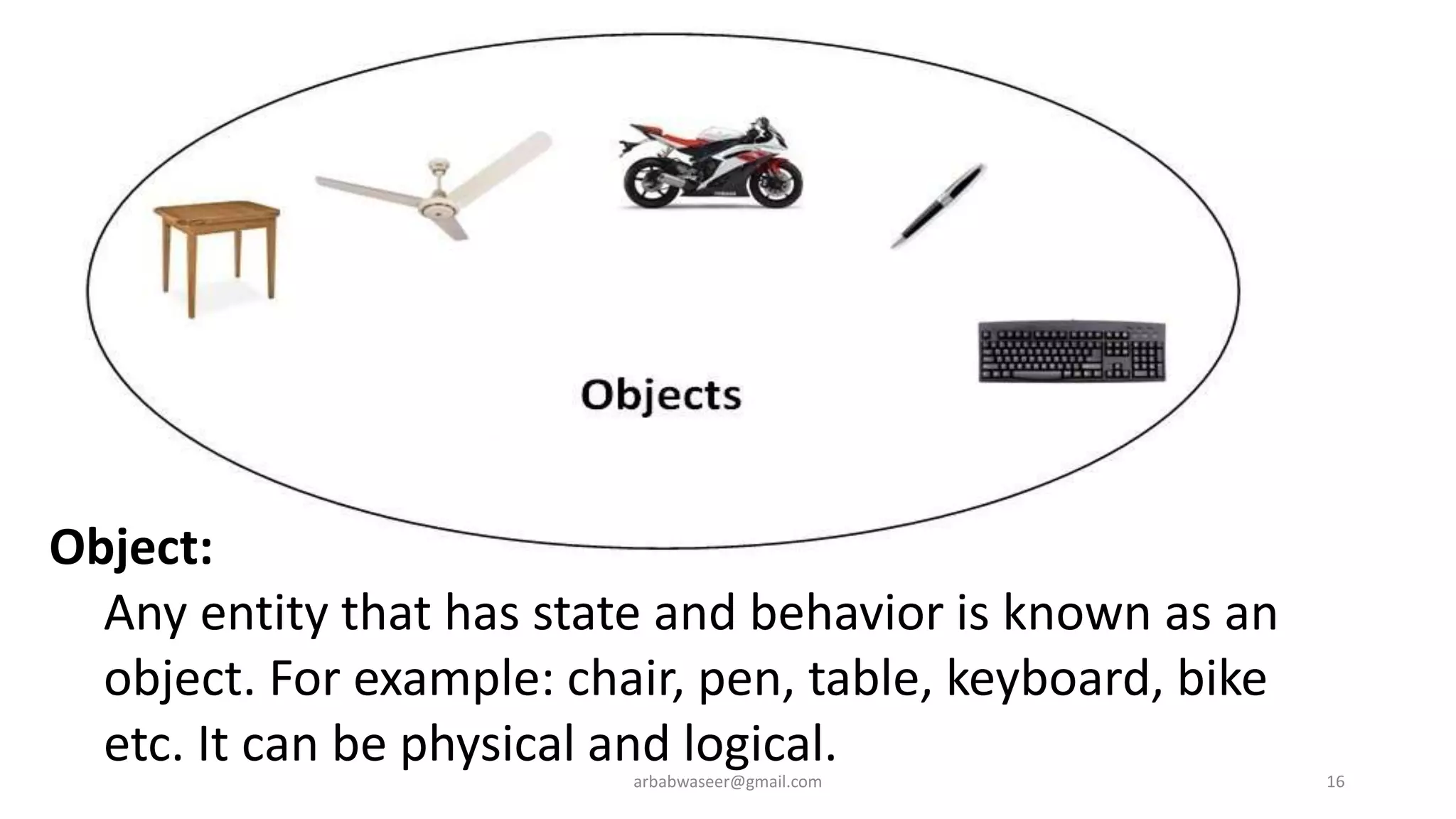
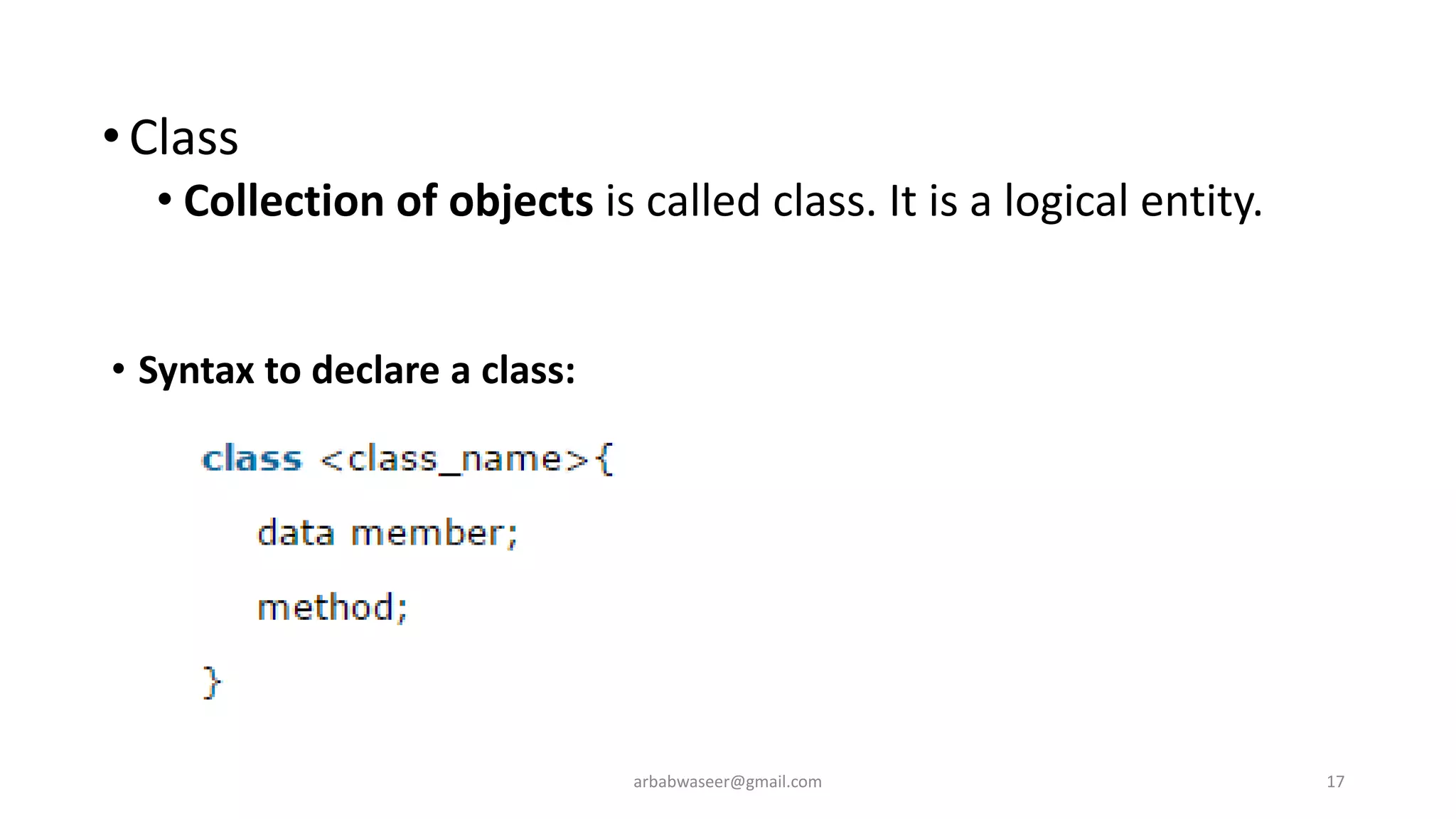
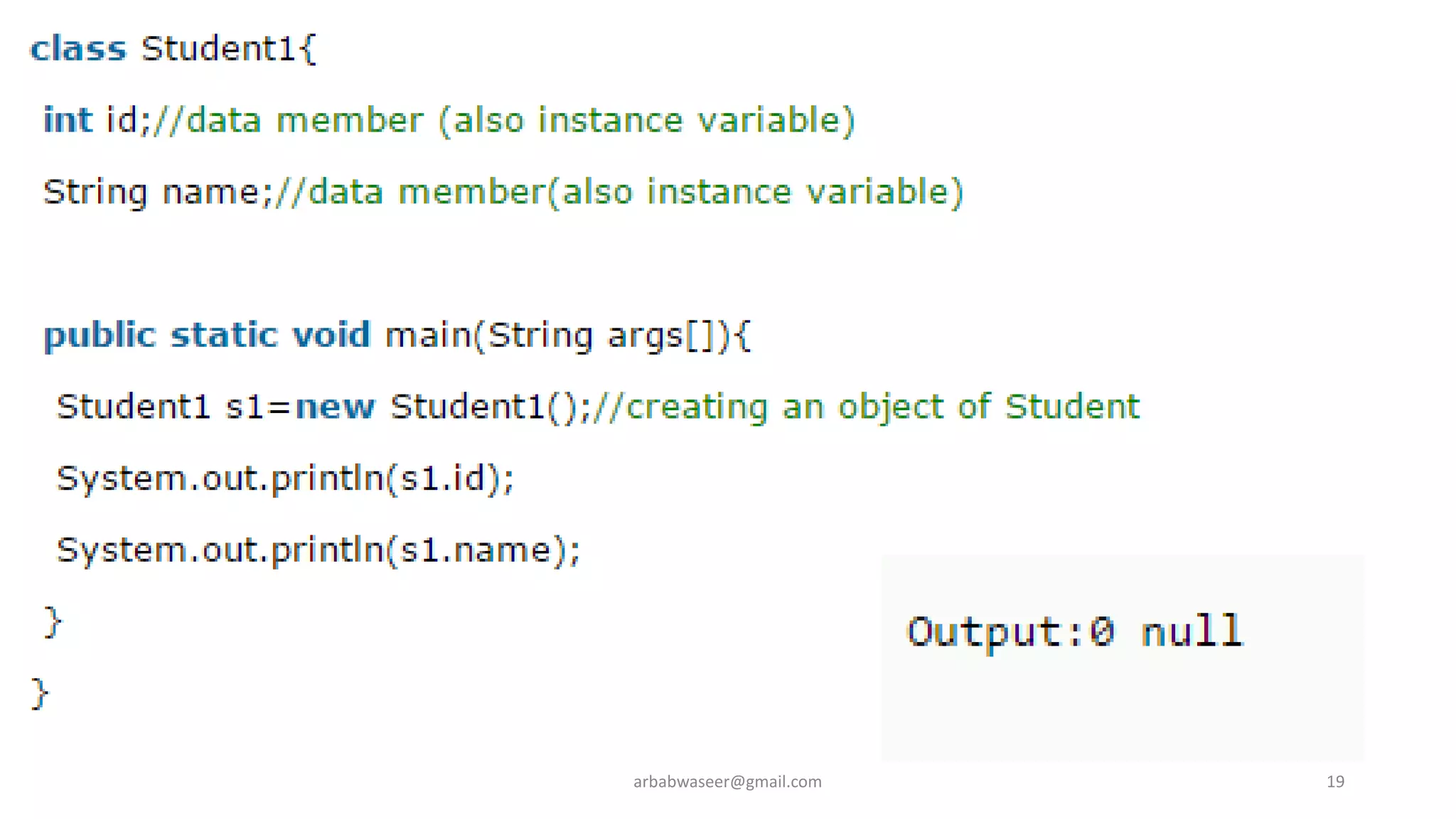
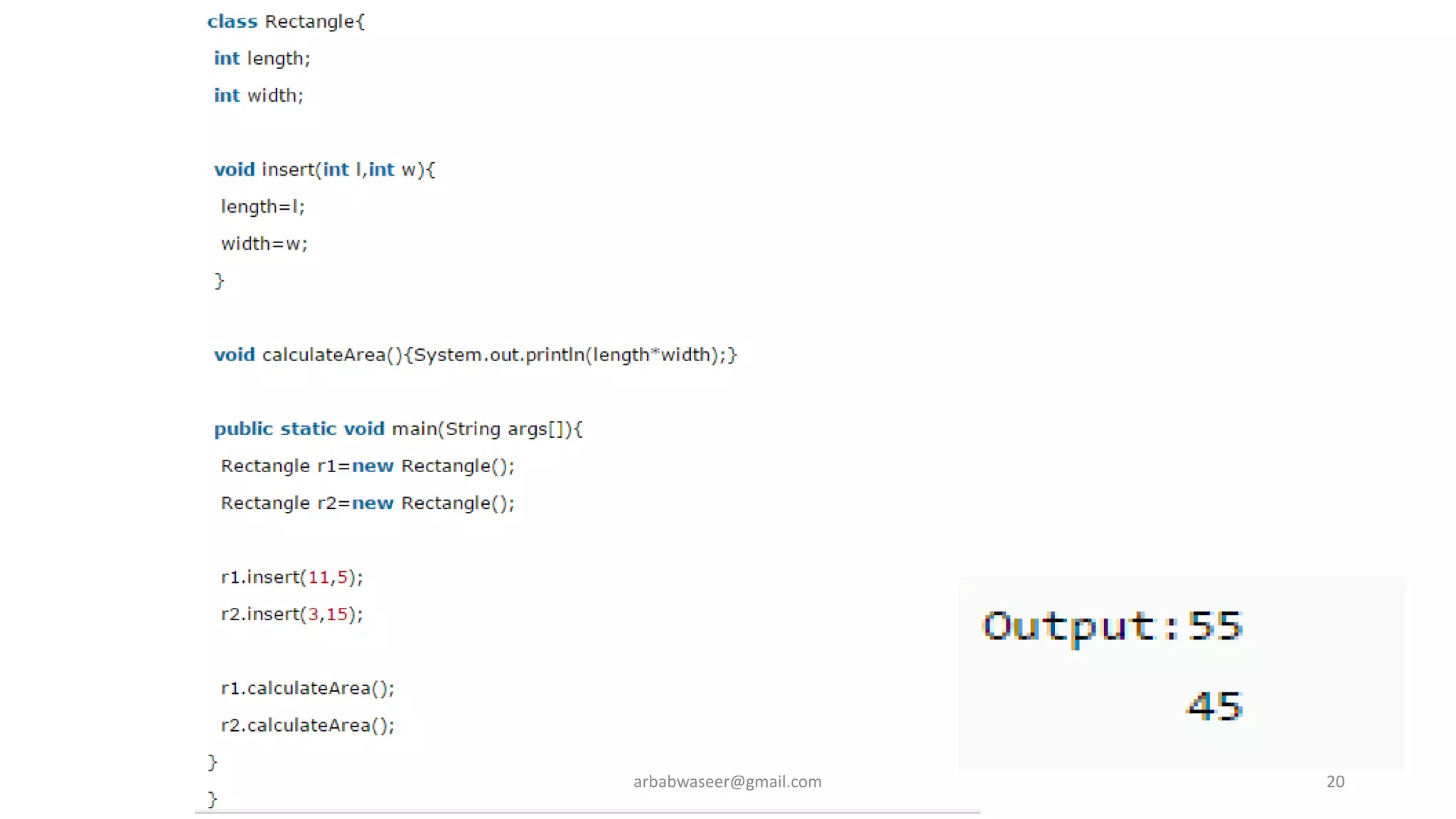
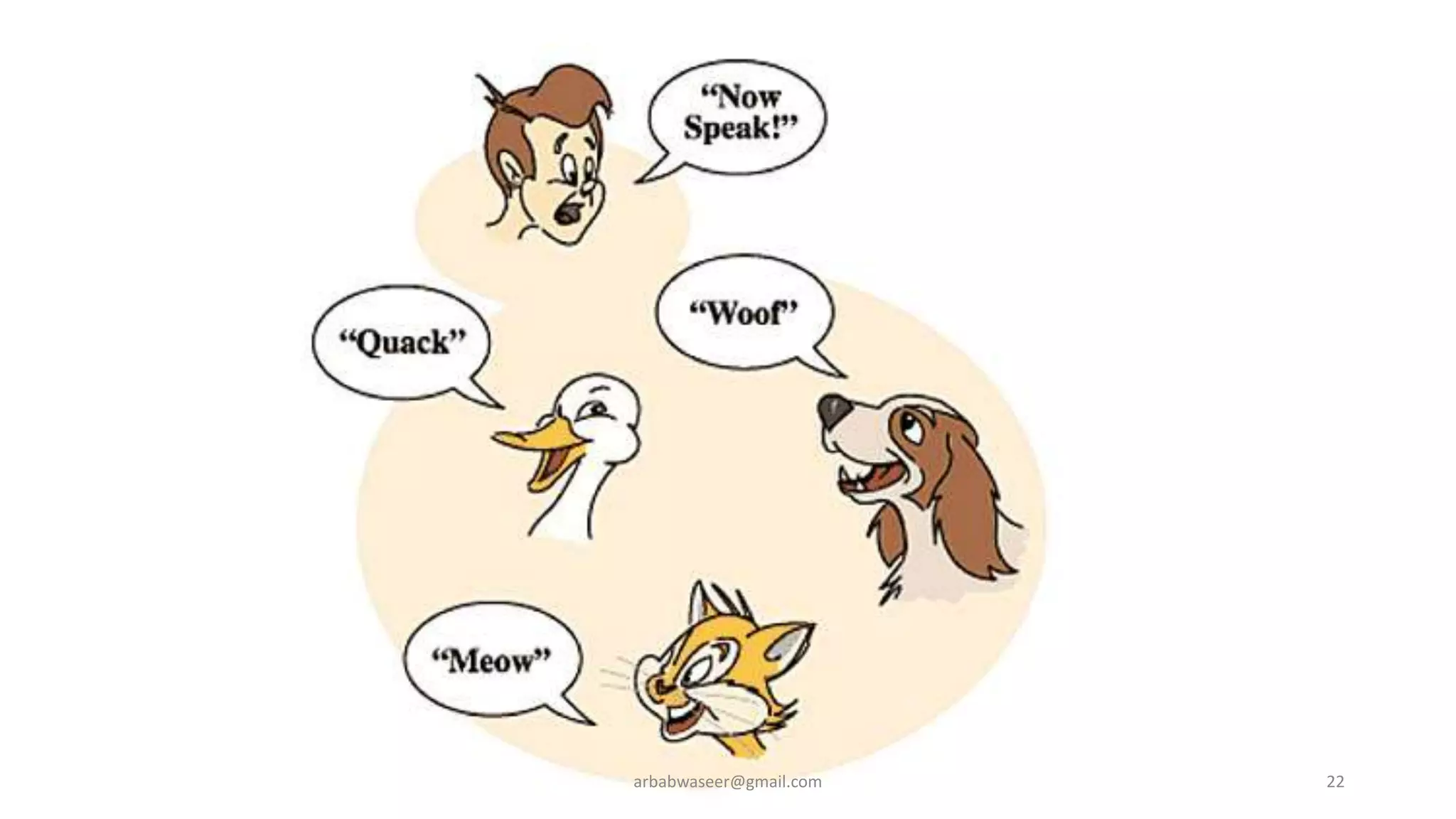
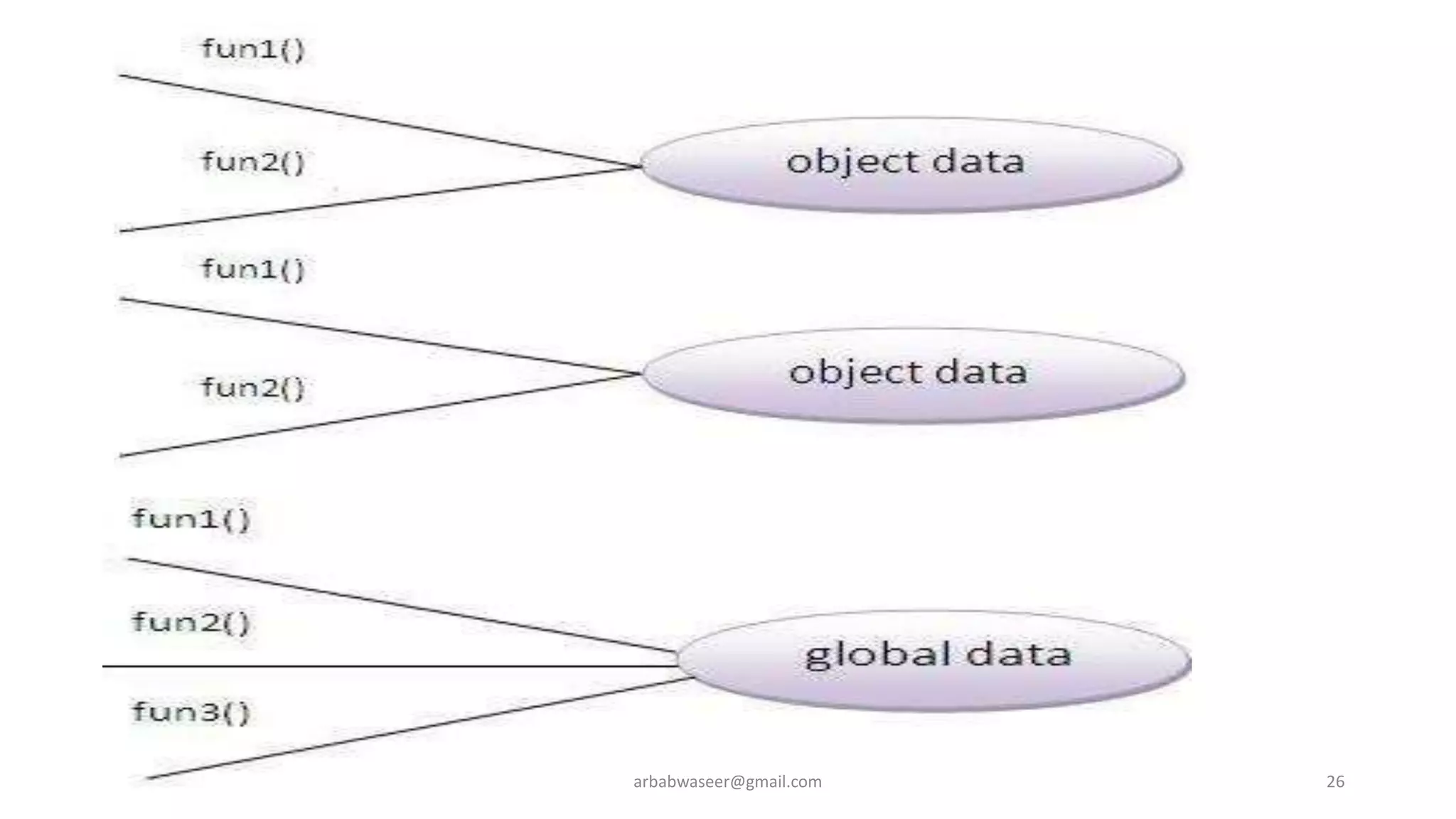
This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming concepts through a lecture on a CMP-2123 Object Oriented Programming course. It defines key OOP concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. It also lists textbooks and materials for the course and provides an overview of topics to be covered, including objects and classes, inheritance, interfaces, exceptions, GUI programming, and more.